Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classification of Antibacterial Agents: 1-Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis 2 - Inhibitors of Cell Membrane Function
Classification of Antibacterial Agents: 1-Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis 2 - Inhibitors of Cell Membrane Function
Uploaded by
omar ahmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pages1. The document discusses factors to consider when selecting antimicrobial agents, including microbial, patient-related, and drug-related factors. Microbe-related factors include gram stain and culture results. Patient factors include site of infection, immune status, renal and hepatic function, age, and pregnancy. Drug factors include safety, cost, and whether the drug is bactericidal or bacteriostatic.
2. Microbial resistance can develop through natural resistance, spontaneous mutation, acquisition from other organisms, or long-term antibiotic use. Mechanisms of resistance include altered drug targets, decreased drug accumulation, and enzymatic deactivation of the drug.
3. Complications of antimicrobial therapy include direct toxic effects, allergic
Original Description:
Original Title
lec_10_abx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses factors to consider when selecting antimicrobial agents, including microbial, patient-related, and drug-related factors. Microbe-related factors include gram stain and culture results. Patient factors include site of infection, immune status, renal and hepatic function, age, and pregnancy. Drug factors include safety, cost, and whether the drug is bactericidal or bacteriostatic.
2. Microbial resistance can develop through natural resistance, spontaneous mutation, acquisition from other organisms, or long-term antibiotic use. Mechanisms of resistance include altered drug targets, decreased drug accumulation, and enzymatic deactivation of the drug.
3. Complications of antimicrobial therapy include direct toxic effects, allergic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesClassification of Antibacterial Agents: 1-Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis 2 - Inhibitors of Cell Membrane Function
Classification of Antibacterial Agents: 1-Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis 2 - Inhibitors of Cell Membrane Function
Uploaded by
omar ahmed1. The document discusses factors to consider when selecting antimicrobial agents, including microbial, patient-related, and drug-related factors. Microbe-related factors include gram stain and culture results. Patient factors include site of infection, immune status, renal and hepatic function, age, and pregnancy. Drug factors include safety, cost, and whether the drug is bactericidal or bacteriostatic.
2. Microbial resistance can develop through natural resistance, spontaneous mutation, acquisition from other organisms, or long-term antibiotic use. Mechanisms of resistance include altered drug targets, decreased drug accumulation, and enzymatic deactivation of the drug.
3. Complications of antimicrobial therapy include direct toxic effects, allergic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
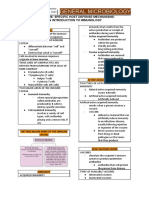
Antimicrobial Agents
Antimicrobial vs Selection of Antimicrobials Microbial Resistance Complications of AB Prophylactic Empiric
Antibiotic m.o. related factors Patient-related factors Drug-related factors therapy therapy therapy
Antimicrobial: any substance that 1. Gram stain: used as a preliminary rapid assessment (e.g. G+ve 1. Site of infection: 1. Safety (e.g. ototoxicity of aminglycosides) Causes: 1. Direct toxic effect: Used w/ caution when the • Given before
inhibits or kills m.o. w/o harming the → penicillins, G-ve → quinolones) ◦ BBB penetration is affected by ◦ aminoglycosides → oto & benefits outweigh the risks identification of the
2. Cost (1) Naturally resistant strains (e.g. vancomycin-resistant G-ve
host lipophilicity, mwt & pp binding nephrotoxicity Examples: m.o.
