Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 viewsCoal Resources and Their Status in Nepal, BASKOTA, Shiv Kumar, Nepal
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal, BASKOTA, Shiv Kumar, Nepal
Uploaded by
Subash MahatThis document summarizes the coal resources and status of coal mining in Nepal. It describes the four main types of coal deposits in Nepal, including lignite, Siwalik coal, Cretaceous-Eocene coal, and Gondwana coal. Production of coal in Nepal peaked at around 10,000 metric tons per year from 2011-2013 but has since declined. Nepal imports more coal than it produces domestically. Challenges facing the coal mining industry in Nepal include small reserves, low coal quality, traditional mining methods, and bureaucratic hurdles. Mechanized mining is not viable, but efficiency could be improved through better tools. The government has stopped further coal exploration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Rumus Blending Batubara ADocument16 pagesRumus Blending Batubara AEka Setia0% (1)
- Sinai Auction 2020-2021Document64 pagesSinai Auction 2020-2021SinaiAcademyNo ratings yet
- Boq For Box CulvertDocument2 pagesBoq For Box CulvertDaniel Okere100% (1)
- Advanced Corporate Finance Quiz 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesAdvanced Corporate Finance Quiz 2 SolutionslaurenNo ratings yet
- Mr. Fahad Ali Rabbani: Name Roll No. Presented byDocument62 pagesMr. Fahad Ali Rabbani: Name Roll No. Presented byHajra AamirNo ratings yet
- KPK NGS Web Min Resources FinalDocument18 pagesKPK NGS Web Min Resources FinalAditya mahatoNo ratings yet
- Process of Cement Production in NepalDocument13 pagesProcess of Cement Production in NepalMadanKarkiNo ratings yet
- 07092014124702imyb - 2012 - 11 - 29 West BengalDocument9 pages07092014124702imyb - 2012 - 11 - 29 West BengalPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Presentation,,SohagDocument23 pagesPresentation,,SohagProgramming & Developing with Al-AminNo ratings yet
- WG 93035Document31 pagesWG 93035Ahmed ElgendyNo ratings yet
- Pandey and BanskotaDocument8 pagesPandey and BanskotaCentral Department of GeologyNo ratings yet
- Malkani Et Al. 2017b-Mineral Resources of North and South PunjabDocument55 pagesMalkani Et Al. 2017b-Mineral Resources of North and South PunjabEmRan LeghariNo ratings yet
- MCP Training Report by M-TECH (Min Pro)Document49 pagesMCP Training Report by M-TECH (Min Pro)Pranay khinvasaraNo ratings yet
- CBM PresentationDocument14 pagesCBM PresentationiconchandraNo ratings yet
- Coal Bed MethaneDocument61 pagesCoal Bed MethaneBiswarup Akhuli100% (1)
- Mineral Resources of Nepal and Their Present StatusDocument26 pagesMineral Resources of Nepal and Their Present StatusSanjay KarkiNo ratings yet
- 1.1-Introduction: 1.2.1 - Maddhyapara Hard Rock Mining Company Limited (MHMCL)Document39 pages1.1-Introduction: 1.2.1 - Maddhyapara Hard Rock Mining Company Limited (MHMCL)Delwar Jahan RonyNo ratings yet
- NTPC Coal Block StatusDocument25 pagesNTPC Coal Block StatusnathansolaiNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel: Coal: Mremi, WilliamDocument41 pagesFossil Fuel: Coal: Mremi, WilliamZanuraNo ratings yet
- EPC1318 Geological ReportDocument27 pagesEPC1318 Geological ReportSemuel Filex Baok100% (1)
- Report On Visit To Maddhapara Granite Mine & Boropukuria Coal MineDocument28 pagesReport On Visit To Maddhapara Granite Mine & Boropukuria Coal MineMd Faisal Karim100% (1)
- CoalDocument18 pagesCoalKishore Kumar KamisettiNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Mineral Resources of NepalDocument17 pagesTerm Paper Mineral Resources of NepalPranit KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Mineral Resources of NepalDocument17 pagesTerm Paper Mineral Resources of NepalPranit Kushwaha0% (1)
- Economic Mineral Deposits of PakistanDocument12 pagesEconomic Mineral Deposits of PakistanOolasyar Khattak67% (12)
- Krishna Godavari Basin: By: - Rishabh TripathiDocument36 pagesKrishna Godavari Basin: By: - Rishabh TripathiRishabhTripathiNo ratings yet
- Quality Assessment of Igaliwo and Olokwu Coals in The Northern Anambra Basin of NigeriaDocument9 pagesQuality Assessment of Igaliwo and Olokwu Coals in The Northern Anambra Basin of NigeriaPremier PublishersNo ratings yet
