Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amnioreduction in Emergency Rescue Cervical Cerclage With Bulging Membranes
Amnioreduction in Emergency Rescue Cervical Cerclage With Bulging Membranes
Uploaded by
Amelia FebrinaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amnioreduction in Emergency Rescue Cervical Cerclage With Bulging Membranes
Amnioreduction in Emergency Rescue Cervical Cerclage With Bulging Membranes
Uploaded by
Amelia FebrinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Amnioreduction in Emergency Rescue Cervical Cerclage with Bulging Membranes
CASE REPORT Amnioreduction in Emergency Rescue
Cervical Cerclage with Bulging
doi: 10.5455/medarh.2020.74.151-152
MED ARCH. 2020 APR; 74(2): 151-152
Membranes
RECEIVED: JAN 12, 2020019 | ACCEPTED: FEB 12, 2020
Edin Medjedovic1,2, Zijo Begic3, Alma Suljevic4, Amela Muftic1, Ema Dzihic5,
1
Clinic of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Clinical
Center University of Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia
Asim Kurjak6
and Herzegovina
2
Department of Gynecology, School of ABSTRACT
Medicine, Sarajevo School of Science and Introduction: Emergency cerclage in the second trimester is aestablished treatment for a di-
Technology, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina lated cervix. Aim: To report a case of a successful cerclage performed in a 33-year old woman
3
Department of Cardiology, Pediatric Clinic, in her secondpregnancy, after 5 years of non-successfulpregnancy outcomes. Case report: In
Clinical Center University of Sarajevo, Sarajevo, her fourth month of pregnancy, the patient was hospitalized because of suprapubic pressure.
Bosnia and Herzegovina After complete laboratory results, ultrasound and vaginal examination the patient was diag-
4
Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, nosed with cervical shortening, cervical canal was opened 3cm, with prolapse and bulging
General Hospital, Konjic, Bosnia and of the fetal membranes in vagina. An amount of 120 ml of clear amniotic fluid was removed
Herzegovina transabdominally under ultrasound guidance, and sent to the microbiological and genetical
5
Department of Gynecology, Health Care Center analysis. McDonald emergency cerclage of the cervical canal was performed. Patient was
Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina monitored few days on department and released home with advice of strict reduction of ac-
6
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, tivity to minimum, and prescribed therapy due to that: antithrombotic, progesterone and an-
Medical School University of Zagreb, Zagreb, tibiotic therapy. Conclusion: Amnioreduction at the time of emergency cerclage placement is
Croatia associated with a lower rate of extreme prematurity and related neonatal morbidity. Success-
ful outcome is not impossible, along with adequate antibiotic regimen, bed rest and regular
Corresponding author: Edin Medjedovic, MD. obstetrical control/checkup.
Clinic of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Clinical
Keywords: cervix, amniotic fluid, pregnancy, treatment.
Center University of Sarajevo, Bosnia and
Herzegovina. E-mail: medjedovic.e@gmail.com.
ORCID ID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2357-
9580. 1. INTRODUCTION ical Center University of Sarajevo.
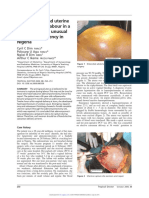
Emergency cerclage in the second After complete laboratory results,
trimester is aestablished treatment ultrasound and vaginal examina-
for a dilated cervix (1, 2). In cases tion the patient was diagnosed with
with advanced cervical dilatation cervical shortening, cervical canal
and bulging membranes, it has been was opened 3cm, with prolapse and
referred to as “heroic cerclage” due bulging of the fetal membranes in
to its poor success rate (1). vagina. There were no clinical and
laboratory signs of infection. Ultra-
2. AIM sound examination revealed normal
To report a case of a successful amniotic fluid index and dynamically
cerclage performed in a 33-year old vital fetus. Patients routine antenatal
woman in her second pregnancy, screen failed to reveal any abnor-
after 5 years of non-successfulpreg- mality. Amniotic fluid reduction was
nancy outcomes. performed. The protruding sac of
membranes was under considerably
3. CASE REPORT less tension. An amount of 120 ml
Patient was trying for 5 years to of clear amniotic fluid was removed
get pregnant. In May 2017, she had transabdominally under ultrasound
one spontaneous abortion in very guidance, and sent to the microbio-
early gestation week (biochemical logical and genetical analysis. Prior
pregnancy). Husband’s spermio- to the operative procedure, patient
© 2020 Edin Medjedovic, Zijo Begic, Alma Suljevic, gram test was normal. Patient was was administered with two antibiot-
Amela Muftic, Ema Dzihic, Asim Kurjak regularly gynecologically examined ics (ceftriaxone, azithromycin), and
with regular PAP smear. Patient was as a tocolytic agent hydroxyproges-
This is an Open Access article distributed under the
terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-
moderately obese. Current pregnan- terone 250mg/ml and indomethacin
Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/ cy was spontaneously conceived, In- tablets 100mg were used. McDonald
licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted eighteen week because of suprapubic emergency cerclage of the cervical
non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction pressure the patient was hospitalized canal was performed. During the op-
in any medium, provided the original work is properly at Pathology department, Clinic of eration, as a tocolytic agent intrave-
cited.
