Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Softcopy Science Form 2 (Book A)
Softcopy Science Form 2 (Book A)
Uploaded by
VANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN MoeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Softcopy Science Form 2 (Book A)
Softcopy Science Form 2 (Book A)
Uploaded by
VANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN MoeCopyright:
Available Formats
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
(919810-T)
No.35, Jalan 5/10B, Spring Crest Industrial Park,
68100 Batu Caves, Selangor, Malaysia.
Tel: 03-6178 7989 ● Fax: 03-6185 2402
www.nilampublication.com.my ● nilampublication@yahoo.com
All rights reserved®. No parts of this book may be reproduced, distributed or transmitted in any form
either in electronic or mechanical without the prior written permission of Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. (919810-T)
Printed by World Line For better discount and stock
No.61, Persiaran Mewah,
availability
Kawasan Perindustrian Bandar Tun Razak,
Cheras, 56000 Kuala Lumpur. Please contact
KANDUNGAN / CONTENTS
SK Aktiviti TP Halaman Tarikh Catatan
SK Activity TP Page Date Remarks
1 Biodiversiti / Biodiversity
A. Menghuraikan dan Berkomunikasi Mengenai Biodiversiti
Describe and Communicate About Biodiversity 1, 2 1
1.1
B. Pengurusan Biodiversiti yang Berkesan
Effective Biodiversity Management 1, 2 3
A. Pengelasan Haiwan
Classification of Animals 1, 2 4
B. Pengenalan Tumbuhan
1.2 Classification of Plants 2 5
C. Membina Kekunci Dikotomi
Constructing Dichotomous Exercise 3 6
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 7
2 Ekosistem / Ecosystem
A. Pengeluar, Pengguna dan Pengurai
1, 2 8
Producer, Consumer and Decomposer
2.1
B. Rantai Makanan dan Siratan Makanan
2, 3 9
Food Chain and Food Web
A. Kitar Air dalam suatu Ekosistem
2 11
Water Cycle in an Ecosystem
B. Kitar Oksigen dan Kitar Karbon dalam Ekosistem
2.2 2 12
Oxygen Cycle and Carbon Cycle in the Ecosystem
C. Menyelesaikan Masalah Gangguan kepada Kitar Nutrien
2 13
Solving Problems of Disruption to the Nutrient Cycle
A. Keseimbangan Ekosistem
1, 2 14
Ecosystem Balance
B. Interaksi antara Organisma Hidup
1, 2 15
Interactions between Living Organisms
2.3 C. Faktor-faktor yang Mempengaruhi Saiz Populasi dalam Suatu
Ekosistem 2 17
Factors Affecting the Size of the Population in an Ecosystem
D. Perubahan dalam Ekosistem
2 17
Changes in Ecosystem
A. Peranan Manusia dalam Mengekalkan Keseimbangan Alam
2.4 4, 5 18
Role of Humans in Maintaining a Balanced Nature
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 19
i © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Contents Book A_F.indd 1 25/10/2021 1:02 PM
SK Aktiviti TP Halaman Tarikh Catatan
SK Activity TP Page Date Remarks
3 Nutrisi / Nutrition
A. Kelas Makanan
3.1 Classes of Foods 2 21
A. Gizi Seimbang
Balanced Diet 1, 2 25
B. Nilai Kalori Makanan dan Merancang Gizi Seimbang
The Calorific Value of Foods and Planning a Balance Diet 1.3 28
3.2
C. Kepentingan Gizi Seimbang, Senaman dan Gaya Hidup Sihat
dalam Mengekalkan Kesihatan
Importance of Balanced Diet, Exercise and Healthy Lifestyle in 2 29
Maintaining Health
A. Struktur Sistem Pencernaan Manusia
3.3 Human Digestive System Structure 1, 2 30
A. Struktur Dalaman Usus Kecil
Internal Structure of Small Intestine 2 33
B. Proses Pengangkutan Hasil Pencernaan
3.4 Transportation Process of Digestive Product 2 34
C. Penyerapan Semula Air dan Penyahtinjaan
Reabsorption of Water and Defaecation 1, 2 34
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 35
4 Kesihatan Manusia / Human Health
A. Penyakit Berjangkit dan Penyakit Tidak Berjangkit
1, 2 37
Infectious and Non-infectious Disease
B. Bagaimana Penyakit Berjangkit Disebarkan?
4.1 2 38
How Infectious Diseases are Spreaded?
C. Mekanisme Menghalang Penularan Penyakit Berjangkit
2 39
Mechanisms to Prevent the Spreads of Infectious Disease
A. Fungsi Sistem Pertahanan Badan
1, 2 40
Functions of Body’s Defence System
B. Antigen, Antibodi dan Keimunan
1 42
Antigen, Antibody and Immunity
C. Kepentingan Imunisasi
4.2 2 42
The Importance of Immunisation
D. Keimunan Pasif dan Keimunan Aktif
1, 2 43
The Passive Immunity and Active Immunity
E. Sistem Keimunan yang Mantap
2 44
Strong Immune System
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 45
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. ii
Modul Sains T2-Contents Book A_F.indd 2 25/10/2021 1:02 PM
SK Aktiviti TP Halaman Tarikh Catatan
SK Activity TP Page Date Remarks
5 Air dan Larutan / Water and Solution
A. Air
Water 1, 2 46
B. Penyejatan Air
5.1 Evaporation of Water 2 47
C. Aplikasi Penyejatan Air
Application of Evaporation of Water 3 48
A. Larutan dan Keterlarutan
Solution and Solubility 1, 2 49
B. Koloid
Colloid 1 50
5.2
C. Air sebagai Pelarut Semesta
Water as a Universal Solvent 3 51
D. Pelarut Bukan Air dan Kegunaannya dalam Kehidupan
Non-water Solvent and its Uses in Life 1, 3 51
A. Kaedah Pembersihan Air
Water Purification Method 6 52
B. Sistem Pembekalan Air
5.3 The Water Supply System 2 54
C. Kelestarian Air
Water Substainability 4 55
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 56
6 Asid dan Alkali / Acid and Alkali
A. Sifat-sifat Asid
1 57
Properties of Acids
B. Sifat-sifat Alkali
1 59
Properties of Alkalis
C. Peranan Air untuk Menunjukkan Sifat-sifat Asid dan Alkali
2 61
Role of Water in Showing the Properties of Acids and Alkalis
6.1
D. Bahan Berasid dan Beralkali dalam Kehidupan Seharian
2 62
Acidic and Alkaline Substances in Daily Life
E. Kekuatan Asid dan Alkali
3 63
The Strength of Acid and Alkali
F. Kegunaan Asid dan Alkali dalam Kehidupan Harian
2, 3 64
Uses of Acid and Alkali in Daily Life
A. Proses Peneutralan
3 66
Neutralisation Process
6.2
B. Aplikasi Peneutralan dalam Kehidupan Harian
3 67
Application of Neutralisation in Daily Life
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 68
iii © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Contents Book A_F.indd 3 25/10/2021 1:02 PM
SK Aktiviti TP Halaman Tarikh Catatan
SK Activity TP Page Date Remarks
7 Keelektrikan dan Kemagnetan / Electricity and Magnetism
A. Tenaga
Energy 1, 2 69
B. Cas Elektrostatik
Electrostatic Charges 1, 2, 3, 4 71
C. Arus Elektrik
7.1 Electric Current 1, 2, 3 73
D. Hubungan antara Arus Elektrik, Voltan dan Rintangan
The Relationship between Electric current, Voltage and Resistance 4 74
E. Hukum Ohm
Ohm’s Law 1 75
A. Komponen Litar Elektrik
Electrical Circuit Components 2, 4 76
7.2
B. Litar Bersiri dan Litar Selari
Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit 1, 2 76
A. Sifat-sifat Magnet
Properties of Magnet 3 79
B. Medan Magnet
7.3 Magnetic Field 3 80
C. Elektromagnet
Electromagnet 6 81
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 82
8 Daya dan Gerakan / Force and Motion
A. Daya
1, 2 84
Force
B. Daya Mempunyai Magnitud, Arah dan Titik Aplikasi
8.1 1, 3 85
Forces have Magnitude, Direction and Point of Application
C. Pasangan Daya Tindakan-Daya Tindak Balas
1 86
Action-Reaction Pair
A. Tuas
3 88
Lever
B. Momen Daya
1, 2 89
The Moment of Force
C. Tekanan
1 91
Pressure
8.2
D. Tekanan Gas
2 92
Gas Pressure
E. Aplikasi Konsep Tekanan Udara dalam Kehidupan Harian dan
Kesan Altitud kepada Tekanan Atmosfera
1, 2, 3 92
Application of the Concept of Air Pressure in Daily Life and Effect
of Altitude to Atmospheric Pressure
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 95
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. iv
Modul Sains T2-Contents Book A_F.indd 4 25/10/2021 1:02 PM
SK Aktiviti TP Halaman Tarikh Catatan
SK Activity TP Page Date Remarks
9 Haba / Heat
A. Haba dan Suhu
9.1 Heat and Temperature 2 97
A. Pengaliran Haba Secara Konduksi, Perolakan dan Sinaran
Heat Flow via Conduction, Convection and Radiation 3 98
B. Pengaliran Haba dalam Fenomena Alam
Heat Flows in Natural Phenomena 3 99
9.1
C. Konduktor Haba dan Penebat Haba
Heat Conductor and Heat Insulator 1, 3 100
D. Kebolehan Bahan Berlainan Sebagai Penebat Haba
Abilities of Different Materials as Heat Insulator 2 101
A. Pengembangan dan Pengecutan Jirim
The Expansion and Contraction of Matter 3 102
9.3 B. Aplikasi Pengembangan dan Pengecutan Jirim dalam Kehidupan
Harian 6 104
Applications of Expansion and Contraction of Matters in Daily Life
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 106
10 Gelombang Bunyi / Sound Waves
A. Pemindahan Bunyi
10.1 2 108
Transfer of Sound
A. Frekuensi Bunyi dan Unitnya serta Amplitud Getaran
1 109
Frequency of Sounds with Its Unit and Amplitude of Vibration
10.2
B. Kesan Doppler
3 110
Doppler Effect
A. Fenomena Pantulan Gelombang Bunyi
4 111
Phenomena of Reflection of Sound Wave
B. Aplikasi Pantulan Gelombang Bunyi
3 111
Application of Reflection of Sound Waves
10.3
C. Had Pendengaran
2 113
Limitations of Hearing
D. Mengatasi Had Pendengaran Manusia
2 114
Overcome the Hearing Limit
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 114
v © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Contents Book A_F.indd 5 25/10/2021 1:02 PM
SK Aktiviti TP Halaman Tarikh Catatan
SK Activity TP Page Date Remarks
11 Bintang dan Galaksi Dalam Alam Semesta / Stars and Galaxie In The Universe
A. Ciri-ciri Objek Angkasa
Characteristics of Objects in Space 1, 2 117
11.1
B. Bintang
Stars 1, 2 121
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 121
12 Sistem Suria / Solar System
A. Jarak antara Planet-planet daripada Matahari
1, 4 124
Distance of the Planets from the Sun
B. Perbandingan dan Perbezaan antara Planet dalam Sistem Suria
dengan Bumi
2 126
Comparison and Difference between Planets of Solar System with
Earth
12.1
C. Pasangan Daya Tindakan-Daya Tindak Balas
2 129
Action-Reaction Pair
D. Situasi Hipotetikal Berkaitan dengan Sistem Suria
1, 4, 5 136
Hypothetical Situations Related to the Solar System
E. Bumi Merupakan Planet Paling Sesuai untuk Hidupan
2 130
Earth is The Most Suitable Place for Living Things
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 131
13 Meteroid, Asteroid dan Komet / Meteroids, Astroids and Comets
A. Meteoroid, Asteroid dan Komet
13.1 Meteoroids, Asteroids and Comets 2 132
B. Pergerakan Meteoroid, Asteroid dan Komet
13.1 Movements of Meteoroid, Asteroid and Comet 2 134
Latihan Pengukuhan / Enrichment Exercise 136
Pernyataan Umum Tafsiran Tahap Penguasaan Pengetahuan Bagi Mata Pelajaran Sains
TAHAP PENGUASAAN TAFSIRAN
1 Mengingat kembali pengetahuan dan kemahiran asas sains.
Memahami pengetahuan dan kemahiran sains serta dapat menjelaskan kefahaman
2
tersebut.
Mengaplikasikan pengetahuan dan kemahiran sains untuk melaksanakan tugasan
3
mudah.
Menganalisis pengetahuan dan kemahiran sains dalam konteks penyelesaian
4
masalah.
Menilai pengetahuan dan kemahiran sains dalam konteks penyelesaian masalah
5
dan membuat keputusan untuk melaksanakan satu tugasan.
Merekacipta menggunakan pengetahuan dan kemahiran sains dalam konteks
6 penyelesaian masalah dan membuat keputusan atau dalam melaksanakan satu
tugasan dalam situasi baru secara kreatif dan inovatif.
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. vi
Modul Sains T2-Contents Book A_F.indd 6 25/10/2021 1:02 PM
Pembelajaran Berasaskan Projek
Project Based Learning
Kriteria-kriteria utama
Main criteria
Kriteria / Criteria Aspek yang dinilai / Assessed aspects
• Tema / Theme
• Standard kandungan / Content standard
• Standard pembelajaran / Learning standard
• Kertas kerja / Paper work:
✓ Tajuk projek / Project title
Reka bentuk ✓ Tarikh dan masa / Date and time
Design ✓ Tempat / Place
20% ✓ Sasaran / Target
✓ Jenis produk / Type of product
✓ Bilangan produk / Number of product
✓ Senarai AJK / List of committee member
✓ Anggaran perbelanjaan / Budget expenditure
• Langkah: / Steps:
Proses ✓ Senarai bahan-bahan yang digunakan / List of materials used
Process ✓ Sumber rujukan / Reference sources
20% ✓ Penghasilan buku skrap / The scrap book created
✓ Penghasilan projek / The project created
• Kemahiran yang terlibat / Skills involved
✓ Penyelesaian masalah / Problem solving
Aplikasi ✓ Kemahiran mengeksperimen / Skill of experimenting
Application ✓ Kemahiran mengukur / Skill of measuring
20% ✓ Kemahiran berkomunikasi / Skill of communicating
✓ Kemahiran membuat keputusan / Skill of making decision
• Produk yang dihasilkan menepati konsep
Pengetahuan Product produced must meet the concept
Knowledge • Sumber maklumat atau rujukan dalam menghasilkan produk
20% The sources and references in producing the products
• Eviden (folio / buku skrap) / Evidence ( folio / scrap book)
Persembahan • Kreativiti (persembahan produk, kelancaran komunikasi)
Presentation Creativity (product presentation, smooth communication)
20% • Kerjasama / Cooperation
Borang Penilaian Pelajar Borang Penilaian Guru
Student Assessment Form Teacher Assessment Form
vii © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Contents Book A_F.indd 7 25/10/2021 1:02 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Biodiversiti
1 Biodiversity
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES 1
1.1 Kepelbagaian Organisma
Diversity of Organisms
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
SP 1.1.1 Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai biodiversiti. / Elaborate and communicate about biodiversity.
LS 1.1.2 Mewajarkan keperluan pengurusan biodiversiti yang berkesan. / Justify the needs of effective biodiversity management.
EMK Kelestarian alam sekitar / Nature preservation
Nilai Murni
Minat dan sifat ingin tahu tentang alam sekitar / Interest and curiosity about the environment
Moral Value
A. Menghuraikan dan Berkomunikasi Mengenai Biodiversiti Buku teks muka surat 4
Describe and Communicate About Biodiversity Textbook page 4
1 Biodiversiti merujuk kepada kepelbagaian organisma, termasuk haiwan, tumbuhan dan mikroorganisma.
Biodiversity refers to diversity of organisms, including animals, plants and microorganisms. TP1
2 Biodiversiti merupakan sistem sokongan hidupan antara satu sama lain yang merangkumi
tumbuhan dan haiwan (vertebrata dan invertebrata).
Biodiversity is a living support system that includes plants and animals (vertebrates
and invertebrates). TP1
3 Lengkapkan peta konsep di bawah tentang kepentingan biodiversiti.
Complete the concept map below about the importance of biodiversity. TP2
(a)
Membekalkan sumber makanan Untuk mengekalkan keseimbangan
(e)
kepada manusia dan haiwan. alam sekitar.
Supply source of food to To maintain environmental
the human and animals. Kepentingan balance .
Biodiversiti
Importance of
Biodiversity
(b) Sebagai sumber perubatan . (d) Untuk pendidikan .
Act as medical resources. education
For .
(c) Dapat menjana ekonomi seperti pelancongan , perubatan, tempat
rekreasi, bioteknologi dan bahan mentah industri.
Economy can be generated such as tourism , medicine, recreation,
biotechnology and industrial raw materials.
3 (a) makanan / food
(f) pendidikan / education (c) ekonomi; pelancongan / Economy; tourism 2 hidupan; tumbuhan / living; plants
(e) keseimbangan / balance (b) perubatan / medical A. 1 kepelbagaian / diversity
1 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab1 Book A_F.indd 1 25/10/2021 12:24 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Activiti / Activity 1.1
Malaysia merupakan salah sebuah negara Mega Biodiversiti, bagaimana ia boleh mengekalkan dan memelihara
khazanah Negara?
Malaysia is one of the 12 Mega Biodiversity country, how to maintain and preserve this national treasures?
Kerana Malaysia mempunyai spesies-spesies
1 1 Mengapakah Malaysia terpilih majoriti di Bumi dan dianggap mempunyai
menjadi salah sebuah negara kepelbagaian biodiversiti yang besar.
Mega Biodiversiti?
Because Malaysia has the majority of species
Why Malaysia is in a group of
Mega Biodiversity country? in the world and is considered to have a large
diversity of biodiversity .
2
Berikan 3 contoh sumber (a) Hutan paya laut (bakau) / Swamp forest (mangrove)
biodiversiti utama Malaysia.
(b) Hutan tanah gambut / Peatland forest
Give 3 examples of main sources
of biodiversity in Malaysia. (c) Hutan tanah pamah / Lowland forest
(a) Pengekalan kitar hidrologi
Hydrology cycle retention
(b) Modifikasi iklim / Climate modification
3
Apakah kebaikan yang diperoleh (c) Kawal hakisan tanah / Control soil erosion
daripada sumber biodiversiti ini?
(d) Sumber makanan
What are the benefits obtained
from this biodiversity source? Food
sources
riadah
(e) Tempat yang baik
Good recreation park
(f) Sumber ubat-ubatan / Sources of medicine
(a) Mewujudkan hutan simpan dan kekal
Create a reserved and permanent forest
4 (b) Melakukan penyelidikan hutan
Langkah-langkah pengurusan
biodiversiti yang berkesan. Doing a forest research
Steps of effective biodiversity kempen kesedaran
management. (c) Mengadakan
Conducts awareness campaigns
(d) Kesedaran teknologi hijau
Green technology awareness
(c) makanan / Food
Kesedaran / awareness (d) 3 (a) hidrologi / Hydrology
kempen kesedaran / awareness campaigns (c) (c) Hutan tanah pamah / Lowland forest
penyelidikan / research (b) (b) Hutan tanah gambut / Peatland forest
kekal / permanent 4 (a) 2 (a) Hutan paya laut (bakau) / Swamp forest (mangrove)
riadah / recreation (d) 1 spesies-spesies; kepelbagaian biodiversiti / species; diversity of biodiversity
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 2
Modul Sains T2-Bab1 Book A_F.indd 2 25/10/2021 12:24 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B. Pengurusan Biodiversiti yang Berkesan Buku teks muka surat 6
Effective Biodiversity Management Textbook page 6
1 Lengkapkan pernyataan di bawah. / Complete the statements below. TP1
(a) (b)
Pembalakan Penggunaan baja kimia dan racun perosak
yang tidak terkawal akan
secara berlebihan untuk pertanian menyebabkan
menyebabkan kemusnahan hutan yang akan
pencemaran air dan tanah.
menjejaskan habitat flora dan fauna, kesan rumah
banjir kilat Tanah juga menjadi tidak subur akibat kehabisan
hijau, , hakisan tanah dan
mineral .
kehilangan kawasan tadahan air.
deforestation The use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides
Uncontrolled will destroy the
excessively to agricultural will pollute
forest and affect the habitat of flora and fauna,
water and soil. Land also become
greenhouse effect, flash floods , soil erosion
infertile due to the depletion of minerals .
and loss of watersheds.
2 Spesies endemik ialah spesies yang hanya dijumpai di kawasan tersebut dan tiada di tempat
lain. Tahap ekologi sesuatu spesies menjadi unik untuk sesetengah lokasi geografi seperti pulau tertentu,
habitat tertentu, negara atau zon-zon lain yang tertentu. / Endemic species are species that only found
in that area and not elsewhere. Ecology level of a species become unique to certain geographical locations such
as certain islands, certain habitats, certain state or certain other zones. TP1
i-THINK
(a) Mewujudkan taman botani (f) Mewujudkan pusat perlindungan
dan hutan simpan hidupan liar
Langkah-langkah dan zoo
Create botanical garden untuk memelihara Create wildlife
and reserved forest dan memulihara sanctuary and zoo
organisma hidup
Ways to preserve
and conserve living (e) Menguatkuasakan
(b) Penanaman semula organism undang-undang
Re-plantation
Enforcement of
laws
(c) Mengawal penebangan hutan
deforestation (d) Mendidik masyarakat
Control the
Educate the public
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
water; minerals
(f) hidupan liar / wildlife (c) penebangan hutan / deforestation (b) air; mineral
i-THINK
(e) undang-undang / laws (a) taman botani / botanical garden deforestation; flash floods
(d) Mendidik / Educate 2 endemik / endemic B. 1 (a) Pembalakan; banjir kilat
3 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab1 Book A_F.indd 3 25/10/2021 12:24 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
1.2 Pengelasan Organisma / Classification of Organisms
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Membezakan organisma dengan kekunci dikotomi berdasarkan ciri-ciri sepunya.
1.2.1
SP Differentiate organisms using a dichotomous key based on common characteristics.
LS Mencirikan kumpulan taksonomi utama.
1.2.2
Characterise the major taxonomy groups.
EMK Kelestarian alam sekitar / Nature preservation
Nilai Murni Minat dan sifat ingin tahu tentang alam sekitar
Moral Value Interest and curiosity about nature
1
Buku teks muka surat 7
A. Pengelasan Haiwan / Classification of Animals Textbook page 7
1 Lengkapkan peta pokok di bawah untuk mengelaskan haiwan-haiwan.
Complete the tree map below to classify animals. TP1
Haiwan / Animals
(a) Vertebrata / Vertebrates (b) Invertebrata / Invertebrates
Mamalia Reptilia Ikan Berkaki Tanpa kaki
Mammals Reptile Fish With legs Without legs
Amfibia Burung
Amphibia Bird
2 Invertebrata merupakan haiwan yang tidak bertulang belakang. Lengkapkan Peta Pokok di bawah dengan
mengelaskan invertebrata berikut mengikut ciri-ciri umumnya.
Invertebrates are animals that do not have backbone. Complete the Tree Map below by classifying the following
invertebrates according to their common characteristics. TP2
Cacing tanah Lipan Lintah Lalat Kerang Semut Kala jengking Siput
Earthworm Centipede Leech Housefly Cockles Ant Scorpion Snail
Invertebrata / Invertebrates
Berkaki / With legs Tanpa kaki / Without legs
(a) 3 pasang (b) Lebih daripada 3 pasang (c) Badan bersegmen (d) Badan tidak bersegmen
3 pairs More than 3 pairs Segmented body Non-segmented body
Lalat Lipan Cacing tanah Siput
Housefly Centipede Earthworm Snail
Semut Kala jengking Lintah Kerang
Ant Scorpion Leech Cockles
2 (a) Lalat; Semut / Housefly; Ant (c) Cacing tanah, Lintah / Earthworm; Leech
(d) Siput; Kerang / Snail; Cockles A. 1 (a) Reptilia; Amfibia; Burung / Reptile; Amphibia; Bird (b) Lipan; Kala jengking / Centipede; Scorpion
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 4
Modul Sains T2-Bab1 Book A_F.indd 4 25/10/2021 12:24 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
3 Haiwan yang bertulang belakang dikenali sebagai vertebrata. Terdapat lima kelas vertebrata mengikut ciri-ciri
umum mereka. / Animals that have backbone are known as vertebrate. There are five classes of vertebrates
according to their common characteristics. TP2
(a) Mamalia • Homoioterma / Homeothermic
Mammal • Dilitupi dengan bulu atau rambut / Covered with fur or hair
• Bernafas melalui peparu / Breathe through lungs
• Melakukan persenyawaan dalam / Undergo internal fertilisation
• Melahirkan anak dan menyusukan anak semasa kecil / Give birth and nurse their 1
young
(b) Reptilia • Poikiloterma / Poikilothermic
Reptiles • Menghasilkan telur yang bercengkerang / Produce eggs with shell
• Bernafas melalui peparu / Breathe through lungs
• Mempunyai sisik dan kulit yang keras / Have scale and hard skin
• Melakukan persenyawaan dalam / Undergo internal fertilisation
(c) Ikan • Poikiloterma / Poikilothermic
Fish • Bertelur / Lay eggs
• Bernafas melalui insang / Breathe through
gills
• Badan dilitupi dengan sisik yang keras / Covered in hard scales
• Mempunyai sirip dan ekor / Have fins and tail
• Melakukan pernyawaan luar / Undergo external fertilisation
(d) Burung • Homoioterma / Homeothermic
Bird • Menghasilkan telur yang bercengkerang keras / Produce eggs with hard shell
• Badan dilitupi bulu pelepah untuk mengekalkan suhu badan
Body covered with feathers to maintain body temperature
• Mempunyai sayap dan sepasang kaki bersisik / Have wings and a pair of scaly feet
• Bernafas melalui peparu / Breathe through lungs
• Melakukan persenyawaan dalam / Undergo internal fertilisation
(e) Amfibia • Poikiloterma / Poikilothermic
Amphibian • Dilitupi dengan kulit lembap / Covered with moist skin
• Hidup di darat dan air / Live in land and in water
• Menghasilkan telur seperti jeli tanpa cengkerang / Produce jelly-like eggs without shell
• Bernafas melalui insang semasa kecil / Young amphibians breathe through gills
• Bernafas melalui peparu dan kulit lembap semasa dewasa
Adult amphibians breathe through lungs and moist skin
• Melakukan persenyawaan luar / Undergo external fertilisation
Buku teks muka surat 12
B. Pengelasan Tumbuhah / Classification of Plants Textbook page 12
1 Lengkapkan peta pokok di bawah untuk mengelaskan tumbuhan. / Complete the tree map below to classify
plants. TP2
Tumbuhan / Plants
(a) Berbunga / Flowering (b) Tidak berbunga / Non-flowering
• Monokotiledon / Monocotyledon • Lumut / Moss
• Paku-pakis / Ferns
• Dikotiledon / Dicotyledons
• Konifer / Conifer
Poikiloterma; shell; hard; internal (e) luar / external
(b) Tidak berbunga; Paku-pakis / Non-flowering; Ferns (d) dalam / internal
(b) Poikiloterma; bercengkerang; keras; dalam
B. 1 (a) Berbunga; Dikotiledon / Flowering; Dicotyledons A. 3 (a) peparu; dalam / lungs; internal (c) insang; sisik; sirip; luar / gills; scales; fins; external
5 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab1 Book A_F.indd 5 25/10/2021 12:24 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Bandingkan ciri-ciri tumbuhan monokotiledon dan dikotiledon.
Compare the characteristics of monocotyledon and dicotyledon plants. TP2
(a) Monokotiledon (b) Dikotiledon
Monocotyledons Dicotyledons
Selari / Parallel Urat daun / Leaf veins Jejala / Network
1 Kotiledon / Cotyledon 2
1 Serabut / Fibrous Akar / Root Tunjang / Tap
Batang lembut / Non-woody Batang / Stem Berkayu / Woody
3 Tumbuhan tidak berbunga dikelaskan kepada tiga kumpulan.
Non-flowering plants are classified into three groups. TP2
(a) Paku-pakis / Ferns (b) Lumut / Moss (c) Konifer / Conifer
Menghasilkan spora Menghasilkan spora Membiak dengan menghasilkan
untuk pembiakan. Vaskular. untuk pembiakan. Bukan kon . Vaskular.
spore vaskular.
Produce for Reproduce by producing
spore
reproduction. Vascular. Produce for cone . Vascular.
reproduction. Non-vascular.
C. Membina Kekunci Dikotomi Buku teks muka surat 14
Constructing Dichotomous Keys Textbook page 14
Kelaskan lima haiwan berikut menggunakan kekunci dikotomi.
Classify the following five animals using a dichotomous key. TP3
1 (a) Poikiloterma / Poikilothermic Ke 2 / To 2 Kucing
Cat
(b) Homoioterma / Homeothermic Ke 3 / To 3
Katak
2 (a) Bersisik / With scales Ke 4 / To 4 Frog
(b) Tidak bersisik / No scales Katak / Frog Burung merpati
Pigeon
3 (a) Tidak berbulu pelepah / No feather Kucing / Cat Ular
(b) Berbulu pelepah / With feather Burung merpati / Pigeon Snake
Ikan tenggiri
4 (a) Tidak berinsang / No gills Ular / Snake Mackerel
(b) Berinsang / With gills Ikan tenggiri / Mackerel
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
Kucing / Cat 3 (a) 3 (a) spora / spore
(b) Ikan tenggiri / Mackerel Katak / Frog C. 2 (b) (b) Jejala; 2; Tunjang; Berkayu / Network; 2; Tap; Woody
4 (a) Ular / Snake kon / cone (c) Parallel; 1; Fibrous; Non-woody
(b) Burung merpati / Pigeon spora / spore (b) 2 (a) Selari; 1; Serabut; Batang lembut
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 6
Modul Sains T2-Bab1 Book A_F.indd 6 25/10/2021 12:24 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Kuiz / Quiz
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan spesies 2 Berikut adalah ciri-ciri sejenis tumbuhan.
endemik? The following are the characteristics of a plant.
What is the definition of endemic species?
• Mempunyai satu kotiledon / Has one cotyledon 1
A Spesies yang mengalami kepupusan
• Mempunyai akar serabut / Has fibrous root
An extinction species • Mempunyai urat daun selari
B Spesies yang terdapat di beberapa negara di Has parallel veins leaves
dunia • Mempunyai batang tidak berkayu
Species found in several country in the world Has non-woody stem
C Spesies yang hidup dalam kumpulan dalam
Antara berikut, yang manakah mempunyai ciri-ciri
habitat yang terhad di lokasi yang spesifik
tersebut?
Species that lives in clusters within a restricted
Which of the following has these characteristics?
habitat in a specific location
A Pokok durian dan pokok padi
D Spesies yang membiak di tempat yang sama
Durian tree and paddy plant
Species that reproduces within the same place
B Pokok jagung dan pokok padi
Maize plant and paddy plant
C Pokok rambutan dan pokok getah
Rambutan tree and rubber tree
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
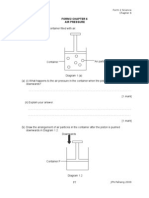
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan kitar hidup katak dan buaya. / Diagram 1 shows the life cycles of a frog and a crocodile.
Kitar hidup katak / Life cycle of a frog Kitar hidup buaya / Life cycle of a crocodile
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
(a) Katak dan buaya dikelaskan sebagai vertebrata. Mengapa?
Frogs and crocodiles are classified as vertebrate. Why?
Kedua-duanya mempunyai tulang belakang. / Both have backbones.
[1 markah/mark]
(b) Nyatakan kelas vertebrata dua haiwan ini. / State the vertebrate classes of these two animals.
Katak / Frog : Amfibia / Amphibian Buaya / Crocodile : Reptilia / Reptile
[2 markah/marks]
(c) Nyatakan satu ciri yang unik bagi setiap haiwan. / State one feature that is unique for each animal.
Katak / Frog : Badan berkulit lembap / Moist skined body
Buaya / Crocodile : Badan bersisik kering / Dry scales body
[2 markah/marks]
(d) Berdasarkan Rajah 1, berikan pendapat anda haiwan manakah yang boleh bernafas dalam air? Wajarkan
pendapat anda.
Based on Diagram 1, give your opinion which animal can breathe in the water? Justify your opinion.
Hanya katak yang boleh bernafas di dalam air kerana ia mempunyai insang yang membolehkannya bernafas
di dalam air. Buaya tidak boleh bernafas di dalam air. Ia hanya mempunyai peparu dan tiada insang.
Only frog can breathe in water because it has gills that allow it to breath in water. The crocodile cannot
breathe in water. It only has lungs but no gills.
[2 markah/marks]
7 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab1 Book A_F.indd 7 25/10/2021 12:24 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Ekosistem
2 Ecosystem
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
2.1 Aliran Tenaga dalam Ekosistem
2 Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
SP 2.1.1 Menerangkan dengan contoh; pengeluar, pengguna dan pengurai. / Explain through examples; producer, consumer and decomposer.
LS 2.1.2 Menginterpretasi rantai makanan dan siratan makanan. / Interpreting food chain and food web.
EMK Kelestarian alam sekitar / Nature preservation
Nilai Murni Minat dan sifat ingin tahu tentang alam sekitar
Moral Value Interest and curiosity about nature
A. Pengeluar, Pengguna dan Pengurai Buku teks muka surat 22
Producer, Consumer and Decomposer Textbook page 22
1 Pengeluar ialah organisma yang membuat makanan sendiri menggunakan tenaga daripada
cahaya matahari melalui proses fotosintesis.
Producer is an organism which can make their own food using energy from sunlight
through photosynthesis process. TP1
2 Pengguna ialah organisma yang memakan organisma lain. Pengguna primer ialah haiwan herbivor dan omnivor
yang memakan pengeluar .
Consumer is an organism which eat other organisms. Primary consumer is herbivore and omnivore animals which
eat producer . TP1
3 Pengguna sekunder ialah haiwan omnivor dan karnivor yang makan pengguna primer .
Secondary consumer is omnivore and carnivore animals which eat the primary consumer . TP1
4 Pengguna tertier ialah haiwan karnivor sekunder yang makan pengguna sekunder.
Tertiary consumer is secondary carnivore animals which eat the secondary consumer. TP1
5 Pengurai ialah organisma yang mengurai haiwan dan tumbuhan yang mati.
Decomposer is an organism which decompose dead animals and plants. TP1
6 Kenal pasti pengeluar, pengguna primer, pengguna sekunder dan pengurai dalam jadual berikut.
Identify the producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer and decomposer in the following table. TP2
Organisma Aktiviti pemakanan Peranan organisma dalam rantai makanan
Organism Feeding activity Function of organism in food chain
(a)
Memakan ikan, sotong,
Pengguna sekunder
kerang-kerangan dan ketam
Secondary consumer
Eat fish, squids, shellfish and
crabs
Singa laut / Sea lion
mengurai / decompose 5 pengguna primer / primary consumer 3 organism; food; sunlight
Pengguna tertier / Tertiary consumer 4 pengeluar / producer 2 A. 1 organisma; makanan; cahaya matahari /
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 8
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 8 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Organisma Aktiviti pemakanan Peranan organisma dalam rantai makanan
Organism Feeding activity Function of organism in food chain
(b)
Memakan ubi-ubian dan buah- Pengguna primer
buahan Primary consumer
Eat tubers and fruits
Landak / Porcupine
(c)
Mengurai organisma mati Pengurai
Decompose dead organism Decomposer
Bakteria pengurai bangkai
Carcass decomposer bacteria
2
(d)
Menggunakan cahaya matahari
bagi membuat makanan Pengeluar
sendiri Producer
Use sunlight to make own
Rumput gajah lokal foods
Local elephant grass
B. Rantai Makanan dan Siratan Makanan Buku teks muka surat 24
Food Chain and Food Web Textbook page 24
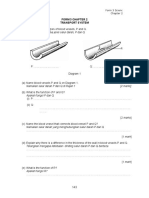
1 Rajah di bawah menunjukkan satu rantai makanan. Setiap anak panah mewakili makanan yang dimakan oleh
setiap haiwan. / The diagram below shows a food chain. Each arrow represents food eaten by each animal.
Susun pernyataan di bawah berkaitan rantai makanan mengikut susunan yang betul.
Arrange the statements about the food chain below with correct arrangement. TP2
Pernyataan Susunan
Statement Arrangement
(a) Matahari menghasilkan tenaga cahaya 1
Sun produces sunlight
(b) Ular mendapat tenaga dengan memakan katak 4
Snake obtains energy by eating frog
(c) Padi menghasilkan makanan sendiri dengan menggunakan tenaga daripada
Matahari 2
Paddy produces its own food by using energy from the Sun
(d) Helang yang mati diurai oleh bakteria dan fungus dalam persekitaran 6
Dead eagle decomposed by bacteria and fungus in surrounding
(e) Apabila belalang memakan padi, sebahagian tenaga berpindah ke belalang 3
When grasshopper eats paddy, some of the energy transferred to the grasshopper
(f) Helang mendapat tenaga dengan memakan ular 5
Eagle obtains energy by eating snake
(f) 5 (c) 2 (d) Pengeluar / Producer
(e) 3 (b) 4 (c) Pengurai / Decomposer
(d) 6 B. 1 (a) 1 A. 6 (b) Pengguna primer / Primary consumer
9 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 9 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Bina tiga rantai makanan menggunakan organisma yang diberi di bawah.
Construct three food chains using the organisms given below. TP3
Helang Sawi Ulat beluncas Belalang Burung pipit Tikus
Eagle Mustard Caterpillar Grasshopper Sparrow Rat
(i) Sawi / Mustard ➝ Ulat beluncas / Caterpillar ➝ Burung pipit / Sparrow ➝ Helang / Eagle
(ii) Sawi / Mustard ➝ Belalang / Grasshopper ➝ Burung pipit / Sparrow ➝ Helang / Eagle
(iii) Sawi / Mustard ➝ Tikus / Rat ➝ Helang / Eagle
3 (a) Siratan makanan berikut merupakan rantai makanan yang telah anda senaraikan.
2 The following food web is the food chain that you have listed. TP3
Ulat beluncas
Caterpillar
Sawi Belalang Burung pipit Helang
Mustard Grasshopper Sparrow Eagle
Tikus
Rat
(b) Daripada siratan makanan, kenal pasti organisma yang memainkan peranan berikut.
From the food web, identify the organism that plays the following role. TP2
(i) Pengeluar / Producer: Sawi / Mustard
(ii) Pengguna primer / Primary consumer: Ulat beluncas, belalang, tikus / Caterpillar, grasshopper, rat
(iii) Pengguna sekunder / Secondary consumer : Burung pipit, helang / Sparrow, eagle
(iv) Pengguna tertier / Tertiary consumer : Helang / Eagle
4 Aliran tenaga dan kehilangan tenaga berlaku dalam satu siratan makanan.
Energy flow and losing of energy occurs in a food web. TP2
Kunci / Key:
Aliran tenaga dalam siratan makanan
Energy flow in food web
Tenaga yang hilang sebagai haba
Energy lost as heat
(a) Sumber tenaga dalam siratan makanan ialah cahaya matahari .
Ekstra / Extra
Source of energy in a food web is sunlight .
(b) Tumbuhan menggunakan tenaga daripada Matahari untuk menjalankan fotosintesis .
Plant uses energy from the Sun to carry out photosynthesis .
(b) fotosintesis / photosynthesis (b) (i) Sawi / Mustard 3
4 (a) cahaya matahari / sunlight (iii) Sawi / Mustard ➝ Tikus / Rat ➝ Helang / Eagle
(iii) Burung pipit, helang / Sparrow, eagle (ii) Sawi / Mustard ➝ Belalang / Grasshopper ➝ Burung pipit / Sparrow ➝ Helang / Eagle 2
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 10
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 10 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(c) Tenaga mengalir melalui tumbuhan pada setiap organisma dalam satu siratan makanan melalui
pemakanan .
Energy flow through plant to each organism in a food web through eating .
(d) Pada setiap aras, tenaga akan hilang apabila benda hidup menjalankan respirasi , pergerakan,
pertumbuhan, dan pengekalan suhu badan menyebabkan tenaga yang dipindahkan bermula daripada
sumber tenaga semakin berkurangan.
At every level, the energy will lose when living things carry out respiration , moving, growth, and
maintaining body temperature cause the energy transferred starting from the energy source decrease.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
2
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
2.2 Kitar Nutrien dalam Ekosistem / Nutrient Cycle in Ecosystem
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai peranan benda hidup dalam kitar oksigen dan kitar karbon dalam ekosistem.
2.2.1
SP Elaborate and communicate the role of living things in oxygen and carbon cycles in an ecosystem.
LS Mewajarkan peranan organisma dalam kitar air suatu ekosistem.
2.2.2
Justify the role of organisms in water cycle in an ecosystem.
Menyelesaikan masalah apabila terdapat gangguan ke atas kitaran disebabkan aktiviti manusia.
2.2.3
Solve the problems when there is an interference to the cycles due to human activities.
EMK Kelestarian alam sekitar / Nature preservation
Nilai Murni Minat dan sifat ingin tahu tentang alam sekitar
Moral Value Interest and curiosity about nature
Buku teks muka surat 25
A. Kitar Air dalam suatu Ekosistem / Water Cycle in an Ecosystem Textbook page 25
1 Lengkapkan peta alir di bawah mengikut urutan yang betul bagi kitar air.
Complete flow chart below with the correct sequence of water cycle. TP2
(a) (b)
Air tersejat dan membentuk kondensasi
Wap air mengalami dan
wap air dan naik ke udara. berubah menjadi titisan air.
Water is evaporated and change Water vapour is condensed and
into water vapour and rise up to the air. changed into water drops.
(d) (c)
Air akan mengalir atau meresap ke Titis-titis air bergabung menjadi awan
dalam tanah, menjadi air sungai, laut atau dan apabila berat, ia turun sebagai
air kolam. hujan .
The rain will flow or seeps into the Water drops combine into clouds and when
ground as a river, ocean or ponds.
it is heavy, it drops as rain .
(d) meresap / seeps (b) kondensasi / condensed (d) respirasi / respiration
(c) hujan / rain A. 1 (a) Air / Water B. 4 (c) pemakanan / eating
11 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 11 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Rajah di bawah menunjukkan kitar air yang berlaku dalam alam sekitar. Lengkapkan.