- Chattaraj Et Al 2019 - Comparative Study On Sorption Characteristics of Coal Seams FromDocument38 pagesChattaraj Et Al 2019 - Comparative Study On Sorption Characteristics of Coal Seams Fromkanhaiya mishraNo ratings yet
- Granite of SindhDocument11 pagesGranite of SindhMuhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 6 MINERAL RESOURCES OF KERALA 12 - 28 - 2011 HTTP ...Document6 pagesPage 1 of 6 MINERAL RESOURCES OF KERALA 12 - 28 - 2011 HTTP ...Charley 02No ratings yet
- Indian Coal and Lignite Resources-2017: Government of India Geological Survey of IndiaDocument46 pagesIndian Coal and Lignite Resources-2017: Government of India Geological Survey of IndiasachinismuNo ratings yet
- Methane Adsorption Characteristics of Coals From Sambaliung Area, Berau, East Kalimantan and Sawahlunto Area, West Sumatra, IndonesiaDocument8 pagesMethane Adsorption Characteristics of Coals From Sambaliung Area, Berau, East Kalimantan and Sawahlunto Area, West Sumatra, IndonesiaNoviantiNo ratings yet
- Report On Coal Resources of The Philippines, November 1985Document51 pagesReport On Coal Resources of The Philippines, November 1985Gfour MaseratiNo ratings yet
- Imyb2011 (03) - Arunachal PradeshDocument3 pagesImyb2011 (03) - Arunachal Pradeshmujib uddin siddiquiNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument10 pages1 PBCatherine SzNo ratings yet
- A Review of Open Cast Coal Mining in IndiaDocument62 pagesA Review of Open Cast Coal Mining in IndiaAbhiram ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Oil and Gas PotentialDocument85 pagesUnconventional Oil and Gas PotentialAngelina RandaNo ratings yet
- Mineral Resources of KeralaDocument10 pagesMineral Resources of Keralaabhinnadh0002No ratings yet
- Resume PaperDocument4 pagesResume PaperMuhammad Dhani Gumilang 249No ratings yet
- Indian Minerals Yearbook 2018: 57 EditionDocument33 pagesIndian Minerals Yearbook 2018: 57 EditionJEFY JEAN ANo ratings yet
- Technical Report Alluvial Gold Mining in Melak (PT. NIKM)Document126 pagesTechnical Report Alluvial Gold Mining in Melak (PT. NIKM)Gunawan Tabrani100% (2)
- Penyusunan Neraca Batubara Dan GambutDocument8 pagesPenyusunan Neraca Batubara Dan GambuthamzahNo ratings yet
- CBM Development in IndiaDocument7 pagesCBM Development in IndiaNimisha VedantiNo ratings yet
- Chandeep Singh XI-A PhysicsDocument16 pagesChandeep Singh XI-A Physicschandeep singhNo ratings yet
- MRP MiningDocument32 pagesMRP MiningAshish PatelNo ratings yet
- Indian Feasibility ReportDocument16 pagesIndian Feasibility ReportДанило ГадайчукNo ratings yet
- Vinayak R V Synbpr (8519) PDFDocument22 pagesVinayak R V Synbpr (8519) PDFravibelavadiNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Oil and Gas Potential PDFDocument85 pagesUnconventional Oil and Gas Potential PDFRizka100% (1)
- Quantitative Clay Mineralogy For A Calcrete-Hosted Uranium Deposit - Innovative Application of Existing Technology On An Unprecedented ScaleDocument8 pagesQuantitative Clay Mineralogy For A Calcrete-Hosted Uranium Deposit - Innovative Application of Existing Technology On An Unprecedented ScaleAldoNo ratings yet
- Central Indo Coal Data SheetDocument4 pagesCentral Indo Coal Data Sheettri darma adi waluyoNo ratings yet
- 3 Sumaryanto Indonesian CRTDocument16 pages3 Sumaryanto Indonesian CRTdesdm kalbarNo ratings yet
- Background Results and Discussion: Geology RegionalDocument1 pageBackground Results and Discussion: Geology RegionalYou FirhadNo ratings yet
- A Review of Coal and Water Resources of PakistanDocument19 pagesA Review of Coal and Water Resources of PakistanNauman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Coal Bed MethaneDocument28 pagesCoal Bed MethaneMohammed Kabiruddin0% (1)
- 2005 - Keep The Cream - Reconciling Coal Recovery at BMA Goonyella RivDocument8 pages2005 - Keep The Cream - Reconciling Coal Recovery at BMA Goonyella Rivanuar piresNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Metode Simpleks BB 101426-24833-1-PB-dikonversiDocument10 pagesJurnal Metode Simpleks BB 101426-24833-1-PB-dikonversiatha angelyNo ratings yet
- Coal Reserve of IndiaDocument14 pagesCoal Reserve of IndiaanantaNo ratings yet
