Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EIA Notes - Week 4
EIA Notes - Week 4
Uploaded by
BHARAT NIKKAMCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 002 - DrivetrainDocument88 pages002 - DrivetrainCarlos PinedaNo ratings yet
- SIMATIC S7 S7-1200 SM 1222 16-Point Digital Output SpecificationsDocument5 pagesSIMATIC S7 S7-1200 SM 1222 16-Point Digital Output SpecificationsMarcio GNo ratings yet
- Papaercraft 29239232392Document15 pagesPapaercraft 29239232392Moony CorbeauNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument27 pagesDC MotorAnonymous AFFiZn100% (2)
- Fundamental of Electrical Engineering EMT 113/4 DC MachinesDocument64 pagesFundamental of Electrical Engineering EMT 113/4 DC Machinesluiz pauloNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project DC Motor and Ac GeDocument29 pagesInvestigatory Project DC Motor and Ac Gemuskansaini1306No ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument14 pagesDC MotorShreyash SargarNo ratings yet
- EMI Unit 4 Part 2 - DC, AC, Stepper Motot and RelaysDocument25 pagesEMI Unit 4 Part 2 - DC, AC, Stepper Motot and RelaysAyushman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Type of NC SystemDocument20 pagesType of NC Systemamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Ktu Module 6Document36 pagesMechatronics Ktu Module 6Adarsh s nairNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DC Electric MotorsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To DC Electric MotorsJames Adrian Abalde SaboNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument4 pagesDC MotorTarakNo ratings yet
- Theory Class - 4Document7 pagesTheory Class - 4MOUSIN PASHANo ratings yet
- Electric Drives - Brushless DC and Reluctance MotorsDocument5 pagesElectric Drives - Brushless DC and Reluctance Motorsfauzi endraNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument38 pagesElectrical Machineshephzi28100% (1)
- 19P205 Electrical MachinesDocument34 pages19P205 Electrical Machinessumanthlogn007No ratings yet
- Assignment # 6Document7 pagesAssignment # 6Jay Ey100% (1)
- DC MotorDocument8 pagesDC Motorven_avv3382No ratings yet
- ECEL LAB#3 AngeladaDocument19 pagesECEL LAB#3 AngeladaAlehamarie AngeladaNo ratings yet
- BEEE e Content Unit 2 DC Gene and DC MotorDocument80 pagesBEEE e Content Unit 2 DC Gene and DC MotorSIVAPRASAD KOLLATI GIEREEE100% (2)
- Types of Electrical Motors1Document12 pagesTypes of Electrical Motors1AnilNo ratings yet
- DC & Ac MotorsDocument13 pagesDC & Ac MotorsYash Jude NathanNo ratings yet
- Direct Current MotorDocument5 pagesDirect Current Motorjamesbergano18No ratings yet
- ECNG-4010 Lecture 05Document37 pagesECNG-4010 Lecture 05Abel BatuNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument16 pagesElectrical MachinesJay kirarNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (Ac) Electrical MachineDocument18 pagesAlternating Current (Ac) Electrical MachineLaw Boon Khang TennarasuNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument14 pagesElectrical Machinesdeepakreddy1226No ratings yet
- Electric DrivesDocument16 pagesElectric DrivesvigneshNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (Assignment)Document7 pagesThermodynamics (Assignment)abdulmajeedabdussalam09No ratings yet
- Shaded Pole Induction MotorDocument7 pagesShaded Pole Induction MotorRahul BhumkarNo ratings yet
- What Is The Commutation ProcessDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Commutation Processكرار قاسم صبيح ابنيانNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Synchronous MachinesDocument34 pagesChapter4 Synchronous Machinessatyakar_vvk100% (2)
- Introduction To Basic MachinesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Basic MachinesFaizan SaeedNo ratings yet
- BLDC Brushless DC MotorDocument22 pagesBLDC Brushless DC MotorNyn SoniNo ratings yet
- Aiet 383 Plcs 04Document13 pagesAiet 383 Plcs 04talha 8byt TalhaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument7 pagesDocumentakhilnandanNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor: Types of MotorsDocument8 pagesElectric Motor: Types of MotorsPlutoNo ratings yet
