Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Using The Kepner Tregoe Matrix'
Using The Kepner Tregoe Matrix'
Uploaded by
Marilyn SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Development and Deployment of Multiplayer Online Games, Vol. IIDocument437 pagesDevelopment and Deployment of Multiplayer Online Games, Vol. IItiyihis146100% (1)
- Laboratory Activities Computer Engineering Drafting and DesignDocument74 pagesLaboratory Activities Computer Engineering Drafting and DesignPaul Santos Nonat75% (4)
- Engineering Management (CH 2: Decision Making)Document2 pagesEngineering Management (CH 2: Decision Making)oddonekun100% (5)
- Kepner Tregoe Decision MakingDocument4 pagesKepner Tregoe Decision Makingarie_susantoNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document11 pagesModule 7Kharxz Hanz Christian Galendez100% (1)
- Chapter 7 p1Document20 pagesChapter 7 p1hasan jabrNo ratings yet
- Decision Matrix - Selection GridDocument4 pagesDecision Matrix - Selection GridSmriti ShahNo ratings yet
- 10.11 Effectiveness Review PUB 5519Document3 pages10.11 Effectiveness Review PUB 5519Yu-Chih PuNo ratings yet
- Guide To Case AnalysisDocument21 pagesGuide To Case AnalysisJayson TasarraNo ratings yet
- KepnerDocument2 pagesKepnerLavanya BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- In This Post, I Will Discuss The DMAIC Approach To Project Management. The Full Form of DMAIC Is Define, Measure, Analysis, Improve and ControlDocument7 pagesIn This Post, I Will Discuss The DMAIC Approach To Project Management. The Full Form of DMAIC Is Define, Measure, Analysis, Improve and ControlVenkatramani GireesanNo ratings yet
- Mansci TermsDocument6 pagesMansci TermsKrisshaNo ratings yet
- 490 14Document15 pages490 14Riski Fitri DamayNo ratings yet
- BUS 433 Lecture NoteDocument11 pagesBUS 433 Lecture NoteukachiNo ratings yet
- Tradeoff Analysis ExampleDocument2 pagesTradeoff Analysis ExampleAdrián PérezNo ratings yet
- Kepner TregoeDocument8 pagesKepner TregoebuckianNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving PPT Neww2023Document33 pagesProblem Solving PPT Neww2023Seham AlyNo ratings yet
- ProblemsolvingmodelDocument5 pagesProblemsolvingmodelnizam.ramlanNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document2 pagesActivity 6Kaye Joy TendenciaNo ratings yet
- The Six Step Problem Solving ModelDocument9 pagesThe Six Step Problem Solving Modeleswaa1979No ratings yet
- Evaluating Public-Private Partnerships: Mst. Sahiba Mahbub Assistant Professor Department of Public AdministrationDocument15 pagesEvaluating Public-Private Partnerships: Mst. Sahiba Mahbub Assistant Professor Department of Public AdministrationzamNo ratings yet
- 5068 Preskill Chapter 5Document80 pages5068 Preskill Chapter 5pj501No ratings yet
- Prescriptive Model Report DummyDocument5 pagesPrescriptive Model Report DummyMaestro GallaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Approaches, Framework, and DesignsDocument15 pagesEvaluation Approaches, Framework, and DesignsDanson Githinji ENo ratings yet
- Multicriteria Decision MakingDocument3 pagesMulticriteria Decision MakingNicole AutrizNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Decision Making in MaintaiananceDocument17 pagesChapter3 Decision Making in Maintaianancemolla biyadgieNo ratings yet
- Effective Decision MakingDocument41 pagesEffective Decision MakingAjanthan AlagaratnamNo ratings yet
- Background: D - Define M - Measure A - AnalyzeDocument13 pagesBackground: D - Define M - Measure A - Analyzehaseeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- 8D Methodology and Line BalancingDocument4 pages8D Methodology and Line BalancingMd Nayeemur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Model - 207Document6 pagesProblem Solving Model - 207Cristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making: Paolo E. Mamaspas Kimberly C. Vallesterol Junuel T. Malbas Jackson S. Joanino Christian L. LeddaDocument12 pagesDecision-Making: Paolo E. Mamaspas Kimberly C. Vallesterol Junuel T. Malbas Jackson S. Joanino Christian L. LeddaEdfandy CatusalemNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving in OperationDocument3 pagesProblem Solving in OperationMohammad RakibNo ratings yet
- Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Tools: Developed by Dr. Martyn Jones, The University of Manchester, January 2016Document29 pagesMulti-Criteria Decision Analysis Tools: Developed by Dr. Martyn Jones, The University of Manchester, January 2016Narmada NandanaNo ratings yet
- Chap - 3 QC ToolsDocument12 pagesChap - 3 QC ToolsSnehlata SarafNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Answer The FollowingDocument2 pagesExercise 1: Answer The FollowingArc Angel Matias SerranoNo ratings yet
- 6 Step Problem Solving ProcessDocument9 pages6 Step Problem Solving ProcessLalitha VbNo ratings yet
- 4 Levels of Training KPIsDocument8 pages4 Levels of Training KPIsSonal ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Decision Matrix Selection MatrixDocument2 pagesDecision Matrix Selection MatrixEng Muhammad MarzoukNo ratings yet
- Operation ResearchDocument25 pagesOperation Researchaishdesai31No ratings yet
- Part 1: This Business of PerformanceDocument4 pagesPart 1: This Business of PerformancesheeshgarNo ratings yet
- Managing Continuous Improvement SystemDocument18 pagesManaging Continuous Improvement SystemDark KnightNo ratings yet
- TQM, Lecture-11+12Document18 pagesTQM, Lecture-11+12Shakeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Design SynthesisDocument19 pagesDesign SynthesisSA Le AsasNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal MethodDocument11 pagesPerformance Appraisal MethodShibly100% (2)
- Metodologia de 4 CuadrantesDocument7 pagesMetodologia de 4 CuadrantesJolukalel Camargo0% (1)
- Activity 2..Document1 pageActivity 2..hyunsuk fhebieNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Evaluating Employee PerformanceDocument16 pagesChapter-6 Evaluating Employee PerformanceSaimon AbedinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document7 pagesChapter 14chinggay_chingNo ratings yet
- Problem Tooles BinitaDocument50 pagesProblem Tooles Binitapaulyn ramosNo ratings yet
- Springer MCADocument32 pagesSpringer MCANguyet Thanh DuongNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Management Canadian 8Th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesFundamentals of Management Canadian 8Th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFyvonne.simmons102100% (21)
- Fundamentals of Management Canadian 8th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesFundamentals of Management Canadian 8th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual 1paulwoodpiszdfckxy100% (36)
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1hassantamer2005a1No ratings yet
- Presentation OPJ Corrective ActionDocument7 pagesPresentation OPJ Corrective Actionmaadhu MNo ratings yet
- On Potential Problem Analysis: Under The Guidance ofDocument7 pagesOn Potential Problem Analysis: Under The Guidance ofMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Model For Case AnalysisDocument10 pagesModel For Case AnalysisRekininternetuNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Program EvaluationDocument6 pagesApproaches To Program EvaluationicaNo ratings yet
- Optimization ProblemsDocument39 pagesOptimization ProblemsRohit NaiduNo ratings yet
- The Kirk Patrick Model of Training EvaluationDocument17 pagesThe Kirk Patrick Model of Training EvaluationarywisesaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Kaizen BaDocument87 pagesPresentation Kaizen BaAbela DrrsNo ratings yet
- Apply Problem Solving Edited For StudentsDocument27 pagesApply Problem Solving Edited For StudentsFelekePhiliphosNo ratings yet