Gynecology and Obstetrics, Clin- nous nitroglycerin was used in dose
CASE REPORT | Med Arch. 2020 APR; 74(2): 151-152 151
Amnioreduction in Emergency Rescue Cervical Cerclage with Bulging Membranes
of 100mcg. Patient was monitored few days on depart- 5. CONCLUSION
ment and released home with advice of strict reduction Amnioreduction at the time of emergency cerclage
of activity to minimum, and prescribed therapy due to placement is associated with a lower rate of extreme pre-
that: antithrombotic, progesterone and antibiotic ther- maturity and related neonatal morbidity. The procedure
apy. Regular checkups were done. First control checkup prolonged pregnancy from18 to 35 week of gestation
was performed one week later, and after that followed successfully, with delivery of a healthy eutrophic new-
regularly every ten days. Vaginal and vulvar smear was born with high Apgar score. The need for cerclage in the
done at35 week of gestation. Enterococcus faecalis was second trimester of pregnancy is not rare. According to
isolated and antibiotic regimen of amoxicillin was ad- our experience, we advise cervical cerclage with amnio
ministered for 5 days. Local vaginal antibiotic therapy reduction in pregnant women with advanced dilatation
was administered twice during the checkup period. On and bulging membranes in the second trimester. Despite
29. 03. 2018., the patient comes to the clinic in 35+2 generally bad prognosis, successful outcome is not im-
week of gestation, with regular contractions, ruptured possible, along with adequate antibiotic regimen, bed
membranes and the suture of cerclage in place. During rest and regular obstetrical control/checkup.
vaginal exam, we removed cerclage and it showed dila-
tation of 6 cm, head presentation with evident preterm • Declaration of patient consent: The authors certify that they have
premature rupture of membranes (PPROM) (clear color obtained all appropriate patient consent forms.
of amniotic fluid noted). She was admitted immediately • Author’s contribution: EM, AK, ZB and AM gave substantial contri-
to the delivery room where she delivered eutrophic fe- bution to the conception or design of the work and in the acquisi-
male newborn, weight 2250 grams, length 47cm, with tion, analysis and interpretation of data for the work. AK had role in
Apgar score of 9/10. During delivery umbilical cord was drafting the work and revising it critically for important intellectual
tied 1x around baby’s right ankle- thus inverting the foot. content. Each author gave final approval of the version to be pub-
Placenta was delivered short after. After revision of birth lished and they agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work
canal, perineal rupture of I degree was noted, and su- in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any
tured accordingly. Patient continued antibiotic regimen part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
(cefazolin), with control of laboratory values. • Conflicts of interest: There are no conflicts of interest.
• Financial support and sponsorship: Nil.
4. DISCUSSION
Cervical incompetence is shortening of cervix before REFERENCES
term, treated when it threatens pregnancy using a sur- 1. Stefanovic M, Vukomanovic P, Kutlesic R, et al. Amnioreduc-
gical technique: cervical cerclage. It is well recognized tion and emergency cerclage with bulging membranes. Acta
cause of recurrent mid-trimester pregnancy loss (3, 4, Fac Med Naiss. 2008; 25(1): 55-58.
5). This surgical technique reinforces the cervical mus- 2. Zhu LQ, Chen H, Chen LB, et al. Effects of emergency cervi-
cle by placing sutures above the opening of the cervix to cal cerclage on pregnancy outcome: a retrospective study of
narrow the cervical canal, usually done between 12-16 158 cases. Med Sci Monit. 2015; 21: 1395-1401.
week of gestation or urgently later during second trimes- 3. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
ter. Under the ideal conditions, the fetal survival rate in- ACOG Practice Bulletin. Cervical insufficiency. Obstet Gy-
creases from 20% to 78-87% after elective cerclage (6, 7). necol. 2003; 102: 1091-1099.
