Professional Documents
Culture Documents
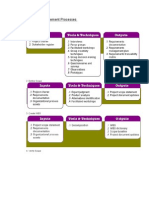
Project Management Knowledge Areas and Processes Mind Map
Project Management Knowledge Areas and Processes Mind Map
Uploaded by
Afiq AbdullahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Project Management Knowledge Areas and Processes Mind Map
Project Management Knowledge Areas and Processes Mind Map
Uploaded by
Afiq AbdullahCopyright:
Available Formats
Covers the approach to managing all the phases of the project lif ecycle including project planning, directing
and monitoring work, and closing down the project.
T he procedures in this knowledge area are used in order to identif y, acquire, and manage the resources required to complete the project successf ully.
Details the change control process where change requests that occur during the project are evaluated, approved and recorded.
A project manager is responsible f or considering the resources to be used f or the project completion. It includes people, equipment, f acilities, f undings, etc. Project resource management has the f ollowing processes.
Development of the project charter It is f or initiating the project and def ining the stakeholders of the project.
1 Integration
identif ies the roles/positions required by the project, the minimum requirements f or those roles, and how they f it into the overall project structure. Plan Resource Management 6 Human Resource Development of the project management plan It includes the outline of the project plan and how to get the desired results f or f avorable outcomes.
T o ensure the necessary resources are available, the quantity of each resources needs to be estimated. Estimate Activity Resources Directing and managing the project work It includes the production and the release of project deliverables.
Project Integration Management is describe as the knowledge
Identif y, Def ine, Combine & Coordinate with various Project Management Processes
Once the required number of resources has been estimated, the resources can be can be acquired. Acquire Resources area that holds every other part of the project together
Human resource management has to with obtaining the suitable and qualified members that Identif y, acquire & manage resources needed to complete the project Monitor and control project work Ref ers to project perf ormance monitoring and ensuring the project deliverables are on schedule.
would form the project team and then developing and managing them as the project progresses.
Ref ers to providing the team with the necessary training and it also includes team-building and improving the interaction among the team T eam Development Perf ormed integrated change control Ref ers to any changes with respect to project sponsors, or administrative tasks etc.
T he project team is actively managed to ensure their production is maximized and they are satisf ied. T eam Management Closing of the project It includes the tasks and activities f or closing the project.
T he resources are monitored and their perf ormance evaluated to ensure maximum productivity. Resource Control
T his knowledge area involves the project scope, that is, the work that is included within the project.
T he processes in this knowledge area are used to ensure that project inf ormation is planned, created, distributed, stored, retrieved, managed, controlled, monitored, and f inally disposed of in a timely and suitable manner.
Since scope changes are one of the top causes of project changes and grief in general, it is very important that the boundaries of the project be well def ined f rom the outset and monitored rigorously.
Consider anyone impacted by the project or who inf luences its success. T his list should include stakeholders,
Identif y Stakeholder
team members, sponsors, customers, and other interested parties. 2 Scope Collect Requirements Ref ers to gathering the requirements f or f urther ref ining the deliverables and def ining the requirements of the project stakeholders.
identif ies the regular communication requirements of each stakeholder, such as investor circulars, progress updates, and so f orth.
It also identif ies any specif ic communications procedures f or unexpected issues or project changes.
Plan Communication Management 7 Communication Def inition of the scope statement Ref ers to creating a detailed description f or the project scope.
Includes processes required to ensure only essential work is included Scope Management is the knowledge area relating
An appropriate medium should be selected at this step to ensure that the inf ormation is delivered successf ully to the stakeholders Distribute Inf ormation T he Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Ref ers to the graphical representation of the entire project into dif f erent work components.
to what work needs to be done by the project
Communication with stakeholders is often the key factor that allows stakeholders to be satisfied even when
unexpected changes happen. It is essential to develop a communications plan to keep all stakeholders Def ine, manage & control project communication needs as def ined by stakeholders Validate scope, which makes sure the deliverables are approved Ref ers to stakeholders approving and accepting the project deliverables.
During project execution the communications plan is put into practice and communications are actively managed. Manage Communications
“in the loop” throughout the project and communicate early and often when unexpected issues occur.
During regular status points the project communications are reviewed and revisions to the communications plan are initiated. Monitor Communications Acceptance and control of the scope deliverables Ref ers to ensuring the project deliverables are completed in accordance to the set scope and requirements.
