Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Insulin Glargine
Insulin Glargine
Uploaded by
Patricia MaglasangCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Gilbert Renaud IV PDFDocument142 pagesGilbert Renaud IV PDFAlexandra Craciun94% (17)
- Case Questions For Medical Nutrition Therapy: A Case Study Approach 4 EdDocument5 pagesCase Questions For Medical Nutrition Therapy: A Case Study Approach 4 Edrouzait abdullahNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Insulin AspartDocument2 pagesInsulin AspartPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Gliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameDocument8 pagesGliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameIsabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Reg InsulinDocument2 pagesReg InsulinBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- BHC Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBHC Drug StudyLeah Reese VersonNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDan HizonNo ratings yet
- GlipizideDocument2 pagesGlipizideFeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnDocument17 pagesType 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study1Document3 pagesDrug Study1marieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Template - Module 12Document3 pagesDrug Study Template - Module 12Alex WagnerNo ratings yet
- Clozapine DiazepamDocument2 pagesClozapine Diazepamalteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (CHF)Document9 pagesDrug Study (CHF)Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyErika Nena Castillo AlamoNo ratings yet
- Insulin Glulisine (rDNA Origin) : (In-Su-Lin Gloo-Lye-Seen)Document3 pagesInsulin Glulisine (rDNA Origin) : (In-Su-Lin Gloo-Lye-Seen)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Hyper - and HypoglycemiaDocument3 pagesHyper - and HypoglycemiaaerugiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study JONDocument2 pagesDrug Study JONjean19.goNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKim CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studykrizzia raymundoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- ENCPDocument12 pagesENCPShin PenielNo ratings yet
- ENCPDocument12 pagesENCPShin PenielNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- PH 106.1 Activity HeheDocument10 pagesPH 106.1 Activity Heheja_QuinineNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Insulin LisproDocument2 pagesDrug Study Insulin LisproEzron Kendrick Duran100% (1)
- Drug GlucotrolDocument1 pageDrug GlucotrolSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersDocument23 pagesEndocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersJoaquim RodriguezNo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument2 pagesFUROSEMIDEjbespiritu100% (3)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Insulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)Document2 pagesInsulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Material, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)Document6 pagesMaterial, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)vincent materialNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroid PrednisoneDocument3 pagesCorticosteroid Prednisone1adie1907No ratings yet
- Drug Study MafDocument5 pagesDrug Study MafSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Generic Name: Mechanism of ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Generic Name: Mechanism of ActionSheferely BayauaNo ratings yet
- mebendazole-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesmebendazole-WPS OfficeDenvicNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Monsalud - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMonsalud - Drug StudyJanielle Christine MonsaludNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBea Lee VenturanzaNo ratings yet
- REFERENCE: Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th Edition, Volume 1, Page 1026Document3 pagesREFERENCE: Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th Edition, Volume 1, Page 1026Charissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Insulin - Pharmacology Group 1 4Document2 pagesInsulin - Pharmacology Group 1 4Hanna Violeza Velasco CayetanoNo ratings yet
- CU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3Document7 pagesCU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3FERMIL PASGALANo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument3 pagesDrug Study DRGershom Perez AcaboNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CardioDocument7 pagesDrug Study CardioCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- RosuvastatinDocument2 pagesRosuvastatinShaira Richelle OmagapNo ratings yet
- Metformin GlucophageDocument1 pageMetformin GlucophageENo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument6 pagesFUROSEMIDEPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument12 pagesCHFganda akoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Regular InsulinDocument8 pagesDrug Study - Regular InsulinRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- KlindexDocument2 pagesKlindexPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Actos Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActos Drug StudyNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Far Eastern UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Far Eastern UniversityChoy DacanayNo ratings yet