- Coal & Lignite Deposits of Jammu & KashmirDocument7 pagesCoal & Lignite Deposits of Jammu & KashmirPurushottam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Coal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective: Volume 5: Case Studies – Advances in Field and Laboratory ResearchFrom EverandCoal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective: Volume 5: Case Studies – Advances in Field and Laboratory ResearchGlenn B. StracherNo ratings yet
- Alumina to Zirconia: The History of the CSIRO Division of Mineral ChemistryFrom EverandAlumina to Zirconia: The History of the CSIRO Division of Mineral ChemistryRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Recent Advances in Mining and Processing of Low-Grade and Submarginal Mineral Deposits: Centre for Natural Resources, Energy and Transport, United Nations, New YorkFrom EverandRecent Advances in Mining and Processing of Low-Grade and Submarginal Mineral Deposits: Centre for Natural Resources, Energy and Transport, United Nations, New YorkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry and Metallurgy: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionFrom EverandChemistry and Metallurgy: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionA. SherryNo ratings yet
- What Is Wireless Spectrum and Why Is It Important?: 19.6% $81.17 BillionDocument1 pageWhat Is Wireless Spectrum and Why Is It Important?: 19.6% $81.17 BillionSubash MahatNo ratings yet
- Mine IlluminationDocument142 pagesMine IlluminationSubash MahatNo ratings yet
- खानी तथा खनिज पदार्थ नियमावली २०५६Document58 pagesखानी तथा खनिज पदार्थ नियमावली २०५६Subash MahatNo ratings yet
- खानी तथा खनिज पदार्थ ऐन २०४२Document8 pagesखानी तथा खनिज पदार्थ ऐन २०४२Subash MahatNo ratings yet
- Cim Definition Standards - 2014Document10 pagesCim Definition Standards - 2014Subash MahatNo ratings yet
- Curriculam 3rd SemDocument4 pagesCurriculam 3rd SemchotuNo ratings yet
- ADR TopicsDocument14 pagesADR TopicsSathvik ReddyNo ratings yet
- A Management Information SystemDocument15 pagesA Management Information SystemFRAkfurdNo ratings yet
- Week 3 & 4Document12 pagesWeek 3 & 4elbaNo ratings yet
- Tuned To Yesterday Schedule May 2021Document5 pagesTuned To Yesterday Schedule May 2021Mark L.No ratings yet
- OIPD in LinguisticsDocument7 pagesOIPD in LinguisticsBela AtthynaNo ratings yet
- Phillips V NACS National Attorney Collection Services Inc FDCPA Civil Cover SheetDocument2 pagesPhillips V NACS National Attorney Collection Services Inc FDCPA Civil Cover SheetghostgripNo ratings yet
- A Study On Adoption of Digital Payment Through Mobile Payment Application With Reference To Gujarat StateDocument6 pagesA Study On Adoption of Digital Payment Through Mobile Payment Application With Reference To Gujarat StateEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- What Is Literature?Document6 pagesWhat Is Literature?MsVerna GingoNo ratings yet
- BattleNight - Red HalidomsDocument47 pagesBattleNight - Red HalidomsWinner ElbertNo ratings yet
- Customary Law Take Home TestDocument10 pagesCustomary Law Take Home TestGcina MaqoqaNo ratings yet
- Adler Chapter01Document41 pagesAdler Chapter01Rishabh Zak100% (1)
- 1Document108 pages1NguyễnDũngNo ratings yet
- cd1 t02Document1 pagecd1 t02elena expoNo ratings yet
- ESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollerDocument10 pagesESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollergessycaNo ratings yet
- LUN Provisioning FormDocument4 pagesLUN Provisioning FormluckysrvstvNo ratings yet
- Book Decade SDocument555 pagesBook Decade STrey MaklerNo ratings yet
- De Cuong On Tap Giua Ki 1tieng Anh Lop 6 Ilearn Smart WorldDocument4 pagesDe Cuong On Tap Giua Ki 1tieng Anh Lop 6 Ilearn Smart Worldanhpham209kmNo ratings yet
- Muh Immersion Addon Pack v1.5.3 ReadmeDocument6 pagesMuh Immersion Addon Pack v1.5.3 ReadmeacemaclaceNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Research's: MidoriDocument17 pagesMicrosoft Research's: Midorisanthosh859No ratings yet
- Mas PrelimsDocument8 pagesMas PrelimsChristopher NogotNo ratings yet
- Christmas DollDocument20 pagesChristmas Dollcraftycow62No ratings yet
- IronbutterplyDocument3 pagesIronbutterplyCiliaNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Developments in The Built EnvironmentDocument25 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Developments in The Built EnvironmentPutri DartamanNo ratings yet