Communicate and document to keep the team and stakeholders inf ormed and productive Manage Stakeholder Expectation
During planning, the project manager must divide the project into tasks and create both a schedule (start and f inish dates f or each task) and budget f or each task.
T he report has the progress inf ormation of the project. T his can be in detailed to tell about the
Report Perf ormance
various status part of the project. It can be put in the f orm of a documented detailed report During the project, earned value management determines the project status at regular status intervals.
Def ine activities Ref ers to explaining the activities of the project in detail with respect to the WBS.
3 Time
Risk management planning, identif ication, analysis, reaction planning, response implementation, and risk monitoring are all processes that f all under this knowledge area.
Project Management Knowledge Areas and Process Sequence of tasks and activities
Ref ers to the sequence that the project team is going to f ollow. It includes the allocation
of times such as f inish-to-start (FS), Finish-to-f inish (FF), Start-to-start (SS), and start-to-f inish (SF)
Risks are an inevitable part of projects, and that is why project risk management plays a crucial role in minimizing the risk f actor.
Estimate activity resource Ref ers to def ining the resources that should take f or each task.
T he Risk Management Plan identif ies how the risks will be itemized, categorized, and prioritized. Plan Risk Management Required to manage the timely completion of project The Time Management knowledge area ensures that
the project is running according to a schedule
Estimate activity duration Ref ers to def ining the time that should take f or each task.
T he major risks to the project are identif ied and placed into a risk register (list of risks). Most projects have one or
Identif y Risks
8 Risk
two risk that take signif icant precedence over all others, and these should of ten get special attention.
Involves creating a diagram with a critical path. Schedule development also includes tying
Develop schedule
dif f erent tasks along with the necessary resources with their start time and end time.
Once the biggest risks are identif ied, they are classif ied into categories of likelihood and impact, and then ranked according to priority. Perf orm Qualitative Risk Analysis
Conduct risk management planning to identif y & analyze the risks on a project Control schedule to ensure project is proceeding as planned. Ref ers to evaluating the project progress as per the def ined schedule.
Risk management involved identifying the risk that may occur in the course of the project and putting plan in place to handle them. Once the risks are ranked according to priority, the biggest priority risks are numerically analyzed
Perf orm Quantitative Risk Analysis
according to their impact to the project budget, schedule, or any other part of the project.
For the most important risks, response plans are draf ted such that all parties are aware of how to respond to the occurrence of the risk. Plan Risk Responses T he project buget is usually one of the most sensitive parts of a project.
T he risk responses identif ied in the previous step are carried out. Implement Risk Responses T he budget must be established through rigorous estimating techniques and monitored to ensure there are no unnecessary changes that make stakeholders unhappy
At regular status points the risk register is inspected and risks that have expired are crossed of f . Monitor and Control Risks Planning the cost management A project manager determines the procedures and methodologies to def ine the project budget and an overall cost.
4 Cost
Estimating the cost T he cost of each task is estimated, taking into account the resources, labor, materials, equipment, and any other item of cost necessary to complete the task.
T he processes in this knowledge area are used in order to buy or acquire products, services, or results that are required outside of the project. Determining the budget Here the separate budget estimations are combined to f orm a detailed project budget. T he task budgets are rolled up into an overall project budget.
The Project Cost Management relates with the project budget.
Plan, estimate, budget f unds, manage & control cost to complete the project This means making good estimates about how much funds is
T he Procurement Management Plan identif ies the outside procurement needs of the project and parameters under which the contractors will be procured. Plan Procurement Management 9 Procurement Ref ers to the analysis of the budget spent going f orward. Earned value analysis is perf ormed on regular
Controlling the cost as the project progresses
project status intervals to determine the project status at that status point. needed to cover the expenses of the project
The procurement management has to do with purchasing needed materials
T he contractors are hired. T his process involves producing the statements of work, terms of ref erence, request f or proposals, and such, as well as soliciting the responses and choosing a vendor. Conduct Procurements Includes processes required to acquire products & services needed f rom outside the project
from the outside. It may also include hiring of sub-contractors fort the project.