- Ac Motor Les4Document4 pagesAc Motor Les4Mamadou CissokhoNo ratings yet
- Week 3 B 2 Electric MotorsDocument59 pagesWeek 3 B 2 Electric MotorsCharlton S.InaoNo ratings yet
- What Is A DC Motor?Document14 pagesWhat Is A DC Motor?karthick LNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 BedcDocument61 pagesUnit 2 BedcASHISHNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument25 pagesDC MachinesKristoffer PascualNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Prime MoversDocument90 pagesChapter 2 Prime Moversaimi wahabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Machine IIIDocument24 pagesLecture 1 Machine IIIfrankmogul12No ratings yet
- Ee-120 DC MachineDocument6 pagesEe-120 DC Machinesmk30150No ratings yet
- Answer: Control System (Unit 1)Document18 pagesAnswer: Control System (Unit 1)Ajeet Kumar shuklaNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFDocument29 pagesHTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFVigneshwaran J vNo ratings yet
- Salman Salu ElectricalDocument9 pagesSalman Salu ElectricalAzeem AsgharNo ratings yet
- Induction and Synchronous Motor FundamentalsDocument9 pagesInduction and Synchronous Motor FundamentalsfitxvNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electric MotorsDocument121 pagesIntroduction To Electric MotorsAmged AlbazeliNo ratings yet
- DC & AC Machines and Speed ControlDocument53 pagesDC & AC Machines and Speed ControlInsane Clown Prince60% (5)
- What Is A DC MotorDocument9 pagesWhat Is A DC MotorKylaeunice GuerraNo ratings yet
- Brushless DC MotorsDocument21 pagesBrushless DC MotorsSRL MECHNo ratings yet
- Share ElectricalDocument7 pagesShare ElectricalIsaac Stephen ApenyoNo ratings yet
- Separately Excited DC MotorDocument3 pagesSeparately Excited DC MotorMaitri ShahNo ratings yet
- Basics and Working of AC Motors & Basics of Power GeneratorDocument37 pagesBasics and Working of AC Motors & Basics of Power GeneratorYasir ShaikhNo ratings yet
- A698111855 - 16061 - 12 - 2019 - Unit 3 - 2.Document30 pagesA698111855 - 16061 - 12 - 2019 - Unit 3 - 2.mat mrkNo ratings yet
- Commutator in DC MotorDocument2 pagesCommutator in DC MotorArmy Joel Mariano100% (1)
- DC ServomotorDocument16 pagesDC ServomotorNSS18EE048 BILINE KCNo ratings yet
- AC MachinesDocument3 pagesAC MachinesjelizajordanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III DC MachinesDocument29 pagesUNIT-III DC MachinesK PushyanthNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- Delmars Standard Textbook of Electricity 6th Edition Herman Test BankDocument6 pagesDelmars Standard Textbook of Electricity 6th Edition Herman Test Bankphelandieuz7n100% (32)
- CDH 821C Yedek Prça 2005Document345 pagesCDH 821C Yedek Prça 2005Sales Aydinkaya100% (1)
- Eagle Most Comp UsedDocument4 pagesEagle Most Comp UsedJay-r AustriaNo ratings yet
- Jackalope MASK by LapaStudiosDocument23 pagesJackalope MASK by LapaStudiosJorge Luis Valenzuela SalazarNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of BLDC MotorDocument25 pagesLiterature Review of BLDC MotorOcean PaudelNo ratings yet
- Hxl80 Trans ValveDocument3 pagesHxl80 Trans ValveJay MobNo ratings yet
- Sample Boq of FF WorkDocument115 pagesSample Boq of FF WorkZAHID IQBALNo ratings yet
- Serie 45 Catalogo TecnicoDocument116 pagesSerie 45 Catalogo Tecnicoangel silvaNo ratings yet
- 422ZX JCB Service Manual 89 PaginasDocument89 pages422ZX JCB Service Manual 89 PaginasVinicius LimaNo ratings yet
- Parts List パーツリスト: Published in July 2016 2RVPL070 842RV120 First Edition 2016 年 7 月 初版 2RVPL010Document94 pagesParts List パーツリスト: Published in July 2016 2RVPL070 842RV120 First Edition 2016 年 7 月 初版 2RVPL010newalexdNo ratings yet
- Whitehall Compact Surgical Scrub Sink One StationDocument2 pagesWhitehall Compact Surgical Scrub Sink One StationAndreas SawarsoNo ratings yet
- Wire Assignments: RearrangeDocument4 pagesWire Assignments: RearrangesyimacomNo ratings yet
