Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsCore Java
Core Java
Uploaded by
Sarang1. An applet is a Java program that runs in a web browser. The applet lifecycle includes initialization, starting, stopping, painting, and destruction methods.
2. An interface defines the behavior of a class but not the implementation. Interfaces are used for abstraction, multiple inheritance, and loose coupling between classes.
3. The Java Collection framework provides classes and interfaces to store and manipulate groups of objects. Common collection classes include ArrayList, which implements a resizable array list, and HashMap, which stores key-value pairs in a hash-based data structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Mori Seiki SL Series Service ManualDocument16 pagesMori Seiki SL Series Service ManualMerauke 1No ratings yet
- Gregory R. Andrews-Foundations of Multithreaded, Parallel, and Distributed Programming-Addison-Wesley (1999)Document682 pagesGregory R. Andrews-Foundations of Multithreaded, Parallel, and Distributed Programming-Addison-Wesley (1999)Emil24100% (4)
- Java: Programming: Your Step by Step Guide to Easily Learn Java in 7 DaysFrom EverandJava: Programming: Your Step by Step Guide to Easily Learn Java in 7 DaysRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Software TestingDocument4 pagesSoftware TestingSarangNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is The Difference Between An Abstract Class and Interface?Document8 pages1) What Is The Difference Between An Abstract Class and Interface?Janelle Zimmerman-HrpcekNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions C and JavaDocument39 pagesInterview Questions C and JavaSaiKrishnaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentsnehaNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions On JAVADocument32 pagesInterview Questions On JAVAMo AlamNo ratings yet
- Garbage Collection Is One of The Most Important Feature of Java, Garbage Collection Is Also CalledDocument7 pagesGarbage Collection Is One of The Most Important Feature of Java, Garbage Collection Is Also Calledkalicharan13No ratings yet
- Java QuestionDocument29 pagesJava QuestionSudeep MishraNo ratings yet
- 002 (6 1st Module TopicDocument6 pages002 (6 1st Module TopicShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Nov Dec 18Document20 pagesNov Dec 18Sheryl VinibaNo ratings yet
- JAVADocument29 pagesJAVAsanthiya govindNo ratings yet
- Mca 4030Document9 pagesMca 4030Armaan loverNo ratings yet
- 115 Java QuestionsDocument11 pages115 Java QuestionsThink BoxNo ratings yet
- Assignment For BC0047Document7 pagesAssignment For BC0047Padam ThapaNo ratings yet
- Java - Rahul OopjDocument6 pagesJava - Rahul OopjRahul KumawatNo ratings yet
- OOC Module 2Document24 pagesOOC Module 2Vinayak TelsangNo ratings yet
- 150java QuesDocument20 pages150java QuesMovva TejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Java Questions AnswersDocument68 pagesJava Questions AnswersAbraham FidouNo ratings yet
- BC0047 - Java ProgrammingDocument6 pagesBC0047 - Java Programmingchakraborty.joyjeet1423No ratings yet
- Made by - Bhumika Dikola Divyasha Mishra J.Jenusha ShinyDocument42 pagesMade by - Bhumika Dikola Divyasha Mishra J.Jenusha ShinyBHAAJI0001No ratings yet
- Java 2 MarksDocument9 pagesJava 2 MarksGnanambalNo ratings yet
- Java QuestionsDocument9 pagesJava QuestionsRacolta Daniel0% (1)
- Sample Oral Questions: JAVA Programming TY Btech CSEDocument12 pagesSample Oral Questions: JAVA Programming TY Btech CSECrazy StuffsNo ratings yet
- Java Notes 13Document4 pagesJava Notes 13Fortune MinerNo ratings yet
- Java, JDBC, Servlets and JSP FaqsDocument12 pagesJava, JDBC, Servlets and JSP FaqssanthoshkarthikNo ratings yet
- Java Interview Questions: 1.2? The Stop, Suspend and Resume Methods Have Been Deprecated in JDKDocument3 pagesJava Interview Questions: 1.2? The Stop, Suspend and Resume Methods Have Been Deprecated in JDKmillan100No ratings yet
- Java Interview QuestionsDocument21 pagesJava Interview QuestionsAnand BiradarNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is Java?Document11 pages1) What Is Java?Jijitha MjNo ratings yet
- Java VIVA QuestionsDocument2 pagesJava VIVA QuestionsVASUDEVAN N (RC2113003011006)No ratings yet
- 2 Mark Questions and Answer: IT2301-Java ProgrammingDocument10 pages2 Mark Questions and Answer: IT2301-Java ProgrammingJohn BerkmansNo ratings yet
- JAVA Basics Who Developed Java?: Platform IndependenceDocument10 pagesJAVA Basics Who Developed Java?: Platform IndependencesaithejaNo ratings yet
- Java Basic Questions For Interview PreparationDocument20 pagesJava Basic Questions For Interview Preparationjaihari88No ratings yet
- Nov Dec 19Document26 pagesNov Dec 19Sheryl VinibaNo ratings yet
- Index: Back End Tool: Oracle 10g Express EditionDocument33 pagesIndex: Back End Tool: Oracle 10g Express EditionPraveen PorwalNo ratings yet
- 1) What Are The Data Types Supported by Java?Document22 pages1) What Are The Data Types Supported by Java?Akash BettadNo ratings yet
- Final JavaDocument35 pagesFinal JavaAiyaNo ratings yet
