Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Education During The British Period: in India"
Education During The British Period: in India"
Uploaded by
Meghna Tripathi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesThe document discusses the evolution of education in British India from the 18th century onwards. It highlights some key developments such as the establishment of institutions like Calcutta Madrasah, Sanskrit College and Fort William College in the late 18th century. In the 19th century, the Charter Act of 1813 allocated funds for education, and Macaulay's Minute of 1835 established English as the medium of instruction. Subsequent reforms included Wood's Despatch of 1854, Hunter Commission's recommendations and the Indian Universities Act of 1904. The Saddler Commission of 1917-19 advocated for reforms in university education. In the 20th century, the Wardha Scheme of 1937 focused on basic education through local languages.
Original Description:
Original Title
Education English 70
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the evolution of education in British India from the 18th century onwards. It highlights some key developments such as the establishment of institutions like Calcutta Madrasah, Sanskrit College and Fort William College in the late 18th century. In the 19th century, the Charter Act of 1813 allocated funds for education, and Macaulay's Minute of 1835 established English as the medium of instruction. Subsequent reforms included Wood's Despatch of 1854, Hunter Commission's recommendations and the Indian Universities Act of 1904. The Saddler Commission of 1917-19 advocated for reforms in university education. In the 20th century, the Wardha Scheme of 1937 focused on basic education through local languages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesEducation During The British Period: in India"
Education During The British Period: in India"
Uploaded by
Meghna TripathiThe document discusses the evolution of education in British India from the 18th century onwards. It highlights some key developments such as the establishment of institutions like Calcutta Madrasah, Sanskrit College and Fort William College in the late 18th century. In the 19th century, the Charter Act of 1813 allocated funds for education, and Macaulay's Minute of 1835 established English as the medium of instruction. Subsequent reforms included Wood's Despatch of 1854, Hunter Commission's recommendations and the Indian Universities Act of 1904. The Saddler Commission of 1917-19 advocated for reforms in university education. In the 20th century, the Wardha Scheme of 1937 focused on basic education through local languages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
www.byjusexamprep.
com
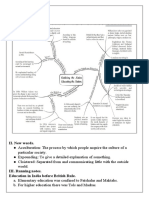
Education during the British Period
• Calcutta Madrasah was established by Warren Hastings in
1781 to study Muslim laws and customs.
• Jonathan Duncan established Sanskrit college at Banaras in
Individual efforts under 1791 for Hindu laws and philosophy.
company rule • Fort William College was set up in 1800 by Wellesley for
the training of civil servants of the Company. (It was closed
in 1802).
• 1 lakh rupees were to be spent by the company for the
Charter Act of 1813 promotion of education in India.
• Amidst Orientalist-Anglicist controversy, Macaulay
supported the latter view.
• English language was chosen as the sole medium of
education.
• Government decided to spend the limited resources for
teaching western sciences and literature.
• They adopted ‘downward filtration theory’ instead of mass
Lord Macaulay’s Minute of education.
1835
Note: ‘Downward filtration theory’ means teaching a few
upper- and middle-class people would produce interpreters
which would eventually penetrate to the masses. However, this
theory failed miserably as envisaged by the British but has
helped in growth of Modern Intelligentsia who shaped the
struggle for independence.
• This was also known as “Magna Carta of English Education
in India”.
• It rejected ‘downward filtration theory’.
• It recommended English for higher studies and vernaculars
Wood’s Despatch, 1854 at school level.
• Secular education.
• Encouraged private enterprises.
• Its objective was to assess the Wood Dispatch.
• It emphasized on state’s role in improving education.
Hunter Education Commission,
• Advocated for transfer of control to local bodies (district
1882-83 and municipal boards).
• To review the performance of universities in India.
Rayleigh Commission, 1902
www.byjusexamprep.com
On the recommendation of Rayleigh commission, the act
provided for:
• greater control over universities
• Universities were given due importance for research and
Indian Universities Act, 1904 studies.
• number of fellows reduced.