Without screeningand surveillance, cervical incompe- 4. MacDougall J, Sidddle N. Emergency cervical cerclage. Br J
tence may not be diagnosed until patient presents with ObstetGynaecol. 1991; 98: 1234-1238.
painless dilatation of the cervix and fetal membranes 5. Debbs RH, Chen J. Contemporary use of cerclage in preg-
protruding through dilated cervix. Unexpected cervical nancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2009; 52(4): 597-610.
incompetence sometimes followed by lower abdominal 6. Cerqui AJ, Olive E, Bennett MJ, et al. Emergency cervical cer-
pain, pain in the back or as premenstrual pain with in- clage. Is there a role for amnioreduction?. Aust N Z J Obstet
creased vaginal secretion and sometimes blood (8). Such Gynaecol. 1999; 39(2): 155-158.
presentation is high risk for both mother and fetus, de- 7. Yip SK, Fung HYM, Fung TY. Emergency cervical cerclage:
manding emergency management if the pregnancy is to a study between duration of cerclage in situ with gestation
be salvaged. Fetal survival rates of 48-68% have been re- at cerclage, herniation of forewater, and cervical dilatation
ported after emergency cerclage (1, 9). By vaginal specu- at presentation. European Journal of Obstetrics Gynecology
lum examination, the burst of fetal membranes should be and Reproductive Biology. 1998; 78(1): 63-67.
excluded. If fetal membranes are visible and are bulging 8. Deb P, Aftab N, Muzaffar S. Prediction of outcomes for emer-
into the vagina, the prognosis of the neonatal survival is gency cervical cerclage in the presence of protruding mem-
dramatically decreased, but emergency cerclage can be branes. ISRN Obstet Gynecol. 2012; 2012: 842841.
attempted (1, 3). The decrease of intra amniotic pressure 9. Lee HJ, Park TC, Norwitz ER. Management of pregnancies
facilitates the reposition of bulging fetal membranes and with cervical shortening: a very short cervix is a very big prob-
insertion of cerclage (1). Infection is the most frequent lem. Rev Obstet Gynecol. 2009; 2(2): 107-115.
cause and complication that follow this state, so it is im- 10. Benifla JL, Goffinet F, Darai E, et al. Emergency cervical cer-
portant to find the signs of infection (1, 2). It is important clage after 20 weeks’ gestation: a retrospective study of 6 years’
to point out that every effort should be made to perform practice in 34 cases. Fetal Diagn Ther. 1997; 12(5): 274-278.
cervical cerclage at or before 26 weeks of gestation (4).
152 CASE REPORT | Med Arch. 2020 APR; 74(2): 151-152
You might also like
- Case Note 13: Patient DetailsDocument3 pagesCase Note 13: Patient DetailsBINCY0% (1)
- Induction and Augmentation of LaborDocument22 pagesInduction and Augmentation of LaborDagnachew kasaye100% (1)
- Jurnal 2Document18 pagesJurnal 2Muhammad Pebri Nilhakim ZavbmNo ratings yet
- Forgotten Transvaginal Cervical Cerclage Stitch in First Pregnancy Benefits Reaped Till The Second PregnancyDocument2 pagesForgotten Transvaginal Cervical Cerclage Stitch in First Pregnancy Benefits Reaped Till The Second PregnancyAna AdamNo ratings yet
- Anterior Cervical Wall Rupture As A Result of Induced AbortionDocument4 pagesAnterior Cervical Wall Rupture As A Result of Induced AbortionnawriirwanNo ratings yet
- Successful Conservative Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer During PregnancyDocument3 pagesSuccessful Conservative Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer During PregnancyEres TriasaNo ratings yet
- Adenomyosis and Uterine Rupture During Labour in A Primigravida: An Unusual Obstetric Emergency in NigeriaDocument2 pagesAdenomyosis and Uterine Rupture During Labour in A Primigravida: An Unusual Obstetric Emergency in NigeriaMariam Carolina Viloria VargasNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2468900918300161 MainDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S2468900918300161 MainayissiNo ratings yet
