Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Monorails ES-14-403-20: Version No. 5.0 Page 1 of 29 Document Last Modified: 30 June 2014
Monorails ES-14-403-20: Version No. 5.0 Page 1 of 29 Document Last Modified: 30 June 2014
Uploaded by
Parthasarathi DalaiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Esd TR20.20 2016Document5 pagesEsd TR20.20 2016Sunseeker Nguyen0% (7)
- WBS For Wedding ProjectDocument1 pageWBS For Wedding ProjectKhushboo Katyayan50% (2)
- Activity Based Costing - Case StudyDocument8 pagesActivity Based Costing - Case StudyViksit Choudhary100% (1)
- Pamphlet 96 - Edition 5 - September 2017Document124 pagesPamphlet 96 - Edition 5 - September 2017中西文香100% (1)
- Pamphlet 88 - Edition 3 - March 2010Document44 pagesPamphlet 88 - Edition 3 - March 2010Jacques BlueqNo ratings yet
- Cap Bud ProbDocument9 pagesCap Bud ProbJulie Mark JocsonNo ratings yet
- Strength Graded Structural Timber - Square Edged Logs With Wane - SoftwoodDocument28 pagesStrength Graded Structural Timber - Square Edged Logs With Wane - SoftwoodNikolic DejanNo ratings yet
- 542935b Atys P M Nmo ENDocument76 pages542935b Atys P M Nmo ENb400013No ratings yet
- TR 512Document97 pagesTR 512RafnunNo ratings yet
- 20201103101151963Document90 pages20201103101151963long0200405No ratings yet
- User Manual Euro 4 Mod - Eng - Nc-2592Document189 pagesUser Manual Euro 4 Mod - Eng - Nc-2592Ricardo RONo ratings yet
- Pre Feasibility Study for Offshore Wind Farm Development in Gujarat-AnnotatedDocument186 pagesPre Feasibility Study for Offshore Wind Farm Development in Gujarat-AnnotatedRituraj Singh SujawatNo ratings yet
- Global India Aortic Valve Replacement Devices Market To 2030Document92 pagesGlobal India Aortic Valve Replacement Devices Market To 2030cvmentorgeraNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice For Buses 26102016Document27 pagesCode of Practice For Buses 26102016dmontoyaNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia-Djibouti Transport Corridor Project-RAP-Adama Awash Lot 1 (60km) Expressway Lot 1Document93 pagesEthiopia-Djibouti Transport Corridor Project-RAP-Adama Awash Lot 1 (60km) Expressway Lot 1Rediet meredNo ratings yet
- ZB - Tenant Handbook - Annex A - Tenant Fit-Out and Leasehold Improvements Manual - 2017Document51 pagesZB - Tenant Handbook - Annex A - Tenant Fit-Out and Leasehold Improvements Manual - 2017Mike TabaderoNo ratings yet
- Palm Valley International School, Meerut - MEP Concept Design Brief ReportDocument75 pagesPalm Valley International School, Meerut - MEP Concept Design Brief ReportArun Kumar GNo ratings yet
- Etag 032 Part 4 May 2013Document34 pagesEtag 032 Part 4 May 2013coolkaisyNo ratings yet
- AzSPU SSOW Procedure For Confined Space EntryDocument34 pagesAzSPU SSOW Procedure For Confined Space EntryAmir M. ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 299 GUIDANCE FOR REINFORCEMENT & SPLICING OF CAGES - FPS-splicing-and-sonic-10-07-20Document40 pages299 GUIDANCE FOR REINFORCEMENT & SPLICING OF CAGES - FPS-splicing-and-sonic-10-07-20gmpintorNo ratings yet
- EIA Chakdara ShamozaiDocument165 pagesEIA Chakdara ShamozaiFariaNo ratings yet
- TNRI Final Design Report R01Document48 pagesTNRI Final Design Report R01Bunyamin SelimogluNo ratings yet
- Cellenium 30Jr Service Manual Ver - 1.01Document63 pagesCellenium 30Jr Service Manual Ver - 1.01Jackson NjarambaNo ratings yet
- Atys P M Instruction Manual 2017-11-542935 enDocument78 pagesAtys P M Instruction Manual 2017-11-542935 enValdemar BarrosNo ratings yet
- Style ManualDocument42 pagesStyle Manualh_romeu_rsNo ratings yet
- BOMBA NEUMATICA ARGAL-ASTRA-EVO-DDE-Instruction-Manual-rev-11-2021Document58 pagesBOMBA NEUMATICA ARGAL-ASTRA-EVO-DDE-Instruction-Manual-rev-11-2021Jose Luis Ari AchahuiNo ratings yet
- ANSYS, Inc. Documentation ErrataDocument14 pagesANSYS, Inc. Documentation ErrataHiếu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- FPS Splicing and Sonic 09 04 20Document40 pagesFPS Splicing and Sonic 09 04 20Poh T KhoNo ratings yet
- H&M Group Requirements For Quality System: Textile ProductsDocument30 pagesH&M Group Requirements For Quality System: Textile Productssaidurtex100% (1)
- Hazop - Vide Exemplo ICIDocument248 pagesHazop - Vide Exemplo ICIHelton SantanaNo ratings yet
- Ume Ingepac Ef PB EngDocument270 pagesUme Ingepac Ef PB EngFelipe De NadaiNo ratings yet
- Pages From HM 27 Metering Systems Section 2 Guide To Gas Metering Systems Mar 2002Document9 pagesPages From HM 27 Metering Systems Section 2 Guide To Gas Metering Systems Mar 2002mounrNo ratings yet
- Api RP 1111 E5Document3 pagesApi RP 1111 E5Oğuzcan Şahin0% (1)
- AutoBatch UserManual Jan2018 PDFDocument78 pagesAutoBatch UserManual Jan2018 PDFHan ArifNo ratings yet
- Construction MethodologyDocument102 pagesConstruction MethodologyDagnachew TassewNo ratings yet
- FEASIBILITY STUDY OF MALAYSIA KEMAMAN WHARF PROJECT (FINALúDocument113 pagesFEASIBILITY STUDY OF MALAYSIA KEMAMAN WHARF PROJECT (FINALúatikahasfiworkNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Design Construction andDocument108 pagesOverview of The Design Construction andMoses Kiting'oNo ratings yet
- MANUAL SGI REV11 Iilzoz2Document45 pagesMANUAL SGI REV11 Iilzoz2LARLUI PATRICK TORRES OLIVARESNo ratings yet
- User Manual MRI 508Document76 pagesUser Manual MRI 508Firdaus YasinNo ratings yet
- Maintenance For Air ConDocument99 pagesMaintenance For Air ConMMTMNo ratings yet
- 45 ST WM 0002 Engineering Standards 2019Document47 pages45 ST WM 0002 Engineering Standards 2019chrisNo ratings yet
- EHS DOC 001 - LaboratorySafetyManualDocument94 pagesEHS DOC 001 - LaboratorySafetyManualankur_haldarNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Structural Master Plan - Norms and StandardsDocument30 pagesAddis Ababa Structural Master Plan - Norms and StandardsRobel WendwesenNo ratings yet
- 7-31k D 07252012 PDFDocument67 pages7-31k D 07252012 PDFerfan_nugroho9063No ratings yet
- Xdisp19.3 ManualDocument149 pagesXdisp19.3 ManualAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Value Engineering ManualDocument193 pagesValue Engineering Manualswetang prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Value Engineearing ManualDocument193 pagesValue Engineearing ManualWirya MuradNo ratings yet
- 1002910-40-SPE-ET-0002 - SubstationsDocument63 pages1002910-40-SPE-ET-0002 - SubstationsAMARPALNo ratings yet
- AORG351: Implementation of Tax Policy Reform in Uganda: The Case Study of Uganda Revenue Authority (URA)Document123 pagesAORG351: Implementation of Tax Policy Reform in Uganda: The Case Study of Uganda Revenue Authority (URA)Tatuh PerryNo ratings yet
- Booklet LSDocument100 pagesBooklet LSAbram SidabutarNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-08-14 at 12.33.02 PMDocument61 pagesScreenshot 2022-08-14 at 12.33.02 PMMahmoud AdlyNo ratings yet
- RFG 048597Document102 pagesRFG 048597Rister ZinnNo ratings yet
- Subsea Wet Gas Compressor Dynamics - TESISDocument118 pagesSubsea Wet Gas Compressor Dynamics - TESISVILLANUEVA_DANIEL2064No ratings yet
- Design Management ManualDocument70 pagesDesign Management ManualShanae RyderNo ratings yet
- AzSPU SSOW Procedure For ScaffoldingDocument20 pagesAzSPU SSOW Procedure For ScaffoldingAmir M. ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Vanne de Control Adoucisseur Fleck 9000-Sxt Im A enDocument110 pagesVanne de Control Adoucisseur Fleck 9000-Sxt Im A enEtienne NASALANDINo ratings yet
- Castellini C22 OM PDFDocument75 pagesCastellini C22 OM PDFHaitham AlbajawiNo ratings yet
- DAMAC SPM - (Rev 6 - 270122)Document223 pagesDAMAC SPM - (Rev 6 - 270122)Xtreme-DesignsNo ratings yet
- GRP Pipe Report-SudanDocument37 pagesGRP Pipe Report-Sudanlehmanwolf100% (1)
- Supra 850Document84 pagesSupra 850Dajmon DajmonNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet 9 - Recommnended Practices For Handling Chlorine Bulk Highway TransportDocument62 pagesPamphlet 9 - Recommnended Practices For Handling Chlorine Bulk Highway TransportJacques BlueqNo ratings yet
- Datastream - How To Search For ESG Data - July 2022Document17 pagesDatastream - How To Search For ESG Data - July 202224a4010600No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For A First Course in Differential Equations With Modeling Applications 10th EditionDocument23 pagesSolution Manual For A First Course in Differential Equations With Modeling Applications 10th Editiondisbenchcrang9xds100% (45)
- BSBHRM415 Assessment 3Document24 pagesBSBHRM415 Assessment 3Michael FelixNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management QB: Part - ADocument7 pagesMarketing Management QB: Part - ASe SathyaNo ratings yet
- Counterparty Credit Exposure and CVA - An Intergrated Approch (UBS)Document34 pagesCounterparty Credit Exposure and CVA - An Intergrated Approch (UBS)Mo MokNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: Performance Task # 1Document3 pagesBusiness Plan: Performance Task # 1Jan BrettNo ratings yet
- Effect of Advertisement On ConsumersDocument59 pagesEffect of Advertisement On Consumersvishal394% (49)
- Sugar Industry: Sugar Breaking Out of Bitter CyclesDocument53 pagesSugar Industry: Sugar Breaking Out of Bitter CyclesPrasun PandeyNo ratings yet
- IIFBM at 12 23Document13 pagesIIFBM at 12 23r.phaniKrishna krishnaNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy With Indian ExamplesDocument21 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy With Indian ExamplesSwetha Asokan60% (5)
- NG-018-XX-PNL-023030 - Rev03 UnsignedDocument26 pagesNG-018-XX-PNL-023030 - Rev03 UnsignedFolarin AyodejiNo ratings yet
- Gilat White Paper Cellular Cellular Backhaul Myths and FactsDocument13 pagesGilat White Paper Cellular Cellular Backhaul Myths and FactsAFF NO LIMITNo ratings yet
- Report On NMB Bank Limited: HIRE Verified WriterDocument24 pagesReport On NMB Bank Limited: HIRE Verified WriterSantosh ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MNGT-3711: Ethics and Social Responsibility in Business and SocietyDocument13 pagesAssignment 2 MNGT-3711: Ethics and Social Responsibility in Business and SocietySam rockzs0% (1)
- Qp-Luxm-Gs & SJDocument2 pagesQp-Luxm-Gs & SJRaksha StarNo ratings yet
- Question Paper - Mock AristoDocument33 pagesQuestion Paper - Mock AristoTONI POOH100% (1)
- Pfrs 13 Fair Value MeasurementDocument22 pagesPfrs 13 Fair Value MeasurementShane PasayloNo ratings yet
