Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Restrictions For Loop Detection Guard
Restrictions For Loop Detection Guard
Uploaded by
Muhamad DimasCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Port Monitor-MirrorDocument16 pagesPort Monitor-MirrorHai LeNo ratings yet
- AOS-CX Switch Simulator - Loop Protect Lab GuideDocument9 pagesAOS-CX Switch Simulator - Loop Protect Lab Guidetest testNo ratings yet
- Native VLAN and Default VLANDocument6 pagesNative VLAN and Default VLANAaliyah WinkyNo ratings yet
- Network Security in Cisco Packet TracerDocument9 pagesNetwork Security in Cisco Packet TracerHritika RawatNo ratings yet
- B 166 Mpls 3850 CG Chapter 011Document18 pagesB 166 Mpls 3850 CG Chapter 011karam yousifNo ratings yet
- Restrictions For Configuring Layer 3 SubinterfacesDocument6 pagesRestrictions For Configuring Layer 3 SubinterfacesCarlos Jose Perez SanchezNo ratings yet
- ACI Best Practice ConfigurationsDocument15 pagesACI Best Practice ConfigurationsR2D2 SanshiroNo ratings yet
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic ControlDocument14 pagesConfiguring Port-Based Traffic ControlAhmed Al-hamdaniNo ratings yet
- Lab No.5 CCNDocument6 pagesLab No.5 CCNMaham AkramNo ratings yet
- Configuring Layer 3 SubinterfacesDocument4 pagesConfiguring Layer 3 SubinterfacesM Alby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security - InstructorDocument8 pages6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security - InstructorKazuo Taro YamiNo ratings yet
- Cisco Discovery Protocol BypassDocument4 pagesCisco Discovery Protocol BypassRichard CrothersNo ratings yet
- Eliminating Layer 2 LoopsDocument6 pagesEliminating Layer 2 LoopsluisNo ratings yet
- Cisco Security Troubleshooting: Part III - Intrusion Prevention SystemsDocument14 pagesCisco Security Troubleshooting: Part III - Intrusion Prevention SystemshoadiNo ratings yet
- B 166 Sys MGMT 9300 CG Chapter 01100Document26 pagesB 166 Sys MGMT 9300 CG Chapter 01100sdfsfNo ratings yet
- B Consolidated 3650 3se CG Chapter 01101100Document30 pagesB Consolidated 3650 3se CG Chapter 01101100Soma KatiavalaNo ratings yet
- Ss Torm ControlDocument6 pagesSs Torm ControlMorteza alizadehNo ratings yet
- SCOR 06 - p1Document14 pagesSCOR 06 - p1Ahmed El kayalNo ratings yet
- Router On A Stick PDFDocument4 pagesRouter On A Stick PDFBedpiny James100% (1)
- PT Activity: Layer 2 Security: Instructor VersionDocument4 pagesPT Activity: Layer 2 Security: Instructor VersionEdwin MarinNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Case Study: RADULKO Transport: CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP NetworksDocument30 pagesTroubleshooting Case Study: RADULKO Transport: CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP NetworksAustin SpillerNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument3 pages6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityMatrix31415No ratings yet
- IT6223BDocument14 pagesIT6223BTREMsZ GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument6 pages6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityAndrés Montenegro MedellínNo ratings yet
- Intervaln RoutingDocument94 pagesIntervaln RoutingSheik ShareefNo ratings yet
- 6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument5 pages6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Securitytuantuan1996100% (1)
- 14.9.10 Packet Tracer - Implement STP SecurityDocument2 pages14.9.10 Packet Tracer - Implement STP SecurityTest MailNo ratings yet
- Vyatta FirewallDocument4 pagesVyatta Firewallduranduran11No ratings yet
- CCNA - CCNPTraining Virtual Local Area Network VLAN Tutorial 2Document2 pagesCCNA - CCNPTraining Virtual Local Area Network VLAN Tutorial 2okotete evidenceNo ratings yet
- Ccna Lab GuideDocument13 pagesCcna Lab GuideAhmed Mahmoud Ahmed100% (1)
- Sniffer ModeDocument6 pagesSniffer Modejcbodoque0406No ratings yet
- 4 7362 Mini Olt Turn Up Procedure - CompressDocument38 pages4 7362 Mini Olt Turn Up Procedure - Compresssuman.k.das83No ratings yet