- Placenta AccretaDocument5 pagesPlacenta AccretaF3rcitaNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Scar Ectopic Pregnancies: Etiology, Diagnosis, and ManagementDocument9 pagesCesarean Scar Ectopic Pregnancies: Etiology, Diagnosis, and ManagementDinorah MarcelaNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Scar Pregnancies and Their ManagementDocument7 pagesCesarean Scar Pregnancies and Their ManagementClinton SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: A ReviewDocument13 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: A ReviewDinorah MarcelaNo ratings yet
- Liao 2016Document4 pagesLiao 2016cristian vivasNo ratings yet
- EJHM - Volume 89 جامعه الزقازيقDocument9 pagesEJHM - Volume 89 جامعه الزقازيقفاطمة الزهراء أسامةNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa 1Document2 pagesPlacenta Previa 1Gunther MirandaNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Management of Cervical-Isthmic Pregnancy: A Proposal MethodDocument4 pagesLaparoscopic Management of Cervical-Isthmic Pregnancy: A Proposal MethodDinorah MarcelaNo ratings yet
- Aogs 14255Document6 pagesAogs 14255Christian YzaguirreNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Gastroschisis in The First TrimesterDocument5 pagesDiagnosis of Gastroschisis in The First TrimesterhakimrosliNo ratings yet
- Delayed Interval Delivery in Twin Pregnancy Without Cerclage: CaseDocument2 pagesDelayed Interval Delivery in Twin Pregnancy Without Cerclage: Caselailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Fetal TransfusionsDocument10 pagesIntrauterine Fetal TransfusionsSaddam FuadNo ratings yet
- Cervical Dysgenesis With Transverse Vaginal Septum With Imperforate Hymen in An 11 Year Old Girl Presenting With Acute AbdomenDocument4 pagesCervical Dysgenesis With Transverse Vaginal Septum With Imperforate Hymen in An 11 Year Old Girl Presenting With Acute Abdomenshe-docNo ratings yet
- Maternal and FDocument3 pagesMaternal and FNununkNo ratings yet
- Clinical StudyDocument6 pagesClinical StudyAmelia FebrinaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Non-Puerperal Uterine Inversion Mimicking Complete Uterine ProlapsedDocument6 pagesChronic Non-Puerperal Uterine Inversion Mimicking Complete Uterine ProlapsedCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Management of AUB in A Bicornuate Uterus - Endometrial Ablation in A CompDocument1 pageManagement of AUB in A Bicornuate Uterus - Endometrial Ablation in A Comptipu42No ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Appendicectomy in All Trimesters of PregnancyDocument7 pagesLaparoscopic Appendicectomy in All Trimesters of PregnancyJason CalvinNo ratings yet
- Normal Vaginal Delivery at Term After Expectant Management of Heterotopic Caesarean Scar Pregnancy: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesNormal Vaginal Delivery at Term After Expectant Management of Heterotopic Caesarean Scar Pregnancy: A Case Reportdiaaabdallah209No ratings yet
- Case Report: Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy in Caesarean Section Scar: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesCase Report: Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy in Caesarean Section Scar: A Case ReportwennyNo ratings yet
- Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy in The Presence of An Intrauterine DeviceDocument5 pagesRuptured Ectopic Pregnancy in The Presence of An Intrauterine DevicePatrick NunsioNo ratings yet
- Sigmoid Volvulus in Pregnancy: Case Report and Review OfliteratureDocument4 pagesSigmoid Volvulus in Pregnancy: Case Report and Review OfliteratureIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Alborzi2014Document5 pagesAlborzi2014dw21541No ratings yet
- Ovarian Pregnancy: Two Case Reports.: Jayeeta Roy, Anindita Sinha BabuDocument5 pagesOvarian Pregnancy: Two Case Reports.: Jayeeta Roy, Anindita Sinha BabuAndriyani MuslimNo ratings yet
- Blighted Ovum: A Case ReportDocument2 pagesBlighted Ovum: A Case Reportakhmad ikhwanNo ratings yet
- Managment of Scar PregnancyDocument43 pagesManagment of Scar Pregnancyvacha sardarNo ratings yet
- Twins PecepDocument8 pagesTwins Pecepjj_cani91No ratings yet
