Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Keratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's Spots
Keratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's Spots
Uploaded by
Nimish BajareOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Keratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's Spots
Keratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's Spots
Uploaded by
Nimish BajareCopyright:
Available Formats
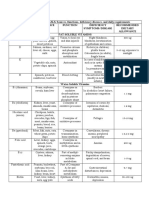
Table 8.
Major biochemical functions Dietary sources RDA (per day)
Vitamin
Deficiency nifestations
Normal vision (dim light vision Fish liver oils, whole milk, Men: 3,500 IU
A
and colour vision) eggs, butter, meat, leafy (or) 1,000 ug
Night blindness (nyctalopia)
Cell growth and differentiation, vegetables and carrots
Women: 2,800 IU
Xerophthalmia, Bitot's spots,
immunity, maintenance of
Keratomalacia in eyes
epithelium and antioxidant (or) 800 ug Skin lesions, atrophy of the
-function. epithelium leading to respiratory
and genitourinary infections
Blood calcium homeostasis Synthesised in the body with Adults: 200 IU Rickets in children
the help of sunlight (or) 5 ug
It contributes to blood Ca2+
(UV-rays). Osteomalacia in adults
levels. Growing children,
It regulates plasma Ca2+ levels Oily fish, egg yolk, organ pregnant and lactating
along with parathormone and meat, butter and cheese. women: 400 IU (or)
Foods fortified with vitamin 10 ug
calcitonin.
D such as milk, margarine,
Bone mineralisation vanaspathi and baby foods
Natural anti-oxidant Vegetable edible oils such as Men: 10 mg
wheat germ oil, sunflower
Hemolytic anemia in premature
Prevents lipid peroxidation Women: 8 mg infants
and protects the integrity of oil, cotton seed oil and
In adults, degenerative changes
biological membranes. soyabean oil, corn oil
in muscles, sterility in animals
Required for blood coagulation Synthesised by intestinal Adults:70-140 ug Prolonged bleeding and
It activates the bacteria
clotting Newborn babies clotting times
factors II, VII, IX and X by Leafy vegetables, eggs and
carboxylating their glutamate should be given 1 mg
dairy products intramuscular injection in
residues.
a single dose
Antioxidant role, collagen Fresh fruits (citrus fruits,
synthesis Children and adults: Scurvy
amla and guava), green leafy 60-75 mg9
Plays a role in the metabolism vegetables (cabbage and Capillary fragility, increasing
of lipid, amino Pregnancy and lactation: hemorrhagic tendeneies
acids, iron, spinach) 9germinating pulses
100-120 mg manifested as petechiae
hemoglobin and some drugs ecchymoses and hematomas
(usually characterised by
Swollen and bleeding gums)
Generalised poor wound-healing
of vitamins
sources, RDA and deficiency manifestations
Table 8.7 (Contd) Summary of the major functions, dietary
Vitamin Major biochemical functions Dietary sources
RDA (per day) Deficiency manifestations
Adults: 1-1.5 mg Wet beri-beri is
B It functions through
Whole grain cereals (Hand characterised
or parboiled, Pregnancy and lactation: by cardiovascular signs such
its coenzyme thiamine pounded
unpolished rice), yeast,
as edema, palpitation and
pyrophosphate(TPP) in the 2m
tachycardia
legumes, oil seeds such
as
following reactions:
groundnut and animals foods Dry beri-beri is characterised by
Oxidative decarboxylation such as pork and beef signs of nervous system such as
(Pyruvate dehydrogenase, muscle wasting and peripheral
a-KG dehydrogenase) neuropathy
Transketolation (transketolase
Beri-beri is usually of the mixed
of HMP shunt)
type
Milk and dairy products, Adults: 1.5 mg Glossitis (magenta tongue),
It functions through its
B2 angular stomatitis, cheilosis,
coenzymes-FMN and FAD meat, fish and eggs. Whole Pregnancy and lactation:
which take part in oxidation- grain cereals, legumes and 2 mg
pharyngitis
reduction reactions catalysed germinating seeds
by many enzymes e.g. L-amino
acid oxidase (FMN)
PDH/succinate
dehydrogenase
lacyl CoA FAD
dehydrogenase/
xanthine oxidase
3 It functions through its Meat, beans, legumes, whole Adults: 20 mg Pellagra
coenzymes NAD and NADP grains, eggs and dried yeast characterised by diarrhea,
Pregnancy and lactation:
which take part in a variety dementia and dermatitis
25 mg
of oxidation-reduction
reactions where the transfer
of hydride ion is involved
NAD dependent enzymes:
e.g, PDH, LDH, B-hydroxy
acyl CoA dehydrogenase,
alcohol dehydrogenase
NADP dependent enzymes:
e.g, Glucose-6-phosphate
dehydrogenase and malic
enzyme
B It acts through its coenzyme Bran of cereals, dried Adults: 2 mg Neurological manifestations
pyridoxal phosphate yeast, legumes, nuts, leafy such as peripheral neuropathy.