- Lab 3Document14 pagesLab 3Fyon ChinNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security: (Instructor Version)Document17 pagesPacket Tracer - Layer 2 Security: (Instructor Version)giovanni saldarriagaNo ratings yet
- En Security Chp6 PTActA L2-Security StudentDocument3 pagesEn Security Chp6 PTActA L2-Security Studentluis alexisNo ratings yet
- Cisco: CCIE Routing and Switching Written Qualification Exam v4.0Document24 pagesCisco: CCIE Routing and Switching Written Qualification Exam v4.0etseNo ratings yet
- 05-Port Additional Characteristic ConfigurationDocument8 pages05-Port Additional Characteristic ConfigurationiwanbudakjambiNo ratings yet
- Interview Report - EHDocument21 pagesInterview Report - EHJose OspinoNo ratings yet
- Turniton STPTDocument2 pagesTurniton STPTcallingrohitNo ratings yet
- Firewalls 1Document36 pagesFirewalls 1alvintejvNo ratings yet
- Inter VLAN RoutingDocument18 pagesInter VLAN Routingvarelac_cunNo ratings yet
- CCIE EI Playbook - Switched CampusDocument34 pagesCCIE EI Playbook - Switched CampusМаниш Нахтвандерер100% (1)
- Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityRichard Inoa JimenezNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 Practice Final Answered 100%Document16 pagesCCNA 3 Practice Final Answered 100%BlueDwarf100% (3)
- Howto L3 IntervlanroutingDocument7 pagesHowto L3 Intervlanroutinga_agustamaNo ratings yet
- Configure InterVLAN RoutingDocument5 pagesConfigure InterVLAN RoutingJuan Felipe Corso AriasNo ratings yet
- Catalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootDocument19 pagesCatalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootSugumar DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- 6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security - InstructorDocument5 pages6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security - InstructorEric Martial AZOMBO BALLANo ratings yet
- Exit Exam - NDCDocument34 pagesExit Exam - NDChaileNo ratings yet
- Cisco Network EngineerDocument20 pagesCisco Network EngineerAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Brocade Bottel Neck CMDDocument32 pagesBrocade Bottel Neck CMDragservNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument14 pages6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityAndres MoraNo ratings yet
- Err Disable RecoveryDocument12 pagesErr Disable Recoveryvinod singh bishtNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Advanced Penetration Testing for Highly-Secured Environments - Second EditionFrom EverandAdvanced Penetration Testing for Highly-Secured Environments - Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Mastering Python Network Automation: Automating Container Orchestration, Configuration, and Networking with Terraform, Calico, HAProxy, and IstioFrom EverandMastering Python Network Automation: Automating Container Orchestration, Configuration, and Networking with Terraform, Calico, HAProxy, and IstioNo ratings yet
- Multitech Datasheet PDFDocument4 pagesMultitech Datasheet PDFRavi PeethaNo ratings yet
- DameWare Server Administrator GuideDocument59 pagesDameWare Server Administrator GuideAaron Teza AngelesNo ratings yet
- E Series Command Reference ManualDocument132 pagesE Series Command Reference ManualHai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Avionics: Digital Data BusesDocument63 pagesAvionics: Digital Data BusesMohamedAlAmineNo ratings yet
- CDMADocument25 pagesCDMAnilabh singhNo ratings yet
- Developing P2P Protocols Across NATDocument7 pagesDeveloping P2P Protocols Across NATBinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Final - RyDocument5 pagesReaction Paper Final - RyRyzagrail Binha-on Chavez50% (2)
- SFP Monitoring MRBTS-533773 4534345E LTE BANJENGAN MANDIRAJA SBTS23R3 ENB 0000 001336 000000 20240329-0950Document20 pagesSFP Monitoring MRBTS-533773 4534345E LTE BANJENGAN MANDIRAJA SBTS23R3 ENB 0000 001336 000000 20240329-0950lisaci6244No ratings yet
- WN Course FileDocument11 pagesWN Course FilePrince PavanNo ratings yet
- Backup DataDocument6 pagesBackup DataKrishyll TamakenNo ratings yet
