Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 2
Lecture 2
Uploaded by
reena devi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views20 pagesJava was created in 1991 by James Gosling and others at Sun Microsystems. It was initially called Oak but renamed to Java in 1995. Java is similar to C++ but aims to be simpler, safer, and platform independent. Java code can run on any device that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) without needing to be recompiled. The Java programming language and its platforms include Java SE for core functionality, Java EE for enterprise applications, Java ME for small devices, and JavaFX for rich internet applications. All Java platforms provide a JVM and APIs to allow platform-independent applications.
Original Description:
Original Title
lecture2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentJava was created in 1991 by James Gosling and others at Sun Microsystems. It was initially called Oak but renamed to Java in 1995. Java is similar to C++ but aims to be simpler, safer, and platform independent. Java code can run on any device that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) without needing to be recompiled. The Java programming language and its platforms include Java SE for core functionality, Java EE for enterprise applications, Java ME for small devices, and JavaFX for rich internet applications. All Java platforms provide a JVM and APIs to allow platform-independent applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views20 pagesLecture 2
Lecture 2
Uploaded by
reena deviJava was created in 1991 by James Gosling and others at Sun Microsystems. It was initially called Oak but renamed to Java in 1995. Java is similar to C++ but aims to be simpler, safer, and platform independent. Java code can run on any device that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) without needing to be recompiled. The Java programming language and its platforms include Java SE for core functionality, Java EE for enterprise applications, Java ME for small devices, and JavaFX for rich internet applications. All Java platforms provide a JVM and APIs to allow platform-independent applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 20
2.
• Java was conceived by James Gosling, Patrick
Naughton, Chris Warth, Ed Frank, and Mike
Sheridan at Sun Microsystems, Inc. in 1991
• This language was initially called “Oak,” but was
renamed “Java” in 1995.
• Java is related to C++, which is a direct
descendant of C. Much of the character of Java is
inherited from these two languages.
• Java programs are platform independent which
means they can be run on any operating system
with any processor as long as the Java
interpreter is available on that system.
• Java code that runs on one platform does not
need to be recompiled to run on another
platform; it's called write once, run
anywhere(WORA).
• Java Virtual Machine(JVM) executes Java
code, but it has been written in
platform-specific languages such as C/C++,
etc. JVM is not written in Java and
hence cannot be platform independent.
• Java technology is both a programming
language and a platform.
• The Java programming language is a high-level
object-oriented language that has a particular
syntax and style.
• A Java platform is a particular environment in
which Java programming language
applications run.
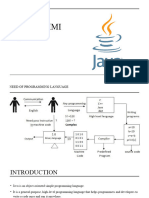
The Java Programming Language Platforms
There are four platforms of the Java
programming language:
• Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE)
• Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE)
• Java Platform, Micro Edition (Java ME)
• JavaFX
• All Java platforms consist of a Java Virtual Machine
(VM) and an application programming interface (API).
• The Java Virtual Machine is a program, for a particular
hardware and software platform, that runs Java
technology applications.
• An API is a collection of software components that you
can use to create other software components or
applications.
• Each Java platform provides a virtual machine and an
API, and this allows applications written for that
platform to run on any compatible system with all the
advantages of the Java programming language:
platform-independence, power, stability,
ease-of-development, and security.
• Java SE's API provides the core functionality of the Java
programming language.
– It defines everything from the basic types and objects of
the Java programming language to high-level classes that
are used for networking, security, database access,
graphical user interface (GUI) development, and XML
parsing.
• The Java EE platform is built on top of the Java SE platform.
The Java EE platform provides an API and runtime
environment for developing and running large-scale,
multi-tiered, scalable, reliable, and secure network
applications.
• The Java ME platform provides an API and a small-footprint
virtual machine for running Java programming language
applications on small devices, like mobile phones.
• JavaFX is a platform for creating rich internet
applications using a lightweight user-interface
API.
– JavaFX applications use hardware-accelerated
graphics and media engines to take advantage of
higher-performance clients and a modern
look-and-feel as well as high-level APIs for
connecting to networked data sources.
– JavaFX applications may be clients of Java EE
platform services.
• The Java EE platform uses a distributed multitiered application
model for enterprise applications.
• Application logic is divided into components according to function,
and the application components that make up a Java EE application
are installed on various machines depending on the tier in the
multitiered Java EE environment to which the application
component belongs.
• Figure 1-1 shows two multitiered Java EE applications divided into
the tiers described in the following list.