- Significance of Searching Class PathDocument12 pagesSignificance of Searching Class PathsajeerNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks Question With AnswersDocument13 pages2 Marks Question With AnswersJyothi PNo ratings yet
- IT51 JAVA PROGRAMMING 2-MARK Questions and Answers UNIT-1Document16 pagesIT51 JAVA PROGRAMMING 2-MARK Questions and Answers UNIT-1Thalapathy Raj KamalNo ratings yet
- My Java NotesDocument52 pagesMy Java NotesNikhil BhardwajNo ratings yet
- What Is Java?Document21 pagesWhat Is Java?Shivanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- Java Training ReportDocument30 pagesJava Training ReportFaltu YadavNo ratings yet
- All in One Core Java FaqDocument136 pagesAll in One Core Java FaqvenkateshNo ratings yet
- CS8651-Internet Programming Notes 1Document206 pagesCS8651-Internet Programming Notes 1palanicse86No ratings yet
- Java QuestionsDocument19 pagesJava QuestionsMayur DarkundeNo ratings yet
- Javaunit1 130907015927Document29 pagesJavaunit1 130907015927UjjWal MahAjanNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Introduction - Advanced JavaDocument48 pagesCh1 Introduction - Advanced Javatsegab bekele100% (1)
- 2 Mark Questions and Answer: IT2301-Java ProgrammingDocument11 pages2 Mark Questions and Answer: IT2301-Java Programmingvimal kiranNo ratings yet
- CHAPT1Document12 pagesCHAPT1isayashpbende26No ratings yet
- Top 371 Java FAQs Useful For Freshers and ExperiencedDocument55 pagesTop 371 Java FAQs Useful For Freshers and ExperiencedJavaEra.com86% (14)
- IT2301 2markDocument10 pagesIT2301 2marksampathaboNo ratings yet
- Java - All in One (FAQs)Document138 pagesJava - All in One (FAQs)api-3728136No ratings yet
- JAVA Notes GistDocument230 pagesJAVA Notes Gistf_ahamedshaNo ratings yet
- Java 70 SheetDocument26 pagesJava 70 SheetAlishad KhanNo ratings yet
- Q1. Explain JDK, JRE and JVM?Document21 pagesQ1. Explain JDK, JRE and JVM?Bogdan BasilescuNo ratings yet
- Core Java-2Document216 pagesCore Java-2Saumya SwainNo ratings yet
- JAVA NotesDocument8 pagesJAVA Notescohoti1106No ratings yet
- Java Basic InterviewDocument15 pagesJava Basic InterviewOmkar JingarNo ratings yet
- Java Package Mastery: 100 Knock Series - Master Java in One Hour, 2024 EditionFrom EverandJava Package Mastery: 100 Knock Series - Master Java in One Hour, 2024 EditionNo ratings yet
- Software TestingDocument4 pagesSoftware TestingSarangNo ratings yet
- And Answers Guide.: Global GuidelineDocument9 pagesAnd Answers Guide.: Global GuidelineSarangNo ratings yet
- University Institute of Engineering & Technology Kurukshetra University, KurukshetraDocument2 pagesUniversity Institute of Engineering & Technology Kurukshetra University, KurukshetraSarangNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions For BCA 6 SemesterDocument11 pagesMCQ Questions For BCA 6 SemesterSarangNo ratings yet
- Csc466/566 Computer Security Midterm Exam Cheat-SheetDocument3 pagesCsc466/566 Computer Security Midterm Exam Cheat-SheetSarangNo ratings yet
- Compiled By: Afaq Alam KhanDocument56 pagesCompiled By: Afaq Alam KhanSarangNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Quiz Answer KeyDocument4 pagesCybersecurity Quiz Answer KeySarangNo ratings yet
- DEL Lab ManualDocument68 pagesDEL Lab ManualMohini AvatadeNo ratings yet
- ECE SyllabusDocument4 pagesECE SyllabuswelcometonceNo ratings yet
- Standard Single Purpose Processors: PeripheralsDocument17 pagesStandard Single Purpose Processors: Peripheralskank1234No ratings yet
- XXXXX Macro Copy-PasteDocument2 pagesXXXXX Macro Copy-PasteJovic SrdjanNo ratings yet
- (MS-MCI) : Microsoft ZIP (MSZIP) Compression and Decompression Data StructureDocument12 pages(MS-MCI) : Microsoft ZIP (MSZIP) Compression and Decompression Data Structuregaby_munteanNo ratings yet
- FPA 5000 Installation Manual enUS 1218442507Document172 pagesFPA 5000 Installation Manual enUS 1218442507Hernan PortilloNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Windows FirewallDocument14 pagesMicrosoft Windows Firewallgamlgus2kNo ratings yet
- Admiral+Ef3212+Jylt 1000d+ +5ab22lt100dmaDocument33 pagesAdmiral+Ef3212+Jylt 1000d+ +5ab22lt100dmaJuan Manuel PalayaNo ratings yet
- Tentative Schedule For End Odd Semester Exam 2023-24 - 2Document8 pagesTentative Schedule For End Odd Semester Exam 2023-24 - 2Harsh SinghNo ratings yet
- MultiZone Limitations and HintsDocument2 pagesMultiZone Limitations and HintsRubén Darío Becerra GalindoNo ratings yet
- Parag Ray: Professional Experience Executive SummaryDocument3 pagesParag Ray: Professional Experience Executive SummaryankushNo ratings yet
- Process Confirmation - Manage Accounting and Control Data: Project XYZ Initiative April 18, 2008Document32 pagesProcess Confirmation - Manage Accounting and Control Data: Project XYZ Initiative April 18, 2008barbarabolognesiNo ratings yet
- Test & Evaluation Report: Asphalt Technologies, IncDocument1 pageTest & Evaluation Report: Asphalt Technologies, IncJORGE SANTANDERNo ratings yet
- Package-Lock JsonDocument149 pagesPackage-Lock JsonBruno MottaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Software Deployment Checklist: New Linux ServerDocument3 pagesOracle Software Deployment Checklist: New Linux ServerVinu3012No ratings yet