- CRT-271 Salesforce Certification Dumps QuestionsDocument7 pagesCRT-271 Salesforce Certification Dumps QuestionsJasmine DengNo ratings yet
- Zhone: FTTX SolutionsDocument11 pagesZhone: FTTX SolutionsMani_3ipNo ratings yet
- Top 40 Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Are The Advantages of Using Cloud Computing?Document8 pagesTop 40 Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Are The Advantages of Using Cloud Computing?Divya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Section 1: Basic Introduction To Cyber Security and Information SecurityDocument5 pagesSection 1: Basic Introduction To Cyber Security and Information SecuritynadaNo ratings yet
- Network Book New - 1Document476 pagesNetwork Book New - 1sawpyae PhyokyawNo ratings yet
- Infineon CYW43439 DataSheet v03 - 00 ENDocument88 pagesInfineon CYW43439 DataSheet v03 - 00 ENDenes MarschalkoNo ratings yet
- Net Net 4000 S C610 MIB Reference GuideDocument112 pagesNet Net 4000 S C610 MIB Reference Guidesergey62No ratings yet
- GSM Sniffing: Basic InterceptDocument3 pagesGSM Sniffing: Basic InterceptAli Zohrevand0% (1)
- Cisco VoIP CME Lab 14 - Music On HoldDocument5 pagesCisco VoIP CME Lab 14 - Music On HoldSyed KhanNo ratings yet
- Backhaul RequirementsDocument25 pagesBackhaul RequirementsChetan BhatNo ratings yet
- 98-367.exam.69q: Website: VCE To PDF Converter: Facebook: TwitterDocument35 pages98-367.exam.69q: Website: VCE To PDF Converter: Facebook: TwittersergeNo ratings yet
- CCIE Standard QuestionsDocument460 pagesCCIE Standard Questionssiriom0% (1)
- Ethical Hacking BrochureDocument7 pagesEthical Hacking BrochureMR. EASYNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking Prelims ExamDocument7 pagesData Communication and Networking Prelims ExamSagarAnchalkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter19 enDocument52 pagesChapter19 enwoodali9115991No ratings yet
- Digital Audio Networking in The FieldDocument4 pagesDigital Audio Networking in The FieldEdoardo PacchiottiNo ratings yet
- Modbus Application Protocol V1 1b3Document50 pagesModbus Application Protocol V1 1b3cjalanisNo ratings yet
- Advanced Computer Networking (CS 723) : Addis Ababa University Department of Computer ScienceDocument79 pagesAdvanced Computer Networking (CS 723) : Addis Ababa University Department of Computer ScienceabdulazizNo ratings yet
- NebDocument114 pagesNebSundeep RakranNo ratings yet
- AD and Azure ADDocument63 pagesAD and Azure ADsanthiram635No ratings yet
Restrictions For Loop Detection Guard
Restrictions For Loop Detection Guard
Uploaded by
Muhamad DimasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Restrictions For Loop Detection Guard
Restrictions For Loop Detection Guard
Uploaded by
Muhamad DimasCopyright:
Available Formats
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
• Restrictions for Loop Detection Guard, on page 1
• Information About Loop Detection Guard, on page 1
• How to Configure Loop Detection Guard, on page 3
• Additional References for Configuring Loop Detection Guard, on page 5
• Feature History for Loop Detection Guard, on page 5
Restrictions for Loop Detection Guard
Loop detection guard can be configured only on Layer 2 physical interfaces. Layer 3 ports and virtual interfaces,
such as port channels, switch virtual interfaces (SVIs), and tunnels, are not supported.
Information About Loop Detection Guard
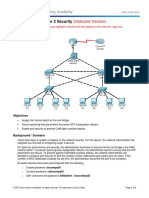
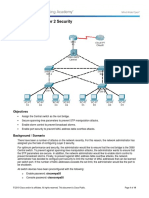
A computer network can experience a network loop where there is more than one Layer 2 path between two
endpoints. This is possible when there are multiple connections between two switches in a network or two
ports on the same switch are connected to each other. The following figure shows a few examples of a network
loop:
Example 1: Switch SW A, which is within the network, is sending traffic to an unmanaged switch on one port
and receiving traffic from the same unmanaged switch, on another port. On the unmanaged switch, the port
receiving traffic is connected to the port sending traffic back to the SW A in the network, resulting in a network
loop.