- BAED Bens Short Quiz 1Document5 pagesBAED Bens Short Quiz 1Luisa RadaNo ratings yet
- Matabuena vs. CervantesDocument1 pageMatabuena vs. CervantesAndrew GallardoNo ratings yet
- Family MembersDocument2 pagesFamily MembersCecilia Scarlett Arriagada SanchezNo ratings yet
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal, BASKOTA, Shiv Kumar, Nepal
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal, BASKOTA, Shiv Kumar, Nepal
Uploaded by
Subash Mahat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views19 pagesThis document summarizes the coal resources and status of coal mining in Nepal. It describes the four main types of coal deposits in Nepal, including lignite, Siwalik coal, Cretaceous-Eocene coal, and Gondwana coal. Production of coal in Nepal peaked at around 10,000 metric tons per year from 2011-2013 but has since declined. Nepal imports more coal than it produces domestically. Challenges facing the coal mining industry in Nepal include small reserves, low coal quality, traditional mining methods, and bureaucratic hurdles. Mechanized mining is not viable, but efficiency could be improved through better tools. The government has stopped further coal exploration.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the coal resources and status of coal mining in Nepal. It describes the four main types of coal deposits in Nepal, including lignite, Siwalik coal, Cretaceous-Eocene coal, and Gondwana coal. Production of coal in Nepal peaked at around 10,000 metric tons per year from 2011-2013 but has since declined. Nepal imports more coal than it produces domestically. Challenges facing the coal mining industry in Nepal include small reserves, low coal quality, traditional mining methods, and bureaucratic hurdles. Mechanized mining is not viable, but efficiency could be improved through better tools. The government has stopped further coal exploration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views19 pagesCoal Resources and Their Status in Nepal, BASKOTA, Shiv Kumar, Nepal
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal, BASKOTA, Shiv Kumar, Nepal
Uploaded by
Subash MahatThis document summarizes the coal resources and status of coal mining in Nepal. It describes the four main types of coal deposits in Nepal, including lignite, Siwalik coal, Cretaceous-Eocene coal, and Gondwana coal. Production of coal in Nepal peaked at around 10,000 metric tons per year from 2011-2013 but has since declined. Nepal imports more coal than it produces domestically. Challenges facing the coal mining industry in Nepal include small reserves, low coal quality, traditional mining methods, and bureaucratic hurdles. Mechanized mining is not viable, but efficiency could be improved through better tools. The government has stopped further coal exploration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 19
COAL RESOURCES
AND THEIR
STATUS IN NEPAL
BASKOTA, Shiv Kumar
Senior Divisional Geologist
Department of Mines & Geology (DMG),
Ministry of Industry
Government of Nepal
INTRODUCTION
Inner Himalaya (Tethys Himalaya)
------- South Tibetan Detachment Fault System------
Higher Himalaya
-------------- Main Central Thrust -----------
Lesser Himalaya
-------- Main Boundary Thrust--------
Sub- Himalaya
-------- Himalayan Frontal Thrust----------
Terai Plain
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 2
COAL RESOURCES
1.Quaternary Lignite Deposits of Kathmandu
Valley
2.Siwalik Coal of the Sub-Himalayas
3.Cretaceous- Eocene Coal of the Lesser
Himalayas
4. Gondwana Coal of the Lesser Himalayas
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 3
COAL RESOURCES
In: Mineral Resources of Nepal, 2016 DMG
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 4
COAL RESOURCES
1.Quaternary Lignite Deposits of Kathmandu Valley
• Geological Setting: In Fluvio-lacustrine sediments of Lukundol
Formation
• Reserve and Quality: Quantitative Evaluation not performed; seam
thickness varies from few centimeters to 1.83 m with maximum
extensions of 750 m. Peat to Lignite Quality
• Mining Activities: Exploited since early 1960’s to 1990’s. None of
them are in operation due to lack of proper market.