The diagram below shows water cycle in environment. Complete it. TP2
(b) Penyejatan / Evaporation
(a) Kondensasi / Condensation
Atmosfera Tanah
Atmosphere Soil
Hujan
an Penyerapan
j at ion Tra
Rain
e t Absorption
e ny ora Tran nspiras
P ap spir i
atio
Ev n Tumbuhan
Laut, kolam, sungai Plant
2 Sea, pond, river
(c) Respirasi, penyahtinjaan
dan perkumuhan Dimakan oleh
Respiration, defaecation Eaten by
and excretion
Haiwan
Animal
Diminum / Drunk by
B. Kitar Oksigen dan Kitar Karbon dalam Ekosistem Buku teks muka surat 26
Oxygen Cycle and Carbon Cycle in the Ecosystem Textbook page 26
1 Lengkapkan kitar oksigen dan kitar karbon pada rajah di bawah.
Complete the diagram below on oxygen cycle and carbon cycle. TP2
Menggunakan / Use, O2 Oksigen
(a) di atmosfera
Membebaskan / Release, CO2 Oxygen
in atmosphere
Membebaskan / Release, O2
(b) Karbon dioksida di atmosfera
Carbon dioxide in atmosphere
Fotosintesis
Respirasi tumbuhan
Photosynthesis
Plant respiration
Pembakaran
Combustion
Haiwan mati
Respirasi haiwan Animals die
Tumbuhan mati Animal respiration
Plant die
Pengurai / Decomposer
Pereputan
Decomposition Pereputan / Decomposition
(c) Respirasi, penyahtinjaan dan perkumuhan / Respiration, defaecation and excretion
(b) Karbon dioksida / Carbon dioxide (b) Penyejatan / Evaporation
B. 1 (a) Oksigen / Oxygen A. 2 (a) Kondensasi / Condensation
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 12
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 12 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Kitar oksigen. / Oxygen cycle. TP2
Karbon dioksida Oksigen dibebaskan di atmosfera
Carbon dioxide Oxygen is released in the atmosphere
(b) Respirasi
Digunakan untuk / Used for
Respiration
(a) Fotosintesis
Photosynthesis
(c) Pembakaran (e) Pengaratan
Combustion (d) Pereputan Rusting
Decomposition 2
C. Menyelesaikan Masalah Gangguan kepada Kitar Nutrien Buku teks muka surat 27
Solving Problems of Disruption to the Nutrient Cycle Textbook page 27
1 Suai padankan aktiviti berikut dengan penyelesaian masalah yang patut diambil terhadap gangguan kitaran.
Match the following activities with the problem solving of cycle distraction. TP2
Aktiviti / Activity Masalah / Problem Penyelesaian / Solution
(a)
Pembakaran bahan
api fosil Kempen penjimatan air
Fossil fuel Water saving campaign
combustion
(b)
Penggunaan air
secara berlebihan
Membina sistem saliran yang efisien
untuk domestik
Build efficient drainage system
Domestic water
usage excessively
(c)
Penanaman semula, mewartakan
Penebangan hutan
hutan simpan dan menguatkuasakan
secara tidak terkawal
undang-undang
Uncontrolled
Replanting, gazetting reserve forest
deforestation
and law enforcement
(d)
Memastikan ketinggian cerobong
Penggunaan air
asap lebih daripada 30 m dan
secara berlebihan
menggunakan penapis asap
dalam pertanian
Make sure the height of chimneys
Excessive water
are more than 30 m and use smoke
usage in agriculture
filters
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
(e) Pengaratan / Rusting
(d)
(d) Pereputan / Decomposition
(c) (c) Pembakaran / Combustion
(b) (b) Respirasi / Respiration
C. 1 (a) B. 2 (a) Fotosintesis / Photosynthesis
13 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 13 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Saling Bersandaran dan Interaksi antara Organisma dan antara Organisma dengan
2.3 Persekitaran / Interdependence and Interaction among Organisms and between
Organisms with the Environment
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Menjelaskan dengan contoh saling bersandaran antara benda hidup dan persekitaran untuk keseimbangan ekosistem.
2.2.1
Explain through examples the interdependence among living things and the environment in maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
2.2.2 Mewajarkan kepentingan penyesuaian hidupan terhadap alam sekitar. / Justify the importance of adaption of living things to the environment.
Berkomunikasi mengenai contoh interaksi antara organisma hidup dan mengaplikasi interaksi tersebut dalam kehidupan harian.
SP 2.2.3
Communicate through examples the interaction between organisms and apply these interactions in daily life.
LS
Mencerakinkan faktor yang mempengaruhi saiz populasi dalam suatu ekosistem.
2.2.4
Separate the factors that affect the size of population in an ecosystem.
Meramalkan bagaimana perubahan dalam ekosistem mempengaruhi sumber yang ada dan keseimbangan antara populasi.
2.2.5
Predict how the changes in ecosystem affect resources and balance of population.
2 EMK
Nilai Murni
Kelestarian alam sekitar / Nature preservation
Minat dan sifat ingin tahu tentang alam sekitar
Moral Value Interest and curiosity about nature
Buku teks muka surat 28
A. Keseimbangan Ekosistem / Ecosystem Balance Textbook page 28
1 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan istilah dan maksudnya.
Complete the table below with their terms and meaning. TP2
Rajah / Diagram Istilah / Terms Maksud / Meaning
(a) Sekumpulan organisma yang mempunyai ciri-ciri yang sama dan
Spesies boleh menghasilkan zuriat melalui pengawanan.
Species A group of organisms that have common characteristics and can
reproduce through mating.
(b)
Tempat tinggal semula jadi bagi organisma.
Habitat
Habitat Natural place of organisms.
(c) Sekumpulan organisma yang sama spesies hidup bersama di
Populasi habitat yang sama.
Population A group of organisms of same species that live together in
the same habitat.
(d)
Beberapa populasi organisma berbeza yang tinggal bersama
Komuniti dalam satu habitat dan saling berinteraksi antara satu sama lain.
Community A few populations of different organism that live together in one
habitat and have mutual interaction with one another.
(e) Beberapa komuniti yang tinggal bersama dalam satu habitat dan
Ekosistem saling berinteraksi antara satu sama lain dengan persekitaran
Ecosystem komponen bukan hidup. / A few communities that live together
in one habitat and have mutual interactions with one another with
non-living component’s surrounding.
2 Keseimbangan ekosistem ialah saling bersandaran antara organisma hidup dengan komponen bukan hidup
dalam keadaan harmoni.
non-living components
Balanced ecosystem is the interdependence between living organisms with in a
harmony situation. TP1
interdependence; non-living components (e) Ekosistem / Ecosystem (b) semula jadi / Natural
saling bersandaran; komponen bukan hidup 2 (c) Populasi; sama spesies / Population; same species A. 1 (a) Spesies / Species
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 14
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 14 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 33
B. Interaksi antara Organisma Hidup / Interactions between Living Organisms Textbook page 33
1 Lengkapkan peta pokok di bawah dengan menyatakan jenis interaksi organisma hidup.
Complete the tree map below by specifying the type of living organism interaction. TP1
Jenis Interaksi / Type of Interactions
(a) (b) (c)
Persaingan Simbiosis Mangsa-pemangsa
Competition Symbiosis Prey-predator
2
(d) (e) (f)
Mutualisme Komensalisme Parasitisme
Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism
2 Dalam interaksi berikut, nyatakan organisma yang memainkan peranan bagi setiap interaksi. Nyatakan tujuan
setiap interaksi dan contoh-contoh lain bagi setiap interaksi tersebut.
In the following interaction, state the animal that play the role of each interaction. State the purpose and other
examples of each interaction. TP2
Jenis interaksi Peranan organisma Tujuan interaksi Contoh-contoh lain
Type of interaction Role of organism Purpose of interaction Other examples
(a) Mangsa: Kuda belang Pemangsa memburu mangsa 1 Katak dan lalat.
Prey: Zebra sebagai makanan. Frog and fly.
Pemangsa: Singa Predator hunts prey for food.
Predator: Lion 2 Kucing dan tikus.
Mangsa-pemangsa
Cat and mouse.
Prey-predator
(b) Sekumpulan singa Dua organisma bersaing 1 Rumput dan semalu.
B bersaing merebut untuk mendapatkan makanan, Grass and mimosa.
A makanan. pasangan dan habitat.
A group of lion Two organisms compete to 2 Harimau dan singa.
competing for food. get food, mate and habitat. Tiger and lion.
Pesaing 1 / Competitor
Singa A / Lion A
Persaingan
Pesaing 2 / Competitor
Competition
Singa B / Lion B
(c) Komensal / Comensal: Komensal berlindung di 1 Ikan yu dan ikan
Orkid / Orchid perumah dan mendapat remora .
Orkid
Perumah / Host: kebaikan manakala perumah
Orchid A shark and a
Batang pokok / Tree tidak mendapat keuntungan
Pokok remora fish.
stem atau mengalami kerugian.
Tree
Commensal being protected
2 Paku pakis dan
by host and get benefit while
Komensalisme the host does not get any pohon besar.
Commensalism benefit nor loss. Ferns and
a big tree.
(c) 1 remora / remora (d) Mutualisme / Mutualism
Paku pakis / Ferns 2 2 (b) Singa A; Singa B / Lion A; Lion B B. 1 (a) Persaingan / Competition
15 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 15 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Jenis interaksi Peranan organisma Tujuan interaksi Contoh-contoh lain
Type of interaction Role of organism Purpose of interaction Other examples
(d) Umang-umang Dua organisma hidup 1 Alga dan fungi
Buran membekalkan makanan. bersama dan membantu satu (liken). / Algae and
Anemone The hermit crab sama lain. Kedua-duanya
supplies food. mendapat keuntungan. fungi (lichen).
Buran memberi
Two organisms live together 2 Tumbuhan
and help each other. Both kekacang dan
Umang-umang perlindungan.
Hermit crab getbenefits.
The anemone gives bakteria.
Mutualisme protection.
Legume and
Mutualism
2 bacteria.
(e) Perumah: manusia Parasit mendapat 1 Rafflesia dan pohon
Host: human makanan manakala besar.
perumah mengalami Rafflesia and big tree.
Parasit: cacing pita
yang menyerap nutrien kerugian . 2 Kutu di atas kulit
daripada manusia. The parasite gets mamalia.
Parasite: tapeworm foods
Parasitisme while the Fleas on mammalians
that absorbs nutrient
Parasitism from human. host suffer loss . head.
3 Kawalan biologi ialah satu kaedah yang menggunakan interaksi mangsa-pemangsa untuk membunuh dan
mengurangkan bilangan perosak.
Biological control is a method using interaction of prey-predator to kill and reduce the numbers of pest. TP1
4 Kenal pasti agen, perosak dan jenis interaksi dalam contoh kawalan biologi yang berikut.
Identify the agent, pest and the type of interaction in the following examples of the biological control. TP2
Kawalan biologi Agen Perosak Jenis interaksi
Biological control Agent Pests Types of interaction
(a) Tikus yang merosakkan
Ular pokok kelapa sawit Mangsa-pemangsa
Snake Rat Prey-predator
that destroys oil
palm tree
(b)
Afid yang merupakan perosak
Kumbang kura-kura pada tumbuhan berbatang lembut Mangsa-pemangsa
Ladybird beetle pest Prey-predator
The aphids are to
plant
(c)
Tikus memakan padi di
sawah padi Mangsa-pemangsa
Burung hantu
Owl The rats eat paddy at Prey-predator
paddy field
(c) sawah padi; Mangsa-pemangsa / paddy field; Prey-predator 4 (a) Ular; Tikus / Snake; Rat 2 kekacang / Legume
(b) perosak; Mangsa-pemangsa / pest; Prey-predator (e) makanan; kerugian / foods; loss B. 2 (d) 1 fungi / fungi
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 16
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 16 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
5 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah tentang kebaikan dan kelemahan kawalan biologi.
Complete the table belows on advantages and disadvantages of biological control. TP3
(a) Kebaikan / Advantages (b) Kelemahan / Disadvantages
Tidak mencemarkan alam sekitar Mungkin memberi kesan kepada organisma lain
Does not pollute the environment May affect other organisms
Murah / Low cost Lambat / Slow
C. Faktor-faktor yang Mempengaruhi Saiz Populasi dalam Suatu Ekosistem Buku teks muka surat 37
Factors Affecting the Size of the Population in an Ecosystem
2
Textbook page 37
1 Lengkapkan peta buih bagi faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi saiz populasi dan kesannya dalam suatu ekosistem.
Complete the bubble map of factors that affect population size and its effect to the ecosystem. TP2
(a) Kehadiran pemangsa (c) Sumber makanan berkurangan
Presence of predator Source of food reduce
Saiz populasi akan
berkurang jika,
Population size
will decrease if,
penyakit (d) Perubahan cuaca
(b) Diserang
Disease outbreak Change of weather
D. Perubahan dalam Ekosistem Buku teks muka surat 38
Changes in Ecosystem Textbook page 38
1 Lengkapkan maklumat di bawah tentang perubahan dalam ekosistem terhadap perubahan populasi yang
mengganggu keseimbangan alam.
Complete the information below about the changes in ecosystems to the changes in population that disturbing
natural balance. TP2
(a) Kekurangan bekalan air (b) Migrasi (c) Perubahan saiz populasi
Shortage of water supply Migration Change in population size
Populasi pengeluar yang berkurang Haiwan berpindah dari satu tempat Pertambahan populasi serangga
disebabkan keadaan kemarau ke tempat lain disebabkan perosak menyebabkan populasi
menjejaskan siratan makanan. perubahan musim. tumbuhan menurun.
Decrease in producer population Animals move from a place to Increase in population of pest
because of drought will affect the other place because of change of causes the population of plants
food web. seasons. decrease.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
(b) Migrasi / Migration C. 1 (b) penyakit / outbreak
D. 1 (a) Kekurangan bekalan air / Shortage of water supply (b) Lambat / Slow
(c) Perubahan saiz populasi / Change in population size (d) cuaca / weather 5 (a) Murah / Low cost
17 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 17 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2.4 Peranan Manusia dalam Mengekalkan Keseimbangan Alam
Role of Humans in Maintaining a Balanced Nature
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
SP Mewajarkan dan berkomunikasi bahawa manusia memerlukan ekosistem yang stabil dan produktif demi kelestarian hidup.
2.4.1
LS Justify and communicate why humans need a stable and productive ecosystem for the sustainability of life.
EMK Kelestarian alam sekitar / Nature preservation
Nilai Murni Minat dan sifat ingin tahu tentang alam sekitar
Moral Value Interest and curiosity about nature
Activiti / Activity 2.1
Lengkapkan carta alir mengenai isu-isu alam sekitar di bawah.
2 Complete a flowchart on environmental issues below.
Punca / Causes Akibat / Impact
Bilangan kenderaan bermotor
bertambah Hujan asid
The number of motor vehicles Acid rain
increases
Pembebasan asap kilang Kematian hidupan akuatik
Emission of factory smoke The death of aquatic life
Pembalakan haram Hakisan tanah
Illegal logging Soil erosion
Pembuangan sisa kilang dan
pertanian ke dalam sungai Kesan rumah hijau
The waste of factory and Green house effect
agriculture waste into the river
Langkah-langkah mengekalkan keseimbangan alam:
Steps in maintaining a balanced nature:
1 Penguatkuasaan undang-undang . / Reinforcement of law .
2 Meningkatkan kesedaran orang awam. / Increase public awareness.
3 Mengamalkan 5R – Elak, Kurangkan, Guna semula, Kitar semula, Kegunaan lain.
Practise 5R – Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Repurpose.
4 Penggunaan kaedah kawalan biologi . / Use of biological control method.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
biologi / biological 4
undang-undang / law 1 Aktiviti / Activity 2.1
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 18
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 18 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu rantai makanan. 3 Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu eksperimen bagi
Diagram 1 shows a food chain. mengkaji taburan organisma hidup terhadap
pengaruh komponen bukan hidup.
Belalang Burung pipit Ular
Grasshopper Sparrow Snake
Diagram 2 shows an experiment to investigate the
contribution of living organisms with the influence
of non-living component.
Kertas hitam 2
Rumput Black paper
Grass
Burung hantu M N
P Owl Air / Water
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1 Rajah 2 / Diagram 2
Apakah P? / What is P? Apakah kesimpulan bagi eksperimen ini?
A Semut What is the conclusion of this experiment?
Ant A Organisma lebih suka berkumpul di kawasan
B Cacing tanah suhu sederhana
Earthworm Organisms are more likely gather in medium
C Kulat temperature region
Fungi B Organisma lebih suka berkumpul di tempat
D Cahaya matahari gelap
Sunlight Organisms are more likely gather in dark region
C Organisma lebih suka berkumpul di tempat
2 Pernyataan di bawah menunjukkan proses yang yang lembap
melibatkan gas P dan gas Q.
Organisms are more likely gather in damp place
The statement below shows processes that involve
D Organisma lebih suka berkumpul di kawasan
gas P and gas Q.
yang kering
Organisms more likely gather in dry place
Gas P digunakan dalam proses fotosintesis
oleh tumbuhan. 4 Antara padanan berikut, yang manakah
Gas Q digunakan dalam proses respirasi oleh menunjukkan interaksi yang betul?
tumbuhan. Which of the following match shows the correct
Gas P is used for a photosynthesis process by interaction?
plant.
Gas Q is used for a respiration process by plant. Organisma Interaksi
Organism Interaction
Antara berikut, yang manakah gas P dan Q?
Which of the following is gas P and Q? A Buran dan umang-
umang Mutualisme
P Q Sea anemone and Mutualism
hermit crab
A Nitrogen Karbon dioksida
Nitrogen Carbon dioxide B Ikan remora dan ikan
Mangsa-pemangsa
jerung
B Karbon dioksida Nitrogen Remora fish and shark
Prey-predator
Carbon dioxide Nitrogen
C Cacing tanah dan
C Oksigen Karbon dioksida Parasitisme
ayam / Earthworm
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Parasitism
and chicken
D Karbon dioksida Oksigen D Kutu dan manusia Komensalisme
Carbon dioxide Oxygen Lice and human Commensalism
19 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 19 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions Ekstra / Extra
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan dua jenis interaksi antara organisma hidup.
Diagram 1 shows two types of interaction among living organisms.
Interaksi A / Interaction A Interaksi B / Interaction B
2 Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
(a) Namakan jenis interaksi dalam Rajah 1. / Name the interaction in Diagram 1.
Interaksi A / Interaction A : Mutualisme / Mutualism
Interaksi B / Interaction B : Mangsa-pemangsa / Prey-predator
[2 markah/marks]
(b) Nyatakan peranan burung dan kerbau dalam interaksi A. / State the role of bird and buffalo in interaction A.
Burung : memberi perlindungan daripada dihisap pacat atau lintah
Birds: Give protection from being sucked by leech or bloodsucker
Kerbau: membekalkan makanan / Buffalo: supplying foods
[2 markah/marks]
(c) Berdasarkan interaksi yang ditunjukkan, interaksi manakah yang digunakan dalam kawalan biologi?
Terangkan. / Based on the interaction shown, which interaction is used in a biological control? Explain.
– Interaksi B / Interaction B
– Larva adalah mangsa dan ikan gapi adalah pemangsa / Larvae is the prey and guppy fish is the predator
[2 markah/marks]
(d) Nyamuk aedes sangat merbahaya dan mudah membiak di kawasan air bertakung. Gigitan nyamuk aedes
boleh menyebabkan penyakit demam denggi yang boleh membawa maut. Sekumpulan pelajar telah
menjalankan kajian bagaimana untuk menghalang dan mengurangkan pembiakan nyamuk. Mereka telah
meletakkan sejumlah 20 ekor larva nyamuk dan dua ekor ikan gapi di dalam satu bekas. Jadual di bawah
menunjukkan bilangan larva dalam tempoh tiga hari. / Aedes mosquitoes are very dangerous and easily
breed in a stagnant water area. Aedes bite can cause dengue fever and cause death. A group of students
did an investigation on how to prevent and reduce mosquito breeding. They put 20 mosquitoes and two
guppy fish in a container. The table below shows the number of larvae within three days.
Hari / Days 1 2 3
Bilangan Larva / Larvae 18 8 2
Number Ikan gapi / Guppy fish 4 4 4
(i) Mengapakah bilangan larva semakin berkurang dan bilangan ikan gapi kekal? Terangkan.
Why does the number of larva decrease and the number of guppy fish remain? Explain.
– Larva dimakan oleh ikan gapi. / Larvae are eaten by guppy fish.
– Larva adalah makanan ikan gapi. / Larvae are the food for guppy fish.
[2 markah/marks]
(ii) Wajarkan kesan interaksi ini terhadap salah satu cara mengawal pembiakan nyamuk aedes.
Justify the effect of this interaction as one of the way to control aedes mosquito breeding.
Kesan interaksi mangsa-pemangsa adalah baik kerana murah dan tidak melibatkan penggunaan racun
yang mencemarkan air. / Effects on prey-predator interactions is good because it is cheap and not
involve the uses of poison that will pollute the water.
[2 markah/marks]
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 20
Modul Sains T2-Bab2 Book A_F.indd 20 25/10/2021 12:25 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Nutrisi
3 Nutrition
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
3.1 Kelas Makanan
Classes of Food
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
SP 3.1.1 Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai kelas makanan. / Elaborate and communicate on classes of food.
LS 3.1.2
EMK
Menguji kehadiran kanji, glukosa, protein dan lemak dalam makanan. / Test the presence of starch, glucose, protein and fat in food.
Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
3
Nilai Murni Jujur dan tepat dalam merekod dan mengesahkan data.
Moral Value Honest and accurate in recording and verifying data.
Buku teks muka surat 46
A. Kelas Makanan / Classes of Food Textbook page 46
Simulasi
1 Nyatakan fungsi kelas makanan berikut dan berikan tiga contoh makanan yang mengandungi kelas Simulation
makanan tersebut.
State the functions of the following classes of food and give three examples of foods that contain
the particular classes of food. TP1
Kelas Makanan Fungsi
Classes of Food Function
(a) Karbohidrat / Carbohydrates • Membekalkan tenaga kepada badan
Contoh / Example: energy
Supplies our body with
1 Nasi / Rice
2 Mee / Noodle
3 Roti / Bread
(b) Protein / Proteins • Menghasilkan sel baru bagi pertumbuhan serta
Contoh / Example: membaiki
Ikan / Fish sel yang rosak
1
Produces new cells
2 Daging / Meat
repaired
3 Ayam / Chicken for growth and damaged cells
• Kekurangannya akan menyebabkan penyakit kwasyiorkor
Dificiency of protein will cause kwashiorkor disease
(c) Lemak / Fats • Membekalkan tenaga / Supply energy
Contoh / Example: suhu
• Mengekalkan badan
1 Mentega / Butter
Maintain our body temperature
2 Minyak kelapa / Coconut oil
• Pelarut vitamin ( A, D, E dan K )
3 Kacang tanah / Groundnut
Solvent for vitamins ( A, D, E and K )
Kacang tanah / Groundnut 3 Ayam / Chicken 3
Minyak kelapa / Coconut oil 2 Daging / Meat 2
A, D, E dan K / A, D, E and K • Mentega / Butter (c) 1 Ikan / Fish (b) 1
tenaga; suhu / energy; temperature • sel baru; membaiki / new cells; repaired • tenaga / energy A. 1 (a) •
21 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 21 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Kelas Makanan Fungsi
Classes of Food Function
(d) Garam mineral / Minerals • Untuk mengekalkan kesihatan
Contoh / Example: To maintain health
1 Susu / Milk
2 Buah-buahan / Fruits
3 Sayur-sayuran / Vegetables
(e) Vitamin / Vitamins • Untuk mengekalkan kesihatan
Contoh / Example: To maintain health
1 Susu / Milk
2 Buah-buahan / Fruits
3 Sayur-sayuran / Vegetables
3 (f) Pelawas / Fibre • Membantu makanan melalui salur pencernaan dengan mudah
Contoh / Example: Helps food to pass through the alimentary cannal easily
1 Bijirin / Cereals • Mengelakkan sembelit
2 Buah-buahan / Fruits constipation
Prevents
3 Sayur-sayuran / Vegetables
(g) Air / Water • Medium untuk tindak balas kimia dalam sel
Contoh / Example: The medium for chemical reactions in cell
Jus buah / Fruit juice • Pelarut bahan tercerna dalam badan
1 Solvent for digested food
2 Buah-buahan / Fruits • Mengekalkan suhu badan
3 Minuman / Drinks Maintain body temperatures
2 Kenal pasti fungsi mineral dan kesan kekurangannya.
Identify the functions of the minerals and their effects of deficiency. TP2
Mineral Fungsi Kesan kekurangan
Minerals Function Effects of deficiency
(a) Besi / Iron
• Pembentukan hemoglobin dalam sel darah Anemia
Sumber / Sources:
1 Daging merah merah untuk pengangkutan oksigen Anaemia
Red meat Formation of haemoglobin in red blood
2 Hati cells for transporting oxygen
Liver
(b) Iodin / Iodine pertumbuhan Beguk
Sumber / Sources: • Mengawal dan pembebasan
1 Makanan laut hormon Goiter
Controls the growth and release of
Seafood
2 Buah-buahan hormones
Fruits
(g) 1 Jus buah / Fruit juice (e) 1 Susu / Milk
Beguk / Goiter • sembelit / constipation • kesihatan / health
(b) pertumbuhan / growth (f) 3 Sayur-sayuran / Vegetables 3 Sayur-sayuran / Vegetables
Anemia / Anaemia • kesihatan / health 2 Buah-buahan / Fruits
2 (a) hemoglobin / haemoglobin 2 Buah-buahan / Fruits A. (d) 1 Susu / Milk
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 22
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 22 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Mineral Fungsi Kesan kekurangan
Minerals Function Effects of deficiency
(c) Natrium / Sodium • Komponen penting dalam pengaliran bendalir Kekejangan otot
Sumber / Sources: badan untuk memastikan fungsi saraf yang baik Muscle cramp
1 Garam masakan Important component in the flow of body fluids to
Table salt ensure the nerves function properly
2 Telur
Eggs
(d) Kalsium, fosforus • Diperlukan dalam pembentukan tulang 1 Riket / Ricket
Calcium, phosphorus gigi 2 Osteoporosis
dan
Sumber / Sources: bones Osteoporosis
Susu / Milk Needed in the formation of
1 teeth 3 Gigi reput
Sayur-sayuran and Tooth decayed
2
Vegetables 4 Pembekuan darah 3
Ikan bilis lambat
3 Delayed blood
Anchovies
clotting
(e) Kalium / Potassium saraf 1 Lemah otot
• Mengekalkan sistem yang
Sumber / Sources: sihat Weak muscles
1 Haiwan nervous 2 Lumpuh
Maintains a healthy system
Animals Paralyse
2 Tumbuhan
Plants
3 Kenal pasti fungsi vitamin dan kesan kekurangannya.
Identify the functions of the vitamins and their effects of deficiency. TP2
Vitamin Fungsi Kesan kekurangan
Vitamins Function Effects of deficiency
(a) Vitamin A / Vitamin A • Membolehkan kita memiliki 1 Rabun malam
Sumber / Sources: penglihatan yang baik
1 Tomato / Tomatoes Enables us to maintain good vision Night blindness
2 Hati / Liver 2 Sakit kulit
3 Sayur hijau / Green vegetables Skin diseases
(b) Vitamin B / Vitamin B • Diperlukan untuk kulit yang sihat dan 1 Beri-beri / Beri-beri
Sumber / Sources: sistem saraf yang sihat 2 Dermatitis
1 Bijirin / Cereals Needed for healthy skin and proper Dermatitis
Telur / Eggs system of the nerves
2 • Mengawal pelepasan tenaga dari
3 Susu / Milk karbohidrat
Control the release of energy from
carbohydrates
Susu / Milk 3 • saraf / nervous 2 Sayur-sayuran / Vegetables
Telur / Eggs 2 2 Tumbuhan / Plants (d) 1 Susu / Milk
Bijirin / Cereals (b) 1 (e) 1 Haiwan / Animals Kekejangan otot / Muscle cramp
Sakit kulit / Skin diseases 2 • tulang; gigi / bones; teeth 2 Telur / Eggs
Rabun malam / Night blindness 3 (a) 1 3 Ikan bilis / Anchovies A. (c) 1 Garam masakan / Table salt
23 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 23 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Vitamin Fungsi Kesan kekurangan
Vitamins Function Effects of deficiency
(c) Vitamin C / Vitamin C tisu yang sihat Skurvi / Scury
• Untuk dan
Sumber / Sources:
penyembuhan luka
1 Sayur-sayuran / Vegetables
Buah-buahan / Fruits For healthy tissue and
2
healing of wounds
• Untuk membina sistem pertahanan
For the formation of the immune
system
(d) Vitamin D / Vitamin D
3 Sumber / Sources:
• Pembentukan tulang 1 Riket / Ricket
dan gigi yang kuat Gigi reput
Hati / Liver 2
1
Formation of bones Tooth decayed
2 Minyak ikan / Fish oil
teeth 3 Osteoporosis
and
3 Telur / Eggs
Osteoporosis
(e)
Vitamin E / Vitamin E • Mengekalkan sistem pembiakan Kemandulan
Sumber / Sources:
yang sihat Sterility
1 Sayur-sayuran hijau
Maintain a healthy reproduction
Green vegetables
system
Bijirin • Mengekalkan kulit
2
Cereals yang cantik
Maintain a beautiful skin
(f)
Vitamin K / Vitamin K pembekuan Pendarahan yang
• Membolehkan
Sumber / Sources:
darah berterusan
1 Sayur-sayuran hijau clotting
Enables blood Prolonged bleeding
Green vegetables
2 Tomato / Tomatoes
Pendarahan yang berterusan / Prolonged bleeding Bijirin / Cereals 2 2 Minyak ikan / Fish oil
• pembekuan / clotting Sayur-sayuran hijau / Green vegetables (e) 1 (d) 1 Hati / Liver
2 Tomato / Tomatoes Osteoporosis / Osteoporosis 3 • pertahanan / immune
(f) 1 Sayur-sayuran hijau / Green vegetables Gigi reput / Tooth decayed 2 healthy tissue; healing of wounds
Kemandulan / Sterility Riket / Ricket 1 • tisu yang sihat; penyembuhan luka
• kulit / skin • tulang; gigi / bones; teeth 2 Buah-buahan / Fruits
• pembiakan / reproduction Telur / Eggs 3 A. 3 (c) 1 Sayur-sayuran / Vegetables
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 24
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 24 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
3.2 Kepentingan Gizi Seimbang / Importance of a Balanced Diet
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
3.2.1 Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai gizi seimbang. / Elaborate and communicate on a balanced diet.
SP
LS Menganggar kalori makanan yang diambil dalam setiap hidangan dan merancang satu gizi seimbang.
3.2.2
Estimate calories of food intake in a meal and plan a balanced diet.
Membuat kajian dan mewajarkan kepentingan gizi seimbang, senaman dan gaya hidup yang sihat dalam mengekalkan kesihatan badan.
3.2.3
Conduct a research and justify the importance of a balanced diet, exercise and a healthy lifestyle in order to maintain a healthy body.
EMK Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Nilai Murni Berfikiran terbuka / Open minded
Moral Value Sistematik, yakin dan beretika / Systematic, confident and ethical
Buku teks muka surat 53
A Gizi Seimbang / Balanced Diet Textbook page 53
1 Gizi seimbang merujuk kepada pemakanan yang mengandungi semua kelas makanan yang diperlukan
oleh tubuh badan dalam nisbah yang betul.
all
3
Balanced diet refers to the diet that involve all classes of food needed by the body in the correct
ratio . TP1
2 Lengkapkan rajah di bawah.
Complete the diagram below. TP2
(a) (b)
Menghasilkan sel baru semasa
pertumbuhan serta membaiki
Mengekalkan kesihatan kita.
sel dan tisu yang rosak.
Maintain our health .
Produce new cells in growth
and repair damaged cells
and tissues.
Kepentingan
Gizi Seimbang
The Importance
of a Balanced
Diet
(c) (d)
Membekalkan tenaga
kepada kita untuk menjalankan Membantu kita menentang penyakit .
aktiviti harian.
Help us to fight against diseases .
Supply energy for us to
carry out daily activities .
(c) tenaga; aktiviti / energy; activities 2 (a) kesihatan / health
(d) penyakit / diseases (b) sel baru; membaiki / new cells; repair A. 1 semua; nisbah / all; ratio
25 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 25 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
3 Rajah di bawah menunjukkan piramid makanan.
The diagram below shows a food pyramid.
Isi tempat kosong dengan contoh makanan pada setiap tingkat.
Fill in the blank with the examples of food at each level. TP1
(a) Lemak, gula
Fat, sugar
(b) Susu, tenusu (c) Ikan, daging, ayam, kekacang
Milk, dairy Fish, meat, chicken, nuts
3
(d) Sayur-sayuran (e) Buah-buahan
Vegetables Fruits
(f) Bijirin, kanji, nasi, roti
Cereal, starch, rice,
bread
(i) Faktor yang mempengaruhi Gizi Seimbang / Factors that affect the Balanced Diet TP2
(a) Umur / Age
• Pada tahap bayi, protein , kalsium dan fosforus
diperlukan dalam kuantiti yang banyak untuk pertumbuhan sel baru, tulang
dan gigi.
At infant stage, protein , calcium and phosphorus are
needed in big quantity for the growth of new cells, bones and teeth.
• Pada tahap kanak-kanak atau remaja, seseorang memerlukan banyak
karbohidrat kerana mereka sangat aktif.
At childhood or teenage stage, a person needs a lot of carbohydrate as they
are very active.
• Pada usia tua, seseorang memerlukan kurang protein dan karbohidrat tetapi
memerlukan lebih banyak kalsium untuk menguatkan tulangnya.
At old age, a person needs less protein and carbohydrate but needs more
calcium to strengthen his bones.
(f) Bijirin; kanji; nasi; roti / Cereal; starch; rice; bread Fish; meat; chicken; nuts
protein; calcium; phosphorus (e) Buah-buahan / Fruits (c) Ikan; daging; ayam; kekacang
3 (i) (a) protein; kalsium; fosforus (d) Sayur-sayuran / Vegetables A. 3 (b) Susu, tenusu / Milk, dairy
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 26
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 26 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(b) Jantina / Gender
• Secara umum, lelaki memerlukan lebih banyak karbohidrat dan
protein berbanding perempuan .
In general, male needs more carbohydrate and protein compared
to female .
(c) Pekerjaan atau aktiviti / Occupation or activity
• Orang yang terlibat dalam pekerjaan atau aktiviti yang memerlukan kekuatan
fizikal (seperti atlet dan pekerja di tapak pembinaan ) memerlukan lebih banyak
karbohidrat untuk memberi tenaga kepada mereka dan juga lebih banyak
protein untuk membina otot yang kuat.
People involved in occupations or activities which require physical strength
(such as athletes and construction site workers) need more carbohydrate to
3
give them energy and also more protein to build strong muscles.
(d) Saiz badan / Body size
• Saiz badan yang lebih besar memerlukan lebih banyak karbohidrat
kerana ia perlu menghasilkan lebih banyak tenaga untuk menjalankan aktiviti.
Bigger body size requires more carbohydrate as it needs to
generate more energy to carry out activities.
(e) Iklim / Climate
• Orang yang tinggal di kawasan beriklim sejuk mengambil lebih banyak
lemak dan karbohidrat untuk mengekalkan badan mereka
panas.
People staying in cold climate regions consume more fat and
carbohydrate
to keep their body warm.
(f) Keadaan kesihatan / State of health
• Orang yang sakit perlu mengubah gizinya supaya penyakitnya tidak menjadi
lebih teruk. / People who are sick need to adjust their diet so that the diseases
will not beworsened.
• Seorang pesakit kencing manis tidak boleh mengambil terlalu banyak kanji
kerana ini akan meningkatkan tahap gula darah. / A diabetic patient cannot
take too much starch as this will increase the blood sugar level.
(e) lemak; karbohidrat / fat; carbohydrate (d) lebih besar / Bigger A. 3 (i) (b) lelaki; perempuan / male; female
27 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 27 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B. Nilai Kalori Makanan dan Merancang Gizi Seimbang Buku teks muka surat 55
The Calorific Value of Foods and Planning a Balance Diet Textbook page 55
Jadual di bawah menunjukkan nilai kalori kelas makanan bagi setiap gram.
The table below shows the calorific value of each class of food in each gram. TP2
Kelas makanan Nilai kalori bagi setiap gram (kJ/g)
Class of foods Calorific value in each gram (kJ/g)
Lemak / Fats 37
Karbohidrat / Carbohydrates 17
Protein / Proteins 17
* 1 kilokalori (kcal) = 4.2 kilojoule (kJ) / 1 kilocalorie (kcal) = 4.2 kilojoule (kJ)
3
Berdasarkan jadual di atas, hitung nilai kalori untuk setiap kelas makanan bagi sampel makanan di bawah.
Based on the table above, calculate the calorific value for each of these classes of food. TP3
(i) Mentega kacang
Peanut butter Tenaga dalam: / Energy in:
Nilai kalori untuk satu hidangan (a) Lemak / Fat: 16 × 37 = 592 kJ
Calorific value per serving 7 × 17 = 119 kJ
(b) Karbohidrat / Carbohydrate:
Satu hidangan (c) Protein / Protein: 8 × 17 = 136 kJ
Per serving
Lemak / Fats 16 g Jumlah tenaga satu hidangan: / Total energy in one serving:
Karbohidrat / Carbohydrates 7g 592 + 119 + 136 = 847 kJ
Protein / Proteins 8g
(ii) Roti putih
White bread Tenaga dalam: / Energy in:
Nilai kalori untuk satu hidangan (a) Lemak / Fat: 4 × 37 = 148 kJ
Calorific value per serving
(b) Karbohidrat / Carbohydrate: 49.7 × 17 = 844.9 kJ
Satu hidangan 0.5 × 17 = 8.5 kJ
Per serving (c) Protein / Protein:
Lemak / Fats 4g Jumlah tenaga satu hidangan: / Total energy in one serving:
Karbohidrat / Carbohydrates 49.7 g
148 + 844.9 + 8.5 = 1 001.4 kJ
Protein / Proteins 0.5 g
Ekstra / Extra
(b) 844.9 kJ (c) 136 kJ
1 001.4 kJ (ii) (a) 148 kJ (b) 119 kJ
(c) 8.5 kJ 847 kJ B. (i) (a) 592 kJ
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 28
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 28 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
C. Kepentingan Gizi Seimbang, Senaman dan Gaya Hidup Sihat dalam
Buku teks muka surat 58
Mengekalkan Kesihatan / Importance of Balanced Diet, Exercise and Textbook page 58
Healthy Lifestyle in Maintaining Health
1 Senaraikan punca dan kesan obesiti.
List the causes and effects of obesity. TP2
(a) Punca Obesiti (b) Kesan Obesiti
Cause of Obesity Effect of Obesity
Pemakanan yang tidak seimbang Sakit jantung
Unbalanced diet Heart disease
Kurang bersenam Kolestrol tinggi
Lack of exercise High cholestrol
Genetik Tekanan darah tinggi
Genetic High blood pressure
3
Gaya hidup tidak sihat Kencing manis
Unhealthy lifestyle Diabetes
Projek / Project
Arahan / Instructions:
Obesiti dalam kalangan murid sekolah semakin meningkat di Malaysia. Ini sangat berkait dengan cara pemakanan
dan gaya hidup yang tidak sihat. Kumpul data bagi rakan-rakan anda di dalam kelas.
Obesity among school children is increasing in Malaysia. This is very much related to improper eating habits and
lifestyle. Collect the following data for your friends in the classroom.
Bil / No Nama / Name Berat, kg / Weight, kg Tinggi, m / Height, m BMI
* Jika kawan anda memiliki indeks BMI lebih daripada 30 kg m–2, teruskan kajian dengan mengaitkan pengambilan
makanan yang diproses seperti burger atau makanan bergoreng. Cadangkan cara untuk menyelesaikan
masalah tersebut bagi peringkat sekolah.
If your friend has BMI index more than 30 kg m–2, continue to study by associating processed meals such as
burgers or fried foods. Suggest ways to solve the problems at school level.
Jisim / Mass (kg)
Indeks jisim badan / Body mass index (BMI) =
Tinggi / Height (m) × Tinggi / Height (m)
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
Kencing manis / Diabetes (b) Kolestrol tinggi / High cholestrol Genetik / Genetic
Tekanan darah tinggi / High blood pressure Gaya hidup tidak sihat / Unhealthy lifestyle C. (a) Kurang bersenam / Lack of exercise
29 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 29 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
3.3 Sistem Pencernaan Manusia / Human Digestive System
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
SP Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai pencernaan.
3.3.1
LS Elaborate and communicate on digestion.
EMK Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Nilai Murni Berfikiran terbuka / Open minded
Moral Value Sistematik, yakin dan beretika / Systematic, confident and ethical
A. Struktur Sistem Pencernaan Manusia Buku teks muka surat 60
Human Digestive System Structure Textbook page 60
1 Isikan tempat kosong dengan perkataan-perkataan yang diberikan untuk menerangkan proses pencernaan dan
peristalsis.
Fill in the blanks with the words provided below to explain the digestion and peristalsis process. TP2
3 ringkas meresap enzim besar mekanik
simple diffuse enzyme bigger mechanically
besar dan kompleks kecil dan ringkas pemotongan kimia pengisaran
large and complex small and simple cutting chemically grinding
(a) Pencernaan / Digestion
Pencernaan ialah satu proses di mana molekul makanan yang besar dan kompleks dipecahkan kepada
molekul kecil dan ringkas
supaya mereka boleh diserap ke dalam aliran darah.
Digestion is a process where large and complex food molecules are broken down into
small and simple molecules so that they can be absorbed into bloodstream.
(b) Pencernaan Fizikal / Physical Digestion
1 Pencernaan fizikal ialah pemecahan secara mekanik ; cebisan makanan yang besar kepada
cebisan yang kecil melalui gerakan pengoyakan, pemotongan dan pengisaran gigi.
Physical digestion is when the large pieces of food is broken down into a smaller pieces of food
mechanically through the tearing, cutting and grinding action of teeth.
2 Ketulan makanan yang kecil mempunyai luas permukaan yang besar bagi pencernaan
kimia. / Smaller pieces of food have a bigger surface area for chemical digestion.
(c) Pencernaan Kimia / Chemical Digestion
1 Pencernaan kimia
ialah pemecahan molekul makanan yang besar dan kompleks secara
kimia kepada molekul ringkas melalui tindakan enzim .
Chemical digestion is the breaking down of large complex food molecules chemically into
simple molecules by the action of enzyme .
2 Molekul ringkas kecil boleh meresap melalui dinding usus kecil semasa penyerapan.
Small and simple molecules can diffuse through the wall of the small intestine during
absorption.
(b) 1 mekanik; pemotongan; pengisaran
2 meresap / diffuse 2 besar / bigger large and complex; small and simple
(c) 1 kimia; ringkas; enzim / chemically; simple; enzyme mechanically; cutting; grinding A. 1 (a) besar dan kompleks; kecil dan ringkas
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 30
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 30 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Labelkan rajah di bawah dengan nama organ yang betul.