Example 2: This example shows a network loop involving four switches, two within the network (SW A and
SW B) and two unmanaged switches (Un A and Un B). Traffic is moving in the following direction SW A
to SW B to Un A to Un B and back to SW A, resulting in a network loop.
Example 3: Two ports on the unmanaged switch are connected to each other, resulting in a network loop.
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
1
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
Information About Loop Detection Guard
While Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is normally the protocol that is configured for this purpose (to prevent
network loops), loop detection guard is suited to situations where there may be unmanaged switches in a
network that do not understand STP, or where STP is not configured on the network.
Loop detection guard is enabled at the interface level. To detect loops, the system sends loop-detect frames
from the interface, at preconfigured intervals. When a loop is detected, the configured action is taken.
Loop detection guard is disabled by default. When you enable the feature, you can configure one of these
actions:
• Error-disable the port sending traffic.
• Error-disable the port receiving traffic (default).
• Display an error message and not disable any port.
When a port is error-disabled, no traffic is sent or received on that port.
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
2
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
Interaction of Loop Detection Guard with Other Features
Interaction of Loop Detection Guard with Other Features
STP and Loop Detection Guard
When both loop detection guard and STP are enabled on a device, STP takes over monitoring the network
for loops. In this case loop-detect packets are neither received nor processed in the network.
VLANs and Loop Detection Guard
We do not recommend configuring this feature on a switch that is connected to a hub for these reasons: The
hub floods traffic to all of its interfaces. If the switch in your network is receiving traffic from the same hub,
but on a port in a different VLAN, you may be inadvertently error-disabling those destination ports. The figure
below illustrates such a situation. The port in VLAN 1 is sending traffic to the hub. The switch is also receiving
traffic from the same hub, but on a port in a different VLAN, that is, VLAN 10. If you configure loop detection
guard (and you have configured the default action of error-disabling the destination port), then the port in
VLAN 10 is blocked. Configuring the option to display a message (instead of error-disabling a port) is not
recommended either, because the system displays as many messages as the number of interfaces configured
in the hub, resulting in a CPU overload.
How to Configure Loop Detection Guard
Enabling Loop Detection Guard and Error-Disabling the Required Port
The feature is disabled by default. Complete the following steps to enable loop detection guard and configure
the action you want the system to take when a loop is detected:
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
3
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
Enabling Loop Detection Guard and Error-Disabling the Required Port
Procedure
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1 enable Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your
password if prompted.
Example:
Device> enable
Step 2 configure terminal Enters global configuration mode.
Example:
Device# configure terminal
Step 3 interface Enters interface configuration mode. Specify
{interface-id|subinterface-id|vlan-id} only a physical interface to configure loop
detection guard on the device. Layer 3 ports
Example:
and virtual interfaces like PortChannels, switch
Device(config)# interface virtual interfaces (SVIs), and tunnels are not
tengigabitethernet 1/0/20
Device(config-if)# supported.
Step 4 [no] loopdetect Enables loop detection guard on the device.
Loopdetect frames are sent from the configured
Example:
interface. Use the loopdetect command without
Device(config-if)# loopdetect any keyword to enable loop detection guard.
Use the no form of this command to disable
this feature.
Note You can enable the feature on trunk
ports, but a warning message is
displayed, for the following reason:
A trunk port carries traffic for
several VLANs, simultaneously. A
loop detected in one VLAN can
result in the error-disabling of all
VLAN traffic associated with the
trunk port.
Step 5 [no] loopdetect{time|action Specifies the frequency at which loop-detect
syslog|source-port} frames are sent and the action the system takes
when a loop is detected. If you do not specify
Example:
an action, the destination port is error-disabled
Device(config-if)# loopdetect 7 by default.
You can configure the following:
• time—Time interval to send loop-detect
frame, in seconds. The range is from 0 to
10. The default is 5.
• action syslog—Displays a system message
and does not error-disable any port. If you
use the no form of this command, the
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
4
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
Additional References for Configuring Loop Detection Guard
Command or Action Purpose
system reverts to the last configured
option.