- STM PDFDocument184 pagesSTM PDFSANDHYA MISHRANo ratings yet
- Furniture ManufacturerDocument9 pagesFurniture ManufacturerUniversal PrideNo ratings yet
- Title:: MTP 36203 (Accounting For Manufacturing)Document17 pagesTitle:: MTP 36203 (Accounting For Manufacturing)Che Rosnor Che HaronNo ratings yet
- BH Tif08Document24 pagesBH Tif08Andres R. OlguinNo ratings yet
- Abrar Alam Electrical Foreman CVDocument2 pagesAbrar Alam Electrical Foreman CVGUDDUNo ratings yet
- Boarding PassDocument1 pageBoarding PassΓιωργος ΜουστακηςNo ratings yet
- 18-12-2023 09-22-39 1702884159 Dailynews PDFDocument24 pages18-12-2023 09-22-39 1702884159 Dailynews PDFCeles NubesNo ratings yet
- Company Management: Shruti Reddy, Upes SolDocument72 pagesCompany Management: Shruti Reddy, Upes Solvishal bagariaNo ratings yet
- 1988 Motorola Annual Report PDFDocument40 pages1988 Motorola Annual Report PDFmrinal1690No ratings yet
- ExxonMobil PD-5340Document2 pagesExxonMobil PD-5340蔡佾呈No ratings yet
Monorails ES-14-403-20: Version No. 5.0 Page 1 of 29 Document Last Modified: 30 June 2014
Monorails ES-14-403-20: Version No. 5.0 Page 1 of 29 Document Last Modified: 30 June 2014
Uploaded by
Parthasarathi DalaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Monorails ES-14-403-20: Version No. 5.0 Page 1 of 29 Document Last Modified: 30 June 2014
Monorails ES-14-403-20: Version No. 5.0 Page 1 of 29 Document Last Modified: 30 June 2014
Uploaded by
Parthasarathi DalaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
This is a Controlled Document that complies with
Wesfarmers Chemicals, Energy & Fertilisers formatting and Quality Control standards.
Please check that this is the latest available version before use.
Title: MONORAILS
Number: ES-14-403-20
Version Number: 5.0
Date Revised: 30 June 2014
Owner: Harish Chopra
Authoriser: Manoj Thakur
Reasons for Creating
or Amending Full Review of Document
Document
Actual Change Details: Standards Association of Australia list updated.
The word 'Superintendent' replaced with 'Responsible Officer'.
Section 7.4 and 18 has been updated.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. SCOPE ....................................................................................................................................... 4
2. PURPOSE .................................................................................................................................. 4
3. RESPONSIBILITY ................................................................................................................... 4
4. DEFINITION OF TERMS ....................................................................................................... 4
5. STANDARDS ............................................................................................................................ 5
6. OVERVIEW .............................................................................................................................. 9
6.1 DESIGN PHASE – FIGURE 1 (3 SHEETS) ...................................................................... 9
6.2 INSTALLATION PHASE – FIGURE 2 ............................................................................... 9
6.3 OPERATIONAL PHASE – FIGURE 3 .............................................................................. 10
7. BASIS OF DESIGN ................................................................................................................ 16
7.1 EXISTING MONORAIL OF UNKNOWN CAPACITY ................................................... 16
7.2 CONDITION OF EXISTING STEELWORK .................................................................... 16
7.3 DESIGN STANDARDS ..................................................................................................... 16
7.4 DESIGN .............................................................................................................................. 16
7.5 INDEPENDENT DESIGN REVIEW ................................................................................. 17
Version No. 5.0 Page 1 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
7.6 STATUTORY AUTHORITY APPROVAL ....................................................................... 17
8. DESIGN METHODS .............................................................................................................. 17
8.1 WORKING STRESS DESIGN METHOD ......................................................................... 17
8.2 LIMIT STATES METHOD ................................................................................................ 17
9. MONORAIL SECTION SIZE ............................................................................................... 17
9.1 SAFE LOAD / CAPACITY TABLES ................................................................................ 17
9.2 FLANGE THICKNESS ...................................................................................................... 17
9.3 WEB THICKNESS ............................................................................................................. 18
9.4 DEFLECTION LIMITS ...................................................................................................... 18
9.5 LONG SPAN MONORAIL BEAMS .................................................................................. 18
10. END STOP DESIGN............................................................................................................... 18
11. INDEPENDENT DESIGN REVIEW .................................................................................... 20
12. CALCULATIONS................................................................................................................... 20
12.1 DESIGN CALCULATIONS ............................................................................................... 20
12.2 INDEPENDENT DESIGN REVIEW ................................................................................. 20
13. APPROVAL BY STATUTORY AUTHORITY ................................................................... 21
14. MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT SELECTION ............................................................... 21
15. ELECTRICAL CONTROLS ................................................................................................. 21
16. HANDLING OF STRUCTURAL STEELWORK & EQUIPMENT ................................. 21
17. FABRICATION ...................................................................................................................... 21
18. WELDING ............................................................................................................................... 22
19. BOLTING ................................................................................................................................ 22
20. SITE MODIFICATIONS ....................................................................................................... 22
21. PROTECTIVE COATINGS .................................................................................................. 22
21.1 STRUCTURAL STEEL ...................................................................................................... 22
21.2 HOIST AND TROLLEY..................................................................................................... 22
21.3 BOLTS ................................................................................................................................ 23
22. INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................... 23
22.1 CIVIL / STRUCTURAL / MECHANICAL ........................................................................ 23
22.2 ELECTRICAL ..................................................................................................................... 23
23. IDENTIFICATION................................................................................................................. 23
23.1 BEAMS ............................................................................................................................... 24
23.2 HOIST AND TROLLEY..................................................................................................... 25
24. INSPECTION AND TESTING .............................................................................................. 25
24.1 WELD TESTING AND INSPECTION .............................................................................. 25
24.2 EXISTING STRUCTURAL STEELWORK INSPECTION .............................................. 25
24.3 NEW FABRICATED STEELWORK INSPECTION ......................................................... 26
24.4 INSPECTION DURING ERECTION ................................................................................. 26
Version No. 5.0 Page 2 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
24.5 COMMISSIONING ............................................................................................................ 26
24.6 INSPECTION DURING OPERATIONAL PHASE ........................................................... 27
25. RECORDS MANAGEMENT ................................................................................................ 29
25.1 AS - BUILT DRAWINGS .................................................................................................. 29
25.2 ENGINEERING PROJECT FILES ..................................................................................... 29
25.3 MAINTENANCE WORK ORDERS .................................................................................. 29
25.4 MONORAIL SYSTEM ANNUAL INSPECTION ............................................................. 29
FIGURES
Figure 1 Monorail Design Process Flow Diagram Sheet 1 of 3 11
Figure 2 Monorail Installation Process Flow Diagram 14
Figure 3 Monorail Maintenance Process Flow Diagram 15
Figure 4 Minimum Interference between Monorail and Trolley End Stops 19
TABLES
Table 1 Size of Monorail Beam Identification Markings 24
Version No. 5.0 Page 3 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
1. SCOPE
This Standard covers the minimum technical requirements for the design, approval, fabrication,
installation, testing and commissioning, preventative maintenance and inspection, and record
keeping of new and upgrades to existing monorails.
