Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Minerals 2
Plant Minerals 2
Uploaded by
zaijah taylor4ACopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sample Operative Dictation OBGYNDocument66 pagesSample Operative Dictation OBGYNEli Eid100% (2)
- Nutrient Functions and Deficiency SymptomsDocument2 pagesNutrient Functions and Deficiency Symptomsdelacruzjoby100% (1)
- Standards Reference Guide PDFDocument4 pagesStandards Reference Guide PDFmusNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 3 Form 5 Presentation (Latest)Document28 pagesBiology Chapter 3 Form 5 Presentation (Latest)Alexander Yong Jin RongNo ratings yet
- Bio CH3 F5 StudywithadminDocument5 pagesBio CH3 F5 StudywithadminariananitafahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Five - Nutrient Requirements and TestingDocument45 pagesLesson Five - Nutrient Requirements and TestingBangjoNo ratings yet
- 1.1.11 Nutrition in PlantsDocument6 pages1.1.11 Nutrition in PlantsAhenkan kwameNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument13 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectBalajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nutrition in Plants (Biology SPM)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Nutrition in Plants (Biology SPM)ALAMEL MANZGHAI A/P GANESONNo ratings yet
- Plant Fertilizer Label Activity DoneDocument3 pagesPlant Fertilizer Label Activity DoneBianca PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 12 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- Nutrients DeficiencyDocument56 pagesNutrients DeficiencykeerthirajanjaisankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nutrition in PlantsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Nutrition in PlantsALAMEL MANZGHAI A/P GANESONNo ratings yet
- FSSAI Ebook Principles Basics Food ChemistryDocument12 pagesFSSAI Ebook Principles Basics Food ChemistrybalwanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Chemistry of Life Unit One Molecules For LifeDocument26 pagesTopic 1 The Chemistry of Life Unit One Molecules For LifekhotsoNo ratings yet
- CopperDocument7 pagesCopperkimberlymphiningoNo ratings yet
- Bio 49 Lecture Assignment (Mineral Nutrition)Document5 pagesBio 49 Lecture Assignment (Mineral Nutrition)Niña Shanen IwagNo ratings yet
- 6.9 Macronutrients and Micronutrients in PlantsDocument13 pages6.9 Macronutrients and Micronutrients in Plants143davbecNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis MineralsDocument14 pagesPhotosynthesis MineralsMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Mineral Deficiencies & Hydroponics PDFDocument75 pages3 Mineral Deficiencies & Hydroponics PDFChezca Alexine QuerbinNo ratings yet
- Essential Plant Nutrients and Their Functions: NitrogenDocument4 pagesEssential Plant Nutrients and Their Functions: NitrogenradhesharmaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Fact SheetDocument1 pagePhotosynthesis Fact SheetamanyNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Plant GrowthDocument11 pagesMinerals and Plant GrowthAadhya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Soil FertilityDocument84 pagesSoil FertilityakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Planet and Tissue CulturelDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Planet and Tissue CulturelsunfonemmaNo ratings yet
- لمحاضرة الاولى نقص العناصرDocument40 pagesلمحاضرة الاولى نقص العناصرAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Plant Micro and Macro Nutrient DeficiencyDocument26 pagesPlant Micro and Macro Nutrient DeficiencyMariano Edz0% (1)
- Organic Manures - 17.12.12Document59 pagesOrganic Manures - 17.12.12Ananda Preethi100% (1)