Label the diagram below with the correct organ. TP1
Kuiz / Quiz
(e)
(a) Mulut
Kelenjar liur Mouth
Salivary gland
(f)
Esofagus
Oesophagus
(g)
(b) Perut
Hati Stomach
Liver
(h)
(c) Pankreas
Pundi hempedu
Gall bladder
Pancreas 3
(i)
Usus besar
(d)
Usus kecil Large intestine
Small intestine
(j)
Rektum
Rectum
3 Jadual di bawah menunjukkan organ-organ dalam sistem pencernaan dan fungsinya.
The table below shows the organs in the digestive systems and their functions. TP2
Organ / Organs Fungsi / Function
Mengunyah makanan kepada cebisan yang lebih kecil dan memulakan pencernaan
(a) Mulut
kanji
Mouth
Urutan aliran makanan / The flow of food particles
Chews food into smaller pieces and starts the digestion of starch
(b) Esofagus Menolak makanan dari mulut ke perut melalui proses peristalsis
Oesophagus Pushes the food from the mouth to the stomach through peristalsis process
(c) Perut Memulakan pencernaan protein
Stomach Starts the digestion of proteins
(d) Duodenum Memulakan pencernaan lemak
Duodenum Starts the digestion of fats
(e) Usus kecil Menyempurnakan pencernaan dan menyerap hasil pencernaan melalui dindingnya
Small intestine Completes the digestion and absorbs end products of digestion
(f) Usus besar Menyerap semula air dan garam mineral
Large intestine Reabsorbs water and mineral salts
(g) Rektum Menyimpan tinja sementara
Rectum Stores faeces temporarily
(h) Dubur Melaksanakan penyahtinjaan
Anus Carries out defeacation
(f) Esofagus / Oesophagus (c) Pundi hempedu / Gall bladder
(j) Rektum / Rectum (h) Pankreas / Pancreas (e) Mulut / Mouth (b) Hati / Liver
(i) Usus besar / Large intestine (g) Perut / Stomach (d) Usus kecil / Small intestine A. 2 (a) Kelenjar liur / Salivary gland
31 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 31 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
4 Isikan tempat kosong dengan kata kunci yang diberi untuk membincangkan rembesan dalam pelbagai organ
dalam salur pencernaan. / Fill in the blanks with the keywords provided to discuss about the secretion in various
organs in the digestive tracts. TP2
maltosa medium bakteria Asid amino kanji
maltose medium bacteria amino acids starch
hidroklorik enzim lipase enzim protease polipeptida
Hydrochloric lipase enzyme protease enzyme polypeptide
Organ Rembesan Fungsi Hasil pencernaan
Organ Secretion Function Product of digestion
(a) Mulut Mencernakan kanji
Enzim amilase Maltosa
Mouth Amylase enzyme starch Maltose
Digest
3 (b) Perut 1 Membekalkan medium
Stomach berasid untuk aktiviti enzim
protease.
Asid hidroklorik Provides acidic medium
Hydrochloric
for protease enzyme activity.
acids
2 Membunuh bakteria di
dalam makanan.
Kills bacteria in the food.
Enzim protease Mencernakan protein Polipeptida
Protease enzyme Digest protein Polypeptide
(c) Duodenum Enzim amilase Mencernakan kanji Maltosa
Duodenum Amylase enzyme Digest starch Maltose
Enzim protease Mencernakan polipeptida Dipeptida
Protease enzyme Digest polypeptide Dipeptide
Enzim lipase Mencernakan lemak Asid lemak dan gliserol
Lipase enzyme Digest fats Fatty acid and glyserol
(d) Usus kecil Enzim maltase Mencernakan maltosa Glukosa
Small intestine Maltase enzyme maltose Glucose
Digest
Mencernakan dipeptida Asid amino
Enzim protease
Protease enzyme Digest dipeptides Amino acids
Sistem Pencernaan Manusia
5 Pelawas tidak dicernakan kerana tiada enzim untuk mencernakan pelawas di dalam sistem Human Digestive System
pencernaan manusia.
Fibres are not digested because there is no enzyme to digest fibre in the human digestive
system. TP2 https://goo.gl/g2VfHK
Asid amino / Amino acids (c) polipeptida / polypeptide Enzim protease / Protease enzyme
(d) maltosa / maltose 2 bakteria / bacteria (b) hidroklorik / Hydrochloric
Enzim lipase / Lipase enzyme 1 medium / medium 4 (a) kanji / starch
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 32
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 32 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
3.4 roses Penyerapan dan Pengangkutan Hasil Pencernaan serta Penyahtinjaan
P
Process of Absorption and Transportation of Digestive Products and Defeacation
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Menjalankan eksperimen bagi menerangkan proses penyerapan hasil pencernaan.
3.4.1
SP Conduct an experiment to explain the absorption of the end products of digestion.
LS Menghubungkaitkan fungsi sistem pencernaan, sistem peredaran darah dan sistem respirasi.
3.4.2
Relate the function of digestive system, blood circulatory system and respiratory system.
3.4.2 Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai penyahtinjaan. / Elaborate and communicate on defecation.
EMK Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Nilai Murni Jujur dan tepat dalam merekod dan mengesahkan data.
Moral Value Honest and accurate in recording and verifying data.
A. Struktur Dalaman Usus Kecil Buku teks muka surat 66
Internal Structure of Small Intestine Textbook page 66
3
Q
Rajah di atas menunjukkan suatu struktur yang terdapat dalam usus kecil.
The diagram above shows a structure found in the small intestine. TP2
1 Struktur yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah ialah vilus .
The structure shown in the diagram is a villus .
2 Struktur ini menambahkan luas permukaan untuk penyerapan makanan tercerna dalam usus kecil.
This structure increases the surface area for the absorption of digested food in the small intestine.
3 Struktur ini mempunyai dinding yang setebal satu sel. Ini membolehkan makanan tercerna diserap dengan
mudah. / This structure has a one-cell thick wall. This enables the digested food to be absorbed easily.
4 Struktur berlabel Q dalam rajah ialah kapilari darah . Fungsinya adalah untuk menyerap dan mengangkut
glukosa dan asid amino.
The structure labelled Q in the diagram is a blood capillary . Its function is to absorb and transport glucose
and amino acid.
5 Struktur berlabel R dalam rajah ialah lakteal. Fungsinya adalah untuk menyerap dan mengangkut asid lemak,
gliserol dan vitamin yang larut dalam lemak (A, D, E dan K).
The structure labelled R in the diagram is a lacteal. Its function is to absorb and transport fatty acids, glycerol
and fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K).
kapilari darah / blood capillary 4 luas permukaan / surface area 2 vilus / villus A. 1
33 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 33 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B. Proses Pengangkutan Hasil Pencernaan Buku teks muka surat 68
Transportation Process of Digestive Product Textbook page 68
Proses pengagihan hasil akhir pencernaan untuk kegunaan sel-sel badan.
Asimilasi
Assimilation The process of distribution of final product of digestions for the use of body cells.
Memecahkan partikel makanan kepada molekul kecil dan ringkas supaya boleh
Sistem pencernaan
diserap ke dalam vilus. / Break down food particles to small and simple molecules
Digestive system
so that it can be absorbed into villus.
Sistem peredaran darah Mengangkut molekul kecil dan ringkas ke sel-sel badan.
Blood circulatory system Transport small and simple molecules to the body cells.
3
Agihan hasil akhir untuk: / Distribution of final product for:
Asimilasi • Pembentukan sel-sel baharu / Formation of new cells
Assimilation • Respirasi / Respiration
• Pengawalan suhu badan / Body temperature controls
C. Penyerapan Semula Air dan Penyahtinjaan Buku teks muka surat 69
Reabsorption of Water and Defaecation Textbook page 69
B
C
1 Nyatakan fungsi bagi struktur yang berlabel. / State the function of the structure labelled. TP1
A : Menyerap semula air / To reabsorb water
B : Menyimpan tinja sementara / To store faeces temporary
C : Membolehkan pengeluaran tinja / To allow the removal of faeces
2 Proses di mana tinja dikeluarkan daripada badan dikenali sebagai penyahtinjaan .
The process where faeces is removed out of the body is known as defaecation . TP1
3 Pelawas membolehkan pergerakan tinja melalui organ-organ ini dengan mudah.
Fibre allows faeces to move easily through the organ. TP2
4 Apabila kekurangan pelawas dalam gizi, kita akan mengalami sembelit , iaitu kesukaran untuk
mengeluarkan tinja. / When we lack of fibre in our diet, we may experience constipation , which is the
difficulty to remove faeces. TP2
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
2 penyahtinjaan / defaecation To store faeces temporary
sembelit / constipation 4 To allow the removal of faeces C. 1 B. Menyimpan tinja sementara
Pelawas / Fibre 3 C. Membolehkan pengeluaran tinja B. pengagihan / distribution
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 34
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 34 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan Amir menghidapi satu Antara berikut, yang manakah padanan yang betul
penyakit. bagi pemerhatian dan kesimpulan bagi eksperimen?
Diagram 1 shows Amir is suffering from a disease. Which of the following is the correct matching for
the observation and conclusion for the experiment?
Pemerhatian Kesimpulan
Observation Conclusion
A Mendakan jingga Glukosa hadir
Orange precipitate Glucose is presence
B Mendakan biru tua Protein hadir
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1 Dark blue precipitate Protein is presence
3
Apakah yang menyebabkan masalah ini? C Mendakan merah bata Protein hadir
What is the cause of this problem? Brick-red precipitate Protein is presence
A Lemak berlebihan / Excess fat B Mendakan jingga Kanji hadir
B Gula berlebihan / Excess sugar Orange precipitate Starch is presence
C Kekurangan iodin / Lack of iodine
D Kekurangan kalsium / Lack of calcium 3 Rajah 3 menunjukkan sistem pencernaan manusia.
Diagram 3 shows a human digestive system.
2 Rajah 2 menunjukkan susunan radas untuk
mengesan kehadiran satu kelas makanan di dalam
sampel makanan X.
Diagram 2 shows a set up of apparatus to
investigate a class of food in food sample of X.
Q P
Larutan albumen R S
+ Kukus air
Reagen Millon Water bath
Albumen solution
+
Millon’s reagent Rajah 3 / Diagram 3
Panaskan Di manakah protein mula tercerna?
Heat
Where does protein start to digest?
A P C R
Rajah 2 / Diagram 2 B Q D S
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
1 Elizabeth menjalankan eksperimen untuk mengkaji penyerapan makanan dalam usus kecil. Susunan radas adalah
seperti ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 1. Dua jenis tiub Visking digunakan dalam dua set radas yang berlainan.
Elizabeth carries out an experiment to study the absorption of food in small intestine. The set-up of apparatus
is as shown in Diagram 1. Two types of Visking tubes are used in two sets of different apparatus.
Air suling
Tiub Visking Distilled Tiub Visking
jenis A water jenis B
Visking tube Visking tube
type A type B
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
35 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 35 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Satu campuran kanji dan larutan glukosa diisi ke dalam kedua-dua tiub Visking pada permulaan eksperimen.
Selepas 20 minit, ujian iodin dan Benedict dijalankan ke atas air suling. Pemerhatian adalah seperti ditunjukkan
dalam Jadual 1.
A mixture of starch and glucose solution is filled into both Visking tubes at the beginning of the experiment.
After 20 minutes, iodine and Benedict’s tests are carried out on the distilled water. The observations are shown in
Table 1.
Ujian Tiub Visking jenis A Tiub Visking jenis B
Test Visking tube type A Visking tube type B
Ujian iodin Kuning Biru tua
Iodine test Yellow Dark blue
Ujian Benedict Mendakan merah bata Mendakan merah bata
Benedict’s test Brick-red precipitate Brick-red precipitate
Jadual 1 / Table 1
3
(a) Bahan jenis apakah yang boleh bergerak melalui tiub Visking?
What type of substance can move through a Visking tube?
Bahan yang mempunyai molekul kecil / A substance which has small molecule
[1 markah/mark]
(b) Berdasarkan pemerhatian, apakah bahan-bahan yang terdapat dalam air suling yang mana tiub Visking jenis
B direndam? / Based on the observation, what are the substances found in the distilled water in which
Visking tube type B is immersed?
Kanji dan glukosa / Starch and glucose
[2 markah/marks]
(c) Jenis tiub Visking yang manakah lebih sesuai digunakan dalam eksperimen ini? Terangkan.
Which type of Visking tube is suitable to be used in this experiment? Explain.
Tiub Visking A. Hanya glukosa yang mempunyai molekul kecil boleh bergerak melaluinya.
Visking tube A. Only glucose which has small molecule can move through it.
[2 markah/marks]
2 Alex seorang kanak-kanak berusia 3 tahun telah menghidapi penyakit kwasyiorkor. Alex telah berhenti minum
susu ibunya kerana ingin memberikan susu tersebut pada adiknya, Abib yang berusia 3 bulan. Disebabkan itu,
gizi badannya lebih mengandungi karbohidrat dan pelawas.
Alex a 3 years old child has suffers kwashiorkor disease. He has stopped drinking his mother’s milk because he
want to give the milk to his brother, Abib, a 3 months old baby. Due to that, his diet contains more carbohydrates
and fibre.
Pada pendapat anda, mengapakah abdomen Alex membengkak apabila dia mengubah gizinya? Terangkan dan
wajarkan pendapat anda.
In your opinion, why is Alex’s abdomen swelling when he changes his diet? Explain and justify your opinion.
Badan Alex boleh mencernakan susu dengan baik. Walau bagaimanapun, badannya mungkin belum bersedia
untuk mencernakan karbohidrat. Alex mungkin belum ada set gigi yang lengkap untuk mengunyah makanan.
Pencernaan fizikal yang tidak baik mempengaruhi penyerapan nutrisi makanan. Maka, ini menyebabkan
pertumbuhan abdomennya yang tidak seimbang.
Alex’s body can digest milk well. However, his body may not be ready to digest carbohydrate yet. Alex may
not have full set of teeth to chew food. Poor physical digestion affected the absorption of nutrient from
food. Thus, it causes imbalance growth of his abdomen.
[4 markah/marks]
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 36
Modul Sains T2-Bab3 Book A_F.indd 36 25/10/2021 12:26 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Kesihatan Manusia
4 Human Health
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
4.1 Penyakit Berjangkit dan Penyakit Tidak Berjangkit
Infectious and Non-infectious Diseases
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Membezakan dan berkomunikasi mengenai penyakit berjangkit dan penyakit tidak berjangkit.
SP 4.1.1
Differentiate and communicate infectious and non-infectious diseases.
LS
4.1.2 Menerangkan bagaimana penyakit berjangkit disebarkan. / Explain how infectious diseases are spread.
4.1.3 Mencerakinkan penyebab dan penularan penyakit berjangkit. / Separate the cause and spread of infectious diseases.
Menjana idea mekanisme menghalang penularan penyakit berjangkit negara.
4.1.4
Generate ideas on the mechanism to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
EMK
Nilai Murni
Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Menghargai dan mengamalkan kehidupan yang sihat.
4
Moral Value Appreciate and practice a healthy life.
A. Penyakit Berjangkit dan Penyakit Tidak Berjangkit Buku teks muka surat 76
Infectious and Non-infectious Diseases Textbook page 76
1 Penyakit berjangkit ialah penyakit yang boleh tersebar dan biasanya disebabkan oleh
mikroorganisma .
Infectious diseases are the diseases that can be spreaded and normally caused by the microorganisms .
TP1
2 Penyakit tidak berjangkit adalah penyakit yang tidak boleh tersebar .
Non-infectious diseases are the diseases that cannot be spreaded . TP1
3 Lengkapkan maklumat di bawah.
Complete the information below. TP2
Contoh penyakit berjangkit Contoh penyakit tidak berjangkit
(a) (b)
Examples of infectious diseases Examples of non-infectious diseases
Selesema Asma
Influenza Athma
Tibi Kanser
Tuberculosis Cancer
Demam denggi Diabetes
Dengue fever Diabetes
Sifilis Tekanan darah tinggi
Syphilis High blood pressure
Tekanan darah tinggi / High blood pressure Sifilis / Syphilis 2 tidak boleh tersebar / cannot be spreaded
Diabetes / Diabetes Demam denggi / Dengue fever spreaded; microorganisms
(b) Kanser / Cancer 3 (a) Tibi / Tuberculosis A. 1 tersebar; mikroorganisma
37 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab4 Book A_F.indd 37 25/10/2021 12:33 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B. Bagaimana Penyakit Berjangkit Disebarkan? Buku teks muka surat 76
How Infectious Diseases are Spreaded? Textbook page 76
1 Patogen : Mikroorganisma yang berbahaya dan boleh menyebabkan penyakit .
Pathogen : Harmful microorganisms that can cause diseases .
2 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah. / Complete the table below. TP2
Medium untuk merebak Penyakit dan cara merebak
Medium of spreading Disease and ways of spreading
A Udara / Air 1 Tuberkulosis (TB) / Tuberculosis (TB)
• Pemindahan titisan air H1N1
Droplet transmission SARS
• Pemindahan habuk • Melalui udara yang disedut oleh hidung atau
Dust transmission mulut semasa bernafas
Through air sucked through the nose and
mouth during breathing
2 Infuenza (demam selesema)
4 Influenza (common cold)
• Melalui udara yang disedut masuk melalui
hidung
Through the air that is breathe in through nose
B Air / Water 1 Kolera (Taun) / Cholera
• Bekalan air tidak terancang • Melalui pengambilan air dan makanan
Inadequate water supply yang tercemar
• Sanitasi yang lemah Through consumption of contaminated water
Poor sanitation food
and
• Banjir / Flood
C Sentuhan / Touch 1 Kurap / Ringworm
• Sentuhan kulit Panau / Tinea
Skin touch • Menerusi sentuhan kulit contohnya dengan berkongsi tuala
• Pakaian orang yang dijangkiti mandi
Clothes of infected person Through skin contact such as sharing of towels
D Vektor (Haiwan yang membawa 1 Kencing tikus / Leptospirosis
patogen) / Vectors (Animal that • Menerusi makanan , minuman dan tanah
transmit pathogen) yang dijangkiti bakteria daripada kencing tikus
• Lipas foods drinks
Cockroach Through , and soil
• Lalat which are infected by bacteria from the urine of rodents
Fly 2 Denggi / Dengue
• Nyamuk • Menerusi gigitan nyamuk Aedes
Mosquito Through the bites of Aedes
• Tikus 3 Malaria
Rat • Menerusi gigitan nyamuk Anopheles
Through the bites of Anopheles mosquitoes
4 Zika
• Menerusi gigitan nyamuk Aedes
Through the bites of Aedes mosquitoes
D 1 makanan, minuman / foods, drinks 2 udara / air Harmful, diseases
B 1 air, makanan / water, food 2 A 1 udara / air B. 1 berbahaya, penyakit
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 38
Modul Sains T2-Bab4 Book A_F.indd 38 25/10/2021 12:33 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
C. Mekanisme Menghalang Penularan Penyakit Berjangkit Buku teks muka surat 81
Mechanisms to Prevent the Spreads of Infectious Disease Textbook page 81
1 Tiga peringkat pencegahan penyakit berjangkit:
Three stages of prevention of infectious disease: TP2
(a) Primer
Primer
• Meningkatkan tahap kesihatan dan kebersihan
Improve health and hygiene
• Meningkatkan daya tahan badan (contoh: vaksin, imunisasi)
Improve immunity (examples: vaccine, immunisation)
• Pemeriksaan kesihatan berkala
Regular health check
• Mengamalkan gaya hidup sihat
Practising healthy lifestyle
(b) Sekunder
Secondary
4
• Memutuskan transmisi jangkitan (contoh: rawatan awal dan pengasingan pesakit)
Cut the transmission of infection (examples: early treatment and patient isolation)
(c) Tertier
Tertiary
• Mengawal populasi vektor (contoh: semburan untuk membunuh vektor)
Control vector population (example: spray to kill vectors)
• Melindungi hos (contoh: menggunakan kelambu atau ubat nyamuk)
Protect the host (examples: using mosquito net or mosquito coil)
Projek / Project
Arahan / Instructions:
Anda dikehendaki membuat kajian kes berdasarkan statistik Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia untuk
membincangkan perkara berikut:
You are required to do a case study based on the statistics of Ministry of Health Malaysia to discuss the statement
below.
1 Penyakit yang paling banyak dihidapi di Malaysia.
The most common disease in Malaysia.
2 Jenis-jenis penyakit yang boleh berjangkit, penyebab dan cara menanganinya.
Types of infectious diseases, causes and ways to prevent the diseases.
3 Meramalkan perkembangan penyakit berdasarkan graf statistik oleh Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia.
Predicts the progression of diseases based on the statistic by Ministry of Health Malaysia.
4 Cadangkan langkah untuk menyelesaikan masalah ini.
Suggests the steps to solve the problems.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
39 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab4 Book A_F.indd 39 25/10/2021 12:33 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
4.2 Pertahanan Badan / Body Defence
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai fungsi sistem pertahanan badan.
SP 4.2.1
Elaborate and communicate the function of body defence system.
LS
4.2.2 Mendefinisikan antigen, antibodi dan keimunan badan. / Define antigens, antibodies and immunity.
4.2.3 Mewajarkan kepentingan imunisasi. / Justify the importance of immunisations.
4.2.4 Membezakan keimunan pasif dan keimunan aktif. / Differentiate passive immunity and active immunity.
4.2.5 Mewajarkan amalan yang baik ke arah keimunan yang mantap. / Justify good practices towards strong immune system.
Mewajarkan dan berkomunikasi mengenai kepentingan imunisasi dan tahap kesihatan individu terhadap keluarga, sosial, ekonomi dan negara.
4.2.6
Justify and communicate the importance of immunisation and health level of individuals to the family, social, economy and nation.
EMK Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Nilai Murni Menghargai dan mengamalkan kehidupan yang sihat.
Moral Value Appreciate and practice a healthy life
Buku teks muka surat 82
A. Fungsi Sistem Pertahanan Badan / Functions of Body's Defence System Textbook page 82
Sistem Pertahanan Badan / Body’s Defence System
Patogen / Pathogen
4
(a) Barisan Pertahanan Pertama / The First Line of Defence
Kulit Mukus
Skin Mucus
Pertahanan tidak spesifik
Non-specific defence system
(b) Barisan Pertahanan Kedua / The Second Line of Defence
Fagosit
Phagocytes
(c) Barisan Pertahanan Ketiga / The Third Line of Defence
Sistem pertahanan spesifik
Specific defence system Limfosit
Lymphocytes
1 Sistem pertahanan badan pertama merupakan mekanisme pertahanan tidak spesifik iaitu sistem
pertahanan badan yang tidak terhad kepada sejenis patogen sahaja.
First body defence system is non specific, which is the body defence system is not limited
to one type of pathogen only. TP1
2 Struktur dan tindak balas yang terlibat: / Structure and reaction involved:
• Mulut / Mouth • Hidung / Nose
• Kulit / Skin • Salur respirasi / Respiration
• Tindak balas pembekuan darah / Blood clotting reaction
• Rembesan oleh kulit dan membran mukus / Secretion by skin and mucus membrane
• Kulit / Skin (c) Limfosit / Lymphocytes
mukus / mucus • • Hidung / Nose 2 (b) Fagosit / Phagocytes
darah / blood • tidak; terhad / non; limited 1 A. (a) Kulit; Mukus /Skin; Mucus
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 40
Modul Sains T2-Bab4 Book A_F.indd 40 25/10/2021 12:33 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
3 Peranan kulit barisan pertanan pertama adalah seperti berikut:
The roles of the skin in first line defence system are as follows: TP2
• Epidermis kulit terdiri daripada sel-sel yang tersusun padat dan ditebalkan dengan keratin. Ini membentuk
satu halangan fizikal yang kukuh terhadap kemasukan patogen ke dalam badan.
The skin epidermis consists of cells that are compacted and thickened by keratin. It forms a strong physical
barriers for the entry of pathogens into the body.
• Kelenjar sebum pada kulit merembeskan sebum untuk membentuk satu lapisan perlindungan kulit. Sebum
merupakan antiseptik dan mengandungi asid laktik. Ia mencegah pertumbuhan mikroorganisma.
Sebaceous glands on the skin secrete sebum to form a layer of protection on the skin. Sebum is an antiseptic
and contains lactic acid. It prevents the growth of microorganisms.
• Mikroorganisma pada kulit akan dihalang oleh bahan kimia di dalam peluh yang dirembeskan oleh kelenjar
peluh. / Microorganisms on the skin will be prevented by the chemicals in the sweat that is secreted by the
sweat glands.
• Mikroorganisma hanya dapat menembusi kulit jika terdapat luka atau kecederaan.
Microorganism can only entering the skin if there is a wound or injury.
• Namun begitu, proses pembekuan darah yang berlaku dengan segera dapat mencegah kemasukan
mikroorganisma dengan banyak.
However, the blood clotting that instantly occurs can prevent the entering of microorganisms. 4
• Air mata yang dirembeskan oleh kelenjar air mata dan sebum yang dirembeskan oleh kelenjar sebum
mengandungi enzim yang memusnahkan bakteria.
Tears secreted by the tears gland and sebum secreted by the sebum glands consist of enzyme that can
destroy bacteria.
• Mikroorganisma yang masuk melalui lubang hidung akan diperangkap oleh lapisan mukus.
Microorganisms that enter through the nose tract, will be trapped by the mucus layer.
Barisan pertahanan pertama
Halangan mekanikal Halangan kimia Refleks
Mechanical barriers Chemical barriers Reflexes
First line of defence
Sel
(a) (b) (c) (d) pembunuh
semula jadi
Natural killer
(NK) cells
Kulit dan membran
mukus / Skin
and mucous Bersin
membranes Sneezing
Keimunan tidak spesifik
Non-specific immunity
(h)
(e) (f) (g)
Protein pelindung
Protective protein
Pelengkap
Fagositosis Radang Complement
Phagocytosis Demam
Inflammation Fever Bakteria
Bacterium
Barisan pertahanan kedua / Second line of defence
(d) Sel pembunuh semula jadi / Natural killer (NK) cells (f) Redang / Information
(g) Demam / Fever A. 3 (a) Kulit dan membran mukus / Mucous membranes (e) Fagositosis / Phagocytosis
41 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab4 Book A_F.indd 41 25/10/2021 12:33 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 83
B. Antigen, Antibodi dan Keimunan / Antigen, Antibody and Immunity Textbook page 83
1 Padankan terma dan definisi yang tepat. / Match the correct terms with its meaning. TP1
Terma / Terms Definisi / Definition
(d) Keupayaan sistem badan melawan suatu patogen sebelum badan
(a) Antigen dijangkiti patogen. Antibodi dihasilkan apabila patogen memasuki badan.
Antigen The ability of body system to fight against a pathogen before the body is
infected with pathogens. Antibodies are produced when the pathogens
enter the body.
(b) Antibodi
(e) Jasad atau bahan asing yang lain mendorong penghasilan antibodi.
Antibody
A body or other foreign substances which induces the production of
antibody.
(c) Keimunan (f) Protein yang dihasilkan oleh sel darah putih sebagai tindak balas terhadap
Immunity antigen tertentu.
Protein produced by white blood cell as response to a specific antigen.
4
Buku teks muka surat 84
C. Kepentingan Imunisasi / The Importance of Immunisation Textbook page 84
1 Membantu mencegah penyakit daripada merebak.
Helps to prevent diseases from spreading. TP2
• Imunisasi memberi faedah kesihatan kepada kanak-kanak kerana dapat mengelakkan penyakit berjangkit
dengan serius yang boleh menyebabkan kecacatan dan kematian.
Immunisation will give health benefits to children as it can prevent serious infectious disease which can cause
disability and death.
• Melalui suntikan vaksin dan antiserum seperti BCG, campak, rubella dan tetanus dapat mencegah pelbagai
jenis penyakit. / Through vaccine and antiserum injections such as BCG, measles, rubella and tetanus can
prevent various diseases.
• Jadual berikut menerangkan jenis vaksin serta kepentingan vaksin secara spesifik:
The following table describes the specific types of vaccines and the importance of the vaccine:
Jenis vaksin Keterangan
Type of vaccine Explanation
(a) BCG Mengelakkan penyakit tuberkulosis / Prevent from tuberculosis disease
(b) Hepatitis B Mengelakkan penyakit hepatitis B / Prevent from hepatitis B
(c) Polio (IPV) Mengelakkan penyakit polio / Prevent from polio
2 Ia merupakan satu pembentukan imunisasi atau perlindungan kepada penyakit melalui
penggunaan vaksin.
It is a formation of immunity or protection to disease through the use of vaccines. TP2
3 Imunisasi adalah cara paling berkesan untuk mengawal penyakit-penyakit berjangkit .
Immunisation is the most effective way to control the infectious diseases. TP2
(c) polio / polio (c) – (d)
berjangkit / infectious 3 • (b) hepatitis B / hepatitis B (b) – (f)
imunisasi; penyakit / immunity; disease 2 C. 1 mencegah / prevent B. 1 (a) – (e)
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 42
Modul Sains T2-Bab4 Book A_F.indd 42 25/10/2021 12:33 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
D. Keimunan Pasif dan Keimunan Aktif Buku teks muka surat 85
The Passive Immunity and Active Immunity Textbook page 85
1 Pengimunan melibatkan tindak balas biokimia yang membolehkan badan membina keimunan terhadap sesuatu
jenis penyakit. / Immunisation is a biochemical reaction that enables the body to build immunity against diseases.
TP1 TP2
Keimunan / Immunity
Aktif / Active Pasif / Passive
(a) Antibodi dihasilkan oleh badan (b) Antibodi diterima daripada sumber luar
Antibody produced by the body Antibody received from outside sources
Keimunan aktif semula jadi Keimunan pasif semula jadi
(i) (i)
Natural active immunity Natural passive immunity
Antibodi yang diperoleh individu Antibodi yang diperoleh daripada
apabila sembuh daripada sesuatu penyakit. susu ibu oleh bayi baru
tidak
Badan individu akan mengeluarkan antibodi lahir yang antibodinya 4
sepanjang hayat bagi penyakit itu. tahan lama.
Antibodies acquired by an individual when Antibodies that are acquired from
mother's milk by newborn baby
he / she recovers from the diseases. The body
which the antibodies do not
of the individual will gain a lifelong
last long.
antibody for the disease.
Keimunan aktif buatan
(ii)
Artificial active immunity Keimunan pasif buatan
(ii) Artificial passive immunity
Antibodi diperoleh menerusi pemvaksinan apabila
vaksin yang mengandungi patogen yang dilemahkan Individu akan memperoleh antibodi serta-merta
atau mati disuntik pada badan individu untuk dengan menyuntik antiserum ke dalam badan.
merangsang penghasilan antibodi sepanjang hayat. Walaubagaimanapun, antibodi yang diperoleh
Antibodies are acquired through vaccination in which adalah bersifat sementara.
vaccine that contains weakened or death pathogens An individual will acquire immediate antibodies
are injected to an individual' body to stimulate the
by injecting antiserum into the body. However,
production of a lifelong antibody.
the antibodies acquired are temporary.
Suntikan vaksin kedua disebut dos penggalak
supaya antibodi di dalam darah akan melebihi aras
Amount of antibodies
Jumlah antibodi di
keimunan.
dalam darah
in the blood
The second injection is known as a booster dose in Aras keimunan
which antibodies in the blood will increase above Immunity level
the immunity level.
Masa (hari)
Jumlah antibodi
di dalam darah
Time (days)
antibodies in
Aras keimunan
Amount of
the blood
Immunity level Suntikan antiserum Suntikan antiserum
pertama kedua
First antiserum Second antiserum
Masa (hari) injection injection
Time (days)
Suntikan vaksin Suntikan vaksin Aras antibodi selepas suntikan pertama dan kedua
pertama kedua
First vaccine Second vaccine Level of antibodies after the first and second injections
injection injection
(i) ibu; tidak / mother's; do not (i) diperoleh; sepanjang hayat / acquired; lifelong
(b) sumber luar / outside sources D. (a) badan / body
43 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab4 Book A_F.indd 43 25/10/2021 12:33 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 87
E. Sistem Keimunan yang Mantap / Strong Immune System Textbook page 87
Amalan yang menggalakkan Makanan / Food
keimunan
(b)
Practices that strengthen the
1 Buah-buahan sitrus / Citrus fruits
immunity system TP2
Contoh: Oren, lemon, limau nipis
Example: Orange, lemon, lime
4 (a) 2 Makanan yang mempunyai antioksidan yang
1 Tidur secukupnya sekurang- tinggi seperti bawang putih.
kurangnya 8 jam sehari. Food that contains high anti-oxidant such as
garlic.
Sleep well at least 8 hours daily.
3 Makanan yang mengandungi antibiotik
2 Bersenam sekurang-kurangnya 3 kali seminggu. seperti yogurt.
Exercise at least 3 times a week. Food that contains antibiotic such as
yogurt.
3 Berehat secukupnya.
Rest well. 4 Minum air dengan banyak.
Drink
tekanan a lot of water.
4 Mengurangkan .
Reduce stress . 5 Pengambilan protein yang banyak seperti
telur dan ayam.
5 Menjaga kesihatan .
Consume a lot of protein such as eggs
Take care of health . and chicken.
6 Berfikiran positif . 6 Pengambilan sayur-sayuran hijau seperti bayam
Positive thinking. dan brokoli.
Consume green vegetables such as spinach and
7 Tidak mengambil barang terlarang seperti arak brocolli.
dan dadah.
Do not take prohibitted item such as alcohol and
Ekstra / Extra
drug.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
5 kesihatan / health
5 telur / eggs (b) 3 antibiotik / antibiotic 4 tekanan / stress
4 Minum / Drink 6 positif / Positive E. (a) 1 Tidur / Sleep
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 44
Modul Sains T2-Bab4 Book A_F.indd 44 25/10/2021 12:33 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Wati telah disahkan menghidap tuberkulosis. 3 Antara berikut, yang manakah menerangkan
Doctor telah menasihatkan Wati sentiasa memakai tentang patogen?
topeng muka jika berada di luar atau tidak meludah Which of the following explain about pathogen?
merata-rata untuk mengelakkan beliau menjangkiti A Keupayaan badan melawan penyakit
orang lain. Bagaimanakah cara penyakit tersebut Ability of body to fight disease
boleh berjangkit? B Molekul yang merangsang penghasilan antibodi
Wati has been diagnosed with tuberculosis. Doctor Molecule which stimulate antibody production
has advised Wati to wear a face mask when going C Organisma yang menyebabkan penyakit
outside or do no spit around to avoid infecting Organisms that cause disease
other people. How the disease can be transmitted? D Haiwan yang menyebarkan penyakit
A Air / Water Animal that spread disease
B Udara / Air
C Sentuhan / Contact 4 Rajah 1 menunjukkan kepekatan suatu antibodi
D Vektor / Vector dalam darah Sheila. / Diagram 1 shows the
2 Rajah 2 menunjukkan sel darah putih dalam satu
concentration of antibody in Sheila’s blood.
4
Kepekatan antibodi dalam darah (%)
sistem pertahanan badan. Concentration of antibody in the blood (%)
Diagram 2 shows white blood cell in a body’s
defence system.
Aras keimunan
Immunity level
Masa (minggu)
Time (weeks)
Suntikan antiserum pertama Suntikan antiserum kedua
First antiserum injection Second antiserum injection
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
Rajah 2 / Diagram 2 Berdasarkan graf, apakah jenis keimunan yang
Pada barisan pertahanan badan yang keberapakah diterima oleh Sheila? / Based on graph, what type
proses ini berlaku? of immunity does Sheila receive?
At which body defence does this process occur? A Keimunan pasif semulajadi
A Barisan pertahanan pertama / First line of defence Natural passive immunity
B Barisan pertahanan kedua / Second line of defence B Keimunan pasif buatan
C Barisan pertahanan ketiga / Third line of defence Artificial passive immunity
D Barisan pertahanan keempat C Keimunan aktif semulajadi
Fourth line of defence Natural active immunity
D Keimunan aktif buatan
Artificial active immunity
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
Arif tinggal di sebuah asrama dan sering berkongsi pakaian dengan rakan-rakannya. Akibatnya,
dia mengalami kegatalan dan mendapati badannya seperti dalam rajah. / Arif lives in a hostel.
He often shares clothes with his friends and gets irritated and finds the body as in the diagram.
(a) Namakan penyakit yang dihidapi oleh Arif dan punca terjadinya penyakit itu.
Name the disease faced by Arif and the cause of the disease.
Panau. Arif berkongsi pakaian dengan rakan-rakannya. / Tinea. Arif sharing clothes with his friends.
[1 markah/mark]
(b)
Untuk mengelakkan penyakit ini daripada berjangkit kepada rakan-rakan yang lain, apakah yang perlu dilakukan
oleh Arif? / To prevent this disease from infecting others, what should be done by Arif?
1 Memastikan badan dilap dengan kain yang bersih. / Make sure his body is wiped with clean towel.
2 Tidak berkongsi tuala atau baju dengan orang lain. / Does not share towel or cloth with others.
[2 markah/marks]
45 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab4 Book A_F.indd 45 25/10/2021 12:33 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Air dan Larutan
5 Water and Solution
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
5.1 Sifat Fizik Air
Physical Characteristics of Water
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
5.1.1 Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai air. / Elaborate and communicate about water.
SP
LS Menjalankan eksperimen dan berkomunikasi mengenai proses penyejatan air dalam kehidupan harian.
5.1.2
Carry out experiments and communicate about water evaporation process in daily life.
EMK Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Nilai Murni Jujur dan tepat dalam merekod dan mengesahkan data
Moral Value Honest and accurate in recording and verifying data
Buku teks muka surat 96
A. Air / Water Textbook page 96
sumber
5 1 Air merupakan bagi kemandirian semua benda hidup.
Water is source to sustain for all living things. TP1
2 Air ialah suatu sebatian. Ia terdiri daripada hidrogen dan oksigen.
Water is a compound. It consists of hydrogen and oxygen. TP1
3 Lengkapkan peta buih di bawah dengan menyatakan ciri-ciri fizik air:
Complete the bubble map below by stating the physical characteristics of water: TP2
1 g cm–3
(d) Ketumpatan pada 4 ºC =
1 g cm–3
(a) Takat beku = 0 ºC Density at 4 ºC =
warna
0 (f) Tiada
Freezing point = ºC
No colour
(b) Takat lebur = 0 ºC bau
(g) Tiada
Melting point = 0 ºC
Air No smell
Water
(c) Takat didih = 100 ºC (h) Tiada rasa
Boiling point = 100 ºC No taste
(e) Tegangan permukaan yang tinggi
High surface tension
(h) rasa / taste (e) tinggi / High (b) 0
(g) bau / smell (d) 1 g cm–3 3 (a) 0
(f) warna / colour (c) 100 A. 1 sumber / source
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 46
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 46 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
4 Tindakan kapilari: Daya lekitan dan daya lekatan antara molekul air dengan dinding xilem membolehkan air
dibawa dari akar ke daun.
Capillary action: Cohesive force and adhesion force between water molecules and xylem walls allow water to be
carried from root to leaf. TP1
5 Kesan penyerapan dan pembebasan haba terhadap keadaan jirim air.
Effect of absorption and release of heat on state of matter of water. TP2
Pemejalwapan / Sublimation
Petunjuk / Key:
Peleburan Pendidihan Tenaga haba diserap dari
Melting Boiling persekitaran
Heat energy is absorbed from
the surrounding
Pembekuan Kondensasi
Freezing Condensation
Tenaga haba dibebaskan ke
Pepejal Cecair Gas persekitaran
Solid Liquid Gas Heat energy is released to the
surrounding
Pemejalwapan / Sublimation
B. Penyejatan Air / Evaporation of Water Buku teks muka surat 101 5
Textbook page 101
Penyejatan air: Proses di permukaan air yang menukarkan air menjadi wap air.
Evaporation of water: Process on the surface of water that change water to water vapour. TP2
(a) (c)
Kelembapan udara Suhu persekitaran
Humidity of air Surrounding temperature
Faktor-faktor yang
mempengaruhi
kadar penyejatan air
Factors that
affect the rate of
evaporation of
water
(b) (d) Kawasan permukaan
Pergerakan udara air terdedah
Movement of air Exposed surface area
of water
Exposed surface area of water Surrounding temperature Movement of air Humidity of air
(d) Kawasan permukaan air terdedah (c) Suhu persekitaran (b) Pergerakan udara B. (a) Kelembapan udara
47 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 47 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
C. Aplikasi Penyejatan Air Buku teks muka surat 105
Application of Evaporation of Water Textbook page 105
Konsep penyejatan air diaplikasikan dengan meluas dalam aktiviti harian kita serta operasi perkilangan. Perhatikan
rajah berikut dan terangkan cara penyejatan diaplikasikan dalam setiap aktiviti berikut.
The concept of evaporation of water is widely applied in our daily activities and industrial operation. Observe the
diagram below and explain the way evaporation is applied in each of the following activity. TP2
(a) • Alat pengering rambut menghasilkan udara panas yang bergerak.
Hair dryer produces hot, moving air.
• Apabila menggunakan alat pengering rambut, rambut diselerakkan untuk
meningkatkan kawasan permukaan terdedah.
When using a hair dryer, the hair is spread out to increase the exposed surface area.
(b)
• Makanan laut dikeringkan di bawah Matahari untuk menyingkirkan air.
Sea food is dried under the hot Sun to eliminate the water.
• Apabila kering, pertumbuhan mikroorganisma dapat dikurangkan.
When dried, the growth of microorganism will be decrease.
(c) • Susu tepung dihasilkan dengan menuangkan susu melalui udara bergerak
yang panas.
Milk powder is produced by pouring milk through hot moving air.
5 • Apabila dituang, kawasan permukaan terdedah akan ditingkatkan.
When poured out, the exposed surface area increased.
• Air di dalam susu menyejat dan susu tepung terbentuk.
Water in milk evaporates and milk powder is formed.
(d) • Mesin pengering digunakan untuk mengeringkan pakaian.
Drying machine is used to dry up washed clothes.
• Udara panas ditiup ke atas pakaian.
Hot air is blown over the clothes.
• Mesin memutarkan pakaian di dalamnya untuk meningkatkan luas permukaan
terdedah. / The machine spins the clothes in it to increase the exposed surface
area.
(e) • Garam dihasilkan dengan mengeringkan air laut bawah Matahari.
Salt is produced by drying up sea water under the Sun.
• Haba daripada Matahari dan angin meningkatkan
kadar penyejatan air dan meninggalkan garam.
Heat from the Sun and wind increase the rate of
evaporation of water and leave the salt behind.
(f) • Ubat tradisi dikeringkan di bawah Matahari untuk mengelakkan pertumbuhan
mikroorganisma. / Traditional medicine is dried up under the Sun to prevent the
growth of microorganisms.
• Penyelerakan ubat di atas lantai meningkatkan luas permukaan terdedah.
Spreading the medicine on the floor increases the exposed surface area.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
• mikroorganisma / microorganism
(e) Haba; angin / Heat; wind (d) • panas / Hot C. (b) • menyingkirkan / eliminate
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 48
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 48 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
5.2 Larutan dan Kadar Keterlarutan / Solution and Rate of Solubility
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
4.2.1 Menerangkan dengan contoh maksud larutan dan keterlarutan. / Explain with examples the meaning of solution and solubility.