2.Siwalik Coal of the Sub-Himalayas
• Geological Setting: In the form of lenses and stringers within
the Siwalik Rocks ; mm to few centimeters in thickness and few
meters long.
• Reserve and Quality: No commercially feasible deposits.
Lignite to Semi- Anthracite Quality
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 5
COAL RESOURCES
3.Cretaceous- Eocene Coal of the Lesser Himalayas
• Geological Setting: Carbonaceous shale with ferruginous quartzite
and black shale of Oligocene age serve as host rock
• Reserve and Quality: Possible Reserve of 5 million tons of coal;
seam thickness varies from few centimeters to 2.5 m with
maximum extensions of 3000 m. Sub- Bituminous Grade with
calorific value upto 7212 kcal/kg.
• Mining Activities: Some of the reserves are still mined
4. Gondwana Coal of the Lesser Himalayas
• Geological Setting: Carbonaceous shale serve as host rock; Fault
controlled
• Reserve and Quality: Possible Reserve of <1 million tons of coal;
seam thickness upto 8 m with maximum extensions of 50 m.
Anthracite Grade with calorific value upto 7521 kcal/kg.
• Mining Activities: Some of the reserves are still mined
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 6
COAL RESOURCES
DMG Brochure
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 7
COAL QUALITY
DMG Brochure
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 8
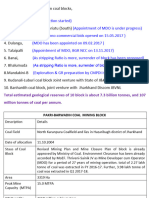
PRESENT STATUS
14 Mining Licences
4 Prospecting Licenses
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 9
PRODUCTION
Production (Metric Tons)
Fiscal Year
Fiscal Year Production( metric ton)
2009/10 7867.24
2010/11 9934.51
2011/12 10499.26
2012/13 13838.3
2013/14 8151.23
2014/15 6754.12
2015/16 2900.3
2016/17 7024.96
DMG, Mineral Resources Division
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 10
CONSUMPTION
Economic Survey, 2016/17
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 11
PRODUCTION AND IMPORT
Production Data: DMG
Import Data: Foreign Trade Statistics of Nepal, TEPC
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 12
PROBLEMS WITH COAL MINES
1. Quantity:
Small Geological Reserves
2. Quality:
Mostly Sub- Bituminous Grade
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 13
PROBLEMS WITH COAL MINES
3. Mining Method:
Traditional Mining
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 14
PROBLEMS WITH COAL MINES
3. Mining Method:
Traditional Mining
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 15
PROBLEMS WITH COAL MINES
3. Mining Method:
Traditional Mining
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 16
PROBLEMS WITH COAL MINES
4. Cross Cutting Issues
Lengthy Governmental Procedure
Difficulties in Land acquisition
Conflict within different acts and regulations
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 17
WAY AHEAD
1. Mechanised mining is NOT viable due to small
resources and low quality
2. Improved tools, use of electric pumps and
compressors can increase efficiency to some extent
3. Government of Nepal has stopped further
exploration of coal in its regular programme!
