Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F3 Chapter 1 (SOALAN) - Respiration
F3 Chapter 1 (SOALAN) - Respiration
Uploaded by
leong cheng liyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 33.3 WorksheetDocument4 pagesChapter 33.3 WorksheetMING ZHU0% (1)
- Respiratory Physiology Lab ReportDocument15 pagesRespiratory Physiology Lab ReportThalia PacamalanNo ratings yet
- Lung Collapse: A Review: Dr. Girish Kukade Radiology Department, AFHDocument61 pagesLung Collapse: A Review: Dr. Girish Kukade Radiology Department, AFHkukadegirishNo ratings yet
- Science's Notes 2.1-2.5 Chloe 3 TulipDocument8 pagesScience's Notes 2.1-2.5 Chloe 3 Tulipjessiejoanna59No ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 2 RespirationJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- f3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesf3 Chapter 2 RespirationCheng JimmyNo ratings yet
- 1: Respiration Functional Model LungsDocument1 page1: Respiration Functional Model LungsNana TanNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing SystemDocument10 pagesGas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing Systemka klklklNo ratings yet
- PT3 C1Document5 pagesPT3 C1MilkNo ratings yet
- PT3 C1Document5 pagesPT3 C1MilkNo ratings yet
- Science-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinDocument14 pagesScience-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- U4 Ans CoursebookDocument2 pagesU4 Ans CoursebookSuyathi MugunthanNo ratings yet
- B3A Animal Physiology Edexcel Gcse BiologyDocument5 pagesB3A Animal Physiology Edexcel Gcse BiologySuki ChanNo ratings yet
- Inhaling and Exhaling Air Breathing Human Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesInhaling and Exhaling Air Breathing Human Respiratory SystemMSZeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Gas ExchangeDocument11 pagesChapter 11. Gas Exchangerep.0mar13No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesChapter 2 Tutorial 1Tanisa SaminNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Respiratory System DinDocument13 pagesModule 2 Respiratory System DinAhmad NajmuddinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Process of RespirationDocument24 pagesLesson 2 Process of RespirationKRISTA MAE BALANAYNo ratings yet
- 11.0 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument10 pages11.0 Gas Exchange in HumansObert MarongedzaNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 RespirationDocument30 pagesScience Chapter 2 RespirationWei LinNo ratings yet
- Breathing Is The Process That Brings Oxygen in The Air Into Your Lungs and MovesDocument6 pagesBreathing Is The Process That Brings Oxygen in The Air Into Your Lungs and MovesJaimeCrispinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Respiration Doc1Document6 pagesChapter 1 Respiration Doc1api-248021925No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Biology 11Document36 pagesChapter 11 Biology 11ax1leNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010Document34 pagesRespiration: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010Hazmaniran HarunNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Respiratory - System - Worksheet - 3Document4 pagesKami Export - Respiratory - System - Worksheet - 3abdalla abdelhamidNo ratings yet
- Mastering Biology BK1B NotesDocument20 pagesMastering Biology BK1B NotesAlva WongNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Apec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesApec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- 37-3 Notes RespiratoryDocument2 pages37-3 Notes RespiratoryjaimearuojNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDDocument7 pagesScience 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument8 pagesRESPIRATIONRochelle BlackNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument2 pagesBreathing and Respirationjenn78No ratings yet
- Respiration Class 10Document3 pagesRespiration Class 10unknownuwugirl2442No ratings yet
- 1r3ntvbfve - Ipa Kelas 8 Bab 9Document19 pages1r3ntvbfve - Ipa Kelas 8 Bab 9aulyamaltha.2008No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesHuman Resource ManagementKIPNGENO EMMANUELNo ratings yet
- S 2 Unit 4 Course Book, Work Book Ques and KeysDocument19 pagesS 2 Unit 4 Course Book, Work Book Ques and KeysHein Aung Zin100% (2)