SP
LS Menjalankan eksperimen bagi menentukan faktor yang mempengaruhi kadar keterlarutan.
4.2.2
Carry out experiment to determine the factors affecting the rate of solubility.
4.2.3 Menjelaskan dengan contoh maksud koloid dalam kehidupan harian. / Explain with examples the meaning of colloids in daily life.
Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai kegunaan air sebagai pelarut universal dalam kehidupan harian dan industri pembuatan.
4.2.4
Elaborate and communicate the uses of water as a universal solvent in daily life and manufacturing industry.
Menunjuk cara contoh pelarut bukan air dan kegunaannya dalam kehidupan.
4.2.5
Demonstrate examples of organic solvents and their uses in daily life.
EMK Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Nilai Murni Menghargai dan mengamalkan kehidupan yang sihat
Moral Value Appreciate and practice a healthy life
Buku teks muka surat 106
A. Larutan dan Keterlarutan / Solution and Solubility Textbook page 106
1 Isikan tempat kosong dengan perkataan-perkataan yang diberi untuk memberi definisi kepada istilah-istilah
berikut. / Fill in the blanks with the given words to define the following terms. TP1
Zat terlarut Ampaian Larutan Pelarut
Solute Suspension Solution Solvent
(a) Zat terlarut ialah bahan yang terlarut di dalam sesuatu cecair.
A solute is a substance that dissolves in a liquid. 5
(b) Pelarut ialah cecair yang melarutkan sesuatu bahan.
A solvent is a liquid that dissolves a substance.
(c) Larutan ialah campuran yang dihasilkan apabila sesuatu bahan terlarut di dalam sesuatu cecair.
A solution is a mixture produced when a substance dissolves in a liquid.
(d) Ampaian ialah campuran sesuatu cecair dan bahan tidak terlarut di dalamnya.
A suspension is a mixture of a liquid and insoluble substances in it. Ekstra / Extra
2 Labelkan istilah pada rajah di bawah. / Label the term on the diagram. TP2
+ =
(a) Zat terlarut (b) Pelarut (c) Larutan
Solute Solvent Solution
3 Keterlarutan sesuatu bahan ialah jumlah zat terlarut yang boleh larut di dalam 100 ml pelarut tertentu pada
suatu suhu tertentu. / Solubilty of a substance is the amount of solute that can dissolve in 100 ml of solvent
at a certain temperature. TP1
4 Kadar keterlarutan merujuk kepada berapa cepat zat terlarut boleh larut dalam suatu pelarut.
Rate of solubility refers to how fast a solute can dissolve in a solvent. TP1
cepat / fast 4 (b) Pelarut / Solvent (c) Larutan / solution
jumlah zat terlarut / amount of solute 3 2 (a) Zat terlarut / Solute (b) Pelarut / solvent
(c) Larutan / Solution (d) Ampaian / suspension A. 1 (a) Zat terlarut / solute
49 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 49 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
5 Jenis larutan.
Types of solution. TP2
Campuran Jenis larutan Definisi
Mixture Type of solution Definition
(a) Larutan yang terbentuk dengan melarutkan
sedikit zat terlarut dalam pelarut
Larutan cair dan dapat melarutkan zat terlarut yang
Dilute solution lebih banyak . / A solution formed by
dissolving a little solute in a solvent and is
able to dissolve a lot more solute.
(b) Larutan yang terbentuk dengan melarutkan
banyak zat terlarut dalam pelarut
Larutan pekat dan dapat melarutkan zat terlarut yang
Concentrated sedikit sahaja lagi . / A solution formed by
solution
dissolving a lot of solute in a solvent and is
able to dissolve a little more solute.
(c) Larutan yang terbentuk dengan melarutkan jumlah
zat terlarut yang maksimum dalam pelarut
5 Larutan tepu dan tidak dapat melarutkan zat terlarut lagi.
Saturated solution
A solution formed by dissolving the maximum
amount of solute in a solvent and cannot
dissolve any more solute.
Buku teks muka surat 111
B. Koloid / Colloid Textbook page 111
1 Perbezaan larutan, koloid dan ampaian. / The differences of solution, colloid and suspension. TP1
Jenis larutan (a) Larutan (b) Koloid (c) Ampaian
Type of solution Solution Colloid Suspension
Definisi Campuran dua atau lebih Zarah-zarah tersebar Ada molekul yang tidak
secara merata tetapi belum
molekul yang homogen
Definition bercampur dan mudah
membentuk ampaian terpisah
The mixture of two or more
Partilces are spread evenly
molecules which are Contain molecule which are
but the suspension is not
homogen not mix and
forming yet.
easily separated
Contoh Larutan gula, larutan garam Mayonis, agar-agar, ais Air teh dengan daun teh, air
Examples Sugar solution, salt solution krim, busa krim pencukur kopi dengan biji kopi
Mayonnaise, jelly, ice Tea with tea leaf, coffee with
cream, shaving cream foam coffee bean
B 1 (a) homogen / homogen (b) banyak; sedikit sahaja lagi / a lot of; a little more
(c) tidak; terpisah / not; separated (c) maksimum; tidak dapat / maximum; cannot A. 5 (a) sedikit; lebih banyak / a little; a lot more
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 50
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 50 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 112
C. Air sebagai Pelarut Semesta / Water as a Universal Solvent Textbook page 112
1 Isi tempat kosong dengan kata-kata yang diberi di dalam kotak.
Fill in the blanks with the words provided in the box. TP3
kesihatan makanan dan minuman larutan akueus pencuci pelarut semesta ubat
health food and drinks aqueous solutions cleaning universal solvent medicines
(a) Air boleh melarutkan banyak bahan, maka air dikenali sebagai pelarut semesta .
Water can dissolve most of the substances, so it is known as a universal solvent .
(b) Tindak balas kimia dalam badan manusia berlaku dalam larutan akueus .
Chemical reactions in the human body occurs in aqueous solutions .
(c) Air digunakan untuk menyediakan makanan dan minuman .
Water is used to prepare foods and drinks .
(d) Air merupakan pelarut bagi agen pencuci , ubat dan racun serangga.
Water is a solvent for cleaning agents, medicines and insecticides.
(e) Air tidak mengancam kesihatan . Manakala sesetengah pelarut lain boleh mengancam kesihatan.
Water does not threaten health . Meanwhile other solvents can threaten health.
D. Pelarut Bukan Air dan Kegunaannya dalam Kehidupan Buku teks muka surat 112 5
Non-water Solvent and Its Uses in Life Textbook page 112
1 Pelarut selain daripada air merupakan pelarut organik. Sesetengah bahan hanya boleh dilarutkan dalam
pelarut organik.
Solvents other than water are organic solvents. Certain subtances can only dissolve in organic solvent. TP1
2 Lengkapkan peta buih di bawah. / Complete the bubble map below. TP3
(a)
(b)
• Kerosin / Kerosene
• Minyak lampu Tupertin / Tupertine
Lamp oil • Penanggal cat
(e) Paint remover
Aseton / Acetone • Pencair cat
Paint thinner
• Varnis kuku
Nail varnish
• Lakuer Contoh Pelarut
Lacquer Organik
Example of
Organic (c)
(d) Solvent Eter / Ether
Alkohol / Alcohol • Pengekstrak
minyak
• Minyak wangi
Oil extractor
Perfume
• Antiseptik
Antiseptic
(e) Aseton / Acetone D. 2 (b) Tupertin / Tupertine (c) makanan dan minuman / foods and drinks
(d) Alkohol / Alcohol (e) kesihatan / health (b) larutan akueus / aqueous solutions
(c) Eter / Ether (d) pencuci; ubat / cleaning; medicines C. 1 (a) pelarut semesta / universal solvent
51 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 51 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
5.3 Pembersihan dan Pembekalan Air / Water Purification and Water Supply
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
4.2.1 Menunjuk cara kaedah pembersihan air. / Demonstrate the water purification method.
SP
LS Menyelesaikan masalah mendapatkan bekalan air untuk kegunaan harian.
4.2.2
Solve the problems in getting water supply for daily life usage.
Membina model dan berkomunikasi mengenai sistem pembekalan air.
4.2.3
Build a model and communicate about water supply system.
4.2.4 Mewajarkan kelestarian air sebagai kunci kehidupan yang sihat. / Justify water sustainability as a key to healthy living.
EMK Kreativiti dan inovasi / Creativity and innovation
Nilai Murni Menghargai dan mengamalkan kehidupan yang sihat
Moral Value Appreciate and practice a healthy life
Buku teks muka surat 113
A. Kaedah Pembersihan Air / Water Purification Method Textbook page 113
TUJUAN Untuk mengkaji kebaikan pelbagai kaedah penulenan air
AIM To investigate the advantages of various water purification methods
RADAS Slaid kaca, mikroskop, corong turas, kertas turas, piring penyejat, penunu Bunsen, kasa
APPARATUS dawai, tungku kaki tiga, penuras batu kelikir dan pasir, bikar, kaki retort, kelalang penyulingan,
termometer, kelalang kon, kondenser Liebig
Glass slide, microscope, filter funnel, filter paper, evaporating dish, Bunsen burner, wire gauze,
tripod stand, gravel and sand filters, beaker, retort stand, distillation flask, thermometer,
conical flask, Liebig condenser
5 BAHAN Air kolam, larutan klorin, serpihan porselin
MATERIALS Pond water, chlorine solution, porcelain chips
Jalankan aktiviti-aktiviti berikut untuk mengkaji kebaikan dan keburukan kaedah-kaedah penulenan air.
Carry out the following activities to study the advantage and disadvantage of water purification methods.
Kaedah / Method Pemerhatian / Observation Kesimpulan / Conclusion
(a) Penurasan Hasil turasan adalah jernih Penurasan menyingkirkan
Filtration tetapi mikroorganisma dan zarah terampai
Lalukan sedikit air kolam melalui penuras batu bakteria masih hadir. daripada air kolam.
kelikir dan pasir seperti yang ditunjukkan The filtrate is clear but micro Filtration removes
dalam rajah. Perhatikan mikroorganisma, zarah organisms and bacteria are suspended particles
terampai dan mineral terlarut dalam air yang still present.
ditulenkan di bawah mikroskop. from pond water.
Pour some water through the gravel and sand
filters as shown in the diagram. Observe the
purified water for microorganisms, suspended
particles and dissolved minerals under a
microscope.
Air kolam / Pond water
Pasir halus / Fine sand
Tiub kaca
Pasir kasar / Coarse sand
Glass
tube Batu kelikir / batu kecil
Gravel / small stones
Batu kecil / Pebbles
Gabus
Cork
Hasil turasan / Filtrate
A. (a) zarah terampai / suspended particles
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 52
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 52 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(b) Pendidihan Air didih tidak mengandungi Pendidihan membunuh
Boiling mikroorganisma . mikroorganisma dalam air
Didihkan sedikit air kolam dalam bikar dan kolam.
The boiled water does not
perhatikannya di bawah mikroskop. Boiling kills microorganisms
Boil some pond water in a beaker and contain microorganisms . in pond water.
observe it under a microscope.
(c) Pengklorinan Air ditambahkan klorin tidak Pengklorinan membunuh
Chlorination mengandungi mikroorganisma. mikroorganisma dalam air
Tambahkan beberapa titis larutan klorin ke The chlorinated water does kolam.
dalam bikar yang mengandungi air kolam dan not contain microorganisms. Chlorination kills
perhatikannya di bawah mikroskop. microorganisms in pond
Add a few drops of chlorine solution into a water.
beaker of pond water and observe it under a
microscope.
(d) Penyulingan 1 Di bawah mikroskop, tiada Penyulingan menyingkirkan
Distillation kesan mikroorganisma atau mikroorganisma
1 Susunkan radas seperti dalam rajah. zarah-zarah terampai.
Set up the apparatus as shown in the Under the microscope, dan zarah terampai
diagram. there is no trace of daripada air kolam.
2 Perhatikan air suling yang terkumpul di microorganisms or Distillation removes
bawah mikroskop. suspended particles. microorganisms and
Observe the distilled water collected 2 Selepas semua air
suspended particles from
under a microscope. menyejat, tiada air yang 5
3 Panaskan sedikit air suling yang tertinggal di dalam pond water.
terkumpul di dalam mangkuk penyejat mangkuk penyejat.
sehingga semua air menyejat. After all water evaporated,
Heat up some distilled water collected no water is left in the
in an evaporating dish until all water evaporating dish.
evaporates.
Termometer
Thermometer
Air keluar
Water out
Kondenser Liebig
Liebig condenser
Air kolam
Pond water
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Serpihan Air masuk
porselin Water in
Panaskan Porcelain chips
Heat up
(Air suling / Distilled water)
Penyelesaian masalah / Problem solving
Negara yang tiada bekalan air dapat menyediakan air:
The country which lack of water provide water: TP6
1 Mendapat air dari kabus / Getting water from mist
2 Kitar semula air / Water recycle
3 Mendapatkan air dari lautan / Getting water from the sea
(c) mikroorganisma; zarah terampai / microorganisms; suspended particles A. (b) mikroorganisma / microorganisms
53 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 53 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 115
B. Sistem Pembekalan Air / The Water Supply System Textbook page 115
Lengkapkan rajah untuk menerangkan proses rawatan air sebelum dibekalkan kepada pengguna.
Complete the diagram to explain the process of water treatment before water is supplied to consumers. TP2
Stesen pam (c)
(a) (b) Pump station
Sistem Pembekalan Air
Alum Water Supply System
Alum Kapur mati
(e)
Slake lime
(d)
(g) https://goo.gl/gnd8rt
(f) Pam
Pump
Tangki air bersih
Clean water tank
(h)
Ke rumah dan bangunan
To homes and buildings
(a)
Air dari sungai disimpan selama beberapa hari untuk membolehkan zarah terampai
Empangan seperti daun, kotoran dan mendapan termendap di dasar.
Reservoir Water from the river is stored for a few days to allow suspended particles like leaves,
dirt and silt to settle to the bottom.
5
(b) Tangki penapisan Air dari empangan disalurkan melalui penapis logam untuk menyingkirkan objek
besar seperti ranting, daun, ikan dan sampah. / Water from the reservoir is channelled
Filtration tank through a metal screen to remove big objects like twigs, leaves, fish and rubbish.
(c) Oksigen dipam ke dalam air untuk menyingkirkan bau dan rasa yang kurang
Tangki pengoksidaan
menyenangkan.
Oxidation tank Oxygen is pumped into the water to remove unpleasant smell and taste.
(d) Aluminium sulfat (alum) ditambahkan untuk menggumpalkan zarah terampai untuk
Tangki
membentuk gumpalan yang lebih besar. Kalsium hidroksida (kapur) ditambahkan
penggumpalan kepada air untuk mengurangkan keasidan air. / Aluminium sulphate (alum) is added
Coagulation tank to make the suspended particle clump together and form larger lumps. Calcium
hydroxide (slaked lime) is added to reduce the acidity of water.
(e)
Tangki pengenapan Gumpalan pejal zarah terampai dibiarkan tenggelam ke dasar tangki.
Sedimentation tank Solid lumps of suspended particles are allowed to sink to the bottom of the tank.
(f) Air dialirkan melalui penuras batu kelikir dan pasir untuk menyingkirkan sebarang
Tangki penurasan
zarah terampai yang tertinggal.
Filtration tank
The water is passed through sand and gravel filters to remove any remaining particles.
(g) Tangki pengklorinan Klorin ditambahkan untuk membunuh mikroorganisma dan fluorin ditambahkan
dan pemfluoridaan untuk mencegah pereputan gigi.
Chlorination and Chlorine is added to kill microorganisms and fluorine is added to prevent tooth
fluoridation tank decay.
(h) Tangki penyimpanan Air yang dirawat disimpan sebelum dibekalkan kepada pengguna.
Storage tank The treated water is stored before being supplied to consumers.
(h) Tangki penyimpanan / Storage tank (c) Tangki pengoksidaan / Oxidation tank
(d) Tangki penggumpalan / Coagulation tank B. (b) Tangki penapisan / Filtration tank
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 54
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 54 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 118
E. Kelestarian Air / Water Substainability Textbook page 118
(f)
Kurangkan
penerokaan
(a) hutan
Reduce forest (e)
exploration Tidak membuang
Mengguna semula air sampah ke dalam
Reuse of water sumber air
Do not throw
the rubbish into
water sources
Cara
Melestarikan
Air
Ways to
Sustain Water
(b) (d)
Jimatkan Kawal sisa
penggunaan air pembuangan kilang
Save water usage (c) Control the factory
Kawal sisa
waste disposal
5
pembuangan
pertanian
Control the
agricultural waste
disposal
Projek / Project
Arahan / Instructions:
Secara berkumpulan anda dikehendaki untuk membuat persembahan multimedia mengenai perkara berikut:
In a group, you are required to create a multimedia presentation on the following area:
1 Mengumpul jumlah penggunaan air di kawasan perumahan anda. Cari penggunaan purata bagi setiap
penduduk di kawasan tempat tinggal anda.
Collect the total usage of water in your residential area. Calculate the average usage of water for each of the
resident in your area.
2 Cadangkan langkah penjimatan yang perlu dilakukan.
Suggest the ways to conserve the water.
3 Kemukakan satu inovasi kaedah menjimatkan air dan kecekapan penggunaan air.
Present an innovation to save water and conserve the usage of water.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
Reduce forest exploration Control the factory waste disposal Save water usage
(f) Kurangkan penerokaan hutan (d) Kawal sisa pembuangan kilang E. (b) Jimatkan penggunaan air
55 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 55 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan perubahan fizikal air. 2 Antara berikut, yang manakah adalah faktor kadar
Diagram 1 shows the physical change of water. penyejatan air? / Which of the followings are the
factors for rate of water evaporation?
Wap air I Suhu persekitaran / Surrounding temperature
Water vapour
II Kelembapan / Humidity
III Cahaya / Light
K
Pepejal Cecair IV Luas permukaan terdedah / Exposed surface area
Solid Liquid A I, II dan / and III C I, III dan / and IV
L
B I, II dan / and IV D I, II, III dan / and IV
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
3 Rajah 2 menunjukkan seekor pencakar air di atas
Antara berikut, yang manakah proses K dan L? permukaan air. / Diagram 2 shows a daddy longlegs
Which of the followings are processes K and L? on the surface of water.
K L
A Pembekuan Pemejalwapan
Freezing Sublimation
B Pembekuan Peleburan
5 Freezing Melting Rajah 2 / Diagram 2
C Peleburan Pembekuan Apakah sifat fizik air yang membolehkan serangga
Melting Freezing ini boleh bergerak tanpa tenggelam?
What is the physical properties of water that enable
D Peleburan Pemejalwapan this insect move without sinking?
Melting Sublimation A Tindakan kapilari / Capillary action
B Daya lekitan yang tinggi / High cohesive force
C Daya lekatan yang tinggi / High adhesive force
D Ketegangan permukaan yang tinggi
High surface tension
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
Rajah 1 menunjukkan tiga sumber air yang berbeza. / Diagram 1 shows three different sources of water.
Ekstra / Extra
Air paip / Tap water Air sungai / River water Air perigi / Well water
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
Pada pendapat anda, sumber air yang manakah paling mudah tercemar? Bincangkan jawapan anda dengan alasan
yang sesuai.
In your opinion, which source of water will be the most easily polluted? Discuss your answer with appropriate reasons.
Air sungai kerana sungai mudah dicemari oleh udara, manusia dan haiwan. Air sungai juga tidak ditapis dan
diproses. Oleh itu, air sungai tidak sesuai untuk diminum secara terus.
River water because river were easily polluted by air, human and animals. River water also not filtered and
processed. Therefore, it is not suitable to drink directly
[4 markah/marks]
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 56
Modul Sains T2-Bab5 Book A_F.indd 56 25/10/2021 12:35 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Asid dan Alkali
6 Acid and Alkali
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
6.1 Sifat Asid dan Alkali
Properties of Acid and Alkali
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
6.1.1 Mendefinisikan secara operasi asid dan alkali. / Define operationally acid and alkali.
6.1.2 Menerangkan dengan contoh bahan berasid dan beralkali. / Explain with examples of acidic and alkaline substances.
SP
LS Menunjukkan cara menentukan kekuatan asid dan alkali berdasarkan nilai pH.
6.1.2
Demonstrate the technique to determine the strength of acid and alkali based on pH value.
6.1.2 Mengenal pasti kegunaan asid dan alkali dalam kehidupan seharian. / Identify the uses of acids and alkalis in daily life.
EMK Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Nilai Murni Jujur dan tepat dalam merekod dan mengesahkan data
Moral Value Honest and accurate in recording and verifying data
Buku teks muka surat 126
A. Sifat-sifat Asid / Properties of Acids Textbook page 126
TUJUAN Untuk mengkaji sifat-sifat asid
AIM To study the properties of acids
6
RADAS Tabung uji, penitis, jubin putih, penunu Bunsen
APPARATUS Test tubes, droppers, white tiles, Bunsen burner
BAHAN Asid hidroklorik cair, asid sulfurik pekat, pita magnesium, cuka, jus limau, kertas
MATERIALS litmus merah, kertas litmus biru, penunjuk semesta, putik kapas, kertas turas dan
kayu uji bernyala.
Dilute hydrochloric acid, concentrated sulphuric acid, magnesium ribbon, vinegar,
lime juice, red and blue litmus paper, universal indicator, cotton buds, filter paper
and wooden splinter.
Prosedur Pemerhatian Kesimpulan
Procedure Observation Conclusion
(a) Celupkan putik kapas ke dalam secawan cuka Cuka dan jus limau Asid mempunyai rasa
dan letakkannya pada lidah anda. Ulang aktiviti masam masam
berasa . .
ini dengan putik kapas yang baru dengan The vinegar and lime Acids have a
mencelupkannya pada jus limau.
juice taste sour . sour
Dip a cotton bud into a cup of vinegar and place
it on your tongue. Repeat this activity with a new taste.
cotton bud using a lime juice.
masam / sour
A. (a) masam / sour
57 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 57 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(b) Titiskan setitis asid sulfurik pekat pada kertas turas Kertas turas terkakis Asid mengakis
.
yang diletakkan di atas jubin putih. dan lubang terbentuk corrosive
Acids are .
Drip a drop of concentrated sulphuric acid on a pada kertas turas.
filter paper placed on a white tile. The filter paper is
Penitis corroded and a
Dropper
hole is formed on the
Asid sulfurik pekat filter paper.
Concentrated
sulphuric acid Jubin putih
White tile
Kertas turas
Filter paper
(c) Letakkan secebis kertas litmus biru dan kertas litmus • Kertas litmus biru Asid menukarkan
merah ke dalam tabung uji yang mengandungi asid bertukar merah . kertas litmus biru
hidroklorik cair. / Place a piece of blue litmus paper kepada merah.
The blue litmus paper
and a piece of red litmus paper into a test tube blue
change to red . Acids turn
containing dilute hydrochloric acid.
• Kertas litmus merah litmus paper to red.
Asid hidroklorik cair tidak berubah.
Dilute hydrochloric acid The red litmus paper
Kertas litmus biru
remains unchanged.
Blue litmus paper Kertas litmus merah
Red litmus paper
(d) • Tambah beberapa titis penunjuk semesta ke • Penunjuk universal Asid mempunyai nilai
dalam tabung uji yang mengandungi asid berubah warna kurang
pH
hidroklorik cair. daripada hijau kepada
daripada
6 Add a few drops of universal indicator to a test merah. 7.
tube containing dilute hydrochloric acid. The universal indicator
Acids have a pH value
• Dengan menggunakan carta warna penunjuk changes colour from
semesta, tentukan pH asid tersebut. green to red. less than 7.
Using a colour chart for the universal indicator, • Asid mempunyai nilai
determine the pH of the acid. pH kurang daripada
7.
Penunjuk The acid has a pH of
semesta
Universal less than 7.
indicator
Asid hidroklorik cair
Dilute hydrochloric acid
(e) • Letakkan pita magnesium ke dalam tabung Gelembung udara Asid bertindak balas
uji yang mengandungi asid hidroklorik cair. muncul di dalam asid. dengan logam untuk
Perhatikan perkara yang berlaku. Apabila diuji dengan membebaskan gas
Place a strip of magnesium ribbon into a kayu uji beryala, hidrogen.
test tube containing dilute hydrochloric acid. bunyi 'pop' Acids react with metals
Observe what happens. to release hydrogen
• Letakkan kayu uji bernyala pada mulut tabung kedengaran. gas.
uji. / Place a burning wooden splinter at the Air bubbles
mouth of the test tube. appears in acid.
When tested with a
burning wooden splinter,
Asid hidroklorik cair a 'pop' sound is
Pita magnesium
Dilute hydrochloric acid heard.
Magnesium ribbon
sound (c) bertukar merah; biru / change to red; blue
(e) Gelembung udara, bunyi 'pop' / Air bubbles, 'pop' (d) kurang daripada / less than (b) terkakis; corroded / mengikis; corrosive
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 58
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 58 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 126
B. Sifat-sifat Alkali / Properties of Alkalis Textbook page 126
TUJUAN Untuk mengkaji sifat-sifat alkali
AIM To study the properties of alkalis
RADAS Tabung uji, penitis, jubin putih, penunu Bunsen
APPARATUS Test tubes, droppers, white tiles, Bunsen burner
BAHAN Larutan natrium hidroksida cair, larutan kalium hidroksida pekat, ammonium
MATERIALS klorida, soda penaik, kertas litmus merah, kertas litmus biru, penunjuk semesta,
putik kapas dan kertas turas.
Dilute sodium hydroxide solution, concentrated potassium hydroxide solution,
ammonium chloride, baking soda, red and blue litmus paper, universal indicator,
cotton buds and filter paper.
Prosedur Pemerhatian Kesimpulan
Procedure Observation Conclusion
(a) Celupkan putik kapas ke dalam soda penaik • Soda penaik berasa • Alkali mempunyai rasa
dan letakkan pada lidah anda. pahit. pahit
.
Dip a cotton bud into a cup of baking soda The baking soda tastes
Alkalis have a bitter
and place it on your tongue. bitter.
• Larutan natrium taste.
NOTA / NOTE
hidroksida cair adalah
Jangan telan soda penaik tetapi kumur licin apabila disentuh.
mulut anda. / Do not swallow the baking The dilute sodium • Alkali adalah licin 6
soda but rinse your mouth. hydroxide solution is apabila disentuh.
slippery when touch. Alkalis are soapy / slippery
Celupkan jari telunjuk anda ke dalam when touch.
bikar yang mengandungi larutan natrium
hidroksida cair dan gosokkannya dengan
ibu jari.
Dip your index finger in a beaker containing
dilute sodium hydroxide solution and rub it
against your thumb.
(b) Titiskan setitis larutan kalium hidroksida Kertas turas terkakis Alkali mengakis.
pekat pada kertas turas yang diletakkan di lubang Alkalis are corrosive.
atas jubin putih. dan
Drip a drop of concentrated potassium terbentuk pada kertas
hydroxide solution on a filter paper placed turas.
on a white tile. The filter paper is
corroded and a
Penitis
Dropper hole is
Larutan kalium formed on the filter paper.
hidroksida pekat
Concentrated
potassium Jubin putih
hydroxide solution White tile
Kertas turas
Filter paper
(b) terkakis; lubang / corroded; hole (a) pahit; licin; / bitter; soapy / slippery
59 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 59 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(c) Letakkan secebis kertas litmus biru dan • Kertas litmus merah Alkali menukarkan kertas
secebis kertas litmus merah ke dalam bertukar biru litmus merah kepada biru.
.
tabung uji yang mengandungi larutan Alkalis turn red litmus paper
The red litmus paper
natrium hidroksida cair. to blue.
Place a piece of blue litmus paper and changes to blue .
a piece of red litmus paper into a test • Kertas litmus biru
tube containing dilute sodium hydroxide
tidak berubah .
solution.
The blue litmus paper
Larutan natrium remains unchanged
hidroksida cair .
Dilute sodium
hydroxide solution
Kertas
litmus biru Kertas litmus merah
Blue litmus Red litmus paper
paper
(d) Tambah beberapa titis penunjuk semesta • Penunjuk semesta berubah Alkali mempunyai nilai pH
ke dalam tabung uji yang mengandungi warna daripada hijau lebih daripada 7.
larutan natrium hidroksida cair. Dengan kepada biru.
Alkalis have a pH value
menggunakan carta warna penunjuk The universal indicator
semesta, tentukan pH alkali tersebut. changes colour from green more than 7.
Add a few drops of universal indicator to blue.
to a test tube containing dilute sodium • Alkali mempunyai nilai pH
hydroxide solution. Using a colour chart for lebih daripada 7.
the universal indicator, find the pH of the The alkali has a pH of more
alkali. than 7.
6 Penunjuk Kuiz / Quiz
semesta
Universal
indicator
Larutan natrium
hidroksida cair
Dilute sodium
hydroxide solution
(e) Tambah sedikit ammonium klorida ke dalam • Gas yang terbebas Alkali bertindak balas
tabung uji yang mengandungi larutan menukarkan kertas litmus dengan garam ammonium
natrium hidroksida cair dan panaskan lembap yang berwarna untuk membebaskan gas
campuran. Letakkan secebis kertas litmus merah ammonia.
kepada
merah lembap pada mulut tabung uji. Alkalis react with
Perhatikan perkara yang berlaku. Hidu gas biru . ammonium salts to release
yang terbebas daripada campuran. The gas emitted turns the ammonia gas.
Add some ammonium chloride to a test red
moist litmus
tube containing dilute sodium hydroxide
solution and heat the mixture. Place a piece paper to blue .
of moist red litmus paper at the mouth of • Gas itu mempunyai bau
the test tube. Observe what happens. Smell
yang sengit .
the gas emitted by the mixture.
The gas has a pungent
smell.
changes to blue; remains unchanged
(e) merah; biru; sengit / red; blue; pungent (d) lebih daripada / more than B. (c) bertukar biru; tidak berubah
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 60
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 60 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Lengkapkan peta buih berganda di bawah. / Complete the double bubble map below. TP1
(b)
(a) (c)
Rasa / Taste Sifat mengakis
Rasa / Taste
Masam Corrosive Pahit
Sour Bitter
properties
(d) (e)
Sifat fizik bagi Sifat fizik bagi
asid alkali
Nilai pH: / pH value: Physical Physical Nilai pH: / pH value:
kurang daripada 7 properties of properties of lebih daripada 7
less than 7 acid alkali
more than 7
(f) (g)
Menukarkan warna Menukarkan warna
kertas litmus biru kepada kertas litmus merah
merah kepada biru 6
Change blue Change red litmus
litmus paper to paper to
red blue
C. Peranan Air untuk Menunjukkan Sifat-sifat Asid dan Alkali Buku teks muka surat 128
The Role of Water in Showing the Properties of Acids and Alkalis Textbook page 128
1 Radas di sebelah digunakan untuk mengkaji kesan alkali. Kertas litmus merah
The apparatus on the right is used to study the effect of alkali. TP2 Red litmus paper
(a) Apakah yang akan berlaku kepada kertas litmus merah? Terangkan Natrium hidroksida
jawapan anda. kering / Dry sodium
What will happen to the red litmus paper? Explain your answer. hydroxide
Tiada perubahan kerana tiada air.
No change because water is not present.
(b) Nyatakan dua pemerhatian yang boleh diperhatikan apabila air dituang ke atas natrium hidroksida kering.
State two observations when water is poured onto the dry sodium hydroxide.
(i) Natrium hidroksida melarut / Sodium hydroxide dissolved
(ii) Kertas litmus merah bertukar biru / Red litmus paper changes to blue
Red litmus paper changes to blue No change because water is not present. lebih daripada 7 / more than 7 (e)
(ii) Kertas litmus merah bertukar biru C. 1 (a) Tiada perubahan kerana tiada air. Pahit / Bitter (c)
Sodium hydroxide dissolved (g) biru / blue mengakis / Corrosive (b)
(b) (i) Natrium hidroksida melarut (f) merah / red Masam / sour (a)
61 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 61 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Radas di sebelah kanan digunakan untuk mengkaji kesan asid.
The apparatus on the right is used to study the effect of acid. TP2
(a) Apakah yang akan berlaku kepada kertas litmus biru? Terangkan jawapan anda.
Kertas litmus biru
What will happen to the blue litmus paper? Explain your answer. Blue litmus paper
Tiada perubahan kerana tiada air. Pepejal asid malik
No change because water is not present. Solid malic acid
(b) Nyatakan dua pemerhatian yang boleh dibuat apabila air dituang ke atas pepejal asid malik.
State two observations when water is poured onto the solid malic acid.
(i) Asid malik melarut / Malic acid dissolved
(ii) Kertas litmus biru bertukar merah / Blue litmus paper changes to red
Kesimpulan / Conclusion:
Alkali dan asid hanya menunjukkan sifatnya dengan kehadiran air.
Alkali and acid only show their properties with the present of water.
D. Bahan Berasid dan Beralkali dalam Kehidupan Seharian Buku teks muka surat 129
Acidic and Alkaline Substances in Daily Life Textbook page 129
TUJUAN Untuk menentukan bahan berasid dan beralkali dalam kehidupan seharian.
AIM To determine the acidic and alkaline substances in daily life.
6 RADAS Bikar, meter pH
APPARATUS Beaker, pH meter
BAHAN Air suling, ubat gigi, sabun, cuka, air pili, minuman bergas, jus oren, minyak masak,
MATERIALS detergen, kertas litmus, penunjuk semesta, metil jingga dan fenolftalein.
Distilled water, toothpaste, soap, vinegar, pipe water, carbonated drink, orange
juice, cooking oil, detergent, litmus paper, universal indicator, methyl orange and
phenolphthalein
BAHAN 1 Letakkan ubat gigi dalam 5 bikar berasingan.
MATERIALS Put the toothpaste into 5 beakers.
2 Bikar A diuji dengan kertas litmus.
Beaker A is tested using litmus paper.
3 Bikar B diuji dengan penunjuk semesta.
Beaker B is tested using universal indicator.
4 Bikar C diuji dengan metil jingga.
Beaker C is tested using methyl orange.
5 Bikar D diuji dengan fenolftalein.
Beaker D is tested using phenolphthalein.
6 Bikar E diuji dengan meter pH.
Beaker E is tested using pH meter.
7 Ulang langkah 1 hingga 6 dengan menggunakan air suling, sabun, cuka, air
pili, minuman bergas, jus oren, minyak masak dan detergen.
Repeat steps 1 to 6 by using distilled water, soap, vinegar, pipe water,
carbonated drink, orange juice, cooking oil and detergent.
Blue litmus paper changes to red Malic acid dissolved No change because water is not present.'
(ii) Kertas litmus biru bertukar merah (b) (i) Asid malik melarut C. 2 (a) Tiada perubahan kerana tiada air.
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 62
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 62 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
TUJUAN
AIM
Pertukaran warna bagi pelbagai petunjuk
Colour change of various indicators
Bahan Kertas Penunjuk Metil Kesimpulan
Substances litmus semesta jingga Fenolftalein Meter pH Conclusion
Litmus Universal Methyl Phenolphthalein pH meter
paper indicator orange
(a) Ubat gigi Biru Biru Kuning Merah jambu >7 Alkali
Toothpaste Blue Blue Yellow Pink Alkali
(b) Air suling Hijau Kuning Tiada warna 7 Neutral
–
Distilled water Green Yellow Colourless Neutral
(c) Sabun Biru Biru Kuning Merah jambu >7 Alkali
Soap Blue Blue Yellow Pink Alkali
(d) Cuka Merah Merah Merah Tiada warna <7 Asid
Vinegar Red Red Red Colourless Acid
(e) Air pili Hijau Kuning Tiada warna 7 Neutral
–
Pipe water Green Yellow Colourless Neutral
(f) Minuman bergas Merah Merah Merah Tiada warna <7 Asid
Carbonated drink Red Red Red Colourless Acid
(g) Jus oren Merah Merah Merah Tiada warna <7 Asid
Orange juice Red Red Red Colourless Acid 6
(h) Minyak masak Hijau Kuning Tiada warna 7 Neutral
–
Cooking oil Green Yellow Colourless Neutral
(i) Detergen Biru Biru Kuning Merah jambu >7 Alkali
Detergent Blue Blue Yellow Pink Alkali
E. Kekuatan Asid dan Alkali Buku teks muka surat 130
The Strength of Acid and Alkali Textbook page 130
1 Asid dan alkali mempunyai kekuatan yang berbeza.
Acid and alkalis have different strength .
2 Para saintis menggunakan skala pH untuk menyatakan kekuatan asid dan alkali.
Scientists use pH scale to state the strength of acids and alkalis.
3 Nilai pH adalah dari 1 hingga 14.
The pH values range from 1 to 14.
4 Asid mempunyai nilai pH kurang dari 7 , manakala jika larutan itu neutral , pH adalah 7, jika
pH melebihi 7, ia adalah alkali.
An acid has pH values less than 7 , while if the solution is neutral , the pH is 7, if the pH values
is more than 7, it is alkali. TP2
(h) 7 (d) <7
4 7; neutral / 7; neutral (g) <7 (c) >7
E. 1 kekuatan / strength (f) <7 (b) 7
(i) >7 (e) 7 D. (a) >7
63 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 63 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
pH bahan / pH of substances
1 Asid hidroklorik / Hydrochloric acid
Asid sulfurik / Sulphuric acid
Bertambah keasidan 2 Cuka / Vinegar
Increasing acidity
3 Jus limau / Lime juice
Jus lemon / Lemon juice
4 Jus nanas / Pineapple juice
Air soda / Soda water
5 Jus epal / Apple juice
Minuman bergas / Carbonated drinks
Susu segar / Fresh milk
6
Neutral 7 Air suling / Distilled water
Neutral
pH 8 Darah / Blood
Natrium hidrogen / Sodium hydrogen
9 Larutan karbonat / Carbonate solution
Sabun / Soap
Ubat gigi / Toothpaste
Bertambah kealkalian
10
Increasing alkalinity
Ammonia / Ammonia
Susu magnesia / Milk of magnesia
11
Air kapur / Limewater
12 Larutan pencuci longkang dan sinki / Drain and sink cleaning solutions
6 13 Larutan natrium hidroksida / Sodium hydroxide solution
14 Larutan kalium hidroksida / Potassium hydroxide solution
F. Kegunaan Asid dan Alkali dalam Kehidupan Harian Buku teks muka surat 131
Uses of Acid and Alkali in Daily Life Textbook page 131
1 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah. / Complete the table below. TP3
Kegunaan asid / Uses of acid
Asid / Acid Kegunaan / Uses
detergen
(a) Asid sulfurik Digunakan dalam bateri kereta, dalam pembuatan baja, kertas,
Sulphuric acid dan tekstil buatan seperti nilon dan rayon.
Used in car batteries, in making fertilisers, paper, detergent and
artificial textile such as nylon and rayon.
Digunakan untuk membuang karat dan membersihkan logam
(b) Asid hidroklorik
Hydrochloric acid untuk kimpalan dan elektrolisis. Dihasilkan dalam perut untuk pencernaan
makanan dan membunuh bakteria.
Used to remove rust and clean metals for welding and electrolysis.
Produced in our stomach to digest food and kills bacteria.
(b) karat / rust F. 1 (a) detergen / detergent
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 64
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 64 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Asid / Acid Kegunaan / Uses
(c) Asid nitrik Untuk membuat bahan letupan dan baja seperti ammonium nitrat.
Nitric acid explosives
Used to make and fertilisers such as ammonium nitrate.
(d) Asid karbonik Digunakan dalam pembuatan minuman berkarbonat .
Carbonic acid carbonated
Used in drinks.
(e) Asid sitrik Digunakan dalam pembuatan jus buahan dan makanan.
Citric acid Used in fruit juices and foods.
(f) Asid tartarik Digunakan dalam garam kesihatan dan pembuatan kek.
Tartaric acid Used in health salts and baking.
(g) Asid askorbik Digunakan dalam pembuatan vitamin C .
Ascorbic acid vitamin C
Used in making .
(h) Asid benzoik Digunakan untuk mengawet makanan dan dalam pembuatan sos.
Benzoic acid Used to preserved food and in making sauce.
(i) Asid asetik (cuka) Digunakan untuk mengawet makanan dan dalam industri pembuatan
Acetic acid (vinegar) jeruk preseve pickles
. / Used to food and in making of .
(g) Asid formik Untuk menggumpalkan lateks.
Formic acid To coagulate latex.
6
Kegunaan alkali / Uses of alkali
Alkali / Alkali Kegunaan / Uses
(a) Natrium hidroksida Digunakan dalam pembuatan sabun, detergen, rayon, plastik dan pembuatan
Sodium hydroxide tekstil buatan.
Used in making soaps, detergent, rayon, plastic and artificial fibres.
(b) Kalium hidroksida Digunakan dalam pembuatan sabun dan pewarna.
Potassium hydroxide Used in making soap and dyes.
(c) Kalsium hidroksida Digunakan dalam pembuatan simen dan meneutralkanasid dalam empangan
Calcium hydroxide air. / Used in making cement and neutralise acid in the water reservoir.
(d) Magnesium hidroksida Digunakan dalam pembuatan susu magnesia dan ubat gigi.
Magnesium hydroxide Used in making magnesia milk and toothpaste.
(e) Larutan ammonia Digunakan dalam pembuatan agen pembersihan, pencuci tingkap, asid nitrik
Ammonia solution dan baja serta mengelakkan pembekuan lateks.
Used in making cleaning agent, window cleaners, nitric acid and fertilisers and
also prevent the coagulation of latex.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
(d) berkarbonat / carbonated
(i) mengawet; jeruk / preseve; pickles (g) vitamin C / vitamin C F. 1. (c) letupan / explosives
65 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 65 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
6.2 Peneutralan / Neutralisation
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
6.2.1 Menerangkan proses peneutralan. / Explain the neutralisation reaction.
SP
LS Menerangkan dengan contoh penggunaan proses peneutralan dalam kehidupan seharian.
6.2.2
Explain with examples the applications of neutralisation reaction in daily life.
EMK Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Nilai Murni Menghargai sumbangan sains dan teknologi
Moral Value Appreciate the contribution of science and technology
Buku teks muka surat 133
A. Proses Peneutralan / Neutralisation Process Textbook page 133
1 Peneutralan ialah proses tindak balas asid dan alkali untuk menghasilkan garam dan air.
Neutralisation is the process which acid
reacts with alkali to produce salt and water. TP2
2 Kaedah yang digunakan untuk tindak balas peneutralan ialah pentitratan .
Method used for neutralisation reaction is titration .