Coal Resources and Their Status in Nepal 18
19
Wel-come you all in the land of the Mt. Everest
You might also like
- Rumus Blending Batubara ADocument16 pagesRumus Blending Batubara AEka Setia0% (1)
- Sinai Auction 2020-2021Document64 pagesSinai Auction 2020-2021SinaiAcademyNo ratings yet
- Boq For Box CulvertDocument2 pagesBoq For Box CulvertDaniel Okere100% (1)
- Advanced Corporate Finance Quiz 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesAdvanced Corporate Finance Quiz 2 SolutionslaurenNo ratings yet
- Mr. Fahad Ali Rabbani: Name Roll No. Presented byDocument62 pagesMr. Fahad Ali Rabbani: Name Roll No. Presented byHajra AamirNo ratings yet
- KPK NGS Web Min Resources FinalDocument18 pagesKPK NGS Web Min Resources FinalAditya mahatoNo ratings yet
- Process of Cement Production in NepalDocument13 pagesProcess of Cement Production in NepalMadanKarkiNo ratings yet
- 07092014124702imyb - 2012 - 11 - 29 West BengalDocument9 pages07092014124702imyb - 2012 - 11 - 29 West BengalPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Presentation,,SohagDocument23 pagesPresentation,,SohagProgramming & Developing with Al-AminNo ratings yet
- WG 93035Document31 pagesWG 93035Ahmed ElgendyNo ratings yet
- Pandey and BanskotaDocument8 pagesPandey and BanskotaCentral Department of GeologyNo ratings yet
- Malkani Et Al. 2017b-Mineral Resources of North and South PunjabDocument55 pagesMalkani Et Al. 2017b-Mineral Resources of North and South PunjabEmRan LeghariNo ratings yet
- MCP Training Report by M-TECH (Min Pro)Document49 pagesMCP Training Report by M-TECH (Min Pro)Pranay khinvasaraNo ratings yet
- CBM PresentationDocument14 pagesCBM PresentationiconchandraNo ratings yet
- Coal Bed MethaneDocument61 pagesCoal Bed MethaneBiswarup Akhuli100% (1)
- Mineral Resources of Nepal and Their Present StatusDocument26 pagesMineral Resources of Nepal and Their Present StatusSanjay KarkiNo ratings yet
- 1.1-Introduction: 1.2.1 - Maddhyapara Hard Rock Mining Company Limited (MHMCL)Document39 pages1.1-Introduction: 1.2.1 - Maddhyapara Hard Rock Mining Company Limited (MHMCL)Delwar Jahan RonyNo ratings yet
- NTPC Coal Block StatusDocument25 pagesNTPC Coal Block StatusnathansolaiNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel: Coal: Mremi, WilliamDocument41 pagesFossil Fuel: Coal: Mremi, WilliamZanuraNo ratings yet
- EPC1318 Geological ReportDocument27 pagesEPC1318 Geological ReportSemuel Filex Baok100% (1)
- Report On Visit To Maddhapara Granite Mine & Boropukuria Coal MineDocument28 pagesReport On Visit To Maddhapara Granite Mine & Boropukuria Coal MineMd Faisal Karim100% (1)
- CoalDocument18 pagesCoalKishore Kumar KamisettiNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Mineral Resources of NepalDocument17 pagesTerm Paper Mineral Resources of NepalPranit KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Mineral Resources of NepalDocument17 pagesTerm Paper Mineral Resources of NepalPranit Kushwaha0% (1)
- Economic Mineral Deposits of PakistanDocument12 pagesEconomic Mineral Deposits of PakistanOolasyar Khattak67% (12)
- Krishna Godavari Basin: By: - Rishabh TripathiDocument36 pagesKrishna Godavari Basin: By: - Rishabh TripathiRishabhTripathiNo ratings yet
- Quality Assessment of Igaliwo and Olokwu Coals in The Northern Anambra Basin of NigeriaDocument9 pagesQuality Assessment of Igaliwo and Olokwu Coals in The Northern Anambra Basin of NigeriaPremier PublishersNo ratings yet
- Chattaraj Et Al 2019 - Comparative Study On Sorption Characteristics of Coal Seams FromDocument38 pagesChattaraj Et Al 2019 - Comparative Study On Sorption Characteristics of Coal Seams Fromkanhaiya mishraNo ratings yet
- Granite of SindhDocument11 pagesGranite of SindhMuhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 6 MINERAL RESOURCES OF KERALA 12 - 28 - 2011 HTTP ...Document6 pagesPage 1 of 6 MINERAL RESOURCES OF KERALA 12 - 28 - 2011 HTTP ...Charley 02No ratings yet
- Indian Coal and Lignite Resources-2017: Government of India Geological Survey of IndiaDocument46 pagesIndian Coal and Lignite Resources-2017: Government of India Geological Survey of IndiasachinismuNo ratings yet
