Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BBA-Semester III Course Name-Environment Management Topic-Natural Resources
BBA-Semester III Course Name-Environment Management Topic-Natural Resources
Uploaded by
Mitali GuptaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BBA-Semester III Course Name-Environment Management Topic-Natural Resources
BBA-Semester III Course Name-Environment Management Topic-Natural Resources
Uploaded by
Mitali GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
BBA-Semester III
Course Name-Environment Management
Topic-Natural Resources
Reference Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f14oBaPNhdc
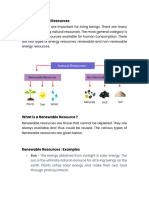
The materials we use from nature such as wind energy, water, plants, animals, and fossil
fuels to make the things we need are called natural resources. They are the basis of life
on Earth.
1. In terms of the source of origin
o Biotic Resources
o These are obtained from the biosphere, such as forests and their products,
animals, birds and their products, from fish and marine organisms.
o Abiotic Resources
o Abiotic resources include non-living things like Examples of abiotic
resources are water, land, ores and air.
2. based on their renewability
o Renewable Resources:
o Renewable resources are ones that can be replenished or reproduced easily.
Some of them, like sunlight, air, wind, etc., are continuously available and their
quantity is not affected by human consumption.
o Solar Energy: Since earth formed, the sun has produced energy in the
form of heat and light. It is considered unlimited (the sun isn’t going
anywhere!)
o Wind Power: Wind is moving air created as the sun heats the earth’s
surface. As long as the sun is shining, the wind remains an infinite,
renewable resource.
o Hydroelectric power :Flowing water creates energy that can be captured
and turned into electricity which is called Hydroelectric power. Water is
constantly renewed by the water cycle which makes this a renewable
resource.
o Biomass :Biomass is any material made by plants and animals that we
can convert into energy. It is considered renewable because we can
always grow more plants and trees.
o Non-renewable resources
o Non-renewable resources are formed over very long geological periods. Minerals
and fossil fuels are included in this category. Since their rate of formation is
extremely slow, they cannot be replenished once they get depleted.
o Fossil fuels release heat energy when they are burned and they are used
to create energy and electricity. They were formed from the remains of
living organisms millions of years ago.
Coal is a black or brownish rock. We burn coal to create energy.
Oil is a liquid fossil fuel. Most of the world’s oil is still deep under
the ground.
Natural Gas We rely on natural gas to give power to lights, TVs, air
conditioners, and kitchen appliances.
3. Based on Exhausting capability
o Inexhaustible Natural Resources: Those resources which are present in
unlimited quantity in nature and are not likely to be exhausted easily by human
activity are inexhaustible natural resources. e.g. – sunlight, air etc.
o Exhaustible Natural Resources:
The amount of these resources is limited. They can be exhausted by human
activity in the long run. E.g. coal, petroleum, natural gas etc..
The modern life-style and the advance in technology have had a very bad impact
on the natural resources. Natural resources like coal and petroleum are depleting
at a very fast rate, and once they are depleted, we will have to depend on other
sources of energy. Therefore it is very necessary for us humans to act in a way
which ensures the conservation of natural resources. There are thousands of
ways of conserving natural resources. The main idea of conservation is to use the
natural resources with optimization, and do not waste any natural resources.
Methods of Conservation of Natural Resources
1. Use of alternative sources of power such as solar and wind energy. These
alternative sources of energy are bio friendly particular because they do not
produce harmful gases that damage the ozone layer.
2. Plant trees to prevent soil erosion. This entails planting trees and vegetation to
control soil erosion caused by wind and water.
3. Practicing of judicious ways to conserve water in our homes. This entails simple
practices like ensuring that taps are closed when they are not in use. Taking less
time in the shower aids to conserve gallons of water per month. Reusing some of
the water for watering the kitchen gardens in our homes is also an important
practice.
4. Treatment of industrial wastes and sewages before they are released in the
water bodies. Rapid industrialization has resulted to wastes that are harmful to
the ecosystem. The release of these effluents directly into the water bodies has
led to massive water pollution to some areas in the world especially in
developing countries. Therefore, industrial and human waste should be treated
to prevent thermal and chemical pollution of water.