- Adenomyosis Excision Followed by Successful Live Birth After Three Consecutive IVFDocument5 pagesAdenomyosis Excision Followed by Successful Live Birth After Three Consecutive IVFPyuzz RemakeNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Ijscr 2020 01 020Document4 pages10 1016@j Ijscr 2020 01 020ari naNo ratings yet
- Leong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument2 pagesLeong Et Al-2004-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Rare Case of Bicornuate Uterus With Fetal Death in A Multipara WomanDocument2 pagesRare Case of Bicornuate Uterus With Fetal Death in A Multipara WomanInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Case Reports in Women's HealthDocument4 pagesCase Reports in Women's Healthowadokunquick3154No ratings yet
- Case Report Rare Cesarean Section Scar Ectopic Pregnancy Successfully Treated by Methotrexate: A CaseDocument5 pagesCase Report Rare Cesarean Section Scar Ectopic Pregnancy Successfully Treated by Methotrexate: A Casemustafaali9711No ratings yet
- Atb of Amniotic Fluid SludgeDocument20 pagesAtb of Amniotic Fluid SludgeSantiago RollanNo ratings yet
- Ballon Fluoroscopy As Treatment For Intrauterine Adhesions. A Novel ApproachDocument5 pagesBallon Fluoroscopy As Treatment For Intrauterine Adhesions. A Novel ApproachAldito GlasgowNo ratings yet
- Artigo Gravidez EctópicaDocument2 pagesArtigo Gravidez EctópicaKevin UchoaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cerclage and It's Significance in Preventing Second Trimester Abortions Because of Cervical IncompetenceDocument7 pagesCervical Cerclage and It's Significance in Preventing Second Trimester Abortions Because of Cervical IncompetenceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Journal of Pediatric Surgery Case ReportsDocument3 pagesJournal of Pediatric Surgery Case ReportsKhaidar Ismail JuWiNo ratings yet
- Rupture of The Cervix During Pregnancy After Cervical Pessary Insertion For Preventing Preterm BirthDocument4 pagesRupture of The Cervix During Pregnancy After Cervical Pessary Insertion For Preventing Preterm BirthNuril AzizahNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument7 pagesResearch ArticleHazbullah AisyNo ratings yet
- Interstitial Ectopic Pregnancy A Case ReportDocument4 pagesInterstitial Ectopic Pregnancy A Case ReportRina Auliya WahdahNo ratings yet
- Hysterosalpingography A Re - Emerging Study With CDocument7 pagesHysterosalpingography A Re - Emerging Study With CTuyul Yelsi 1No ratings yet
- Medicine: Intrauterine Device Found in An Ovarian TumorDocument5 pagesMedicine: Intrauterine Device Found in An Ovarian TumorRezky amalia basirNo ratings yet
- Stepwise Devascularization Versus B-LyncDocument57 pagesStepwise Devascularization Versus B-LyncBagusHibridaNo ratings yet
- Mitric 2018Document3 pagesMitric 2018Lely WidiawatiNo ratings yet
- A New Technique To Preserve The Uterus in PatientsDocument9 pagesA New Technique To Preserve The Uterus in PatientsMor OB-GYNNo ratings yet
- Sister Mary Joseph Nodule As Cutaneous.9Document3 pagesSister Mary Joseph Nodule As Cutaneous.9Fernando MartinezNo ratings yet
- Prophylactic Uterine Artery Embolization in Second-Trimester Pregnancy Termination With Complete Placenta PreviaDocument8 pagesProphylactic Uterine Artery Embolization in Second-Trimester Pregnancy Termination With Complete Placenta PreviaAs AsNo ratings yet
- MainDocument4 pagesMainselvia oktavianiNo ratings yet
- Women's Health and WellnessDocument4 pagesWomen's Health and WellnessLau RenNo ratings yet
- General Gynaecology:, Leo Francis AquilizanDocument15 pagesGeneral Gynaecology:, Leo Francis AquilizanesjayemNo ratings yet
- Uog 16935Document1 pageUog 16935Razi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Evaluation of The Uterine Scar After.13Document6 pagesUltrasound Evaluation of The Uterine Scar After.13Jessy MacNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Childhood Glaucoma: Clinical Considerations and TechniquesFrom EverandSurgical Management of Childhood Glaucoma: Clinical Considerations and TechniquesAlana L. GrajewskiNo ratings yet