2. Culture of the m.o. ◦ meningitis (inflammation) → ↑ BBB 3. Bactericidal vs bacteriostatic bacteria ) ◦ chloramphenicol → grey baby
Antibiotics: natural or semisynthetic 1. to prevent streptococcal • Broad spectrum
permeability → ↑ penicillin penetration A. bactericidal requires actively replicating m.o (2) Spontaneous mutation syndrome infections → rheumatic heart
antimicrobials (ABs are a type of 3. Detection of microbial antigens using PCR (e.g. hepatitis) • Used for severe
antimicrobials) ◦ prostate → ↓ penetration due to acidic Therefore, combination of cidal + static → (3) Acquired resistance (i.e. from another organism) 2. Allergic rxn (hypersensitivity) disease
medium antagonism infections that
◦ penicillins 2. to prevent TB or meningitis require immediate
2. Immune system B. combination of 2 bactericidal agents → ↑ in individuals who are in
Forms of resistance: ◦ sulfonamides ttt
3. Renal function resistance, superinfection & toxicity → should close contact w/ patients
be used w/ caution (e.g. B-lactams + 1. Altered targets (e.g. alteration of DNA gyrase → resistance to 3. Superinfections:
4. Hepatic function aminoglycosides) fluoroquinolones) 3. prior to prosthetic implant
◦ due to long-term use of broad surgeries (e.g. artificial heart
5. Age 2. Decreased accumulation of the drug due to: spectrum AB → resistance valves or dental prosthesis)
6. Pregnancy & lactation ◦ ↓ permeability (e.g. B-lactams cannot pass through the porins in 4. immunocompromised
the LPS of G-ve bacteria) patients
◦ ↑ efflux (e.g. tetracyclines)
3. Enzymatic deactivation of the drug (e.g. B-lactamase)
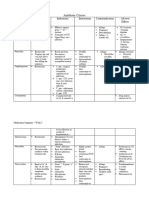
Classification of Antibacterial Agents
Class
1- Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis 2- Inhibitors of Cell membrane function
Beta-Lactams Vancomycin Carbapenems Monobactams Fosfomycin Isoniazide (INH) Ethambutol
Penicillins Cephalosporins
General • Highly selective cuz human cells lack cell walls • Same as penicillins MOA: Synthetic β-lactams Aztreonam (IV, IM): • Bactericidal synthetic Active against mycobacterium TB
properties • Bactericidal → therefore, they require actively proliferating bacteria → • cephalosporins are derived from Inhibits polymerization of the • active against pseudomonas derivative of phosphonic acid
antagonized by bacteriostatic cephalosporium mold cell wall e.g. imipenem, meropenem & TB therapy consists of:
ertapenem • Not active against G+ve or • unique structure → no cross
• cephamycins are derived from streptomyces 1. Isoniazide (INH)
anaerobes reactivity → used in case of
Uses: 2. Rifampicin (RNA synthesis inhibitor)
MOA Inhibit penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) which regulate the cross-linking of peptidoglycan → exposure of the cell membrane (osmotically • MRSA & MRE→ Imipenem (IV): • ↓ immunogenicity → alternative hypersensitivity
unstable) → cell lysis
bacteremia, endo-carditis, broad-spectrum (including to the previous drugs in case of 3. Ethambutol or Pyrazinamide
peritonitis, pneumonia, pseudomonas) → empiric therapy in allergy Uses:
Resistance 1. Production of β-lactamase Same as penicillins, but they are less susceptible to critical cases UTIs (E.coli & E. fecalis)
etc..
2. Camouflaged target (PBP) → penicillin cannot bind to PBPs (e.g. MRSA & MRE) β-lactamase → no need for clavulanic a'
• β-lactam allergic patients Imipenem is taken in combination
3. ↓ permeability of the drug (e.g. porins in G-ve)
w/ cilastatin (why?)
4. Efflux pumps Resistance: • Imipenem is metabolized by
VRSA & VRE dehydropeptidase enzyme in the
Spectrum • G+ve → susceptible A) First generation
renal PCT → nephrotoxic metabolite
• G-ve → not susceptible due to LPS membrane G+ve & some G-ve
• Cilastatin inhibits dehydropeptidase
Cannot cross the BBB
e.g.
• Cefadroxil (Duricef) → oral
Types A) Natural penicillins: • Cephalexin → oral
1. Benzylpenicillin = penicillin G (IV & IM) • Cephradine (Velosef) → parenteral
◦ short duration
◦ acid unstable B) Second generation
◦ β-lactamase sensitive Wider spectrum of activity against G-ve
◦ unstable in solution form (must be freshly prepared) Unreliable CSF penetration
2. Phenoxymethylpenicillin = penicillin V (oral) e.g.
◦ acid stable → oral • Cefaclor → oral
• Cefuroxime → oral
B) Semisynthetic penicillins (by altering the side chain):
• Cefoxitine (cephamycin not cephalosporin) →
1. β-lactamase resistant penicillins → active against staph. (e.g. methicillin &
parenteral
cloxacillin)
2. Extended spectrum penicillins → active against G-ve & G+ve C) Third generation:
◦ Aminopenicillins (ampicillin & amoxicillin) G+ve, G-ve & anaerobic m.o.