- Conventional Detector Bases: Ns6 and Ns4 Series BaseDocument2 pagesConventional Detector Bases: Ns6 and Ns4 Series BasecauvongkhongmauNo ratings yet
- D-Tect 2 Quad Pir DatasheetDocument2 pagesD-Tect 2 Quad Pir DatasheetAdrian DeoancaNo ratings yet
- Belt DrivesDocument43 pagesBelt DrivesSugianto BarusNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Bypass Cabinet For Nfinity and GXT 10kvaDocument36 pagesMaintenance Bypass Cabinet For Nfinity and GXT 10kvaAhmedNo ratings yet
- CHM Installation ManualDocument16 pagesCHM Installation ManualconimecNo ratings yet
- Don'T: The Safe Use of LPG Blow TorchesDocument2 pagesDon'T: The Safe Use of LPG Blow TorchesRAMANo ratings yet
- Doosan Forklift b15 20t 2 Testing and Adjusting System OperationDocument10 pagesDoosan Forklift b15 20t 2 Testing and Adjusting System Operationmaria100% (57)
- Primado 2Document15 pagesPrimado 2gadhang dewanggaNo ratings yet
- Aeroneb Pro Service Instruction: TitleDocument4 pagesAeroneb Pro Service Instruction: TitleGABRIELNo ratings yet
- QAP - Rev - 0Document4 pagesQAP - Rev - 0Ravindra YogiNo ratings yet
- SSR Ingersoll RandDocument50 pagesSSR Ingersoll RandMuhamad Luthfi FaisalNo ratings yet
- Price List of Zencelo: Product Cat. No. Description WE (White) SZ (Silver Bronze) Flush SwitchesDocument8 pagesPrice List of Zencelo: Product Cat. No. Description WE (White) SZ (Silver Bronze) Flush SwitchesMuteeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety - Indian Standards - Print DoneDocument6 pagesElectrical Safety - Indian Standards - Print DoneKritika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement of Gases & Clear Liquids With Series 6001 & 6002Document8 pagesFlow Measurement of Gases & Clear Liquids With Series 6001 & 6002Jani WidodoNo ratings yet
EIA Notes - Week 4
EIA Notes - Week 4
Uploaded by
BHARAT NIKKAMOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EIA Notes - Week 4
EIA Notes - Week 4
Uploaded by
BHARAT NIKKAMCopyright:
Available Formats
Elements of Industrial Automation 20ME44P
WEEK -4
ADC: An analog-to-digital converter is any device that converts analog signals (continuous
quantity) into digital signals (discrete time digital representation). The analog signal is a
continuous sinusoidal wave form that cannot be read by a computer, hence the need for
conversion. By converting the analog signal, data can be amplified, added or taken from the
original signal.
DAC: A digital-to-analog converter (DAC) is a device, usually consisting of a single chip,
for converting binary or digital code into an analog signal. A DAC device converts an
abstract finite precise number, typically a fixed-point binary number, into a definite physical
variable such as voltage or pressure.
Motor: An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into
mechanical energy.
Types of motors:
1.DC motor
2.AC motor
3.Stepper Motor
4.Serve Motor
Types of D.C Motors:
1. Series wound motor
2. Shunt wound motor
3. Compound motor
4. Separately excited motor
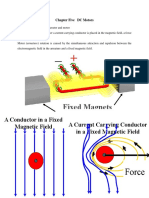
D.C. motors: Figure the basic principle of the d. c. motor,
a loop of wire which is free to rotate in the field of a
permanent magnet. When a current is passed through the
coil, the resulting forces acting on its sides at right angles
to the field cause forces to act on those sides to give
rotation. However, for the rotation to continue, when the
coil passes through the vertical position the current
direction through the coil has to be reversed.
In the conventional d.c. motor, coils of wire are mounted in slots on a cylinder of magnetic
material called the armature. The armature is mounted on bearings and is free to rotate. It is
mounted in the magnetic field produced by field poles. These may be, for small motors,
permanent magnets or electromagnets with their magnetism produced by a current through
the field coils.
Types of A.C. Motors:
1.Single phase A.C. motor
i.Induction motor
iiSynchronous motor.
2.Poly phase A.C. motor
Compiled by Shri.Bharat Nikkam Dept. of Mechanical Engg. Page 1
Elements of Industrial Automation 20ME44P
i.Induction motor
ii.Synchronous motor.
