Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5689794613
5689794613
Uploaded by
DEEPAK KHANDELWALOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5689794613
5689794613
Uploaded by
DEEPAK KHANDELWALCopyright:
Available Formats
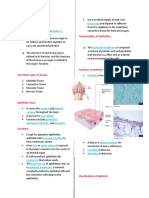
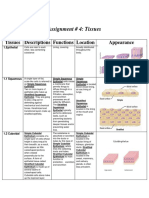
Meristem Location Function
Apical Tips of root & stem Increases the length of root &
stem
lateral Lateral sides of root & Stem Increases the girth of root &
Stem
Intercalary Near the nodes, at the base of Increases the length of
the leaves internodes, increases the
length of the leaves.
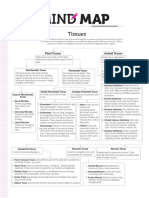
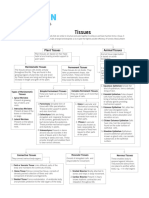
Simple permanent Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma
tissue
Structure Thin cell wall, loosely Elongated cells , Fibrous cells with
packed with irregular thickening at tapering ends.
intercellular spaces the inner corners of Lignified cell wall.
the cell wall with
Pectin and cellulose:
Living / dead Living cells Living cells Dead cells
Location All parts of the plant - At the base of the Stem, hard coat of
roots, stem, leaves, petiole of the leaf , seeds , veins of leaves,
flowers & seeds Stem & branches outer covering of
coconut.
Functions Storage of food, fill Provide support & Provide strength &
vacant spaces, provide flexibility to various rigidity to various
support. parts. plant parts.
Sub-type 1.Aerenchyma:
Help aquatic plants
float in water.
2. Chlorenchyma:
Contains
chloroplasts.it helps to
perform
photosynthesis.
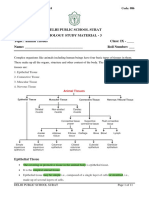
Epithelial tissue Location Structure Function
Squamous epithelium Inner lining of the Thin, small and flat Helps in selective
mouth, blood vessels, cells transportation of
alveoli 10 esophagus, substances
etc.
Stratified squamous Outer layer of the skin Multilayered made up Protection of organs,
of thin small and flat preventing wear and
cells tear of the organs
Columnar epithelium Small interestine Cells are tall and pillar Secretion of digestive
like with upper free juices and absorption
ends showing multiple of digested food
foldings at the site of
absorption
Ciliated columnar Inner surface of the Cells are tall and pillar Cilia push air and
respiratory tract like with upper free mucus forward to
ends having hair like keep the respiratory
projections tract clean
Cuboidal epithelium Kidney tubule Cuboidal cells Reabsorption of water
(nephrons), salivary and other useful
glands substances to form
urine, secretion of
saliva
Glandular epithelium Inner layer of the skin Cells contain glands Secretion of mucus,
which can secrete oil, sweat, etc.
various materials
Connective tissue Location Structure Function
Blood Closed circulatory RBCS, WBCS, Platelets Transportation of
system suspended within the gases, hormones,
liquid plasma. nutrients, waste retic
Bone Form the skeleton Osteocytes are Helps in movement,
embedded within the Supports and protects
solid matrix made up various organs
of calcium phosphate.
Cartilage Ears, nose, larynx Different type of cells Provides shape &
,trachea supported by fibrous , support to organs,
flexible jelly like Lubricates the surface
matins. of the cells.
Ligament At the joints Strong, fibrous & Joins two bones to
highly flexible each other
Tendons At the end of a muscle Strong. Fibrous, less Joins muscles to bones
elastic
Areolar Present between skin Different type of cells Acts as a packaging
& muscles, around the & elastic fibres tissue between the
blood vessels supported by a jelly organs. It supports
like matrix. many delicate organs.
It helps in repair of
tissues.
Adipose Below the skin,around cells filled with fat Storage of fats, supply
the internal organs. droplets embedded energy, provide
within a jelly like insulation.
ground substance.