- Gas Exchange in Humans Grade 9Document49 pagesGas Exchange in Humans Grade 9harliv2.5chandhokNo ratings yet
- Gr.8 Ch.5 Chapter Review AnswerDocument10 pagesGr.8 Ch.5 Chapter Review Answerson GokuNo ratings yet
- Biology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabanDocument3 pagesBiology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabannoorlailyNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 MIDTERM TRANSES UjmDocument23 pagesNCM 109 MIDTERM TRANSES UjmRayanna MaligaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory SystemSudip NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Emergency Plan 1Document4 pagesEmergency Plan 1Iman Hassan Ahmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 RespirationDocument4 pagesChapter 16 Respiration24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊No ratings yet
- Study Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesStudy Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemosamaNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Respiratory System SEM 2 SESI 2019/2020 Group: A: Name: Mohamad Aiman Iqbal Bin Nordin MATRIC NO: D20192091516Document8 pagesModule 2: Respiratory System SEM 2 SESI 2019/2020 Group: A: Name: Mohamad Aiman Iqbal Bin Nordin MATRIC NO: D20192091516muhd ariffNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument5 pagesENGLISHArmida SisonNo ratings yet
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationDocument5 pagesCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- 9 Science q2Document44 pages9 Science q2Gerald LosanesNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Full HBDocument26 pagesTopic 5 Full HBazankha1990No ratings yet
- Management of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationDocument13 pagesManagement of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationClyde CapadnganNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - Exchange - Carbon Dioxide - BreatheDocument2 pagesRespiratory - Exchange - Carbon Dioxide - BreatheLina UribeNo ratings yet
- Tamilnadu Board Class 11 Zoology Chapter 6Document22 pagesTamilnadu Board Class 11 Zoology Chapter 6Varshini PeraNo ratings yet
- Respiration G810FD6Document10 pagesRespiration G810FD6Tifa NassimNo ratings yet
- Rev Notes ch07 eDocument4 pagesRev Notes ch07 ejokes NerdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Gas Exchange in Humans: Learning ObjectivesDocument13 pagesChapter 8 - Gas Exchange in Humans: Learning Objectivesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Food Calorific ValueDocument2 pagesFood Calorific Valueleong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- CH 1.4 Electrolytic Cell Chemistry F5 KSSMDocument87 pagesCH 1.4 Electrolytic Cell Chemistry F5 KSSMleong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- CH 1.6 Rusting Chemistry F5 KSSMDocument51 pagesCH 1.6 Rusting Chemistry F5 KSSMleong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- Skema PPT Kimia P2 Ting 4 2021, 2Document9 pagesSkema PPT Kimia P2 Ting 4 2021, 2leong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- PN Leong Cheng LiyDocument201 pagesPN Leong Cheng Liyleong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- 07-08 - Cursped1zcxxDocument103 pages07-08 - Cursped1zcxxAlex AlexNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam in Nursing Set ADocument38 pagesPractice Exam in Nursing Set AGo IdeasNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NotesDocument43 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NotesJapani TutorNo ratings yet
- Respiratory History and ExaminationDocument7 pagesRespiratory History and Examinationjen262004No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange and Transport (Physiology)Document31 pagesGas Exchange and Transport (Physiology)Arsalan khanNo ratings yet
- Test A Unit 2 PDFDocument5 pagesTest A Unit 2 PDFAnabela Torres MendesNo ratings yet
- Insulin Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes UpdateDocument83 pagesInsulin Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes UpdateasupicuNo ratings yet
- "We Heal As One": Department of EducationDocument11 pages"We Heal As One": Department of EducationJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper ChemDocument2 pagesReaction Paper ChemAlexis Dela Cruz RoguelNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease - CSDocument88 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease - CSMASII100% (8)
