Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SBC 304-07 Sulphate & Chloride Exposure
SBC 304-07 Sulphate & Chloride Exposure
Uploaded by
إسلام عليOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SBC 304-07 Sulphate & Chloride Exposure
SBC 304-07 Sulphate & Chloride Exposure
Uploaded by
إسلام عليCopyright:
Available Formats
Manfouha Sewage Treatment Plant Fourth Stream
Concrete Durability Report
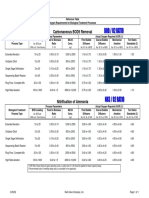
Table 9-8 SBC 304-07 Requirements for Sulphate Exposure
Sulphate Water- Sulphate Cement Type Max. Water- Min. Min. f’c,
Exposure Soluble (SO4) in Cementitious Cementitious MPa
Sulphate Water, ppm Ratio, by Materials
(SO4) Weight* Content,
in Soil, % by kg/m3
Weight
Negligible 0.00 to 0.1 0 to 150 - - - -
Moderate+ 0.1 to 0.2 150 to 500 II 0.50 330 28
Severe 0.2 to 2.0 1500 to 10000 V 0.45 350 30
Very Over 2.0 Over 10000 V plus 0.45 350 30
Severe+ Pozzolan
++
+ If sulphate ions are associated with magnesium ions, supplementary protection, such as application of a
barrier coating, is required,
++Pozzolan that conforms to relevant ASTM standards or that is shown to improve the sulphate resistance
by service records should only be used.
SBC 304-07 table below provides requirements for chloride exposure conditions as summarised in the table
below:
Table 9-9 SBC 304-07 Requirements for Chloride Exposure
Chloride Water- Chloride (Cl-) Cement Type Max. Water- Min. Min. f’c,
Exposure Soluble in Water, Cementitious Cementitious MPa
Chloride (Cl-) ppm Ratio, by Materials
in Soil, % by Weight* Content,
Weight kg/m3
Negligible < 0.05 < 500 - - - -
Moderate 0.05 to 0.1 500 to 2000 - 0.50 330 28
Severe 0.1 to 0.5 2000 to 10000 I 0.45 350 30
Very > 0.5 > 10000 I plus 0.40 370 35
Severe Pozzolan
+
+ Pozzolan that conforms to relevant standards shall only be used.
SBC 304-07 Clause 4.5.1 provides recommendations for durability when concrete is subject to sulphate plus
chloride exposure. This provision states that if concrete is exposed to both chlorides and sulphates, the
lowest applicable maximum water-cementitious materials ratio and highest minimum cementitious materials
content of above tables shall be selected. The corresponding highest fc shall be the governing value for
quality control purposes. The cement type shall be the one required by Table above. The provisions of this
clause are based upon the principle that since reinforcement corrosion is the major form of concrete
deterioration in a chloride-sulphate environment and as sulphate ions do not penetrate deeper into the
concrete cover, it is suggested to use the cement type specified in Table above, rather than that dictated by
the severity of the sulphate exposure conditions.
The Requirements from CS163
Similar to the provisions of BS 8500-1 and BRE SD1, Concrete Society report CS163 assesses the ground
conditions by analysis of groundwater and water/soil extracts and consideration of groundwater mobility and
pH to give an Arabian Peninsula sulphate classification.