5. This is an important practice of ensuring water conservation. It is done by
harvesting of rainwater during the wetter seasons of the year and using it during
the dry seasons.
6. Such practices include switching off the lights when not in use, unplugging
electrical appliances when not in use. Plugged-in appliances continue to use
electricity even when not in use. Other practices include spending less time when
taking hot showers.
7. Ensure the recycling of wastes. These wastes include plastics, paper bags that
have resulted to tones of garbage. Recycling entails re-manufacturing of already
used materials. This reduces the amount of waste available reducing soil and
water pollution.
You might also like
- Sefox Spray Adhesi̇ve MSDSDocument6 pagesSefox Spray Adhesi̇ve MSDSAljameel ShowroomNo ratings yet
- OLF Drill Cuttings SummaryDocument12 pagesOLF Drill Cuttings SummaryReza Ismail HasanNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources - Google DriveDocument20 pagesNatural Resources - Google DriveKajol HNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument8 pagesNatural ResourcesTigerNo ratings yet
- Vaishali Evs ProjectDocument32 pagesVaishali Evs Projectvaishali TMU studentNo ratings yet
- Elcano Arpeco Assign 1Document4 pagesElcano Arpeco Assign 1Joemer SiplocNo ratings yet
- EVS Chapter 2 Sem2Document17 pagesEVS Chapter 2 Sem2rishigoel284No ratings yet
- Land Resources IntroductionDocument10 pagesLand Resources Introductionprabinforever75% (4)
- 4.unit - II, Subunit-A, Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources. Role of Individual in Conservation of Natural Resources For Sustainable Life Styles.Document4 pages4.unit - II, Subunit-A, Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources. Role of Individual in Conservation of Natural Resources For Sustainable Life Styles.milf hunterNo ratings yet
- Types of Natural ResourcesDocument3 pagesTypes of Natural ResourcesSoumendra RoyNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources: and Their ConservationDocument18 pagesNatural Resources: and Their Conservationnihal_sawyerNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sistema Ni KaloyDocument39 pagesLesson Plan Sistema Ni KaloyJohn Carlo CericoNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 Coal and PetroleumDocument5 pagesCh-5 Coal and PetroleumZara SmithNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Non Renewable ResourcesDocument14 pagesRenewable and Non Renewable ResourcesSittie Ainie100% (1)
- Natural Resource-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesNatural Resource-WPS OfficeMD ALI100% (1)
- Natural Resources and Their ManagementDocument24 pagesNatural Resources and Their Managementshilpaverma2106No ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument4 pagesNatural ResourcesShalini C G100% (1)
- File On Topic Renewable and Nonrenewable Source of EnergyDocument2 pagesFile On Topic Renewable and Nonrenewable Source of EnergyJoban SandhuNo ratings yet
- Final Report EnergyDocument52 pagesFinal Report EnergymangalamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sistema Ni Kaloy UpgradedDocument39 pagesLesson Plan Sistema Ni Kaloy UpgradedJohn Carlo CericoNo ratings yet
- Earth's Resources: 6 GradeDocument13 pagesEarth's Resources: 6 GradeJordyn IzenstarkNo ratings yet
- Grade-7 Renewable ResourcesDocument3 pagesGrade-7 Renewable ResourcesJay r DomingoNo ratings yet
- Module-Earth-Science-Q2 w456Document6 pagesModule-Earth-Science-Q2 w456Aaron Paul TañedoNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document1 pageNotes 1Kanak GargNo ratings yet
- Makapasar Sa Sci CutieDocument18 pagesMakapasar Sa Sci CutieChristian MonterroyoNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document15 pagesModule 3SumanpalNo ratings yet
- Sources of Energy in NatureDocument3 pagesSources of Energy in NatureChandan Kumar BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Handout 2.10.f PDFDocument3 pagesHandout 2.10.f PDFToru -No ratings yet
