Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Insulin Aspart
Insulin Aspart
Uploaded by
Patricia MaglasangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Insulin Aspart
Insulin Aspart
Uploaded by
Patricia MaglasangCopyright:
Available Formats
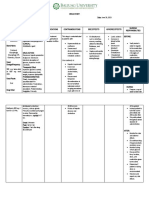
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
RESPONSIBILITIES
GENERIC NAME: Regulates the metabolism of To improve glycemic control in CNS: headache, seizures, BEFORE:
Insulin Aspart glucose. It promotes the adults with diabetes mellitus asthenia, fever, fatigue, Administer by subcutaneous
storage and inhibits the sensory disturbance injection only in the thigh,
BRAND NAME: breakdown of glucose, fat, and CV: hypertensin, peripheral abdominal wall, or upper arm.
Novorapid amino acids. Insulin lowers edema Rotate sites within same region
blood glucose by increasing CONTRAINDICATION: EENT: nasopharyngitis from one injection to the next
CLASSIFICATION: peripheral glucose uptake, Contraindicated during GI: nausea, diarrhea to reduce risk of lipodystrophy
Antidiabetic particularly in the skeletal episodes of hypoglycemia GU: UTI, dysmenorrhea
muscle and fat Metabolic: hypoglycemia, Inspect visually for particulate
DOSAGE: Contraindicated in patients with hypokalemia, weight gain matter and discoloration before
8 “U” a history of hypersensitivity to Musculoskeletal: myalgia administration, whenever
drug or its components. Severe Respiratory: URI, bronchitis, solution and container permit;
ROUTE: life-threatening, generalized cough: bronchospasm, throat use only if solution appears
Subcutaneous allergic reaction, including pain or irritation, decreased clear and colorless
anaphylaxis, can occur with pulmonary function
FREQUENCY: insulin products Skin: injection-site reactions, Instructions for priming and
TID lipodystrophy, pruritus, rash using pens vary from one to
Use cautiously in patients Other: allergic reactions, another, are very detailed, and
TIMING: susceptible to hypokalemia, flulike symptoms, involve multiple steps. Refer to
5AM-11AM-5PM such as patients who are manufacturer’s instructions for
fasting, are takin potassium- use
lowering drugs, or are
concurrently taking drugs that DURING:
may affect potassium levels Monitor patient carefully for
signs and symptoms of
hypoglycemia, especially in
long-standing disease
Instruct patient to keep hard
candy or glucose tablets on
hand to treat mild cases of
hypoglycemia
Teach patient that alcohol may
affect glucose levels and should
be avoided
AFTER:
Assess patient for signs and
symptoms of hypoglycemia
(sweating, shaking, trembling,
confusion) and hyperglycemia
(drowsiness, fruity breath odor,
frequent urination, thirst).
Notify prescriber if any of these
signs or symptoms occur
Inform patient that any insulin
change should be made
cautiously and only under
medical supervision
Instruct patient not to stop
insulin abruptly or change
amount injected without
consulting prescriber
You might also like
- Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ)Document2 pagesDiabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ)Wayan SugitaNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Insulin GlargineDocument2 pagesInsulin GlarginePatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Gliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameDocument8 pagesGliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameIsabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Reg InsulinDocument2 pagesReg InsulinBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnDocument17 pagesType 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDan HizonNo ratings yet
- BHC Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBHC Drug StudyLeah Reese VersonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKim CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Insulin LisproDocument2 pagesDrug Study Insulin LisproEzron Kendrick Duran100% (1)
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Insulin Glulisine (rDNA Origin) : (In-Su-Lin Gloo-Lye-Seen)Document3 pagesInsulin Glulisine (rDNA Origin) : (In-Su-Lin Gloo-Lye-Seen)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- GlipizideDocument2 pagesGlipizideFeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (CHF)Document9 pagesDrug Study (CHF)Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Template - Module 12Document3 pagesDrug Study Template - Module 12Alex WagnerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyErika Nena Castillo AlamoNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Clozapine DiazepamDocument2 pagesClozapine Diazepamalteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studykrizzia raymundoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MafDocument5 pagesDrug Study MafSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study1Document3 pagesDrug Study1marieNo ratings yet
- Insulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)Document2 pagesInsulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Drug GlucotrolDocument1 pageDrug GlucotrolSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Insulinas de OsmosisDocument3 pagesInsulinas de OsmosisDennise A. Hernández JuárezNo ratings yet
- PH 106.1 Activity HeheDocument10 pagesPH 106.1 Activity Heheja_QuinineNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Hyper - and HypoglycemiaDocument3 pagesHyper - and HypoglycemiaaerugiNo ratings yet
- ENCPDocument12 pagesENCPShin PenielNo ratings yet
- ENCPDocument12 pagesENCPShin PenielNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBea Lee VenturanzaNo ratings yet
- Monsalud - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMonsalud - Drug StudyJanielle Christine MonsaludNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersDocument23 pagesEndocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersJoaquim RodriguezNo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument2 pagesFUROSEMIDEjbespiritu100% (3)
- Humalog Drug StudyDocument3 pagesHumalog Drug StudyKristinelou Marie ReynaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Med WardDocument13 pagesDrug Study - Med WardFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument3 pagesDrug Study DRGershom Perez AcaboNo ratings yet