◦ carbenicillin & piperacillin → active against pseudomonas highly resistant to β-lactamase
penetrate BBB
C) β-lactamase inhibitors combinations: parenteral administration
1. amoxicillin + clavulanic a' = Augmentin e.g. ceftriaxone & cefotaxime
2. ampicillin + sulbactam = Unasyn
3. piperacillin + tazobactam = Zosyn (IV) D) Fourth generation:
wider spectrum
N.B. the β-lactamase inhibitor has no AB activity on its own
parenteral administration
reserved for severe infections
e.g. Cefepime → active against pseudomonas
Uses • Natural penicillins → G+ve • G-ve bacterial meningitis → ceftriaxone
• penicillinase resistant (e.g. methicillin) → G+ve • gonorrhea
• aminopenicillins → G+ve & G-ve but not pseudomonas • UTI
• extended spectrum (e.g carbenicillin & ticarcillin) → G-ve & pseudomonas • MRSA
N.B. some strains of staph. & enterococci became resistant to methicillin due to • mixed infection esp. anaerobes → 3rd gen.
camouflaged PBPs → MRSA & MRE
Adverse 1) Hypersensitivity: ranging from rashes to angioedema & anaphylaxis → Same as penicillins but less risk of hypersensitivity
effects therefore, SC skin testing is a must before parenteral administration
cross reactivity is observed among natural & semisynthetic penicillins Disadv: most cephalosporins have low oral activity
→ IV or IM
2) GIT disturbance & diarrhea due to normal flora disruption
3) Nephrotoxicity (uncommon)
4) Neurotoxicity: GABAergic inhibition → used w/ caution with epileptic patients
5) ↓ blood cells count (irrelevant)
Pharmaco • Absorption • Poor oral absorption (except for some 1st & 2nd
kinetics ◦ broad spectrum → kills gut flora generation drugs)
◦ taken on empty stomach (↓ gastric acidity) • renal elimination
• Distribution
◦ Cannot reach CSF unless there is inflammation (meningitis) Ceftriaxone:
◦ Cannot reach prostate • can cross the BBB
• biliary elimination → used in renally impaired
patients
• long t1/2
Class
3- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors 4- Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid 5- Antimetabolites (anti-folates)
30 S 50 S Synthesis
Tetracyclines Aminoglycosides Glycyl- Macrolides Lincosamides Chloramphenicol Quinolones Rifamycins Sulfonamides Trimethoprim Cotrimoxazole Dapson
cyclines
MOA Bind to 30S subunit → Bind to 30S subunit → interfere w/ the assembly of ____ Bind irreversibly to 50S Bind to 50S Binds to 50S Inhibition of: RNA polymerase Compete w/ PABA → inhibit DHFR inhibitor Combination of Similar to sulfa
prevent binding of tRNA to ribosomes (i.e. prevent binding of 30S & 50S) → inhibit the 1. Topoisomerase II (gyrase) in G-ve bacteria inhibitor dihydropteroate synthase trimethoprim + drugs
the mRNA-ribosome cpx translocation of protein 2. Topoisomerase IV in G+ve bacteria sulfamethoxazole in a
bacterioSTATIC BacteriCIDAL bacterioSTATIC bacterioSTATIC bacterioSTATIC e.g. Rifampicin & bacterioSTATIC ratio of 1:5
bacteriCIDAL Rifapentin (longer
Examples Doxycycline (Vibramycin) Can be combined w/ β-lactams (as both are CIDAL) 1) Clarithromycin → H. Clindamycin (Dalacin) • Broad spectrum First generation: nonfluorinated FQ t1/2) Spectrum: Similar to sulfonamides Advantages: Uses:
demclocycline Pylori • Reserved for life-threatening nalidixic acid → narrow spectrum (G-ve only) • G+ve, G-ve (shigella & E.coli) • synergism Leprosy
Broad spectrum • used in dental Uses: TB &
minocycline infections for which no • Chlamydia trachomatis (STD) • ↓ resistance
procedures & buccal leprosy
2) Azithromycin
Uses broad spectrum → reserved Uses: infections alternatives exist Second generation: • potent AB effect
1) Streptomycin → TB, plague & tularemia (Zithromax)→ Ciprofloxacin & norfloxacin → active against G-ve
for severe infections • active against Adverse effects: Uses: • both have similar
Respiratory tract & atypical bacteria t1/2
• RTIs 2) Neomycin (Entocid, Bacitracin) & Kanamycin infections (MRSA) anaerobes LME inducer • Meningitis (can cross the BBB)
• UTIs (Kenacomb) → too toxic for parenteral use → taken • UTIs
Third generation: Uses:
• Acne orally or topically → intestinal & skin infections • Sulphasalazine → intestinal
Levofloxacin (respiratory FQ) → RTIs • prostate & vaginal
infections (e.g. ulcerative colitis)
• Gonorrhea 3) Gentamycin (Garamycin) → parenterally for infections
due to its anti-inflammatory &
severe infections Fourth generation: immunosupressant effects • respiratory, intestinal
Moxifloxacin → active against G+ve , G-ve & & UTIs
4) Amikacin → gentamycin-resistant infections • Topical uses
anaerobes
5) Tobramycin (Tobrex eye drops) → active against
N.B. FQs are alternatives to B-lactams in case of
pseudomonas
allergy
Pharmaco • Can cross the BBB → ttt Poor oral absorption → parenteral or topical ____ ____ ____ Form cpx w/ divalent ions (e.g. Ca) → ↓ absorption ____ ____
kinetics of meningitis
• Can reach the prostate CYP inhibitors → risk of drug interactions
→ ttt of prostatitis
Adverse • Bind to Ca in bones & • Ototoxicity • Broad spectrum → • ↓ blood count → CI in anemia • Phototoxicity • Nausea, vomiting & headache • Megaloblastic
effects teeth • Nephrotoxicity kills gut flora & leukemia • Cardiotoxicity → torsade de pointes • Serious SE → stop administration anemia (esp. when
• CI in pregnancy & • Neurotoxicity • CYP 450 inhibitors → • CI in pregnancy & infants → • Joint swelling combined w/ MTX)
◦ Crystalluria (CI in urolithiasis)
children • allergic rxn drug interactions w/ grey baby syndrome due to low • CI in pregnancy • CI in pregnancy →
◦ Hypersensitivity
• drug food interaction w/ warfarin, digoxin, etc... capacity of glucuronidation neural tube defects
◦ plasma protein displacement→ can
Ca
displace bilirubin → kernicterus → CI
in infants, pregnancy & breastfeeding
Selectivity • Selective cuz bacterial ribosomes (30S & 50S) differ structurally from mammalian ribosomes (40S & 60S) _____ _____
• at high doses → interact w/ human ribosomes → toxicity
Indication AB of choice
Respiratory tract infections Azithromycin (Zithromax)
Levofloxacin (resp. FQ)
H. Pylori Clarithromycin
Chlamydia trachomatis Sulfonamides
Pseudomonas Imipenem
Aztreonam
Cefepime (4th gen.)