3 Persamaan perkataan untuk tindak balas peneutralan adalah seperti di bawah:
The word equation for the neutralisation is as below: TP2 TP3
Asid Alkali Garam Air
+ + Water
Acid Alkali Salt
Contoh / Example
6
(a) Asid hidroklorik Natrium hidroksida Natrium klorida Air
+ +
Hydrochloric acid Sodium hydroxide Sodium chloride Water
Asid hidroklorik Kalsium hidroksida Kalsium klorida Air
(b) + Calcium chloride + Water
Hydrochloric acid Calcium hydroxide
Asid sulfurik Natrium hidroksida Natrium sulfat Air
(c) + +
Sulphuric acid Sodium hydroxide Sodium sulphate Water
Asid sulfurik Kalsium hidroksida Kalsium sulfat Air
(d) + +
Sulphuric acid Calcium hydroxide Calcium sulphate Water
Asid nitrik Natrium hidroksida Natrium nitrat Air
(e) + +
Nitric acid Sodium hydroxide Sodium nitrate Water
Acid; Alkali; Salt
3 Asid; Alkali; Garam
(e) Natrium sulfat / Sodium sulphate + Air / Water (c) Natrium sulfat / Sodium sulphate + Air / Water 2 pentitratan / titration
(d) Kalsium klorida / Calcium chloride + Air / Water (b) Kalsium klorida / Calcium chloride + Air / Water A. 1 asid / acid
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 66
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 66 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B. Aplikasi Peneutralan dalam Kehidupan Harian Buku teks muka surat 134
Application of Neutralisation in Daily Life Textbook page 134
TP3
1 Ubat gigi mengandungi alkali. Alkali akan meneutralkan asid yang telah terhasil daripada tindak
balas antara bakteria dan makanan di dalam mulut.
Toothpaste contains an alkali. The alkali will neutralise the acid formed by the action of bacteria
and food in the mouth.
2 Ketidakcernaan adalah disebabkan penghasilan asid yang berlebihan di dalam perut. Ubat yang
mengandungi alkali seperti magnesium hidroksida atau susu magnesia digunakan untuk meneutralkan asid
dalam perut.
Indigestion is due to excess of acid produced in the stomach. Medicine containing alkali such as
magnesium hydroxide or magnesia milk is used to neutralise the acids in the stomach.
3 Jika seseorang tercedera disebabkan alkali seperti natrium hidroksida pekat, rawatan segera perlu
diberikan dengan menyapukan asid seperti cuka atau asid borik pada tempat yang tercedera.
If a person injured by alkali such as concentrated sodium hydroxide, immediate treatment should
be done by applying acid such as vinegar or boric acid onto the injured area.
4 Apabila seseorang terkena sengatan lebah, lebah akan memasukkan asid ke dalam kulit mangsa.
Alkali seperti losyen ‘calamine’, larutan ammonia atau soda penaik disapu pada bahagian yang terkena sengatan
untuk meneutralkan asid tersebut. 6
When a bee stings a person, it injects acid into the skin. An alkali solution such as calamine lotion,
ammonia solution or baking soda is applied on wound to neutralise the acid.
5 Luka akibat gigitan tebuan adalah bersifat alkali . Asid lemah seperti cuka boleh
disapukan ke tempat yang terkena sengatan untuk meneutralkan alkali.
The wound from the sting of a wasp is alkaline. A weak acid such as vinegar can be
applied to neutralise the alkali.
6 Kalsium hidroksida digunakan untuk meneutralkan air dalam empangan. Ia juga digunakan untuk
meneutralkan tanah yang berasid.
Calcium hydroxide is used to neutralise water at the reservoir. It is also used to neutralise
acidity of soil.
7 Sabun digunakan untuk meneutralkan urea yang dihasilkan oleh peluh.
Soap is used to neutralise the urea produced by sweat.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
3 alkali; asid / alkali; acid
urea / urea 7 alkali; cuka; meneutralkan / acid; vinegar; neutralise 5 2 asid; meneutralkan / acid; neutralise
meneutralkan; meneutralkan / neutralise; neutralise 6 asid; meneutralkan / acid; neutralise 4 B. 1 Ubat gigi; meneutralkan / Toothpaste; neutralise
67 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 67 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Badan Amirul telah disengat obor-obor semasa 3 Susunkan bahan di bawah mengikut susunan
sedang mandi di laut bersama dengan kawan- menurun nilai pH.
kawannya. Bahagian badannya yang disengat Arrange the substances below in descending order
menjadi merah dan bengkak. Cadangkan cara of pH value.
pertolongan awal yang boleh dilakukan oleh kawan-
kawannya bagi mengurangkan kesakitan Amirul. • Jus oren / Orange juice
Amirul’s body has been stained with a jellyfish while • Jus peria / Bitter gourd juice
bathing in the sea with his friends. The stinged body • Asid hidroklorik / Hydrochloric acid
part becomes red and swollen. Suggest the first aid • Air mineral / Mineral water
way his friends can do to reduce the pain of Amirul.
A Menyapu ubat gigi / Apply some toothpaste A Jus peria, air mineral, jus oren, asid hidroklorik
B Membasuh dengan air laut Bitter gourd juice, mineral water, orange juice,
Clean with the sea water hydrochloric acid
C Membasuh dengan sabun / Clean using a soap B Asid hidroklorik, jus oren, air mineral, jus peria
D Menyapu dengan cuka / Apply with vinegar Hydrochloric acid, orange juice, mineral water,
bitter gourd juice
2 Kenal pasti bahan yang terhasil bagi tindak balas C Air mineral, jus peria, jus oren, asid hidroklorik
peneutralan di bawah. / Identify the product of Mineral water, bitter gourd juice, orange juice,
neutralisation process below. hydrochloric acid
D Jus oren, asid hidroklorik, air mineral, jus peria
Asid sulfurik + Kalium hidroksida ➝ ? Orange juice, hydrochloric acid, mineral water,
Sulphuric acid + Potassium hydroxide ➝ ? bitter gourd juice
6 A Kalium sulfat / Potassium sulphate
B Kalium oksida / Potassium oxide
C Kalium sulfat + Air / Potassium sulphate + Water
D Kalium oksida + Air / Potassium oxide + Water
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
1 Kertas litmus boleh digunakan untuk menguji keasidan dan kealkalian suatu Serbuk pencuci Kertas litmus
kering merah
bahan. Kertas litmus merah disentuh pada serbuk pencuci kering seperti yang Dried washing Red litmus
ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 1. Namun begitu, tiada perubahan warna diperhatikan. powder paper
Berikan alasan bagi keadaan ini dan cadangan untuk membolehkan serbuk
pencuci menunjukkan sifatnya.
Litmus paper can be used to test the acidity and alkalinity of a substance. Red
litmus paper is being touched onto the dried washing powder as shown in
Diagram 1. However, no colour change is observed. Give reason for this situation
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
and suggestion for the washing powder to show its property.
Tanpa kehadiran air, sifat bahan tidak dapat ditunjukkan. Tambahkan air kepada serbuk pencuci tersebut.
In the absence of water, the substance cannot show its properties. Add water to the washing powder.
[2 markah/marks]
2 Qayum merupakan usahawan tani muda. Beliau mengusahakan ladang strawberi. Untuk memastikan tanamannya
subur, beliau memastikan baja dari jenis ammonia sentiasa diletak secara berkala. Wajarkan tindakan Qayum.
Qayum is a young agricultural entrepreneur. He works on a strawberry farm. To make sure the plants are fertile,
he ensures the ammonia fertilisers are always put regularly. Justify his action.
Ekstra / Extra
Tanahnya berasid. Baja ammonia akan meneutralkan tanah.
The soil is acidic. The ammonia will neutralise the soil.
[2 markah/marks]
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 68
Modul Sains T2-Bab6 Book A_F.indd 68 25/10/2021 12:38 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Keelektrikan dan Kemagnetan
7 Electricity and Magnetism
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
Keelektrikan
7.1
Electricity
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
7.1.1 Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai tenaga. / Describe and communicate about energy.
SP 7.1.2 Menerangkan dan berkomunikasi mengenai kewujudan cas elektrostatik. / Explain and communicate the existence of electrostatic charges.
LS 7.1.3 Menjelaskan dengan contoh elektrostatik dalam kehidupan seharian. / Explain with examples electrostatic in daily life.
7.1.4 Merumuskan cas yang mengalir menghasilkan arus elektrik. / Draw a conclusion that the flow of charges produces electric current.
7.1.5 Mencirikan arus, voltan dan rintangan serta unitnya. / Characterise current, voltage and resistance, and their units.
7.1.6 Merumuskan perkaitan antara arus, voltan dan rintangan. / Draw a conclusion on the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Jujur dan tepat dalam merekod dan mengesahkan data
Moral Value Honest and accurate in recording and verifying data
Buku teks muka surat 142
A. Tenaga / Energy Textbook page 142
1 Tenaga ialah kebolehan untuk melakukan kerja. Unit S.I. bagi tenaga ialah joule (J).
Energy is the ability to carry out work. The S.I. for energy is joule (J). TP1
2 Tenaga boleh ditemui dalam pelbagai bentuk.
Energy can be found in different forms. TP1 TP2
7
Jenis tenaga Maksud Contoh
Types of energy Meaning Example
(a) Tenaga keupayaan
elastik
Elastic potential
energy Tenaga yang disimpan dalam suatu objek disebabkan
kedudukan dan keadaannya.
(b) Tenaga keupayaan Energy stored in an object due to its position and condition.
graviti
Gravitational
potential energy
(c) Tenaga kinetik Tenaga yang dimiliki oleh suatu objek yang sedang
Kinetic energy bergerak .
Energy possessed by a moving object.
(d) Tenaga haba Suatu bentuk tenaga dalam suatu objek yang panas .
Heat energy hot
A form of energy in a object.
(d) panas / hot A 2. (c) bergerak / moving
69 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 69 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Jenis tenaga Maksud Contoh
Types of energy Meaning Example
(e) Tenaga cahaya melihat
Tenaga yang membolehkan kita .
Light energy
The energy which enables us to see .
(f) Tenaga bunyi
Sound energy Tenaga yang dihasilkan oleh objek yang bergetar.
The energy produced by a vibrating object.
(g) Tenaga elektrik elektron
Electrical energy Tenaga yang dihasilkan oleh aliran .
The energy produced by the flow of electron .
(h) Tenaga kimia Tenaga yang tersimpan dalam suatu bahan .
Chemical energy substance
The energy stored in a .
(i) Tenaga nuklear Dibebaskan daripada tindak balas pembelahan atau pelakuran
Nuclear energy yang berlaku dalam nukleus atom.
It is released from fission or fusion reactions which occur in
atomic nucleus.
3 Sumber tenaga. / Sources of energy. TP1
(a)
(b)
Matahari
The Sun Ombak
Waves
7 (h)
Angin (c)
Wind
Geoterma
Geothermal
Sumber
tenaga
Energy
(g)
sources
Biojisim (d)
Biomass
Air
Water
(f) (e)
Bahan radioaktif
Bahan api fosil
Radioactive
Fossil fuel
substances
(h) bahan / substance
(h) Angin / Wind (e) Bahan radioaktif / Radioactive substances (g) elektron / electron
(f) Bahan api fosil / Fossil fuel 3 (c) Geoterma / Geothermal (e) melihat / see
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 70
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 70 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 144
B. Cas Elektrostatik / Electrostatic Charges Textbook page 144
1 Elektrostatik adalah kajian cas elektrik statik iaitu cas-cas yang pegun (statik).
Electrostatic is a study of static electrical charges, that is charges which are stationary (static). TP1
2 Cas elektrik statik boleh dihasilkan melalui geseran.
Static electrical charges are produced by friction. TP1
(a) Semua atom terdiri daripada proton (bercas positif) dan elektron (bercas negatif).
All atoms are made up of proton (positive charges) and electron (negative charges). TP1
(b) Apabila geseran berlaku antara dua jenis atom yang berlainan, elektron boleh berpindah dari satu jenis
atom ke satu jenis atom yang lain seperti dalam rajah berikut.
When friction happens between two different types of atoms, electrons can transfer from one
type of atom to another type of atom as shown in the following diagram. TP2
Elektron Elektron dipindahkan
Electron Electron is transferred
Proton
Proton
Atom A Atom B
Atom A Atom B
(i) Atom A bercas positif kerana bilangan elektron di dalamnya menjadi kurang; manakala Atom B bercas
negatif kerana bilangan elektron di dalamnya bertambah.
Atom A is positively charged because the amount of electron in it has reduced; whereas Atom B is 7
negatively charged because the amount of electron in it has increased.
neutral
(ii) Bahan mempunyai jumlah cas positif (proton) dan cas negatif (elektron) yang sama.
A neutral object contains same amount of positive charges (protons) and negative charges
(electrons).
3 Elektroskop digunakan untuk mengesan kewujudan cas elektrik pada sesuatu objek.
Electroctroscope is use to detect the existence of electric charges on an object.
(ii) neutral / neutral 2 (b) berpindah / transfer B. 1 pegun / stationary
71 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 71 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
4 Apabila pencapahan kerajang emas di dalam elektroskop semakin besar, kuantiti cas elektrostatik semakin
banyak terkumpul.
When the divergence of a gold leaf in an elctroscope is larger, the quantity of electrostatic charges is higher
accumulated. TP4
Langkah Pemerhatian Penerangan
Step Observation Explanation
(a) Sebatang pembaris Pembaris plastik neutral
Ceper logam
plastik dibawa mendekati Metal cap neutral
ceper logam elektroskop. Elektroskop The plastic ruler is
A plastic ruler is brought Electroscope Kerajang emas
near to the metal cap of Gold leaf
an electroscope.
Tiada perubahan pada kerajang emas
No change at the gold leaf
(b) Sebatang pembaris Pembaris digosok dengan Pembaris plastik mempunyai
kain bulu / Ruler rubbed with
plastik dibawa mendekati woollen cloth cas
ceper logam elektroskop charge
setelah digosok dengan Ceper logam
The plastic ruler has
kain bulu. Metal cap
A plastic ruler which Elektroskop
Electroscope Kerajang emas
has been rubbed with a Gold leaf
woollen cloth is brought
near to the metal cap of mencapah
Kerajang emas
an electroscope.
diverge
The gold leaves
5 Terangkan langkah-langkah keselamatan dalam pengendalian cas elektrostatik dengan mengisi tempat kosong
dengan perkataan yang diberi. / Explain the following safety masures in handling electrostatics charges by filling
in the blanks with the words provided. TP3
7
rantai logam dinyahcas konduktor kilat roda
metal chain discharged lightning conductors wheels
(a)
Bangunan-bangunan yang tinggi dilengkapi dengan
konduktor kilat yang menghantar kilat ke bumi
secara langsung.
Tall buildings are equipped with lightning conductors that
send lightning to the earth directly.
(b) Kapal terbang perlu dinyahcas
sebelum mendarat. Ini dilakukan
dengan mengumpulkan cas-cas pada bahagian roda .
Cas-cas melompat ke bumi apabila kapal terbang mendekati
permukaan darat semasa mendarat. / An aeroplane needs to be
discharged before landing. This is done by accumulating
charges at the wheels . Charges jump to the earth when the
aeroplane is near to the earth when landing.
(b) dinyahcas, roda / discharged, wheels (b) mencapah; diverge / cas; charge
5 (a) konduktor kilat / lightning conductors A. 4 (a) neutral / neutral
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 72
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 72 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(c) Lori minyak yang membawa minyak dan bahan-bahan mudah terbakar
mempunyai satu rantai logam yang menyentuh lantai untuk
menyahcas.
An oil tanker that carries oil and flammable substances has a
metal chain that touches the earth to discharge.
Projek / Project
Arahan / Instructions:
Jalankan simulasi kejadian kilat dengan menggunakan penjana Van de Graaff.
Conduct a simulation of lightning by using Van de Graaff generator. TP4
1 Hidupkan penjana Van de Graaff. / Switch on Van de Graaff generator.
2 Selepas beberapa minit, dekatkan sfera logam pada kubah.
After a few minutes, bring the metal sphere near to the dome.
3 Perhatikan apa yang berlaku dan bincangkan di dalam kelas.
Observe what happens and discuss it in the class.
Projek / Project
Arahan / Instructions:
Secara berkumpulan, kaji situasi berikut: / In group, study the following situations:
(a) Pemilihan jenis fabrik yang sesuai dipakai ketika cuaca panas
Choosing type of fabric that suitable to wear during hot weather 7
(b) Kawasan perlindungan yang selamat semasa ribut petir (konsep Faraday’s Cage)
Safe protection area during thunder storm (Faraday’s Cage)
Bincangkan cara penyelesaian situasi tersebut berdasarkan konsep elektrostatik. Bentangkan hasil perbincangan
dalam kelas. / Discuss ways to solve these situations based on electrostatic concept. Present the findings of the
discusssion inclass. TP6
Buku teks muka surat 148
C. Arus Elektrik / Electric Current Textbook page 148
1 Berikut merupakan istilah-istilah yang digunakan dalam litar elektrik.
The following terms shows the terms used in electrical circuit. TP1
(a) Tenaga elektrik – tenaga yang dihasilkan apabila cas-cas mengalir dalam satu arah
Electrical energy – energy that is produced when charges flow in one direction
(b) Arus elektrik – kadar pengaliran cas elektrik
Electric current – the rate of flow of electrical charges
(c) Voltan – daya elektrik yang diperlukan untuk menggerakkan cas dari satu titik ke titik lain dalam satu litar lengkap
Voltage – electrical force that is needed to move charges from one point to another in a complete circuit
(d) Rintangan – faktor-faktor dalam konduktor yang mengurangkan jumlah arus elektrik
Resistance – factors in a conductor that reduce the amount of electric current
5 (c) rantai logam / metal chain
73 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 73 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Cas-cas statik dihasilkan apabila sesuatu objek menggosok objek yang lain. Cas-cas yang dihasilkan dengan
cara ini adalah pegun. Malah jika cas-cas yang pegun ini mengalir dari satu tempat ke tempat lain,
arus elektrik dihasilkan. / Static charges are produced when an object rubs against another object. Charged
produced in this way are stationary. However, if these stationary charges flow from one place to
another, electric current is produced. TP2
3 Untuk memerhatikan aliran arus elektrik, sebuah penjana Van de Graaff dicaskan dan disambungkan
dengan pili air seperti berikut. / To observe the flow of electrical current, a Van de Graaff generator is
charged up and join to the water tap as follow. TP3
Susunan radas Pemerhatian Perbincangan
Arrangement of apparatus Observation Discussion
Penunjuk • Kubah penjana Van de Graaff dicaskan
galvanometer apabila suis ditutup. / The dome of the
Pili air Kubah
Dome
terpesong Van de Graaff generator is charged up
Water tap
Wayar The pointer of when the switch is closed.
bertebat
Insulated Tali getah the galvanometer • Cas-cas mengalir ke bumi apabila
wire Rubber belt deflected kubah penjana Van de Graaff
Roda plastik disambungkan dengan pili air.
Plastic wheel The charges flow to the earth when the
dome of the Van de Graaff generator is
Galvanometer Penjana Van de joined to the water tap.
Galvanometer Graaff
Van de Graaff • Galvanometer digunakan untuk
generator mengesan arus kecil yang mengalir
melaluinya.
Galvanometer is used to detect small
current that flows through it.
D. Hubungan antara Arus Elektrik, Voltan dan Rintangan Buku teks muka surat 148
The Relationship between Electric current, Voltage and Resistance
7
Textbook page 148
Arus / Current Voltan / Voltage Rintangan / Resistance
Simbol
(a) I V R
Symbol
Unit ukuran Ampere Volt Ohm
(b)
Measuring unit
Simbol unit A V Ω
(c)
Unit symbol
Alat pengukuran Ammeter Voltmeter –
(d)
Measuring tool
Simbol alat ukur –
(e)
Symbol of measuring tool
Cara menyambung alat
ukur (bersiri / selari) Bersiri Selari
(f) Ways to connect –
Series Parallel
measuring tool (series /
parallel)
(d) Ammeter / Voltmeter D. (a) I; V; R
Selari; Parallel (c) A; V; Ω 3 Van de Graaff / Van de Graaff
(f) Bersiri; Series (b) Ampere; Volt; Ohm C. 2 mengalir / flow
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 74
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 74 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 152
E. Hukum Ohm / Ohm’s Law Textbook page 152
Hukum Ohm / Ohm’s law:
V= IR "Arus elektrik yang mengalir melalui suatu konduktor berkadar terus dengan voltan."
"Electric current that flows through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage."
Selesaikan masalah berikut dengan menggunakan Hukum Ohm.
Arahan: / Instructions:
Solve the following problems by applying Ohm’s Law. TP4
Contoh / Example 1 5V Kira rintangan mentol.
3V Calculate the resistance of
Kira rintangan mentol.
the light bulb.
Calculate the resistance of 1A A
the light bulb.
2A A
V
V
V =R V =R
V
I I
3 =R I R tutup yang dicari 5 =R
2 close what we looking for 1
R = 1.5 Ω R=5Ω
2 5V Kira bacaan ammeter jika 3 4V
Kira bacaan ammeter jika
rintangan mentol ialah 2 Ω. rintangan mentol ialah 2 Ω.
Calculate the reading of Calculate the reading of
A A
ammeter if the resistance ammeter if the resistance
of the bulb is 2 Ω. of the bulb is 2 Ω.
V
V =R
I
V V =R
I
7
5 =2 4 =2
I I
I = 2.5 A I=2A
4 5
Kira bacaan voltmeter jika Kira bacaan voltmeter jika
2A A rintangan mentol ialah 2 Ω. 1A A rintangan mentol ialah 3 Ω.
Calculate the reading of Calculate the reading of
voltmeter if the resistance voltmeter if the resistance
of the bulb is 2 Ω. of the bulb is 3 Ω.
V V
V =R V =R
I I
V =2 V =3
2 1
V=4V V=3V
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
V = 4 V 4 I = 2.5 A 2
V=3V 5 I=2A 3 R=5Ω E. 1
75 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 75 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
7.2 Pengaliran Arus Elektrik dalam Litar Bersiri dan Litar Selari
Electrical Current Flows in Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
SP Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai pengaliran arus elektrik dalam litar bersiri dan litar selari.
7.2.1
LS Elaborate and communicate about the flow of electric current in series circuit and parallel circuit.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Jujur dan tepat dalam merekod dan mengesahkan data
Moral Value Honest and accurate in recording and verifying data
Buku teks muka surat 152
A. Komponen Litar Elektrik / Electrical Circuit Components Textbook page 152
1 Suatu litar yang lengkap membenarkan arus mengalir melaluinya dan alat elektrik yang disambung
dalamnya boleh berfungsi .
A complete circuit allows a current to flow through it and the electrical appliances in it can
function . TP2
2 Lukiskan simbol-simbol bagi semua komponen di bawah. / Draw the symbol of all components. TP1
Komponen Simbol Komponen Simbol
Component Symbol Component Symbol
(a) Sel kering (f) Perintang
Dry cell Resistor
(b) Suis (g) Fius
Switch Fuse
(c) Voltmeter (h) Galvanometer
V G
Voltmeter Galvanometer
7 (d) Ammeter
A
(i) Perintang boleh
Ammeter ubah
Rheostat (variable atau / or
(e) Mentol + –
resistor)
Bulb
Buku teks muka surat 153
B. Litar Bersiri dan Litar Selari / Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit Textbook page 153
+ –
+ –
Litar bersiri / Series circuit Litar selari / Parallel circuit
+ –
(i) (f) V (c)
G (h) (e) 2
(g) A (d) A. 1 arus; berfungsi / current; function
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 76
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 76 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
1 Lengkapkan kelebihan dan kelemahan litar bersiri dalam jadual di bawah.
Complete the advantages and disadvantages of series circuit in the table below. TP4
(a) Kelebihan litar bersiri (b) Kelemahan litar bersiri
Advantages of series circuit Disadvantages of series circuit
satu suis • Apabila satu mentol terbakar, mentol lain
• Menggunakan hanya untuk
menghidupkan semua mentol. terpadam . / When one bulb burns out, all the
Use only one switch to switch on all go off
other bulbs .
bulbs.
• Kecerahan mentol berkurang apabila lebih banyak
• Voltan akan meningkat apabila sel-sel mentol disambungkan. / The brightness of the bulbs
kering disambungkan secara bersiri . decreases when more bulbs are connected.
Voltage • Mentol tidak boleh dipadam berasingan.
increases when dry cells are
connected in series . Light bulb cannot switched off separately.
2 Lengkapkan kelebihan dan kelemahan litar selari dalam jadual di bawah.
Complete the advantages and disadvantages of parallel circuit in the table below. TP4
(a) Kelebihan litar selari (b) Kelemahan litar selari
Advantages of parallel circuit Disadvantages of parallel circuit
• Kecerahan mentol bertambah apabila lebih banyak • Voltan setiap alat elektrik tidak dapat dikawal
mentol disambungkan. / The brightness of the bulb kerana voltannya sama dengan voltan sumber.
increases when more bulbs are connected. Voltage for each of electrical appliance cannot
• Mentol boleh dihidupkan dan dipadamkan secara be controlled because its voltage same as
berasingan . source voltage.
separately • Tenaga sel kering dihabiskan dengan lebih
Bulbs can be switched on or off .
cepat .
• Jika terdapat satu mentol atau alat elektrik rosak, faster .
berfungsi Energy of the dry cells is used up
alat lain masih . / If one bulb or
electrical appliance burns out, the other appliances 7
still function .
3 Bandingkan arus, voltan dan rintangan dalam litar bersiri dan litar selari dalam jadual di bawah.
Compare the current, voltage and resistance in a series circuit and a parallel circuit in the table below. TP2
Ciri-ciri / Properties (a) Litar bersiri / Series circuit (b) Litar selari / Parallel circuit
V
V
Susunan komponen I I V1R1
Arrangement of I1
V1R1 V2R2
components
V2R2
I1 I2 I2
Arus / Current I1 = I2 I1 + I2
I= I=
Voltan / Voltage V1 + V2 V1 = V2
V= V=
Rintangan berkesan 1 1 1
R1 + R2 = +
Effective resistance R= R R1 R2
dipadam / switched off •
R 1 R2 (b) • cepat / faster terpadam / go off (b) •
+ (c) I1 + I2; V1 + V2;
1 1 • berfungsi / function Voltan; bersiri / Voltage; series •
3 (a) I1 = I2; V1 + V2; R1 = R2 2 (a) • berasingan / separately satu suis / one switch B. 1 (a) •
77 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 77 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Penyelesaian masalah pengiraan / Problem solving on calculation
1 Selesaikan masalah berikut tentang voltan, arus dan rintangan dalam litar bersiri atau selari.
Solve the following problems on voltage, current and resistance in a series or parallel circuit. TP2
(a) Diberi voltan dalam litar ialah 9 V dan jumlah arus ialah 2 A.
Given the voltage in the circuit is 9 V and the total current is 2 A.
2Ω r
(i) Kirakan jumlah rintangan dalam litar (ii) Kemudian, cari rintangan r.
tersebut. Then, find out the resistance of r.
Calculate the total resistance in the circuit. R = R1 + R2
V
R = 4.5 = 2 + r
I
9 r = 2.5 Ω
=
2
= 4.5 Ω
(b) Diberi bacaan voltmeter ialah 6 V dan jumlah arus dalam litar ialah 3 A.
Dua mentol tersebut adalah sama.
Given the reading of the voltmeter is 6 V and the total current in the
circuit is 3 A. The two bulbs are identical.
(i) Apakah voltan yang dibekalkan (ii) Kirakan rintangan setiap mentol.
kepada setiap mentol? Calculate the resistance of one light bulb.
7 What is the voltage supplied to each V 1
=
1
+
1
light bulb? R = R R R
I 1 2
6V 6 1 1 1
= = + (R = R1)
3 2 R1 R2 2
= 2 Ω 1 2
=
2 R1
R1 = R2 = 4Ω
Projek / Project
1 Sediakan satu lakaran ringkas litar yang sesuai digunakan di rumah.
Prepare a sketch on simple suitable circuit used at home.
2 Wajarkan pemilihan jenis litar yang anda gunakan dalam lakaran di (1).
Justify the sketch you draw in (1).
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
(ii) R1 = R2 = 4Ω (ii) 2.5 Ω
(b) (i) 6 V 1 (a) (i) 4.5 Ω
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 78
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 78 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
7.3 Kemagnetan
Magnetism
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
7.3.1 Merumuskan ciri magnet. / Draw a conclusion about the characteristics of a magnet.
SP 7.3.2 Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai elektromagnet. / Describe and communicate about electromagnets.
LS
Menjalankan eksperimen dan berkomunikasi mengenai kegunaan magnet dan elektromagnet dalam kehidupan seharian.
7.3.3
Carry out an experiment and communicate the uses of magnets and electromagnets in daily life.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Jujur dan tepat dalam merekod dan mengesahkan data
Moral Value Honest and accurate in recording and verifying data
Buku teks muka surat 158
A. Sifat-sifat Magnet / Properties of Magnet Textbook page 158
1 Magnet ialah oksida sesetengah logam. Daya magnetik magnet menarik bahan-bahan magnet.
A magnet is an oxide of certain metals. The magnetic force of a magnet attracts magnetic substances. TP1
2 Antara berikut, yang manakah merupakan bahan-bahan magnet? Tandakan (✓) dalam kotak.
Which of the following are magnetic substances? Tick (✓) in the box. TP1
(a) Besi / Iron ✓ (c) Karbon / Carbon (e) Keluli / Steel ✓
(b) Nikel / Nickel ✓ (d) Kobalt / Cobalt ✓ (f) Aluminium / Aluminium
3 Magnet ada dua kutub, iaitu kutub utara dan kutub selatan .
A magnet has two poles, north pole and south pole. TP2
(a) (b)
7
Kutub yang sama menolak antara satu Kutub yang berbeza menarik antara satu sama lain.
sama lain. Different poles attract each other.
Same poles repel each other.
4 Apabila sebatang magnet bar digantung bebas, kutub utaranya menghala ke Utara Bumi.
When a bar magnet is hung free, its north pole points to North of Earth. TP2
Disebabkan sifat magnet ini, kompas
dicipta untuk menentukan arah.
Due to this characteristic of magnet, compass
is invented to determine direction.
U/N
5 Medan magnet: Kawasan sekitar magnet yang wujud kesan daya oleh magnet.
Magnetic field: The area around the magnet that has the effect of force by the magnet. TP1
(a) menolak / repel (d) ✓
3 utara; selatan / north; south (b) ✓
4 Utara; North / kompas; compas (e) ✓ A. 2 (a) ✓
79 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 79 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 159
B. Medan Magnet / Magnetic Field Textbook page 159
1 Rajah di bawah menunjukkan sebatang magnet bar. Bagi mengkaji corak medan magnet:
Diagram below shows a bar magnet. To study the pattern of a magnetic field:
(a) Arah jarum kompas-kompas tersebut ditunjukkan (b) Garisan medan magnet yang terbentuk
di bawah. / The direction of the pointers of the ditunjukkan di bawah. The magnetic field lines
compasses shown below. formed shown below.
U/N S/S
U/N S/S
2 Arah garisan medan magnet bermula dari kutub utara dan tamat pada kutub selatan
magnet bar. Garisan medan magnet adalah lebih dekat di kutub dan berpisah lebih jauh antara satu sama lain
di sisi magnet bar. Ini adalah kerana medan magnet di sekitar kutub adalah lebih kuat .
The direction of the magnetic field lines begins from the north pole and ends at the south
pole of the bar magnet. The magnetic field lines are closer at the poles and further apart from one another at
the side of the bar magnet. This is because the magnetic field around the poles is stronger .
Rajah berikut menunjukkan corak medan magnet.
The following diagram shows the pattern of magnetic field. TP3
7 (a) (b)
U/N S/S
U/N S/S
S/S U/N
U/N S/S
(c) (d)
U/N S/S
U/N
S/S
north; south; side; stronger
B. 2 utara; selatan; sisi; lebih kuat
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 80
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 80 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 160
C. Elektromagnet / Electromagnet Textbook page 160 Ekstra / Extra
1 Elektromagnet merupakan medan magnet yang dihasilkan oleh konduktor yang dikenakan
arus dan hanya bersifat sementara.
An electromagnet is a field of magnetic that produced by the conductor with flowing
current and it is temporary.
2 Apabila arus terhenti, medan magnet juga hilang. / When the current is stopped, magnetic field also stopped.
3 Arah medan magnet disongsangkan apabila arus elektrik disongsangkan.
The direction of the magnetic field is reversed when the direction of the current is reversed.
4 Arah medan magnet boleh ditentukan dengan menggunakan petua genggaman tangan kanan seperti dalam
rajah di bawah. / The direction of the magnetic field can be determined by using the right-hand grip rule as in
the following diagram.
I (arus)
I (arus)
I (current)
I (current)
(a) Ibu jari tangan kanan menunjukkan arah arus.
The thumb of the right hand shows the direction of current.
(b) Jari-jari lain menunjukkan arah medan magnet apabila
dipandang dari atas.
Other fingers show the direction of the magnetic field when
Tangan kanan seeing from above.
Medan magnet
Magnetic field Right hand
5 Contoh corak medan magnet yang disebabkan oleh: / Example of the pattern of the magnetic field due to: TP3
(a) Arus dalam wayar lurus Penyelesaian
Current in a straight wire Solution
(b) Arus dalam gegelung tunggal Penyelesaian
Current in a single coil Solution
Projek / Project
Arahan / Instructions:
Secara berkumpulan, cari maklumat mengenai aplikasi elektromagnet dari sebarang sumber dan persembahkan
dalam bentuk slaid kepada rakan sekelas.
In group, find information about application of electromagnet from any source and present it in slide show to
the classmates. TP6
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
81 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 81 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu simbol komponen 3 Dalam elektroskop, apabila satu rod asetat yang
elektrik. bercas positif didekatkan pada ceper logam,
Diagram 1 shows a symbol of an electric component. kerajang emas akan / In an electroscope, when a
positively charged acetate rod is brought near to
the metal cap, the gold leaf will
A kekal pada kedudukan yang sama.
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1 remain in the same position.
B mencapah dengan lebih banyak.
Namakan komponen elektrik yang ditunjukkan.
diverges more.
Name the electrical component shown.
C bergerak ke arah plat logam.
A Suis
moves towards the metal plate.
Switch
D bergetar sebelum merapat ke plat logam.
B Transformer
vibrates before getting closer to the metal plate.
Transformer
C Reostat
4 Rajah 3 menunjukkan kedudukan tiga kompas R, S
Rheostat
dan T. / Diagram 3 shows three compasses R, S and T.
D Fius
Fuse S
2 Rajah 2 menunjukkan sebuah litar selari. T R
Diagram 2 shows a parallel circuit.
4V
Rajah 3 / Diagram 3
P=3 Ω
Antara berikut, yang manakah menunjukkan arah
Q=6 Ω
jarum kompas yang betul? / Which of the following
shows the correct direction of the compass needle?
7 V
Rajah 2 / Diagram 2 R S T
Kira nilai arus yang mengalir bagi setiap perintang. A
Calculate the value of resistance for each resistance.
B
A P & Q = 0.4 A
B P & Q = 2.0 A C
C P = 0.25 A, Q = 0.25 A
D
D P =1.33 A, Q = 0.67 A
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan dua jenis litar, J dan K. / Diagram 1 shows two types of circuits, J and K.
J K 3
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
(a) Jika salah satu mentol dalam litar telah rosak, litar yang manakah akan berfungsi? Sila tandakan (✓) pada
kotak yang betul. / If one of the bulbs in the circuit is malfunctioned, which of the circuit will still be
functioning? Please tick (✓) in the box correctly. [1 markah/mark]
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 82
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 82 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(b) Jika dua sel kering 1.5 V digunakan dalam litar J, apakah rintangan bagi setiap mentol jika arus yang
direkodkan oleh ammeter ialah 0.5 A? / If two 1.5 V dry cells are used in circuit J, what is the resistance for
each bulb if the current recorded by the ammeter is 0.5 A?
V = IR
V 2 × 1.5 V
R= = =6Ω
I 0.5 A
Rintangan 2 mentol / Resistance 2 bulbs = 6 Ω
Rintangan 1 mentol / Resistance 1 bulb = 6 Ω = 3 Ω
2
[3 markah/marks]
(c) Berikan dua kelebihan jenis litar K. / Give two advantages of circuit K.
– Jika satu mentol terbakar, satu mentol lagi masih menyala.
If one bulb burns out, another bulb still lights up.
– Setiap mentol menerima voltan penuh daripada sumber dan kecerahan yang sama.
Each bulb receives full voltage from the source and have the same brightness.
[2 markah/marks]
2 Rajah 2 menunjukkan sebatang paku besi dililitkan dengan wayar yang disambungkan kepada sebiji bateri.
Diagram 2 shows an iron nail coiled with wire and connected to a battery.
Paku besi
Iron nail
Wayar
Wire
Bateri – +
Battery
Rajah 2 / Diagram 2
(a) Apakah yang terhasil dalam eksperimen ini? / What is produced in this experiment?
7
Elektromagnet / Electromagnet
[1 markah/mark]
(b) Cadangkan dua cara yang boleh menambahkan kekuatan produk di (a).
Suggest two methods that can increase the strength of the product in (a).
– Menambah lilitan wayar. / Increase the number of coils of the wire.
– Menambah bilangan bateri. / Increase the number of batteries.
[2 markah/marks]
(c) Berikan satu contoh mesin yang menggunakan prinsip eksperimen ini.
Give one example of machine that uses the principle of this experiment.
Kren / Crane
[1 markah/mark]
Ekstra / Extra
83 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab7 Book A_F.indd 83 25/10/2021 1:09 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Daya dan Gerakan
8 Force and Motion
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
8.1 Daya
Force
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
8.1.1 Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai daya. / Describe and communicate about force.
Menerangkan daya mempunyai magnitud, arah dan titik aplikasi.
8.1.2
SP Explain that force has magnitude, direction and point of application.
LS 8.1.3 Mengukur daya dalam unit S.I. / Measure force in S.I. unit.
Menjelaskan dengan contoh setiap daya tindakan terdapat daya tindak balas yang sama magnitud tetapi bertentangan arah.
8.1.4
Explain with examples that every action force has an equal (same magnitude) reaction force but in the opposite direction.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Jujur dan tepat dalam merekod dan mengesahkan data
Moral Value Honest and accurate in recording and verifying data
Buku teks muka surat 168
A. Daya / Force Textbook page 168
1 Daya merupakan tolakan dan tarikan ke atas suatu objek.
Force is push and pull on an object. TP1
2 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah.
Complete the table below. TP2
Jenis daya Penerangan Contoh
Types of force Explanation Example
(a) Daya graviti Daya yang mengarah ke pusat Bumi. Daya ini menyebabkan
Gravitational jatuh
8 force
sesuatu objek ke Bumi.
Force that directed to the centre of the Earth. This force causes
the object falls to the Earth.
(b) Berat Daya graviti yang bertindak ke atas sesuatu objek.
Weight Daya ditunjuk oleh penimbang adalah magnitud daya tindak
balas.
The gravitational force that acts on an object.
The force appointed by the scales is the magnitude of the
reaction force.
(c) Daya geseran Daya yang menentang gerakan dan bertindak pada Gerakan
Movement
Frictional force dua permukaan yang bersentuhan.
The force that against the movement and acts on
two surfaces that in contact.
Daya geseran
Frictional force
(c) menentang / against (b) graviti / gravitational A. 2 (a) jatuh / falls
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 84
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 84 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Jenis daya Penerangan Contoh
Types of force Explanation Example
(d) Daya elastik Daya apabila suatu bahan diregangkan atau
Elastic force
dimampatkan .
Force when a material is stretched or
compressed .
(e) Daya apungan Daya tujah yang bertindak pada suatu objek Daya apungan
Buoyant force
Buoyant force yang terapung di dalam sesuatu bendalir.
Thrust force that acts on an object that floats on
the surface of fluid.
(f) Daya normal Daya sokongan apabila ia bersentuhan dengan sesuatu Normal
Normal force objek. Normal
Supporting force when it is in touch with an
object.
B. Daya Mempunyai Magnitud, Arah dan Titik Aplikasi Buku teks muka surat 171
Forces have Magnitude, Direction and Point of Application Textbook page 171
1 Magnitud daya ialah kuantiti daya
yang dikenakan ke atas objek. Contohnya, jika kita mampu
melonjak ke atas dengan magnitud daya yang besar, bermakna kita melompat dengan lebih tinggi .
Magnitude is the quantity of
force
which applied to the object. For example, if we are able to
jump with bigger magnitude, means that we are jumping higher . TP1
2 Arah daya ialah arah di mana daya dikenakan ke atas objek. 8
The direction of force is where force is applied on the object. TP1
3 Titik aplikasi daya adalah pada bahagian daya yang dikenakan tertumpu.
The point of application of force is at the part of the applied force were focused. TP1
4 Labelkan jenis daya yang terlibat dan tandakan ‘•’ untuk titik aplikasi daya dalam rajah di bawah.
Label the type of force and mark ‘•’ for the point of application of force in the diagram below. TP3
Daya tolakan
Pushing force
4 Daya tolakan / Pushing force (f) bersentuhan / touch stretched; compressed
B. 1 daya; lebih tinggi / force; higher (e) tujah / Thrust A. 2 (d) diregangkan; dimampatkan
85 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 85 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
C. Pasangan Daya Tindakan-Daya Tindak Balas Buku teks muka surat 173
Action-Reaction Pair Textbook page 173
Setiap daya tindakan terdapat daya tindak balas yang sama magnitud
Hukum Newton Ketiga bertentangan
Newton’s Third Law tetapi arah. / Every action force has reaction force with the
same magnitude but in opposite direction. TP1
Daya tindakan Daya tindak balas
(a) (b) (c)
Daya normal Action force Reaction force
(Daya tindak
balas) Daya apungan
Normal force Buoyant force
(Reaction
force)
Spring dimampatkan
Spring is compressed
Berat Daya tindakan Daya tindak balas
(Daya Action force Reaction force
tindakan)
Weight
(Action Berat
force) Weight
Situasi 1 – Jasad yang kekal di atas Situasi 2 – Jasad yang terapung Situasi 3 – Dua troli yang
meja di air bersentuhan dilepaskan
Situation 1 – A body fix on a table Situation 2 – A body floats on water menggunakan mekanisme
spring akan bergerak pada arah
Magnitud berat (daya tindakan) Magnitud berat (daya tindakan) bertentangan dengan jarak yang
= daya normal (daya tindak balas) = daya apungan (daya tindak sama
Weight (action force) balas)
= normal force (reaction force) Weight (action force) Situation 3 – Two trolleys in
= buoyant force (reaction force) contact, when released using the
spring mechanism, will move in
the opposite direction of the
8 same distance
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
(c) sama / same = normal force (reaction force)
= buoyant force (reaction force) Weight (action force)
Weight (action force) = daya normal (daya tindak balas)
= daya apungan (daya tindak balas) (a) Magnitud berat (daya tindakan)
(b) Magnitud berat (daya tindakan) C. magnitud; bertentangan / magnitude; opposite
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 86
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 86 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
8.2 Kesan Daya
Effects of Force
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
8.2.1 Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai kesan tindakan daya. / Describe and communicate the effects of force.