- The Pathway: The Human Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesThe Pathway: The Human Respiratory SystemKenneth Decker PrietoNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 01Document11 pagesCbjescpu 01Karthy JanaviNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument107 pagesMedical TerminologyonmcvNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathic MCQ Book For Upsc and MD 9788131932575Document26 pagesHomoeopathic MCQ Book For Upsc and MD 9788131932575NIYAS TTNo ratings yet
- Adverse Reactions To Furazolidone and Other Drugs. A Comparative ReviewDocument11 pagesAdverse Reactions To Furazolidone and Other Drugs. A Comparative ReviewmaryNo ratings yet
- CKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTDocument1 pageCKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTInah Floresta BesasNo ratings yet
- PranayamaDocument18 pagesPranayamaVERITYjnanaZETETIC100% (1)
- Acute Pancreatitis Case PresDocument29 pagesAcute Pancreatitis Case Preskristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- Your Lung Nodule Is More Likely To Be Benign If: You Are Younger Than Age 40. You Are A Nonsmoker. There Is in The Nodule. The Nodule Is SmallDocument3 pagesYour Lung Nodule Is More Likely To Be Benign If: You Are Younger Than Age 40. You Are A Nonsmoker. There Is in The Nodule. The Nodule Is SmallK CheungNo ratings yet
- Gynecology and Obstretics Assignment (MCQS)Document9 pagesGynecology and Obstretics Assignment (MCQS)Jehanzeb AkramNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pediatrics MsMMaMDocument40 pagesClinical Pediatrics MsMMaMGoha Basha100% (3)
- KS4 The Breathing SystemDocument54 pagesKS4 The Breathing SystemNur narzwinNo ratings yet
- ClubbingDocument42 pagesClubbingRhomizal MazaliNo ratings yet
- DVM Curriculum-Booklet (Draft)Document100 pagesDVM Curriculum-Booklet (Draft)Elina aliNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy in Critically Ill Adult Patients PDFDocument17 pagesPhysical Therapy in Critically Ill Adult Patients PDFSoledad Cayupi TrafilafNo ratings yet
- Class 4 Subject Science Chapter 3 Animal KingdomDocument3 pagesClass 4 Subject Science Chapter 3 Animal KingdomShubhjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Complications PDFDocument21 pagesPostoperative Complications PDFDoctor's BettaNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels: Artery Capillary VeinDocument27 pagesBlood Vessels: Artery Capillary Veinapi-19641337No ratings yet
F3 Chapter 1 (SOALAN) - Respiration
F3 Chapter 1 (SOALAN) - Respiration
Uploaded by
leong cheng liyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F3 Chapter 1 (SOALAN) - Respiration
F3 Chapter 1 (SOALAN) - Respiration
Uploaded by
leong cheng liyCopyright:
Available Formats
Intensive SCIENCE INTENSIVE PROGRAMME FOR FROM 3
SSCCIIIE CHAPTER 1 : RESPIRATION
NAMA: CLASS: DATE:
ENCCEE
FFOORR
FFOORRMM
1 Respiration
33 is a chemical process whereby glucose 5 Transport of oxygen from the ______ into the cells
react
WW W.S with oxygen to produce energy, carbon dioxide
MKSP.COM
and water.
Words equation
Glucose + → Energy + + Water
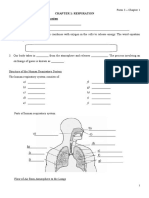
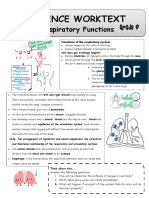
2 Huamn Respiratory System
1.
Trap dust,
warmed and
moistens air
1 Oxygen from alveolus diffuses into the blood
2.
capillaries and combines with haemoglobin in
Trap dust and
the red blood cells to form ________________
microorganisms
2. The oxygenated blood then transport to the
3. 6.
heart and ________to all parts of the body.
Direct air into Protects lungs
3. When reach the body cells, oxyhaemoglobin
brochiole and heart
break down and the oxygen diffuses into the
4. 7
cells and carries out the process of ________
Direct air into Moves ribs
4. At the same time, carbon dioxide in the cells
Alveoli
diffuses into the _______________________
5. 8. Diaphragm
5. The deoxygenated blood then transport to the
Diffuses air into Helps breathing
heart and pumps to the _______________
blood capillaries mechanism
6 Harmful substances Effects
Tar - blackens the lungs.
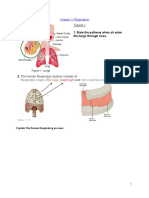
3 Pathway of air flow from the nose to the alveolus Cigarette smoke Nicotine - causes lung cancer
during inhalation : Acid - corrodes lung's cells.