Muscular tissue Striated Nonstriated Cardiac
Structure Long, cylindrical, Short, spindle shaped, Cylindrical, branched
multinucleated and uninucleated and & uninucleated.
unbranched. unbranched.
Striations They show alternate No striations Light striations
dark & light
bands(Striations).
Work Voluntary Involuntary Involuntary
Location attached to the Present in the internal Walls of the heart.
skeleton organs like:
Tris of the eye,
alimentary canal,
blood vessels, etc
Functions Help in physical Movement of eye lids, Rhythmic contraction
movement of the contraction or dilation and relaxation of the
body. of pupils passage of heart.
food through
alimentary canal , etc
Important terms:
1. Tissue- Tissue is a group of cells having similar origin, structure and function.
2. Differentiation- the process by which a cell attains permanent shape size and function.
3. Voluntary muscles- muscles which can be controlled according to our will.
4. Involuntary muscles -muscles which are not under the control of our will.
5. Impulse: an electrical signal transmitted along a nerve fibre as a response to a stimulus.
You might also like
- Weight Watchers Food List For Gamers: Index of FoodsDocument62 pagesWeight Watchers Food List For Gamers: Index of FoodsPamm100% (7)
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument32 pagesAnaphy Reviewerpatientsafety100% (1)
- Men Are From Mars SummaryDocument7 pagesMen Are From Mars SummaryDeepak Rao Rao100% (2)
- Rio Tinto - Procedure For Compliance Risk AssessmentDocument24 pagesRio Tinto - Procedure For Compliance Risk AssessmentHer Huw100% (1)
- Ix BioDocument4 pagesIx Biokartikvarshney98No ratings yet
- Tissues: Animal Tissues Plant TissuesDocument1 pageTissues: Animal Tissues Plant TissuesAbhishek NarwariyaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Cell Biology and Organisation: 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsDocument47 pages2.0 Cell Biology and Organisation: 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsFHATIN AMIRA BINTI MUSA MoeNo ratings yet
- Revision-Map Chapter 6Document1 pageRevision-Map Chapter 6garv.garimaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuessrianshNo ratings yet
- Histology of Cell and Tissue: Chapter 7: TissuesDocument53 pagesHistology of Cell and Tissue: Chapter 7: TissuesAmirah AdlinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document49 pagesChapter 6Jidnyasa DambhareNo ratings yet
- BIO 9 SM3 23-24pDocument11 pagesBIO 9 SM3 23-24pNandini Pritesh PatelNo ratings yet
- (Lecture - 3) Tissue OrganisationDocument38 pages(Lecture - 3) Tissue OrganisationN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues-Full NotesDocument12 pagesChapter-6 Tissues-Full NotesAdithya VinodNo ratings yet
- Living Processes of Multicellular OrganismsDocument5 pagesLiving Processes of Multicellular Organismsboloqpiau boloqbokNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Tissues - Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab 5 Tissues - Lab ReportbrittNo ratings yet
- Class Ix - Science - Biology - Chapter 6 - Tissues (Animal Tissues) - NotesDocument4 pagesClass Ix - Science - Biology - Chapter 6 - Tissues (Animal Tissues) - NotesVipul TehlanNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheets Animal Cell TypesDocument4 pagesFact Sheets Animal Cell Typessamsung picturesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9-Plant and Animal TissueDocument32 pagesLesson 9-Plant and Animal TissueDarlene FrueldaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissue OwnDocument43 pagesPlant and Animal Tissue Ownapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- Single Squamous EpitheliumDocument28 pagesSingle Squamous EpitheliumLyndonn Santos100% (1)
- TissuesDocument2 pagesTissuesapi-569181610No ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument9 pagesTissues NotesPrathiba AugustineNo ratings yet
- Grade-09 Science Chapter06 TissuesnotesDocument22 pagesGrade-09 Science Chapter06 Tissuesnotesrohitparihar1720No ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life & Tissues - NotesDocument25 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life & Tissues - NotesNaman VatsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TissuesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Tissuesnaziakhaqan14No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 or 4 - Body Tissues and GlandsDocument11 pagesChapter 3 or 4 - Body Tissues and GlandsAlthea BayolaNo ratings yet
