Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pandas Basics: Learn Python For Data Science Interactively
Pandas Basics: Learn Python For Data Science Interactively
Uploaded by
Sofia HerreraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pandas Basics: Learn Python For Data Science Interactively
Pandas Basics: Learn Python For Data Science Interactively
Uploaded by
Sofia HerreraCopyright:
Available Formats
Asking For Help Dropping
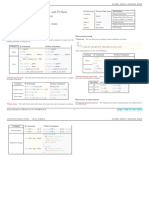
Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet
>>> help(pd.Series.loc)
>>> s.drop([‘a’, ‘c’]) Drop values from rows (axis=0)
Pandas Basics
>>> df.drop(‘Country’, axis=1) Drop values from columns(axis=1)
Selection Also see NumPy Arrays
Getting Sort & Rank
>>> s[‘b’] Get one element
-5 >>> df.sort_index() Sort by labels along an axis
Learn Python for Data Science Interactively >>> df[1:]
Country Capital Population
Get subset of a DataFrame >>> df.sort_values(by=’Country’)
>>> df.rank()
Sort by the values along an axis
Assign ranks to entries
1 India New Delhi 1303171035
Pandas 2 Brazil Brasília 207847528
The Pandas library is built on NumPy and provides easy-to-use data structures and data analysis tools for
the Python programming language.
Retrieving Series/DataFrame Information
Selecting, Boolean Indexing & Setting
Use the following import convention:
>>> import pandas as pd
By>>>Position
df.iloc[[0],[0]] Select single value by row &
Basic Information
‘Belgium’ column
>>> df.iat([0],[0]) >>> df.shape (rows,columns)
Pandas Data Structures ‘Belgium’ >>> df.index Describe index
By Label >>> df.columns Describe DataFrame columns
>>> df.loc[[0], [‘Country’]] Select single value by row & >>> df.info() Info on DataFrame
Series >>> df.count() Number of non-NA values
‘Belgium’ column labels
A one-dimensional labeled array a a 3 >>> df.at([0], [‘Country’])
capable of holding any data type
Index b -5 ‘Belgium’
c 7 By Label/Position
Summary
>>> df.ix[2] Select single row of
d 4
Country Brazil subset of rows
>>> s = pd.Series([3, -5, 7, 4], index=[‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’]) Capital Brasília >>> df.sum() Sum of values
Population 207847528 >>> df.cumsum() Cummulative sum of values
>>> df.min()/df.max() Minimum/maximum values
>>> df.ix[:,’Capital’] Select a single column of
DataFrame 0 Brussels subset of columns
>>> df.idxmin()/df.idxmax() Minimum/Maximum index value
>>> df.describe() Summary statistics
Columns Country Capital Population A two-dimensional labeled 1 New Delhi >>> df.mean() Mean of values
data structure with columns 2 Brasília >>> df.median() Median of values
Index 0 Belgium Brussels 11190846 of potentially different types >>> df.ix[1,’Capital’] Select rows and columns
1 India New Delhi 1303171035 ‘New Delhi’
2 Brazil Brasília 207847528 Boolean Indexing
>>> s[~(s > 1)] Series s where value is not >1
>>> data = {‘Country’: [‘Belgium’, ‘India’, ‘Brazil’], >>> s[(s < -1) | (s > 2)] s where value is <-1 or >2
‘Capital’: [‘Brussels’, ‘New Delhi’, ‘Brasília’],
>>> df[df[‘Population’]>1200000000] Use filter to adjust DataFrame Applying Functions
‘Population’: [11190846, 1303171035, 207847528]}
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data, Setting
columns=[‘Country’, ‘Capital’, ‘Population’]) >>> s[‘a’] = 6 Set index a of Series s to 6 >>> f = lambda x: x*2
>>> df.apply(f) Apply function
>>> df.applymap(f) Apply function element-wise
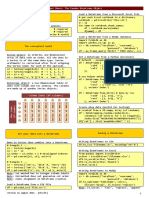
I/O
Data Alignment
Read and Write to CSV Read and Write to SQL Query or Database Table
>>> pd.read_csv(‘file.cvs’, header=None, nrows=5) >>> from sqlalchemy import create_engine Internal Data Alignment
>>> df.to_csv(‘myDataFrame.csv’) >>> engine = create_engine(‘sqlite:///:memory:’) NA values are introduced in the indices that don’t overlap:
>>> pd.read_sql(“SELECT * FROM my_table;”, engine)
>>> pd.read_sql_table(‘my_table’, engine) >>> s3 = pd.Series([7, -2, 3], index=[‘a’, ‘c’, ‘d’])
>>> s + s3
Read and Write to Excel >>> pd.read_sql_query(“SELECT * FROM my_table;”, engine)
a 10.0
b NaN
>>> pd.read_excel(‘file.xlsx’)
c 5.0
>>> df.to_excel(‘dir/myDataFrame.xlsx’, sheet_name=’Sheet1’)
d 7.0
read_sql()is a convenience wrapper around read_sql_table() and read_sql_query()
Read multiple sheets from the same file
>>> xlsx = pd.ExcelFile(‘file.xlsx’)
>>> df = pd.read_excel(xlsx, ‘Sheet1’) >>> df.to_sql(‘myDf’, engine)
Summary
You can also do the internal data alignment yourself with
the help of the fill methods:
>>>
s.add (s3,fill_value=0)
a 10.0
b -5.0
c 5.0
d 7.0
>>> s.sub (s3,fill_value=2)
>>> s.div (s3,fill_value=4)
>>> s.mul (s3,fill_value=3)
You might also like
- XML Final Exam (42/50) : Question TextDocument41 pagesXML Final Exam (42/50) : Question TextJhansen Feliciano /JHAZPRINT/50% (6)
- CDBM Mod02 AnswersDocument22 pagesCDBM Mod02 AnswersMoin Kabir MoinNo ratings yet
- Learning JavaScript Data Structures and Algorithms - Second EditionFrom EverandLearning JavaScript Data Structures and Algorithms - Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Pandas Python For Data ScienceDocument1 pagePandas Python For Data Sciencechowdamhemalatha100% (1)
- Python SciPy Cheat Sheet Linear Algebra PDFDocument1 pagePython SciPy Cheat Sheet Linear Algebra PDFTech and HacksNo ratings yet
- How Does A Relational Database Work - Coding Geek PDFDocument68 pagesHow Does A Relational Database Work - Coding Geek PDFFosnxbxksNo ratings yet
- Cheat PythonDocument8 pagesCheat PythonhectordelosriosdiazNo ratings yet
- Pandas Python For Data ScienceDocument1 pagePandas Python For Data ScienceaaaaNo ratings yet
- Pandas: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelyDocument1 pagePandas: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelySofia HerreraNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet: Learn Python For Data Science Interactively atDocument1 pageCheat Sheet: Learn Python For Data Science Interactively atJuan GalvanNo ratings yet
- Python数据科学速查表 - Pandas 进阶Document1 pagePython数据科学速查表 - Pandas 进阶Keith NgNo ratings yet
- Data Wrangling Cheat SheetDocument1 pageData Wrangling Cheat Sheetcuneyt noksanNo ratings yet
- Python For Data Science: Advanced Indexing Data Wrangling in Pandas Cheat Sheet Combining DataDocument1 pagePython For Data Science: Advanced Indexing Data Wrangling in Pandas Cheat Sheet Combining DatalocutoNo ratings yet
- Pandas Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePandas Cheat Sheetcuneyt noksanNo ratings yet
- Pandas Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Retrieving Series/Dataframe InformationDocument1 pagePandas Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Retrieving Series/Dataframe InformationlocutoNo ratings yet
- Data WranglingGUIA PYTHON-05Document1 pageData WranglingGUIA PYTHON-05Danilo ZanichelliNo ratings yet
- Conversion Guide R Python Data ManipulationDocument2 pagesConversion Guide R Python Data ManipulationJAVIERA NATALIA CONTADORNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet: The Pandas Dataframe Object: Column Index (DF - Columns)Document6 pagesCheat Sheet: The Pandas Dataframe Object: Column Index (DF - Columns)Nirmala ShindeNo ratings yet
- 3 Pandasadvanced PDFDocument1 page3 Pandasadvanced PDFcunhafccNo ratings yet
- PandasGUIA PYTHON-04Document1 pagePandasGUIA PYTHON-04Danilo ZanichelliNo ratings yet
- Advance Operations On DataframesDocument20 pagesAdvance Operations On DataframesPranav Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- PySpark SQL Cheat Sheet PythonDocument1 pagePySpark SQL Cheat Sheet PythonKetan BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- PySpark SQL Cheat Sheet PythonDocument1 pagePySpark SQL Cheat Sheet PythonTrung Nguyen100% (1)