• Rules were made stricter for private college affiliations.
• Gopal Krishna Gokhale called this move a “retrograde
measure”.
• Government refused to take up the responsibility of
compulsory education.
Government Resolution on • It urged the provincial government to do the same.
Education Policy, 1913 • Even private players were encouraged.
• The commission was set up to review Calcutta University
which later extended to all universities.
• 12+3 program (12-year schooling and 3-year degree)
Saddler University • A separate board of secondary and intermediate education
Commission, 1917-19 were to be set up.
• It laid stress on Female education, applied scientific and
technological education, teachers’ training.
• Laid emphasis on primary education.
• Quality of education was given priority over a number of
Hartog Committee, 1929 schools and colleges.
• Admissions were highly restricted.
• Zakir Hussain committee formulated this national scheme
for basic education.
• The main principle of ‘learning through activity’.
Wardha Scheme of Basic
• secular in approach.
Education (1937) • First seven years of schooling through mother tongue and
English after 8th.
• Sergeant was the educational advisor to the British
Government.
• He advocated number of reforms and aimed to make
Sergeant Plan of Education,
Indian education system equivalent to that of England in 40
1944 years. But it seriously lacked methodology for
implementation. It was just lip service of the government.
You might also like
- Woods Despatch of 1854Document12 pagesWoods Despatch of 1854Richa Raj67% (12)
- Admission LetterDocument2 pagesAdmission Lettersodlarge100% (1)
- Education Commissions in IndiaDocument19 pagesEducation Commissions in IndiaJay Singh90% (10)
- Education During British Rule English 73Document2 pagesEducation During British Rule English 73aman kumarNo ratings yet
- Development of Education in British IndiaDocument2 pagesDevelopment of Education in British Indiawebwork25No ratings yet
- Status of Secondary Education During British PeriodDocument9 pagesStatus of Secondary Education During British PeriodRadheya KarnaNo ratings yet
- Macaulay's MinuteDocument10 pagesMacaulay's MinuteharleynunutaNo ratings yet
- Notes On English Language HistoryDocument28 pagesNotes On English Language HistoryAnushka SejalNo ratings yet
- Education Policy of British IndiaDocument33 pagesEducation Policy of British IndiaGeorgia EvansNo ratings yet
- English in India Free Study Material For UGC NET English Paper 2 - 2685Document12 pagesEnglish in India Free Study Material For UGC NET English Paper 2 - 2685PriyaramalingamNo ratings yet
- PuuuDocument8 pagesPuuuEnd Pro GamingNo ratings yet
- Hunter CommissionDocument6 pagesHunter CommissionharleynunutaNo ratings yet
- Education 2Document9 pagesEducation 2maham sanayaNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document153 pagesWeek 4Vaibhav RathoreNo ratings yet
- Education Commissions in India PDFDocument19 pagesEducation Commissions in India PDFNiroj Kumar Sahoo100% (2)
- Education Commissions in India PDFDocument19 pagesEducation Commissions in India PDFNidhi Prakriti100% (1)
- CBSE - G+08 - Civilising The Native Educating The Nation - NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE - G+08 - Civilising The Native Educating The Nation - Notesdhruvkapasia101No ratings yet
- Role of Higher Education Before Independence Eng File 49Document5 pagesRole of Higher Education Before Independence Eng File 49Ishani NayakNo ratings yet
- Education and British RuleDocument50 pagesEducation and British RuleShah Drshann100% (1)
- Week 4Document153 pagesWeek 4RBNo ratings yet
- Crux EH - Educational Development in British India - 1679916248Document38 pagesCrux EH - Educational Development in British India - 1679916248Amogh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Colonial EducationDocument2 pagesColonial EducationShivangi Kumari -Connecting Fashion With HistoryNo ratings yet
- Wood DespatchDocument2 pagesWood DespatchAyan DasNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Education in IndiaDocument6 pagesEvolution of Education in Indiaidharma1947No ratings yet