A.C Motor: The single-phase squirrel-cage induction motor
consists of a squirrel-cage rotor, this being copper or aluminum bars
that fit into slots in end rings to form complete electrical circuits .
There are no external electrical connections to the rotor. The basic
motor consists of this rotor with a stator having a set of windings.
When an alternating current passes through the stator windings an
alternating magnetic field is produced. As a result of
electromagnetic induction, e.m.f’s are induced in the conductors of
the rotor and currents flow in the rotor.
Stepper Motor : The stepper motor is a device that produces
rotation through equal angles when digital pulses are supplied as
input.
Types of Stepper Motor:
1.Variable reluctance stepper
2.Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor
3.Hybrid Stepper Motor
Variable reluctance stepper motor: Figure shows the basic
form of the variable reluctance stepper motor. With this form
the rotor is made of soft steel and is cylindrical with four poles.
i.e fewer poles than on the stator. When an opposite pair of
windings has current switched to them, a magnetic field is
produced with lines of force which pass from the stator poles
through the nearest set of poles on the rotor. Since lines of
force can be considered to be rather like elastic thread and
always trying to shorten themselves, the rotor will move until
the rotor and stator poles line up. This is termed the position of
minimum reluctance. This form of stepper generally gives step
angles of 7.5° or 15 °.
Servo motor:
1.DC servo motor
2.AC servo motor
3.Positive rotation
4.Continuous rotation
5.Linear servo motor
Compiled by Shri.Bharat Nikkam Dept. of Mechanical Engg. Page 2
Elements of Industrial Automation 20ME44P
Working Principle of AC Servomotor:
Initially, a constant ac voltage is provided at the main winding of the stator of the ac
servomotor. The other stator terminal of the servomotor is connected to the control
transformer through the control winding.
Due to the provided reference voltage, the shaft of the synchro generator rotates with a
particular speed and attains a certain angular position.
Also, the shaft of the control transformer has a certain specific angular position which is
compared with the angular position of the shaft of the synchro generator.
Further, the comparison of two angular positions provides the error signal. More specifically,
the voltage levels of the corresponding shaft positions are compared which generates the
error signal.
This error signal corresponds to the voltage level present at the control transformer. This
signal is then provided to the servo amplifier which generates variable control voltage.
With this applied voltage, the rotor again attains a specific speed and starts rotation and
sustains until the value of the error signal reaches 0, thereby attaining the desired position of
the motor in the AC servomotors.
Compiled by Shri.Bharat Nikkam Dept. of Mechanical Engg. Page 3
You might also like
- 002 - DrivetrainDocument88 pages002 - DrivetrainCarlos PinedaNo ratings yet
- SIMATIC S7 S7-1200 SM 1222 16-Point Digital Output SpecificationsDocument5 pagesSIMATIC S7 S7-1200 SM 1222 16-Point Digital Output SpecificationsMarcio GNo ratings yet
- Papaercraft 29239232392Document15 pagesPapaercraft 29239232392Moony CorbeauNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument27 pagesDC MotorAnonymous AFFiZn100% (2)
- Fundamental of Electrical Engineering EMT 113/4 DC MachinesDocument64 pagesFundamental of Electrical Engineering EMT 113/4 DC Machinesluiz pauloNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project DC Motor and Ac GeDocument29 pagesInvestigatory Project DC Motor and Ac Gemuskansaini1306No ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument14 pagesDC MotorShreyash SargarNo ratings yet
- EMI Unit 4 Part 2 - DC, AC, Stepper Motot and RelaysDocument25 pagesEMI Unit 4 Part 2 - DC, AC, Stepper Motot and RelaysAyushman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Type of NC SystemDocument20 pagesType of NC Systemamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Ktu Module 6Document36 pagesMechatronics Ktu Module 6Adarsh s nairNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DC Electric MotorsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To DC Electric MotorsJames Adrian Abalde SaboNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument4 pagesDC MotorTarakNo ratings yet