- ROADBLOCKS: Checklist of 101 Idea Stoppers For Negative ThinkersDocument1 pageROADBLOCKS: Checklist of 101 Idea Stoppers For Negative ThinkersMarilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Kepner Tregoe Matrix - TemplateDocument3 pagesKepner Tregoe Matrix - TemplateMarilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Example 03Document4 pagesTutorial 1: Example 03Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Example 02: SADT Analysis of Job Shop Production at Massy Energy Fabric Maintenance (MEFM)Document3 pagesExample 02: SADT Analysis of Job Shop Production at Massy Energy Fabric Maintenance (MEFM)Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Tut01 SADT Example01Document4 pagesTut01 SADT Example01Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Tut01 Analysis Sample (FoodCart) Feb2021Document17 pagesTut01 Analysis Sample (FoodCart) Feb2021Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- TQM T01 SADTSAnalysis Jan202122Document1 pageTQM T01 SADTSAnalysis Jan202122Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Minimum Wage Act PowerPointDocument9 pagesMinimum Wage Act PowerPointMarilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Test: Module 7 Vocabulary: PIONEER Beginners - American EditionDocument3 pagesTest: Module 7 Vocabulary: PIONEER Beginners - American EditionMiguel Angel Alvarado50% (2)
- All ABOUT ELECTRICAL MOTORSDocument160 pagesAll ABOUT ELECTRICAL MOTORSkajale.shrikant100% (2)
- Slyp 818Document39 pagesSlyp 818ASWINNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document9 pagesLesson 1Brian MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Timothy Leary Bibliography: ArticlesDocument8 pagesTimothy Leary Bibliography: ArticlesLeandroNo ratings yet
- Lab NoDocument8 pagesLab NoAli MohsinNo ratings yet
- Information TheoryDocument16 pagesInformation TheoryPrajwal MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 23.401: Technical SpecificationDocument418 pages3GPP TS 23.401: Technical SpecificationDani SusantoNo ratings yet
- A Quick Guide To Digital Video Resolution and Aspect Ratio ConversionsDocument17 pagesA Quick Guide To Digital Video Resolution and Aspect Ratio ConversionsRupert WalkerNo ratings yet
- KivyDocument776 pagesKivyNabil SouakiNo ratings yet
- দুই পেজের সিভি 2 Page CvDocument4 pagesদুই পেজের সিভি 2 Page Cvibrahimcomputershop01No ratings yet
- Rashid MahdiDocument2 pagesRashid Mahdiandreea9827No ratings yet
- 4 - SPC-FD-Part 4 of 5-Division 26Document1 page4 - SPC-FD-Part 4 of 5-Division 26Fathy RamadanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Data MiningDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Data MiningbharathimanianNo ratings yet
- BMW Ksd2!09!2018 Service InformationDocument23 pagesBMW Ksd2!09!2018 Service Informationnatashagutierrez240187rio100% (117)
- MiviiDocument8 pagesMiviiVencislav SlavovNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Shikha Agrawal: Initialization of 80386DX, Debugging and Virtual 8086 ModeDocument14 pagesPrepared by Shikha Agrawal: Initialization of 80386DX, Debugging and Virtual 8086 Modeshikhamailme84No ratings yet
- Lab Journal 4 14032023 104921amDocument8 pagesLab Journal 4 14032023 104921amHammad MashwaniNo ratings yet
- WOLFKING PRESENTATION ÀÇÍõ éÉÜDocument45 pagesWOLFKING PRESENTATION ÀÇÍõ éÉÜzackerzhuNo ratings yet
- CheckPoint VPN-1 FireWall-1 NG Management I Instructor SlidesDocument198 pagesCheckPoint VPN-1 FireWall-1 NG Management I Instructor SlidesdanilofantinatoNo ratings yet
- Control Systems: Dr. Anilesh DeyDocument20 pagesControl Systems: Dr. Anilesh DeyTanay ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- About Me: LinkedinDocument2 pagesAbout Me: LinkedinsoftifyrankNo ratings yet
- 8-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTDocument10 pages8-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTMerab KvitsaridzeNo ratings yet
- Revision Test 5 Maximum Marks 50 Answer All Questions Duration 2.00 HrsDocument1 pageRevision Test 5 Maximum Marks 50 Answer All Questions Duration 2.00 HrsGlan DevadhasNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2021-22 SWE2001 ELA VL2021220504513 Reference Material I 01-03-2022 Challenging1 and 2Document6 pagesWINSEM2021-22 SWE2001 ELA VL2021220504513 Reference Material I 01-03-2022 Challenging1 and 2Sri Pritika BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- egrzvs4-65d-r6n43-product-specificationsDocument6 pagesegrzvs4-65d-r6n43-product-specificationsantlozNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Document4 pagesApplied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- STAT-205 (IT) Mid Term PaperDocument2 pagesSTAT-205 (IT) Mid Term PaperMuhammad SaqlainNo ratings yet
Using The Kepner Tregoe Matrix'
Using The Kepner Tregoe Matrix'
Uploaded by
Marilyn SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Using The Kepner Tregoe Matrix'
Using The Kepner Tregoe Matrix'
Uploaded by
Marilyn SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
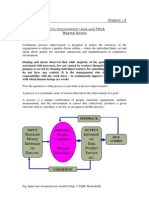
Kepner Tregoe Matrix
The Kepner Tregoe matrix is a tool used to support organisational decision making. Through
a focus on risk assessment and prioritisation, it aims to achieve a course of action or
outcome with the least negative consequences. The approach guides users through the
setting of objectives, prioritising alternatives, exploring the weaknesses of these
alternatives, and ultimately identifying the solution that is ‘best’. Additionally, the method
assists with the preparation of plans for problems that may arise as a consequence of the
decision made.
There are four major steps in this approach. Situation appraisal: the present situation is
clarified and priorities are set; Problem analysis: the problem is defined and its root cause is
determined; Decision analysis: a risk analysis is performed for alternative courses of action
or solutions; and Potential problem analysis: the best courses of action are analysed and
potential problems and responses to minimise their risk are identified.
Using the ‘Kepner Tregoe Matrix’
Step 1: A problem statement is developed, clarifying the objectives of the decision and
actions that are required.
Step 2: A summary is created of the strategic requirements (must-haves), operational
objectives (want-to-haves), and limits.
Step 3: The operational objectives are quantitatively ranked from most to least important,
using a predetermined scale.
Step 4: A list of alternative courses of action is generated.
Step 5: Only courses of action that align with the ‘must-have’ requirements are retained.
The remaining courses of action are scored against each objective using a scale from 1 to 10,
where 1 is used to represent a course of action that is not suitable to achieving the
objectives and 10 for courses of action that are suitable for achieving the objectives. This
should be referred to as the satisfaction score.
Step 6: Each objective is given a weight, or assigned a numerical value between 1-10, on the
basis of its importance. 1 represents an objective of low importance and 10 an objective of
high importance. A weighted score is calculated for each objective for each course of action
by multiplying the value assigned for the weight, by the satisfaction score assigned to it in
the previous step.
Step 7: Potential problems or issues with the top three courses of action are considered. The
probability and significance of these is scored.
Step 8: An ‘adversity rating’ is calculated that scores all adverse effects for each course of
action.
Step 9: The adversity rating for each course of action is subtracted from its weighted score
and the option with the highest total is selected.
Step 10: All negative consequences of the ‘winning’ course of action are determined and
plans derived to minimise their effects.