- 15EC62T - Embedded Systems Electronics 6th Sem Syllabus For Diploma DTE Karnataka C15 Scheme - All About VTUDocument11 pages15EC62T - Embedded Systems Electronics 6th Sem Syllabus For Diploma DTE Karnataka C15 Scheme - All About VTURajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Webbing eSIM End User Activation - Home-Country Use CaseDocument5 pagesWebbing eSIM End User Activation - Home-Country Use CaseKamito YloverNo ratings yet
- SOAL CA - Etika Profesi Dan Tatakelola Korporat 2015 PDFDocument147 pagesSOAL CA - Etika Profesi Dan Tatakelola Korporat 2015 PDFWilly Arief YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Kalaiselvi2017 Li-Fi TechnologyDocument4 pagesKalaiselvi2017 Li-Fi TechnologyMadhu YadwadNo ratings yet
- Tests Starters 8 Key PDFDocument2 pagesTests Starters 8 Key PDFchamikahewanadugala1996No ratings yet
- Lab Manual: University of HailDocument39 pagesLab Manual: University of HailCoolie YagitNo ratings yet
- Assignment01 1Document2 pagesAssignment01 1Ahsan JavedNo ratings yet
- Results: What Electronic Gadgets Do You Use For Online Learning? Choose OneDocument5 pagesResults: What Electronic Gadgets Do You Use For Online Learning? Choose OneCarlo FlojoNo ratings yet
- Shopee FB CPAS UTM Tagging GuideDocument23 pagesShopee FB CPAS UTM Tagging GuidetestNo ratings yet
- Physical Unclonable Function (PUF) Based Random Number GeneratorDocument7 pagesPhysical Unclonable Function (PUF) Based Random Number GeneratorAnonymous IlrQK9HuNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Cli RefDocument1 pageFortigate Cli RefPham Minh TaiNo ratings yet
- Solving The Job-Shop Scheduling Problem by Arena Simulation SoftwareDocument7 pagesSolving The Job-Shop Scheduling Problem by Arena Simulation SoftwareEssam KaoudNo ratings yet
- Python Scientific IntroDocument335 pagesPython Scientific IntrosuperbuchNo ratings yet
Core Java
Core Java
Uploaded by
Sarang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pages1. An applet is a Java program that runs in a web browser. The applet lifecycle includes initialization, starting, stopping, painting, and destruction methods.
2. An interface defines the behavior of a class but not the implementation. Interfaces are used for abstraction, multiple inheritance, and loose coupling between classes.
3. The Java Collection framework provides classes and interfaces to store and manipulate groups of objects. Common collection classes include ArrayList, which implements a resizable array list, and HashMap, which stores key-value pairs in a hash-based data structure.
Original Description:
Original Title
Core java
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. An applet is a Java program that runs in a web browser. The applet lifecycle includes initialization, starting, stopping, painting, and destruction methods.
2. An interface defines the behavior of a class but not the implementation. Interfaces are used for abstraction, multiple inheritance, and loose coupling between classes.
3. The Java Collection framework provides classes and interfaces to store and manipulate groups of objects. Common collection classes include ArrayList, which implements a resizable array list, and HashMap, which stores key-value pairs in a hash-based data structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesCore Java
Core Java
Uploaded by
Sarang1. An applet is a Java program that runs in a web browser. The applet lifecycle includes initialization, starting, stopping, painting, and destruction methods.
2. An interface defines the behavior of a class but not the implementation. Interfaces are used for abstraction, multiple inheritance, and loose coupling between classes.
3. The Java Collection framework provides classes and interfaces to store and manipulate groups of objects. Common collection classes include ArrayList, which implements a resizable array list, and HashMap, which stores key-value pairs in a hash-based data structure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
1) List any two restriction for applet. 14)List any two differences between HashMap and HashTable.
1.If we are running an applet from a provider who is not HashMap :-
trustworthy than security is important. 1.HashMap is non-synchronized. It is not thread-safe and can't be
2.Applet itself cannot run or modify any application on the local shared between many threads without proper synchronization
system. code
3.Applets has no access to client-side resources such as files , OS 2.HashMap allows one null key and multiple null values
etc. 3.Multiple threads can operate simultaneously and hence
2)What are different ways of creating string object ? hashmap's object is not thread-safe.
There are two ways to create a String object: Hashtable:-
By string literal : Java String literal is created by using double 1.Hashtable is synchronized. It is thread-safe and can be shared
quotes. For Example: String s=“Welcome”; with many threads.
By new keyword : Java String is created by using a keyword “new 2.Hashtable doesn’t allow any null key or value.
”. For example: String s=new String(“Welcome”); 3.At a time only one thread is allowed to operate the Hashtable’s
3)Can we use super() and this() within the same object. Hence it is thread-safe.