Atkins Concrete Durability Report | Rev 1 | 5 April 2017 | 5147554 44
You might also like
- ASME-boiler GuidelinesDocument4 pagesASME-boiler GuidelinesJayanath Nuwan Sameera71% (7)
- PTE Reading Practice Test 4Document7 pagesPTE Reading Practice Test 4Ilda KapajNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water LimitsDocument5 pagesBoiler Water Limitskokkulan0% (1)
- SAES Q 001 Table ExposureDocument4 pagesSAES Q 001 Table ExposureKhurram ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Altret Industries Private LimitedDocument5 pagesAltret Industries Private LimitedJinalNo ratings yet
- O2 Ratio TableDocument1 pageO2 Ratio TableMashaelNo ratings yet
- Hakkani Paper BoilerDocument1 pageHakkani Paper BoilerpacificoneassociatesNo ratings yet
- Kimberlite Water Additive Polymers Product Selection GuideDocument6 pagesKimberlite Water Additive Polymers Product Selection GuideAshish RathoreNo ratings yet
- B S Recommendation For Treatment of Water of Steam Boilers & Water HeatersDocument5 pagesB S Recommendation For Treatment of Water of Steam Boilers & Water HeatersMahmoud Mahmoudm100% (3)
- AdditivsDocument40 pagesAdditivsMohsin MalikNo ratings yet
- Approximate BOQ For Limestone Crusher & Load CentreDocument8 pagesApproximate BOQ For Limestone Crusher & Load CentreSasanka SekharNo ratings yet
- RCC Formula Notes 1 17Document36 pagesRCC Formula Notes 1 17Wajahat KhanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Boiler Feedwater - LenntechDocument1 pageCharacteristics of Boiler Feedwater - LenntechjagjitNo ratings yet
- Lampiran (Data BLH)Document4 pagesLampiran (Data BLH)bella carollineNo ratings yet
- Biomass Boiler Report 11-02-2022Document1 pageBiomass Boiler Report 11-02-2022Mohammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Desulphurization of Hot Metal and Liquid Steel For RAILDocument16 pagesOptimization of Desulphurization of Hot Metal and Liquid Steel For RAILratul_sarkarNo ratings yet
- Cor-Ten B Structural SteelDocument2 pagesCor-Ten B Structural SteelJitendra AmbaselkarNo ratings yet
- My DataDocument36 pagesMy DataPapa K. TokpahNo ratings yet
- 1-Designing and Proportioning Normal Concrete MixturesDocument50 pages1-Designing and Proportioning Normal Concrete MixturesMa ThiNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument1 pageCase StudyDevendra FoniaNo ratings yet
- Sucker Rods Couplings PsDocument2 pagesSucker Rods Couplings PsAlfonso RamosNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Welding ConsumablesDocument17 pagesAssessment of Welding Consumablesmahmoud_allam3No ratings yet
- Carbonation Chloride Penetration of Concrete StructuresDocument4 pagesCarbonation Chloride Penetration of Concrete StructuresAshrafNo ratings yet
- A0176257 PDFDocument1 pageA0176257 PDFZac NastNo ratings yet
- California Bearing Ratio (CBR)Document18 pagesCalifornia Bearing Ratio (CBR)Usman AfzalNo ratings yet
- Material Chemical Composition - Cast Analysis: Brand, Source, Tests Etc. Units RequirementDocument4 pagesMaterial Chemical Composition - Cast Analysis: Brand, Source, Tests Etc. Units RequirementNandika MilindaNo ratings yet
- Grating Raw Material Tolerance & SpecificationDocument4 pagesGrating Raw Material Tolerance & SpecificationBASKARANNo ratings yet
- Sae-J403-2001 - TolDocument2 pagesSae-J403-2001 - TolNorberto A. GhiggiNo ratings yet
- Weighing BalanceDocument4 pagesWeighing BalanceNishit SuvaNo ratings yet
- ASTM A335 Pipe Specification1Document8 pagesASTM A335 Pipe Specification1Rupam BaruahNo ratings yet