– Client-tier components run on the client machine.
– Web-tier components run on the Java EE server.
– Business-tier components run on the Java EE server.
– Enterprise information system (EIS)-tier software runs on the EIS
server.
A First Simple Program
• For this example, the name of the source file should be
Example.java
• In Java, all code must reside inside a class.
• By convention, the name of the main class should match the
name of the file that holds the program.
Compiling the Program
• The javac compiler creates a file called
Example.class that contains the bytecode
version of the program.
• The Java bytecode is the intermediate
representation of your program that contains
instructions the Java Virtual Machine will
execute.
• The public keyword is an access modifier, which allows the
programmer to control the visibility of class members.
• When a class member is preceded by public, then that member
may be accessed by code outside the class in which it is
declared.
• The keyword static allows main( ) to be called without having to
instantiate a particular instance of the class.
• This is necessary since main( ) is called by the Java Virtual
Machine before any objects are made.
• The keyword void simply tells the compiler that main( ) does
not return a value.
• String args[ ] declares a parameter named args,
which is an array of instances of the class
String.
• Objects of type String store character strings.
• In this case, args receives any command-line
arguments present when the program is
executed.
• System is a class predefined by Java that is
automatically included in your programs.
You might also like
- BMW Key Ews Dme Cas Sync ProcedureDocument5 pagesBMW Key Ews Dme Cas Sync ProceduregoogleheadNo ratings yet
- Website Development ProposalDocument5 pagesWebsite Development ProposalAlex100% (1)
- CONTROL-M - Basic ConceptsDocument42 pagesCONTROL-M - Basic ConceptsakrivenetsNo ratings yet
- 9.introduction To JavaDocument46 pages9.introduction To JavadoneyNo ratings yet
- Java CoreDocument123 pagesJava CoreEr Bhargav ModiNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument36 pagesIntroductionREESHU RANJANNo ratings yet
- Java APIUnitIDocument41 pagesJava APIUnitI82Neha PalNo ratings yet
- 1 BasicsDocument152 pages1 BasicsBhuvana GowthamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Introduction To JavaDocument31 pagesChapter 2-Introduction To JavaSasinikhila JogiNo ratings yet
- BSCS 7th Java 3Document212 pagesBSCS 7th Java 3m.saadbaloch4892No ratings yet
- Basics of Java Programming LanguageDocument32 pagesBasics of Java Programming LanguageDr Narayana Swamy RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Java Unit 1 - Fundamentals of Java ProgrammingDocument66 pagesJava Unit 1 - Fundamentals of Java ProgrammingREDNo ratings yet
- CT-6611 Chapter-9Document37 pagesCT-6611 Chapter-9bazezew belewNo ratings yet
- Basic FeaturesDocument19 pagesBasic FeaturesumangNo ratings yet
- Java Note 1Document16 pagesJava Note 1Anu VermaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document101 pagesModule 2Arghadeep GhoshNo ratings yet
- 220245-MSBTE-22412-Java (Unit 1)Document40 pages220245-MSBTE-22412-Java (Unit 1)Nomaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Thopstech Java NotesDocument90 pagesThopstech Java NotesVijayNo ratings yet
- JAVA Unit 1Document297 pagesJAVA Unit 1momap92001No ratings yet
- Java Full Notes Unit 1-6 V2V by Rajan SirDocument156 pagesJava Full Notes Unit 1-6 V2V by Rajan SirYash GawareNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document18 pagesLecture 01Oluwapelumi EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Java Basics NotesDocument23 pagesJava Basics NotesDJNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java Programming: Fairose Binti MohtarDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Java Programming: Fairose Binti MohtarPabbura_HatiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ProgrammingDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Programmingayushdwivedy73No ratings yet
- TUTORIAL About The Java TechnologyDocument3 pagesTUTORIAL About The Java Technologylaura vanesaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document40 pagesUnit 1ranajitsenkoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Introducing JavaDocument22 pagesChapter Two: Introducing JavaEnqu kNo ratings yet