- Methane Adsorption Characteristics of Coals From Sambaliung Area, Berau, East Kalimantan and Sawahlunto Area, West Sumatra, IndonesiaDocument8 pagesMethane Adsorption Characteristics of Coals From Sambaliung Area, Berau, East Kalimantan and Sawahlunto Area, West Sumatra, IndonesiaNoviantiNo ratings yet
- Report On Coal Resources of The Philippines, November 1985Document51 pagesReport On Coal Resources of The Philippines, November 1985Gfour MaseratiNo ratings yet
- Imyb2011 (03) - Arunachal PradeshDocument3 pagesImyb2011 (03) - Arunachal Pradeshmujib uddin siddiquiNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument10 pages1 PBCatherine SzNo ratings yet
- A Review of Open Cast Coal Mining in IndiaDocument62 pagesA Review of Open Cast Coal Mining in IndiaAbhiram ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Oil and Gas PotentialDocument85 pagesUnconventional Oil and Gas PotentialAngelina RandaNo ratings yet
- Mineral Resources of KeralaDocument10 pagesMineral Resources of Keralaabhinnadh0002No ratings yet
- Resume PaperDocument4 pagesResume PaperMuhammad Dhani Gumilang 249No ratings yet
- Indian Minerals Yearbook 2018: 57 EditionDocument33 pagesIndian Minerals Yearbook 2018: 57 EditionJEFY JEAN ANo ratings yet
- Technical Report Alluvial Gold Mining in Melak (PT. NIKM)Document126 pagesTechnical Report Alluvial Gold Mining in Melak (PT. NIKM)Gunawan Tabrani100% (2)
- Penyusunan Neraca Batubara Dan GambutDocument8 pagesPenyusunan Neraca Batubara Dan GambuthamzahNo ratings yet
- CBM Development in IndiaDocument7 pagesCBM Development in IndiaNimisha VedantiNo ratings yet
- Chandeep Singh XI-A PhysicsDocument16 pagesChandeep Singh XI-A Physicschandeep singhNo ratings yet
- MRP MiningDocument32 pagesMRP MiningAshish PatelNo ratings yet
- Indian Feasibility ReportDocument16 pagesIndian Feasibility ReportДанило ГадайчукNo ratings yet
- Vinayak R V Synbpr (8519) PDFDocument22 pagesVinayak R V Synbpr (8519) PDFravibelavadiNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Oil and Gas Potential PDFDocument85 pagesUnconventional Oil and Gas Potential PDFRizka100% (1)
- Quantitative Clay Mineralogy For A Calcrete-Hosted Uranium Deposit - Innovative Application of Existing Technology On An Unprecedented ScaleDocument8 pagesQuantitative Clay Mineralogy For A Calcrete-Hosted Uranium Deposit - Innovative Application of Existing Technology On An Unprecedented ScaleAldoNo ratings yet
- Central Indo Coal Data SheetDocument4 pagesCentral Indo Coal Data Sheettri darma adi waluyoNo ratings yet
- 3 Sumaryanto Indonesian CRTDocument16 pages3 Sumaryanto Indonesian CRTdesdm kalbarNo ratings yet
- Background Results and Discussion: Geology RegionalDocument1 pageBackground Results and Discussion: Geology RegionalYou FirhadNo ratings yet
- A Review of Coal and Water Resources of PakistanDocument19 pagesA Review of Coal and Water Resources of PakistanNauman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Coal Bed MethaneDocument28 pagesCoal Bed MethaneMohammed Kabiruddin0% (1)
- 2005 - Keep The Cream - Reconciling Coal Recovery at BMA Goonyella RivDocument8 pages2005 - Keep The Cream - Reconciling Coal Recovery at BMA Goonyella Rivanuar piresNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Metode Simpleks BB 101426-24833-1-PB-dikonversiDocument10 pagesJurnal Metode Simpleks BB 101426-24833-1-PB-dikonversiatha angelyNo ratings yet
- Coal Reserve of IndiaDocument14 pagesCoal Reserve of IndiaanantaNo ratings yet
- Coal & Lignite Deposits of Jammu & KashmirDocument7 pagesCoal & Lignite Deposits of Jammu & KashmirPurushottam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Coal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective: Volume 5: Case Studies – Advances in Field and Laboratory ResearchFrom EverandCoal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective: Volume 5: Case Studies – Advances in Field and Laboratory ResearchGlenn B. StracherNo ratings yet