• source-port—Error-disables the source
port. If you use the no form of this
command, the destination port is
error-disabled.
In the example configuration on the left
(Device(config-if)# loopdetect 7), the
interface is configured to send loop-detect
frames every 7 seconds, and to error-disable the
destination port if a loop is detected (The default
applies, because neither the action syslog option
nor the source-port option has been
configured).
Step 6 end Returns to privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Device(config-if)# end
Step 7 show loopdetect Displays all the interfaces where loop detection
guard is enabled, the frequency at which
Example:
loop-detect packets are sent, and the status of
the physical interface.
Device# show loopdetect
Additional References for Configuring Loop Detection Guard
Related Documents
Related Topic Document Title
For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in See the Layer 2/3 Commands
this chapter. section of the Command Reference
(Catalyst 9600 Series Switches)
Feature History for Loop Detection Guard
This table provides release and related information for features explained in this module.
These features are available on all releases subsequent to the one they were introduced in, unless noted
otherwise.
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
5
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
Feature History for Loop Detection Guard
Release Feature Feature Information
Cisco IOS XE Amsterdam Loop Detection Guard Loop detection guard prevents network loops in
17.2.1 either networks that are not configured with STP
or unmanaged devices in networks configured with
STP.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform and software image support. To access Cisco
Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn.
Configuring Loop Detection Guard
6
You might also like
- Port Monitor-MirrorDocument16 pagesPort Monitor-MirrorHai LeNo ratings yet
- AOS-CX Switch Simulator - Loop Protect Lab GuideDocument9 pagesAOS-CX Switch Simulator - Loop Protect Lab Guidetest testNo ratings yet
- Native VLAN and Default VLANDocument6 pagesNative VLAN and Default VLANAaliyah WinkyNo ratings yet
- Network Security in Cisco Packet TracerDocument9 pagesNetwork Security in Cisco Packet TracerHritika RawatNo ratings yet
- B 166 Mpls 3850 CG Chapter 011Document18 pagesB 166 Mpls 3850 CG Chapter 011karam yousifNo ratings yet
- Restrictions For Configuring Layer 3 SubinterfacesDocument6 pagesRestrictions For Configuring Layer 3 SubinterfacesCarlos Jose Perez SanchezNo ratings yet
- ACI Best Practice ConfigurationsDocument15 pagesACI Best Practice ConfigurationsR2D2 SanshiroNo ratings yet
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic ControlDocument14 pagesConfiguring Port-Based Traffic ControlAhmed Al-hamdaniNo ratings yet
- Lab No.5 CCNDocument6 pagesLab No.5 CCNMaham AkramNo ratings yet
- Configuring Layer 3 SubinterfacesDocument4 pagesConfiguring Layer 3 SubinterfacesM Alby KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security - InstructorDocument8 pages6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security - InstructorKazuo Taro YamiNo ratings yet
- Cisco Discovery Protocol BypassDocument4 pagesCisco Discovery Protocol BypassRichard CrothersNo ratings yet
- Eliminating Layer 2 LoopsDocument6 pagesEliminating Layer 2 LoopsluisNo ratings yet
- Cisco Security Troubleshooting: Part III - Intrusion Prevention SystemsDocument14 pagesCisco Security Troubleshooting: Part III - Intrusion Prevention SystemshoadiNo ratings yet
- B 166 Sys MGMT 9300 CG Chapter 01100Document26 pagesB 166 Sys MGMT 9300 CG Chapter 01100sdfsfNo ratings yet
- B Consolidated 3650 3se CG Chapter 01101100Document30 pagesB Consolidated 3650 3se CG Chapter 01101100Soma KatiavalaNo ratings yet
- Ss Torm ControlDocument6 pagesSs Torm ControlMorteza alizadehNo ratings yet
- SCOR 06 - p1Document14 pagesSCOR 06 - p1Ahmed El kayalNo ratings yet
- Router On A Stick PDFDocument4 pagesRouter On A Stick PDFBedpiny James100% (1)