- Em Unit-1Document10 pagesEm Unit-1Hemant Kumar AhirwarNo ratings yet
- TYPES:1.solar Energy 2.wind e 3hydropower e 5.biomass:: Economic Value Oil Natural GasDocument6 pagesTYPES:1.solar Energy 2.wind e 3hydropower e 5.biomass:: Economic Value Oil Natural GasswatiNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources of The Earth: Our ResponsibilityDocument22 pagesNatural Resources of The Earth: Our ResponsibilityGRACE VERIDIANONo ratings yet
- Land Resource and Energy ResourcesDocument11 pagesLand Resource and Energy ResourcesGautam GopalNo ratings yet
- Digital AssignmentDocument14 pagesDigital AssignmentVedha NayakamNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourceDocument16 pagesNatural ResourceMarathi DhinganaNo ratings yet
- Examples of Nonrenewable Energy SourcesDocument4 pagesExamples of Nonrenewable Energy SourcesY D Amon GanzonNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow and Conservation of ResourcesDocument10 pagesEnergy Flow and Conservation of ResourcesnitikanehiNo ratings yet
- Comprehension EnergyDocument3 pagesComprehension EnergyArlet SastreNo ratings yet
- Lesson Presentation 3-EcosystemDocument7 pagesLesson Presentation 3-Ecosystemian abocadoNo ratings yet
- Krishna Sraf - Ix-A - Computer Practical Question 1.Document43 pagesKrishna Sraf - Ix-A - Computer Practical Question 1.Krishna SarafNo ratings yet
- 16 - Academic English NREM - Jan21Document78 pages16 - Academic English NREM - Jan21tranhoangquant67No ratings yet
- Evs Imp - (25)Document14 pagesEvs Imp - (25)labdhigandhi2003No ratings yet
- Toddle Dbcde904 132c 4afc b6b6 2a237bef7220 Renewable and NonrenewableDocument6 pagesToddle Dbcde904 132c 4afc b6b6 2a237bef7220 Renewable and Nonrenewable76t8n6vdg7No ratings yet
- Energy Renewable EnergyDocument16 pagesEnergy Renewable EnergyMd IshteyaqueNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources Handout (C)Document3 pagesEnergy Resources Handout (C)PunchyDoodlesNo ratings yet
- Example - Sustainable DevelopmentDocument3 pagesExample - Sustainable DevelopmentsurenikaNo ratings yet
- Renewable ResourcesDocument5 pagesRenewable ResourcessumitrochakrabortiNo ratings yet
- Inder Evs 2-2Document25 pagesInder Evs 2-2inderisurdaddy12No ratings yet
- Conservation of Natural ResourcesDocument2 pagesConservation of Natural ResourcesRoshan KumarNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument3 pagesNatural ResourcesNikhil LondheNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Solid Waste ManagementDocument4 pagesEnvironmental and Solid Waste ManagementLOMIBAO, JC HUBBER P.No ratings yet
- Chaprter 2: Environmental ScienceDocument9 pagesChaprter 2: Environmental Sciencejeboy DaquizNo ratings yet
- Unit Energy Part 5Document20 pagesUnit Energy Part 5Maurya AdeshraNo ratings yet
- SCI7 Q4 SLK2W2 The Philippine EnvironmentDocument15 pagesSCI7 Q4 SLK2W2 The Philippine Environmentms.ilaganirineNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Natural Resources and Biodiversity: 2.0 ObjectivesDocument25 pagesUNIT 2 Natural Resources and Biodiversity: 2.0 Objectivesyo boNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 EVSDocument13 pagesUnit 1 EVSVarshaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Environmental ScienceDocument6 pagesAssignment of Environmental ScienceAakar SethNo ratings yet
- Biology - Project On Human ImpactDocument15 pagesBiology - Project On Human ImpactShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- 8 Ag 1Document4 pages8 Ag 1archanagnair2002No ratings yet
- What Are Natural Resources?Document5 pagesWhat Are Natural Resources?Lucrari de LicentaNo ratings yet
- Luis Landa American School and Institute: StudentDocument9 pagesLuis Landa American School and Institute: StudentAlejandradeAguilarNo ratings yet
- 6d7b83 Natural Resources and Associated ProblemDocument3 pages6d7b83 Natural Resources and Associated ProblemAyushi Singh100% (3)