(PLP) which is mostly vegetables, milk, eggs, meat Pregnancy and lactation:
2.5 mg mental confusion and
involved in reactions of and fish
amino acid metabolism depression. Microcytic
such as transamination, hypochromic anemia,
seborrheic dermatitis, carpal
decarboxylation,
transsulfuration. tunnel syndrome
Enzymes dependent on PLP:
e.g, ALP, AST, cystathionine
synthase
Takes part in carboxylation
by Soyabean, yeast, egg yolk, 200 to
reactions in gluconeogenesis, whole grains and organ Deficiency is uncommon
fatty acid synthesis. meat 300 mg since the minimal amounts
required are synthesised by the
Enzymes dependent on Biotin:
intestinal microflora
e.g, Pyruvate carboxylase and
acetyl CoA carboxylase
tamins
Vitamin Major biochemical functions Dietary sources RDA (perday)
It acts through coenzyme A in
Deficiency nifestations
Whole grains, vegetables, 10 mg
bs a wide variety of reactions. egumes, yeast, egg yolk and Deficiency is uncommon.
Enzymes dependent on organ meat Burning feet syndrome,
condition associated with mild
a
coenzyme A: Examples
include PDH, thiokinase, a-KG pantothenate deficieney
dehydrogenase and HMG COA
synthase
lt acts through its coenzymne Green leafy vegetables, Adults: 200 ug
tetrahydrofolate which whole grains, fruits, eggs
Macrocytic anemia with
plays a central role in one- and dairy products
Pregnancy: 400 ug megaloblastic changes in the
bone marrow
carbon metabolism. Folate is Lactation: 300 ug
associated with DNA, RNA and Neural tube defects in the
fetus
protein synthesis; amino acid
metabolism Hyperhomocysteinemia linked
to coronary artery disease
B2 It functions through its Organ meat (liver), meat, Adults: 1-2 ug Megaloblastic anemia,
coenzymes methyl cobalamin fish, eggs, milk, curd and subacute combined
Children: 0.5-1 ug
and deoxyadenosyl cobalamin. cheese degeneration, demyelination;
There are only two reactions in Pregnancy and pernicious anemia
humans known to involve B2 lactation: 3 ug/day
Synthesis of methionine from
homocysteine
Conversion of methylmalonyl
CoA to succinyl CoA
You might also like
- US Army Medical Course MD0937-200 - The Operating Room Specialist in The Centralized Materiel ServiceDocument134 pagesUS Army Medical Course MD0937-200 - The Operating Room Specialist in The Centralized Materiel ServiceGeorges100% (2)
- Rewiting PDFDocument107 pagesRewiting PDFEmmanuelOliveira75% (4)
- Module 1-Ergonomics and Facilities PlanningDocument12 pagesModule 1-Ergonomics and Facilities Planninglei melendrez100% (6)
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartGerarld Immanuel Kairupan100% (1)
- Vitamin/Mineral Chart Health Psychology: Vitamins Minerals Health Benefits Vitamin Source Recommended Daily IntakeDocument3 pagesVitamin/Mineral Chart Health Psychology: Vitamins Minerals Health Benefits Vitamin Source Recommended Daily IntakeQuarmina HesseNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument5 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartKaye Tubungbanua MatunogNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Notes Science Form 2Document9 pagesNutrition Notes Science Form 2Yi YingNo ratings yet
- Lab Values: Interpreting Chemistry and Hematology For Adult PatientsDocument36 pagesLab Values: Interpreting Chemistry and Hematology For Adult PatientsBrian Johnson100% (1)
- BCH 211 Lecture NoteDocument13 pagesBCH 211 Lecture NotemanomistephenNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)Document1 pageFat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)Satyam AnandNo ratings yet
- Christine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument5 pagesChristine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Cielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADocument10 pagesCielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- Nutrient ChartDocument7 pagesNutrient ChartDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument3 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsRan And SanNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential NutrientsDocument5 pages6 Essential NutrientsRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartJagan LogaiyaNo ratings yet
- जीवनसत्वे (VIDARBH IAS) -Document2 pagesजीवनसत्वे (VIDARBH IAS) -adityasjadhav2505No ratings yet
- Macronutrient Distribution Functions Utilization Food Sources RNI or Requirements MalnutritionDocument6 pagesMacronutrient Distribution Functions Utilization Food Sources RNI or Requirements MalnutritionCedrick AgresanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Table FormDocument7 pagesVitamins Table FormR-Chian Jose GermanpNo ratings yet