Existing structures shall be analysed in accordance with the criteria established in this Standard and
appropriate action taken, before upgrades to existing monorails are carried out or a new monorail is
installed in an existing structure.
Note: For electric hoists and motorised trolleys, this Standard is to be read in conjunction with
CSBP Engineering Standard Electric Hoists (ES-14-403-21).
2. PURPOSE
To ensure that all monorails in CSBP facilities are in compliance with WorkSafe WA regulations
and other relevant codes and practices and that the company’s requirements for operability, safety
and reliability are assured at all times.
3. RESPONSIBILITY
During the development phase it is the responsibility of the Responsible Officer to ensure that all
approvals have been obtained before the Works are carried out and that the requirements of this
Standard are adhered to.
Following completion of project handover, it is the responsibility of each business unit to ensure
that their monorails remain compliant with this Standard and are safe to use.
4. DEFINITION OF TERMS
Contractor/Vendor
The company that provides the equipment and services needed.
Sub-Contractor
A third party to be employed by the Contractor/Vendor, who has been approved by the Responsible
Officer.
Responsible Officer
Functional title for the Wesfarmers CSBP Limited Officer, or authorised representative,
responsible for the development and implementation of the Works, including liaison with and
obtaining internal and external approvals from appropriate personnel, statutory authorities etc.
CSBP
Wesfarmers CSBP Limited.
Version No. 5.0 Page 4 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
Works
The scope of work that a Contractor is or may be required to execute under an agreement including
variations and remedial work.
Monorail
Light industrial crane comprising a beam, a trolley and a hoisting device. The trolley travels along
the bottom flange of the beam.
Jib Crane
A cantilevered monorail, that is pivoted about a vertical axis at the supported end.
Verification
Examination of objective evidence to determine conformity with stated requirements for that
activity.
5. STANDARDS
The Contractor shall perform the Works in accordance with this Standard, the latest issue of
referenced standards and Contractor regulations for on-site work. Should there be a conflict
between the Works, Statutory Requirements and the Standards, the Contractor shall notify the
Responsible Officer in writing for resolution. In general, the most stringent requirement will
prevail.
CSBP Engineering Standards
ES-14-101-02 Drawing Management
ES-14-101-03 Drawing Preparation
ES-14-101-04 Drawing Numbering
ES-14-101-06 Equipment Numbering System
ES-14-102-09 Labels & Signs: Plant and Equipment
ES-14-102-12 Protective Coatings
ES-14-202-10 Concrete
ES-14-202-14 Grouting
ES-14-302-01 Fabrication of Structural Steelwork
ES-14-302-02 Erection of Structural Steelwork
ES-14-401-01 Mechanical Preferred Equipment
ES-14-402-01 Mechanical Equipment Design, Supply and Installation
ES-14-402-02 Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical Equipment
ES-14-403-21 Electric Hoists
ES-14-701-01 Electrical/Instrument Preferred Equipment
ES-14-902-01 Materials and Workmanship for Electrical Installations
ES-14-902-02 Testing and Commissioning of Electrical Installations
Version No. 5.0 Page 5 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
CSBP Procedures
DP-05-011-03 Maintenance Daily Schedule
DP-05-013-01 Work Order Entry and Approval
DP-05-013-04 Closing Maintenance Work Orders
DP-05-013-05 Developing Maintenance Strategies
DP-05-014-01 Maintenance Breakdown Repairs
EP-08-030-05 Engineering Project Files
EP-08-030-19 Engineering Project Design Review
EP-08-030-38 Engineering Project Handover
CSBP Guides
GM-05-043-01 Technical Data Requirements for Plant and Equipment
GM-05-050-01 Engineering Modification
GM-10-020-04 Contractor’s Site Instructions
GM-11-035-02 Basic Safety Rules
GM-11-038-02 Slings, Rigging and Lifting Equipment Safety
CSBP Standard Forms
ES-14-101-12 Technical Data Sheets – Mechanical, Electrical and Instrument
IF1463 Technical Data Sheets – Hoist, Winch, Crane
Stage 1 Commissioning Inspection Reports
M101 General Mechanical
M152 Hoist, Monorail and/or Monorail Jib Crane
Stage 2 Commissioning Test Reports
M201 General Mechanical
M252 Hoist, Monorail and/or Monorail Jib Crane
CSBP Standard Drawings
9900-3-0005/001 Standard Beam and Bracing Connection Details
9900-3-0005/002 Standard Beam Connection Details & Member Schedule
9900-3-0005/003 Structural Base Plates
9900-3-0005/004 Standard Column & Beam Bolted Splice Connection Details
Version No. 5.0 Page 6 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
Standards Association of Australia
AS 1111 (all parts) ISO Metric Hexagon Bolts and Screws
AS 1112 (all parts) ISO Metric Hexagon Nuts Cold Formed
AS 1163 Structural Steel Hollow Sections
AS 1170 SAA Loading Code
AS 1214 Hot-Dip Galvanised Coatings on Threaded Fasteners
AS 1237 (all parts) Plain Washers for Metallic Bolts, Screws and Nuts for General
Purposes
AS 1252 High-Strength Steel Bolts with Associated Nuts and Washers for
Structural Engineering
AS 1418.1 Cranes - General Requirements
AS 1418.2 Cranes - Serial Hoists and Winches
AS 1554.1 Welding of Steel Structures
AS 1594 Hot Rolled Steel Flat Products
AS 1666.2 Wire Rope Slings - Care and Use
AS 1674 Safety in Welding and Allied Processes
AS 1796 Certification of Welders and Welding Supervisors
AS 1858.1 Electrodes and Fluxes for Submerged-Arc Welding – Carbon Steel
and Carbon Manganese Steels.
AS 1939 Degrees of Protection Provided by Enclosures of all Electrical
Equipment
AS 2053 Conduits and Fittings for Electrical Installations
AS 2214 Certification of Welding Supervisors – Structural Steel Welding
AS 2550 Cranes – Safe Use
AS 2700 Colour Standards for General Purposes
AS 3600 Concrete Structures
AS 3678 Structural Steel Hot Rolled Plates, Floor Plates and Slabs
AS 3679.1 Structural Steel Hot Rolled Bars and Sections
AS 3679.2 Structural Steel Welded I Sections
AS 3990 Mechanical Equipment – Steelwork
AS 3992 Welding and Brazing Qualifications
AS 4024 Safe Guarding of Machinery
AS 4100 Steel Structures
AS 4600 Cold-Formed Steel Structures
AS 4680 Hot-Dip Galvanised (Zinc) Coatings on Fabricated Ferrous Articles
AS 4855 Welding Consumables – Covered Electrodes for Manual Metal Arc
Welding of Non-Alloy and Fine Grain Steels.
AS/NZS ISO 9002 Quality Systems – Model for Quality Assurance in Production,
Installation and Servicing
Version No. 5.0 Page 7 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
Other Engineering Standards and Publications
AISC Design Capacity Tables for Structural Steel
AISC Design of Structural Connections
AISC Safe Load Tables 6th Edition 1987
Version No. 5.0 Page 8 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
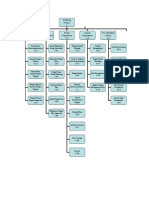
6. OVERVIEW
Flow diagrams Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the high level activities involved in the
management of monorail systems through design, installation and operational phases.