- Gs Prelims 5 Years Modern HistoryDocument130 pagesGs Prelims 5 Years Modern HistorykanishkNo ratings yet
- Important Commissions and Committees During BritishDocument9 pagesImportant Commissions and Committees During BritishSatish SiddharthaNo ratings yet
- EDUCATION AND BRITISH RULE - Common NotesDocument4 pagesEDUCATION AND BRITISH RULE - Common NotesManjula ManjulaNo ratings yet
- Civilizing The NativeDocument13 pagesCivilizing The NativeMishkat MishkatNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 History Notes Chapter 7 - Civilising The Native, Educating The NationDocument1 pageCBSE Class 8 History Notes Chapter 7 - Civilising The Native, Educating The Nationvanshbhadauria55No ratings yet
- Reviewer RizalDocument10 pagesReviewer RizalHugh CasanasNo ratings yet
- Handout on EducationDocument7 pagesHandout on EducationbellawillchesterkittyNo ratings yet
- 1854-1944 Educational Commissions & Committees in British IndiaDocument5 pages1854-1944 Educational Commissions & Committees in British IndiaDr. Molla Abdus SattarNo ratings yet
- Important Commissions and Committees During British - ClearIASDocument25 pagesImportant Commissions and Committees During British - ClearIASShibasis DakuaNo ratings yet
- Woods Dispatch C24f3ec2Document4 pagesWoods Dispatch C24f3ec2naseemhyderNo ratings yet
- Charter Act 1813Document25 pagesCharter Act 1813satya100% (1)
- Assignment - MuqeemDocument13 pagesAssignment - MuqeemHaseeb RoyNo ratings yet
- WoodsDocument6 pagesWoodsGurbani BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Beena Ke LiyDocument10 pagesBeena Ke LiyRITHIK MONDALNo ratings yet
- Education System in India During British Rule UPSC Notes1Document3 pagesEducation System in India During British Rule UPSC Notes1dfkjvlnsfn bgb100% (1)
- Colonial EraDocument45 pagesColonial Eratitusmunikwa2001No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Lesson 1-4Document54 pagesUnit 1 - Lesson 1-4Ani rudhNo ratings yet
- Hunter Commission Upsc Notes 58Document3 pagesHunter Commission Upsc Notes 58kumardeyapurbaNo ratings yet
- PMFIAS MIH 10 Spread of English EducationDocument26 pagesPMFIAS MIH 10 Spread of English EducationrhinocharmersNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8. Civilising The "Native", Educating The Nation Education For CommerceDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 8. Civilising The "Native", Educating The Nation Education For Commercerajan_dunNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 08 History Civilising The Native' Educating The NationDocument2 pagesChapter - 08 History Civilising The Native' Educating The NationMerajNo ratings yet
- Education in Colonial EraDocument17 pagesEducation in Colonial EraAnanda PadhanNo ratings yet
- Civilising The Native Educating The NationDocument2 pagesCivilising The Native Educating The NationABHINAV 8-C100% (1)
- History - Ch 8. History NotesDocument2 pagesHistory - Ch 8. History Notespushkarshrivastava90No ratings yet
- HunterDocument14 pagesHunternathxeroxNo ratings yet
- Wood's Despatch of 1854Document5 pagesWood's Despatch of 1854Aman YadavNo ratings yet
- 1630245058Document7 pages1630245058Punitha gowdaNo ratings yet
- Indian Education Commission - 1882Document7 pagesIndian Education Commission - 1882surajitpal4uNo ratings yet
- (Prelims Spotlight) Important British Commissions and Committees - CivilsdailyDocument9 pages(Prelims Spotlight) Important British Commissions and Committees - CivilsdailysuryajayanthNo ratings yet
- Woods DespatchDocument2 pagesWoods DespatchkumardeyapurbaNo ratings yet
- British Education SystemDocument3 pagesBritish Education SystemQu KhanNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of The Teacher Preparation and Professionalization in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesHistorical Development of The Teacher Preparation and Professionalization in The PhilippinesArianne Rose FangonNo ratings yet