Carbon monoxide - reduce
Vehicles smoke ability of blood to transport
oxygen
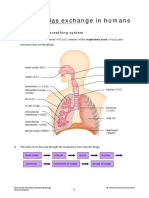
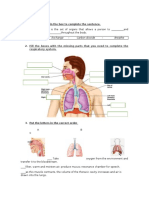
4 Using a functional model of the lungs to explain the process of inhalation.
Y-Shape tube represented
Balloon represented
Air space represented
Bell jar represented
Rubber sheet represented
Using a model to explain the inhalation Process of inhalation
1 When the rubber sheet is pulled down. represented 1 When the diaphragm is move downward & flattens
2. Volume of bell jar increase. 2. Volume of thoracic cavity is increase.
3. Air pressure inside the bell jar increase. 3. Air pressure inside the thoracic cavity increase.
4. Air from outside flow into the balloon and expand. 4. Air from outside flow into the lung and inflate.
1
You might also like
- Chapter 33.3 WorksheetDocument4 pagesChapter 33.3 WorksheetMING ZHU0% (1)
- Respiratory Physiology Lab ReportDocument15 pagesRespiratory Physiology Lab ReportThalia PacamalanNo ratings yet
- Lung Collapse: A Review: Dr. Girish Kukade Radiology Department, AFHDocument61 pagesLung Collapse: A Review: Dr. Girish Kukade Radiology Department, AFHkukadegirishNo ratings yet
- Science's Notes 2.1-2.5 Chloe 3 TulipDocument8 pagesScience's Notes 2.1-2.5 Chloe 3 Tulipjessiejoanna59No ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 2 RespirationJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- f3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesf3 Chapter 2 RespirationCheng JimmyNo ratings yet
- 1: Respiration Functional Model LungsDocument1 page1: Respiration Functional Model LungsNana TanNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing SystemDocument10 pagesGas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing Systemka klklklNo ratings yet
- PT3 C1Document5 pagesPT3 C1MilkNo ratings yet
- PT3 C1Document5 pagesPT3 C1MilkNo ratings yet
- Science-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinDocument14 pagesScience-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- U4 Ans CoursebookDocument2 pagesU4 Ans CoursebookSuyathi MugunthanNo ratings yet
- B3A Animal Physiology Edexcel Gcse BiologyDocument5 pagesB3A Animal Physiology Edexcel Gcse BiologySuki ChanNo ratings yet
- Inhaling and Exhaling Air Breathing Human Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesInhaling and Exhaling Air Breathing Human Respiratory SystemMSZeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Gas ExchangeDocument11 pagesChapter 11. Gas Exchangerep.0mar13No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesChapter 2 Tutorial 1Tanisa SaminNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Respiratory System DinDocument13 pagesModule 2 Respiratory System DinAhmad NajmuddinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Process of RespirationDocument24 pagesLesson 2 Process of RespirationKRISTA MAE BALANAYNo ratings yet
- 11.0 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument10 pages11.0 Gas Exchange in HumansObert MarongedzaNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 RespirationDocument30 pagesScience Chapter 2 RespirationWei LinNo ratings yet
- Breathing Is The Process That Brings Oxygen in The Air Into Your Lungs and MovesDocument6 pagesBreathing Is The Process That Brings Oxygen in The Air Into Your Lungs and MovesJaimeCrispinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Respiration Doc1Document6 pagesChapter 1 Respiration Doc1api-248021925No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Biology 11Document36 pagesChapter 11 Biology 11ax1leNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010Document34 pagesRespiration: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010Hazmaniran HarunNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Respiratory - System - Worksheet - 3Document4 pagesKami Export - Respiratory - System - Worksheet - 3abdalla abdelhamidNo ratings yet
- Mastering Biology BK1B NotesDocument20 pagesMastering Biology BK1B NotesAlva WongNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Apec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesApec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- 37-3 Notes RespiratoryDocument2 pages37-3 Notes RespiratoryjaimearuojNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDDocument7 pagesScience 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument8 pagesRESPIRATIONRochelle BlackNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument2 pagesBreathing and Respirationjenn78No ratings yet
- Respiration Class 10Document3 pagesRespiration Class 10unknownuwugirl2442No ratings yet
- 1r3ntvbfve - Ipa Kelas 8 Bab 9Document19 pages1r3ntvbfve - Ipa Kelas 8 Bab 9aulyamaltha.2008No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesHuman Resource ManagementKIPNGENO EMMANUELNo ratings yet
- S 2 Unit 4 Course Book, Work Book Ques and KeysDocument19 pagesS 2 Unit 4 Course Book, Work Book Ques and KeysHein Aung Zin100% (2)
- Gas Exchange in Humans Grade 9Document49 pagesGas Exchange in Humans Grade 9harliv2.5chandhokNo ratings yet
- Gr.8 Ch.5 Chapter Review AnswerDocument10 pagesGr.8 Ch.5 Chapter Review Answerson GokuNo ratings yet
- Biology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabanDocument3 pagesBiology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabannoorlailyNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 MIDTERM TRANSES UjmDocument23 pagesNCM 109 MIDTERM TRANSES UjmRayanna MaligaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory SystemSudip NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Emergency Plan 1Document4 pagesEmergency Plan 1Iman Hassan Ahmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 RespirationDocument4 pagesChapter 16 Respiration24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊No ratings yet