6.1 DESIGN PHASE – FIGURE 1 (3 SHEETS)
The process commences with an engineering project request to either upgrade an existing monorail
system, or design and install a new one.
If the Safe Working Load (SWL) of an existing monorail is unknown it is necessary to check
through maintenance records, archived project files etc, to determine the monorail’s history, initial
usage and whether design calculations are available.
The condition of the existing monorail, connections and support structure shall be checked for
corrosion, deformation etc as this could impact the design and consequently the Works.
Based on findings, the SWL of existing monorail and loads on existing support structure shall be
determined, enabling engineering design modifications to monorail and/or support structure to be
established.
ALL design work for monorail systems with a SWL of ten (10) tonne or greater shall be carried out
and checked by an external engineering company / consultant. Monorail systems less than ten (10)
tonne shall be either designed / checked externally or, designed internally by CSBP and checked
externally by a suitably qualified and experienced structural engineer.
An Independent Design Review shall be carried out on ALL monorail systems with a SWL of ten
(10) tonne or greater, to ensure proposed modifications and loading conditions comply with
relevant standards and regulations. Independent Design Review of monorail systems less than ten
(10) tonnes shall ONLY be carried out if specified in the Works by the Responsible Officer.
Monorail systems with a SWL of ten (10) tonne or greater shall be reviewed and approved by
WorkSafe or their authorised agency, prior to commencement of fabrication or remedial work.
A new monorail in an existing plant basically has the same design steps as previously outlined,
whilst a new monorail with a new support structure follows normal design activities as indicated in
the flow diagram.
Reference to relevant clauses in this Standard and other CSBP and Australian Standards are made
in Figure 1, covering design phase activities.
6.2 INSTALLATION PHASE – FIGURE 2
This process commences with an approved monorail design and includes design modifications and
structural strengthening of existing structural steelwork where required.
Normal project development sequence activities are followed through to Customer handover and
project file close out.
Version No. 5.0 Page 9 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
Reference to relevant clauses in this Standard and other CSBP Engineering Standards are made in
Figure 2, covering installation phase activities.
6.3 OPERATIONAL PHASE – FIGURE 3
This process commences with a commissioned monorail system that has been handed over to the
Customer.
The maintenance strategy, monorail system technical details and the inspection and preventative
maintenance requirements are finalised and recorded in the JDE Maintenance System, (activities
commenced in the design / installation phases).
Based on inspection findings, maintenance work is carried out in accordance with work priority or
if an engineering modification is required, changes are implemented in accordance with Figure 1
and Figure 2. Closure details are recorded in the JDE System. Reference to relevant clauses in this
Standard and other CSBP Engineering Standards and Departmental Procedures are made in Figure
3, covering operational phase activities.
Version No. 5.0 Page 10 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
No Eng Project MONORAILS
AS3990 Source historical info /
AS1418 Calculate SWL.
7.1 Upgrade
Exit SWL New or New Exit No
7.3 A
8. known? Upgrade? struct?
9. Yes
Yes
9.
Cals for exist No Calculate AS4100
8.
Structure? existing loads AS3990
7.3
Yes
24.2 Inspect existing 24.2
7.2 Inspect existing
Monorail. 7.2
structure
Extent of corrosion.
No Condition Condition of bolts.
Extent of corrosion. OK? Extent of Structural
Condition of end stops deformation etc..
and connection to Yes
structure. ES-14-101-02
Prepare layout/detail ES-14-101-03
drawings. ES-14-101-04
ES-14-101-06
10.
Carry out monorail 9. AS4100 / AS3990
calculations. 8. AS1418
7.4
7.3
Check existing 8.
structure imposed 7.4
loads. 7.3
Within Yes SWL No
Condition of existing 24.2 ≥ 10t? End
7.2 code?
structure and monorail
to be factored into No Yes
design.
Design structural
B
stiffening.
12.
10.
Recheck design 9. B
calculations 8.
7.4
7.3 Yes
No Within Yes SWL No
≥ 10t? End
code?
Figure 1 Monorail Design Process Flow Diagram Sheet 1 of 3
Version No. 5.0 Page 11 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
Intergrated design
monorail and
structure
ES-14-101-02
ES-14-101-03
Prepare layouts and
detail drawings ES-14-101-04
ES-14-101-06
12.
10.
Carry out design AS4100
9.
8. calculations AS1418
7.4
7.3
Yes SWL No
Within
code? ≥ 10t? End
No Yes
Revise design B
12.
10.
9. Recheck design
8. calculations
7.4
7.3
No Yes SWL No
Within
code? ≥ 10t? End
Yes
Figure 1 Monorail Design Flow Diagram Sheet 2 of 3
Version No. 5.0 Page 12 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
7.5
Independent 11.
Design Review 12.
Within No
Advise
code? Superintendent
Yes
Action as
required
Statutory 7.6
Authority 13.
review/approval
Within No Advise
code? Superintendent
Yes
File approvals in Action as
project file required
End
Figure 1 Monorail Design Process Flow Diagram Sheet 3 of 3
Version No. 5.0 Page 13 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
Approved monorail
design.
Tender, evaluate,
approval to proceed,
award.
ES-14-101-02
Prepare shop/ vendor ES-14-101-03
drawing and ES-14-101-04
documents. Submit ES-14-402-01
and review/ approve. ES-14-902-01
24.3 ES-14-302-01
24.1 ES-14-401-01
Fabricate/
23. ES-14-402-01
manufacture, inspect.
21. ES-14-701-01
14. ---> 19. ES-14-902-01
24.4
24.1 ES-14-302-02
Install ES-14-402-01
. 22.
14. ---> 19. ES-14-902-01
Test / Commission 24.5 ES-14-402-02
ES-14-902-02
Remedial work No
Accepted?
as
required.
Yes
Finalise handover
and close out
documentation,
As built Drawings
Remedial work as No Customer MDR's
required accept? Data Sheets
. H/O Certificate
Yes
File project
documentation
25.2
End
Figure 2 Monorail Installation Process Flow Diagram
Version No. 5.0 Page 14 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
Commissioned
monorail system.
Finalise maintenance DP-05-013-05
Activities commence in strategy. GM-11-038-02
the design and
installation phases as
information becomes Equipment number
available. Complete recording SWL
details in JDE Registration numbers
Maintenance System. Hoist details
Inspection Reqts etc.
25.4
24.6 Carry out inspection GM-11-038-02
according to plan.
Yes Record details in
Accepted? End
JDE system.
No
MAINTENANCE Identify remedial ENGINEERING
WORK work required. MODIFICATION
DP-05-011-03 Initiate maintenance Initiate engineering
GM-05-050-01
DP-05-013-01 work work
DP-05-014-01 . .
Carry out design
work. Fig 1
Carry out
maintenance work.
Carry out
engineering work. Fig 2
Close out - record
DP-05-013-04 details in JDE
system. Close out - record
details in JDE
25.3 system. 25.2
25.1
End
Figure 3 Monorail Maintenance Process Flow Diagram
Version No. 5.0 Page 15 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
7. BASIS OF DESIGN
7.1 EXISTING MONORAIL OF UNKNOWN CAPACITY
The safe working load of an existing monorail of unknown capacity shall be established by a search
through existing records and/or a design check, dependant on results of search.
This information search will include archived project records, maintenance, inspection and testing
records in order to determine equipment history, initial and current usage and availability of
original calculations.
If required, design calculations shall be carried out in accordance with applicable standards and
based on the properties and condition of existing structural steelwork members and the current
loading requirements. Refer Sections 7.2 to 7.4, 12 and 24.2.
Note: Where the strength or serviceability of an existing monorail or structure is to be
evaluated, the actual properties of the existing structural steelwork shall be used, NOT the
properties of sections currently available, which have replaced superseded sections.
7.2 CONDITION OF EXISTING STEELWORK
Existing structural steelwork, including monorails to be rated or upgraded, shall be inspected prior
to commencement of design work for structural adequacy, as condition could impact on the extent
of remedial and strengthening work that may be required. Refer to Section 24.2.
7.3 DESIGN STANDARDS
Monorails and supporting structures, including strengthening of existing steelwork members where
required, shall be designed in accordance with this Standard and Australian Standards AS3990,
AS4100 and AS1418.1 as applicable. Refer to Sections 8, 9, 10 and 12 for details.
For free standing monorail structures concrete footings shall be designed in accordance with
AS3600 and CSBP Engineering Standard Concrete (ES-14-202-10).
7.4 DESIGN
All Design work shall be performed in accordance with applicable CSBP specifications and
relevant Australian Standards. All loading including impact effect shall be considered as per
Australian Standards.