- Alumina to Zirconia: The History of the CSIRO Division of Mineral ChemistryFrom EverandAlumina to Zirconia: The History of the CSIRO Division of Mineral ChemistryRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Recent Advances in Mining and Processing of Low-Grade and Submarginal Mineral Deposits: Centre for Natural Resources, Energy and Transport, United Nations, New YorkFrom EverandRecent Advances in Mining and Processing of Low-Grade and Submarginal Mineral Deposits: Centre for Natural Resources, Energy and Transport, United Nations, New YorkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry and Metallurgy: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionFrom EverandChemistry and Metallurgy: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionA. SherryNo ratings yet
- What Is Wireless Spectrum and Why Is It Important?: 19.6% $81.17 BillionDocument1 pageWhat Is Wireless Spectrum and Why Is It Important?: 19.6% $81.17 BillionSubash MahatNo ratings yet
- Mine IlluminationDocument142 pagesMine IlluminationSubash MahatNo ratings yet
- खानी तथा खनिज पदार्थ नियमावली २०५६Document58 pagesखानी तथा खनिज पदार्थ नियमावली २०५६Subash MahatNo ratings yet
- खानी तथा खनिज पदार्थ ऐन २०४२Document8 pagesखानी तथा खनिज पदार्थ ऐन २०४२Subash MahatNo ratings yet
- Cim Definition Standards - 2014Document10 pagesCim Definition Standards - 2014Subash MahatNo ratings yet
- Curriculam 3rd SemDocument4 pagesCurriculam 3rd SemchotuNo ratings yet
- ADR TopicsDocument14 pagesADR TopicsSathvik ReddyNo ratings yet
- A Management Information SystemDocument15 pagesA Management Information SystemFRAkfurdNo ratings yet
- Week 3 & 4Document12 pagesWeek 3 & 4elbaNo ratings yet
- Tuned To Yesterday Schedule May 2021Document5 pagesTuned To Yesterday Schedule May 2021Mark L.No ratings yet
- OIPD in LinguisticsDocument7 pagesOIPD in LinguisticsBela AtthynaNo ratings yet
- Phillips V NACS National Attorney Collection Services Inc FDCPA Civil Cover SheetDocument2 pagesPhillips V NACS National Attorney Collection Services Inc FDCPA Civil Cover SheetghostgripNo ratings yet
- A Study On Adoption of Digital Payment Through Mobile Payment Application With Reference To Gujarat StateDocument6 pagesA Study On Adoption of Digital Payment Through Mobile Payment Application With Reference To Gujarat StateEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- What Is Literature?Document6 pagesWhat Is Literature?MsVerna GingoNo ratings yet
- BattleNight - Red HalidomsDocument47 pagesBattleNight - Red HalidomsWinner ElbertNo ratings yet
- Customary Law Take Home TestDocument10 pagesCustomary Law Take Home TestGcina MaqoqaNo ratings yet
- Adler Chapter01Document41 pagesAdler Chapter01Rishabh Zak100% (1)
- 1Document108 pages1NguyễnDũngNo ratings yet
- cd1 t02Document1 pagecd1 t02elena expoNo ratings yet
- ESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollerDocument10 pagesESP32 Tutorial What Do You Have To Know About The ESP32 MicrocontrollergessycaNo ratings yet
- LUN Provisioning FormDocument4 pagesLUN Provisioning FormluckysrvstvNo ratings yet
- Book Decade SDocument555 pagesBook Decade STrey MaklerNo ratings yet
- De Cuong On Tap Giua Ki 1tieng Anh Lop 6 Ilearn Smart WorldDocument4 pagesDe Cuong On Tap Giua Ki 1tieng Anh Lop 6 Ilearn Smart Worldanhpham209kmNo ratings yet
- Muh Immersion Addon Pack v1.5.3 ReadmeDocument6 pagesMuh Immersion Addon Pack v1.5.3 ReadmeacemaclaceNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Research's: MidoriDocument17 pagesMicrosoft Research's: Midorisanthosh859No ratings yet
- Mas PrelimsDocument8 pagesMas PrelimsChristopher NogotNo ratings yet
- Christmas DollDocument20 pagesChristmas Dollcraftycow62No ratings yet
- IronbutterplyDocument3 pagesIronbutterplyCiliaNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Developments in The Built EnvironmentDocument25 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Developments in The Built EnvironmentPutri DartamanNo ratings yet
- BAED Bens Short Quiz 1Document5 pagesBAED Bens Short Quiz 1Luisa RadaNo ratings yet
- Matabuena vs. CervantesDocument1 pageMatabuena vs. CervantesAndrew GallardoNo ratings yet
- Family MembersDocument2 pagesFamily MembersCecilia Scarlett Arriagada SanchezNo ratings yet