You might also like
- Development and Deployment of Multiplayer Online Games, Vol. IIDocument437 pagesDevelopment and Deployment of Multiplayer Online Games, Vol. IItiyihis146100% (1)
- Laboratory Activities Computer Engineering Drafting and DesignDocument74 pagesLaboratory Activities Computer Engineering Drafting and DesignPaul Santos Nonat75% (4)
- Engineering Management (CH 2: Decision Making)Document2 pagesEngineering Management (CH 2: Decision Making)oddonekun100% (5)
- Kepner Tregoe Decision MakingDocument4 pagesKepner Tregoe Decision Makingarie_susantoNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document11 pagesModule 7Kharxz Hanz Christian Galendez100% (1)
- Chapter 7 p1Document20 pagesChapter 7 p1hasan jabrNo ratings yet
- Decision Matrix - Selection GridDocument4 pagesDecision Matrix - Selection GridSmriti ShahNo ratings yet
- 10.11 Effectiveness Review PUB 5519Document3 pages10.11 Effectiveness Review PUB 5519Yu-Chih PuNo ratings yet
- Guide To Case AnalysisDocument21 pagesGuide To Case AnalysisJayson TasarraNo ratings yet
- KepnerDocument2 pagesKepnerLavanya BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- In This Post, I Will Discuss The DMAIC Approach To Project Management. The Full Form of DMAIC Is Define, Measure, Analysis, Improve and ControlDocument7 pagesIn This Post, I Will Discuss The DMAIC Approach To Project Management. The Full Form of DMAIC Is Define, Measure, Analysis, Improve and ControlVenkatramani GireesanNo ratings yet
- Mansci TermsDocument6 pagesMansci TermsKrisshaNo ratings yet
- 490 14Document15 pages490 14Riski Fitri DamayNo ratings yet
- BUS 433 Lecture NoteDocument11 pagesBUS 433 Lecture NoteukachiNo ratings yet
- Tradeoff Analysis ExampleDocument2 pagesTradeoff Analysis ExampleAdrián PérezNo ratings yet
- Kepner TregoeDocument8 pagesKepner TregoebuckianNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving PPT Neww2023Document33 pagesProblem Solving PPT Neww2023Seham AlyNo ratings yet
- ProblemsolvingmodelDocument5 pagesProblemsolvingmodelnizam.ramlanNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document2 pagesActivity 6Kaye Joy TendenciaNo ratings yet
- The Six Step Problem Solving ModelDocument9 pagesThe Six Step Problem Solving Modeleswaa1979No ratings yet
- Evaluating Public-Private Partnerships: Mst. Sahiba Mahbub Assistant Professor Department of Public AdministrationDocument15 pagesEvaluating Public-Private Partnerships: Mst. Sahiba Mahbub Assistant Professor Department of Public AdministrationzamNo ratings yet
- 5068 Preskill Chapter 5Document80 pages5068 Preskill Chapter 5pj501No ratings yet
- Prescriptive Model Report DummyDocument5 pagesPrescriptive Model Report DummyMaestro GallaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Approaches, Framework, and DesignsDocument15 pagesEvaluation Approaches, Framework, and DesignsDanson Githinji ENo ratings yet
- Multicriteria Decision MakingDocument3 pagesMulticriteria Decision MakingNicole AutrizNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Decision Making in MaintaiananceDocument17 pagesChapter3 Decision Making in Maintaianancemolla biyadgieNo ratings yet
- Effective Decision MakingDocument41 pagesEffective Decision MakingAjanthan AlagaratnamNo ratings yet
- Background: D - Define M - Measure A - AnalyzeDocument13 pagesBackground: D - Define M - Measure A - Analyzehaseeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- 8D Methodology and Line BalancingDocument4 pages8D Methodology and Line BalancingMd Nayeemur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Model - 207Document6 pagesProblem Solving Model - 207Cristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making: Paolo E. Mamaspas Kimberly C. Vallesterol Junuel T. Malbas Jackson S. Joanino Christian L. LeddaDocument12 pagesDecision-Making: Paolo E. Mamaspas Kimberly C. Vallesterol Junuel T. Malbas Jackson S. Joanino Christian L. LeddaEdfandy CatusalemNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving in OperationDocument3 pagesProblem Solving in OperationMohammad RakibNo ratings yet
- Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Tools: Developed by Dr. Martyn Jones, The University of Manchester, January 2016Document29 pagesMulti-Criteria Decision Analysis Tools: Developed by Dr. Martyn Jones, The University of Manchester, January 2016Narmada NandanaNo ratings yet
- Chap - 3 QC ToolsDocument12 pagesChap - 3 QC ToolsSnehlata SarafNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Answer The FollowingDocument2 pagesExercise 1: Answer The FollowingArc Angel Matias SerranoNo ratings yet
- 6 Step Problem Solving ProcessDocument9 pages6 Step Problem Solving ProcessLalitha VbNo ratings yet
- 4 Levels of Training KPIsDocument8 pages4 Levels of Training KPIsSonal ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Decision Matrix Selection MatrixDocument2 pagesDecision Matrix Selection MatrixEng Muhammad MarzoukNo ratings yet
- Operation ResearchDocument25 pagesOperation Researchaishdesai31No ratings yet
- Part 1: This Business of PerformanceDocument4 pagesPart 1: This Business of PerformancesheeshgarNo ratings yet
- Managing Continuous Improvement SystemDocument18 pagesManaging Continuous Improvement SystemDark KnightNo ratings yet
- TQM, Lecture-11+12Document18 pagesTQM, Lecture-11+12Shakeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Design SynthesisDocument19 pagesDesign SynthesisSA Le AsasNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal MethodDocument11 pagesPerformance Appraisal MethodShibly100% (2)
- Metodologia de 4 CuadrantesDocument7 pagesMetodologia de 4 CuadrantesJolukalel Camargo0% (1)
- Activity 2..Document1 pageActivity 2..hyunsuk fhebieNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Evaluating Employee PerformanceDocument16 pagesChapter-6 Evaluating Employee PerformanceSaimon AbedinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document7 pagesChapter 14chinggay_chingNo ratings yet
- Problem Tooles BinitaDocument50 pagesProblem Tooles Binitapaulyn ramosNo ratings yet
- Springer MCADocument32 pagesSpringer MCANguyet Thanh DuongNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Management Canadian 8Th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesFundamentals of Management Canadian 8Th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFyvonne.simmons102100% (21)
- Fundamentals of Management Canadian 8th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesFundamentals of Management Canadian 8th Edition Robbins Solutions Manual 1paulwoodpiszdfckxy100% (36)
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1hassantamer2005a1No ratings yet
- Presentation OPJ Corrective ActionDocument7 pagesPresentation OPJ Corrective Actionmaadhu MNo ratings yet
- On Potential Problem Analysis: Under The Guidance ofDocument7 pagesOn Potential Problem Analysis: Under The Guidance ofMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Model For Case AnalysisDocument10 pagesModel For Case AnalysisRekininternetuNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Program EvaluationDocument6 pagesApproaches To Program EvaluationicaNo ratings yet
- Optimization ProblemsDocument39 pagesOptimization ProblemsRohit NaiduNo ratings yet
- The Kirk Patrick Model of Training EvaluationDocument17 pagesThe Kirk Patrick Model of Training EvaluationarywisesaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Kaizen BaDocument87 pagesPresentation Kaizen BaAbela DrrsNo ratings yet
- Apply Problem Solving Edited For StudentsDocument27 pagesApply Problem Solving Edited For StudentsFelekePhiliphosNo ratings yet
- ROADBLOCKS: Checklist of 101 Idea Stoppers For Negative ThinkersDocument1 pageROADBLOCKS: Checklist of 101 Idea Stoppers For Negative ThinkersMarilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Kepner Tregoe Matrix - TemplateDocument3 pagesKepner Tregoe Matrix - TemplateMarilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Example 03Document4 pagesTutorial 1: Example 03Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Example 02: SADT Analysis of Job Shop Production at Massy Energy Fabric Maintenance (MEFM)Document3 pagesExample 02: SADT Analysis of Job Shop Production at Massy Energy Fabric Maintenance (MEFM)Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Tut01 SADT Example01Document4 pagesTut01 SADT Example01Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Tut01 Analysis Sample (FoodCart) Feb2021Document17 pagesTut01 Analysis Sample (FoodCart) Feb2021Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- TQM T01 SADTSAnalysis Jan202122Document1 pageTQM T01 SADTSAnalysis Jan202122Marilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Minimum Wage Act PowerPointDocument9 pagesMinimum Wage Act PowerPointMarilyn SinghNo ratings yet