Amounts of project and management reserves are outlined
During project execution the contractors must be managed and the contracts monitored to provide early warning of project changes. Control Procurements
Summing up the estimates
T he processes in this knowledge area is use to identif y people, groups, or organizations that may have an impact on or can be af f ect by the project, analyze stakeholder expectations
and develop suitable management techniques f or ef f ectively engaging stakeholders in project decisions and execution, as well as their inf luence on the project. T he desired quality of the output can have a signif icant inf luence on project time and cost
uring the project initiation phase the major stakeholders are identif ied and their concerns established. Identif y Stakeholders 10 Stakeholder It’s important to decide the quality level and standards at project initiation phase
T he Stakeholder Management Plan lists each stakeholder and prioritizes their concerns and potential impacts on the project. Plan Stakeholder Engagement
5 Quality
Creation of the quality management plan It ref ers to documenting the specif ications f or def ining the quality of the deliverables.
Identify the stakeholders of the project and then proceed by planning how to keep them satisfied. Identif y stakeholders to analyze their expectations and impact on the project and its development
During project execution the stakeholders must have their needs addressed and communication lines must remain open. Manage Stakeholder Engagement The Project Quality Management performed to incorporate the organization’s
T he processes that ensure the quality of the deliverables
Incorporate the organisation policy regarding planning, managing and controlling project quality Quality assurance (making sure quality standards are f ollowed in the process)
must be inspected regularly to ensure they are working. quality policy about planning, managing, and controlling project and product
During status intervals each stakeholder must be considered to determine if their needs and being addressed and if changes need to made to ensure that they are. Monitor Stakeholder Engagement quality requirements to meet stakeholder’s expectations
T he deliverables themselves are inspected to ensure
Quality control (checking that the deliverables meet the quality standards)
they conf orm to the quality standards.
You might also like
- Engineering Economy 9Th Edition Leland T Blank Full ChapterDocument67 pagesEngineering Economy 9Th Edition Leland T Blank Full Chaptereleanor.gamble412100% (10)
- It Is Ongoing and RepetitiveDocument49 pagesIt Is Ongoing and RepetitiveGino0% (1)
- Process Flow Chart of A FoundryDocument1 pageProcess Flow Chart of A Foundrykshitij-mehta-4210100% (1)
- BSBMGT517 Assessor Marking Guide v2.0Document28 pagesBSBMGT517 Assessor Marking Guide v2.0Manreet KaurNo ratings yet
- OB ProjectDocument38 pagesOB ProjectAli KumaylNo ratings yet
- Film PrioritizationDocument7 pagesFilm PrioritizationPrashanthi Priyanka ReddyNo ratings yet
- Scheduling Tool Procurement: Joseph M. Rivard Phase 2 - Contract Selection Dr. Antonio Prensa October 15, 2010Document14 pagesScheduling Tool Procurement: Joseph M. Rivard Phase 2 - Contract Selection Dr. Antonio Prensa October 15, 2010jojolax36No ratings yet
- PMP CheatSheetDocument1 pagePMP CheatSheetalfri121No ratings yet
- Phase 4 - Project Management Financial Assessments Value in Using PERT, Risk Matrices, and Earned Value Management Memo Joseph M. Rivard Professor: Dr. Gonzalez PM620-1003B-01 September 10, 2010Document5 pagesPhase 4 - Project Management Financial Assessments Value in Using PERT, Risk Matrices, and Earned Value Management Memo Joseph M. Rivard Professor: Dr. Gonzalez PM620-1003B-01 September 10, 2010jojolax36No ratings yet
- PMP ITTO Process Chart PMBOK Guide 6th Edition-1aDocument14 pagesPMP ITTO Process Chart PMBOK Guide 6th Edition-1aSyed SadiqNo ratings yet