“this()” and “super()” cannot be used inside the same 15)What are the different ways to create an object in Java ?
constructor, as both cannot be executed at once (both cannot be There are five different ways to create an object in Java:
the first statement). “this” can be passed as an argument in the 1.Java new Operator.
method and constructor calls. 2.Java Class. newInstance() method.
4)State the use of wrapper class. 3.Java newInstance() method of constructor.
The wrapper class implements the technique to convert the 4.Java Object. clone() method.
primitive into object and object into primitive. There is a concept 5.Java Object Serialization and Deserialization.
of autoboxing and unboxing in the wrapper class, which 16)Can you save a Java source file by name than class name ?
transform the primitives into objects and objects into primitives Yes,you can save your java source code file with any other name,
automatically. not same as your main class name but when you comiple it than
5)How to create and access the package in Java ? byte code file name will be same as your main class name.
1.First create a directory within name of package. alization.
2.Create a java file in newly created directory. 17)What is instance variable ?
3.In this java file you must specify the package name with the help An instance variable is a variable which is declared in a class but
of package keyword. outside of constructors, methods, or blocks. Instance variables
4.Save this file with same name of public class. are created when an object is instantiated, and are accessible to
5.Now you can use this package in your program. all the constructors, methods, or blocks in the class. Access
6)State the purpose of throw keyword. modifiers can be given to the instance variable.mplementation.
The throws keyword is used to declare which exceptions can be 18)List Java non-access modifiers.
thrown from a method, while the throw keyword is used to Modifiers in Java fall into one of two groups - access and non-
explicitly throw an exception within a method or block of code. Access:
The throws keyword is used in a method signature and declares Access:- public , private , protected .
which exceptions can be thrown from a method. Non-Access:- static, final, abstract, synchronized, volatile,
7)State the use of jar file. transient and native .
JAR files are packaged with the ZIP file format, so you can use 19) Swing :-
them for tasks such as lossless data compression, archiving, Java Swing is a lightweight Java graphical user interface (GUI)
decompression, and archive unpacking. These tasks are among widget toolkit that includes a rich set of widgets. It is part of the
the most common uses of JAR files, and you can realize many JAR Java Foundation Classes (JFC) and includes several packages for
file benefits using only these basic features. developing rich desktop applications in Java.
8)Which container use border layout as its default layout ? 20) AWT :-
The window, Frame and Dialog classes use a border layout as their AWT stands for Abstract window toolkit is an Application
default layout. programming interface (API) for creating Graphical User
9)Does the order of public static void matter in main method. Interface (GUI) in Java. It allows Java programmers to develop
It doesn't matter but void should always come before main(). window-based applications. AWT provides various components
10)List the types of Applet. like button, label, checkbox, etc. used as objects inside a Java
1.Form applet , 2.List applet , 3.Pick applet , 4.Multi-value group Program.
applet , 5.Chart applet , 6.Association applet , 7.Explorer or Tree 21)Container :-
applet , 8.File attachment applet. Containers are the interface between a component and the low-
11)What is exception ? level, platform-specific functionality that supports the component
An exception is an event, which occurs during the execution of a . Before it can be executed, a web, enterprise bean, or application
program, that disrupts the normal flow of the program's client component must be assembled into a Java EE module and
instructions. When an error occurs within a method, the method deployed into its container.
creates an object and hands it off to the runtime system. 23)Event:-
12)What is collection framework ? An event in Java is an object that is created when something
The Java collections framework is a set of classes and interfaces changes within a graphical user interface. If a user clicks on a
that implement commonly reusable collection data structures. button, clicks on a combo box, or types characters into a text field
Although referred to as a framework, it works in a manner of a , etc., then an event triggers, creating the relevant event object.
library. The collections framework provides both interfaces that 24)Event handling :-
define various collections and classes that implement them. Event Handling is the mechanism that controls the event and
13)What is JVMA Java virtual machine is a virtual machine that decides what should happen if an event occurs. This mechanism
enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs have the code which is known as event handler that is executed
written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode. when an event occurs. Java Uses the Delegation Event Model to
The JVM is detailed by a specification that formally describes handle the events.
what is required in a JVM implementation.
1)What is applet ? Explain life cycle of applet. 5)What is Interface ? Why are they used in Java ? Explain
Applet is a class in Java. The applet life cycle can be defined as the An Interface in Java programming language is defined as an abstract
process of how the object is created, started, stopped, and destroyed type used to specify the behavior of a class. An interface in Java is a
during the entire execution of its application. It basically has five blueprint of a class. A Java interface contains static constants and
core methods namely init(), start(), stop(), paint() and destroy(). abstract methods.
1.init(): The init() method is the first method to run that initializes the 1.It is used to achieve total abstraction.
applet. It can be invoked only once at the time of initialization. 2.Since java does not support multiple inheritances in the case of
2.start(): The start() method contains the actual code of the applet class, by using an interface it can achieve multiple inheritances.
and starts the applet. It is invoked immediately after the init() 3.It is also used to achieve loose coupling.
method is invoked. 4.Interfaces are used to implement abstraction.
3.stop(): The stop() method stops the execution of the applet. The 6)Define collection. Explain any two classes used with collection.
stop () method is invoked whenever the applet is stopped, minimized The Collection in Java is a framework that provides an architecture to
, or moving from one tab to another in the browser, the stop() store and manipulate the group of objects.A Collection represents a
method is invoked single unit of objects, i.e., a group.