- Anglicist Movement Presentation 2.ppsxDocument8 pagesAnglicist Movement Presentation 2.ppsxAriiba SaliimNo ratings yet
- Historical Perspective of Education SystemDocument18 pagesHistorical Perspective of Education SystemWong Jay Ying0% (1)
- 3-Development of Education During British Period in IndiaDocument3 pages3-Development of Education During British Period in IndiaSeharNo ratings yet
- Delphi Complete Works of Thomas Babington Macaulay (Illustrated)From EverandDelphi Complete Works of Thomas Babington Macaulay (Illustrated)No ratings yet
- 18mec34e U2Document80 pages18mec34e U2Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- G-8 & G-20Document17 pagesG-8 & G-20Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Mark-Up PricingDocument8 pagesMark-Up PricingMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- 2022 Question Paper-4Document3 pages2022 Question Paper-4Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mcom Applied EconomicsDocument29 pagesSyllabus Mcom Applied EconomicsMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- 2015 AccDocument4 pages2015 AccMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument21 pagesUntitledMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- 2022 Question Paper-1Document3 pages2022 Question Paper-1Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument40 pagesUntitledMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- 2018 AccDocument8 pages2018 AccMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Press English 13Document4 pagesPress English 13Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- India COVID LOCKDOWN UpdatesDocument1 pageIndia COVID LOCKDOWN UpdatesMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Right To Information (RTI) Act, 2005Document3 pagesRight To Information (RTI) Act, 2005Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- "Law Without Justice Is Wound Without Care.": Public Interest Litigation (PIL)Document3 pages"Law Without Justice Is Wound Without Care.": Public Interest Litigation (PIL)Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Nation Movement 2 Englih 27Document6 pagesNation Movement 2 Englih 27Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Revolutionary Movements During British EraDocument4 pagesRevolutionary Movements During British EraMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Famous Temples in India: No. Famous Temple Location Nearest River/LakeDocument2 pagesFamous Temples in India: No. Famous Temple Location Nearest River/LakeMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Art & Architecture of Delhi SultanateDocument3 pagesArt & Architecture of Delhi SultanateMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- News Paper English 77Document2 pagesNews Paper English 77Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Mughal Architecture Period: BaburDocument4 pagesMughal Architecture Period: BaburMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian Architecture English 90Document10 pagesAncient Indian Architecture English 90Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Forest and Wildlife: Forests and Natural Flora in Uttar PradeshDocument2 pagesForest and Wildlife: Forests and Natural Flora in Uttar PradeshMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Classical Dances, Folk Dances and Martial ArtsDocument4 pagesClassical Dances, Folk Dances and Martial ArtsMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Writ Eng 49Document5 pagesWrit Eng 49Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 English 37Document9 pagesLecture 3 English 37Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Delhi Sultanate Part-1: Dynasty Period of Rule Prominent RulersDocument4 pagesDelhi Sultanate Part-1: Dynasty Period of Rule Prominent RulersMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminology of Environment and EcologyDocument3 pagesBasic Terminology of Environment and EcologyMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- The Revolt of 1857: A. Economic CausesDocument3 pagesThe Revolt of 1857: A. Economic CausesMeghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- What Was The Need For Anti-Defection Law?Document4 pagesWhat Was The Need For Anti-Defection Law?Meghna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Resume Nayeem Rahman ChowdhuryDocument2 pagesResume Nayeem Rahman ChowdhuryJoycelynn BlackmonNo ratings yet