- PT Activity: Layer 2 Security: Instructor VersionDocument4 pagesPT Activity: Layer 2 Security: Instructor VersionEdwin MarinNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Case Study: RADULKO Transport: CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP NetworksDocument30 pagesTroubleshooting Case Study: RADULKO Transport: CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP NetworksAustin SpillerNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument3 pages6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityMatrix31415No ratings yet
- IT6223BDocument14 pagesIT6223BTREMsZ GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument6 pages6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityAndrés Montenegro MedellínNo ratings yet
- Intervaln RoutingDocument94 pagesIntervaln RoutingSheik ShareefNo ratings yet
- 6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument5 pages6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Securitytuantuan1996100% (1)
- 14.9.10 Packet Tracer - Implement STP SecurityDocument2 pages14.9.10 Packet Tracer - Implement STP SecurityTest MailNo ratings yet
- Vyatta FirewallDocument4 pagesVyatta Firewallduranduran11No ratings yet
- CCNA - CCNPTraining Virtual Local Area Network VLAN Tutorial 2Document2 pagesCCNA - CCNPTraining Virtual Local Area Network VLAN Tutorial 2okotete evidenceNo ratings yet
- Ccna Lab GuideDocument13 pagesCcna Lab GuideAhmed Mahmoud Ahmed100% (1)
- Sniffer ModeDocument6 pagesSniffer Modejcbodoque0406No ratings yet
- 4 7362 Mini Olt Turn Up Procedure - CompressDocument38 pages4 7362 Mini Olt Turn Up Procedure - Compresssuman.k.das83No ratings yet
- Lab 3Document14 pagesLab 3Fyon ChinNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security: (Instructor Version)Document17 pagesPacket Tracer - Layer 2 Security: (Instructor Version)giovanni saldarriagaNo ratings yet
- En Security Chp6 PTActA L2-Security StudentDocument3 pagesEn Security Chp6 PTActA L2-Security Studentluis alexisNo ratings yet
- Cisco: CCIE Routing and Switching Written Qualification Exam v4.0Document24 pagesCisco: CCIE Routing and Switching Written Qualification Exam v4.0etseNo ratings yet
- 05-Port Additional Characteristic ConfigurationDocument8 pages05-Port Additional Characteristic ConfigurationiwanbudakjambiNo ratings yet
- Interview Report - EHDocument21 pagesInterview Report - EHJose OspinoNo ratings yet
- Turniton STPTDocument2 pagesTurniton STPTcallingrohitNo ratings yet
- Firewalls 1Document36 pagesFirewalls 1alvintejvNo ratings yet
- Inter VLAN RoutingDocument18 pagesInter VLAN Routingvarelac_cunNo ratings yet
- CCIE EI Playbook - Switched CampusDocument34 pagesCCIE EI Playbook - Switched CampusМаниш Нахтвандерер100% (1)
- Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityRichard Inoa JimenezNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 Practice Final Answered 100%Document16 pagesCCNA 3 Practice Final Answered 100%BlueDwarf100% (3)
- Howto L3 IntervlanroutingDocument7 pagesHowto L3 Intervlanroutinga_agustamaNo ratings yet
- Configure InterVLAN RoutingDocument5 pagesConfigure InterVLAN RoutingJuan Felipe Corso AriasNo ratings yet
- Catalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootDocument19 pagesCatalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootSugumar DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- 6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security - InstructorDocument5 pages6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 Security - InstructorEric Martial AZOMBO BALLANo ratings yet
- Exit Exam - NDCDocument34 pagesExit Exam - NDChaileNo ratings yet
- Cisco Network EngineerDocument20 pagesCisco Network EngineerAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Brocade Bottel Neck CMDDocument32 pagesBrocade Bottel Neck CMDragservNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityDocument14 pages6.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Layer 2 SecurityAndres MoraNo ratings yet