Menerangkan dan berkomunikasi mengenai perkaitan antara perbezaan ketumpatan dengan kesan keapungan dalam kehidupan harian.
8.2.2
SP Explain and communicate the relationship between the differences in density and the effects of buoyancy in daily life.
LS Mengelas dan menyelesaikan masalah tuas berdasarkan kedudukan fulkrum, beban dan daya.
8.2.3
Classify and solve problems involving levers based on the position of fulcrum, load and effort.
8.2.4 Menerangkan dan berkomunikasi mengenai momen daya. / Explain and communicate about moment of force.
Menjalankan eksperimen dan berkomunikasi mengenai tekanan serta aplikasinya dalam kehidupan harian.
8.2.5
Carry out experiment and communicate about pressure and its application in daily life.
Menghuraikan dan berkomunikasi mengenai tekanan gas dengan merujuk kepada teori kinetik gas.
8.2.6
Carry out experiment and communicate about pressure based on the kinetic theory of gas.
Menerangkan dan berkomunikasi mengenai kewujudan tekanan atmosfera dan kesan altitud kepada tekanan atmosfera.
8.2.7
Explain and communicate the existence of atmospheric pressure and the effects of altitude on atmospheric pressure.
8.2.8 Menerangkan kesan kedalaman terhadap tekanan cecair. / Explain the effects of depth on liquid pressure.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Jujur dan tepat dalam merekod dan mengesahkan data
Moral Value Honest and accurate in recording and verifying data
Isikan tempat kosong dengan jawapan yang sesuai untuk menunjukkan bagaimana kapal kargo mengekalkan
keapungannya.
Fill in the blanks with suitable answers to show how the cargo ship maintains its buoyancy. TP3
(i) Isi padu air yang disesarkan oleh kapal kargo adalah besar kerana isi padu
kapal yang besar. / Volume of water displaced by cargo ship is large because the
volume of the ship is higher.
(ii) Daya tujah ke atas (iii) Isi padu air yang
kapal kargo yang besar disesarkan
membolehkan kapal kargo
= daya tujah ke atas
terapung . Volume of water
The higher upthrust force displaced
of cargo ship enable it to
float = upthrust force 8
.
1 Setiap kapal ditandakan dengan garisan Plimsoll pada badannya yang menandakan paras timbul
kapal dalam air. / Every ship is marked with Plimsoll line at its body which shows the float level of
the ship in the water. TP3
2 Paras di garisan Plimsoll dipengaruhi oleh suhu dan ketumpatan air.
Level of Plimsoll line is affected by temperature and density of water.
3 Sesebuah kapal yang berada di air tidak boleh melebihi garian Plimsoll ini bagi memastikan kapal
tersebut mempunyai keapungan yang mencukupi untuk terapung.
A ship on the water cannot exceed the Plimsoll line to ensure the ship has enough buoyancy
to stay float.
melebihi / exceed 3 1 timbul / float (ii) terapung / float
suhu / temperature 2 (iii) daya tujah ke atas / upthrust force (i) besar; isi padu / large; volume
87 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 87 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 181
A. Tuas / Lever Textbook page 181
1 Lengkapkan peta pokok di bawah tentang tuas.
Complete the tree map below about lever. TP1 TP2
(a) Tuas / Lever
Sebatang rod yang boleh berputar secara bebas pada satu titik yang dikenali sebagai fulkrum apabila
daya dikenakan untuk mengatasi beban .
A rod which can turn about a fixed point called the fulcrum when a force called effort is applied
to overcome a resisting load .
Daya : Tolakan atau tarikan yang
(b) Kepentingan tuas / Importance of lever
dikenakan pada palang
• Membolehkan kita melakukan kerja dengan cepat dan mudah. Effort : Pushing or pulling applied on
the bar
Allows us to do work fast and easily. Beban : Objek yang hendak digerakkan
• Hanya menggunakan daya yang kecil untuk melakukan kerja. Load : Object to be moved
Fulkrum : Titik sokongan tetap
Only use minimal force to do work. Fulcrum : Fixed support point
(c) Tuas kelas pertama (d) Tuas kelas kedua (e) Tuas kelas ketiga
First class lever Second class lever Third class lever
Daya Daya Daya
Effort Effort Effort
8
Fulkrum Beban Fulkrum Beban Fulkrum Beban
Fulcrum Load Fulcrum Load Fulcrum Load
Fulkrum berada di tengah Beban berada di tengah Daya berada di tengah
antara beban dan daya antara fulkrum dan daya antara fulkrum dan beban
Fulcrum Load Effort
is in the middle is in the middle is in the middle
of load and effort of fulcrum and effort of fulcrum and load
Contoh / Example Contoh / Example Contoh / Example
• Gunting / Scissors • Pemecah kekeras / Nutcracker • Joran / Fishing rod
• Pembuka tin / Can opener • Kereta sorong / Wheelbarrow • Forseps / Forceps
and easily.
(e) Daya / Effort cepat dan mudah. / Allows us to do work fast Only use minimal force to do work.
(d) Beban / Load (b) • Membolehkan kita melakukan kerja dengan melakukan kerja.
(c) Fulkrum / Fulcrum A. 1 (a) fulkrum; daya; beban / fulcrum; effort; load • Hanya menggunakan daya yang kecil untuk
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 88
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 88 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Kelaskan alatan berikut berdasarkan kelas tuas dan tandakan kedudukan fulkrum = F, beban = B dan daya = E
pada setiap alat tersebut.
Classify the following tools according the the class of lever and mark the position of fulcrum = F, load = B and
effort = E at each tools. TP2
(a) (b) (c) E
F E
E
F
F B
B B
Tuas kelas ketiga Tuas kelas pertama Tuas kelas pertama
Third class lever First class lever First class lever
(d) E (e) (f) B
F
E
B B F
Tuas kelas kedua Tuas kelas ketiga Tuas kelas kedua
Second class lever Third class lever Second class lever
B. Momen Daya Buku teks muka surat 183
The Moment of Force Textbook page 183
1 Momen daya Sepana Daya
Moment of force Spanner Force
8
Nat
Nut
Jarak tegak
Perpendicular distance
(a) Apabila daya dikenakan pada sesuatu objek, objek berputar pada satu titik pangsi atau fulkrum
dan dikenali sebagai momen daya .
When a force is applied to an object, the object rotates at one pivot or fulcrum point and
known as moment of force . TP1
(b) Momen daya (N m) = Daya (N) × Jarak tegak dari fulkrum (pangsi) ke daya (m)
Moment of force (N m) = Force (N) × Perpendicular distance from the fulcrum (pivot) to the
force (m)
(d) Tuas kelas kedua / Second class lever (F, B, E)
(b) Daya (N) / Force (N) (f) Tuas kelas kedua / Second class lever (E, B, F) (c) Tuas kelas pertama / First class lever (E, F, B)
B. 1 (a) berputar; momen daya / rotates; moment of force (e) Tuas kelas ketiga / Third class lever (F, E, B) A. 2 (b) Tuas kelas pertama / First class lever (B, F, E)
89 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 89 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Prinsip momen menyatakan apabila tuas berada dalam keseimbangan, kedua-dua momen adalah sama .
Principle of moments said when lever is balanced, the two moments are equal . TP1
Jarak daya / Effort distance Jarak beban / Load distance L
E
F
Rumus / Formula
Daya (N) × Jarak Daya (m) = Beban (N) × Jarak Beban (m)
Effort (N) × Effort Distance (m) = Load (N) × Load Distance (m)
(a) Rajah menunjukkan daya sebanyak 5 N dikenakan ke atas pemutar skru
untuk membuka penutup tin. Apakah beban bagi pemutar skru tersebut?
The diagram shows a force of 5 N applied to a screwdriver handle to 5N
open a can lid. What is the load of the screwdriver? 28 cm
2 cm
Beban × Jarak Beban = Daya × Jarak Daya
Beban × 0.02 = 5 × 0.28
Beban = 70 N
Load × Load distance = Effort × Effort distance
Load × 0.02 = 5 × 0.28
Load = 70 N
(b) Tentukan daya yang diperlukan untuk menolak beban di dalam kereta
8 sorong tersebut. 45 kg
Determine the effort needed to push the load inside the wheelbarrow.
Daya × Jarak Daya = Beban × Jarak Beban
Daya × 2 = 450 × 0.5
Daya = 112.5 N
Effort × Effort Distance = Load × Load Distance
Effort × 2 = 450 × 0.5 1.5 m 0.5 m
Effort = 112.5 N
Jarak beban / Load distance
(b) Daya / Effort = 112.5 N Jarak daya / Effort distance
(a) Beban / Load = 70 N B. 2 sama / equal
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 90
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 90 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 187
C. Tekanan / Pressure Textbook page 187
Daya / Force (N) Tekanan ialah daya per unit
Tekanan / Pressure =
Luas permukaan / Surface area (m2) luas permukaan
F (N) Pressure is force applied
P = over a unit surface area
A (m2)
Unit S.I tekanan ialah newton per meter persegi (N m–2) atau pascal (Pa)
S.I unit of pressure is newton per square metre (N m–2) or pascal (Pa)
Sesetengah alat mempunyai luas permukaan yang kecil untuk menghasilkan tekanan yang besar manakala sesetengah
alat mempunyai luas permukaan yang besar untuk menghasilkan tekanan yang kecil dalam prinsip operasinya. Isikan
tempat kosong bagi aplikasi tekanan dalam kehidupan harian. / Some of the tools have small surface area to produce
higher pressure whereas some of the tools have large surface area to produce smaller pressure in its principle of
operation. Fill in the blanks according the application of pressure in daily life. TP2
(a) Mata pisau mempunyai luas permukaan yang sangat kecil untuk
menghasilkan tekanan yang sangat tinggi bagi membolehkan pisau
memotong bahan dengan mudah.
The knife edges has a very small surface area to produce very
high pressure to allow the knife to cut the material easily.
(b) Paku tekan dapat dibenam dengan lebih mudah berbanding skru kerana
hujungnya mempunyai luas permukaan yang kecil. Maka tekanan yang besar
dapat dihasilkan.
Thumbtack can be embedded more easily than screws because the ends have a
small surface area. So great pressure can be generated.
8
(c) Papan luncur salji diperbuat daripada satu papan yang lebar
bagi menghasilkan tekanan yang rendah pada permukaan untuk membolehkan
pergerakan menjadi laju .
The snowboard is made of a wide board to produce low pressure
on the surface to allow the movement to be fast .
(d) tanah lumpur
Traktor dapat bergerak dengan mudah di atas kerana
tayarnya mempunyai luas permukaan yang besar. Tekanan yang rendah
terhasil menyebabkan tayar tidak mudah tenggelam . / The tractor
can move easily on muddy ground because the tire has a large surface
area. The low pressure produced causes the tire not easily
sink .
muddy ground; low; sink surface area; high, cut
(d) tanah lumpur; rendah; tenggelam (c) lebar; laju / wide; fast C. (a) luas permukaan; tinggi, memotong
91 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 91 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 190
D. Tekanan Gas / Gas Pressure Textbook page 190
Isikan tempat kosong tentang teori kinetik gas bagi tekanan udara.
Fill in the blank on kinetic theory of gases for air pressure. TP2
bebas
(a) Zarah gas sentiasa bergerak (b) Kadar perlanggaran antara zarah
dan berlanggar dengan dinding dengan dinding tinggi, tekanan udara
menghasilkan tekanan udara . tinggi
yang terhasil adalah .
Gas particles are always moving Frequency of collision between
freely and colliding with the the gas particles and the wall is high,
air pressure the air pressure is high .
wall produce .
Tekanan udara meningkat apabila isi padu Tekanan udara meningkat apabila suhu gas
bekas berkurang. meningkat.
Air pressure increases when the volume of Air pressure increases as temperature of the
the container decreases. gas increases.
(c) Apabila isi padu berkurang, zarah-zarah gas (d)
Apabila suhu meningkat, zarah-zarah gas
bergerak dalam ruangan yang kecil menyebabkan mendapat lebih tenaga kinetik. Zarah-zarah gas
zarah-zarah berlanggar dengan dinding lebih berlanggar dengan dinding lebih kerap dengan
kerap dan menghasilkan tekanan udara yang daya tinggi dan tekanan udara yang terhasil
tinggi. tinggi.
As the volume decreases, the air particles move As the temperature increases, the air particles
in a smaller space cause the particles collide have more kinetic energy. The particles collide
more frequently with the walls and produce high the wall of the container more frequently with
air pressure. greater force and air pressure produced is higher.
E. Aplikasi Konsep Tekanan Udara dalam Kehidupan Harian dan Kesan Altitud
Buku teks muka surat 194
kepada Tekanan Atmosfera / Application of the Concept of Air Pressure in Daily
8 Life and Effect of Altitude to Atmospheric Pressure
Textbook page 194
1 Isikan tempat kosong. / Fill in the blanks. TP3
(a) Hemisfera Magdeburg
Magdeburg hemisphere Kedua-dua hemisfera tidak dapat dipisahkan walaupun daya yang
tinggi dikenakan apabila udara di dalam hemisfera dipam keluar
Tekanan atmosfera
Atmospheric pressure dan menjadi vakum. Tekanan atmosfera yang sangat tinggi menolak
hemisfera kerana tekanan udara di dalamnya sangat rendah.
Both of Magdeburg hemisphere cannot be separated although
Vakum higher force is exerted when the air in the hemisphere is pump out
Vacuum
and becomes vacuum. The higher atmospheric pressure pushes the
hemisphere because the air pressure inside it is very low.
Tekanan atmosfera
Atmospheric pressure
Kedap udara
Airtight seal
(b) Kadar perlanggaran; tinggi / Frequency of collision; high D. (a) bebas;tekanan udara / freely; air pressure
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 92
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 92 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(b) Pam sedut / Plunger
Pam Tolak ke bawah
sedut Push downwards
Plunger Udara / Air
Apabila pam ditekan ke bawah udara dipaksa keluar
dan tekanan udara rendah terhasil. Tekanan yang lebih
Air Lubang singki
Water
tinggi dalam saluran paip menolak kotoran keluar
Sink
Sumbatan
apabila pam ditarik .
Blockage
Air is forced out when the plunger is pushed downward
Tarik ke atas
Pull upwards
and low air pressure produced. The higher air
pressure inside the pipe push the dirt out when the plunger is
pulled .
Air Sumbatan
Water Blockage
Tekanan udara luaran
External air pressure
(c) Penyedut minuman / Drinking straw
Apabila penyedut minuman disedut, udara di dalam penyedut
Disedut / Sucked minuman berkurang dan tekanan yang rendah terhasil.
Tekanan Air dapat ditolak masuk ke dalam penyedut minuman kerana
rendah
Tekanan Lower tekanan atmosfera yang tinggi.
atmosfera pressure
When the straw is sucked, the air inside the straw decreases and
Atmospheric
pressure low air pressure is produced. The water is pushed inside
the straw because of the high atmospheric pressure .
(d) Sifon / Siphon
Hujung salur getah yang disedut sedikit menyebabkan
Tekanan atmosfera tekanan udara yang rendah terhasil dalam salur getah. Tekanan
menolak
8
Atmospheric pressure
atmosfera yang tinggi air masuk ke dalam salur
getah.
The end of rubber tube which is slightly sucked causes low
air pressure inside the rubber tube. The higher air pressure
pushes the water into the rubber tube.
(e) Picagari / Syringe
Omboh Apabila omboh ditarik ke atas, kawasan bertekanan
Piston rendah terbentuk dalam picagari. Tekanan atmosfera
Silinder
yang lebih tinggi menolak air masuk ke dalam picagari.
Cylinder
When the piston is pulled, the low air pressure is
Tekanan
atmosfera higher
Atmospheric produced in the syringe. The atmospheric pressure
pressure Cecair pushes the water inside the syringe.
Liquid
(e) rendah; tinggi / low; higher low; straw; atmospheric pressure pushed; low air pressure; higer; pulled
(d) disedut; menolak / sucked; pushes (c) rendah; penyedut minuman; tekanan atmosfera E. (b)
ditekan; tekanan udara rendah; tinggi; ditarik
93 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 93 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(f) Pembersih vakum / Vacuum cleaner berputar
Kipas elektrik yang menyedut
udara dalam satu bukaan. Tekanan udara dalam hos
Kipas Tekanan rendah
Fan Low pressure Rod pemegang menjadi rendah . Tekanan atmosfera yang
Hos Holding rod
Hose lebih tinggi menolak kotoran ke dalam hos dan
dikumpul dalam beg kotoran.
Habuk
Dust The electrical fan that is rotating sucked the
air through an opening. The air pressure into the hose
becomes low . The higher atmospheric
Udara
Air pressure push the dirt into the hose and collect it in
Tekanan atmosfera tinggi
High atmospheric pressure the dirt bag.
2 Tekanan atmosfera menurun apabila altitud meningkat disebabkan oleh tarikan graviti .
Atmospheric pressure decreases as altitude increases due to gravitational attraction . TP2
3 Semakin dekat ke permukaan Bumi, molekul udara ditarik bersama oleh tarikan graviti menyebabkan
kenaikan tekanan. / As closer to the surface of the Earth, air molecules are pulled together by
gravitational attraction causing the pressure to rise. TP2
Ekstra / Extra
4 Pada ketinggian yang lebih tinggi, molekul udara kurang terjejas. Udara menjadi kurang berat
dan berkembang dengan mudah. Tekanan atmosfera adalah rendah .
At higher altitude, air molecules are less affected. Air becomes less heavy and expands easily.
Atmospheric pressure is low . TP2
5 Isi tempat kosong tentang aplikasi kedalaman terhadap tekanan cecair dalam kehidupan harian.
Fill in the blanks about the depth on liquid pressure in daily life. TP3
(a) tebal
Kapal selam dibina dengan dinding yang supaya
dapat menahan tekanan air laut yang tinggi sewaktu berada
di dalam air.
The submarine is built with thicker wall to withstand the
8 high pressure of sea water during in the ocean.
Tekanan rendah
(b) Low pressure
Empangan
Dam
Air Empangan menyimpan air pada aras kedalaman yang tinggi.
Water
Dinding Tembok empangan haruslah lebih tebal di bahagian bawah bagi
tebal
Thick wall menahan tekanan yang lebih tinggi berbanding di bahagian atas.
The dam holds water at high depth level. The dam wall
Sungai
River should be thicker at the bottom to withstand higher pressure
than at the top.
Tekanan tinggi
High pressure
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
(b) menyimpan; lebih tebal / holds; thicker rendah / low 4 2 tarikan graviti / gravitational attraction
5 (a)
tebal; tinggi / thicker; high dekat / closer 3 1 (f) berputar; rendah / rotating; low
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 94
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 94 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Antara berikut, yang manakah tindakan yang 3 Rajah 2 menunjukkan Aminah sedang menguli
melibatkan daya tolakan? adunan kuih.
Which of the following action involves pushing Diagram 2 shows, Aminah is kneading the dough.
force? Yis / Yeast
A Membuka buku
Opening the book Gula Air suam
B Menanggalkan paku dengan tukul Sugar Warm water
Removing a nail using a hammer Tepung
C Mengepam tayar basikal dengan pam Flour
Pump a bicycle tire with a pump
D Mengukur berat dengan neraca spring
Measuring weight with a spring balance
2 Rajah 1 menunjukkan corak bunga pada sebiji tayar. Rajah 2 / Diagram 2
Diagram 1 shows the tread pattern on a tyre. Apakah kesan daya yang dikenakan dalam situasi
itu? / What is the effect of the force excreted in the
situation?
A Bentuk doh berubah
The shape of the dough changes
B Jisim doh berubah
The mass of the dough changes
C Kekenyalan doh berubah
The elasticity of the dough changes
D Berat doh menurun
The weight of the dough decreases
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
Apakah fungsi corak bunga pada tayar? 4 Satu bongkah kayu ditarik menggunakan tali melalui
What is the function of tread pattern on tyre? empat jenis permukaan yang berlainan. Permukaan
A Untuk mencantikkan tayar. manakah yang akan menghasilkan geseran yang
To beautify tyre. paling sedikit? / A block of wood is pulled using a
B Untuk menambahkan kelajuan.
To increase speed.
rope across four different types of surfaces. Which 8
surface will produce the least friction?
C Untuk menambahkan geseran. A Simen kasar / Rough cement
To increase friction. B Tar / Tar
D Untuk mengurangkan geseran. C Kertas pasir / Sandpaper
To reduce friction. D Ais / Ice
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
1 Berdasarkan rajah di bawah, tandakan (✓) bagi keadaan yang menunjukkan ciri daya yang sama.
Based on the diagram below, tick (✓) for the situation which shows the same characteristic of force.
[1 markah/mark]
95 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 95 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 (a) Rajah 2(a) menunjukkan seorang lelaki sedang memanjat pokok.
Diagram 2(a) shows a boy climbing a tree.
Rajah 2(a) / Diagram 2(a)
(i) Nyatakan dua faktor yang mempengaruhi magnitud daya berdasarkan Rajah 2(a).
State two factors that affect the magnitude of the force based on Diagram 2(a).
– Graviti / Gravity
– Permukaan bersentuhan / Surface in contact
[2 markah/marks]
(ii) Nyatakan dua kegunaan daya yang ditunjukkan pada Rajah 2(a) dalam kehidupan harian kita.
State two uses of the forces as shown in the Diagram 2(a) in our daily life.
– Menyalakan mancis / Light up matches
– Membolehkan kita berjalan / Allow us to walk
[2 markah/marks]
(b) Rajah 2(b) menunjukkan dua tayar kereta dengan corak yang berbeza.
Diagram 2(b) shows two car tyres with different patterns.
Corak A Corak B
Pattern A Pattern B
Rajah 2(b) / Diagram 2(b)
(i) Tayar kereta yang manakah lebih selamat untuk digunakan pada hari hujan?
Which car tyre is safer to be used on rainy day?
Tayar corak B / Pattern B tyre
[1 markah/mark]
(ii) Senaraikan satu kebaikan menggunakan tayar yang mempunyai bunga yang tebal.
List one advantage of using tyres with thick tread.
Daya geseran lebih besar / Larger frictional force
[1 markah/mark]
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 96
Modul Sains T2-Bab8 Book A_F.indd 96 25/10/2021 12:45 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Haba
9 Heat
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
9.1 Hubung Kait Suhu dengan Haba
Relationship between Temperature and Heat
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
SP Membanding beza antara haba dengan suhu.
9.1.1
LS Make a comparison between heat and temperature.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam.
Moral Value Realising that science is one way to understand nature.
A. Haba dan Suhu Buku teks muka surat 206
Heat and Temperature Textbook page 206
1 Perbezaan antara suhu dan haba adalah seperti berikut:
The differences of temperature and heat is as follows: TP2
Haba / Heat Suhu / Temperature
(a) Suatu bentuk tenaga yang Tahap kepanasan atau kesejukan
menyebabkan suatu objek menjadi
suatu objek
panas degree of hotness or coldness
energy The of
A form of that causes
an object
an object to become hot
Unit SI ialah Kelvin (K) atau darjah
(b) Unit SI ialah joule (J)
joule (J)
Celsius (°C) 9
SI unit is Kelvin (K)
SI unit is or degree
Celsius (°C)
(c) Bergerak dari kawasan panas
ke kawasan sejuk Meningkat dengan peningkatan pergerakan
Moves from a hot zarah-zarah
region to a cold region Increases with the increase of the
movement of particles
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
energy; degree of hotness or coldness
(c) panas; panas; pergerakan / hot; cold; movement (b) joule (J); Kelvin (K) / joule (J); Kelvin (K) A. 1 (a) tenaga; Tahap kepanasan atau kesejukan
97 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 97 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
9.2 Pengaliran Haba dan Keseimbangan Haba
Heat Flow and Thermal Equilibrium
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
9.1.1 Menerangkan haba mengalir dari kawasan panas ke kawasan sejuk. / Explain how heat flows from a hot region to a cold region.
Menerangkan dan berkomunikasi mengenai pengaliran haba dalam fenomena alam.
SP 9.2.2
Explain and communicate about heat flow in natural phenomena.
LS
Berkomunikasi mengenai konduktor haba dan penebat haba serta kegunaan konduktor dan penebat haba dalam kehidupan harian.
9.2.3
Communicate about heat conductors and heat insulators and their uses in daily life.
EMK Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu) / Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam
Moral Value Realising that science is one way to understand nature.
A. Pengaliran Haba secara Konduksi, Perolakan dan Sinaran Buku teks muka surat 207
Heat Flow via Conduction, Convection and Radiotion Textbook page 207
Lengkapkan jadual di bawah untuk menunjukkan perbandingan pemindahan haba secara konduksi, perolakan dan
sinaran. / Complete the table below to show comparison of heat transfer by conduction, convection and radiation. TP2
Konduksi
Perolakan Conduction
Convection
Sinaran
Radiation
Persamaan / Similarities
Pemindahan haba dari kawasan panas ke kawasan sejuk
Transfers of heat from hot region to cold region
Perbezaan / Differences
Keadaan (a) Konduksi (b) Perolakan (c) Sinaran
Condition Conduction Convection Radiation
(a) Medium Melalui pepejal Melalui bendalir (cecair atau gas) Berlaku dalam
Medium (konduktor) fluid vakum .
solid Through (liquid or gas)
Through Occur in
(conductor) vacuum .
9 (b) Pergerakan Zarah bergetar Zarah-zarah yang menerima haba bergerak Haba bergerak
zarah apabila menerima haba dan ke atas kerana ia kurang tumpat dari satu sumber
Movement memindahkan getaran dan zarah yang lebih tumpat akan turun ke haba.
Heat moves from
bawah membentuk arus perolakan
of particles pada zarah bersebelahan. .
a source of heat.
The particles vibrate The particles which receive heat move
when receive heat and upward because it is less dense
transfer the vibration and more dense particles move
that are next to them. downward to form convection current .
(c) Kelajuan Tinggi Perlahan Sangat tinggi
Speed High Slow dalam kelajuan
cahaya .
Very high in speed
of light .
(iii) (a) Tinggi / High vibrate; transfer (b) bendalir / fluid
(c) cahaya / light upward; convection current (ii) (a) bergetar; memindahkan (i) (a) pepejal / solid
(b) Perlahan / Slow (b) ke atas; arus perolakan (c) vakum / vacuum A. panas; sejuk / hot; cold
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 98
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 98 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B. Pengaliran Haba dalam Fenomena Alam Buku teks muka surat 209
Heat Flow in Natural Phenomena Textbook page 209
Lengkapkan tempat kosong di bawah tentang kejadian bayu laut, bayu darat dan pemanasan Bumi oleh Matahari.
Complete the following blanks according to sea breeze, land breeze phenomenon and Earth warming by
the Sun. TP3
Fenomena / Phenomenon Penerangan / Explanation
(a) Bayu laut / Sea breeze Pada waktu siang, kawasan daratan menjadi lebih panas
berbanding lautan kerana pasir di pantai lebih cepat menyerap haba dari
sinaran Matahari. Suhu udara di permukaan daratan lebih tinggi
daripada suhu permukaan lautan. Udara panas di daratan yang
kurang tumpat naik ke atas dan bergerak ke laut
Udara manakala udara sejuk yang lebih tumpat bergerak ke bawah
Udara sejuk panas
bergerak ke naik iaitu ke daratan secara perolakan sebagai bayu laut.
Bayu laut
bawah Hot air hotter
Sea breeze
Cold air moves rises During the day, the land area becomes than
downwards
the sea because the sand at beach absorbs heat from the Sun ray.
Laut / Sea Daratan
The temperature of the air at land surface is higher
Land
than the temperature at the sea surface. Hot air at the land which is
less dense rises upwards and moves to the sea
whereas cold air which is denser move downwards to land
by convection as sea breeze.
(b) Bayu darat / Land breeze Pada waktu malam, kawasan daratan menjadi lebih cepat sejuk
berbanding lautan. Suhu udara di permukaan daratan lebih rendah
Udara sejuk
bergerak ke
daripada suhu di permukaan lautan. Udara panas dari permukaan laut
bawah yang kurang tumpat naik ke atas dan bergerak ke daratan manakala
Cold air moves udara sejuk dari daratan yang lebih tumpat turun ke bawah dan
downwards
Udara
bergerak ke laut secara perolakan sebagai bayu darat.
panas naik Bayu darat At night, the land area becomes colder than the sea. The air
Hot air Land breeze
rises
temperature on the land surface is lower than the temperature at the
surface of the sea. Hot air from the surface of the sea which is less
Laut / Sea dense rises upwards and moves to land while cold water from the land
Daratan
which is denser moves downwards and moves to sea by convection as
9
Land
land breeze.
(c) Pemanasan Bumi / Heating of Earth
Matahari Sinar Matahari memasuki atmosfera bumi dan menyinari
Sun seluruh permukaan Bumi. Haba dari Matahari dipindahkan secara
sinaran melalui vakum.
The Sun ray enters the Earth atmosphere and radiates
Sinar Matahari
Sun radiation throughout the earth surface. Heat from the Sun is transferred by
radiation through vacuum.
Bumi
Earth
hotter; higher; less dense; upwards; denser
B. (a) panas; lebih tinggi; kurang tumpat; atas; lebih tumpat (c) atmosfera; sinaran / atmosphere; radiation
99 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 99 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
C. Konduktor Haba dan Penebat Haba Buku teks muka surat 211
Heat Conductor and Heat Insulator Textbook page 211
1 Konduktor haba ialah bahan yang boleh mengalirkan haba dengan baik.
A heat conductor is a substance which can conduct heat well. TP1
2 Penebat haba ialah bahan yang tidak boleh mengalirkan haba dengan baik.
Insulator of heat is a substance which cannot conduct heat well. TP1
3 Isi tempat kosong untuk membincangkan kegunaan konduktor haba dan penebat haba.
Fill in the blanks to discuss the uses of heat conductor and heat insulator. TP3
(a) Iglu / Igloo
Iglu diperbuat daripada ais iaitu penebat haba
yang baik . Kehilangan haba dapat dihalang.
Igloo is made up from ice which is
good insulator of heat. Lost of heat can be avoided.
(b)
Habuk kayu / Sawdust
Habuk kayu digunakan untuk melambatkan peleburan ais.
Sawdust is used to slow down the melting of ice.
(c) Tingkap dwi-kaca Tingkap di negara yang beriklim sejuk diperbuat daripada dua
Double-glazed window
kepingan kaca yang terpisah oleh satu lapisan udara . Udara
adalah penebat haba yang baik. Haba dapat
dikekalkan .
The windows in the cold climate countries are made of two sheets
of glass which are separated by a layer of air . Air is a good
9 insulator of heat. Heat will be retained .
(d) Seterika / Iron Tapak seterika yang diperbuat daripada logam ialah
Pemegang konduktor
Handle haba yang sangat baik. Ia mengkonduksikan
haba supaya dapat menggosok kain dengan cepat .
The base of iron is made from metal which is a very good heat
conductor . It conduct heat so that clothes can be ironed
quickly .
Tapak seterika / Iron base
layer of air; insulator; retained (b) melambatkan / slow down
(d) konduktor; cepat / conductor; quickly (c) lapisan udara; penebat; dikekalkan C. 3 (a) ais; baik / ice; good
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 100
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 100 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
D. Kebolehan Bahan Berlainan Sebagai Penebat Haba Buku teks muka surat 212
Abilities of Different Materials as Heat Insulator Textbook page 212
Termometer Termometer
Thermometer Thermometer
Kapas Plastik Kertas
Cotton wool Plastic Paper
Air panas Air panas
(95 °C) (95 °C)
Hot water Hot water
(95 °C) (95 °C)
Kelalang dasar leper
Flat-bottomed flasks
1 Kandungan haba bagi ketiga-tiga kelalang leper bulat adalah sama kerana ketiga-tiga kelalang
mempunyai isi padu air dan suhu awal air yang sama.
The amount of heat for the three round bottomed flasks are the same because they have same
volume of water and same initial temperature.
2 Penurunan suhu menunjukkan kehilangan haba.
Drop of temperature shows loss of heat.
3 Kelalang yang dibalut dengan bahan yang mempunyai kehilangan haba paling rendah merupakan penebat haba
yang terbaik .
The flask that is wrapped with the material that has the lowest heat loss is the best heat insulator.
4 Berdasarkan gambar rajah di atas, susunkan bahan-bahan tersebut mengikut urutan menaik bagi kebolehan
menebat haba.
Based on the diagrams above, arrange all materials in ascending order of ability of heat insulating.
Plastik Kertas Kapas
Plastic Paper Cotton wool
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
9
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
9.3 Prinsip Pengembangan dan Pengecutan Jirim
The Principle of Expansion and Contraction of Matter
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Menerangkan bagaimana haba menyebabkan pengembangan dan pengecutan pepejal, cecair dan gas.
9.3.1
SP Explain how heat can cause the expansion and contraction in solid, liquid and gas.
LS Berkomunikasi mengenai pelbagai kegunaan pengembangan dan pengecutan jirim dalam kehidupan harian.
9.3.2
Communicate about the various uses of expansion and contraction of matter in daily life.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam.
Moral Value Realising that science is one way to understand nature.
Kapas / Cotton wool Plastik / Plastic 4 2 kehilangan / loss
Kertas / Paper terbaik / best 3 D. 1 haba / heat
101 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 101 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
A. Pengembangan dan Pengecutan Jirim Buku teks muka surat 213
The Expansion and Contraction of Matter Textbook page 213
1 Isikan tempat kosong bagi mengkonsepsikan pemanasan jirim.
Fill in the blanks to conceptualise the heating of matter. TP2
Apabila jirim dipanaskan, zarah-zarah menyerap haba. Zarah-zarah bergerak semakin laju. Ruang antara
zarah bertambah . Jirim mengembang .
When a matter is heated, the particle absorbs heat. The particles move faster. The space between
the particles increases . Matter expands .
2 Isikan tempat kosong bagi mengkonsepsikan penyejukan jirim.
Fill in the blanks to conceptualise the cooling of matter. TP2
Apabila jirim disejukkan, zarah-zarah membebaskan haba. Zarah-zarah bergerak semakin perlahan .
Ruang antara zarah berkurang . Jirim mengecut .
When a matter is cooled, the particles release heat. The particles move slower . The
space between the particles decreases . Matter contracts .
Aktiviti Pengembangan dan Pengecutan Pepejal, Cecair dan Gas
Activity 9.4 Expansion and Contraction of Solid, Liquid and Gas
Aktiviti / Activity Pemerhatian / Observation
(a) 1 Sebelum dipanaskan, bebola logam dapat masuk melalui
Gelang logam / Metal ring gelang logam dan dapat dikeluarkan melalui gelang logam.
Before heating, the metal ball can go through the metal ring
and can be removed through the metal ring.
2 Selepas dipanaskan, bebola logam tidak dapat masuk melalui
Bebola logam gelang logam.
Metal ball
After heating, the metal ball cannot go through metal ring.
3 Selepas disejukkan, bebola logam boleh masuk melalui
9 Haba / Heat
gelang logam.
After cooling, the metal ball can go through metal ring.
(b) 1 Apabila kelalang kon dimasukkan ke dalam besen kaca yang
mengandungi air panas, aras cecair berpendarfluor meningkat .
Tiup kaca Cecair
Glass tube berpendarfluor When the conical flask is put into the glass basin containing hot water,
Fluorescent rises up
liquid the level of fluorescent liquid .
2 Apabila kelalang kon bulat dimasukkan ke dalam besen kaca yang
mengandungi ketulan ais, aras cecair berpendarfluor menurun .
Kelalang kon Air panas
Conical flask Hot water
When the conical flask is put into the glass basin containing ice cubes,
the level of fluorescent liquid decreases .
3 boleh masuk / can go release; slower; decreases; contracts
2 tidak dapat / cannot 2 perlahan; berkurang; mengecut
2 menurun / decreases go through; be removed absorbs; increases; expands
(b) 1 meningkat / rises up (a) 1 masuk melalui; dikeluarkan A. 1 menyerap; bertambah; mengembang
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 102
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 102 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Aktiviti / Activity Pemerhatian / Observation
(c) 1 Apabila kelalang dasar bulat dipanaskan dengan penunu Bunsen,
Penunu Bunsen gelembung gas keluar melalui tiub kaca dalam air.
Bunsen burner
Kelalang dasar Tiup kaca When the round bottom flask is heated with Bunsen burner,
bulat Glass tube bubbles of gaseous come out through the glass tube in the water.
Round bottom
flask 2 Apabila kelalang dasar bulat disejukkan di bawah air paip, air dari
bikar masuk melalui tiub kaca.
When the round bottom flask is cooled under the tap water, the
Bikar / Beaker Besen kaca / Glass basin water from the beaker enters the glass tube.
Kesimpulan / Conclusion
Aktiviti (a) / Activity (a)
1 Apabila bebola logam dipanaskan, bebola logam tidak dapat melalui gelang logam kerana bebola logam
mengembang menyebabkan saiznya bertambah dari asal. / When the metal ball is heated, the
metal ball cannot go through the metal ring because the metal ball expands and causes its size
increases from the original.
2 Apabila disejukkan, bebola logam itu boleh melalui gelang logam kerana ia mengecut dan saiznya
kembali kepada asal. / When cooling, the metal ball can go through the metal ring because it contracts
and its size returns to original.
Aktiviti (b) / Activity (b)
1 Apabila kelalang dasar bulat direndam dalam air panas, aras cecair berpendarfluor meningkat dalam tiub
kaca kerana cecair mengembang . / When the round bottom flask is soaked into the hot water, the level
of fluorescent liquid in the glass tube increases because the liquid expands .
2 Aras cecair berpendarfluor menurun selepas diletakkan ke dalam bikar yang mengandungi ketulan ais
kerana cecair berpendarfluor mengecut . / The level of fluorescent liquid decreases after put into the
contracts
beaker containing ice cubes because the liquid .
9
Aktiviti (c) / Activity (c)
1 Udara dalam kelalang dasar bulat mengembang apabila dipanaskan menyebabkan isi padu udara
bertambah dan ditolak keluar menghasilkan gelembung gas.
The air in the round bottom flask expands when heated causes the volume of air increase and is
pushed out to produce gas bubbles.
2 Apabila disejukkan, isi padu udara berkurang dan tekanan udara bertambah kerana udara di dalamnya
mengecut. / When cooled, the volume of air decreases and the air pressure increases because the air
inside it contracts.
2 mengecut / contracts 1 mengembang; bertambah / expands; increases
2 tekanan udara bertambah / air pressure increases 1 mengembang / expands Aktiviti (a) / Activity (a)
1 isi padu udara; ditolak keluar / volume of air; pushed out Aktiviti (b) / Activity (b) 2 masuk / enters
Aktiviti (c) / Activity (c) 2 mengecut / contracts (c) 1 gelembung gas / bubbles of gaseous
103 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 103 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B. Aplikasi Pengembangan dan Pengecutan Jirim dalam Kehidupan Harian Buku teks muka surat 214
Applications of Expansion and Contraction of Matters in Daily Life Textbook page 214
Prinsip pengembangan dan pengecutan jirim banyak diaplikasikan dalam kehidupan harian kita. Antaranya adalah
seperti dalam rajah-rajah berikut:
The principles of expansion and contraction of matters are widely applied in our daily lives. Among them are as in
the following diagrams: TP3
(a) Termometer 1 Merkuri dalam bebuli termometer mengembang dan mengecut
Thermometer seragam
secara pada perubahan suhu yang kecil.
Mercury in the thermometer bulb expands and contracts
Merkuri
Mercury uniformly with a small change in temperature.
Tiub kapilari 2 Merkuri mengembang dan menaik dalam tiub kapilari pada suhu
tinggi
35
Capillary tube
36
yang .
37
38
Mercury expands and rises in capillary tube at high
39
40
41
temperature.
42
3 Merkuri mengecut dan menurun dalam tiub kapilari pada
suhu yang rendah.
Mercury contracts and drops in capillary tube at lower
temperature.
(b) Jalur dwilogam di dalam alat 1 Penggera kebakaran menggunakan jalur dwilogam yang terdiri
penggera kebakaran
Bimetallic strip in the fire alarm daripada dua jenis logam yang mempunyai kadar pengembangan
yang berbeza .
The fire alarm uses bimetallic strip that consists of two types of
metals which have different rates of expansion.
Wayar elektrik Loceng penggera
Electrical wiring Alarm bell
2 Semasa kebakaran, jalur dwilogam menjadi panas .
During fire, the bimetallic strip becomes hot .
membengkok
9 Bateri
Battery
3 Jalur dwilogam mengembang dan .
Kuprum / Copper Bimetallic strip expands and bends .
Sebelum
4 Jalur dwilogam menyentuh skru sesentuh dan melengkapkan
pemanasan
Before heating
Besi / Iron litar. / The bimetallic strips touches the connecting screw and
Selepas completes the circuit.
pemanasan
After heating
5 Arus elektrik mengalir di dalam litar menyebabkan
loceng penggera berbunyi .
Electric current flows in the circuit causes the fire bell
rings .
3 membengkok / bends 3 mengecut / contracts
mengalir; berbunyi / flows; rings 5 2 panas / hot 2 tinggi / high
melengkapkan / completes 4 (b) 1 jalur dwilogam; berbeza / bimetallic strip; different B (a) 1 seragam / uniformly
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 104
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 104 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(c) Ruang pada landasan kereta api 1 Celah pengembangan ialah ruang kecil antara dua hujung
Gaps in railway track
landasan besi.
An expansion gap is a small space between two endings of
the metal rail.
2 Dengan ini, hujung logam dapat mengembang secara bebas
Ruang kecil
Small gap
pada hari panas.
Hence, the end of the metal rails can expand freely
during hot day.
3 Landasan kereta api akan membengkok dan putus jika tiada
celah pengembangan.
The railway track will bend and break if there is no
expansion gaps.
( d) Penggolek pada jambatan keluli celahan
1 Jambatan keluli mempunyai bagi membenarkan
Roller on the steel bridges
pengembangan dan pengecutan.
Jambatan Ruang gaps
Bridge Gap The steel bridges has for expansion and
contraction.
2 Penggolek dan sambungan gelongsor membenarkan jambatan
keluli bergerak ketika mengembang dan mengecut.
Penggolek move
Roller Rollers and sliding joints allow the steel bridge to
as it expands and contracts.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
9.4 Hubung Kait Jenis Permukaan Objek dengan Penyerapan dan Pembebasan Haba 9
Relationship between Types of Surface of Object and Heat Absorption and Emission
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Menunjuk cara bagaimana objek yang gelap dan kusam menyerap haba lebih baik daripada objek putih dan berkilat.
9.4.1
Demonstrate how dark, dull objects absorb heat better than white and shiny objects.
SP Menunjuk cara bagaimana objek yang gelap dan kusam membebaskan haba lebih baik daripada objek putih dan berkilat.
9.4.2
LS Demonstrate how dark, dull objects radiate heat better than white and shiny object.