- Unit 2 Agr-105Document85 pagesUnit 2 Agr-105RY4NNo ratings yet
- Plant Mineral NutritionDocument44 pagesPlant Mineral NutritionRencsNo ratings yet
- PEN Plant PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPEN Plant Physiologywehrmacht.refugioNo ratings yet
- NutrientsDocument1 pageNutrientstsupkoNo ratings yet
- Apply The Recommended Kind and Rate of FertilizerDocument20 pagesApply The Recommended Kind and Rate of FertilizerRon EncinasNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument20 pagesBiologySam DanielNo ratings yet
- Mineral Salts For Plants-2 PDFDocument17 pagesMineral Salts For Plants-2 PDFSarah NaelNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Plant GrowthDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis and Plant GrowthzaivrkNo ratings yet
- Bio F5 C3 Nutrition in Plants: Prepared By: Ruksana AshrufDocument12 pagesBio F5 C3 Nutrition in Plants: Prepared By: Ruksana AshrufRuksana AshrufNo ratings yet
- Shova Biology SheetsDocument3 pagesShova Biology Sheetsemdadul2009No ratings yet
- 3.1 Main Inorganic NutrientsDocument14 pages3.1 Main Inorganic NutrientsIYLIA NADHIRAH BINTI MD NADZRI MoeNo ratings yet
- Plant NutrientsDocument8 pagesPlant Nutrientspanashenyika34No ratings yet
- 11.modes of Plant NutritionDocument8 pages11.modes of Plant NutritionRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Functions of Essential Elements in PlantsDocument9 pagesFunctions of Essential Elements in PlantsImtiaz MiahNo ratings yet
- Hopkins4e PPT ch4Document57 pagesHopkins4e PPT ch4api-355298421No ratings yet
- Plant Deficiency & Toxicity Guide! (Garden Talk #28) Part 1Document36 pagesPlant Deficiency & Toxicity Guide! (Garden Talk #28) Part 1mamont12No ratings yet
- Soil Fertility and ProductivityDocument26 pagesSoil Fertility and Productivitypriaj46No ratings yet
- MineralsDocument13 pagesMineralsAima AzharNo ratings yet
- Deficiency of Micro NutrientsDocument21 pagesDeficiency of Micro NutrientsQasim SajjadNo ratings yet
- Plant PhsiologyDocument67 pagesPlant Phsiologyassdsa100% (2)
- Micronutrients Unit2Document30 pagesMicronutrients Unit2hkami6620No ratings yet
- Hydroponics I Plant NutritionDocument18 pagesHydroponics I Plant Nutritionrishit.pal.ug21No ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument44 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISsuggaballNo ratings yet
- Biology SQ3RDocument68 pagesBiology SQ3RJay JustNo ratings yet
- CRS002 AssignmentDocument4 pagesCRS002 Assignmentdennis calizaNo ratings yet
- (24.01) Plant Essential ElementsDocument33 pages(24.01) Plant Essential ElementsTang Tiong Min 郑中铭No ratings yet
- Deficiency and Toxicity SymptomsDocument56 pagesDeficiency and Toxicity SymptomsYamaguchi KumikoNo ratings yet
- Soil 2a - Nutrient DeficiencyDocument5 pagesSoil 2a - Nutrient DeficiencyMARY ANN HUBILLANo ratings yet
- 12 Mineral NutritionDocument5 pages12 Mineral NutritionDe DasNo ratings yet
- q4 Plant Nutrition and Development w2Document48 pagesq4 Plant Nutrition and Development w2Russell AggasidNo ratings yet
- 5 Life at Molecular Level OwnDocument56 pages5 Life at Molecular Level Ownapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Common Nutrient Deficiency SymptomsDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Common Nutrient Deficiency SymptomsdelacruzjobyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Lesson 1 PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesChapter 6 Lesson 1 PhotosynthesisAli waleed AbdalmoatyNo ratings yet
- Annual Plant Reviews, Root DevelopmentFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Root DevelopmentTom BeeckmanNo ratings yet