- N1 A3 BemhDocument4 pagesN1 A3 BemhSarahi MartinezNo ratings yet
- Retinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin ADocument2 pagesRetinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin AsashellNo ratings yet
- Kwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeDocument3 pagesKwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeJASHINEE A/P BASKARAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument23 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- AppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFDocument7 pagesAppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFMaria Christina LagartejaNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients - VitaminsDocument9 pagesMicronutrients - VitaminsKate SantosNo ratings yet
- VitMin - Guide - EN - PortalBranding - NoDate - Indd - Vitmin - GuideDocument4 pagesVitMin - Guide - EN - PortalBranding - NoDate - Indd - Vitmin - GuidepatgarettNo ratings yet
- Vitamin AsDocument37 pagesVitamin AsmarcelaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument6 pagesVitamin and Mineral Chartsellitt ngNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and NutritionDocument10 pagesVitamins and NutritionAnurag KumarNo ratings yet
- Study Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesDocument3 pagesStudy Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesAnugrah MNo ratings yet
- Study Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesDocument3 pagesStudy Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesWaseemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of FoodDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of Foodpclim2010No ratings yet
- Compilation of Fat-Soluble VitaminsDocument4 pagesCompilation of Fat-Soluble VitaminsYhannie PendangNo ratings yet
- Nur Syahirah Binti Mohd Yusri A170291: Nama Dan No. MatrikDocument7 pagesNur Syahirah Binti Mohd Yusri A170291: Nama Dan No. MatrikSyahirah YusriNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument8 pagesVitaminsecho tiongcoNo ratings yet
- IMP BiologyDocument22 pagesIMP Biologyvolesa9875No ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument2 pagesVitamins and MineralsHelen Mae GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Presented By: DR - Eglal Hakeim &DR - Hoda SyaedDocument33 pagesPresented By: DR - Eglal Hakeim &DR - Hoda Syaedbobovovo bobovovoNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument8 pagesVitamins & Mineralswardahmohammad2022No ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminsShivrajNo ratings yet
- Essential Amino AcidsDocument3 pagesEssential Amino Acidssania ziaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin NotesDocument3 pagesVitamin NotesKamran ZaheerNo ratings yet
- 5th Vitamins & MineralsDocument5 pages5th Vitamins & MineralsKennedy HouseNo ratings yet
- 6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietDocument27 pages6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietNigel Subhash BakkerNo ratings yet
- Classes of Food Source Functions Effects of Deficiency CarbohydratesDocument1 pageClasses of Food Source Functions Effects of Deficiency CarbohydratesUlya YeeaaNo ratings yet
- NutrientDocument1 pageNutrientJazz Astucia AzarconNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument61 pagesVitamins and MineralsMackoy LoganNo ratings yet
- Appendix C: Nutrient Chart - Function, Deficiency and Toxicity Symptoms, and Major Food SourcesDocument5 pagesAppendix C: Nutrient Chart - Function, Deficiency and Toxicity Symptoms, and Major Food SourcesMaria Christina LagartejaNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument2 pagesVitamindaroshamchaudhary1237No ratings yet
- Infant Nutrition and Feeding Infant Nutrition and FeedingDocument5 pagesInfant Nutrition and Feeding Infant Nutrition and FeedingGarv JainNo ratings yet
- Vitamins PresentationDocument21 pagesVitamins PresentationClarise MoringNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals TableDocument7 pagesVitamins and Minerals TableDHANUSRI K 1840747100% (1)
- Dietary Guidelines For Different Population Groups: Subject: Human Nutrition and Dietetics Student: Isela MenjivarDocument27 pagesDietary Guidelines For Different Population Groups: Subject: Human Nutrition and Dietetics Student: Isela MenjivarIsela Menjivar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Reaction of Glucose: CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesReaction of Glucose: CarbohydratesADITYA TIWARINo ratings yet