Kreativiti dan inovasi
9.4.3
Creative and inovative
Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam
EMK
Realizing that science is one way to understand nature
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam
Moral Value Realising that science is one way to understand nature
(d) 1 celahan / gaps 2 mengembang / expand
bergerak / move 2 3 membengkok / bend (c) 1 ruang kecil / small space
105 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 105 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Pembelajaran Berasaskan Projek: Bangunan Hijau / Project Based Learning: Green Building
Arahan / Instructions:
Bangunan Hijau adalah satu konsep pembinaan yang bercirikan teknologi mesra alam semula jadi. Matlamat
utama adalah peningkatan penggunaan sumber semula jadi (tenaga, bahan, air) secara efisien. Salah satu elemen
yang perlu ada dalam bangunan hijau adalah kualiti persekitaran dalaman (Indoor environmental quality).
Reka bentukkan satu rumah kediaman hijau dengan mengambil kira perkara-perkara berikut:
i. Penggunaan tenaga dapat dikurangkan
ii. Menyediakan persekitaran dan keadaan rumah yang lebih sejuk
Inovasi anda boleh dihasilkan dalam konteks tempatan atau global mengikut kreativiti anda sendiri.
Anda boleh merujuk halaman belakang buku bagi melihat kriteria-kriteria yang dinilai bagi projek ini.
Green Building is a construction concept that features environmentally friendly technology. The ultimate goal
is to increase the use of natural resources (energy, materials, water) efficiently. One element that needs to be in
green building is the quality of indoor environment (Indoor environmental quality).
Designate a green residential house with regards to the following:
i. Energy consumption can be reduced
ii. Provides a cooler environment and home condition
Your innovation can be created in a local or global context according to your own creativity.
You can refer the book's back cover to see the criteria assesed for this project.
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE Kuiz / Quiz
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Antara berikut, yang manakah merupakan 3 Jadual 1 menunjukkan proses pemindahan haba
konduktor haba yang baik? dan aplikasinya. / Table 1 shows the process of heat
Which of the following is a good heat conductor? transfer and its application.
A Kapas
Pemindahan haba Aplikasi dalam kehidupan
Cotton
Heat transfer Application in daily life
B Getah
Rubber
9 C Bulu P
Tingkap kaca dua lapis
Two layered glass window
Fur
D Aluminium Q Bayu darat / Land breeze
Aluminium
Jadual 1 / Table 1
Berdasarkan Jadual 1, apakah cara pengaliran haba
yang terlibat bagi P dan Q? / Based on Table 1,
2 Antara isi padu air berikut, yang manakah akan
what is the way of heat flow involved in P and Q?
paling cepat mencapai suhu 100°C?
Which of the following volume of water will be the P Q
fastest to reach a temperature of 100°C?
A 50 cm3 A Konduksi / Conduction Sinaran / Radiation
B 67 cm3 Konduksi / Conduction Perolakan / Convection
B
C 80 cm3
D 100 cm3 C Sinaran / Radiation Konduksi / Conduction
D Sinaran / Radiation Perolakan / Convection
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 106
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 106 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
1 Sekumpulan pengakap memasak air semasa mengadakan aktiviti perkhemahan di kawasan sekolah. Satu
kumpulan memasak air menggunakan dapur gas mudah alih manakala satu lagi kumpulan memasak menggunakan
dapur kayu dengan menggantung air tersebut. / A group of scouts boils water during camping activity at the
school area. One group boils the water by using portable cooking gas and another group boils by using wood
by hanging it.
Kaedah A / Method A Kaedah B / Method B
(a) Nyatakan jenis pemindahan haba bagi kedua-dua kaedah di atas.
State the type of heat transfer for both method above.
Kaedah A ialah perolakan dan kaedah B ialah sinaran. / Method A is convection and method B is radiation.
[1 markah/mark]
(b) Kaedah manakah yang membolehkan air masak dengan cepat? Terangkan.
Which method can boil the water faster? Explain.
Kaedah A kerana haba dipindahkan terus dari sumber haba ke air secara perolakan.
Method A because heat is directly transferred from source of heat to the water by convection.
[2 markah/marks]
2 Rajah menunjukkan kesan haba terhadap dua jalur dwilogam.
Diagram shows the effect of heat on the bimetallic strips.
Kuprum / Copper
Pemanasan
Besi / Iron Heating
(a) Apakah prinsip yang digunakan dalam pemanasan jalur dwilogam tersebut?
What is the applicable principle of the heating of the bimetallic strip?
Prinsip pengembangan dan pengecutan jirim
Principles of expansion and contraction of matters
[1 markah/mark]
(b) Jalur dwilogam boleh didapati dalam peralatan yang digunakan dalam kehidupan seharian. 9
Nyatakan dua contoh peralatan tersebut.
Bimetallic strips can be found in many instruments that are used in daily life.
State two examples of the instruments.
Seterika, penggera kebakaran
Iron, fire alarm
[2 markah/marks]
(c) Landasan kereta api turun mengaplikasikan prinsip yang dinyatakan dalam 2(a). Landasan kereta api dibina
dengan terdapat ruang kecil antara dua hujung landasan besi. Berikan justifikasi anda.
Railway track also applied the principle stated in 2(a). Railway track built with a small gap between two
ending of metals rail. Justify.
Untuk membolehkan landasan kereta api hujung logam mengembang pada waktu panas.
To enable end of metal rails can expands during hot day.
[1 markah/mark]
107 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab9 Book A_F.indd 107 25/10/2021 1:08 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Gelombang Bunyi
10 Sound Waves
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
10.1 Ciri-ciri Gelombang Bunyi
Characteristics of Sound Waves
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
SP Berkomunikasi mengenai ciri asas gelombang bunyi.
10.1.1
LS Communicate about the basic characteristics of sound waves.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam
Moral Value Realising that science is one way to understand nature
Buku teks muka surat 226
A. Pemindahan Bunyi / Transfer of Sound Textbook page 226
Isi tempat kosong di bawah dengan jawapan yang betul untuk membincangkan pemindahan bunyi dalam medium
yang berlainan.
Fill in the blanks with the correct answer to discuss the transfer of sounds in different medium. TP2
sangat rapat paling jauh paling perlahan dipindahkan paling jauh dan paling cepat
very close furthest slowest transferred furthest and fastest
(a) Jarak antara zarah-zarah dalam pepejal adalah sangat rapat berbanding cecair dan gas. Bunyi boleh
dipindahkan paling jauh dan paling cepat dalam pepejal.
The distance between particles in solid is very close compared to liquid and gas. Sound can be
transferred furthest and fastest in solid.
(b) Jarak antara zarah-zarah dalam gas adalah paling jauh . Zarah-zarah bergerak dalam jarak yang jauh sebelum
berlanggar dengan zarah yang lain. Ini menyebabkan pemindahan bunyi dalam gas adalah paling perlahan .
Distance between the particles in gas is the furthest . Particles have to move at further distance
10 before they collide with other particles. This makes the transfer of the sound in gas is the slowest .
(c) Tiada zarah terdapat dalam vakum. Bunyi tidak dapat dipindahkan melalui vakum kerana tiada
getaran terhasil.
There are no particles in vacuum. Sound cannot be transferred through vacuum because no vibration
is produced.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
very close; furthest and fastest
(c) dipindahkan / transferred (b) paling jauh; paling perlahan / furthest; slowest A. (a) sangat rapat; paling jauh dan paling cepat
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 108
Modul Sains T2-Bab10 Book A_F.indd 108 25/10/2021 12:51 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
10.2 Kenyaringan dan Kelangsingan Bunyi
Loudness and Pitch of Sound
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
10.2.1 Menerangkan frekuensi bunyi dan unitnya serta amplitud getaran. / Explain frequency and its unit, the amplitude of vibration.
10.2.2 Menghubungkaitkan frekuensi dengan kelangsingan. / Relate frequency to pitch.
SP
LS 10.2.3 Menghubungkaitkan amplitud dengan kenyaringan. / Relate amplitude to loudness.
Menjelaskan menggunakan contoh kekuatan dan kelangsingan menggunakan alatan muzik.
10.2.4
Explain with examples loudness and pitch using musical instruments.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam
Moral Value Realising that science is one way to understand nature
A. Frekuensi Bunyi dan Unitnya serta Amplitud Getaran Buku teks muka surat 229
Frequency of Sound with Its Unit and Amplitude of Vibration Textbook page 229
1 Padankan yang berikut. / Match the following. TP1
(a) Frekuensi
(e) 20 Hz – 20 000 Hz
Frequency
(b) Unit frekuensi (f) Bilangan getaran bunyi dalam satu saat
Unit of frequency Number of sound vibration in one second
(c) Julat bunyi manusia
(g) Hertz (Hz)
Range of sound for human
(d) Amplitud (h) Pengukuran skala magnitud ayunan sesuatu gelombang
Amplitude Magnitude scale measurement of wave oscillation
2 Labelkan amplitud pada rajah di bawah. / Label the amplitude on diagram below. TP1
Amplitud
Amplitude
Projek / Project
Arahan / Instructions: 10
Secara berkumpulan, kumpulkan maklumat berkaitan kekuatan dan kelangsingan bagi beberapa alat muzik
seperti piano, gitar, rekorder dan gendang. Bentangkan kepada rakan sekelas anda dalam bentuk persembahan
multimedia. Pembentangan anda harus mempunyai: / In group, collect information about strengths and pitch for
some musical instruments such as piano, guitar, recorders and drums. Present to your classmates in the form of
multimedia presentations. Your presentation should have:
1 Rakaman audio / Audio recording
2 Bentuk gelombang bunyi yang dihasilkan alat muzik tersebut
The waveforms of the sound produced by the musical instruments
3 Perbandingan antara alat-alat muzik tersebut / Comparison between the musical instruments
Amplitude (d) – (h) (b) – (g)
Amplitud 2 (c) – (e) A. (a) – (f)
109 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab10 Book A_F.indd 109 25/10/2021 12:51 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B Kesan Doppler Buku teks muka surat 231
Doppler Effect Textbook page 231
1 Rajah menunjukkan perubahan panjang gelombang yang terhasil apabila sumber bunyi bergerak.
The diagram shows the change of wavelength when source of sound moving. TP3
Sumber bunyi Arah gerakan sumber
Source of sound Direction of source
Pemerhati
Observer
Panjang gelombang / Wavelength
Kesan Doppler
Doppler Effect
Perubahan frekuensi ketara yang disebabkan oleh pergerakan relatif sumber bunyi, pemerhati atau
kedua-duanya.
Apparent change in frequency
caused by the relative movement of source of sound, observer or both.
Projek / Project
Arahan / Instructions:
1 Bentuk kumpulan seramai dua atau tiga orang ahli.
Form a group consists of two or three members.
2 Secara berkumpulan, pergi berhampiran pagar sekolah dan berdiri berdekatan dengan jalan raya.
In group, go near to the school gate and stand near the road.
3 Perhatikan dan dengar dengan teliti bunyi kenderaan atau siren ambulan yang sedang bergerak melintasi
10 anda. / Observe and listen carefully the sound of vehicles or ambulance's siren that crossing in front of you.
4 Banding beza kelangsingan bunyi tersebut. Rekodkan pemerhatian anda.
Compare and contrast pitch of the sound. Record you observation.
5 Bentangkan pemerhatian anda di kelas.
Present your observation in the class.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
Apparent change in frequency
B. 1 Perubahan frekuensi ketara
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 110
Modul Sains T2-Bab10 Book A_F.indd 110 25/10/2021 12:51 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
10.3 Fenomena dan Aplikasi Pantulan Gelombang Bunyi
Phenomenon and Application of Reflection of Sound Waves
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Menjelaskan dengan contoh fenomena yang berkait dengan pantulan gelombang bunyi seperti gema dan kesan Doppler bunyi.
10.2.1
Explain with example the phenomena related to reflection of sound waves such as echo and Doppler effect.
Menjelaskan dengan contoh aplikasi pantulan gelombang bunyi.
10.2.2
SP Explain with example the applications of reflection of sound waves.
LS Menerangkan dan berkomunikasi mengenai had pendengaran bagi manusia dan haiwan.
10.2.3
Elaborate and communicate the limitations of hearing for humans and animals.
Menerangkan dengan contoh cara mengatasi had pendengaran manusia.
10.2.4
Explain with examples ways to overcome human limitations of hearing.
Kemahiran saintifik (proses pemikiran dan kemahiran manipulatif tertentu)
EMK
Scientific skills (specific processes of thinking and manipulative skills)
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam
Moral Value Realising that science is one way to understand nature
A. Fenomena Pantulan Gelombang Bunyi Buku teks muka surat 232
Phenomena of Reflection of Sound Waves Textbook page 232
1 Isikan tempat kosong di bawah tentang fenomena pantulan bunyi.
Fill in the blanks below on phenomenon of reflection of sound. TP4
(a) Apabila bunyi dipantulkan pada satu permukaan yang keras dalam ruang yang tertutup dan kosong,
gema akan terhasil.
When the sound is reflected on the hard surface in a closed area, echo will produce.
(b) Dinding dewan orkestra biasanya dilitupi dengan permukaan yang lembut untuk mengelakkan
pantulan bunyi. Bunyi yang dipantulkan dari orkestra ke dinding akan memberi gangguan kepada
persembahan.
Wall of orchestra hall is covered with soft surface to prevent reflection. Reflected
sound from the orchestra to the wall will disturb the performance.
B. Aplikasi Pantulan Gelombang Bunyi Buku teks muka surat 232
Application of Reflection of Sound Waves Textbook page 232
1 Gariskan jawapan yang betul tentang aplikasi pantulan gelombang bunyi.
Underline the correct answer about the application of sound wave reflection. TP3
(a) Sonar ialah satu teknik yang menggunakan ( perambatan , hentaman ) bunyi untuk navigasi, komunikasi atau
( mengesan , melihat ) objek di bawah permukaan air dan mengukur kedalaman air. 10
Sonar is a technique that uses sound ( propagation , hit ) to navigate, communication or ( detect , observe )
objects under the surface of water and measure the depth of water.
(b) Sonar banyak digunakan dalam bidang perkapalan dan ( perikanan , pertanian ).
Sonar is widely used in shipping industry and ( fishery , agricultural ) field.
(b) perikanan; fishery (b) lembut; dipantulkan / soft; Reflected
B. 1 (a) perambatan; mengesan / propagation; detect A. 1 (a) gema / echo
111 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab10 Book A_F.indd 111 25/10/2021 12:51 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Lengkapkan peta alir di bawah tentang bagaimana teknologi sonar digunakan untuk mengukur kedalaman laut
atau dalam industri perikanan.
Complete the flow chart below on how sonar technology is used to measure the depth of sea or in fishery
industry. TP3
(a) Sonar mengeluarkan bunyi dengan frekuensi tinggi ke dalam laut.
high
Sonar emits frequency of sound into the sea.
(b) Gelombang bunyi yang terhasil merambat sehingga ke dasar laut dan dipantulkan kembali ke kapal
sebagai gema . / Sound wave produced propagates to the sea bottom and reflected
back to the ship as echo .
(c) Gema yang terhasil akan dikesan oleh satu peranti yang terdapat dalam sonar yang
dikenali sebagai hidrofon. / An echo produced will be detected by a gadget in sonar known
as hydrophone.
(d) Jumlah tempoh bunyi (perambatan dan pantulan) yang terhasil diukur dan dihitung untuk menentukan
kedalaman laut. / Total period of sound (propagation and reflection) produced is measured
and calculated to determine the depth of the sea.
3 Nyatakan ‘Betul’ atau ‘Salah’ bagi pernyataan di bawah tentang teknologi sonogram dalam bidang perubatan.
State ‘True’ or ‘False’ for the statements below about sonogram technology in medical field. TP3
(a) Ultrabunyi merupakan teknik pengimejan yang menggunakan gelombang bunyi Betul
untuk menghasilkan imej. True
Ultrasound is an imaging technique which use sound wave to produce image.
(b) Transduser kecil yang dikenali sebagai hidrofon menghantar gelombang bunyi ke
dalam badan dan menerima isyarat gema yang dipantulkan bagi menghasilkan imej. Salah
Small transducer known as hydrophone emits sound wave into the body and receive False
reflected echo signal to produce image.
10
(c) Pengimejan boleh melihat struktur dan pergerakan organ dalam badan. Betul
Imaging can see the structure and movement of organ in the body. True
(d) Ultrabunyi adalah seperti sinar-X atau imbasan CT yang menggunakan gelombang
bunyi berfrekuensi tinggi untuk menghasilkan imej organ dan struktur dalam badan. Salah
Ultrasound is like X-ray and CT-scan which uses high frequency of sound wave to False
produce organ image and body structure image.
(b) Salah / False (c) dikesan / detected
(d) Salah / False 3 (a) Betul / True (b) gema / echo
(c) Betul / True (d) kedalaman / depth B. 2 (a) tinggi / high
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 112
Modul Sains T2-Bab10 Book A_F.indd 112 25/10/2021 12:51 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
4 Lengkapkan tempat kosong di bawah tentang bagaimana kelawar menganggar jarak semasa terbang.
Complete the blanks below on how bats estimate its distance during fly. TP3
(a) Kelawar lebih banyak menggunakan telinga berbanding
mata kerana struktur matanya kecil dan terbang pada waktu
malam .
Bat uses ears more frequently compare to eyes because
its eyes structure is small and it flies at night .
(d) Bunyi tersebut terkena halangan dan
(b) Menggunakan kaedah pengesanan
dipantul kembali dalam gema semasa terbang.
bentuk gema. / The sound hits the echo
Using detection
obstacles and bounced back
method during fly.
in the echoes form.
(c) Menghasilkan bunyi menjerit yang tinggi
dan nyaring ketika terbang.
Emit high and loud
shouting sound during fly.
C. Had Pendengaran Buku teks muka surat 233
Limitations of Hearing Textbook page 233
1 Isikan tempat kosong dengan perkataan yang terdapat dalam kotak tentang had pendengaran.
Fill in the blanks with the words in the box on limitations of hearing. TP2
merosakkan rendah elastik julat pendengaran / hearing range
damage low elastic 20 000 Hz
(a) Julat pendengaran manusia yang sihat ialah antara 20 Hz hingga 20 000 Hz .
Normal hearing range for human is between 20 Hz to 20 000 Hz .
(b) Spesies haiwan yang berbeza mempunyai julat pendengaran yang berbeza.
hearing range 10
Different animal species have different .
(c) Bunyi yang berfrekuensi terlalu rendah
agak sukar didengari dan bunyi yang berfrekuensi
terlalu tinggi boleh merosakkan deria pendengaran. /
Low
frequency sounds are a bit
damage
difficult to hear and too high frequency sounds may the hearing senses.
(d) Kanak-kanak boleh mendengar dengan lebih baik kerana gegendang telinga mereka lebih elastik
elastic
berbanding orang tua. / Children can hear better because their eardrum is more compare
to elderly.
(b) julat pendengaran / hearing range (c) tinggi; nyaring / high; load
(d) elastik / elastic C. 1 (a) 20 000 Hz (b) gema / echo
(c) rendah; merosakkan / low; damage (d) dipantul / bounced 4 (a) telinga; malam / ears; night
113 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab10 Book A_F.indd 113 25/10/2021 12:51 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
D. Mengatasi Had Pendengaran Manusia Buku teks muka surat 233
Overcome the Hearing Limit Textbook page 233
1 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah tentang alat bagi mengatasi had pendengaran manusia dengan fungsinya.
Complete the table below about the tools to overcome the limitation of human hearing with its functions. TP2
Alat / Tool Fungsi / Function
(a) Mikrofon Menukar gelombang akustik kepada getaran mekanikal
Microphone
Change acoustic wave to mechanical wave
(b) Stetoskop Mendengar bunyi degupan jantung
Stethoscope heartbeats
Listen to
(c) Alat bantu Membantu menguatkan lagi bunyi yang masuk ke dalam telinga
pendengaran amplify
Hearing aid Help to the sound entering the ears
(d) Alat pembesar Menguatkan bunyi yang dihasilkan
suara
Increase the volume of the sound produced
Speaker
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu alat digunakan dalam 2 Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu gelombang bunyi.
bidang perubatan. Diagram 2 shows a sound wave.
Diagram 1 shows a device used in medical field.
Amplitud / Amplitude
Masa
Time
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
10 Nyatakan fungsi alat tersebut. Rajah 2 / Diagram 2
State the function of this device. Nyatakan ciri-ciri gelombang di atas.
A Menguatkan bunyi yang dihasilkan State the characteristics of the wave above.
Increase the volume of the sound produced A Frekuensi rendah, kelangsingan rendah
B Menukarkan gelombang akustik kepada Low frequency, low pitch of sound
getaran mekanikal / Change the acoustic waves B Frekuensi tinggi, kelangsingan tinggi
to mechanical waves High frequency, high pitch of sound
C Membantu menguatkan lagi bunyi yang masuk C Amplitud tinggi, kenyaringan rendah
ke telinga / Help to increase the volume of High amplitude, low loudness
sound entering the ears D Amplitud rendah , kenyaringan tinggi
D Mendengar bunyi degupan jantung Low amplitude, high loudness
Listen to heartbeat
(d) Menguatkan / Increase (b) degupan jantung / heartbeats
(c) menguatkan / amplify D 1 (a) getaran mekanikal / mechanical wave
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 114
Modul Sains T2-Bab10 Book A_F.indd 114 25/10/2021 12:51 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions Kuiz / Quiz
1 Di angkasa lepas sering berlaku letupan manakala di langit sering berlaku guruh. Mengapakah
bunyi letupan di angkasa lepas tidak dapat didengari di Bumi tetapi bunyi guruh dapat didengari
dengan sangat kuat?
In outer space explosions are often occur while in the sky thunders are often occur. Why the explosion sounds
in space cannot be heard on Earth but thunder sounds can be heard strongly?
Di angkasa lepas tiada medium perambatan iaitu berada dalam keadaan vakum manakala di langit terdapat
medium gas. Bunyi tidak boleh merambat dalam vakum.
No medium to propagate in outer space which is in vacuum state while there is gas medium in the sky.
Sound cannot propagate in vacuum.
[2 markah/marks]
2 Pada Mac 2014, Malaysia dikejutkan dengan kehilangan pesawat penumpang MAS MH370 yang hilang dari
radar dan tidak dapat dikesan. Usaha mencari dan menyelamat telah giat dijalankan di laut bagi mengesan
serpihan pesawat tersebut. Rajah 2 menunjukkan gambaran bagaimana sonar dapat membantu mengesan
serpihan pesawat yang hilang tersebut.
In March 2014, Malaysia was shocked by the disappearance of MAS MH370 passenger aircraft from the radar
and were undetected. The search and rescue were actively engaged in the sea to detect the debris of the
aircraft. Diagram 2 shows how the sonar can help to detect the missing aircraft debris.
Rajah 2 / Diagram 2
Terangkan bagaimana sonar digunakan untuk mengesan serpihan pesawat.
Explain how sonar is used to detect the aircraft debris.
Sonar mengeluarkan gelombang bunyi ke dasar laut. Gelombang bunyi yang terkena pada permukaan serpihan
akan terpantul kembali dalam bentuk gema. Gema tersebut akan ditafsirkan oleh alat dalam sonar.
Sonar emits sound wave into the sea. Sound wave that hits the debris surface will reflect back in the form of
echos. The echos is interpreted by the tool in sonar.
[3 markah/marks]
3 (a) Aziz terpaksa bercakap secara menjerit apabila bercakap dengan datuknya. Jelaskan. 10
Aziz has to shout when talking with his grandfather. Explain.
Gegendang telinga datuknya menjadi kurang elastik. Semakin meningkat usia, semakin kurang elastik
gegendang telinga. Gegendang telinga tidak dapat bergetar dengan kuat apabila menerima
gelombang bunyi.
His grandfather’s ear drum becomes less elastic. The longer the age, the less elastic an ear drum.
An ear drum couldn’t vibrate stronger when receive sound wave.
[3 markah/marks]
115 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab10 Book A_F.indd 115 25/10/2021 12:51 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(b) Berikut menunjukkan beberapa peralatan bagi mengatasi had pendengaran manusia. Bulatkan yang
manakah dapat membantu Aziz dalam membantu datuknya untuk dapat mendengar semula dengan normal.
The following shows a a few of tools that use to overcome the human hearing limit. Circle the tool that can
help Aziz to help his grandfather to hear as normal.
[1 markah/mark]
4 Rajah menunjukkan bentuk gelombang bagi tiga jenis bunyi K, L dan M.
The diagram shows the waveforms of three types of sounds K, L and M.
Amplitud Amplitud Amplitud
Amplitude Amplitude Amplitude
Masa Masa Masa
0 Time 0 Time 0 Time
K L M
(a) Susun dalam tertib menurun, kelangsingan tiga bunyi.
Arrange in descending order, the pitch of the three sounds.
L, K,M
[1 markah/mark]
(b) Apakah faktor yang mempengaruhi kelangsingan dan nyatakan hubungan antara kelangsingan dengan
faktor tersebut.
What is the factor that affect the pitch and state the relationship between pitch and that factor.
Frekuensi. Semakin tinggi ferkuensi semakin tinggi kelangsingan.
Frequency. The higher the frequency the higher the pitch of the sound.
[2 markah/marks]
(c) Huraikan bagaimana untuk menghasilkan bunyi yang perlahan pada gelas kosong.
Describe how to produce low sound at an empty glass.
Gelas dibalut dengan tuala. Permukaan lembut adalah penyerap bunyi yang baik. Bunyi yang terhasil akan
diserap oleh tuala dan bunyi yang perlahan terhasil.
The glass is covered with a towel. Soft surface is good absorber of sound. The sound produced is absorbed
10 by the towel and low sound is produced.
[3 markah/marks]
5 Abu mengetuk tala bunyi di dalam tiga bahan yang berbeza iaitu tepung, air susu dan udara. Jelaskan bahan
mana yang dapat memindahkan bunyi paling laju.
Abu hit the tuning fork in three different materials which are flour, milk and air. Explain which materials can
transfer the sound faster.
Tepung. Zarah-zarah tepung tersusun rapat berbanding zarah-zarah air susu dan udara. Zarah tepung
bergetar apabila menerima gelombang bunyi dan memindahkan pada zarah bersebelahan dengan cepat.
Flour. Flour particles are closely arrange compare to milk particle and air particles. Flour particles vibrate
when receive sound wave and transfer the sound to beside particles rapidly.
[3 markah/marks]
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 116
Modul Sains T2-Bab10 Book A_F.indd 116 25/10/2021 12:51 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB Bintang dan Galaksi dalam
CHAPTER
Alam Semesta
11 Stars and Galaxies in the Univers
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
11.1 Bintang dan Galaksi dalam Alam Semesta
Stars and Galaxies in the Universe
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
11.1.1 Berkomunikasi mengenai ciri objek angkasa. / Communicate the characteristics of objects in space.
SP
LS Membanding dan membezakan bintang (termasuk Matahari) berdasarkan ciri bintang dan hubung kaitkan dengan pemerhatian bintang
11.1.2
di Bumi. / Compare and contrast the characteristics of stars (including the Sun) and relate them to the observation of stars on Earth.
EMK Sains dan teknologi / Science and technology
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam.
Moral Value Realising that science is one way to understand nature.
A. Ciri-ciri Objek Angkasa Buku teks muka surat 240
Characteristics of Objects in Space Textbook page 240
1 Galaksi ialah kelompok ribuan atau jutaan bintang dalam susunan tertentu.
stars
Galaxy is a group of thousands or millions of in a particular arrangement. TP1
2 Galaksi mempunyai awan, gas dan debu yang disatukan oleh tarikan graviti antara
gas, clouds and dust
komponen-komponennya di mana bintang baru terhasil. / Galaxies have held
gravitational attraction
together by between their components where is new star is produced. TP1
3 Terdapat tiga jenis galaksi secara umumnya. Lengkapkan peta pokok di bawah berkenaan jenis-jenis galaksi.
There are basically three types of galaxies. Complete the tree map below according to the type of galaxies. TP2
Jenis-jenis galaksi / Types of galaxies
(a) Berpilin / Spiral (b) Elips / Elliptical (c) Tidak seragam / Irregular
• Teras berbentuk cakera dan ada
lengan berlingkar / Disc-shaped • Leper dan berbentuk • Tidak mempunyai
bentuk tetap
bola
core and has spiral-arms 11
lebih tua Flattened and ball-shaped No regular shape
• Bintang di teras
• Kebanyakannya bintang • Kebanyakannya bintang tua
daripada bintang di lengan / The
tua nebula
older dan / Mostly
stars in the core are
old old stars and nebula
than those in the arms Mostly stars
• nebula / nebula • Leper / Flattened attraction
• bentuk tetap / regular shape (b) Elips / Elliptical gas; clouds and dust; gravitational
(c) Tidak seragam / Irregular • lebih tua / older 2 awan; gas dan debu; tarikan graviti
• tua / old 3 (a) • lengan berlingkar / spiral-arms A. 1 bintang / stars
117 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab11 Book A_F.indd 117 25/10/2021 12:54 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
4 Sistem suria kita berada di dalam galaksi yang dipanggil Bima Sakti .
Milky Way
Our solar system is in a galaxy called . TP1
5 Terangkan ciri-ciri galaksi Bima Sakti ini dengan menggariskan jawapan yang betul.
Explain the characteristics of Milky Way galaxy by underline the correct answer. TP2
• Jenis galaksi adalah ( berpilin , elips , tidak seragam ).
Type of galaxy is ( spiral , elliptical , irregular ).
• Bilangan bintang di dalamnya: ( beratus-ratus , berjuta-juta , berbillion-
billion ) bintang.
Number of stars in it: ( hundreds , millions, billions ) of stars.
• Ia ( ada , tiada ) zarah-zarah debu yang boleh membentuk bintang baru.
It ( has , has no ) dust particles that can form new stars.
• Sistem suria terletak di ( tengah , pinggir ) Bima Sakti.
The solar system is situated at the ( middle , edge ) of the Milky Way.
hidrogen helium
6 Nebula ialah awan besar yang terdiri daripada debu dan gas (seperti dan ).
hydrogen helium
Nebula is big cloud made up of dust and gases (such as and ). TP2
7 Susunkan langkah-langkah kelahiran bintang di bawah mengikut urutan.
Arrange orderly the steps of birth of star below. TP2
Apabila saiz bintang semakin mengecil, tekanan gas semakin meningkat dan menyebabkan suhu
gas meningkat. 3
When the size of star becomes smaller, pressure of gas increases thus temperature of gas increases.
Apabila suhu gas mencecah 15 juta °C, gas hidrogen mula terbakar. 4
When the temperature of gas reaches 15 million °C, hydrogen gas starts burning.
Bintang terhasil daripada gumpalan gas dan nebula. 1
Star forms from a group of gas and nebula.
Pembelahan nuklear terjadi dan bintang terhasil. 5
Nuclear fission occurs and star is formed.
11
Graviti bintang menarik gas-gas tersebut dan memisahkan gas-gas tersebut dari nebula. 2
Star’s gravity attracts those gaseous and separate its from nebula.
• berbillion-billion / billions
3, 4, 1, 5, 2 7 • pinggir / edge 5 • berpilin / spiral
hidrogen; helium / hydrogen; helium 6 • ada / has A. 4 Bima Sakti / Milky Way
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 118
Modul Sains T2-Bab11 Book A_F.indd 118 25/10/2021 12:54 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
8 Berikut menerangkan apa yang terjadi apabila bintang mati. Lengkapkan carta alir berikut dengan
perkataan-perkataan yang diberi. / The following explains what happen when a star dies. Complete the
following flow chart with the words provided. TP1
kerdil putih gas hidrogen bintang neutron daya tarikan graviti
white dwarf hydrogen gas neutron star gravitational force
lebih besar mengecut lohong hitam
bigger shrinks black hole
Kitar Hidup Bintang
The Life Cycle of Stars
Pelakuran nuklear berhenti apabila gas hidrogen habis digunakan.
(i)
Nuclear fusions stop when the hydrogen gas is used up.
https://goo.gl/nCe55r
Teras bintang mengecut dan ia menjadi lebih panas.
(ii)
The core of the star shrinks and it becomes hotter.
Lapisan bintang yang paling luar mengembang dan menyejuk, menjadikan bintang lebih besar .
(iii)
The outermost layer of the star expands and cools, causing the star to become bigger .
Apabila lebih banyak lagi haba hilang, daya tarikan graviti yang kuat menarik bintang ke dalam.
(iv)
When more and more heat is lost, the increasingly strong gravitational force pulls the star inwards.
(v) Kejadian berdasarkan saiz asal bintang:
Events based on the original size of the star:
(a) Bintang bersaiz sederhana: Lapisan luar tersebar ke angkasa dan menjadi kerdil putih .
Medium-sized star: The outer layer disperses into space and the star becomes a white dwarf .
(b) Bintang yang besar: Bintang mengembang membentuk super raksasa. Kemudian, meletup dengan
cepat dalam supernova untuk membentuk bintang neutron .
Large star: The star expands to form a supergiant. It explodes quickly in a supernova to form a
neutron star .
(c) Bintang yang sangat besar: Bintang mengembang membentuk super raksasa. Kemudian, meletup 11
dengan cepat dalam supernova untuk membentuk lohong hitam .
Super-large star: The star expands to form a supergiant. It explodes in a supernova to form a
black hole .
(b) bintang neutron / neutron star (iii) lebih besar / bigger
(v) (a) kerdil putih / white dwarf (ii) mengecut / shrinks
(c) lohong hitam / black hole (iv) daya tarikan graviti / gravitational force A. 8 (i) gas hidrogen / hydrogen gas
119 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab11 Book A_F.indd 119 25/10/2021 12:54 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
9 Rajah di bawah menunjukkan kelahiran dan kematian bintang. Labelkan rajah berdasarkan perkataan yang
diberi. / The diagram below shows the birth and death of star. Label the diagram using the words below. TP1
Kerdil putih Bintang neutron Nebula Super raksasa Raksasa merah Lohong hitam Supernova
White dwarf Neutron star Nebula Supergiant Red giant Black hole Supernova
Bintang saiz Raksasa merah (b) Kerdil putih
sederhana Red giant White dwarf
Medium-sized star
Bintang besar Raksasa merah (c) Super raksasa Supernova (d) Bintang neutron
Large star Red giant Supergiant Supernova Neutron star
(a) Nebula
Nebula
Bintang super (e) Raksasa merah Super raksasa (f) Supernova (g) Lohong hitam
besar Red giant Supergiant Supernova Black hole
Super-large star
10 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah tentang perbandingan saiz relatif antara Bumi, planet, sistem suria, galaksi Bima
Sakti dan alam semesta.
Complete the table below on comparison of the relative size of the Earth, the planet, the solar system, the Milky
Way and the universe. TP2
Objek angkasa Saiz relatif Objek angkasa Saiz relatif
Space object Relative size Space object Relative size
(a) Bumi / Earth 12 756 km (h) Neptun / Neptune 155 600 km
(b) Utarid / Mercury 15 329 km (i) Sistem suria
4.503 billion km
Solar system
(c) Zuhrah / Venus 38 025 km
100 000 tahun cahaya
100 000 light years
(d) Marikh / Mars 21 297 km (j) Galaksi Bima Sakti * 1 tahun cahaya
Milky Way galaxy 1 light years
(e) Musytari / Jupiter 439 264 km 9.46 × 1012 km
=
11 (f) Zuhal / Saturn 365 882 km
14.5 billion tahun
(k) Alam semesta
cahaya
(g) Uranus / Uranus 159 354 km Universe
14.5 billion light years
439 264 km (e) (f) Supernova / Supernova
21 297 km (d) (e) Raksasa merah / Red giant
9.46 × 1012 km (j) 38 025 km (c) (d) Bintang neutron / Neutron star
155 600 km (h) 15 329 km (b) (c) Super raksasa / Supergiant
159 354 km (g) 12 756 km 10 (a) (b) Kerdil putih White dwarf
365 882 km (f) Lohong hitam / Black hole (g) 9 (a) Nebula / Nebula
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 120
Modul Sains T2-Bab11 Book A_F.indd 120 25/10/2021 12:54 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Buku teks muka surat 242
B. Bintang / Stars Textbook page 242
Lengkapkan jadual di bawah tentang ciri-ciri pengelasan bintang.
Complete the table below on the characteristics of stars.
Ciri-ciri Penjelasan
Characteristics Explanation
1 Suhu / Temperature <3 500 K hingga / to >25 000 K
2 Jarak / Distance >149 680 000 km
Bergantung pada saiz, jarak dari Bumi dan suhu permukaan.
3 Kecerahan / Brightness
Depends on their size, distance from the Earth and the surface temperature.
Semakin panas
Merah, Jingga, Kuning, Kuning-putih, Putih, Putih-kebiruan, Biru
4 Warna / Colour
Hotter
Red, Orange, Yellow, Yellowish-white, White, Bluish-white, Blue
Paling besar ( super raksasa ), besar ( raksasa ), kecil ( kerdil )
5 Saiz / Size
Really big ( supergiant ), big ( giant ), small ( dwarf )
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Antara berikut, galaksi yang manakah berbentuk 3 Rajah 1 menunjukkan kelahiran dan kematian suatu
Bima Sakti? bintang.
Which of the following galaxies is the Milky Way? Diagram 1 shows the birth and the death of a star.
A C
Bintang besar Raksasa merah X Supernova Bintang neutron
Large star Red giant Supernova Neutron star
B D
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
Nyatakan X.
State X.
A Raksasa putih 11
White giant
2 Nebula ialah awan besar yang terdiri daripada B Kerdil putih
Nebula is a big cloud made up of White dwarf
A hidrogen dan oksigen / hydrogen and oxygen C Super raksasa
B hidrogen dan helium / hydrogen and helium Supergiant
C oksigen dan helium / oxygen and helium D Super kerdil
D oksigen dan nitrogen / oxygen and nitrogen Super dwarf
super raksasa; raksasa; kerdil / supergiant; giant; dwarf 5 B. 4 Semakin panas / Hotter
121 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab11 Book A_F.indd 121 25/10/2021 12:54 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
1 Teori Big Bang merupakan teori saintifik yang menyatakan alam semesta muncul dari keadaan yang sangat
tumpat dan panas lebih kurang 13.7 billion tahun dahulu. Alam semesta telah mengembang ke satu saiz yang
tidak dapat dibayangkan dan terlalu sejuk untuk didiami. Dalam alam semesta terdapat lebih 30 jenis galaksi
yang mana setiap galaksi mempunyai lebih 100 000 bintang.
Big Bang theory is a scientific theory that states the universe comes from a very dense and hot state about
13.7 billion years ago. The universe has expanded to a size that cannot be imagined and too cold to live. In the
universe there are over 30 types of galaxies where each galaxy has over 100 000 stars.
(a) Apakah galaksi?
What is galaxy?
Galaksi merupakan kumpulan bintang-bintang yang terdapat dalam alam semesta.
Galaxy is a group of stars in a universe.
[1 markah/mark]
(b)
Sistem suria kita terletak dalam galaksi Bima Sakti. Nyatakan jenis galaksi Bima Sakti dan bilangan planet
yang terdapat dalam sistem suria.
Our solar system is located in Milky Way. State the type of the Milky Way galaxy and the number of planets
in the solar system.
Berpilin. 8 buah planet.
Spiral. 8 planets.
[2 markah/marks]
(c) Jadual di bawah menunjukkan perbandingan anggaran relatif bagi diameter, jarak dan jisim setiap planet.
(bukan menunjukkan nilai sebenar)
The table below shows a relative approximation of the diameter, distance and the mass of each planet. (not
showing real values)
Planet Diameter (cm) Jarak dari Matahari (cm) Jisim (g atau kg)
Planet Diameter (cm) Distance from Sun (cm) Mass (g or kg)
Utarid / Mercury 1.9 0.10 1.7 g
Zuhrah / Venus 4.7 0.18 25.6 g
Bumi / Earth 5.0 0.25 31.4 g
Marikh / Mars 2.7 0.38 3.4 g
Musytari / Jupiter 56.8 1.32 10.0 kg
Zuhal / Saturn 47.2 2.42 2.99 kg
Uranus / Uranus 20.0 4.87 0.46 kg
Neptun / Neptune 19.7 7.61 0.54 kg
11
(i) Nyatakan dua pasang planet yang diameternya hampir sama.
State two pairs of planet that have almost the same diameter.
Utarid dan Marikh / Mercury and Mars
Zuhrah dan Bumi / Venus and Earth
[2 markah/marks]
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 122
Modul Sains T2-Bab11 Book A_F.indd 122 25/10/2021 12:54 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(ii) Planet manakah yang mungkin mempunyai hidupan seperti Bumi? Wajarkan jawapan anda.
Which planet has living organism such as Earth? Justify your answer.
Zuhrah. Kerana mempunyai ciri-ciri yang hampir sama dengan Bumi.
Venus. Because it has characteristics that are almost same as the Earth.
[2 markah/marks]
2 Rajah berikut menunjukkan jenis-jenis galaksi. / The diagram below shows type of galaxies.
Jenis galaksi / Types of galaxies
i. Tidak seragam / Irregular ii. Berpilin / Spiral iii. Elips / Elliptical
(a) Namakan jenis-jenis galaksi tersebut.
Name the type of galaxies.
[3 markah/marks]
(b) Terangkan jenis galaksi galaksi 2(a)(ii).
Explain type of galaxy at 2(a)(ii).
Galaksi berpilin dinamakan sempena struktur lingkaran yang memanjang dari pusat ke cakera galaksi.
Terdiri daripada cakera rata, berputar dan mengandungi bintang, gas dan habuk.
The spiral galaxy is named after a spherical structure extending from the centre to the galaxy disk. It consists
of a flat disk, rotating and consists of stars, gases, and dust.
[2 markah/marks]
(c) Nyatakan satu bintang yang terdapat di dalam galaksi.
Name a star in the galaxy.
Matahari / Sun
[1 markah/mark]
(d) Ramalkan jika kita terkeluar dari galaksi Bima Sakti, di mana kita akan berada?
Predict if we get out of the Milky Way galaxy, where will we be?
Jika kita terkeluar dari galaksi Bima Sakti, maka kita tidak akan langsung berada di galaksi lain tetapi
memasuki ruang antara galaksi. Hal ini terjadi karena jarak galaksi paling dekat dari Bima Sakti pun sangat
jauh. Galaksi yang dimaksud adalah Canis Major Dwarf, yang berjarak 250 000 tahun cahaya dari Bumi.
If we break out of the Milky Way galaxy, then we will not be directly in another galaxy but enter the space
between galaxies. This is because the closest galaxy distance from the Milky Way is so far away. The galaxy
11
is the Canis Major Dwarf, 250 000 light-years from Earth.
[4 markah/marks]
123 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab11 Book A_F.indd 123 25/10/2021 12:54 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Sistem Suria
12 Solar System
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
12.1 Sistem Suria
Solar Sistem
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Membandingkan jarak planet dalam sistem suria daripada Matahari dengan menggunakan astronomical unit (A.U) dan tahun cahaya.