- Biology MAY 2018Document28 pagesBiology MAY 2018zaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Test MatchDocument2 pagesTest Matchzaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2020 P1 SolutionsDocument16 pagesCSEC Biology June 2020 P1 Solutionszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Transport in Humans - CSEC Past Paper QuestionsDocument27 pagesTransport in Humans - CSEC Past Paper Questionszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Transport in Multicellular OrganismsDocument41 pagesTransport in Multicellular Organismszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- IT - SBA - 2023 - Question With RubricDocument16 pagesIT - SBA - 2023 - Question With Rubriczaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- BerryDocument3 pagesBerryzaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- "A Stone's Throw" by Elma Mitchell Class NotesDocument6 pages"A Stone's Throw" by Elma Mitchell Class Noteszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Transport in Plant - Class NotesDocument32 pagesTransport in Plant - Class Noteszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Mom Luby and The Social WorkerDocument3 pagesMom Luby and The Social Workerzaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Plant Minerals 1Document2 pagesPlant Minerals 1zaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition, DigestionDocument13 pagesHuman Nutrition, Digestionzaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument7 pagesArgumentative EssaynemoviNo ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP TIẾNG ANH 1 CUỐI HPDocument14 pagesÔN TẬP TIẾNG ANH 1 CUỐI HPdty2357203010065No ratings yet
- Metabolic and Complicated Cataract: DR - Ajai Agrawal Additional Professor Department of Ophthalmology AIIMS, RishikeshDocument31 pagesMetabolic and Complicated Cataract: DR - Ajai Agrawal Additional Professor Department of Ophthalmology AIIMS, Rishikeshsai shantanu100% (1)
- NCP Spiritual DistressDocument3 pagesNCP Spiritual DistressAngelo ArabejoNo ratings yet
- Binge Anxiety Killer Cheat Sheet: InstructionsDocument4 pagesBinge Anxiety Killer Cheat Sheet: Instructionsdoppler_No ratings yet
- Air Water Land Noise Pollution Information and PicsDocument10 pagesAir Water Land Noise Pollution Information and PicsHarendra Yadav100% (3)
- The Question of Sex Education in SchoolsDocument2 pagesThe Question of Sex Education in SchoolsPhoebe FranciscoNo ratings yet
- KAMASUTRA IN PRACTICE: The Use of Sexual Positions in Czech and Slovak Citizens and Its Association With Female OrgasmicityDocument2 pagesKAMASUTRA IN PRACTICE: The Use of Sexual Positions in Czech and Slovak Citizens and Its Association With Female OrgasmicityPriya SemwalNo ratings yet
- Hand - Arm Vibration: Training GuideDocument5 pagesHand - Arm Vibration: Training GuideSaddem HadfiNo ratings yet
- Guideline Conduct Bioequivalence Studies Veterinary Medicinal Products Revision 4 - enDocument32 pagesGuideline Conduct Bioequivalence Studies Veterinary Medicinal Products Revision 4 - ensunieljagtap1982No ratings yet
- 2nd Draft FYP - Mental Health Awareness CoursewareDocument24 pages2nd Draft FYP - Mental Health Awareness CoursewareIZZAH FAHMIDAH BINTI ISMAIL -No ratings yet
- 45 and Beyond - How PICC Continues To Be The Premier MICE Venue For Decades - BusinessWorld OnlineDocument5 pages45 and Beyond - How PICC Continues To Be The Premier MICE Venue For Decades - BusinessWorld OnlineRaven Nicole MoralesNo ratings yet
- Shigella PDFDocument2 pagesShigella PDFxpmathNo ratings yet
- A Sacrificial Lov3 Research - NEWDocument21 pagesA Sacrificial Lov3 Research - NEWJustinemae UbayNo ratings yet
- Tpla2: Sample Volumes Sample Sample DilutionDocument3 pagesTpla2: Sample Volumes Sample Sample DilutionhairiNo ratings yet