- Umayam Patho & Drug Study 3rd RotationDocument6 pagesUmayam Patho & Drug Study 3rd RotationRyan Dave UmayamNo ratings yet
- ClonazepamDocument3 pagesClonazepamShane Shaira G PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument1 pageClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyCassandra Ysabel Reyes3210376No ratings yet
- Drug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Kate PedzNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument4 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument1 pageFurosemidePatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- EnoxaparineDocument1 pageEnoxaparinePatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- KlindexDocument2 pagesKlindexPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Insulin AspartDocument2 pagesInsulin AspartPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and HormoneDocument26 pagesVitamin and HormoneMohammad JewelNo ratings yet
- Supplement Black BookDocument33 pagesSupplement Black Booktweetybyrd443013No ratings yet
- Assess For Signs of HyperglycemiaDocument9 pagesAssess For Signs of HyperglycemiaSheril Sularte CasanesNo ratings yet
- Generički Naziv Lijeka (Zabranjena Supstanca) Registrovani Preparati (Komercijalni Naziv) Zaštićeno Ime Lijeka Oznaka U LZS 2015 Oznaka U ATCDocument7 pagesGenerički Naziv Lijeka (Zabranjena Supstanca) Registrovani Preparati (Komercijalni Naziv) Zaštićeno Ime Lijeka Oznaka U LZS 2015 Oznaka U ATCДраган ЧолићNo ratings yet
- Biology 8461/2H: Mark SchemeDocument21 pagesBiology 8461/2H: Mark SchemeMohamad HabbalNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis ReviewDocument7 pagesHomeostasis ReviewMCK1348No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Manufacturing of Biotechnology-Insulin and ErythropoietinDocument10 pagesChapter 3 - Manufacturing of Biotechnology-Insulin and Erythropoietin202110203No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 The Endocrine System Chapter OutlineDocument23 pagesChapter 16 The Endocrine System Chapter OutlineMartina MicicNo ratings yet
- The Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Type 1 and PDFDocument12 pagesThe Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Type 1 and PDFasmawatiNo ratings yet
- GlucagonDocument4 pagesGlucagonElenanana100% (1)
- Correction Factor 2020Document2 pagesCorrection Factor 2020Arshad SyahaliNo ratings yet
- Case Study BkaDocument92 pagesCase Study BkaMaria CabangonNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis UptodateDocument88 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis UptodateYus RendraNo ratings yet
- F4C9 Question 8,13,14,16BDocument2 pagesF4C9 Question 8,13,14,16BCHUA PHEI THNG MoeNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy For Cardiopumonary DisordersDocument101 pagesPhysical Therapy For Cardiopumonary Disorderssunita_h100% (5)
- Manejo HiperglicemiaDocument28 pagesManejo HiperglicemiaLya Mylene VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument58 pagesDiabetes MellitusJai Adora100% (2)
- Print Chapter 18 Endocrine System Flashcards - Easy NotecardsDocument31 pagesPrint Chapter 18 Endocrine System Flashcards - Easy NotecardsTran9716No ratings yet
- Prof. Yaron Ilan - Alimentary Pharmacology & TherapeuticsDocument15 pagesProf. Yaron Ilan - Alimentary Pharmacology & TherapeuticsProf. Yaron IlanNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Related DrugsDocument42 pagesHormones and Related DrugsRamya PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Role of Karela in Diabetes A ReviewDocument10 pagesRole of Karela in Diabetes A ReviewDharmaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Research Paper PDFDocument5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Research Paper PDFaflbrfeij100% (1)
- For Hardgainers Who Can't Get The Scale Where They Want It, Milk May Be The Answer!Document7 pagesFor Hardgainers Who Can't Get The Scale Where They Want It, Milk May Be The Answer!zhuzaiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson Frank100% (1)
- NovomixDocument5 pagesNovomixJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- MCQ Bank PDFDocument38 pagesMCQ Bank PDFShafiq Ur Rahman100% (1)
- Acupressure Masterclass Treatment Chart Manual CDocument114 pagesAcupressure Masterclass Treatment Chart Manual CAkchika0% (2)
- Ito Super ScienceDocument34 pagesIto Super ScienceMiguel Antonio MiladoNo ratings yet
Insulin Glargine
Insulin Glargine
Uploaded by
Patricia MaglasangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Insulin Glargine
Insulin Glargine
Uploaded by
Patricia MaglasangCopyright:
Available Formats
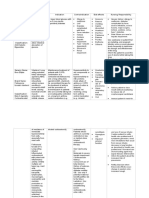
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
RESPONSIBILITIES
GENERIC NAME: Lowers blood glucose level by To improve glycemic control in CNS: headache, pyrexia BEFORE:
Insulin Glargine stimulating peripheral glucose adults with diabetes mellitus CV: peripheral edema Administer by subcutaneous
uptake by binding to insulin EENT: pharyngitis, rhinitis injection only in the thigh,
BRAND NAME: receptors on skeletal muscle GI: abdominal pain, abdominal wall, or upper arm.