- Project Management and PMP OverviewDocument79 pagesProject Management and PMP OverviewLisario CondeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Introduction To Agile and ScrumDocument19 pagesLesson 3 - Introduction To Agile and ScrumDeepak Kumar100% (1)
- Project Scope Management Processes: Collect RequirementsDocument10 pagesProject Scope Management Processes: Collect RequirementsnoorulatharNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Process Pics ShortcutsDocument72 pagesPMBOK Process Pics Shortcutsgesliop global100% (1)
- FormulasDocument5 pagesFormulasRam RamisettiNo ratings yet
- PmiDocument8 pagesPmisalman1arif1No ratings yet
- PMP Certification - 4daysDocument4 pagesPMP Certification - 4dayssahajNo ratings yet
- Understanding Agile Project Management Methods UsingDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Agile Project Management Methods UsingJacquelinNo ratings yet
- Smart Goal ReflectionDocument3 pagesSmart Goal Reflectionapi-405728283No ratings yet
- Project Management TipsDocument10 pagesProject Management Tipstrisno100% (20)
- Capm QuestionsDocument6 pagesCapm QuestionsyenNo ratings yet
- Cracking The PMP Code: Draft PrintDocument5 pagesCracking The PMP Code: Draft PrintMMNo ratings yet
- Agile Project Management - TutorialsPointDocument4 pagesAgile Project Management - TutorialsPointEzra Mikah G. CaalimNo ratings yet
- Tips and Techniques To Pas PMPDocument12 pagesTips and Techniques To Pas PMPkapilkrbhatia100% (1)
- Project Charter TemplateDocument2 pagesProject Charter TemplateHimanshu JauhariNo ratings yet
- AGile and TestingDocument11 pagesAGile and TestingPrasadlee LeeNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Area Quiz-Project Integration ManagementDocument4 pagesKnowledge Area Quiz-Project Integration Managementcrown212No ratings yet
- PMP StudyDocument336 pagesPMP StudysunnyNo ratings yet
- PMP Examination Content Outline June 2019Document15 pagesPMP Examination Content Outline June 2019swathyNo ratings yet
- 08 Mastering ITTO Cheat SheetsDocument6 pages08 Mastering ITTO Cheat SheetsDileep Kumar Motukuri50% (2)
- How To Become A Project ManagerDocument9 pagesHow To Become A Project ManagerLaura LugoNo ratings yet
- Agility Project Manage M NTDocument8 pagesAgility Project Manage M NTAmelia AlresnaNo ratings yet
- PMP Full Process MapDocument14 pagesPMP Full Process MapSIBINNo ratings yet
- List of Requirements For Project PlanDocument11 pagesList of Requirements For Project PlanAdam Ong100% (1)
- 50 Project Management Terms You Should Know - Whizlabs BlogDocument14 pages50 Project Management Terms You Should Know - Whizlabs BlogPhineasGageNo ratings yet
- PMP ProcessesDocument9 pagesPMP ProcessesRobincrusoe100% (3)
- PMP Certification Practice Exam 50Document16 pagesPMP Certification Practice Exam 50ChelixNo ratings yet
- PMP Tools and Techniques in SummaryDocument22 pagesPMP Tools and Techniques in Summaryahmedmoin1159No ratings yet
- PM620 Unit 4 DBDocument3 pagesPM620 Unit 4 DBmikeNo ratings yet
- 200 PMBOK 6th Edition Practice QuestionsDocument86 pages200 PMBOK 6th Edition Practice QuestionsTuan Linh Tran100% (1)
- Rita Process ChartDocument1 pageRita Process Chartaa k100% (1)
- PMP Exam Preparation PlansDocument6 pagesPMP Exam Preparation PlansRogelio RomeroNo ratings yet
- Lynda - PMP - Communication Channels QuestionsDocument2 pagesLynda - PMP - Communication Channels QuestionsSatish Raghupathi100% (1)
- PMP Documents - ExcelDocument3 pagesPMP Documents - ExcelCharlotte LiamNo ratings yet
- Pmp-Course: Mr. Chris McpheeDocument4 pagesPmp-Course: Mr. Chris McpheeSanjiv SinghNo ratings yet
- Agile PMDocument5 pagesAgile PMSatyamNo ratings yet
- Software Process ModelsDocument10 pagesSoftware Process ModelsDexter KamalNo ratings yet
- JIRA Cheat SheetDocument1 pageJIRA Cheat SheetChristian MartiniNo ratings yet
- Project Success CriteriaDocument4 pagesProject Success CriteriayettipenaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Professional (Pmi) Study GuideDocument284 pagesProject Management Professional (Pmi) Study GuideMagdy El-GhobashyNo ratings yet
- PMI-ACP Exam Prep: Glossary of Agile TermsDocument17 pagesPMI-ACP Exam Prep: Glossary of Agile Termspromethuschow100% (1)