- Safety and HealthDocument23 pagesSafety and HealthIan MardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Women's Preference For Vaginal Delivery:determining FactorsDocument55 pagesWomen's Preference For Vaginal Delivery:determining FactorsGifty OsafoNo ratings yet
- WIC Outreach For LAs Planning Guide and ToolsDocument9 pagesWIC Outreach For LAs Planning Guide and ToolsCherotichNo ratings yet
- Poster Chi2 - Ocular Albinism HKDocument1 pagePoster Chi2 - Ocular Albinism HKyollayusticiaNo ratings yet
- Frankenstein Theme EssayDocument5 pagesFrankenstein Theme Essayafabifazv100% (2)
- Jawbone CavitationsDocument8 pagesJawbone CavitationsCAESA96No ratings yet
- Understanding Communication and ConsentDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Communication and ConsentCHRIS FLYNNNo ratings yet
- Katrin Barnard Theory PciDocument34 pagesKatrin Barnard Theory PciArum NingtiasNo ratings yet
- Order of DrawDocument8 pagesOrder of DrawVincent ReyesNo ratings yet
- Soal BAHASA INGGRISDocument20 pagesSoal BAHASA INGGRISAdi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- PROGNOSIS EbmDocument25 pagesPROGNOSIS EbmcarinasheliaNo ratings yet
- USMMA CatalogDocument134 pagesUSMMA CatalogMANUEL ANTONIO DE LA CRUZ SALCEDONo ratings yet
- Final-Psych-Drug StudyDocument5 pagesFinal-Psych-Drug StudySolsona Natl HS MaanantengNo ratings yet
Plant Minerals 2
Plant Minerals 2
Uploaded by
zaijah taylor4ACopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Minerals 2
Plant Minerals 2
Uploaded by
zaijah taylor4ACopyright:
Available Formats
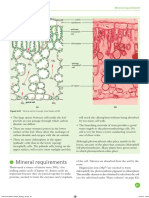
Mineral nutrition in plants
Plants require a variety of minerals for healthy growth and development. These are absorbed from the
soil by plant roots in the form of ions.
Table 7.1 The major minerals required by plants
Element Form in which Functions Results of deficiency
plants obtain
the element
Nitrogen Nitrate ions, • To make proteins used for • Poor growth.
NO3− plant growth. • Chlorosis (yellowing) of leaves,
• To make chlorophyll. especially older leaves.
• Underdeveloped leaves.
Magnesium Magnesium • To make chlorophyll; • Chlorosis of leaves.
ions, Mg2+ magnesium forms part of
the chlorophyll molecule.
Phosphorus Phosphate • To make ATP. • Stunted growth, i.e. short stems.
ions, PO43− • To make some proteins. • Dull, purplish green leaves with
curly brown edges.
• Poor root growth.
Potassium Potassium ions, • To help maintain the • Leaves have yellow-brown margins
K + correct salt balance in and brown spots that give a
cells. mottled appearance.
• To help in photosynthesis. • Premature death of leaves.
Sulfur Sulfate ions, • To make proteins. • Poor growth.
SO42− • Chlorosis of leaves.
Calcium Calcium ions, • To make cell walls in the • Poor, stunted growth.
Ca2+ tips of growing roots and • Death of the growing tips of roots
shoots. and shoots.
• Poor bud development.
Revision questions
1 Distinguish between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition.
2 What happens when an organism feeds saprophytically?
3 Explain in detail how a green leaf manufactures glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
4 Write a balanced chemical equation to summarise the process of photosynthesis.
5 Describe FOUR ways in which the internal structure of a green leaf is adapted to
carry out photosynthesis.
6 Identify THREE environmental factors that affect the rate at which green plants
produce glucose.
7 Suggest THREE ways that plants can utilise the glucose produced in photosynthesis.
8 Why are plants growing in a soil deficient in nitrogen usually small with
yellow leaves?