- Rickets in Children, Osteomalacia in Adults, Osteoporoisis in Oldage Retards Growth. Hairfall & Change in Skin. Reproduction FailureDocument3 pagesRickets in Children, Osteomalacia in Adults, Osteoporoisis in Oldage Retards Growth. Hairfall & Change in Skin. Reproduction FailureHarshan VPNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument17 pagesVitaminsnicholaschungu24No ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Nutrition 6.1 Type of NutritionDocument9 pagesChapter 6: Nutrition 6.1 Type of NutritionmariposillasNo ratings yet
- Vit EDocument2 pagesVit EkingpinNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Name: Miriam Harriott Grade: 10 Mignott Subject: Foods and Nutrition Teacher: Mrs. ThomasDocument22 pagesAssignment: Name: Miriam Harriott Grade: 10 Mignott Subject: Foods and Nutrition Teacher: Mrs. Thomasmiriam harriottNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Unit ThreeDocument49 pagesNutrition Unit ThreeMelchizedek Tagarino TorioNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Classes of FoodDocument16 pages2.1 The Classes of FoodFatin NazirahNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument2 pagesMineralsStacy WinterNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: 416.6 Grams/dayDocument5 pagesNutrition: 416.6 Grams/dayMargaret Nicole AboNo ratings yet
- Epileptic Disorders - 2023 - Tomson - The Pharmacological Treatment of Epilepsy in AdultsDocument21 pagesEpileptic Disorders - 2023 - Tomson - The Pharmacological Treatment of Epilepsy in AdultsIvan MihailovicNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of GITDocument21 pagesPharmacology of GITAlnzeer6No ratings yet
- Pharmacoeconomics 3rd Prof.Document64 pagesPharmacoeconomics 3rd Prof.Ahmed ImranNo ratings yet
- G12 - Pe 4 - Module 4Document14 pagesG12 - Pe 4 - Module 4John Lois VanNo ratings yet
- Interesting Phobias (Fears) : Preda Călin Ștefan Cls. A VII - A B Școala Gimnazială Sfinții Voievozi"Document4 pagesInteresting Phobias (Fears) : Preda Călin Ștefan Cls. A VII - A B Școala Gimnazială Sfinții Voievozi"Preda MirelaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Path Endocrine OutlineDocument46 pagesPath Endocrine Outlineaya derweshNo ratings yet
- Modern TimesDocument58 pagesModern TimesMicah DomingoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - FranciscomarionvelascoDocument10 pagesActivity 1 - FranciscomarionvelascoTek CasoneteNo ratings yet
- Sex-Linked: October 2020Document5 pagesSex-Linked: October 2020Fairus ShafiraNo ratings yet
- Dr. A. Samy TAG Upper Limb - 1Document20 pagesDr. A. Samy TAG Upper Limb - 1DRAHMEDFAHMYORTHOCLINICNo ratings yet
- Social Science & MedicineDocument9 pagesSocial Science & MedicineTriana virgaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge On Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemophilia Among Health Care ProfessionalDocument1 pageKnowledge On Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemophilia Among Health Care ProfessionalAnonymous SMLzNANo ratings yet
- Dysphagia SurgicalDocument75 pagesDysphagia Surgicalian ismail100% (1)
- ENGLISH 10 Q2 Module 5Document20 pagesENGLISH 10 Q2 Module 5Rubelyn CagapeNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Checker X Originality Report: Similarity Found: 12%Document10 pagesPlagiarism Checker X Originality Report: Similarity Found: 12%Project DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Case NoDocument19 pagesCase Nomuttaqin95No ratings yet
- Planetary Axle Wheel Ends PDFDocument64 pagesPlanetary Axle Wheel Ends PDFКонстантин КосаревNo ratings yet
- Functional Approaches To Pet Hospital DesignDocument154 pagesFunctional Approaches To Pet Hospital DesignotaamekiriNo ratings yet
- Libro Ciencia y TecnologiaDocument173 pagesLibro Ciencia y TecnologiaLorenzo FuentesNo ratings yet
- Rekap Jaga 14 Januari 2021 2Document2 pagesRekap Jaga 14 Januari 2021 2yafidyNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Intracranial Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Critical Assessment of Drug Induced CausesDocument10 pagesDrug Induced Intracranial Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Critical Assessment of Drug Induced CausesSerque777No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Papers MSUDocument20 pagesBiochemistry Papers MSUShiv BhattNo ratings yet
- ChloramphenicolDocument3 pagesChloramphenicolMarielyn Gabatin LegionNo ratings yet
- Im Grave's DiseaseDocument28 pagesIm Grave's DiseaseHidvardNo ratings yet
- Approach To Child With Headache: Dr. Vijaya Kumar Chikanbanjar 2nd Year Resident Department of PediatricsDocument49 pagesApproach To Child With Headache: Dr. Vijaya Kumar Chikanbanjar 2nd Year Resident Department of Pediatricsar bindraNo ratings yet