4.destroy(): The destroy() method destroys the applet after its work is 1.ArrayList:-
done. The ArrayList class implements the List interface. It uses a dynamic
5.paint(): The paint() method belongs to the Graphics class in Java. It array to store the duplicate element of different data types. The
is used to draw shapes like circle, square, trapezium, etc. ArrayList class maintains the insertion order and is non-synchronized.
2)Explain the use of super keyword with reference to inheritance. The elements stored in the ArrayList class can be randomly accessed.
The super keyword refers to superclass (parent) objects. 2.LinkedList :-
It is used to call superclass methods, and to access the superclass LinkedList implements the Collection interface. It uses a doubly
constructor.The most common use of the super keyword is to linked list internally to store the elements. It can store the duplicate
eliminate the confusion between superclasses and subclasses that elements. It maintains the insertion order and is not synchronized. In
have methods with the same name. LinkedList, the manipulation is fast because no shifting is required.
1.super variable refers immediate parent class instance. 7)Write similarities and dissimilarities between Abstract Class
2.super variable can invoke immediate parent class method. and Interface.
3.super() acts as immediate parent class constructor and should be Similarities:-
the first line in child class constructor 1.We can't create object for both.
3)Explain exception handling with example. 2.All the abstract methods must be overridden by subclass.
Exception handling is the process of responding to unwanted or 3.Don’t have default constructor.
unexpected events when a computer program runs. such as 4.By using both we can go for dynamic polymorphism.
ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException, 5.Both can contain static and final variable.
RemoteException, etc. 6.Both inherited from common domain of itself using extends
Example ; keyword.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero 7.Both provide static method implementation.
at ExceptionDemo.main(Exception.java:5) Dissimilarities:-
ExceptionDemo : The class name 1.Type of methods: Interface can have only abstract methods. An
main : The method name abstract class can have abstract and non-abstract methods. From
ExceptionDemo.java : The filename Java 8, it can have default and static methods also.
java:5 : Line numberception 2.Final Variables: Variables declared in a Java interface are by default
This message is not user friendly so a user will not be able to final. An abstract class may contain non-final variables.
understand what went wrong. In order to let them know the reason 3.Type of variables: Abstract class can have final, non-final, static and
in simple language, we handle exceptions. We handle such non-static variables. The interface has only static and final variables.
conditions and then prints a user friendly warning message to user, 8)Explain any four methods of file class.
which lets them correct the error as most of the time exception 1. canExecute() :- Tests whether the application can execute the file
occurs due to bad data provided by user. denoted by this abstract pathname. :- boolean
4)How to create user defined package ? How to access it ?Explain 2. canRead() :- Tests whether the application can read the file
with example. denoted by this abstract pathname. :- boolean
Step 1: Creating a package in java class. The format is very simple 3. canWrite() :- Tests whether the application can modify the file
and easy. Just write a package by following its name. denoted by this abstract pathname. :- boolean
package example1; 4. compareTo :- (File pathname) Compares two abstract pathnames
Step 2: Include class in java package, But remember that class only lexicographically. :- int
have one package declaration. 9)Explain the need of garbage collection in java.
package example1; Java applications obtain objects in memory as needed. It is the task of
class gfg { garbage collection (GC) in the Java virtual machine (JVM) to
public static void main(Strings[] args){ automatically determine what memory is no longer being used by a
} Java application and to recycle this memory for other uses.In the
} common language runtime (CLR), the garbage collector (GC) serves as
Step 3: Now the user-defined package is successfully created, we can an automatic memory manager. The garbage collector manages the
import it into other packages and use functions allocation and release of memory for an application. For developers
Example :- working with managed code, this means that you don't have to write
import example.gfg; code to perform memory management tasks.
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
gfg obj = new gfg();
System.out.println(obj.show());
}} . Output :- hello geeks !! How are you ?
1)What is jar file ? Give steps and example of creating jar file. 6)Write a short note on Abstract class.
JAR stands for Java ARchive. It's a file format based on the popular Data abstraction is the process of hiding certain details and showing
ZIP file format and is used for aggregating many files into one. only essential information to the user.
1.-c creates new archive file. Abstraction can be achieved with either abstract classes or interfaces
2.-v generates verbose output. It displays the included or extracted (which you will learn more about in the next chapter).
resource on the standard output. The abstract keyword is a non-access modifier, used for classes and
3.-m includes manifest information from the given mf file. methods:
4.-f specifies the archive file name. Abstract class: is a restricted class that cannot be used to create
5.-x extracts files from the archive file. objects (to access it, it must be inherited from another class).
itC:\> jar cf pack.jar pack Abstract method: can only be used in an abstract class, and it does
create jar file using this command by converting it into Pack.jar not have a body. The body is provided by the subclass.
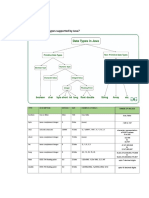
2)Explain data types in Java. 1.An instance of an abstract class can not be created.
Data types specify the different sizes and values that can be stored in 2.Constructors are allowed.
the variable. There are two types of data types in Java that are 3.We can have an abstract class without any abstract method.
divided into two groups. 4.There can be a final method in abstract class but any abstract
Primitive data types :- The primitive data types include boolean, char, method in class(abstract class) can not be declared as final or in
byte, short, int, long, float and double.In Java language, primitive simper terms final method can not be abstract itself as it will yield an
data types are the building blocks of data manipulation. error: “Illegal combination of modifiers: abstract and final”
Non-primitive data types :- The non-primitive data types include We are not allowed to create objects for an abstract class.