- PGI MANIMTIM - Vaginal Delivery, Breech Delivery and Operative Vaginal DeliveryDocument8 pagesPGI MANIMTIM - Vaginal Delivery, Breech Delivery and Operative Vaginal DeliveryKim Adarem Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Dian AnggrainiDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Dian AnggrainiYohanispendriantoNo ratings yet
- Lecture-22 Prolonged PregnancyDocument24 pagesLecture-22 Prolonged PregnancyMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNo ratings yet
- MDWY70 - Week 5 ExamDocument41 pagesMDWY70 - Week 5 ExamHydra Olivar - PantilganNo ratings yet
- NCM109 Prelim (First Notes)Document10 pagesNCM109 Prelim (First Notes)Mary Queenie Tulin100% (2)
- Lorna Pint AsDocument5 pagesLorna Pint Ascharlyn amadoNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum: 2 Stage of LaborDocument46 pagesIntrapartum: 2 Stage of LaborJamie Haravata100% (1)
- What Is Reproduction?: Male Reproductive System GenesDocument4 pagesWhat Is Reproduction?: Male Reproductive System GenesPrada Maya AnggariNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Classes - Sunnybrook HospitalDocument2 pagesPrenatal Classes - Sunnybrook HospitalScribdNo ratings yet
- Template For Printed Summary of Quarterly Reports To IPHODocument21 pagesTemplate For Printed Summary of Quarterly Reports To IPHORoel AbricaNo ratings yet
- Course Information For Current Semester/Term: Maklumat Kursus Untuk Semester/Penggal SemasaDocument5 pagesCourse Information For Current Semester/Term: Maklumat Kursus Untuk Semester/Penggal SemasaNurul IrhamnaNo ratings yet
- Determining Gravidity and Parity: I. GravidaDocument6 pagesDetermining Gravidity and Parity: I. GravidaDanica CorpuzNo ratings yet
- SYNOPSISDocument25 pagesSYNOPSISpriyankaNo ratings yet
- Problems With Passageway & Pelvic Proportion FINALDocument7 pagesProblems With Passageway & Pelvic Proportion FINALZam PamateNo ratings yet
- Case Report On OligohydramniosDocument3 pagesCase Report On OligohydramniosRakhi BhagatNo ratings yet
- Outcomes of Induction of Labour in Women With Previous Caesarean Delivery: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using A Population DatabaseDocument7 pagesOutcomes of Induction of Labour in Women With Previous Caesarean Delivery: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using A Population DatabaseAndinNo ratings yet
- Basic Antenatal Care Handbook ISBNDocument59 pagesBasic Antenatal Care Handbook ISBNAuliamusy100% (1)
- MCN - P2 Post Test (Reviewer)Document3 pagesMCN - P2 Post Test (Reviewer)cianixNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kesehatan Mercusuar: Hubungan Berat Lahir Dengan Kejadian Ikterus Di Rumah Sakit Dr. M. Djamil PadangDocument5 pagesJurnal Kesehatan Mercusuar: Hubungan Berat Lahir Dengan Kejadian Ikterus Di Rumah Sakit Dr. M. Djamil PadangSafita AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Life Vincent Pallotti HospitalMaternity Fee Structure 2021Document1 pageLife Vincent Pallotti HospitalMaternity Fee Structure 2021minentlendelaNo ratings yet
- Fourth Year B SC Nursing Obstetric and Gynaecological Nursing Obstetric NursingDocument35 pagesFourth Year B SC Nursing Obstetric and Gynaecological Nursing Obstetric Nursingsandeepv080% (1)
- Changed Indications For Cesarean Sections: Ylva Vladic Stjernholm, Karin Petersson & Eva EnerothDocument5 pagesChanged Indications For Cesarean Sections: Ylva Vladic Stjernholm, Karin Petersson & Eva EnerothSam Ath SanNo ratings yet
- LaborDocument2 pagesLaborAngelyn FlorenososNo ratings yet
- 2 PLACENTA PREVIA Case PresentationDocument19 pages2 PLACENTA PREVIA Case PresentationAiswarya ThomasNo ratings yet
- Shiloh Veterinary Hospital: Dell Kay Bertino, DVM Marci Cook, DVM Arielle Mansur, DVMDocument3 pagesShiloh Veterinary Hospital: Dell Kay Bertino, DVM Marci Cook, DVM Arielle Mansur, DVMyonasNo ratings yet
- Can Your Baby Get Pregnant If You Have Sex While PregnantDocument6 pagesCan Your Baby Get Pregnant If You Have Sex While Pregnanteng-scribd100% (2)
- Aida Ayu Mailinda SariDocument11 pagesAida Ayu Mailinda SariMay El-MardhatillahNo ratings yet
- Progression of First Stage LaourDocument14 pagesProgression of First Stage LaourAlmira Dyah PuspitariniNo ratings yet