- Theory Class - 4Document7 pagesTheory Class - 4MOUSIN PASHANo ratings yet
- Electric Drives - Brushless DC and Reluctance MotorsDocument5 pagesElectric Drives - Brushless DC and Reluctance Motorsfauzi endraNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument38 pagesElectrical Machineshephzi28100% (1)
- 19P205 Electrical MachinesDocument34 pages19P205 Electrical Machinessumanthlogn007No ratings yet
- Assignment # 6Document7 pagesAssignment # 6Jay Ey100% (1)
- DC MotorDocument8 pagesDC Motorven_avv3382No ratings yet
- ECEL LAB#3 AngeladaDocument19 pagesECEL LAB#3 AngeladaAlehamarie AngeladaNo ratings yet
- BEEE e Content Unit 2 DC Gene and DC MotorDocument80 pagesBEEE e Content Unit 2 DC Gene and DC MotorSIVAPRASAD KOLLATI GIEREEE100% (2)
- Types of Electrical Motors1Document12 pagesTypes of Electrical Motors1AnilNo ratings yet
- DC & Ac MotorsDocument13 pagesDC & Ac MotorsYash Jude NathanNo ratings yet
- Direct Current MotorDocument5 pagesDirect Current Motorjamesbergano18No ratings yet
- ECNG-4010 Lecture 05Document37 pagesECNG-4010 Lecture 05Abel BatuNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument16 pagesElectrical MachinesJay kirarNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (Ac) Electrical MachineDocument18 pagesAlternating Current (Ac) Electrical MachineLaw Boon Khang TennarasuNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument14 pagesElectrical Machinesdeepakreddy1226No ratings yet
- Electric DrivesDocument16 pagesElectric DrivesvigneshNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (Assignment)Document7 pagesThermodynamics (Assignment)abdulmajeedabdussalam09No ratings yet
- Shaded Pole Induction MotorDocument7 pagesShaded Pole Induction MotorRahul BhumkarNo ratings yet
- What Is The Commutation ProcessDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Commutation Processكرار قاسم صبيح ابنيانNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Synchronous MachinesDocument34 pagesChapter4 Synchronous Machinessatyakar_vvk100% (2)
- Introduction To Basic MachinesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Basic MachinesFaizan SaeedNo ratings yet
- BLDC Brushless DC MotorDocument22 pagesBLDC Brushless DC MotorNyn SoniNo ratings yet
- Aiet 383 Plcs 04Document13 pagesAiet 383 Plcs 04talha 8byt TalhaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument7 pagesDocumentakhilnandanNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor: Types of MotorsDocument8 pagesElectric Motor: Types of MotorsPlutoNo ratings yet
- Ac Motor Les4Document4 pagesAc Motor Les4Mamadou CissokhoNo ratings yet
- Week 3 B 2 Electric MotorsDocument59 pagesWeek 3 B 2 Electric MotorsCharlton S.InaoNo ratings yet
- What Is A DC Motor?Document14 pagesWhat Is A DC Motor?karthick LNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 BedcDocument61 pagesUnit 2 BedcASHISHNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument25 pagesDC MachinesKristoffer PascualNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Prime MoversDocument90 pagesChapter 2 Prime Moversaimi wahabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Machine IIIDocument24 pagesLecture 1 Machine IIIfrankmogul12No ratings yet
- Ee-120 DC MachineDocument6 pagesEe-120 DC Machinesmk30150No ratings yet
- Answer: Control System (Unit 1)Document18 pagesAnswer: Control System (Unit 1)Ajeet Kumar shuklaNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFDocument29 pagesHTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFVigneshwaran J vNo ratings yet
- Salman Salu ElectricalDocument9 pagesSalman Salu ElectricalAzeem AsgharNo ratings yet
- Induction and Synchronous Motor FundamentalsDocument9 pagesInduction and Synchronous Motor FundamentalsfitxvNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electric MotorsDocument121 pagesIntroduction To Electric MotorsAmged AlbazeliNo ratings yet
- DC & AC Machines and Speed ControlDocument53 pagesDC & AC Machines and Speed ControlInsane Clown Prince60% (5)