Toujeo and in fat cells, and by gastroenteritis, nausea, Rotate sites within same region
inhibiting hepatic glucose CONTRAINDICATION: vomiting from one injection to the next
CLASSIFICATION: production; also inhibits Contraindicated during Metabolic: hypoglycemia, to reduce risk of lipodystrophy
Antidiabetic lipolysis and proteolysis, and episodes of hypoglycemia or sodium retention, weight gain
enhances protein synthesis diabetic ketoacidosis Musculoskeletal: back pain Inspect visually for particulate
DOSAGE: Use cautiously in elderly Respiratory: URI, bronchitis, matter and discoloration before
20 “U” patients, who may be at risk cough administration, whenever
for increased sensitivity to Skin: injection-site reactions, solution and container permit;
ROUTE: drugs effects. Signs and lipodystrophy, pruritus, rash use only if solution appears
Subcutaneous symptoms of hypoglycemia Other: allergic reactions, clear and colorless
may be more difficult to flulike symptoms
FREQUENCY: recognize in these patients Instructions for priming and
OD Use cautiously in patients using pens vary from one to
susceptible to hypokalemia another, are very detailed, and
TIMING: such as patients who are involve multiple steps. Refer to
8AM fasting, are taking potassium- manufacturer’s instructions for
lowering drugs, or concurrently use
taking drugs that may affect
potassium level DURING:
Monitor patient carefully for
signs and symptoms of
hypoglycemia, especially in
long-standing disease
Instruct patient to keep hard
candy or glucose tablets on
hand to treat mild cases of
hypoglycemia
Teach patient that alcohol may
affect glucose levels and should
be avoided
AFTER:
Assess patient for signs and
symptoms of hypoglycemia
(sweating, shaking, trembling,
confusion) and hyperglycemia
(drowsiness, fruity breath odor,
frequent urination, thirst).
Notify prescriber if any of these
signs or symptoms occur
Inform patient that any insulin
change should be made
cautiously and only under
medical supervision
Instruct patient not to stop
insulin abruptly or change
amount injected without
consulting prescriber
You might also like
- Gilbert Renaud IV PDFDocument142 pagesGilbert Renaud IV PDFAlexandra Craciun94% (17)
- Case Questions For Medical Nutrition Therapy: A Case Study Approach 4 EdDocument5 pagesCase Questions For Medical Nutrition Therapy: A Case Study Approach 4 Edrouzait abdullahNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Insulin AspartDocument2 pagesInsulin AspartPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Gliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameDocument8 pagesGliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameIsabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Reg InsulinDocument2 pagesReg InsulinBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- BHC Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBHC Drug StudyLeah Reese VersonNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDan HizonNo ratings yet
- GlipizideDocument2 pagesGlipizideFeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnDocument17 pagesType 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study1Document3 pagesDrug Study1marieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Template - Module 12Document3 pagesDrug Study Template - Module 12Alex WagnerNo ratings yet
- Clozapine DiazepamDocument2 pagesClozapine Diazepamalteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (CHF)Document9 pagesDrug Study (CHF)Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyErika Nena Castillo AlamoNo ratings yet
- Insulin Glulisine (rDNA Origin) : (In-Su-Lin Gloo-Lye-Seen)Document3 pagesInsulin Glulisine (rDNA Origin) : (In-Su-Lin Gloo-Lye-Seen)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Hyper - and HypoglycemiaDocument3 pagesHyper - and HypoglycemiaaerugiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study JONDocument2 pagesDrug Study JONjean19.goNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKim CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studykrizzia raymundoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- ENCPDocument12 pagesENCPShin PenielNo ratings yet
- ENCPDocument12 pagesENCPShin PenielNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- PH 106.1 Activity HeheDocument10 pagesPH 106.1 Activity Heheja_QuinineNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Insulin LisproDocument2 pagesDrug Study Insulin LisproEzron Kendrick Duran100% (1)
- Drug GlucotrolDocument1 pageDrug GlucotrolSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersDocument23 pagesEndocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersJoaquim RodriguezNo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument2 pagesFUROSEMIDEjbespiritu100% (3)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Insulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)Document2 pagesInsulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Material, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)Document6 pagesMaterial, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)vincent materialNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroid PrednisoneDocument3 pagesCorticosteroid Prednisone1adie1907No ratings yet
- Drug Study MafDocument5 pagesDrug Study MafSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Generic Name: Mechanism of ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Generic Name: Mechanism of ActionSheferely BayauaNo ratings yet
- mebendazole-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesmebendazole-WPS OfficeDenvicNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Monsalud - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMonsalud - Drug StudyJanielle Christine MonsaludNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBea Lee VenturanzaNo ratings yet