ALL design work for monorail systems with a SWL of ten (10) tonne or greater shall be carried out
and checked by an external engineering company / consultant. Monorail systems less than ten (10)
tonne shall be either designed / checked externally or, designed internally by CSBP and checked
externally by a suitably qualified and experienced structural engineer.
Note: Externally produced designs can be checked within the same organisation provided that
the company has in place a QA checking process. If not, design shall be checked by a
suitably qualified and experienced structural engineer from a different company.
Version No. 5.0 Page 16 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
For requirements on design calculations refer to Section 12.1.
7.5 INDEPENDENT DESIGN REVIEW
Completed design work for monorail systems with SWL of ten (10) tonne or greater shall be
subject to an Independent Design Review. Refer to Section 11and 12 for details.
7.6 STATUTORY AUTHORITY APPROVAL
WorkSafe WA or their authorised agency shall approve all CSBP monorail systems with a ten (10)
tonne or greater safe working load prior to commencement of any fabrication or remedial work.
Refer to Section 13 for details.
8. DESIGN METHODS
8.1 WORKING STRESS DESIGN METHOD
Unless directed otherwise by the Responsible Officer, design-involving plants installed during or
before 1990 shall be carried out using the working stress design method. This shall be in
accordance with the provisions of AS3990 except where specified otherwise in AS1418.1.
8.2 LIMIT STATES METHOD
Unless directed otherwise by the Responsible Officer, design - involving new plants, or operating
plants installed after 1990 - shall be carried out using the limit states method. This shall be in
accordance with the provisions of AS4100, except where specified otherwise in AS1418.1.
9. MONORAIL SECTION SIZE
9.1 SAFE LOAD / CAPACITY TABLES
Subject to flange and web thickness and deflection checks (Sections 9.2 to 9.4 inclusive) monorail
section size may be designed using:
a. AISC Safe Load Tables 6th Edition 1987, for plants installed during or before 1990 using
‘old’ steel grades (e.g. Grade 250) and following the working stress design method of
AS3990.
b. AISC Design Capacity Tables for structural steel, for new and existing plants installed after
1990 and following the limit states method of AS4100.
9.2 FLANGE THICKNESS
Flange thickness of proposed beam section; shall be checked for local buckling in accordance with
AS1418.1 Clause 5.7.1.
Version No. 5.0 Page 17 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
9.3 WEB THICKNESS
Web thickness of proposed beam section shall be checked in accordance with AS1418.1 Clause
5.7.2.
9.4 DEFLECTION LIMITS
The calculated deflection of the beam shall satisfy the requirements of AS1418.1 Clause 5.6.
9.4.1 Cantilever Monorails
Calculations for the deflection of cantilever monorails shall include the effects of adjacent spans.
9.4.2 Jib Cranes
Jib Cranes that can rotate through 90ο or more will impose torsional stresses in supporting building
columns.
Deflections due to torsional and other loading on building columns or structure shall be considered
when calculating total effects.
9.5 LONG SPAN MONORAIL BEAMS
Strengthening of long span monorail beams, to increase lateral buckling strength and stability, can
be achieved by the addition of bracing or ties to the top flange of the beam. Design shall be in
accordance with Section 8.
10. END STOP DESIGN
End stop connection to monorail beam, shall be designed to withstand dynamic loads transmitted
by hoist trolley, in accordance with applicable standards.
End stop shall be sized and positioned to suit the actual hoist trolley to be used, such that the
calculated vertical and horizontal interference dimensions, between monorail and trolley end stops,
shall not be less than those specified in Figure 4.
Note: If original hoist trolley is to be replaced a verification check shall be carried out, to ensure
minimum interference dimensions are maintained, PRIOR to putting the new trolley into
service. End stops shall be replaced if needed. Refer to Section 24.5 for commissioning
requirements.
Version No. 5.0 Page 18 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
MONORAIL
WHEELS
MONORAIL
L
END STOP
HOIST TROLLY MONORAIL TROLLY
END STOP
MONORAIL HORIZONTAL
END STOP INTERFERENCE >15mm
(BOTH SIDES)
VERTICAL
INTERFERENCE >15mm
(BOTH SIDES)
TROLLY
END STOP
MANUFACTURERS RECOMENDED
WHEEL FLANGE CLEARANCE
(BOTH SIDES)
TYPICAL CROSS SECTION THROUGH MONORAIL
Figure 4 Minimum Interference between Monorail and Trolley End Stops
Version No. 5.0 Page 19 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
11. INDEPENDENT DESIGN REVIEW
On completion of design and checking of calculations, including details of remedial work and
strengthening of existing structural steelwork where required, as per Section 7.3 and 7.4, an
Independent Design Review shall be carried out for ALL monorail systems with a SWL ten (10)
tonne or greater. Independent Design Review of monorails with SWL less than ten (10) tonne shall
ONLY be carried out when specified in the Works by the Responsible Officer.
The Responsible Officer shall nominate the type and extent of Independent Design Review
activities to be carried out, on a case by case basis. For example:
a. Methodology checks.
b. Conformance with Australian Standards and good engineering practices.
c. Analysis of design by carrying out alternative calculations or analysis methods.
d. Engineering check of prepared design drawings and calculations.
e. Comparison with a proven similar design.
Outcome of the Independent Design Review will enable the Responsible Officer to:
a. Initiate review / approval process with WorkSafe, or their authorised agency, if review
outcome is satisfactory.
b. Initiate appropriate action, if the Independent Design Review identifies problem areas such
as non-conformance to standards and incorrect analysis.
12. CALCULATIONS
12.1 DESIGN CALCULATIONS
Copies of the checked structural design calculations for the monorail and supporting structure, and
where required: concrete footing design - for free standing monorail structures; and the
strengthening of existing steelwork members, shall be submitted to the Responsible Officer in
accordance with the requirements of the Works.
Calculation sheets shall reference preliminary drawings, sketches and layouts by drawing and
revision number, and standards and other publications referred to in the calculations by title,
author, date and publisher.
All calculations shall be checked in accordance with Section 7.4, for accuracy and confirmation of
technical detail. Each sheet shall have the company name and the printed name and signature of the
checking engineer, and be dated.
Copies submitted shall be clearly referenced legible hard copies. If calculations are computer
generated, electronic copies shall be supplied in addition to the hard copy if specified by the
Responsible Officer in the Works.
12.2 INDEPENDENT DESIGN REVIEW
Report and copy of analysis and any calculations prepared by the Independent Design Review shall
be submitted to the Responsible Officer in accordance with the requirements of the Works.
Documentation shall reference drawings and publications and shall be submitted in a similar
manner as Section 12.1.
Version No. 5.0 Page 20 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
13. APPROVAL BY STATUTORY AUTHORITY
All new, re-rated or modified monorail systems, ten (10) tonne or greater safe working load shall
be reviewed and approved by WorkSafe, or their authorised agency.
No fabrication or remedial work shall commence until the Responsible Officer has received written
approval from WorkSafe, or their authorised agency.
14. MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT SELECTION
All materials shall be new unless approved by the Responsible Officer.
Unless otherwise noted on the drawings or approved by the Responsible Officer, materials and
equipment shall comply with the requirements of CSBP Engineering Standards:
• ES-14-302-01 Fabrication of Structural Steelwork
• ES-14-401-01 Mechanical Preferred Equipment
• ES-14-701-01 Electrical/Instrument Preferred Equipment
• ES-14-902-01 Materials and Workmanship for Electrical Installations
Manual lifting equipment shall be designed and comply with the relevant section of AS 1418.1 and
AS 1418.2.
Power operated lifting equipment shall be designed and comply with the relevant section of AS
1418.1 and AS 1418.2, and CSBP Engineering Standard Electric Hoists (ES-14-403-21).
15. ELECTRICAL CONTROLS
Where required, electrical controls shall comply with CSBP Engineering Standard Electric Hoists
(ES-14-403-21).
16. HANDLING OF STRUCTURAL STEELWORK & EQUIPMENT
Care shall be taken at all times during the fabrication, transportation, storage and erection of
monorails, supports and equipment and where applicable the modification and strengthening of
existing structures, to prevent steelwork deformation and/or damage to protective coatings.
Damaged steelwork, equipment and protective coatings shall be repaired to the satisfaction of the
Responsible Officer or replaced.
17. FABRICATION
Unless otherwise specified, fabrication of monorails, supports and strengthening components for
existing structures, shall be in accordance with CSBP Engineering Standard Fabrication of
Structural Steelwork (ES-14-302-01).
Version No. 5.0 Page 21 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
18. WELDING
Unless otherwise specified, all structural welding shall conform to AS 1554.1 Category SP and
CSBP Engineering Standard Fabrication of Structural Steelwork (ES-14-302-01). All welding
procedures shall be submitted to the Responsible Officer for approval.
19. BOLTING
Unless otherwise specified all structural bolted connections shall be torqued bearing type AS 1252
Grade 8.8/TB bolts, installed in accordance with CSBP Engineering Standard Erection of
Structural Steelwork (ES-14-302-02).