- What Is A DC MotorDocument9 pagesWhat Is A DC MotorKylaeunice GuerraNo ratings yet
- Brushless DC MotorsDocument21 pagesBrushless DC MotorsSRL MECHNo ratings yet
- Share ElectricalDocument7 pagesShare ElectricalIsaac Stephen ApenyoNo ratings yet
- Separately Excited DC MotorDocument3 pagesSeparately Excited DC MotorMaitri ShahNo ratings yet
- Basics and Working of AC Motors & Basics of Power GeneratorDocument37 pagesBasics and Working of AC Motors & Basics of Power GeneratorYasir ShaikhNo ratings yet
- A698111855 - 16061 - 12 - 2019 - Unit 3 - 2.Document30 pagesA698111855 - 16061 - 12 - 2019 - Unit 3 - 2.mat mrkNo ratings yet
- Commutator in DC MotorDocument2 pagesCommutator in DC MotorArmy Joel Mariano100% (1)
- DC ServomotorDocument16 pagesDC ServomotorNSS18EE048 BILINE KCNo ratings yet
- AC MachinesDocument3 pagesAC MachinesjelizajordanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III DC MachinesDocument29 pagesUNIT-III DC MachinesK PushyanthNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- Delmars Standard Textbook of Electricity 6th Edition Herman Test BankDocument6 pagesDelmars Standard Textbook of Electricity 6th Edition Herman Test Bankphelandieuz7n100% (32)
- CDH 821C Yedek Prça 2005Document345 pagesCDH 821C Yedek Prça 2005Sales Aydinkaya100% (1)
- Eagle Most Comp UsedDocument4 pagesEagle Most Comp UsedJay-r AustriaNo ratings yet
- Jackalope MASK by LapaStudiosDocument23 pagesJackalope MASK by LapaStudiosJorge Luis Valenzuela SalazarNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of BLDC MotorDocument25 pagesLiterature Review of BLDC MotorOcean PaudelNo ratings yet
- Hxl80 Trans ValveDocument3 pagesHxl80 Trans ValveJay MobNo ratings yet
- Sample Boq of FF WorkDocument115 pagesSample Boq of FF WorkZAHID IQBALNo ratings yet
- Serie 45 Catalogo TecnicoDocument116 pagesSerie 45 Catalogo Tecnicoangel silvaNo ratings yet
- 422ZX JCB Service Manual 89 PaginasDocument89 pages422ZX JCB Service Manual 89 PaginasVinicius LimaNo ratings yet
- Parts List パーツリスト: Published in July 2016 2RVPL070 842RV120 First Edition 2016 年 7 月 初版 2RVPL010Document94 pagesParts List パーツリスト: Published in July 2016 2RVPL070 842RV120 First Edition 2016 年 7 月 初版 2RVPL010newalexdNo ratings yet
- Whitehall Compact Surgical Scrub Sink One StationDocument2 pagesWhitehall Compact Surgical Scrub Sink One StationAndreas SawarsoNo ratings yet
- Wire Assignments: RearrangeDocument4 pagesWire Assignments: RearrangesyimacomNo ratings yet
- Conventional Detector Bases: Ns6 and Ns4 Series BaseDocument2 pagesConventional Detector Bases: Ns6 and Ns4 Series BasecauvongkhongmauNo ratings yet
- D-Tect 2 Quad Pir DatasheetDocument2 pagesD-Tect 2 Quad Pir DatasheetAdrian DeoancaNo ratings yet
- Belt DrivesDocument43 pagesBelt DrivesSugianto BarusNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Bypass Cabinet For Nfinity and GXT 10kvaDocument36 pagesMaintenance Bypass Cabinet For Nfinity and GXT 10kvaAhmedNo ratings yet
- CHM Installation ManualDocument16 pagesCHM Installation ManualconimecNo ratings yet
- Don'T: The Safe Use of LPG Blow TorchesDocument2 pagesDon'T: The Safe Use of LPG Blow TorchesRAMANo ratings yet
- Doosan Forklift b15 20t 2 Testing and Adjusting System OperationDocument10 pagesDoosan Forklift b15 20t 2 Testing and Adjusting System Operationmaria100% (57)
- Primado 2Document15 pagesPrimado 2gadhang dewanggaNo ratings yet
- Aeroneb Pro Service Instruction: TitleDocument4 pagesAeroneb Pro Service Instruction: TitleGABRIELNo ratings yet
- QAP - Rev - 0Document4 pagesQAP - Rev - 0Ravindra YogiNo ratings yet
- SSR Ingersoll RandDocument50 pagesSSR Ingersoll RandMuhamad Luthfi FaisalNo ratings yet
- Price List of Zencelo: Product Cat. No. Description WE (White) SZ (Silver Bronze) Flush SwitchesDocument8 pagesPrice List of Zencelo: Product Cat. No. Description WE (White) SZ (Silver Bronze) Flush SwitchesMuteeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety - Indian Standards - Print DoneDocument6 pagesElectrical Safety - Indian Standards - Print DoneKritika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement of Gases & Clear Liquids With Series 6001 & 6002Document8 pagesFlow Measurement of Gases & Clear Liquids With Series 6001 & 6002Jani WidodoNo ratings yet