- Storage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESDocument14 pagesStorage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESdubeymaya153No ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue TypeDocument7 pagesEpithelial Tissue Typevaynegod5No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument27 pagesPlant and Animal TissuesDoods GaldoNo ratings yet
- TISSUES - Class Notes - SprintDocument40 pagesTISSUES - Class Notes - SprintMr Vinod yadavNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument13 pagesTissuesAdil Khan100% (1)
- Tissues, SkinDocument11 pagesTissues, SkinkimcheeseNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue PDFDocument20 pagesEpithelial Tissue PDFshafa cahyani100% (1)
- Tissues - Comprehensive NotesDocument4 pagesTissues - Comprehensive NotesRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Ang Paggamit NG IbaDocument3 pagesAng Paggamit NG IbakikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsDocument84 pages2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular Organismswickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Meristematic Tis: Plants AnimalsDocument6 pagesMeristematic Tis: Plants AnimalsRajat ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022Document31 pagesPlant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022shalu malani100% (1)
- BIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueDocument19 pagesBIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Levels of OrganisationDocument9 pagesTissues: Levels of OrganisationHarmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- 649539f145572900183c11f2 ## Structural Organisation in Animals ShortDocument4 pages649539f145572900183c11f2 ## Structural Organisation in Animals Shorts.yagyan prasad acharyNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 4: Tissues Explore: 1.: Tissues Descriptions Functions Location AppearanceDocument8 pagesAssignment # 4: Tissues Explore: 1.: Tissues Descriptions Functions Location AppearanceKassandra Shayne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- Biology Notes Chapter 4 Cells and Tissue: 4.2 Cellular Structures and FunctionsDocument10 pagesBiology Notes Chapter 4 Cells and Tissue: 4.2 Cellular Structures and FunctionsFatima Zulqarnain100% (1)
- Class 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23Document4 pagesClass 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23collins thomasNo ratings yet
- Ix Biology 6 1, PPTDocument35 pagesIx Biology 6 1, PPTShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cells and TissuesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Cells and TissuesClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Tissues (FOLW CHART - 1)Document4 pagesTissues (FOLW CHART - 1)RishitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TissuesDocument10 pagesChapter TissuesAarti JainNo ratings yet
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 pagesBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- Biology A-Level OCR A: Specialised Cells & Organism OrganisationDocument2 pagesBiology A-Level OCR A: Specialised Cells & Organism OrganisationSulaimaan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida Class-Ix Biology Handout Topic-Animal TissuesDocument4 pagesAmity International School, Noida Class-Ix Biology Handout Topic-Animal TissuesL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Tissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaDocument3 pagesTissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Tissues Pre LabDocument43 pagesTissues Pre LabCindy-chan DelfinNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL-CELL Group 2Document35 pagesANIMAL-CELL Group 2mjecbjNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Type and Its FunctionDocument36 pagesPlant Cell Type and Its Functionlamberto revecheNo ratings yet
- TISSUES (Prashant Kirad)Document9 pagesTISSUES (Prashant Kirad)abhijotsinghas83No ratings yet
- Quizzes ReviewerDocument8 pagesQuizzes ReviewerAis WallensteinNo ratings yet
- 9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Document29 pages9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Vipul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document11 pagesBiology 1Francois Isabelo EspirituNo ratings yet