- Java Notes (Nep Syllabus)Document133 pagesJava Notes (Nep Syllabus)Tangent Learning SolutionsNo ratings yet
- My Java Notes BasicDocument31 pagesMy Java Notes BasicDivya PawarNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Web Publishing With Java Why Java?Document20 pagesUnit Iii Web Publishing With Java Why Java?srikmarepallyNo ratings yet
- Why JavaDocument21 pagesWhy JavakarthickamsecNo ratings yet
- Java Programming by K. AdiseshaDocument76 pagesJava Programming by K. AdiseshaAdisesha KandipatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Part IIDocument86 pagesChapter 1 - Part IIalsenlegesseNo ratings yet
- Abstract Class in JavaDocument86 pagesAbstract Class in JavaVasanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Merge Final 1.0 PDFDocument146 pagesMerge Final 1.0 PDFlaxmikant solankeNo ratings yet
- Java by Kamalakar DanduDocument284 pagesJava by Kamalakar DanduKamalakar DanduNo ratings yet
- JVM PresentationDocument14 pagesJVM Presentationanshul siwachNo ratings yet
- Features of JavaDocument4 pagesFeatures of JavaNixie Lee MarintesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To JavaDocument37 pagesIntroduction To JavaGanesh NelluriNo ratings yet
- Java Environment and FeaturesDocument34 pagesJava Environment and FeaturesMeena KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Programming: Sheikh Qaisar Ayub, Sulma RashidDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Programming: Sheikh Qaisar Ayub, Sulma RashidQaisar Ayub SheikhNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Use Java?: Glossary Web Publishing With JavaDocument21 pagesWhy Do We Use Java?: Glossary Web Publishing With JavaS Kalyan LakshmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document40 pagesUnit 1rohandasari420No ratings yet
- By: Akanksha YadavDocument15 pagesBy: Akanksha YadavAbhishek NagarajNo ratings yet
- Adv Java24Document102 pagesAdv Java24Rohit AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Java Notes PDFDocument167 pagesJava Notes PDFPraneeth MutnuruNo ratings yet
- Java Notes - Part 1Document39 pagesJava Notes - Part 1Daniel JoshuaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Lecture 1 - Introduction To Java PDFDocument21 pages2018 Lecture 1 - Introduction To Java PDFChris JamesNo ratings yet
- Add This Data Into Your ReportDocument7 pagesAdd This Data Into Your Reportkapoorshahid606No ratings yet
- Unit-I 1JavaBAsic IntroDocument48 pagesUnit-I 1JavaBAsic IntroMochiNo ratings yet
- Day1 JavaintroDocument31 pagesDay1 JavaintrochandanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Java Introduction To JavaDocument2 pages1.1 Introduction To Java Introduction To JavaAnonymous Atg05gpbNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document40 pagesUnit 1Prabesh KarkiNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument187 pagesJavapramodmauryapkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java Programming LanguageDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Java Programming Languagevasanthyogi100% (1)
- JavaDocument14 pagesJavabharanidaran ramalingamNo ratings yet
- Core Java Notes: Chapter-1, 2,3 Features of JAVA EnvironmentDocument31 pagesCore Java Notes: Chapter-1, 2,3 Features of JAVA EnvironmentRUSHIL SHAHNo ratings yet
- T StartDocument26 pagesT Startasdad adNo ratings yet
- Java Platform OverviewDocument25 pagesJava Platform Overviewindu kaurNo ratings yet
- Why Software Developers Choose JavaDocument2 pagesWhy Software Developers Choose JavaAndrew MartinNo ratings yet
- 6 Introduction To JavaDocument17 pages6 Introduction To JavaVasikaran KNo ratings yet
- Assosa University: College of Computing and InformaticsDocument24 pagesAssosa University: College of Computing and InformaticsGebreigziabher M. AbNo ratings yet
- Proceedings2016 40 44Document6 pagesProceedings2016 40 44reena deviNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of An Electric Oven: Akinfaloye Oluwabusayo AkinyemiDocument6 pagesDesign and Construction of An Electric Oven: Akinfaloye Oluwabusayo Akinyemireena deviNo ratings yet
- Lec06-Scan HandoutDocument7 pagesLec06-Scan Handoutreena deviNo ratings yet