- PySpark SQL Cheat Sheet Python PDFDocument1 pagePySpark SQL Cheat Sheet Python PDFAnish goyalNo ratings yet
- PySpark SQL Cheat Sheet Python PDFDocument1 pagePySpark SQL Cheat Sheet Python PDFCamilo AvilaNo ratings yet
- Importing Data Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Pickled Files Exploring Your DataDocument1 pageImporting Data Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Pickled Files Exploring Your DatalocutoNo ratings yet
- Numpy Basics: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelyDocument1 pageNumpy Basics: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelySofia HerreraNo ratings yet
- Informatics Practices: Class XII (As Per CBSE Board)Document20 pagesInformatics Practices: Class XII (As Per CBSE Board)sofia guptaNo ratings yet
- PandasDocument9 pagesPandasAllinagaram AjayNo ratings yet
- Data Science With Python 1620448217Document4 pagesData Science With Python 1620448217Kavin Karthikeyan100% (1)
- Pandas DataFrame NotesDocument13 pagesPandas DataFrame Notespankaj sethiaNo ratings yet
- Scipy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Linear AlgebraDocument1 pageScipy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Linear AlgebraLourdes Victoria UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Pandas DataFrame NotesDocument13 pagesPandas DataFrame Notesalainvalois67% (3)
- Handout - Spark ReferenceDocument2 pagesHandout - Spark ReferencerajasekharNo ratings yet
- Pandas - Jupyter NotebookDocument44 pagesPandas - Jupyter Notebookdisguisedacc511No ratings yet
- Importing Data Python Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageImporting Data Python Cheat Sheet PDFruler3382No ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheets CompilationDocument14 pagesPython Cheat Sheets Compilationraghavandra ethish manickam100% (1)
- Numpy Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat SheetJosh Iz100% (1)
- Numpy Python Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat Sheet PDFAbhijith S AnchanNo ratings yet
- Numpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDocument6 pagesNumpy Basics: Arithmetic Operationsmanish chavhanNo ratings yet
- Numpy Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat Sheetyellow_birdNo ratings yet
- ML CheatsheetsDocument17 pagesML CheatsheetsGhikjh100% (2)
- Numpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDocument7 pagesNumpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDeepak Gupta100% (14)
- SQL Cheat Sheet PythonDocument1 pageSQL Cheat Sheet PythonAndrew KhalatovNo ratings yet
- Pandas DataFrame NotesDocument10 pagesPandas DataFrame NotesSarath Ramineni100% (1)
- DatavischeatsheetDocument2 pagesDatavischeatsheetrcg97.hdNo ratings yet
- Pandas - Cheat - Sheet FULLDocument2 pagesPandas - Cheat - Sheet FULLNANDIKHA THARANIKUMARNo ratings yet
- Python数据科学速查表 - BokehDocument1 pagePython数据科学速查表 - BokehKeith NgNo ratings yet
- Numpy Basics Introduction ToDocument35 pagesNumpy Basics Introduction Topriyanka sharmaNo ratings yet
- Python Libraries Cheat SheetsDocument6 pagesPython Libraries Cheat SheetsSushma MNo ratings yet
- Pandas Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPandas Cheat SheetArvind9407No ratings yet
- Creating Dataframes Reshaping DataDocument2 pagesCreating Dataframes Reshaping Datanikolamil1993100% (1)
- SciPyGUIA PYTHON-02Document1 pageSciPyGUIA PYTHON-02Danilo ZanichelliNo ratings yet
- EDA Unit 2 NotesDocument61 pagesEDA Unit 2 NotessivashankarsrideviNo ratings yet