20. SITE MODIFICATIONS
No site modification or correction to structural steelwork, mechanical or electrical work, other than
those specified on drawings or in the Works, shall be made without the approval of the Responsible
Officer.
Note: Any proposed site change shall be assessed for potential impact on the structural integrity
of the monorail system, or breach of the WorkSafe license agreement.
Where necessary, proposed changes shall be submitted to relevant parties for review and
approval before implementing proposed changes. Refer to Sections 11, 12 and 13.
21. PROTECTIVE COATINGS
21.1 STRUCTURAL STEEL
Surface preparation and protective coating, shall be in accordance with CSBP Engineering
Standard Protective Coatings (ES-14-101-12).
The monorail shall be painted Golden Yellow to AS 2700-colour code Y14.
Support steelwork shall be:
a. Light Grey Blue, AS 2700 - B44 in Chemical Process Plants
b. Cream, AS 2700 – Y34 in other areas such as fertiliser plants, storage and despatch.
Note: If supporting structural steelwork has torqued friction type connections (bolts denoted as
8.8/TF), contact surfaces shall be clean “as-rolled” or equivalent, free from paint or any
other applied finish, which will impact on the effectiveness of the friction developed
between the contact surfaces.
21.2 HOIST AND TROLLEY
Protective coating and finish of mechanical and electrical trolleys and hoists shall be to the
manufacturer’s standard unless specified otherwise by the Responsible Officer.
Version No. 5.0 Page 22 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
21.3 BOLTS
Unless otherwise specified all bolts, nuts and washes shall be hot-dip galvanised in accordance
with AS 1214.
22. INSTALLATION
22.1 CIVIL / STRUCTURAL / MECHANICAL
As applicable, all monorail installation activities including setting out, concrete footings,
modification and strengthening of existing structures, steelwork erection, bolting, field welding and
grouting of structure base plates shall be carried out in accordance with:
a. the drawings;
b. Responsible Officer approved Contractor installation procedures;
c. CSBP Engineering Standards:
• Concrete (ES-14-202-10)
• Erection of Structural Steelwork (ES-14-302-02)
• Grouting (ES-14-202-14)
• Mechanical Equipment Design, Supply and Installation (ES-14-402-01)
d. Statutory Authorities having jurisdiction over the work site.
22.2 ELECTRICAL
Where an electric trolley and /or hoist is fitted, all electrical installation activities shall be in
accordance with CSBP Engineering Standard Electric Hoists (ES-14-403-21).
23. IDENTIFICATION
Monorail beam, hoist and trolley shall be clearly marked with their safe working load, equipment
number, Statutory Authority registration number if applicable, and other identification markings in
accordance with Sections 23.1 and 23.2.
Note: When the safe working load of a trolley and / or hoist is not matched to that of the beam,
the trolley, hoist and beam shall be marked with the lesser safe working load as
appropriate.
Version No. 5.0 Page 23 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
23.1 BEAMS
All monorail beams shall be identified with the following information:
a. Safe Working Load (SWL) shall be specified in metric units as follows:
• kilograms where SWL is less than 1 tonne e.g.; SWL 700kg
• tonnes where SWL is equal to or greater than 1 tonne e.g.; SWL 9t or SWL 9 tonne
b. Equipment number, assigned in accordance with CSBP Engineering Standard Equipment
Numbering System (ES-14-101-06) e.g.; 1121L0221
Note: For a hoist and trolley that is ‘permanently attached’ to a specific monorail beam the
equipment number shall cover the beam, hoist and trolley.
For a hoist and trolley that is ‘portable’, the beam shall have a different equipment
number to that of the hoist and trolley.
c. Statutory Authority registration number for all monorails 10 tonne SWL or greater.
d. Beam orientation (i.e. either north-south OR east-west, as applicable) shall be clearly
marked on the beam. For corresponding markings on electric control switches for
motorised trolleys refer to CSBP Engineering Standard Electric Hoists (ES-14-403-21).
Note: For curved monorails, marking shall be as directed by the Responsible Officer.
Identification labelling shall be black paint stencilled lettering and numerals on both sides of the
monorail.
Markings shall be of sufficient size to be clearly visible and legible from the working area below
the beam. The following minimum sizes specified in Table 1 shall be adhered to wherever
possible.
MINIMUM HEIGHT of MARKINGS in mm
NOMINAL DEPTH of BEAM in mm
(see note)
150 75
200 100
250 125
300 150
350 200
400 200
450 and larger 250
Note: For short span beams, height of markings may be reduced where they cannot be
accommodated over monorail length with standard size text specified above.
Table 1 Size of Monorail Beam Identification Markings
Version No. 5.0 Page 24 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
23.2 HOIST AND TROLLEY
All hoists and trolleys shall be identified by the following information:
a. Equipment number assigned in accordance with CSBP Engineering Standard Equipment
Numbering System (ES-14-101-06) e.g. 1121L0221.
Note: For a hoist and trolley that is ‘permanently attached’ to a specific monorail beam
one (1) equipment number shall be assigned to cover the beam, hoist and trolley
as per Section 23.1.
Hoists and trolleys that are ‘portable’ i.e. they are not attached permanently to a
specific monorail beam, shall be assigned one (1) number for the hoist and trolley
and one (1) number for the beam, specific to the plant area responsible for that
equipment.
For identification and labelling of electric hoists and trolleys refer to CSBP
Engineering Standard Electric Hoists (ES-14-403-21).
b. Labelling details shall be in accordance with CSBP Engineering Standard Labels & Signs:
Plant and Equipment (ES-14-102-09).
24. INSPECTION AND TESTING
24.1 WELD TESTING AND INSPECTION
Weld inspection and testing shall be in accordance with AS 1554.1 and CSBP Engineering
Standards:
• ES-14-302-01 Fabrication of Structural Steelwork
• ES-14-302-02 Erection of Structural Steelwork.
24.2 EXISTING STRUCTURAL STEELWORK INSPECTION
The following areas shall be inspected and results recorded during the design/development phase to
establish the extent of remedial and strengthening work that may be required to existing structural
steel.
Monorail (if fitted)
a. Extent of corrosion and condition of protective coating on monorail steelwork and end
connection bolts.
b. Type, size, connection details and adequacy and condition of existing monorail end stops.
c. Monorail identification markings are on both sides of beam, are correct and clearly visible
from ground level, or operating level in a multi-level situation. Required markings in
accordance with Section 23 to be displayed are:
• Safe Working Load (SWL)
• CSBP equipment numbers
• Statutory Authority registration number where applicable
Version No. 5.0 Page 25 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
Structure
a. Extent of corrosion and condition of protective coating on existing monorail support
structure and connection bolts.
b. Bolted connections are secure in areas subject to vibration.
c. Supporting structure above a proposed monorail does not have excessive deflection or that
supporting columns are not noticeably distorted.
d. Extent of corrosion and condition of protective coating on existing structure that is to be
used to support a proposed monorail.
24.3 NEW FABRICATED STEELWORK INSPECTION
All new fabricated structural steelwork shall be inspected in accordance with the requirements of
CSBP Engineering Standard Fabrication of Structural Steelwork (ES-14-302-01).
24.4 INSPECTION DURING ERECTION
The following areas shall require inspection and approval by the Responsible Officer:
a. Surface preparation of concrete footing prior to erection of structural support steelwork.
b. Setting out and alignment tolerances.
c. Cutting, drilling and welding of existing steelwork.
d. Surface preparation and protective coating of remedial works, modifications and
strengthening existing steelwork and field welds.
e. Cleaning and surface preparation of the underside of support column base plate, holding
down bolts and concrete foundation prior to grouting.
Inspection shall be carried out in accordance with relevant Australian Standards and the following
CSBP Engineering Standards:
• ES-14-102-12 Protective Coatings
• ES-14-202-14 Grouting
• ES-14-302-02 Erection of Structural Steelwork
24.5 COMMISSIONING
Prior to being placed into service the monorail shall comply with the commissioning requirements
of AS1418.
24.5.1 Stage 1 Commissioning
All components within the monorail system shall be inspected to verify that they have been
fabricated / manufactured, supplied and installed in accordance with:
• Contract drawings and documentation;
• Standards and Codes specified in this Standard;
• Statutory Regulations;
• Manufacturer’s requirements.
Version No. 5.0 Page 26 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
Movement of hoist and trolley shall be checked throughout their complete range in all directions
under no-load condition.
Stage 1 Commissioning Inspection Reports General Mechanical (M101) and Hoist, Monorail
and/or Monorail Jib Crane (M152) shall be used to verify equipment details.
Note: Stage 2 Commissioning, shall not commence until the Responsible Officer has accepted
and signed off the Stage 1 Commissioning Inspection Reports, as being successfully
completed.