- Err Disable RecoveryDocument12 pagesErr Disable Recoveryvinod singh bishtNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Advanced Penetration Testing for Highly-Secured Environments - Second EditionFrom EverandAdvanced Penetration Testing for Highly-Secured Environments - Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Mastering Python Network Automation: Automating Container Orchestration, Configuration, and Networking with Terraform, Calico, HAProxy, and IstioFrom EverandMastering Python Network Automation: Automating Container Orchestration, Configuration, and Networking with Terraform, Calico, HAProxy, and IstioNo ratings yet
- Multitech Datasheet PDFDocument4 pagesMultitech Datasheet PDFRavi PeethaNo ratings yet
- DameWare Server Administrator GuideDocument59 pagesDameWare Server Administrator GuideAaron Teza AngelesNo ratings yet
- E Series Command Reference ManualDocument132 pagesE Series Command Reference ManualHai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Avionics: Digital Data BusesDocument63 pagesAvionics: Digital Data BusesMohamedAlAmineNo ratings yet
- CDMADocument25 pagesCDMAnilabh singhNo ratings yet
- Developing P2P Protocols Across NATDocument7 pagesDeveloping P2P Protocols Across NATBinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Final - RyDocument5 pagesReaction Paper Final - RyRyzagrail Binha-on Chavez50% (2)
- SFP Monitoring MRBTS-533773 4534345E LTE BANJENGAN MANDIRAJA SBTS23R3 ENB 0000 001336 000000 20240329-0950Document20 pagesSFP Monitoring MRBTS-533773 4534345E LTE BANJENGAN MANDIRAJA SBTS23R3 ENB 0000 001336 000000 20240329-0950lisaci6244No ratings yet
- WN Course FileDocument11 pagesWN Course FilePrince PavanNo ratings yet
- Backup DataDocument6 pagesBackup DataKrishyll TamakenNo ratings yet
- CRT-271 Salesforce Certification Dumps QuestionsDocument7 pagesCRT-271 Salesforce Certification Dumps QuestionsJasmine DengNo ratings yet
- Zhone: FTTX SolutionsDocument11 pagesZhone: FTTX SolutionsMani_3ipNo ratings yet
- Top 40 Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Are The Advantages of Using Cloud Computing?Document8 pagesTop 40 Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Are The Advantages of Using Cloud Computing?Divya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Section 1: Basic Introduction To Cyber Security and Information SecurityDocument5 pagesSection 1: Basic Introduction To Cyber Security and Information SecuritynadaNo ratings yet
- Network Book New - 1Document476 pagesNetwork Book New - 1sawpyae PhyokyawNo ratings yet
- Infineon CYW43439 DataSheet v03 - 00 ENDocument88 pagesInfineon CYW43439 DataSheet v03 - 00 ENDenes MarschalkoNo ratings yet
- Net Net 4000 S C610 MIB Reference GuideDocument112 pagesNet Net 4000 S C610 MIB Reference Guidesergey62No ratings yet
- GSM Sniffing: Basic InterceptDocument3 pagesGSM Sniffing: Basic InterceptAli Zohrevand0% (1)
- Cisco VoIP CME Lab 14 - Music On HoldDocument5 pagesCisco VoIP CME Lab 14 - Music On HoldSyed KhanNo ratings yet
- Backhaul RequirementsDocument25 pagesBackhaul RequirementsChetan BhatNo ratings yet
- 98-367.exam.69q: Website: VCE To PDF Converter: Facebook: TwitterDocument35 pages98-367.exam.69q: Website: VCE To PDF Converter: Facebook: TwittersergeNo ratings yet
- CCIE Standard QuestionsDocument460 pagesCCIE Standard Questionssiriom0% (1)
- Ethical Hacking BrochureDocument7 pagesEthical Hacking BrochureMR. EASYNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking Prelims ExamDocument7 pagesData Communication and Networking Prelims ExamSagarAnchalkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter19 enDocument52 pagesChapter19 enwoodali9115991No ratings yet
- Digital Audio Networking in The FieldDocument4 pagesDigital Audio Networking in The FieldEdoardo PacchiottiNo ratings yet
- Modbus Application Protocol V1 1b3Document50 pagesModbus Application Protocol V1 1b3cjalanisNo ratings yet
- Advanced Computer Networking (CS 723) : Addis Ababa University Department of Computer ScienceDocument79 pagesAdvanced Computer Networking (CS 723) : Addis Ababa University Department of Computer ScienceabdulazizNo ratings yet
- NebDocument114 pagesNebSundeep RakranNo ratings yet
- AD and Azure ADDocument63 pagesAD and Azure ADsanthiram635No ratings yet