12.1.1
SP Compare the distance between the Sun and the planets in the solar system using astronomical unit (A.U) and light years (ly).
LS Membina jadual untuk membanding dan membezakan antara planet Sistem Suria dengan Bumi.
12.1.2
Construct a table to compare and contrast the planets in the solar system and the Earth.
Meneroka hubungan yang mungkin berdasarkan ciri planet dan memberi penjelasan tentang hubungan tersebut termasuk anomali yang
12.1.3 mungkin wujud. / Explore the possible relationship based on the characteristics of the planets and explain the relationship including anomalies
that may arise.
Menaakul dan menganalogikan situasi hipotetikal berkaitan dengan Sistem Suria.
12.1.4
Reasoning and making analogies in hypothetical situations related to the solar system.
Menjustifikasi Bumi merupakan planet yang paling sesuai untuk kehidupan berdasarkan data tentang Bumi.
12.1.5
Justify why the Earth is the most ideal planet for life based on data collected.
EMK Kelestarian alam sekitar / Nature preservation
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam
Moral Value Realizing that science is one way to understand nature
A. Jarak antara Planet-planet daripada Matahari Buku teks muka surat 252
Distance of the Planets from the Sun Textbook page 252
1 Lengkapkan rajah di bawah: / Complete the diagram below: TP1
(vii) Uranus
Uranus
(viii) Neptun
Neptune
(vi) Zuhal
(iv) Marikh Saturn
Mars
Matahari
Sun
(v) Musytari
Jupiter
(iii) Bumi
Earth
(ii) Zuhrah
(i) Utarid Venus
Mercury
12
(vi) Zuhal / Saturn (iii) Bumi / Earth
(viii) Neptun / Neptune (v) Musytari / Jupiter (ii) Zuhrah / Venus
(vii) Uranus / Uranus (iv) Marikh / Mars A. 1 (i) Utarid / Mercury
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 124
Modul Sains T2-Bab12 Book A_F.indd 124 25/10/2021 12:57 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Sistem Suria terdiri daripada Matahari dan objek astronominya yang terikat oleh
gravitinya dalam orbit sekelilingnya.
Solar system consists of Sun and astronomy objects which tie with its gravity
in its surrounding orbit . TP1
3 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah. / Complete the table below. TP1
1 tahun cahaya
1 light year
= 9.5 × 1012 km
1 A.U.
= 1.5 × 108 km
1 A.U.
Untuk menukar unit dalam unit astronomi (A.U.) dan km:
To convert unit between astronomi unit (A.U.) and km:
Jarak dalam km
Jarak (A.U.) =
1.5 × 108 km
Distance in km
Distance (A.U.) =
1.5 × 108 km
Untuk menukar unit antara tahun cahaya (ly) dan km:
To convert unit between light years (ly) and km:
Jarak dalam km
Jarak (ly) =
9.5 × 1012 km
Distance in km
Distance (ly) =
9.5 × 1012 km
Jarak planet dari Matahari
Distance the planets from the Sun
Planet
Planet Dalam A.U.
Dalam kilometer (km) Dalam tahun cahaya (ly) In A.U.
In kilometre (km) In light years (ly) (unit astronomi)
(astronomical unit)
(a) Utarid / Mercury 5.79 × 107 6.09 × 10–6 0.39
(b) Zuhrah / Venus 1.08 × 108 1.14 × 10–5 0.72
(c) Bumi / Earth 1.50 × 108 1.58 × 10–5 1.0
(d) Marikh / Mars 2.28 × 108 2.40 × 10–5 1.52
(e) Musytari / Jupiter 7.79 × 108 8.19 × 10–5 5.19
(f) Zuhal / Saturn 1.43 × 109 1.51 × 10–4 9.53
(g) Uranus / Uranus 2.87 × 109 3.02 × 10–4 19.13
12
(h) Neptun / Neptune 4.5 × 10 9
4.74 × 10 –4
30.0
(b) 1.08 × 108, 1.14 × 10–5
(h) 30.0 (e) 7.79 × 108, 8.19 × 10–5 3 (a) 6.09 × 10–6
(g) 2.87 × 109 (d) 2.28 × 108, 2.40 × 10–5 Solar system; Sun; graivity; orbit
(f) 1.51 × 10–4, 9.53 (c) 1.50 × 108 A. 1 Sistem Suria; Matahari; gravitinya; orbit
125 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab12 Book A_F.indd 125 25/10/2021 12:57 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B. Perbandingan dan Perbezaan antara Planet dalam Sistem Suria dengan Bumi Buku teks muka surat 254
Comparison and Difference between Planets of Solar System with Earth Textbook page 254
1 Lengkapkan data di bawah. / Complete the data below. TP2 Simulasi
Simulation
(a) (b)
Utarid / Mercury Zuhrah / Venus
–173 - 427 °C T = 462 °C
T =
4 879 km d = 12 104 km
d =
5.4 g cm–3 ρ = 5.2 g cm–3
(c) ρ = (e)
3.7 m s –2
g = 8.87 m s–2
g =
Bumi / Earth Musytari / Jupiter
T = –89.2 - 56.7 °C T = –108 °C
d = 12 756 km d = 142 984 km
• Suhu, T
ρ = 5.5 g cm–3 ρ = 1.3 g cm–3
Temperature, T
g = 9.8 m s–2 • Diameter, d g = 24.79 m s–2
Diameter, d
(d) • Ketumpatan, ρ (f)
Density, ρ
• Tarikan graviti, g
Gravitational force, g
Marikh / Mars Zuhal / Saturn
T = –143 - 35 °C T = –139 °C
d = 6 794 km d = 120 536 km
ρ = 3.9 g cm –3
(g) (h) ρ = 0.7 g cm–3
g = 3.71 m s–2 g = 10.44 m s–2
Uranus / Uranus Neptun / Neptune
T = –197.2 °C T = –201 °C
d = 51 118 km d = 49 528 km
ρ = 1.27 g cm–3 ρ = 1.6 g cm–3
12 g = 8.69 m s–2 g = 11.15 m s–2
B. 1 (a) –173 - 427 °C; 4 879 km; 5.4 g cm–3; 3.7 m s–2 (d) –143 - 35 °C; 6 794 km; 3.9 g cm–3; 3.71 m s–2 (g) –197.2 °C; 51 118cm; 1.27 g cm–3 km; 8.69 m s–2
(b) 12 104 km; 5.2 g cm–3; 8.87 m s–2 (e) –108 °C; 142 984 km; 1.3 g cm–3; 24.79 m s–2 (h) –201 °C; 49 528 km; 1.6 g cm–3; 11.15 m s–2
(c) –89.2 - 56.7 °C; 12 756 km; 5.5 g cm–3; 9.8 m s–2 (f) –139 °C; 120 536 km; 0.7 g cm–3; 10.44 m s–2
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 126
Modul Sains T2-Bab12 Book A_F.indd 126 25/10/2021 12:57 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
2 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah.
Complete the table below. TP2
Perbandingan dengan Bumi
Comparison with Earth
Masa
Halaju Bilangan
Planet Arah putaran mengelilingi
Lapisan Permukaan putaran pada satelit
Planet planet Matahari
atmosfera planet paksi (km/j) semula jadi
Rotation (hari di bumi)
Atmosphere Planet Speeds of Number of
direction of Time orbiting
layers surfaces rotation on natural
the planet the Sun
axis (km/h) satellites
(days on earth)
Tidak berwarna,
kawah diliputi
habuk halus,
(a) Barat ke
dataran, gunung,
Tiada atmosfera timur
lembah 88 10.89 0
Utarid No atmosphere West to east
No colour, crater
Mercury
covered with
fine dust, plains,
mountains, valleys
96.5% karbon
dioksida;
Berwarna jingga,
3.4% nitrogen;
berpasir dan
0.1% argon,
berbatu, dataran-
helium, neon,
dataran besar,
(b) sulfur dioksida, Timur ke
gunung berapi,
wap air barat
kawah yang luas 224.7 6.52 0
Zuhrah 96.5% carbon East to west
Orange colour,
Venus dioxide;
sandy and rocky,
3.4% nitrogen;
large plains,
0.1% argon,
volcanoes, broad
helium, neon,
craters
sulphur dioxide,
water vapour
78% nitrogen;
21% oksigen;
0.97% gas nadir
dan bahan- 71% air dan 29%
bahan lain; daratan (dataran,
(c) 0.03% karbon gunung dan Barat ke
dioksida gunung berapi) timur 365 1 674.4 1
Bumi 78% nitrogen; 71% water and West to east
Earth oxygen; 29% land (plains,
0.97% inert mountains and
gas and other volcanoes)
substances;
0.03% carbon
dioxide
12
(c) Barat ke timur; 365 / West to east; 365 (b) Timur ke barat / East to west B. 2 (a)
Barat ke timur / West to east
127 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab12 Book A_F.indd 127 25/10/2021 12:57 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
96% karbon
dioksida; Berwarna
1.9% nitrogen; kemerahan,
1.9% argon; berpasir dan
0.2% oksigen, berbatu, dataran-
(d) karbon dataran besar, Barat ke
monoksida gunung berapi, timur 687 868.2 2
Marikh 96% carbon kawah yang luas West to east
Mars dioxide; Reddish colour,
1.9% nitrogen; sandy and rocky,
1.9% argon; large plains,
0.2% oxygen, volcanoes, broad
carbon craters
monoxide
89.6% hidrogen;
10.1% helium;
0.3% metana,
Tiada permukaan
ammonia,
(e) yang keras. Hanya Barat ke
etana, air
dilitupi gas. timur
89.6% 4 343.5 45 300 67
Musytari No hard surface. West to east
hydrogen;
Jupiter Only covered with
10.1% helium;
gas.
0.3% methane,
ammonia,
ethane, water
96% hidrogen;
3% helium;
0.4% metana, Tiada permukaan
(f) ammonia, yang keras. Hanya Barat ke
etana, air dilitupi gas. timur 10 767.5 35 500 62
Zuhal 96% hydrogen; No hard surface. West to east
Saturn 3% helium; Only covered with
0.4% methane, gas.
ammonia,
ethane, water
83.3% hidrogen; Tiada permukaan
(g) 15.5% helium; yang keras. Hanya
2.4% metana dilitupi gas. Pada sisinya
On its side 30 660 9 320 27
Uranus 83.3% hydrogen; No hard surface.
Uranus 15.5% helium; Only covered with
2.4% methane gas.
80% hidrogen;
19% helium; Tiada permukaan
(h) 0.1% metana, yang keras. Hanya Barat ke
etana dilitupi gas. timur 60 152 9 660 14
Neptun 80% hydrogen; No hard surface. West to east
Neptune 19% helium; Only covered with
12 0.1% methane,
ethane
gas.
(g) Pada sisinya / On its side (e) Barat ke timur / West to east
(h) Barat ke timur / West to east (f) Barat ke timur / West to east B 2 (d) Barat ke timur / West to east
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 128
Modul Sains T2-Bab12 Book A_F.indd 128 25/10/2021 12:57 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
C. Hubungan Berdasarkan Ciri-ciri Planet Buku teks muka surat 258
Relationships Based on Characteristics of Planets Textbook page 258
1 Hubungan antara suhu planet dengan Matahari.
Relationship between temperatures of the planets with the Sun. TP2
(a) Planet yang tiada atmosfera: / Planet without atmosphere:
Utarid / Mercury:
– Sinaran Matahari secara terus ./ Direct Sun radiation.
–
Bahagian yang menghadap Matahari sangat panas (melebihi 427 °C).
Side facing the Sun is very hot (more than 427 °C).
– Bahagian yang gelap sangat sejuk (sehingga –173 °C).
Dark side is very cold (up to –173 °C).
(b) Planet yang mempunyai atmosfera / Planet with atmosphere:
(i) Bumi / Earth:
– Awan memantulkan sinaran Matahari ke angkasa lepas.
Clouds reflects Sun’s rays to the outer space.
– Atmosfera memerangkap sebahagian haba disebabkan oleh kesan rumah hijau .
Atmosphere traps some heat because of green house effect .
(ii) Zuhrah / Venus:
– Awan tebal memantulkan sinaran Matahari ke angkasa lepas.
Thick cloud reflects Sun’s rays to outer space.
– Atmosfera yang terdiri daripada gas karbon dioksida menyebabkan kesan rumah hijau .
Atmosphere that consist of carbon dioxide gas cause green house effect .
– Suhu permukaan boleh mencapai 462 °C. / Surface temperature can reach 462 °C.
(iii) Marikh / Mars:
– Tekanan permukaan yang sangat rendah memberi kesan pada suhu permukaan
(–143 °C hingga 35 °C).
Very low surface pressure affects the surface temperature (–143 °C to 35 °C).
(c) Planet gergasi / Giant planets:
Musytari, Zuhal, Uranus dan Neptun mempunyai permukaan dilitupi gas dan menerima sinaran Matahari
yang sedikit . Suhu permukaan adalah sangat rendah . / Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
have gas-filled surfaces and receive a little Sun rays. Surface temperature is very low .
2 Hubungan antara ketumpatan dengan tarikan graviti.
Relationship between density with gravitational attraction.
Tarikan graviti di permukaan sesuatu planet dipengaruhi oleh jisim dan ketumpatan planet.
The gravitational attraction on the surface of a planet is affected by mass and density
of the planet. TP2
3 Hubungan jarak, masa dan kelajuan / Relationship between distance, time and speed
Semakin jauh jarak planet dari Matahari, semakin banyak masa diperlukan untuk mengelilingi
Matahari dalam satu orbit. 12
The futher the distance of the planet from the Sun, the more time taken to orbit the Sun. TP2
rendah / low (iii) (b) (i) - memantulkan / reflects
3 banyak / more - kesan rumah hijau / green house effect - gelap / Dark
2 jisim; ketumpatan / mass; density - memantulkan / reflects (ii) - menghadap / facing
(c) sedikit; rendah / a little; low - kesan rumah hijau / green house effect C 1 (a) - terus / direct
129 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab12 Book A_F.indd 129 25/10/2021 12:57 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
D. Situasi Hipotetikal Berkaitan dengan Sistem Suria Buku teks muka surat 260
Hypothetical Situations Related to the Solar System Textbook page 260
Pembelajaran berasaskan penyelesaian masalah Apa akan berlaku sekiranya putaran Bumi terhenti?
Problem solving based learning What will happen if the Earth stops rotating? TP5
1. Sebahagian Bumi hanya mengalami siang dan 2. Bahagian Bumi yang menghadap Matahari akan
sebahagian Bumi hanya mengalami malam. menjadi kawasan gurun.
Part of the Earth only experiences day and part of Part of the Earth that faces the Sun will become
the Earth only experiences night. desert.
4. Suhu bahagian Bumi yang tidak disinari Matahari
3. Paras air laut meningkat.
sangat dingin. / Temperature on the Earth part
Sea level increases.
that not iluminated by the Sun are very cold.
5. Apakah satelit semula jadi? / What is natural satellite? TP1
Satelit semula jadi ialah jasad yang mengelilingi planet pada orbitnya sendiri.
Natural satellite is a body that orbiting planets on its own orbits.
Pembelajaran Berasaskan Projek: Bentuk Bumi / Project Based Learning: Earth's Shape
Arahan / Instructions:
Secara berkumpulan, bincangkan situasi-situasi berikut: / In group, discuss the following situations:
Sekiranya anda berada di Bulan, / If you are at the Moon,
1 Terangkan pemerhatian anda tentang bentuk Bumi. / Explain your observation about the Earth’s shape. TP4
2 Adakah Bumi kelihatan mempunyai fasa? / Is the Earth’s look having phase? TP4
Sediakan persembahan multimedia. / Prepare multimedia presentation.
Borang penilaian boleh didapati pada halaman hadapan buku. / Assesment form can be obtained on the front page.
E. Bumi Merupakan Planet Paling Sesuai Untuk Hidupan Buku teks muka surat 260
Earth is the Most Suitable Planet for Living Things Textbook page 260
1 Lengkapkan rajah di bawah dengan menjustifikasi Bumi sesuai untuk didiami.
Complete the diagram by justify the Earth is the most suitable to live. TP2
(a) Kandungan oksigen yang (c) Sumber air yang banyak untuk
tinggi untuk proses respirasi. Gas di keperluan hidupan.
Sumber air
High oxygen contents for atmosfera Lots of water source for living
Water
respiration process. Gas in needs.
resources
atmosphere
Keadaan
(b) Julat suhu yang tidak terlalu Suhu permukaan (d) Permukaan yang sesuai untuk
panas atau sejuk. Temperature Condition of pelbagai hidupan sama ada laut
Temperature range that are dan darat. / Suitable surface for
surfaces
not too hot or too cold. variety of living either sea or land.
12
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
(d) Permukaan yang sesuai untuk pelbagai hidupan cold.
variety of living either sea or land. Lots of water source for living needs. Temperature range that are not too hot or too
sama ada laut dan darat. / Suitable surface for (c) Sumber air yang banyak untuk keperluan hidupan. E. 1 (b) Julat suhu yang tidak terlalu panas atau sejuk.
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 130
Modul Sains T2-Bab12 Book A_F.indd 130 25/10/2021 12:57 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan sistem suria. 2 1 tahun cahaya bersamaan dengan
Diagram 1 shows a solar system. 1 light year equals to
A 9.5 × 1010 km
B 9.5 × 1012 km
C 1.5 × 108 km
D 1.2 × 108 km
Z
Matahari 3 Bumi berputar dari barat ke timur. Antara berikut,
Sun yang manakah mempunyai arah putaran yang sama
dengan Bumi?
Y Earth rotates from west to east. Which of the
X following has the same rotation direction as the
Earth?
A Utarid, Zuhrah, Marikh
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1 Mercury, Venus, Mars
B Utarid, Zuhrah, Musytari
Namakan planet X, Y dan Z.
Mercury, Venus, Jupiter
Name the planets X, Y and Z.
C Utarid, Marikh, Musytari
X Y Z Mercury, Mars, Jupiter
D Zuhrah, Marikh, Musytari
A Utarid Zuhal Bumi Venus, Mars, Jupiter
Mercury Saturn Earth
4 Antara berikut, planet manakah yang tidak
B Zuhal Utarid Bumi mempunyai satelit semula jadi?
Saturn Mercury Earth Which of the following planets does not have
C Zuhal Bumi Utarid natural satellites?
Saturn Earth Mercury A Utarid / Mercury
B Bumi / Earth
D Utarid Bumi Zuhal C Marikh / Mars
Mercury Earth Saturn D Uranus / Uranus
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
1 (a) Namakan dua planet yang mempunyai permukaan yang sangat keras dan berbatu dalam sistem suria.
Angkasawan mengatakan bahawa mereka boleh berjalan di atas permukaan planet-planet ini.
Name two planets which have hard and rocky surfaces. Astronauts said that they can walk on the surfaces
of these planets.
Zuhrah dan Marikh / Venus and Mars
[2 markah/marks]
(b) Peningkatan bilangan penduduk di Bumi menyebabkan kehabisan bahan-bahan seperti bahan api fosil. Untuk
menampung keperluan penduduk, bolehkah manusia berhijrah ke planet lain? Wajarkan jawapan anda.
The increase number of people on the Earth will cause the depletion of resources such as fossil fuel. To
accommodate the needs of the population, is it possible for human to live in other planets? Justify your answer.
– Planet lain tidak sesuai untuk didiami. / Other planets are not suitable to live.
– Kebanyakannya tidak mengandungi oksigen. / Mostly do not have oxygen. Ekstra / Extra 12
– Contohnya Marikh dipenuhi dengan gas karbon dioksida.
For example, Mars is filled with carbon dioxide.
– Ia tidak sesuai untuk proses kehidupan manusia. / It is not suitable for living process of human
[4 markah/marks]
131 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab12 Book A_F.indd 131 25/10/2021 12:57 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
BAB
CHAPTER Meteoroid, Asteroid dan Komet
13 Meteoroids, Asteroids and Comets
LATIHAN BERKEMAHIRAN / SKILL-BASED ACTIVITIES
13.1 Jasad Lain dalam Sistem Suria iaitu Meteoroid, Asteroid dan Komet
Other Objects in the Solar System, such as Meteoroids, Asteroids and Comets
K.Kejayaan / S.Criteria
Berkomunikasi tentang jasad lain dalam sistem suria iaitu meteoroid, asteroid dan komet.
13.1.1
SP Communicate on other objects in the solar system, such as meteoroids, asteroids and comets.
LS Membincangkan pergerakan meteoroid, asteroid dan komet dan kesannya terhadap Bumi berdasarkan data.
13.1.2
Discuss the movements of meteroids, asteroids and comets and their effects on the Earth based on data.
Menjana idea bagaimana mengurangkan atau mengelakkan kemungkinan berlakunya perlanggaran asteroid dengan Bumi.
13.1.3
Generate ideas on how to reduce or prevent the possibility of asteroids colliding with the Earth.
EMK Kelestarian alam sekitar / Nature preservation
Nilai Murni Menyedari bahawa sains merupakan salah satu cara untuk memahami alam
Moral Value Realising that science is one way to understand nature
A. Meteoroid, Asteroid dan Komet Buku teks muka surat 270
Meteoroids, Asteroids and Comets Textbook page 270
1 Isikan tempat kosong dengan jawapan yang betul tentang meteoroid, asteroid dan komet.
Fill in the blanks with the correct answer about meteoroid, asteroid and comet. TP2
(a) Meteoroid – Sebuah objek padat yang bergerak di angkasa.
Meteoroid – Terbina daripada batuan dan logam seperti besi dan nikel.
– Ukurannya adalah lebih kecil daripada asteroid dan lebih besar daripada
sebuah atom atau molekul (saiznya antara 10 μm hingga 1 m).
0
– Suhu meteoroid di angkasa lepas = °C
42
– Kelajuan adalah berbeza-beza. Paling laju adalah km s–1
– A compact object which moving in space.
– Built from rocks and metals such as iron and nickel.
– Its measurement is smaller than asteroid and bigger than an atom or molecule
(size between 10 μm to 1 m).
0
– Meteoroid temperature in outer space = °C
42
– Speeds are different. The fastest is km s–1
42 0 A 1
13
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 132
Modul Sains T2-Bab13 Book A_F.indd 132 25/10/2021 12:59 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
(b) Asteroid Matahari
– Objek besar yang mengelilingi .
Asteroid besi nikel
– Terbina daripada batuan dan logam seperti dan .
lebih kecil
– Saiz yang daripada planet (saiznya dari 1 m hingga 1 000
km).
jalur asteroid
– Membentuk di antara orbit planet Marikh dan Musytari.
– Suhu permukaan = -73 °C
– Kelajuan purata = 25 km s–1
– Big objects which move around the sun .
– Built from rocks and metals such as iron and nickel .
smaller
– Its size is than planet (size ranging from 1 m to 1 000 km).
asteroid belts
– Forming between orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
-73
– Surface temperature = °C
25
– Average speed = km s–1
(c) Komet kepala ekor
– Terdiri daripada dua bahagian, iaitu dan .
Comet gas ais debu
– Gumpalan , dan yang
mengelilingi Matahari.
– Komet mungkin jatuh ke Bumi, Bulan atau planet-planet lain jika ditarik oleh
graviti
.
elips
– Mempunyai orbit yang berbentuk .
10 70
– Purata julat kelajuan = km s–1 hingga km s–1
head tail
– Consists of two parts, and .
gas ice dust
– Blobs of , and that surround
the Sun.
– The comets may fall to the Earth, Moon or other planets if they are pulled by
gravity
.
eliptical
– Have an orbit.
10 70
– Average speed range = km s–1 to km s–1
gravity; eliptical; 10, 70 -73; 25
13
head; tail; gas; ice; dust sun; iron; nickel; smaller; asteroid belts;
graviti; elips ; 10; 70 jalur asteroid; -73; 25
kepala; ekor; gas; ais; debu (c) Matahari; besi; nikel; lebih kecil; A. 1 (b)
133 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab13 Book A_F.indd 133 25/10/2021 12:59 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
B. Pergerakan Meteoroid, Asteroid dan Komet Buku teks muka surat 272
Movements of Meteoroid, Asteroid and Comet Textbook page 272
1 Lengkapkan peta alir di bawah berkenaan pergerakan meteoroid.
Complete the flow map below on movement of meteoroid. TP2
atmosfera tinggi
(a) Meteoroid memasuki Bumi pada kelajuan disebabkan oleh daya tarikan
geseran atmosphere
graviti dan menghasilkan yang tinggi. / Meteoroids enter the Earth at
high friction
speed due to gravitational attraction and produces high .
(b) Jalur cahaya yang panjang dan halus dipanggil meteor terhasil daripada ketulan jisim angkasa
meteors
lepas yang terbakar. / The long and smooth light paths called are derived from burning
masses of massive space.
(c) Apabila meteor memasuki Bumi dengan banyak pada satu masa, pancuran meteor berlaku.
meteor meteor shower
When the entered the Earth in large quantity at a time, a occurred.
(d) Jika meteoroid tidak terbakar dengan lengkap, serpihan ini akan menghentam permukaan Bumi dan
serpihan yang tertinggal selepas hentaman dikenali sebagai meteorit . Kawah terbentuk.
If the meteoroids are not completely burned, this fragment will hit the surface of the earth and the
meteorites Crater
fragments left behind after the impact are known as . is formed.
2 Isikan tempat kosong tentang pergerakan asteroid. / Fill in the blanks on movements of asteroids. TP2
(a) Asteroid berada dalam jalur asteroid
tetapi terdapat orbit asteroid yang berada di luar jalur
asteroid belt
seperti Apollo, Amor dan Aten. / Asteroids are in the but there are asteroids
that orbit out of the asteroid belts such as Apollo, Amor and Aten.
(b) Orbit-orbit di luar lingkaran asteroid boleh berhampiran atau bersilang dengan orbit Bumi.
intersect
Orbits outside the asteroid enclosure can be near or with Earth's orbit.
(c) Pada titik persilangan atau lintasan berhampiran orbit Bumi dan orbit asteroid, perlanggaran antara
asteroid dengan Bumi boleh berlaku.
collisions
At the intersections or trajectories point near the Earth's orbit and asteroid's orbit,
between asteroids and Earth can occur.
(d) Perlanggaran dengan asteroid bersaiz besar boleh menyebabkan kemusnahan hidupan Bumi.
destruction
A collision with a large size asteroid can cause the of life on Earth.
13
(d) kemusnahan / destruction 2 (a) jalur asteroid / asteroid belt (b) meteor / meteors
(c) perlanggaran / collisions (d) meteorit; Kawah / meteorites; Crater atmosphere; high; friction
(b) bersilang / intersect (c) meteor; pancuran meteor / meteor; meteor shower B 1 (a) atmosfera; tinggi; geseran
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 134
Modul Sains T2-Bab13 Book A_F.indd 134 25/10/2021 12:59 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
3 Isikan tempat kosong tentang pergerakan komet. / Fill in the blanks on movement of comets. TP2
(a) Apabila komet menghampiri Matahari, komet semakin laju , mencair dan
kelihatan seperti berekor panjang.
faster melts
When a comet approaches the Sun, the comet gets , and looks
like long-tailed.
(b) Tiupan angin suria dari Matahari menyebabkan ekor komet sentiasa menjauhi Matahari.
solar wind
The blows from the Sun causes the comet's tails always away from the Sun.
(c) Tarikan graviti planet luar yang kuat menyebabkan komet mudah terkeluar dari orbitnya.
gravitational
The strong attraction of outer planet causes comets to easily out of their orbit.
(d) Berisiko untuk berlanggar dengan Bumi pada kelajuan tinggi.
At risk of colliding with Earth at high speed.
Projek / Project
Arahan / Instructions:
1 Para saintis sejak sekian lama membuat penyelidikan bagi mencari kaedah untuk melindungi Bumi dari
dihentam asteroid dengan cara memperlambat atau mengubah lintasannya. Dalam kumpulan, rancang satu
persembahan multimedia mengenai fenomena perlanggaran asteroid dan jasad lain dengan Bumi. Dalam
pembentangan, anda juga perlu bincangkan:
(i) Kaedah yang dicadangkan oleh saintis.
(ii) Contoh kesan hentaman asteroid yang ada di Bumi.
For a long time scientists have done research to find out the methods to protect Earth from being hit
by asteroid through diverting or slowing their trajectory. In group, plan a multimedia presentation on the
phenomenon of asteroid collision and other objects with the Earth. In the presentation, you also need to
discuss:
(i) Methods proposed by scientists.
(ii) Examples of asteroid impact on Earth.
Refleksi Murid
Sila tandakan (✓)
Studentʼs
Please tick (✓)
Reflection Faham / Understand ( ) Kurang faham / Less understand ( ) Tidak faham / Do not understand ( )
13
(c) graviti / gravitational (b) angin suria / solar wind (a) laju; mencair / faster; melts 3
135 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
Modul Sains T2-Bab13 Book A_F.indd 135 25/10/2021 12:59 PM
SAINS TINGKATAN 2
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu objek terdapat dalam 2 Komet terhasil daripada
Sistem Suria. Comets come from
Diagram 1 shows an object in the Solar System. A gumpalan gas, ais dan air.
lumps of gas, ice and water.
B gumpalan gas, ais dan udara.
lumps of gas, ice and air.
C gumpalan gas, ais dan debu.
lumps of gas, ice and dust.
D gumpalan gas, air dan debu.
lumps of gas, water and dust.
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
Antara berikut, yang manakah merupakan ciri-ciri 3 Jalur cahaya yang panjang dan halus dipanggil
yang terdapat pada objek di atas? The long and streak of light is called
Which of the following is the characteristics found A meteoroid. / meteoroids.
in the above object? B meteor. / meteors.
A Bentuknya tidak teratur C asteroid. / asteroid.
Irregular shape D komet. / comet.
B Tidak mempunyai orbit sendiri
Does not have its own orbit 4 Namakan fenomena yang menyebabkan ekor
C Terbentuk dari serpihan komet atau asteroid komet sentiasa menjauhi Matahari. / Name the
Formed from comet or asteroid debris phenomenon causes the comet's tails to stay away
D Ketulan batu atau logam kecil yang terapung- from the Sun.
apung dalam Sistem Suria A Angin suria / Solar wind
Small pebbles or metals floating in the Solar B Tompok matahari / Sunspot
System C Ribut suria / Solar storm
D Tarikan graviti / Gravitational attraction
Soalan Struktur / Structured Questions
1 Di permukaan Bulan terdapat banyak kawah-kawah besar akibat hentaman asteroid yang kerap. Mengapakah
Bumi terselamat dari hentaman asteroid secara kerap? Terangkan.
There are a lot of craters caused by frequent hits of asteroid on the Moon surface. Why does the Earth survive
from frequent asteroids impact?
Bumi dilindungi oleh lapisan atmosfera. Apabila asteroid tersasar dan memasuki atmosfera,
Bumi ia akan terbakar akibat geseran yang tinggi dengan atmosfera.
The Earth is protected by atmospheric layer. When the asteroid is strayed and entering the atmosphere of the
Earth it will be burned due to high friction with the atmosphere.
[3 markah/marks]
Ekstra / Extra
13
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 136
Modul Sains T2-Bab13 Book A_F.indd 136 25/10/2021 12:59 PM
You might also like
- Form 3 Science, Chapter 1Document47 pagesForm 3 Science, Chapter 1qq23586% (57)
- Science Notes Form 3Document20 pagesScience Notes Form 3Jasmine Kaur KaurNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Mathematics Revision KSSMDocument10 pagesForm 1 Mathematics Revision KSSMAsri BahariNo ratings yet
- Sce Form 2Document22 pagesSce Form 2williamkong123No ratings yet
- Modul F2 Science C2Document14 pagesModul F2 Science C2NorelyanaAli67% (3)
- Form 3 Science Chapter 1Document9 pagesForm 3 Science Chapter 1Mohamad Harith100% (2)
- Form 2 Chapter 2Document7 pagesForm 2 Chapter 2naza977579% (19)
- Softcopy Science Form 1 (Book A) BUKU NILAMDocument152 pagesSoftcopy Science Form 1 (Book A) BUKU NILAMVANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN Moe100% (1)
- Form 2 Chapter 6Document9 pagesForm 2 Chapter 6naza9775100% (7)
- Form 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsDocument11 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsCheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- Modul Science Form 2Document36 pagesModul Science Form 2Nur Atiah Daud94% (18)
- Form 3 Chapter 7Document15 pagesForm 3 Chapter 7naza9775100% (5)
- Biology p2 Form 4Document8 pagesBiology p2 Form 4Simbarashe HondoNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 pagesForm 3 Chapter 2Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Model Pt3Document30 pagesModel Pt3Sean Larson100% (4)
- F3 - CP3 - Consumer MathematicsDocument8 pagesF3 - CP3 - Consumer MathematicsAdelryeNo ratings yet
- Science PT3Document2 pagesScience PT3Veloo Gunasagaran80% (5)
- STF Science Module 1 (PMR) Chapter 1: Introduction To Science Section ADocument8 pagesSTF Science Module 1 (PMR) Chapter 1: Introduction To Science Section AzuaihaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Sciencenaza977583% (18)
- Science Form 2 Paper 1 Exam QuestionDocument10 pagesScience Form 2 Paper 1 Exam Questionchaiseng yongNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 6Document7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 6naza9775100% (6)
- Science Form 2Document6 pagesScience Form 2E's M ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chap 7 Exercise Complete)Document19 pagesScience Form 3 Chap 7 Exercise Complete)Henry Hoe100% (2)
- Science Paper1 MidYear2014 Form 2Document8 pagesScience Paper1 MidYear2014 Form 2Nor AdilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MatterDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Matternaza9775100% (2)
- F2 Chap 3 MCQDocument5 pagesF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Chemistry Form 4 Final ExamDocument11 pagesPaper 3 Chemistry Form 4 Final ExamMelissa Yates85% (13)
- f2 Chapter 2 PDFDocument9 pagesf2 Chapter 2 PDFNurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Form 1Document20 pagesScience Notes Form 1Farah Asnida0% (2)
- TRIAL PT3 SCIENCE 2019 SM Sains PerempuanDocument28 pagesTRIAL PT3 SCIENCE 2019 SM Sains PerempuanSyafiqah Redzuan100% (1)
- Form 3 Module Chapter 6 Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesForm 3 Module Chapter 6 Electricity and MagnetismJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Soalan pt3Document8 pagesSoalan pt3wkt6133No ratings yet
- Form 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesForm 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeJames Wong100% (1)
- Revision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Document21 pagesRevision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Shureen Baskaran100% (1)
- Malaysia Form 4 Physics Chapter 2Document1 pageMalaysia Form 4 Physics Chapter 2lakyn_267% (3)
- Sample Question For Chemistry Form 4 (SPM)Document2 pagesSample Question For Chemistry Form 4 (SPM)Sathish Sarma Sathianarayanan63% (8)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 1Document13 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 1huisin100% (1)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1-10Document16 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1-10Nur Atiah Daud57% (7)
- Exercise On Chapter 8 Science Form 3Document3 pagesExercise On Chapter 8 Science Form 3Sasi RekaNo ratings yet
- Module Heat (QUESTION BASED)Document21 pagesModule Heat (QUESTION BASED)Cart Kartika75% (4)
- Form 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Document6 pagesForm 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Kelvin50% (2)
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1 - 10Document14 pagesScience Form 2 Chapter 1 - 10Nur Atiah Daud88% (8)
- Quiz f3Document10 pagesQuiz f3Hafizah PakahNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITI f2 2017Document54 pagesBIODIVERSITI f2 2017farah6214100% (1)
- Exercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Document2 pagesExercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Nor Adila100% (1)
- Soalansubjektifmidexamt 3Document10 pagesSoalansubjektifmidexamt 3Cikgu Siti RohaizaNo ratings yet
- Module 06 Biodiversity - Significance and ConservationDocument24 pagesModule 06 Biodiversity - Significance and ConservationMarian Grace CanaNo ratings yet
- Bio 2Document17 pagesBio 2Vladimir TacmoNo ratings yet
- BC10TEXTCH02 Sec2Document23 pagesBC10TEXTCH02 Sec2Achintya SettNo ratings yet
- Textbook Examining Ecology Exercises in Environmental Biology and Conservation 1St Edition Paul A Rees Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Examining Ecology Exercises in Environmental Biology and Conservation 1St Edition Paul A Rees Ebook All Chapter PDFgerald.wolfe507100% (16)
- Kami Export - Cycles ActivityDocument9 pagesKami Export - Cycles ActivityEthan BompartNo ratings yet
- Borang Rumusan Standard Kandungan Sains Tingkatan 2 KSSM: 1. Maintenance AND Continuity of LifeDocument3 pagesBorang Rumusan Standard Kandungan Sains Tingkatan 2 KSSM: 1. Maintenance AND Continuity of LifeTecer WaniNo ratings yet
- Environmetal BiotechnologyDocument13 pagesEnvironmetal BiotechnologyNandini KotharkarNo ratings yet
- General EcologyDocument152 pagesGeneral Ecologykidest100% (2)
- PDFDocument7 pagesPDFBrijesh KarkarNo ratings yet
- 21616IIEDDocument48 pages21616IIEDDhanalakshmi BoorlagaddaNo ratings yet
- (Book) General EcologyDocument152 pages(Book) General EcologyAgatha HaselvinNo ratings yet
- Environmental EcologyDocument7 pagesEnvironmental EcologyDivya AryaNo ratings yet
- Quiz: Matter and Energy in Ecosystems: Read Each Question. Circle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesQuiz: Matter and Energy in Ecosystems: Read Each Question. Circle The Letter of The Correct Answerameersadik.27No ratings yet
- RPT Science F2 KSSM 2020Document20 pagesRPT Science F2 KSSM 2020intanNo ratings yet
- Softcopy Science Form 1 (Book A) BUKU NILAMDocument152 pagesSoftcopy Science Form 1 (Book A) BUKU NILAMVANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN Moe100% (1)
- Softcopy Sains Tingkatan 2 (Buku B)Document64 pagesSoftcopy Sains Tingkatan 2 (Buku B)VANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN Moe0% (1)
- Senarai Nama Murid Ikut KelasDocument7 pagesSenarai Nama Murid Ikut KelasVANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN MoeNo ratings yet
- 1 Cekap Analisis Item PSS GeografiDocument6 pages1 Cekap Analisis Item PSS GeografiVANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN MoeNo ratings yet
- The Rocket - : From East To WestDocument15 pagesThe Rocket - : From East To Westsushainkapoor photoNo ratings yet
- About These Lesson Plans and ResourcesDocument8 pagesAbout These Lesson Plans and ResourcesAhmer TariqNo ratings yet
- Compostion Notes Essay C1 and C2 Esolnet HellasDocument11 pagesCompostion Notes Essay C1 and C2 Esolnet HellasΚυριάκος Δινάκης100% (2)
- 5th National Report On Biological Biodiversity PDFDocument157 pages5th National Report On Biological Biodiversity PDFammend100% (2)
- 2022 Media Materiality ReportDocument17 pages2022 Media Materiality ReportMarcelogabrielfranNo ratings yet
- Seaweeds Australia Newsletter - Issue 3.2, Nov 2013Document6 pagesSeaweeds Australia Newsletter - Issue 3.2, Nov 2013Milkwood100% (2)
- Working For Dasuya ForestDocument271 pagesWorking For Dasuya ForestParimal AgrawalNo ratings yet
- What Is in A TangabDocument16 pagesWhat Is in A TangabOrange LemonNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessmnt Module 2 (Darlene Dayuha A8a56)Document2 pagesSelf-Assessmnt Module 2 (Darlene Dayuha A8a56)Darlene KrizianNo ratings yet
- Plenary II 1 - The Conservation and Management of Our Freshwater Ecosystems Rafael D. Guerrero IIIDocument14 pagesPlenary II 1 - The Conservation and Management of Our Freshwater Ecosystems Rafael D. Guerrero IIIFebwin Villaceran100% (1)
- Biodiversity of LianasDocument285 pagesBiodiversity of LianasWille Rmo BenNo ratings yet
- State of Plant Genetic Resources For Food and Agriculture in NigeriaDocument82 pagesState of Plant Genetic Resources For Food and Agriculture in NigeriaAle LlerenaNo ratings yet
- Nparks - Labrador Nature Reserve - Info Kit (6.6)Document26 pagesNparks - Labrador Nature Reserve - Info Kit (6.6)adrian kohNo ratings yet
- The Omnivores Dilemma-Chapter 2Document2 pagesThe Omnivores Dilemma-Chapter 2api-239466415No ratings yet
- MicofagosDocument80 pagesMicofagosJOSE FRANCISCO FRANCO NAVIANo ratings yet
- Linking The Sdgs and Gri: LegendDocument41 pagesLinking The Sdgs and Gri: LegendricardocubagNo ratings yet
- Impact of Armed Conflict On Environment in The State of Jammu and KashmirDocument12 pagesImpact of Armed Conflict On Environment in The State of Jammu and Kashmirproud of kashmir100% (1)
- Classification of Boreal Forest Ecosystem Goods and Services in FinlandDocument197 pagesClassification of Boreal Forest Ecosystem Goods and Services in FinlandSivamani SelvarajuNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment BFC 32403 Sem 2 20192020Document18 pagesIndividual Assignment BFC 32403 Sem 2 20192020abood buriahiNo ratings yet
- Molluscs in Mangroves: A Case Study: Prof. A. Shanmugam and Mrs. S. VairamaniDocument12 pagesMolluscs in Mangroves: A Case Study: Prof. A. Shanmugam and Mrs. S. VairamaniUsdiyantoNo ratings yet
- IiedDocument94 pagesIiedrexyben tuvieraNo ratings yet
- Why Biodiversity and The Interconnected Web of Life Are ImportantDocument3 pagesWhy Biodiversity and The Interconnected Web of Life Are ImportantAzmi AlsayesNo ratings yet
- NEET Chapter Wise Weightage 2021Document6 pagesNEET Chapter Wise Weightage 2021maxzoelNo ratings yet
- Topic 4. Biodiversity and Its Conservation (6 Marks) : Q. No. Option I Option II Option III Option IV Answer KeyDocument2 pagesTopic 4. Biodiversity and Its Conservation (6 Marks) : Q. No. Option I Option II Option III Option IV Answer KeysakshiNo ratings yet
- Ecological RestorationDocument12 pagesEcological RestorationDondon TayabanNo ratings yet
- Forestry Principles and ApplicationsDocument29 pagesForestry Principles and ApplicationsAkash Mahajan67% (3)
- Environment: Coral Reefs Climate ChangeDocument56 pagesEnvironment: Coral Reefs Climate ChangeFitra Wira HadinataNo ratings yet
- Mascher Et Al 2019Document6 pagesMascher Et Al 2019Caty ArenasNo ratings yet
- Onu 2Document30 pagesOnu 2Lenilson FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Schultheiss Et Al 2022, How Many Ants On EarthDocument9 pagesSchultheiss Et Al 2022, How Many Ants On EarthAviv SharonNo ratings yet