- ASTM A335 Pipe Specification1 PDFDocument8 pagesASTM A335 Pipe Specification1 PDFRoberto EliasNo ratings yet
- Bunker Specification Page 2Document15 pagesBunker Specification Page 2mohdfadhirul100% (1)
- Activity: Muhammad Sohaib FA18-GEO-006 10/24/21Document5 pagesActivity: Muhammad Sohaib FA18-GEO-006 10/24/21Abid OwaisNo ratings yet
- Part I - Multiphase Pipeline & Slug Catcher Design GuideDocument1 pagePart I - Multiphase Pipeline & Slug Catcher Design GuideamoghimiNo ratings yet
- Astm-A519 - 06Document13 pagesAstm-A519 - 06claudiaNo ratings yet
- Boiler JIS V2Document4 pagesBoiler JIS V2Nathan BlecharcykNo ratings yet
- Brand, Source, Tests Etc. Units RequirementDocument1 pageBrand, Source, Tests Etc. Units RequirementNandika MilindaNo ratings yet
- Lambada SensorDocument197 pagesLambada SensorTung NguyenNo ratings yet
- California Bearing Ratio (CBR)Document17 pagesCalifornia Bearing Ratio (CBR)ghulam ulaahNo ratings yet
- Extension of Stainless Steel Refining Complex by Twin Tank VOD UnitDocument6 pagesExtension of Stainless Steel Refining Complex by Twin Tank VOD UnitJJNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel 441 UNS S43940Document5 pagesStainless Steel 441 UNS S43940Enrique Ruiz HonoratoNo ratings yet
- RCC Formula Notes 66Document35 pagesRCC Formula Notes 66Pavan kumarNo ratings yet
- pp043-049 ms18Document6 pagespp043-049 ms18Srikanth SrikantiNo ratings yet
- A 514 - A514m - 00 Qtuxnc9bnte0ts1sruqDocument4 pagesA 514 - A514m - 00 Qtuxnc9bnte0ts1sruqdelta lab sangliNo ratings yet
- Article Technical Paper Minimizing F GD CostDocument9 pagesArticle Technical Paper Minimizing F GD CostdsoNo ratings yet
- Tablas de Parametros Agua CalderaDocument4 pagesTablas de Parametros Agua CalderaLeandro BecerraNo ratings yet
- 1786 Amendments 3Document3 pages1786 Amendments 3kiranNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 3 March 2017 TO Is 1786: 2008 High Strength Deformed Bars and Wires For Concrete Reinforcement - SpecificationDocument3 pagesAmendment No. 3 March 2017 TO Is 1786: 2008 High Strength Deformed Bars and Wires For Concrete Reinforcement - SpecificationThetarun75% (4)
- Interaction Between Ceria Nad Hydroxylamine - TamilmaniDocument6 pagesInteraction Between Ceria Nad Hydroxylamine - TamilmaniUmarameshKNo ratings yet
- Carbon - EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCarbon - EquivalentsAliAkarNo ratings yet
- Cation Exchange Resin DUOLITE C20 PDS PDFDocument4 pagesCation Exchange Resin DUOLITE C20 PDS PDFArunkumar ChandaranNo ratings yet
- Sandvik: Stainless Steel Wire ProductsDocument4 pagesSandvik: Stainless Steel Wire ProductsRemo StortiniNo ratings yet
- Plate A36 (2016)Document4 pagesPlate A36 (2016)eko kusumoNo ratings yet
- Re Architecture Adaptive Reuse of BuildiDocument51 pagesRe Architecture Adaptive Reuse of BuildikatarinadjurovicNo ratings yet
- Final Research Paper of Group 3Document36 pagesFinal Research Paper of Group 3mondejar loueljayjustoNo ratings yet
- Thesis Synopsis 2Document3 pagesThesis Synopsis 2anam asgharNo ratings yet
- Department of Education School Form 8 Learner's Basic Health and Nutrition Report (SF8)Document1 pageDepartment of Education School Form 8 Learner's Basic Health and Nutrition Report (SF8)Janna Mae Canubida Lapitan-MañacapNo ratings yet
- Literary AnalysisDocument6 pagesLiterary AnalysisGlademier ShanneNo ratings yet
- PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY - Difference Between Viable Particle and Non-Viable ParticleDocument3 pagesPHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY - Difference Between Viable Particle and Non-Viable ParticleMd Golam Nabi SarnamatNo ratings yet
- The Consequences of Covid-19 On The Sector of Spatial/Urban Planning, Construction, Legalization, and HousingDocument48 pagesThe Consequences of Covid-19 On The Sector of Spatial/Urban Planning, Construction, Legalization, and HousingBlerina BoshnjakuNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Methods and Practices in Indian Leather SectorDocument9 pagesSustainable Methods and Practices in Indian Leather SectorVishwanath SiddhantiNo ratings yet
- Icd ReportDocument118 pagesIcd Reportgurumurthy38No ratings yet
- Drought Monitoring and Assessment Using Landsat TMDocument18 pagesDrought Monitoring and Assessment Using Landsat TMTeddy Arfaansyah PutraNo ratings yet
- Undone Science: Charting Social Movement and Civil Society Challenges To Research Agenda SettingDocument31 pagesUndone Science: Charting Social Movement and Civil Society Challenges To Research Agenda SettingJose LeonNo ratings yet
- Vokabular Za Zavrsni (ENGLESKI 2) - 1622459603Document6 pagesVokabular Za Zavrsni (ENGLESKI 2) - 1622459603Za NoveleNo ratings yet
- 09 Activity 1 - ARGDocument2 pages09 Activity 1 - ARGaeiaNo ratings yet
- (Dynamic Model Simulation of The Effects of Legume Cover Crops (LCC) On Runoff andDocument18 pages(Dynamic Model Simulation of The Effects of Legume Cover Crops (LCC) On Runoff andMUHAMMAD ZIKRON -No ratings yet
- Walthamstow Wetlands Licensing Objection LetterDocument2 pagesWalthamstow Wetlands Licensing Objection LetterAdam WinstanleyNo ratings yet
- Product CatalogueDocument60 pagesProduct CatalogueBogdan MucenicaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Ass. 2Document2 pagesIntroduction Ass. 2Jessabelle RamosNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Resiliensi Masyarakat Terhadap Risiko Bencana Tanah Longsor Di Desa Kayuambon Kabupaten Bandung Ruman SyahfudinDocument13 pagesPengembangan Resiliensi Masyarakat Terhadap Risiko Bencana Tanah Longsor Di Desa Kayuambon Kabupaten Bandung Ruman SyahfudinTreeta GroupNo ratings yet
- Models of Public Policy MakingDocument5 pagesModels of Public Policy MakingdanNo ratings yet
- Upper Thames River Conservation Authority: LegendDocument1 pageUpper Thames River Conservation Authority: LegendDotan NutodNo ratings yet
- Art004 Definite Article The PDFDocument2 pagesArt004 Definite Article The PDFsuzanne_13No ratings yet
- Part A: Listening: Họ và tên: Lớp 8 Trường THCSDocument4 pagesPart A: Listening: Họ và tên: Lớp 8 Trường THCSAlaska EnglishNo ratings yet
- Final Test Revision - (Answer Key)Document10 pagesFinal Test Revision - (Answer Key)Maha AlanjawiNo ratings yet
- Fallingwater, - WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesFallingwater, - WPS OfficeAbdi TirfaNo ratings yet
- Documento Sem TítuloDocument8 pagesDocumento Sem TítuloEuany AlexsandraNo ratings yet
- Practice With Open ClozeDocument2 pagesPractice With Open ClozeAnh Minh HoangNo ratings yet
- Kurukshetra 4-ByjusDocument21 pagesKurukshetra 4-ByjusPriyanka KarnNo ratings yet
- 1st PT in Household Services Grade 8 16-17Document5 pages1st PT in Household Services Grade 8 16-17Marry Jane Lustre CanabalNo ratings yet
- ACI Annual Report: The Voice of The World's AirportsDocument43 pagesACI Annual Report: The Voice of The World's AirportsDewsdeen WalkerNo ratings yet