- REFERENCE: Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th Edition, Volume 1, Page 1026Document3 pagesREFERENCE: Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th Edition, Volume 1, Page 1026Charissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Insulin - Pharmacology Group 1 4Document2 pagesInsulin - Pharmacology Group 1 4Hanna Violeza Velasco CayetanoNo ratings yet
- CU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3Document7 pagesCU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3FERMIL PASGALANo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument3 pagesDrug Study DRGershom Perez AcaboNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CardioDocument7 pagesDrug Study CardioCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- RosuvastatinDocument2 pagesRosuvastatinShaira Richelle OmagapNo ratings yet
- Metformin GlucophageDocument1 pageMetformin GlucophageENo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument6 pagesFUROSEMIDEPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument12 pagesCHFganda akoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Regular InsulinDocument8 pagesDrug Study - Regular InsulinRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- KlindexDocument2 pagesKlindexPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Actos Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActos Drug StudyNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Far Eastern UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Far Eastern UniversityChoy DacanayNo ratings yet
- Umayam Patho & Drug Study 3rd RotationDocument6 pagesUmayam Patho & Drug Study 3rd RotationRyan Dave UmayamNo ratings yet
- ClonazepamDocument3 pagesClonazepamShane Shaira G PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument1 pageClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyCassandra Ysabel Reyes3210376No ratings yet
- Drug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Kate PedzNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument4 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument1 pageFurosemidePatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- EnoxaparineDocument1 pageEnoxaparinePatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- KlindexDocument2 pagesKlindexPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Insulin AspartDocument2 pagesInsulin AspartPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and HormoneDocument26 pagesVitamin and HormoneMohammad JewelNo ratings yet
- Supplement Black BookDocument33 pagesSupplement Black Booktweetybyrd443013No ratings yet
- Assess For Signs of HyperglycemiaDocument9 pagesAssess For Signs of HyperglycemiaSheril Sularte CasanesNo ratings yet
- Generički Naziv Lijeka (Zabranjena Supstanca) Registrovani Preparati (Komercijalni Naziv) Zaštićeno Ime Lijeka Oznaka U LZS 2015 Oznaka U ATCDocument7 pagesGenerički Naziv Lijeka (Zabranjena Supstanca) Registrovani Preparati (Komercijalni Naziv) Zaštićeno Ime Lijeka Oznaka U LZS 2015 Oznaka U ATCДраган ЧолићNo ratings yet
- Biology 8461/2H: Mark SchemeDocument21 pagesBiology 8461/2H: Mark SchemeMohamad HabbalNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis ReviewDocument7 pagesHomeostasis ReviewMCK1348No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Manufacturing of Biotechnology-Insulin and ErythropoietinDocument10 pagesChapter 3 - Manufacturing of Biotechnology-Insulin and Erythropoietin202110203No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 The Endocrine System Chapter OutlineDocument23 pagesChapter 16 The Endocrine System Chapter OutlineMartina MicicNo ratings yet
- The Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Type 1 and PDFDocument12 pagesThe Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Type 1 and PDFasmawatiNo ratings yet
- GlucagonDocument4 pagesGlucagonElenanana100% (1)
- Correction Factor 2020Document2 pagesCorrection Factor 2020Arshad SyahaliNo ratings yet
- Case Study BkaDocument92 pagesCase Study BkaMaria CabangonNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis UptodateDocument88 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis UptodateYus RendraNo ratings yet
- F4C9 Question 8,13,14,16BDocument2 pagesF4C9 Question 8,13,14,16BCHUA PHEI THNG MoeNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy For Cardiopumonary DisordersDocument101 pagesPhysical Therapy For Cardiopumonary Disorderssunita_h100% (5)
- Manejo HiperglicemiaDocument28 pagesManejo HiperglicemiaLya Mylene VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument58 pagesDiabetes MellitusJai Adora100% (2)
- Print Chapter 18 Endocrine System Flashcards - Easy NotecardsDocument31 pagesPrint Chapter 18 Endocrine System Flashcards - Easy NotecardsTran9716No ratings yet
- Prof. Yaron Ilan - Alimentary Pharmacology & TherapeuticsDocument15 pagesProf. Yaron Ilan - Alimentary Pharmacology & TherapeuticsProf. Yaron IlanNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Related DrugsDocument42 pagesHormones and Related DrugsRamya PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Role of Karela in Diabetes A ReviewDocument10 pagesRole of Karela in Diabetes A ReviewDharmaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Research Paper PDFDocument5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Research Paper PDFaflbrfeij100% (1)
- For Hardgainers Who Can't Get The Scale Where They Want It, Milk May Be The Answer!Document7 pagesFor Hardgainers Who Can't Get The Scale Where They Want It, Milk May Be The Answer!zhuzaiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson Frank100% (1)
- NovomixDocument5 pagesNovomixJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- MCQ Bank PDFDocument38 pagesMCQ Bank PDFShafiq Ur Rahman100% (1)
- Acupressure Masterclass Treatment Chart Manual CDocument114 pagesAcupressure Masterclass Treatment Chart Manual CAkchika0% (2)
- Ito Super ScienceDocument34 pagesIto Super ScienceMiguel Antonio MiladoNo ratings yet