- Learning Pandas 2.0: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Manipulation and Analysis for Data Scientists and Machine Learning ProfessionalsFrom EverandLearning Pandas 2.0: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Manipulation and Analysis for Data Scientists and Machine Learning ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionFrom EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Mastering C++ Network Automation: Run Automation across Configuration Management, Container Orchestration, Kubernetes, and Cloud NetworkingFrom EverandMastering C++ Network Automation: Run Automation across Configuration Management, Container Orchestration, Kubernetes, and Cloud NetworkingNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hour Max - Marks: 75: Model Question Paper Diploma in Computer EngineeringDocument4 pagesTime: 3 Hour Max - Marks: 75: Model Question Paper Diploma in Computer EngineeringSam JhonsonNo ratings yet
- Functional Components: Mobile Store ManagementDocument7 pagesFunctional Components: Mobile Store ManagementKingSlayer GamingNo ratings yet
- DBMS Mba 2013Document22 pagesDBMS Mba 2013saif505No ratings yet
- Important SQL Practice Questions With AnswersDocument7 pagesImportant SQL Practice Questions With AnswersmanekdivishaNo ratings yet
- Adam Leszczyński POUG 2018, SopotDocument39 pagesAdam Leszczyński POUG 2018, SopotAdam NowakNo ratings yet
- Software Requirements Specification Introduction: Part - BDocument10 pagesSoftware Requirements Specification Introduction: Part - BGayatri ShindeNo ratings yet
- Modeling Data ObjectsDocument10 pagesModeling Data ObjectsMerera AmsaluNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Complete NotesDocument21 pagesUNIT 5 Complete Notesworks8606No ratings yet
- P - 14 - Object - Relational DatabasesDocument50 pagesP - 14 - Object - Relational DatabasesRoman GolubovskiNo ratings yet
- Case Study-1 7bDocument2 pagesCase Study-1 7bRithvik ShettyNo ratings yet
- JDBC Part-3Document13 pagesJDBC Part-3Saim KeshriNo ratings yet
- B.Tech - CSE and CS Syllabus of 3rd Year 12 Oct 20Document35 pagesB.Tech - CSE and CS Syllabus of 3rd Year 12 Oct 20Basic Of EverythingNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument8 pagesDatabase Management SystemNicola BrownNo ratings yet
- BI Mini Project-Wardrobe AnalysisDocument11 pagesBI Mini Project-Wardrobe AnalysisAnushree ChandraNo ratings yet
- Ausschreibung Rocket App V3Document3 pagesAusschreibung Rocket App V3Viktor KiselevNo ratings yet
- Fantastico FileslistDocument1 pageFantastico FileslistRasheersh JhaNo ratings yet
- SAS Interview Questions & Answers (Basics)Document4 pagesSAS Interview Questions & Answers (Basics)shirisha chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Scripting For Beginners: Qlik Sense September 2020Document52 pagesTutorial - Scripting For Beginners: Qlik Sense September 2020universalNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database 21c - Distributed DataDocument42 pagesOracle Database 21c - Distributed DataNakhla Al-HawiNo ratings yet
- C.S ProjectDocument29 pagesC.S Projectstationcomedy914No ratings yet
- In Comparison With Oracle 8i, 9i Is Have Lot Many New Features. Important IsDocument241 pagesIn Comparison With Oracle 8i, 9i Is Have Lot Many New Features. Important IsBalaji ShindeNo ratings yet
- Linq 2019 PDFDocument47 pagesLinq 2019 PDFZain Alabeeden AlarejiNo ratings yet
- ApacheCon 2018 Geo 3 Calcite Spatial HydeDocument48 pagesApacheCon 2018 Geo 3 Calcite Spatial HydeGokul SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Identify and Resolve Database Performance ProblemsDocument11 pagesIdentify and Resolve Database Performance ProblemsHalid Assen100% (2)
- DBMS Unit 3 Part 2Document29 pagesDBMS Unit 3 Part 2Cine-popcornNo ratings yet
- Monitor and Administer Module AADocument28 pagesMonitor and Administer Module AADo DothingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five (ISR)Document17 pagesChapter Five (ISR)Wudneh AderawNo ratings yet