50 7 Concise Revision Course: CSEC® Biology
You might also like
- Sample Operative Dictation OBGYNDocument66 pagesSample Operative Dictation OBGYNEli Eid100% (2)
- Nutrient Functions and Deficiency SymptomsDocument2 pagesNutrient Functions and Deficiency Symptomsdelacruzjoby100% (1)
- Standards Reference Guide PDFDocument4 pagesStandards Reference Guide PDFmusNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 3 Form 5 Presentation (Latest)Document28 pagesBiology Chapter 3 Form 5 Presentation (Latest)Alexander Yong Jin RongNo ratings yet
- Bio CH3 F5 StudywithadminDocument5 pagesBio CH3 F5 StudywithadminariananitafahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Five - Nutrient Requirements and TestingDocument45 pagesLesson Five - Nutrient Requirements and TestingBangjoNo ratings yet
- 1.1.11 Nutrition in PlantsDocument6 pages1.1.11 Nutrition in PlantsAhenkan kwameNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument13 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectBalajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nutrition in Plants (Biology SPM)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Nutrition in Plants (Biology SPM)ALAMEL MANZGHAI A/P GANESONNo ratings yet
- Plant Fertilizer Label Activity DoneDocument3 pagesPlant Fertilizer Label Activity DoneBianca PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 12 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- Nutrients DeficiencyDocument56 pagesNutrients DeficiencykeerthirajanjaisankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nutrition in PlantsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Nutrition in PlantsALAMEL MANZGHAI A/P GANESONNo ratings yet
- FSSAI Ebook Principles Basics Food ChemistryDocument12 pagesFSSAI Ebook Principles Basics Food ChemistrybalwanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Chemistry of Life Unit One Molecules For LifeDocument26 pagesTopic 1 The Chemistry of Life Unit One Molecules For LifekhotsoNo ratings yet
- CopperDocument7 pagesCopperkimberlymphiningoNo ratings yet
- Bio 49 Lecture Assignment (Mineral Nutrition)Document5 pagesBio 49 Lecture Assignment (Mineral Nutrition)Niña Shanen IwagNo ratings yet
- 6.9 Macronutrients and Micronutrients in PlantsDocument13 pages6.9 Macronutrients and Micronutrients in Plants143davbecNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis MineralsDocument14 pagesPhotosynthesis MineralsMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Mineral Deficiencies & Hydroponics PDFDocument75 pages3 Mineral Deficiencies & Hydroponics PDFChezca Alexine QuerbinNo ratings yet
- Essential Plant Nutrients and Their Functions: NitrogenDocument4 pagesEssential Plant Nutrients and Their Functions: NitrogenradhesharmaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Fact SheetDocument1 pagePhotosynthesis Fact SheetamanyNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Plant GrowthDocument11 pagesMinerals and Plant GrowthAadhya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Soil FertilityDocument84 pagesSoil FertilityakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Planet and Tissue CulturelDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Planet and Tissue CulturelsunfonemmaNo ratings yet
- لمحاضرة الاولى نقص العناصرDocument40 pagesلمحاضرة الاولى نقص العناصرAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Plant Micro and Macro Nutrient DeficiencyDocument26 pagesPlant Micro and Macro Nutrient DeficiencyMariano Edz0% (1)
- Organic Manures - 17.12.12Document59 pagesOrganic Manures - 17.12.12Ananda Preethi100% (1)
- Unit 2 Agr-105Document85 pagesUnit 2 Agr-105RY4NNo ratings yet
- Plant Mineral NutritionDocument44 pagesPlant Mineral NutritionRencsNo ratings yet
- PEN Plant PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPEN Plant Physiologywehrmacht.refugioNo ratings yet
- NutrientsDocument1 pageNutrientstsupkoNo ratings yet
- Apply The Recommended Kind and Rate of FertilizerDocument20 pagesApply The Recommended Kind and Rate of FertilizerRon EncinasNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument20 pagesBiologySam DanielNo ratings yet