Classes, Interfaces, and Arrays. 7)Explain inner class in Java with example.
3)What is adapter class ? Explain its purpose. In Java, inner class refers to the class that is declared inside class or
In JAVA, an adapter class is the default implementation of listener interface which were mainly introduced, to sum up, same logically
interfaces. The notion of listener interfaces stems from the relatable classes as Java is purely object-oriented so bringing it closer
Delegation Event Model. It is one of the many techniques used to to the real world.
handle events in Graphical User Interface (GUI) programming Example :-
languages, such as JAVA. An adapter class in JAVA is therefore class Outer {
purpose is to implement an interface having a set of dummy methods void outerMethod() {
. If a programmer chooses to inherit an adapter class, they will not be int x = 98;
forced to implement all the methods listed under a particular listener System.out.println("inside outerMethod");
interface. class Inner {
4)Differentiate StringBuffer and StringBuilder class. void innerMethod() {
StringBuffer :- System.out.println("x= "+x);
1.StringBuffer is synchronized i.e. thread safe. It means two threads }
can't call the methods of StringBuffer simultaneously. }
2.StringBuffer is less efficient than StringBuilder. Inner y = new Inner();
3.StringBuffer was introduced in Java 1.0 y.innerMethod();
StringBuilder :- }
1.StringBuilder is non-synchronized i.e. not thread safe. It means two }
threads can call the methods of StringBuilder simultaneously. class MethodLocalVariableDemo {
2.StringBuilder is more efficient than StringBuffer. public static void main(String[] args) {
3.StringBuilder was introduced in Java 1.5 Outer x=new Outer();
5)Explain arrays in Java. How does it differ from C++ ? x.outerMethod();
There are three behavioral differences between an array in C++ and a }
similar array in Java: }
1.A Java array is aware of its size while a C++ array is not Output inside innerMethod
2.Java detects and notifies a programmer when an array is indexed x= 98
out of bounds C++ does not
3.In C++ it is possible to create an array of fully constructed objects in
a single operation; Java requires multiple operations to create an
array of objectsThree behavioral differences between an array in C++
and a similar array in Java:Array Size1.A Java array is aware of its size
while a C++ array is not
Array Size :-
An array in Java is an object (i.e., an instance of an unnamed class),
so, like any object, it may have instance fields. Every Java array has a
field defined as public int length; that stores the size of (or the
number of elements in) the array.
Bounds Checking :-
Arrays, in both the C++ and Java programming languages, are zero-
indexed, meaning that legal index values range from 0 to size - 1
(where size is the maximum number of elements in the array).
Arrays Of Objects :-
It is possible in both C++ and in Java to have arrays of objects.
However, creating an array of objects in Java is a multi-step process
of building pointers and pointers-to-pointers (technically, Java has
references, but a Java reference is pretty close to a C++ pointer).
You might also like
- Mori Seiki SL Series Service ManualDocument16 pagesMori Seiki SL Series Service ManualMerauke 1No ratings yet
- Gregory R. Andrews-Foundations of Multithreaded, Parallel, and Distributed Programming-Addison-Wesley (1999)Document682 pagesGregory R. Andrews-Foundations of Multithreaded, Parallel, and Distributed Programming-Addison-Wesley (1999)Emil24100% (4)
- Java: Programming: Your Step by Step Guide to Easily Learn Java in 7 DaysFrom EverandJava: Programming: Your Step by Step Guide to Easily Learn Java in 7 DaysRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Software TestingDocument4 pagesSoftware TestingSarangNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is The Difference Between An Abstract Class and Interface?Document8 pages1) What Is The Difference Between An Abstract Class and Interface?Janelle Zimmerman-HrpcekNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions C and JavaDocument39 pagesInterview Questions C and JavaSaiKrishnaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentsnehaNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions On JAVADocument32 pagesInterview Questions On JAVAMo AlamNo ratings yet
- Garbage Collection Is One of The Most Important Feature of Java, Garbage Collection Is Also CalledDocument7 pagesGarbage Collection Is One of The Most Important Feature of Java, Garbage Collection Is Also Calledkalicharan13No ratings yet
- Java QuestionDocument29 pagesJava QuestionSudeep MishraNo ratings yet
- 002 (6 1st Module TopicDocument6 pages002 (6 1st Module TopicShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Nov Dec 18Document20 pagesNov Dec 18Sheryl VinibaNo ratings yet
- JAVADocument29 pagesJAVAsanthiya govindNo ratings yet