- Kimberly Shipway: Graduate TeacherDocument1 pageKimberly Shipway: Graduate Teacherapi-531136578No ratings yet
- University Grants Commission - XII Plan GuidelinesDocument8 pagesUniversity Grants Commission - XII Plan GuidelinesJanardhan Ch0% (1)
- (Download PDF) Read Reason Write An Argument Text and Reader 13E Ise 13Th Ise Edition Dorothy U Seyler Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pages(Download PDF) Read Reason Write An Argument Text and Reader 13E Ise 13Th Ise Edition Dorothy U Seyler Full Chapter PDFbagtyyldz100% (9)
- Univeristy of Perpetual Help System Dalta Alabang-Zapote Road, Pamplona 3, Las Pinas City College of LawDocument2 pagesUniveristy of Perpetual Help System Dalta Alabang-Zapote Road, Pamplona 3, Las Pinas City College of LawMamerto Egargo Jr.No ratings yet
- Revision Plan-II (DPP # 3) - ChemistryDocument8 pagesRevision Plan-II (DPP # 3) - ChemistryBhriguKansraNo ratings yet
- Proposed Itinerary of Travel: National Defense College of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageProposed Itinerary of Travel: National Defense College of The PhilippinesDenize Nicole PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Perez de Miles Annotated CV 7Document16 pagesPerez de Miles Annotated CV 7api-367444538No ratings yet
- (Nguyen Hoang Nguyen) CVDocument1 page(Nguyen Hoang Nguyen) CVHuynh Thi Cam NhungNo ratings yet
- Primer 2019-2020Document30 pagesPrimer 2019-2020Allen Lois LanuzaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Senior Portfolio RequirementsDocument21 pages2016 Senior Portfolio RequirementsSpartanSpiritNo ratings yet
- Unit 19 (Date 21/2-L P B I Dư NG) : A. VocabularyDocument7 pagesUnit 19 (Date 21/2-L P B I Dư NG) : A. VocabularyLê Quang HuyNo ratings yet
- Higher Education ProgramsDocument14 pagesHigher Education ProgramsSapana ThapaNo ratings yet
- Admissions at Generations 2024Document13 pagesAdmissions at Generations 2024unasbaig17No ratings yet
- Mba Colleges in AndrapradeshDocument3 pagesMba Colleges in Andrapradeshanuragkr85No ratings yet
- Grace Pfenning - In-Class EssayDocument3 pagesGrace Pfenning - In-Class Essayapi-526065196No ratings yet
- Tanya Chahal CVDocument1 pageTanya Chahal CVtanyaNo ratings yet
- Fellowship in Diabetology-Dr Mohan's Diabetes Education Academy, Chennai - Admission-Details - 20231116003050Document3 pagesFellowship in Diabetology-Dr Mohan's Diabetes Education Academy, Chennai - Admission-Details - 20231116003050Aarudh PonnarNo ratings yet
- Application Form 2021 Madhvani ScholarshipDocument8 pagesApplication Form 2021 Madhvani ScholarshipEdgar MugaruraNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC 2002 Scoring Guidelines Form BDocument7 pagesAP Calculus BC 2002 Scoring Guidelines Form BMr. PopoNo ratings yet
- Sri Krishna College of Engineering & Technology (Autonomous)Document1 pageSri Krishna College of Engineering & Technology (Autonomous)woodksdNo ratings yet
- Graduation SpeechDocument3 pagesGraduation SpeechbnetNo ratings yet
- Fall 2019 Inside IR - Institutional Research - Monroe Community CollegeDocument8 pagesFall 2019 Inside IR - Institutional Research - Monroe Community Collegeisaac_maykovichNo ratings yet
- AdvAnat Anatomy CMEDocument3 pagesAdvAnat Anatomy CMErageshkrrmbbsNo ratings yet
- Dorm ApplicationDocument4 pagesDorm Applicationromalino0% (1)
- College Acknowledgement of ModulesDocument1 pageCollege Acknowledgement of ModulesJhoeyAsueroDelosSantosNo ratings yet
- Academic Job SearchDocument8 pagesAcademic Job SearchZaw Ye HtikeNo ratings yet
- 2011 Calendar Journal - SMDocument104 pages2011 Calendar Journal - SMClarisel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Nydrique Barnes 23 UpdatedresumeDocument2 pagesNydrique Barnes 23 Updatedresumeapi-644951053No ratings yet