- Test: Module 7 Vocabulary: PIONEER Beginners - American EditionDocument3 pagesTest: Module 7 Vocabulary: PIONEER Beginners - American EditionMiguel Angel Alvarado50% (2)
- All ABOUT ELECTRICAL MOTORSDocument160 pagesAll ABOUT ELECTRICAL MOTORSkajale.shrikant100% (2)
- Slyp 818Document39 pagesSlyp 818ASWINNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document9 pagesLesson 1Brian MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Timothy Leary Bibliography: ArticlesDocument8 pagesTimothy Leary Bibliography: ArticlesLeandroNo ratings yet
- Lab NoDocument8 pagesLab NoAli MohsinNo ratings yet
- Information TheoryDocument16 pagesInformation TheoryPrajwal MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 23.401: Technical SpecificationDocument418 pages3GPP TS 23.401: Technical SpecificationDani SusantoNo ratings yet
- A Quick Guide To Digital Video Resolution and Aspect Ratio ConversionsDocument17 pagesA Quick Guide To Digital Video Resolution and Aspect Ratio ConversionsRupert WalkerNo ratings yet
- KivyDocument776 pagesKivyNabil SouakiNo ratings yet
- দুই পেজের সিভি 2 Page CvDocument4 pagesদুই পেজের সিভি 2 Page Cvibrahimcomputershop01No ratings yet
- Rashid MahdiDocument2 pagesRashid Mahdiandreea9827No ratings yet
- 4 - SPC-FD-Part 4 of 5-Division 26Document1 page4 - SPC-FD-Part 4 of 5-Division 26Fathy RamadanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Data MiningDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Data MiningbharathimanianNo ratings yet
- BMW Ksd2!09!2018 Service InformationDocument23 pagesBMW Ksd2!09!2018 Service Informationnatashagutierrez240187rio100% (117)
- MiviiDocument8 pagesMiviiVencislav SlavovNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Shikha Agrawal: Initialization of 80386DX, Debugging and Virtual 8086 ModeDocument14 pagesPrepared by Shikha Agrawal: Initialization of 80386DX, Debugging and Virtual 8086 Modeshikhamailme84No ratings yet
- Lab Journal 4 14032023 104921amDocument8 pagesLab Journal 4 14032023 104921amHammad MashwaniNo ratings yet
- WOLFKING PRESENTATION ÀÇÍõ éÉÜDocument45 pagesWOLFKING PRESENTATION ÀÇÍõ éÉÜzackerzhuNo ratings yet
- CheckPoint VPN-1 FireWall-1 NG Management I Instructor SlidesDocument198 pagesCheckPoint VPN-1 FireWall-1 NG Management I Instructor SlidesdanilofantinatoNo ratings yet
- Control Systems: Dr. Anilesh DeyDocument20 pagesControl Systems: Dr. Anilesh DeyTanay ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- About Me: LinkedinDocument2 pagesAbout Me: LinkedinsoftifyrankNo ratings yet
- 8-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTDocument10 pages8-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTMerab KvitsaridzeNo ratings yet
- Revision Test 5 Maximum Marks 50 Answer All Questions Duration 2.00 HrsDocument1 pageRevision Test 5 Maximum Marks 50 Answer All Questions Duration 2.00 HrsGlan DevadhasNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2021-22 SWE2001 ELA VL2021220504513 Reference Material I 01-03-2022 Challenging1 and 2Document6 pagesWINSEM2021-22 SWE2001 ELA VL2021220504513 Reference Material I 01-03-2022 Challenging1 and 2Sri Pritika BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- egrzvs4-65d-r6n43-product-specificationsDocument6 pagesegrzvs4-65d-r6n43-product-specificationsantlozNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Document4 pagesApplied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- STAT-205 (IT) Mid Term PaperDocument2 pagesSTAT-205 (IT) Mid Term PaperMuhammad SaqlainNo ratings yet