- mebendazole-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesmebendazole-WPS OfficeDenvicNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Regular InsulinDocument8 pagesDrug Study - Regular InsulinRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CardioDocument7 pagesDrug Study CardioCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Insulin - Pharmacology Group 1 4Document2 pagesInsulin - Pharmacology Group 1 4Hanna Violeza Velasco CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study JONDocument2 pagesDrug Study JONjean19.goNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Regular (Injection, Concentrated) : (In-Su-Lin)Document3 pagesInsulin, Regular (Injection, Concentrated) : (In-Su-Lin)Tri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- CU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3Document7 pagesCU Task 11 RLE - Urinary Problems in Older Adults - GROUP2E 3FERMIL PASGALANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- ClonazepamDocument3 pagesClonazepamShane Shaira G PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Generic Name: Mechanism of ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Generic Name: Mechanism of ActionSheferely BayauaNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument2 pagesName of DrugSunny Mae T. PuigNo ratings yet
- Actos Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActos Drug StudyNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroid PrednisoneDocument3 pagesCorticosteroid Prednisone1adie1907No ratings yet
- LantusDocument1 pageLantusCassie100% (4)
- Miglitol (Glyset)Document1 pageMiglitol (Glyset)ENo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien HipoglikemiaDocument15 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien HipoglikemiaNaela zenthaNo ratings yet
- Drugs of DiabetesDocument42 pagesDrugs of Diabeteskwennybiang100% (1)
- Drug Study 2Document5 pagesDrug Study 2Bani Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetformin Drug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Furosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaDocument9 pagesFurosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaRanee Diane AnanayoNo ratings yet
- REFERENCE: Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th Edition, Volume 1, Page 1026Document3 pagesREFERENCE: Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th Edition, Volume 1, Page 1026Charissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument1 pageFurosemidePatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- EnoxaparineDocument1 pageEnoxaparinePatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- KlindexDocument2 pagesKlindexPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Insulin GlargineDocument2 pagesInsulin GlarginePatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Endurance Sports: Marathon, Triathlon, and Road CyclingDocument11 pagesNutrition For Endurance Sports: Marathon, Triathlon, and Road CyclingLeonardiniNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia and Anemia Associated With Malaria Among Pregnant Mothers Living With HIV Attending Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital, Kano State-NigeriaDocument6 pagesHypoglycemia and Anemia Associated With Malaria Among Pregnant Mothers Living With HIV Attending Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital, Kano State-NigeriaUMYU Journal of Microbiology Research (UJMR)No ratings yet
- Diabetes and HerbsDocument132 pagesDiabetes and HerbsAjmal KhanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Tests For EndocrinologyDocument6 pagesLaboratory Tests For EndocrinologyAnastasia100% (1)
- Perry Chapter 7,8,9,10,11,12,14 Case Study & DefinitionsDocument15 pagesPerry Chapter 7,8,9,10,11,12,14 Case Study & Definitionstriddle1969100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing QuizDocument9 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Quizapi-3718174100% (27)
- Mendiola-Neonatal Hypoglycemia PPT 1Document49 pagesMendiola-Neonatal Hypoglycemia PPT 1Maysa IsmailNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemDocument30 pagesUser Guide: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemVince CentenoNo ratings yet
- DiabetekDocument15 pagesDiabetekMaira GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Blood SugarDocument18 pagesBlood Sugarlaloo01No ratings yet
- Slemani Pediatric Teaching Hospital GuidelinesDocument93 pagesSlemani Pediatric Teaching Hospital GuidelinesHeersh RaofNo ratings yet
- Janumet PM eDocument62 pagesJanumet PM eRaffi DerderianNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics-in-Review 1989 - Acute Diarrhea in Children PDFDocument10 pagesPediatrics-in-Review 1989 - Acute Diarrhea in Children PDFmob3No ratings yet
- Ampalaya CandyDocument8 pagesAmpalaya CandyCes UniqueNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Neonatal ConvulsionDocument19 pagesLesson Plan On Neonatal ConvulsionASHISH KUMAR YADAV100% (1)
- 100 Beats Per Minute. Many DifferentDocument4 pages100 Beats Per Minute. Many Differentjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Beta-Cell Neoplasia InsulinomaDocument28 pagesChapter 9 - Beta-Cell Neoplasia InsulinomaSteffi AraujoNo ratings yet
- Myrissa Melinda L Alip, MDDocument5 pagesMyrissa Melinda L Alip, MDadnep1991No ratings yet
- NP1 NLE CoverageDocument18 pagesNP1 NLE CoverageAnonymous hDcvpptNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyiiDocument8 pagesDrug Studyiimarie100% (7)
- DTC Guide For Diabetes - Interactive 1 2Document4 pagesDTC Guide For Diabetes - Interactive 1 2sonyjrajNo ratings yet
- EE Tarek Exam Hints 2019-1Document83 pagesEE Tarek Exam Hints 2019-1Ibrahim Sayed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sharief F 2011Document14 pagesSharief F 2011wiwiNo ratings yet
- Metformin For GDMDocument7 pagesMetformin For GDMRoro WidyastutiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Fact SheetsDocument1 pageDiabetes Fact SheetsprincessandthepumpNo ratings yet
- Endo 2 Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension Angina Pectoris BloodDocument18 pagesEndo 2 Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension Angina Pectoris Bloodmildred alidonNo ratings yet
- 10 Ways To Reduce Blood Sugar NaturallyDocument4 pages10 Ways To Reduce Blood Sugar NaturallyAnkur PatelNo ratings yet
- Careworld Philippines Inc.: 3 Floor, Amore BLDG., Brgy. Luciano Trecemartires City, Cavite, PhilippinesDocument6 pagesCareworld Philippines Inc.: 3 Floor, Amore BLDG., Brgy. Luciano Trecemartires City, Cavite, PhilippinesRowena Lalongisip De LeonNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris "Diabetes": Shendy Wira Putra (183310822)Document6 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris "Diabetes": Shendy Wira Putra (183310822)Adilla SyafniNo ratings yet