- 2 33 MergedDocument2 pages2 33 MergedDEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- QA Glass Bottle - CIPLDocument38 pagesQA Glass Bottle - CIPLDEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Hariom GuptaDocument3 pagesHariom GuptaDEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Revision NotesDocument15 pagesClass 9 Science Chapter 1 Revision NotesDEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Beer RecoveryDocument7 pagesBeer RecoveryDEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesDocument46 pagesClass 9 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesDEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Silver Oak School Summer Holiday Homework (2022-23) Class IxDocument6 pagesSilver Oak School Summer Holiday Homework (2022-23) Class IxDEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- 9 Hindi B Test Paper ch1 1Document2 pages9 Hindi B Test Paper ch1 1DEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 Notes - The Story of Village PalampurDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 Notes - The Story of Village PalampurDEEPAK KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Multigrade Teaching: Lesson 1Document4 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Multigrade Teaching: Lesson 1Eda Angela OabNo ratings yet
- Jacqueline Bouvier Kennedy Onassis,' by Barbara Leaming - NYTimesDocument4 pagesJacqueline Bouvier Kennedy Onassis,' by Barbara Leaming - NYTimesCorola_de_minuniNo ratings yet
- IA - Consumer Electronics Servicing CGDocument25 pagesIA - Consumer Electronics Servicing CGGlenn TotzNo ratings yet
- SBS Basalt 101Document4 pagesSBS Basalt 101kelvinyeohNo ratings yet
- Release MergedDocument76 pagesRelease MergedAndri aryanataNo ratings yet
- Annex B - Bdoi Par Facility Business SecureDocument4 pagesAnnex B - Bdoi Par Facility Business SecureMichael PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Document ListDocument64 pagesDocument ListBALACHITRANo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Male and Female Genitals During Coitus and Female Sexual ArousalDocument6 pagesMagnetic Resonance Imaging of Male and Female Genitals During Coitus and Female Sexual Arousalapi-3738541100% (1)
- 2.5. PBM Serie Diverter EriksDocument20 pages2.5. PBM Serie Diverter EriksmguisseNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Test Report: Calibration Test Report - Pressure Recorder SATR-A-2004 22-Jan-18 MechDocument2 pagesSaudi Aramco Test Report: Calibration Test Report - Pressure Recorder SATR-A-2004 22-Jan-18 MechaneeshNo ratings yet
- Essential OilsDocument40 pagesEssential OilsmariyajaisonNo ratings yet
- Allies or Enemies: How Those Needing Help Learned To Help Themselves in The Face of Bad BloodDocument88 pagesAllies or Enemies: How Those Needing Help Learned To Help Themselves in The Face of Bad BloodChantal At HfnzNo ratings yet
- Manganese Removal Suez Water HandbookDocument13 pagesManganese Removal Suez Water HandbookAdam KulikowskiNo ratings yet
- Códigos de Erro P720Document1,322 pagesCódigos de Erro P720Mauricio Cavalcante da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Table HandlingDocument5 pagesTable HandlingbayuNo ratings yet
- Datasheet (10) Fuente ConmutadaDocument11 pagesDatasheet (10) Fuente ConmutadaJose Antonio SeguraNo ratings yet
- Reuter Cleaner - Safety Data SheetDocument12 pagesReuter Cleaner - Safety Data SheetFALCAO2007No ratings yet
- Report BREF Greece EN PDFDocument20 pagesReport BREF Greece EN PDFaegean227No ratings yet
- Ion Test PDFDocument11 pagesIon Test PDFAnderson XiaoNo ratings yet
- The Chaos of Longing NodrmDocument129 pagesThe Chaos of Longing NodrmonlinebookkNo ratings yet
- MBA Unemployment ReportDocument19 pagesMBA Unemployment ReportShiva NandNo ratings yet
- The Aggression of Three Main Characters in The Island of DRDocument13 pagesThe Aggression of Three Main Characters in The Island of DRMuawiyah PramudhitaNo ratings yet
- 1000 Kva 400v c32 Low BSFC PrimeDocument6 pages1000 Kva 400v c32 Low BSFC PrimeelipholebNo ratings yet
- Biological DeodorizerDocument6 pagesBiological DeodorizerPOEM HUBNo ratings yet
- Catálogo EraDocument8 pagesCatálogo EraFRANCO HUACANJULCA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 3 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial Chapter 3 PDFToukaNo ratings yet