- Harold Somers: Feigenbaum, Edward A. and Pamela Mccorduck 1983 Addison-Wesley, Reading, MaDocument2 pagesHarold Somers: Feigenbaum, Edward A. and Pamela Mccorduck 1983 Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mareena deviNo ratings yet
- Index: Date Experiment SignDocument1 pageIndex: Date Experiment Signreena deviNo ratings yet
- Web Tech Ass1Document3 pagesWeb Tech Ass1reena deviNo ratings yet
- Memory Based Paper: IBPS Clerk Mains 2021Document139 pagesMemory Based Paper: IBPS Clerk Mains 2021reena deviNo ratings yet
- Comp JKSSB Fundamentals of ComputerDocument25 pagesComp JKSSB Fundamentals of Computerreena deviNo ratings yet
- Web TechnologyDocument29 pagesWeb Technologyreena deviNo ratings yet
- HTML TablesDocument17 pagesHTML Tablesreena deviNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document26 pagesLecture 4reena deviNo ratings yet
- HTML FormsDocument17 pagesHTML Formsreena deviNo ratings yet
- Student Information System - FDocument12 pagesStudent Information System - Freena deviNo ratings yet
- HTML Elements For ListsDocument11 pagesHTML Elements For Listsreena deviNo ratings yet
- By Shubam Verma Sir: Answer: - (1) HHQKDocument11 pagesBy Shubam Verma Sir: Answer: - (1) HHQKreena deviNo ratings yet
- Lexical Analyzer: Design and Implementation With LEX ToolDocument13 pagesLexical Analyzer: Design and Implementation With LEX Toolreena deviNo ratings yet
- Web Designing Course SyllabusDocument19 pagesWeb Designing Course Syllabusreena deviNo ratings yet
- PLM Fundamentals IIIDocument18 pagesPLM Fundamentals IIIamit chaudhariNo ratings yet
- TimeGlider TutorialDocument11 pagesTimeGlider TutorialDidina RatiuNo ratings yet
- Dnfs Clonedb Oow 2012Document42 pagesDnfs Clonedb Oow 2012vikNo ratings yet
- RHCE QuestionsDocument6 pagesRHCE QuestionsgoharhussainNo ratings yet
- Wondershare Quiz Maker StepsDocument4 pagesWondershare Quiz Maker StepsNorih UsmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1DPNo ratings yet
- Crises Connect Research PaperDocument12 pagesCrises Connect Research PaperVishnu BNo ratings yet
- BitLocker To Go UserguideDocument12 pagesBitLocker To Go UserguideGiorgos AnyfantisNo ratings yet
- Project Keyboard ShortcutsDocument1 pageProject Keyboard ShortcutsRadharaman YadavNo ratings yet
- JSF Tutorial 1Document4 pagesJSF Tutorial 1oriental2008No ratings yet
- HANDS Hadoop CloudDocument10 pagesHANDS Hadoop Cloudbenben08No ratings yet
- Cordova National High School: Quarter 1 Week 4Document17 pagesCordova National High School: Quarter 1 Week 4R TECHNo ratings yet
- Iec 61850 Mms Client DatasheetDocument2 pagesIec 61850 Mms Client DatasheetRishi DhimanNo ratings yet
- Container Positioning Information System: Combination of ExcellenceDocument2 pagesContainer Positioning Information System: Combination of ExcellenceДенис ГильдеевNo ratings yet
- F5 Customer Demo: BIG-IP AFM - Use Global RulesDocument9 pagesF5 Customer Demo: BIG-IP AFM - Use Global RulesAries Raf OndisNo ratings yet
- Release-Information 14.0 enDocument5 pagesRelease-Information 14.0 enAnjali DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Autosys Unix CommandsDocument4 pagesAutosys Unix CommandsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document22 pagesCase Study 2Arsalan ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Hardering OracleDocument40 pagesHardering OracleFabian Alejandro Molina SosaNo ratings yet
- C ProgrammingDocument205 pagesC ProgrammingSrinivasan RamachandranNo ratings yet
- A Step by Step Oracle DB Migration Test Case 1704032098Document11 pagesA Step by Step Oracle DB Migration Test Case 1704032098David BalbucaNo ratings yet
- How To Use Net emDocument6 pagesHow To Use Net emTruong Cong MinhNo ratings yet
- Digital Book Reader: User GuideDocument265 pagesDigital Book Reader: User GuideHammerzorNo ratings yet
- TP - Docker - ISRCDocument8 pagesTP - Docker - ISRCDRISS AIT OMARNo ratings yet
- IFMS Government of MaharashtraDocument17 pagesIFMS Government of MaharashtrakaisermalekNo ratings yet
- Labi Shamsideen Labinjo Resume 04Document3 pagesLabi Shamsideen Labinjo Resume 04shubhamNo ratings yet
- SAP C4C Sales Quote How-Tos Spine Representatives/Agents ManualDocument24 pagesSAP C4C Sales Quote How-Tos Spine Representatives/Agents ManualManishNo ratings yet