24.5.2 Stage 2 Commissioning
Monorail and hoist shall be tested in accordance with the requirements of AS1418. Results shall be
recorded in the Stage 2 Commissioning Test Reports; General Mechanical (M201) and Hoist,
Monorail and/or Monorail Jib Crane (M252).
Note: Monorail system shall not be put into service until the Responsible Officer has accepted
and signed off the Stage 2 Commissioning Test Reports, as being successfully completed.
24.5.2.1 Beam Load Testing
Unless otherwise directed by the Responsible Officer, beam load testing shall be carried out with:
a. Test load equivalent to SWL + 10%
b. Test locations at:
• centre of span or
• end of cantilever (if applicable).
Beam deflection shall be measured at location of test load.
Note: ALL beams shall be load-tested as above, regardless of the monorail safe working load.
ONLY suitably qualified and experienced personnel shall carry out load testing.
Test load shall be kept as close as practical to ground or operating level. The stability and
deformation of supporting structure shall be monitored during testing.
24.6 INSPECTION DURING OPERATIONAL PHASE
In accordance with CSBP Guide Slings, Rigging and Lifting Equipment Safety (GM-11-038-02)
and AS 2550 the monorail system, including all mechanical, electrical and structural components
shall be subject to a complete and documented annual inspection. Dependant upon the
environmental conditions and the type of equipment being used more frequent safety checks shall
be carried out as directed by the applicable business unit.
Note: The person using lifting equipment shall inspect it for safety, before each use. Any lifting
equipment found to be defective, damaged or suspect shall not be used.
Version No. 5.0 Page 27 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
24.6.1 Inspection Plan
In accordance with the Inspection Plan, the following areas shall be inspected and results recorded,
to establish whether any remedial work is required.
Monorail
a. Extent of corrosion and condition of protective coating on monorail steelwork and end
connection bolts.
b. Condition of monorail end stops.
c. Monorail identification markings are clearly visible from ground level, or operating level in
a multi level situation.
Structure
a. Extent of corrosion and condition of protective coating on monorail support structure and
connection bolts.
b. Bolted connections are secure in areas subject to vibration.
c. Supporting structure above monorail does not have excessive deflection or the supporting
columns are not noticeably distorted.
Hoist and Trolley
a. Mechanical
1. Extent of corrosion and condition of protective coating on trolley, end stops, wheels
and connection bolts.
2. Clearance between monorail bottom flange outside face and trolley wheel flange is
within manufacturer’s limits.
3. Actual vertical and horizontal interference dimensions, between monorail and
trolley end stops are not less than those specified in Figure 4.
4. Condition of chains, wire ropes, slings, sheaves, hook and safety latch as applicable.
Refer to CSBP Guide Slings, Rigging and Lifting Equipment Safety (GM-11-038-
02) for requirements.
5. Wear and clearances on all movable components are within manufacturer’s limits.
b. Electrical
Condition and operation of electrical equipment as defined in CSBP Engineering Standard
Electric Hoists (ES-14-403-21).
Version No. 5.0 Page 28 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
Monorails
ES-14-403-20
25. RECORDS MANAGEMENT
25.1 AS - BUILT DRAWINGS
On completion of site modifications and installation, testing and commissioning of the monorail
system, drawings shall be upgraded to reflect any as-built design deviations.
Drawings recording the as-built details shall be prepared/revised, numbered, approved and handed
over in accordance with CSBP Engineering Standards:
• ES-14-101-02 Drawing Management
• ES-14-101-03 Drawing Preparation
• ES-14-101-04 Drawing Numbering
25.2 ENGINEERING PROJECT FILES
On completion of the project all relevant hard-copy documentation, in numbered project files, shall
be archived in the designated work area.
Records in electronic format (such as drawings and JDE data) shall be stored in the appropriate
databases and designated work area.
Refer to CSBP Guide Engineering Modifications (GM-05-050-01) for type of documents to be
retained for historical purposes.
25.3 MAINTENANCE WORK ORDERS
On completion of the maintenance work order, details shall be recorded in accordance with CSBP
Departmental Procedure Closing Maintenance Work Orders (DP-05-013-04).
25.4 MONORAIL SYSTEM ANNUAL INSPECTION
On completion of the annual inspection (or more frequently as determined by each business unit),
results shall be recorded in accordance with CSBP Guide Manual Slings, Rigging and Lifting
Equipment Safety (GM-11-038-02).
Version No. 5.0 Page 29 of 29
Document last modified: 30 June 2014.
You might also like
- Esd TR20.20 2016Document5 pagesEsd TR20.20 2016Sunseeker Nguyen0% (7)
- WBS For Wedding ProjectDocument1 pageWBS For Wedding ProjectKhushboo Katyayan50% (2)
- Activity Based Costing - Case StudyDocument8 pagesActivity Based Costing - Case StudyViksit Choudhary100% (1)
- Pamphlet 96 - Edition 5 - September 2017Document124 pagesPamphlet 96 - Edition 5 - September 2017中西文香100% (1)
- Pamphlet 88 - Edition 3 - March 2010Document44 pagesPamphlet 88 - Edition 3 - March 2010Jacques BlueqNo ratings yet
- Cap Bud ProbDocument9 pagesCap Bud ProbJulie Mark JocsonNo ratings yet
- Strength Graded Structural Timber - Square Edged Logs With Wane - SoftwoodDocument28 pagesStrength Graded Structural Timber - Square Edged Logs With Wane - SoftwoodNikolic DejanNo ratings yet
- 542935b Atys P M Nmo ENDocument76 pages542935b Atys P M Nmo ENb400013No ratings yet
- TR 512Document97 pagesTR 512RafnunNo ratings yet
- 20201103101151963Document90 pages20201103101151963long0200405No ratings yet
- User Manual Euro 4 Mod - Eng - Nc-2592Document189 pagesUser Manual Euro 4 Mod - Eng - Nc-2592Ricardo RONo ratings yet
- Pre Feasibility Study for Offshore Wind Farm Development in Gujarat-AnnotatedDocument186 pagesPre Feasibility Study for Offshore Wind Farm Development in Gujarat-AnnotatedRituraj Singh SujawatNo ratings yet
- Global India Aortic Valve Replacement Devices Market To 2030Document92 pagesGlobal India Aortic Valve Replacement Devices Market To 2030cvmentorgeraNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice For Buses 26102016Document27 pagesCode of Practice For Buses 26102016dmontoyaNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia-Djibouti Transport Corridor Project-RAP-Adama Awash Lot 1 (60km) Expressway Lot 1Document93 pagesEthiopia-Djibouti Transport Corridor Project-RAP-Adama Awash Lot 1 (60km) Expressway Lot 1Rediet meredNo ratings yet
- ZB - Tenant Handbook - Annex A - Tenant Fit-Out and Leasehold Improvements Manual - 2017Document51 pagesZB - Tenant Handbook - Annex A - Tenant Fit-Out and Leasehold Improvements Manual - 2017Mike TabaderoNo ratings yet
- Palm Valley International School, Meerut - MEP Concept Design Brief ReportDocument75 pagesPalm Valley International School, Meerut - MEP Concept Design Brief ReportArun Kumar GNo ratings yet
- Etag 032 Part 4 May 2013Document34 pagesEtag 032 Part 4 May 2013coolkaisyNo ratings yet
- AzSPU SSOW Procedure For Confined Space EntryDocument34 pagesAzSPU SSOW Procedure For Confined Space EntryAmir M. ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 299 GUIDANCE FOR REINFORCEMENT & SPLICING OF CAGES - FPS-splicing-and-sonic-10-07-20Document40 pages299 GUIDANCE FOR REINFORCEMENT & SPLICING OF CAGES - FPS-splicing-and-sonic-10-07-20gmpintorNo ratings yet
- EIA Chakdara ShamozaiDocument165 pagesEIA Chakdara ShamozaiFariaNo ratings yet
- TNRI Final Design Report R01Document48 pagesTNRI Final Design Report R01Bunyamin SelimogluNo ratings yet
- Cellenium 30Jr Service Manual Ver - 1.01Document63 pagesCellenium 30Jr Service Manual Ver - 1.01Jackson NjarambaNo ratings yet