- Mineral Salts For Plants-2 PDFDocument17 pagesMineral Salts For Plants-2 PDFSarah NaelNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Plant GrowthDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis and Plant GrowthzaivrkNo ratings yet
- Bio F5 C3 Nutrition in Plants: Prepared By: Ruksana AshrufDocument12 pagesBio F5 C3 Nutrition in Plants: Prepared By: Ruksana AshrufRuksana AshrufNo ratings yet
- Shova Biology SheetsDocument3 pagesShova Biology Sheetsemdadul2009No ratings yet
- 3.1 Main Inorganic NutrientsDocument14 pages3.1 Main Inorganic NutrientsIYLIA NADHIRAH BINTI MD NADZRI MoeNo ratings yet
- Plant NutrientsDocument8 pagesPlant Nutrientspanashenyika34No ratings yet
- 11.modes of Plant NutritionDocument8 pages11.modes of Plant NutritionRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Functions of Essential Elements in PlantsDocument9 pagesFunctions of Essential Elements in PlantsImtiaz MiahNo ratings yet
- Hopkins4e PPT ch4Document57 pagesHopkins4e PPT ch4api-355298421No ratings yet
- Plant Deficiency & Toxicity Guide! (Garden Talk #28) Part 1Document36 pagesPlant Deficiency & Toxicity Guide! (Garden Talk #28) Part 1mamont12No ratings yet
- Soil Fertility and ProductivityDocument26 pagesSoil Fertility and Productivitypriaj46No ratings yet
- MineralsDocument13 pagesMineralsAima AzharNo ratings yet
- Deficiency of Micro NutrientsDocument21 pagesDeficiency of Micro NutrientsQasim SajjadNo ratings yet
- Plant PhsiologyDocument67 pagesPlant Phsiologyassdsa100% (2)
- Micronutrients Unit2Document30 pagesMicronutrients Unit2hkami6620No ratings yet
- Hydroponics I Plant NutritionDocument18 pagesHydroponics I Plant Nutritionrishit.pal.ug21No ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument44 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISsuggaballNo ratings yet
- Biology SQ3RDocument68 pagesBiology SQ3RJay JustNo ratings yet
- CRS002 AssignmentDocument4 pagesCRS002 Assignmentdennis calizaNo ratings yet
- (24.01) Plant Essential ElementsDocument33 pages(24.01) Plant Essential ElementsTang Tiong Min 郑中铭No ratings yet
- Deficiency and Toxicity SymptomsDocument56 pagesDeficiency and Toxicity SymptomsYamaguchi KumikoNo ratings yet
- Soil 2a - Nutrient DeficiencyDocument5 pagesSoil 2a - Nutrient DeficiencyMARY ANN HUBILLANo ratings yet
- 12 Mineral NutritionDocument5 pages12 Mineral NutritionDe DasNo ratings yet
- q4 Plant Nutrition and Development w2Document48 pagesq4 Plant Nutrition and Development w2Russell AggasidNo ratings yet
- 5 Life at Molecular Level OwnDocument56 pages5 Life at Molecular Level Ownapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Common Nutrient Deficiency SymptomsDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Common Nutrient Deficiency SymptomsdelacruzjobyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Lesson 1 PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesChapter 6 Lesson 1 PhotosynthesisAli waleed AbdalmoatyNo ratings yet
- Annual Plant Reviews, Root DevelopmentFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Root DevelopmentTom BeeckmanNo ratings yet
- Biology MAY 2018Document28 pagesBiology MAY 2018zaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Test MatchDocument2 pagesTest Matchzaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2020 P1 SolutionsDocument16 pagesCSEC Biology June 2020 P1 Solutionszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Transport in Humans - CSEC Past Paper QuestionsDocument27 pagesTransport in Humans - CSEC Past Paper Questionszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Transport in Multicellular OrganismsDocument41 pagesTransport in Multicellular Organismszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- IT - SBA - 2023 - Question With RubricDocument16 pagesIT - SBA - 2023 - Question With Rubriczaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- BerryDocument3 pagesBerryzaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- "A Stone's Throw" by Elma Mitchell Class NotesDocument6 pages"A Stone's Throw" by Elma Mitchell Class Noteszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Transport in