- Mca 4030Document9 pagesMca 4030Armaan loverNo ratings yet
- 115 Java QuestionsDocument11 pages115 Java QuestionsThink BoxNo ratings yet
- Assignment For BC0047Document7 pagesAssignment For BC0047Padam ThapaNo ratings yet
- Java - Rahul OopjDocument6 pagesJava - Rahul OopjRahul KumawatNo ratings yet
- OOC Module 2Document24 pagesOOC Module 2Vinayak TelsangNo ratings yet
- 150java QuesDocument20 pages150java QuesMovva TejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Java Questions AnswersDocument68 pagesJava Questions AnswersAbraham FidouNo ratings yet
- BC0047 - Java ProgrammingDocument6 pagesBC0047 - Java Programmingchakraborty.joyjeet1423No ratings yet
- Made by - Bhumika Dikola Divyasha Mishra J.Jenusha ShinyDocument42 pagesMade by - Bhumika Dikola Divyasha Mishra J.Jenusha ShinyBHAAJI0001No ratings yet
- Java 2 MarksDocument9 pagesJava 2 MarksGnanambalNo ratings yet
- Java QuestionsDocument9 pagesJava QuestionsRacolta Daniel0% (1)
- Sample Oral Questions: JAVA Programming TY Btech CSEDocument12 pagesSample Oral Questions: JAVA Programming TY Btech CSECrazy StuffsNo ratings yet
- Java Notes 13Document4 pagesJava Notes 13Fortune MinerNo ratings yet
- Java, JDBC, Servlets and JSP FaqsDocument12 pagesJava, JDBC, Servlets and JSP FaqssanthoshkarthikNo ratings yet
- Java Interview Questions: 1.2? The Stop, Suspend and Resume Methods Have Been Deprecated in JDKDocument3 pagesJava Interview Questions: 1.2? The Stop, Suspend and Resume Methods Have Been Deprecated in JDKmillan100No ratings yet
- Java Interview QuestionsDocument21 pagesJava Interview QuestionsAnand BiradarNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is Java?Document11 pages1) What Is Java?Jijitha MjNo ratings yet
- Java VIVA QuestionsDocument2 pagesJava VIVA QuestionsVASUDEVAN N (RC2113003011006)No ratings yet
- 2 Mark Questions and Answer: IT2301-Java ProgrammingDocument10 pages2 Mark Questions and Answer: IT2301-Java ProgrammingJohn BerkmansNo ratings yet
- JAVA Basics Who Developed Java?: Platform IndependenceDocument10 pagesJAVA Basics Who Developed Java?: Platform IndependencesaithejaNo ratings yet
- Java Basic Questions For Interview PreparationDocument20 pagesJava Basic Questions For Interview Preparationjaihari88No ratings yet
- Nov Dec 19Document26 pagesNov Dec 19Sheryl VinibaNo ratings yet
- Index: Back End Tool: Oracle 10g Express EditionDocument33 pagesIndex: Back End Tool: Oracle 10g Express EditionPraveen PorwalNo ratings yet
- 1) What Are The Data Types Supported by Java?Document22 pages1) What Are The Data Types Supported by Java?Akash BettadNo ratings yet
- Final JavaDocument35 pagesFinal JavaAiyaNo ratings yet
- Significance of Searching Class PathDocument12 pagesSignificance of Searching Class PathsajeerNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks Question With AnswersDocument13 pages2 Marks Question With AnswersJyothi PNo ratings yet
- IT51 JAVA PROGRAMMING 2-MARK Questions and Answers UNIT-1Document16 pagesIT51 JAVA PROGRAMMING 2-MARK Questions and Answers UNIT-1Thalapathy Raj KamalNo ratings yet
- My Java NotesDocument52 pagesMy Java NotesNikhil BhardwajNo ratings yet
- What Is Java?Document21 pagesWhat Is Java?Shivanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- Java Training ReportDocument30 pagesJava Training ReportFaltu YadavNo ratings yet
- All in One Core Java FaqDocument136 pagesAll in One Core Java FaqvenkateshNo ratings yet
- CS8651-Internet Programming Notes 1Document206 pagesCS8651-Internet Programming Notes 1palanicse86No ratings yet
- Java QuestionsDocument19 pagesJava QuestionsMayur DarkundeNo ratings yet
- Javaunit1 130907015927Document29 pagesJavaunit1 130907015927UjjWal MahAjanNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Introduction - Advanced JavaDocument48 pagesCh1 Introduction - Advanced Javatsegab bekele100% (1)
- 2 Mark Questions and Answer: IT2301-Java ProgrammingDocument11 pages2 Mark Questions and Answer: IT2301-Java Programmingvimal kiranNo ratings yet
- CHAPT1Document12 pagesCHAPT1isayashpbende26No ratings yet
- Top 371 Java FAQs Useful For Freshers and ExperiencedDocument55 pagesTop 371 Java FAQs Useful For Freshers and ExperiencedJavaEra.com86% (14)
- IT2301 2markDocument10 pagesIT2301 2marksampathaboNo ratings yet
- Java - All in One (FAQs)Document138 pagesJava - All in One (FAQs)api-3728136No ratings yet
- JAVA Notes GistDocument230 pagesJAVA Notes Gistf_ahamedshaNo ratings yet
- Java 70 SheetDocument26 pagesJava 70 SheetAlishad KhanNo ratings yet
- Q1. Explain JDK, JRE and JVM?Document21 pagesQ1. Explain JDK, JRE and JVM?Bogdan BasilescuNo ratings yet
- Core Java-2Document216 pagesCore Java-2Saumya SwainNo ratings yet
- JAVA NotesDocument8 pagesJAVA Notescohoti1106No ratings yet
- Java Basic InterviewDocument15 pagesJava Basic InterviewOmkar JingarNo ratings yet