- Qvive PMP Formulas PMBOK6 v1bDocument1 pageQvive PMP Formulas PMBOK6 v1bObi A AgusioboNo ratings yet
- Project Management Sample 2024Document32 pagesProject Management Sample 2024Vibrant PublishersNo ratings yet
- PMP Certification Study Notes 4 - Project Integration ManagementDocument5 pagesPMP Certification Study Notes 4 - Project Integration ManagementlogaritmNo ratings yet
- PMP Downloadable Flash Cards - Predecessor-SuccessorDocument17 pagesPMP Downloadable Flash Cards - Predecessor-Successorridbuzz100% (3)
- Individual and Team Goals - Agile Sparks 2012Document7 pagesIndividual and Team Goals - Agile Sparks 2012Yuval YeretNo ratings yet
- Epfo Online Recruitment Application (Ora) PreviewDocument2 pagesEpfo Online Recruitment Application (Ora) Previewkhushwant kumarNo ratings yet
- Supplier Relations and Supply Chain Performance in Financial ProccessDocument23 pagesSupplier Relations and Supply Chain Performance in Financial Proccessivan platiniNo ratings yet
- Quia - InS 21 Quiz 2 - Session Ins 21 Chapter 2Document5 pagesQuia - InS 21 Quiz 2 - Session Ins 21 Chapter 2toll_meNo ratings yet
- 8-Monthly Project Progress ReportDocument1 page8-Monthly Project Progress ReportHimanshu PawarNo ratings yet
- Retail BankingDocument9 pagesRetail BankingMohan KottuNo ratings yet
- Activity Procter & Gamble (P&G) Balogo, Aljean Kaye S. Bsbaom601ADocument3 pagesActivity Procter & Gamble (P&G) Balogo, Aljean Kaye S. Bsbaom601AOragon LatosaNo ratings yet
- Vision: Innovative Assessment SystemDocument3 pagesVision: Innovative Assessment SystemSachin YadavNo ratings yet
- Kadamba Transport Corporation Limited: (Government of Goa Undertaking)Document3 pagesKadamba Transport Corporation Limited: (Government of Goa Undertaking)Siva Ram kambapuNo ratings yet
- Isaca Code of Professional Ethics Is Auditing Standards Is Auditing Guidelines Tools and TechniquesDocument20 pagesIsaca Code of Professional Ethics Is Auditing Standards Is Auditing Guidelines Tools and TechniquesARTHURNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Account (Motor Vehicle)Document2 pagesDepreciation Account (Motor Vehicle)BELLA CYNTHIA LESMANA WONGSONo ratings yet
- Adjective Plus Preposition WorksheetDocument4 pagesAdjective Plus Preposition WorksheetRUTH MARIBEL MAMANI MAMANINo ratings yet
- Eco AssignmentDocument6 pagesEco Assignmentshashwat shuklaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Strategic ManagementDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Strategic ManagementPermalino Borja Rose AnneNo ratings yet
- Nonprofit VsDocument3 pagesNonprofit VsRoschelle MiguelNo ratings yet
- 56 Brand Management at HCL (Vishal)Document77 pages56 Brand Management at HCL (Vishal)sheemankhanNo ratings yet
- Track & Trace Express - DHL - GlobalDocument2 pagesTrack & Trace Express - DHL - GlobalDragimage JenianNo ratings yet
- Project Handover ChecklistDocument4 pagesProject Handover ChecklistMikeNo ratings yet
- Da Nang Identifies 7 Key Areas For Economic Development 2023Document4 pagesDa Nang Identifies 7 Key Areas For Economic Development 2023NHƯ THƯƠNGNo ratings yet
- Investments Bodie Kane Marcus 9th Edition Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesInvestments Bodie Kane Marcus 9th Edition Solutions ManualMonicaAcostagzqkx100% (91)
- Roles and Challenges of Specialized BanksDocument12 pagesRoles and Challenges of Specialized BanksSadman SafayetNo ratings yet
- Nicolo Di Jerlando ResumeDocument3 pagesNicolo Di Jerlando Resumeapi-376266725No ratings yet
- Shop Supplies & Hand Tools PDFDocument194 pagesShop Supplies & Hand Tools PDFAngelito MuñozNo ratings yet
- BlackbookDocument46 pagesBlackbookunknowgamer9820680832No ratings yet
- Medical Store Rs. 4.64 MillionDocument17 pagesMedical Store Rs. 4.64 MillionMohtashim SolankiNo ratings yet
- Batch2 - Shruti SharmaDocument22 pagesBatch2 - Shruti Sharmashivendra singhNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Economics of Strategy 7th Edition by DranoveDocument14 pagesTest Bank For Economics of Strategy 7th Edition by Dranovewinry100% (1)