Plant - Class NotesDocument32 pagesTransport in Plant - Class Noteszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Mom Luby and The Social WorkerDocument3 pagesMom Luby and The Social Workerzaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Plant Minerals 1Document2 pagesPlant Minerals 1zaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition, DigestionDocument13 pagesHuman Nutrition, Digestionzaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument7 pagesArgumentative EssaynemoviNo ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP TIẾNG ANH 1 CUỐI HPDocument14 pagesÔN TẬP TIẾNG ANH 1 CUỐI HPdty2357203010065No ratings yet
- Metabolic and Complicated Cataract: DR - Ajai Agrawal Additional Professor Department of Ophthalmology AIIMS, RishikeshDocument31 pagesMetabolic and Complicated Cataract: DR - Ajai Agrawal Additional Professor Department of Ophthalmology AIIMS, Rishikeshsai shantanu100% (1)
- NCP Spiritual DistressDocument3 pagesNCP Spiritual DistressAngelo ArabejoNo ratings yet
- Binge Anxiety Killer Cheat Sheet: InstructionsDocument4 pagesBinge Anxiety Killer Cheat Sheet: Instructionsdoppler_No ratings yet
- Air Water Land Noise Pollution Information and PicsDocument10 pagesAir Water Land Noise Pollution Information and PicsHarendra Yadav100% (3)
- The Question of Sex Education in SchoolsDocument2 pagesThe Question of Sex Education in SchoolsPhoebe FranciscoNo ratings yet
- KAMASUTRA IN PRACTICE: The Use of Sexual Positions in Czech and Slovak Citizens and Its Association With Female OrgasmicityDocument2 pagesKAMASUTRA IN PRACTICE: The Use of Sexual Positions in Czech and Slovak Citizens and Its Association With Female OrgasmicityPriya SemwalNo ratings yet
- Hand - Arm Vibration: Training GuideDocument5 pagesHand - Arm Vibration: Training GuideSaddem HadfiNo ratings yet
- Guideline Conduct Bioequivalence Studies Veterinary Medicinal Products Revision 4 - enDocument32 pagesGuideline Conduct Bioequivalence Studies Veterinary Medicinal Products Revision 4 - ensunieljagtap1982No ratings yet
- 2nd Draft FYP - Mental Health Awareness CoursewareDocument24 pages2nd Draft FYP - Mental Health Awareness CoursewareIZZAH FAHMIDAH BINTI ISMAIL -No ratings yet
- 45 and Beyond - How PICC Continues To Be The Premier MICE Venue For Decades - BusinessWorld OnlineDocument5 pages45 and Beyond - How PICC Continues To Be The Premier MICE Venue For Decades - BusinessWorld OnlineRaven Nicole MoralesNo ratings yet
- Shigella PDFDocument2 pagesShigella PDFxpmathNo ratings yet
- A Sacrificial Lov3 Research - NEWDocument21 pagesA Sacrificial Lov3 Research - NEWJustinemae UbayNo ratings yet
- Tpla2: Sample Volumes Sample Sample DilutionDocument3 pagesTpla2: Sample Volumes Sample Sample DilutionhairiNo ratings yet
- Safety and HealthDocument23 pagesSafety and HealthIan MardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Women's Preference For Vaginal Delivery:determining FactorsDocument55 pagesWomen's Preference For Vaginal Delivery:determining FactorsGifty OsafoNo ratings yet
- WIC Outreach For LAs Planning Guide and ToolsDocument9 pagesWIC Outreach For LAs Planning Guide and ToolsCherotichNo ratings yet
- Poster Chi2 - Ocular Albinism HKDocument1 pagePoster Chi2 - Ocular Albinism HKyollayusticiaNo ratings yet
- Frankenstein Theme EssayDocument5 pagesFrankenstein Theme Essayafabifazv100% (2)
- Jawbone CavitationsDocument8 pagesJawbone CavitationsCAESA96No ratings yet
- Understanding Communication and ConsentDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Communication and ConsentCHRIS FLYNNNo ratings yet
- Katrin Barnard Theory PciDocument34 pagesKatrin Barnard Theory PciArum NingtiasNo ratings yet
- Order of DrawDocument8 pagesOrder of DrawVincent ReyesNo ratings yet
- Soal BAHASA INGGRISDocument20 pagesSoal BAHASA INGGRISAdi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- PROGNOSIS EbmDocument25 pagesPROGNOSIS EbmcarinasheliaNo ratings yet
- USMMA CatalogDocument134 pagesUSMMA CatalogMANUEL ANTONIO DE LA CRUZ SALCEDONo ratings yet
- Final-Psych-Drug StudyDocument5 pagesFinal-Psych-Drug StudySolsona Natl HS MaanantengNo ratings yet