- Java Package Mastery: 100 Knock Series - Master Java in One Hour, 2024 EditionFrom EverandJava Package Mastery: 100 Knock Series - Master Java in One Hour, 2024 EditionNo ratings yet
- Software TestingDocument4 pagesSoftware TestingSarangNo ratings yet
- And Answers Guide.: Global GuidelineDocument9 pagesAnd Answers Guide.: Global GuidelineSarangNo ratings yet
- University Institute of Engineering & Technology Kurukshetra University, KurukshetraDocument2 pagesUniversity Institute of Engineering & Technology Kurukshetra University, KurukshetraSarangNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions For BCA 6 SemesterDocument11 pagesMCQ Questions For BCA 6 SemesterSarangNo ratings yet
- Csc466/566 Computer Security Midterm Exam Cheat-SheetDocument3 pagesCsc466/566 Computer Security Midterm Exam Cheat-SheetSarangNo ratings yet
- Compiled By: Afaq Alam KhanDocument56 pagesCompiled By: Afaq Alam KhanSarangNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Quiz Answer KeyDocument4 pagesCybersecurity Quiz Answer KeySarangNo ratings yet
- DEL Lab ManualDocument68 pagesDEL Lab ManualMohini AvatadeNo ratings yet
- ECE SyllabusDocument4 pagesECE SyllabuswelcometonceNo ratings yet
- Standard Single Purpose Processors: PeripheralsDocument17 pagesStandard Single Purpose Processors: Peripheralskank1234No ratings yet
- XXXXX Macro Copy-PasteDocument2 pagesXXXXX Macro Copy-PasteJovic SrdjanNo ratings yet
- (MS-MCI) : Microsoft ZIP (MSZIP) Compression and Decompression Data StructureDocument12 pages(MS-MCI) : Microsoft ZIP (MSZIP) Compression and Decompression Data Structuregaby_munteanNo ratings yet
- FPA 5000 Installation Manual enUS 1218442507Document172 pagesFPA 5000 Installation Manual enUS 1218442507Hernan PortilloNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Windows FirewallDocument14 pagesMicrosoft Windows Firewallgamlgus2kNo ratings yet
- Admiral+Ef3212+Jylt 1000d+ +5ab22lt100dmaDocument33 pagesAdmiral+Ef3212+Jylt 1000d+ +5ab22lt100dmaJuan Manuel PalayaNo ratings yet
- Tentative Schedule For End Odd Semester Exam 2023-24 - 2Document8 pagesTentative Schedule For End Odd Semester Exam 2023-24 - 2Harsh SinghNo ratings yet
- MultiZone Limitations and HintsDocument2 pagesMultiZone Limitations and HintsRubén Darío Becerra GalindoNo ratings yet
- Parag Ray: Professional Experience Executive SummaryDocument3 pagesParag Ray: Professional Experience Executive SummaryankushNo ratings yet
- Process Confirmation - Manage Accounting and Control Data: Project XYZ Initiative April 18, 2008Document32 pagesProcess Confirmation - Manage Accounting and Control Data: Project XYZ Initiative April 18, 2008barbarabolognesiNo ratings yet
- Test & Evaluation Report: Asphalt Technologies, IncDocument1 pageTest & Evaluation Report: Asphalt Technologies, IncJORGE SANTANDERNo ratings yet
- Package-Lock JsonDocument149 pagesPackage-Lock JsonBruno MottaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Software Deployment Checklist: New Linux ServerDocument3 pagesOracle Software Deployment Checklist: New Linux ServerVinu3012No ratings yet
- 15EC62T - Embedded Systems Electronics 6th Sem Syllabus For Diploma DTE Karnataka C15 Scheme - All About VTUDocument11 pages15EC62T - Embedded Systems Electronics 6th Sem Syllabus For Diploma DTE Karnataka C15 Scheme - All About VTURajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Webbing eSIM End User Activation - Home-Country Use CaseDocument5 pagesWebbing eSIM End User Activation - Home-Country Use CaseKamito YloverNo ratings yet
- SOAL CA - Etika Profesi Dan Tatakelola Korporat 2015 PDFDocument147 pagesSOAL CA - Etika Profesi Dan Tatakelola Korporat 2015 PDFWilly Arief YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Kalaiselvi2017 Li-Fi TechnologyDocument4 pagesKalaiselvi2017 Li-Fi TechnologyMadhu YadwadNo ratings yet
- Tests Starters 8 Key PDFDocument2 pagesTests Starters 8 Key PDFchamikahewanadugala1996No ratings yet
- Lab Manual: University of HailDocument39 pagesLab Manual: University of HailCoolie YagitNo ratings yet
- Assignment01 1Document2 pagesAssignment01 1Ahsan JavedNo ratings yet
- Results: What Electronic Gadgets Do You Use For Online Learning? Choose OneDocument5 pagesResults: What Electronic Gadgets Do You Use For Online Learning? Choose OneCarlo FlojoNo ratings yet
- Shopee FB CPAS UTM Tagging GuideDocument23 pagesShopee FB CPAS UTM Tagging GuidetestNo ratings yet
- Physical Unclonable Function (PUF) Based Random Number GeneratorDocument7 pagesPhysical Unclonable Function (PUF) Based Random Number GeneratorAnonymous IlrQK9HuNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Cli RefDocument1 pageFortigate Cli RefPham Minh TaiNo ratings yet
- Solving The Job-Shop Scheduling Problem by Arena Simulation SoftwareDocument7 pagesSolving The Job-Shop Scheduling Problem by Arena Simulation SoftwareEssam KaoudNo ratings yet
- Python Scientific IntroDocument335 pagesPython Scientific IntrosuperbuchNo ratings yet