- Materials Recovery FacilityDocument2 pagesMaterials Recovery FacilityJasper Kenneth PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Review of Waste Tyre Pyrolysis 5240E1114021Document6 pagesComparative Review of Waste Tyre Pyrolysis 5240E1114021DHSanjNo ratings yet
- A Knowledge-Base On Waste Management Through Action Research: The Case of Busia, UgandaDocument9 pagesA Knowledge-Base On Waste Management Through Action Research: The Case of Busia, UgandaMario WhoeverNo ratings yet
- The Circular EconomyDocument30 pagesThe Circular EconomySri JananiNo ratings yet
- Company Profiles - CHINA GROUPDocument8 pagesCompany Profiles - CHINA GROUPAhmad Mursyidi KamaludinNo ratings yet
- Establishment Categorization Checklist FormDocument2 pagesEstablishment Categorization Checklist FormAngelika CalingasanNo ratings yet
- Mangmyb 01Document15 pagesMangmyb 01Saad MotawéaNo ratings yet
- English Sample Paper 2023-24Document12 pagesEnglish Sample Paper 2023-24Tanmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vietnam 2019 - DrinksDocument10 pagesVietnam 2019 - DrinksMinh ThuậnNo ratings yet
- NatRes PPT 04 Brown Laws PDFDocument309 pagesNatRes PPT 04 Brown Laws PDFPatatas SayoteNo ratings yet
- Pasir Gudang 1Document8 pagesPasir Gudang 1Ahmad MuzammilNo ratings yet
- Community and Environmental Health: Learning Competencies: Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesCommunity and Environmental Health: Learning Competencies: Learning ObjectivesRollon, Sherwin B.No ratings yet
- Capstone Project (Draft)Document11 pagesCapstone Project (Draft)Aira BongalaNo ratings yet
- Msds - RInso CairDocument19 pagesMsds - RInso Cairyulia shinsungNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Kindergarten 2Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Kindergarten 2Joyce ZamoroNo ratings yet
- The Issue of Wastewater Is Becoming More and MoreDocument11 pagesThe Issue of Wastewater Is Becoming More and MoreBeerappa RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Bloomberg BNADocument68 pagesBloomberg BNABob MackinNo ratings yet
- E Waste Disposal MethodsDocument12 pagesE Waste Disposal Methodstheunitedindian200No ratings yet
- Name: Subject: Date:: Surname 1Document3 pagesName: Subject: Date:: Surname 1mutua daveNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of A Residential Project in Light Steel Framing According To Leed For HomesDocument12 pagesEvaluation of A Residential Project in Light Steel Framing According To Leed For HomesOsvaldo FariaNo ratings yet
- KLONOPIN (R) Tablets (2.0 MG) : SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocument8 pagesKLONOPIN (R) Tablets (2.0 MG) : SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingSandro AlcobaçaNo ratings yet
- Design of A Rotary Blade Glass Pulverizing MachineDocument12 pagesDesign of A Rotary Blade Glass Pulverizing MachineAhmad S AhmadNo ratings yet
- PDF E Waste Recycling and Management Present Scenarios and Environmental Issues Anish Khan Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF E Waste Recycling and Management Present Scenarios and Environmental Issues Anish Khan Ebook Full Chapterhelen.lomas712100% (3)
- Mat Said 2003Document10 pagesMat Said 2003sarsvathyyNo ratings yet
- Cortaderia Selloana (Pampas Grass) Fibers As An Alternative To Wood Fibers inDocument9 pagesCortaderia Selloana (Pampas Grass) Fibers As An Alternative To Wood Fibers inJamilla Bianca ManuelNo ratings yet
- 7 - Septic Tank SystemsDocument13 pages7 - Septic Tank SystemsSagar ParmarNo ratings yet
- Lithium Batteries and Their Safe Storage Transport Use and Disposal Including Re Use and Re CyclingDocument26 pagesLithium Batteries and Their Safe Storage Transport Use and Disposal Including Re Use and Re CyclingTrainer 01No ratings yet
- The Role of MBT in Europe: Wolfgang MüllerDocument30 pagesThe Role of MBT in Europe: Wolfgang Müllermiroslav11No ratings yet