- Atys P M Instruction Manual 2017-11-542935 enDocument78 pagesAtys P M Instruction Manual 2017-11-542935 enValdemar BarrosNo ratings yet
- Style ManualDocument42 pagesStyle Manualh_romeu_rsNo ratings yet
- BOMBA NEUMATICA ARGAL-ASTRA-EVO-DDE-Instruction-Manual-rev-11-2021Document58 pagesBOMBA NEUMATICA ARGAL-ASTRA-EVO-DDE-Instruction-Manual-rev-11-2021Jose Luis Ari AchahuiNo ratings yet
- ANSYS, Inc. Documentation ErrataDocument14 pagesANSYS, Inc. Documentation ErrataHiếu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- FPS Splicing and Sonic 09 04 20Document40 pagesFPS Splicing and Sonic 09 04 20Poh T KhoNo ratings yet
- H&M Group Requirements For Quality System: Textile ProductsDocument30 pagesH&M Group Requirements For Quality System: Textile Productssaidurtex100% (1)
- Hazop - Vide Exemplo ICIDocument248 pagesHazop - Vide Exemplo ICIHelton SantanaNo ratings yet
- Ume Ingepac Ef PB EngDocument270 pagesUme Ingepac Ef PB EngFelipe De NadaiNo ratings yet
- Pages From HM 27 Metering Systems Section 2 Guide To Gas Metering Systems Mar 2002Document9 pagesPages From HM 27 Metering Systems Section 2 Guide To Gas Metering Systems Mar 2002mounrNo ratings yet
- Api RP 1111 E5Document3 pagesApi RP 1111 E5Oğuzcan Şahin0% (1)
- AutoBatch UserManual Jan2018 PDFDocument78 pagesAutoBatch UserManual Jan2018 PDFHan ArifNo ratings yet
- Construction MethodologyDocument102 pagesConstruction MethodologyDagnachew TassewNo ratings yet
- FEASIBILITY STUDY OF MALAYSIA KEMAMAN WHARF PROJECT (FINALúDocument113 pagesFEASIBILITY STUDY OF MALAYSIA KEMAMAN WHARF PROJECT (FINALúatikahasfiworkNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Design Construction andDocument108 pagesOverview of The Design Construction andMoses Kiting'oNo ratings yet
- MANUAL SGI REV11 Iilzoz2Document45 pagesMANUAL SGI REV11 Iilzoz2LARLUI PATRICK TORRES OLIVARESNo ratings yet
- User Manual MRI 508Document76 pagesUser Manual MRI 508Firdaus YasinNo ratings yet
- Maintenance For Air ConDocument99 pagesMaintenance For Air ConMMTMNo ratings yet
- 45 ST WM 0002 Engineering Standards 2019Document47 pages45 ST WM 0002 Engineering Standards 2019chrisNo ratings yet
- EHS DOC 001 - LaboratorySafetyManualDocument94 pagesEHS DOC 001 - LaboratorySafetyManualankur_haldarNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Structural Master Plan - Norms and StandardsDocument30 pagesAddis Ababa Structural Master Plan - Norms and StandardsRobel WendwesenNo ratings yet
- 7-31k D 07252012 PDFDocument67 pages7-31k D 07252012 PDFerfan_nugroho9063No ratings yet
- Xdisp19.3 ManualDocument149 pagesXdisp19.3 ManualAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Value Engineering ManualDocument193 pagesValue Engineering Manualswetang prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Value Engineearing ManualDocument193 pagesValue Engineearing ManualWirya MuradNo ratings yet
- 1002910-40-SPE-ET-0002 - SubstationsDocument63 pages1002910-40-SPE-ET-0002 - SubstationsAMARPALNo ratings yet
- AORG351: Implementation of Tax Policy Reform in Uganda: The Case Study of Uganda Revenue Authority (URA)Document123 pagesAORG351: Implementation of Tax Policy Reform in Uganda: The Case Study of Uganda Revenue Authority (URA)Tatuh PerryNo ratings yet
- Booklet LSDocument100 pagesBooklet LSAbram SidabutarNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-08-14 at 12.33.02 PMDocument61 pagesScreenshot 2022-08-14 at 12.33.02 PMMahmoud AdlyNo ratings yet
- RFG 048597Document102 pagesRFG 048597Rister ZinnNo ratings yet
- Subsea Wet Gas Compressor Dynamics - TESISDocument118 pagesSubsea Wet Gas Compressor Dynamics - TESISVILLANUEVA_DANIEL2064No ratings yet
- Design Management ManualDocument70 pagesDesign Management ManualShanae RyderNo ratings yet
- AzSPU SSOW Procedure For ScaffoldingDocument20 pagesAzSPU SSOW Procedure For ScaffoldingAmir M. ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Vanne de Control Adoucisseur Fleck 9000-Sxt Im A enDocument110 pagesVanne de Control Adoucisseur Fleck 9000-Sxt Im A enEtienne NASALANDINo ratings yet
- Castellini C22 OM PDFDocument75 pagesCastellini C22 OM PDFHaitham AlbajawiNo ratings yet
- DAMAC SPM - (Rev 6 - 270122)Document223 pagesDAMAC SPM - (Rev 6 - 270122)Xtreme-DesignsNo ratings yet
- GRP Pipe Report-SudanDocument37 pagesGRP Pipe Report-Sudanlehmanwolf100% (1)
- Supra 850Document84 pagesSupra 850Dajmon DajmonNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet 9 - Recommnended Practices For Handling Chlorine Bulk Highway TransportDocument62 pagesPamphlet 9 - Recommnended Practices For Handling Chlorine Bulk Highway TransportJacques BlueqNo ratings yet
- Datastream - How To Search For ESG Data - July 2022Document17 pagesDatastream - How To Search For ESG Data - July 202224a4010600No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For A First Course in Differential Equations With Modeling Applications 10th EditionDocument23 pagesSolution Manual For A First Course in Differential Equations With Modeling Applications 10th Editiondisbenchcrang9xds100% (45)
- BSBHRM415 Assessment 3Document24 pagesBSBHRM415 Assessment 3Michael FelixNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management QB: Part - ADocument7 pagesMarketing Management QB: Part - ASe SathyaNo ratings yet
- Counterparty Credit Exposure and CVA - An Intergrated Approch (UBS)Document34 pagesCounterparty Credit Exposure and CVA - An Intergrated Approch (UBS)Mo MokNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: Performance Task # 1Document3 pagesBusiness Plan: Performance Task # 1Jan BrettNo ratings yet
- Effect of Advertisement On ConsumersDocument59 pagesEffect of Advertisement On Consumersvishal394% (49)
- Sugar Industry: Sugar Breaking Out of Bitter CyclesDocument53 pagesSugar Industry: Sugar Breaking Out of Bitter CyclesPrasun PandeyNo ratings yet
- IIFBM at 12 23Document13 pagesIIFBM at 12 23r.phaniKrishna krishnaNo ratings yet
- Blue Ocean Strategy With Indian ExamplesDocument21 pagesBlue Ocean Strategy With Indian ExamplesSwetha Asokan60% (5)
- NG-018-XX-PNL-023030 - Rev03 UnsignedDocument26 pagesNG-018-XX-PNL-023030 - Rev03 UnsignedFolarin AyodejiNo ratings yet
- Gilat White Paper Cellular Cellular Backhaul Myths and FactsDocument13 pagesGilat White Paper Cellular Cellular Backhaul Myths and FactsAFF NO LIMITNo ratings yet
- Report On NMB Bank Limited: HIRE Verified WriterDocument24 pagesReport On NMB Bank Limited: HIRE Verified WriterSantosh ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MNGT-3711: Ethics and Social Responsibility in Business and SocietyDocument13 pagesAssignment 2 MNGT-3711: Ethics and Social Responsibility in Business and SocietySam rockzs0% (1)
- Qp-Luxm-Gs & SJDocument2 pagesQp-Luxm-Gs & SJRaksha StarNo ratings yet
- Question Paper - Mock AristoDocument33 pagesQuestion Paper - Mock AristoTONI POOH100% (1)
- Pfrs 13 Fair Value MeasurementDocument22 pagesPfrs 13 Fair Value MeasurementShane PasayloNo ratings yet
- STM PDFDocument184 pagesSTM PDFSANDHYA MISHRANo ratings yet
- Furniture ManufacturerDocument9 pagesFurniture ManufacturerUniversal PrideNo ratings yet
- Title:: MTP 36203 (Accounting For Manufacturing)Document17 pagesTitle:: MTP 36203 (Accounting For Manufacturing)Che Rosnor Che HaronNo ratings yet
- BH Tif08Document24 pagesBH Tif08Andres R. OlguinNo ratings yet
- Abrar Alam Electrical Foreman CVDocument2 pagesAbrar Alam Electrical Foreman CVGUDDUNo ratings yet
- Boarding PassDocument1 pageBoarding PassΓιωργος ΜουστακηςNo ratings yet
- 18-12-2023 09-22-39 1702884159 Dailynews PDFDocument24 pages18-12-2023 09-22-39 1702884159 Dailynews PDFCeles NubesNo ratings yet
- Company Management: Shruti Reddy, Upes SolDocument72 pagesCompany Management: Shruti Reddy, Upes Solvishal bagariaNo ratings yet
- 1988 Motorola Annual Report PDFDocument40 pages1988 Motorola Annual Report PDFmrinal1690No ratings yet
- ExxonMobil PD-5340Document2 pagesExxonMobil PD-5340蔡佾呈No ratings yet