- Study Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesStudy Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemosamaNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Respiratory System SEM 2 SESI 2019/2020 Group: A: Name: Mohamad Aiman Iqbal Bin Nordin MATRIC NO: D20192091516Document8 pagesModule 2: Respiratory System SEM 2 SESI 2019/2020 Group: A: Name: Mohamad Aiman Iqbal Bin Nordin MATRIC NO: D20192091516muhd ariffNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument5 pagesENGLISHArmida SisonNo ratings yet
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationDocument5 pagesCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- 9 Science q2Document44 pages9 Science q2Gerald LosanesNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Full HBDocument26 pagesTopic 5 Full HBazankha1990No ratings yet
- Management of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationDocument13 pagesManagement of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationClyde CapadnganNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - Exchange - Carbon Dioxide - BreatheDocument2 pagesRespiratory - Exchange - Carbon Dioxide - BreatheLina UribeNo ratings yet
- Tamilnadu Board Class 11 Zoology Chapter 6Document22 pagesTamilnadu Board Class 11 Zoology Chapter 6Varshini PeraNo ratings yet
- Respiration G810FD6Document10 pagesRespiration G810FD6Tifa NassimNo ratings yet
- Rev Notes ch07 eDocument4 pagesRev Notes ch07 ejokes NerdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Gas Exchange in Humans: Learning ObjectivesDocument13 pagesChapter 8 - Gas Exchange in Humans: Learning Objectivesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Food Calorific ValueDocument2 pagesFood Calorific Valueleong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- CH 1.4 Electrolytic Cell Chemistry F5 KSSMDocument87 pagesCH 1.4 Electrolytic Cell Chemistry F5 KSSMleong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- CH 1.6 Rusting Chemistry F5 KSSMDocument51 pagesCH 1.6 Rusting Chemistry F5 KSSMleong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- Skema PPT Kimia P2 Ting 4 2021, 2Document9 pagesSkema PPT Kimia P2 Ting 4 2021, 2leong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- PN Leong Cheng LiyDocument201 pagesPN Leong Cheng Liyleong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- 07-08 - Cursped1zcxxDocument103 pages07-08 - Cursped1zcxxAlex AlexNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam in Nursing Set ADocument38 pagesPractice Exam in Nursing Set AGo IdeasNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NotesDocument43 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NotesJapani TutorNo ratings yet
- Respiratory History and ExaminationDocument7 pagesRespiratory History and Examinationjen262004No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange and Transport (Physiology)Document31 pagesGas Exchange and Transport (Physiology)Arsalan khanNo ratings yet
- Test A Unit 2 PDFDocument5 pagesTest A Unit 2 PDFAnabela Torres MendesNo ratings yet
- Insulin Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes UpdateDocument83 pagesInsulin Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes UpdateasupicuNo ratings yet
- "We Heal As One": Department of EducationDocument11 pages"We Heal As One": Department of EducationJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper ChemDocument2 pagesReaction Paper ChemAlexis Dela Cruz RoguelNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease - CSDocument88 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease - CSMASII100% (8)
- The Pathway: The Human Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesThe Pathway: The Human Respiratory SystemKenneth Decker PrietoNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 01Document11 pagesCbjescpu 01Karthy JanaviNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument107 pagesMedical TerminologyonmcvNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathic MCQ Book For Upsc and MD 9788131932575Document26 pagesHomoeopathic MCQ Book For Upsc and MD 9788131932575NIYAS TTNo ratings yet
- Adverse Reactions To Furazolidone and Other Drugs. A Comparative ReviewDocument11 pagesAdverse Reactions To Furazolidone and Other Drugs. A Comparative ReviewmaryNo ratings yet
- CKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTDocument1 pageCKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTInah Floresta BesasNo ratings yet
- PranayamaDocument18 pagesPranayamaVERITYjnanaZETETIC100% (1)
- Acute Pancreatitis Case PresDocument29 pagesAcute Pancreatitis Case Preskristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- Your Lung Nodule Is More Likely To Be Benign If: You Are Younger Than Age 40. You Are A Nonsmoker. There Is in The Nodule. The Nodule Is SmallDocument3 pagesYour Lung Nodule Is More Likely To Be Benign If: You Are Younger Than Age 40. You Are A Nonsmoker. There Is in The Nodule. The Nodule Is SmallK CheungNo ratings yet
- Gynecology and Obstretics Assignment (MCQS)Document9 pagesGynecology and Obstretics Assignment (MCQS)Jehanzeb AkramNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pediatrics MsMMaMDocument40 pagesClinical Pediatrics MsMMaMGoha Basha100% (3)
- KS4 The Breathing SystemDocument54 pagesKS4 The Breathing SystemNur narzwinNo ratings yet
- ClubbingDocument42 pagesClubbingRhomizal MazaliNo ratings yet
- DVM Curriculum-Booklet (Draft)Document100 pagesDVM Curriculum-Booklet (Draft)Elina aliNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy in Critically Ill Adult Patients PDFDocument17 pagesPhysical Therapy in Critically Ill Adult Patients PDFSoledad Cayupi TrafilafNo ratings yet
- Class 4 Subject Science Chapter 3 Animal KingdomDocument3 pagesClass 4 Subject Science Chapter 3 Animal KingdomShubhjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Complications PDFDocument21 pagesPostoperative Complications PDFDoctor's BettaNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels: Artery Capillary VeinDocument27 pagesBlood Vessels: Artery Capillary Veinapi-19641337No ratings yet