Piperacillin, Carbenicillin & Ticarcillin
Tobramycin
Meningitis Ceftriaxone & Cefotaxime (3rd gen. cephalo)
(can cross the BBB)
tetracyclines
Sulfonamides (sulfadiazine)
Prostatitis Tetracyclines
Cotrimoxazole
Infections in renally Ceftriaxone (due to biliary elimination)
impaired patients
Anaerobes Ceftriaxone & Cefotaxime (3rd gen. cephalo)
Lincosamides (Clindamycin)
Moxifloxacin (4th gen. FQ)
Gonorrhea Tetracyclines
cephalosporins
MRSA Vancomycin
cephalosporins
Macrolides (azithro)
TB Streptomycin
Isoniazide + Rifampicin + Ethambutol / Pyrazinamide
Leprosy Rifampicin & Rifapentine
Dapson
Tularemia (rabbit fever) Streptomycin
Buccal & dental infections Clindamycin (Dalacin)
Empiric therapy in critical Imipenem (IV)
cases (e.g. accidents)
UTIs Fluoroquinolones (cipro or nalidixic a')
Tetracyclines
sulfonamides
Cotrimoxazole (Septrin)
Fosfomycin
Safe in pregnancy B-lactams (penicillins & cephalo)
Ulcerative colitis Sulphasalazine (due to its anti-inflammatory effect)
You might also like
- Viewpoint: OnlineDocument4 pagesViewpoint: OnlineJoseph Adinolfi Jr.92% (12)
- DSM V Clinical Cases - Chapter 12 Sleep Wake DisordersDocument13 pagesDSM V Clinical Cases - Chapter 12 Sleep Wake DisordersIzzyinOzzieNo ratings yet
- Refresher Course: Preboard Examination Nursing Practice I: Basic Foundation of Nursing and Professional PracticeDocument9 pagesRefresher Course: Preboard Examination Nursing Practice I: Basic Foundation of Nursing and Professional PracticeKristine SingsonNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers IMCIDocument13 pagesQuestions and Answers IMCIEmvie Loyd Pagunsan-Itable100% (10)
- Carmilaa Introduction To AntimicrobialsDocument2 pagesCarmilaa Introduction To AntimicrobialsCARINA-ELENA-MIHAELA STANCUNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument37 pagesImmunityRand Hussein100% (1)
- 6-Introduction To AntibioticsDocument10 pages6-Introduction To AntibioticsKanishka TiwariNo ratings yet
- Morteza Mahmoudi - ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3, 2656-2664Document9 pagesMorteza Mahmoudi - ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3, 2656-2664Tania ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Microbial Control Sterilization & DisinfectionDocument10 pagesMicrobial Control Sterilization & DisinfectionMatt CloudNo ratings yet
- S1473309905700517 - 1 s2.0 S1473309905700517 MainDocument10 pagesS1473309905700517 - 1 s2.0 S1473309905700517 MainwardaninurindahNo ratings yet
- W1 Antimicrobial DrugsDocument8 pagesW1 Antimicrobial Drugsseanne kskwkwkaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistance: Key PointsDocument7 pagesAntibiotic Resistance: Key Pointsgeorgi.annaNo ratings yet
- M.06 MISCELLANEOUS ANTIMICROBIALS (Part 1)Document3 pagesM.06 MISCELLANEOUS ANTIMICROBIALS (Part 1)PAUL ALINGKAYONNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology in EndodonticsDocument7 pagesPharmacology in EndodonticsJanice EstaNo ratings yet
- Biomedicines 08 00405 v2Document30 pagesBiomedicines 08 00405 v2Nguyễn A.ThưNo ratings yet
- Bello 2018Document10 pagesBello 2018Cristian Javier Zamorano GómezNo ratings yet
- Abigail Ann ADocument9 pagesAbigail Ann AAbigail Ann BinalayNo ratings yet
- Pharma-Module 8Document5 pagesPharma-Module 8Myles CardelNo ratings yet
- PHARM - 5. Antibiotics (6p)Document6 pagesPHARM - 5. Antibiotics (6p)mmatthew74No ratings yet
- Antibiotics PharmaDocument4 pagesAntibiotics PharmaJohn Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- L4. Chemotherapeutic Agents IDocument11 pagesL4. Chemotherapeutic Agents IMoNo ratings yet
- Systematic Approach in Selecting AntibioticsDocument5 pagesSystematic Approach in Selecting AntibioticsWu Yi FanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S019665532200880XDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S019665532200880XjrochaoNo ratings yet
- ELE PID Approach To Antibiotic TreatmentDocument12 pagesELE PID Approach To Antibiotic TreatmentSebastian ColinNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY Anti Microbial DrugsDocument17 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Anti Microbial DrugsLeilani Sablan100% (2)
- Antibiotics (Antimicrobials) : Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesAntibiotics (Antimicrobials) : Learning ObjectivesaugustinstefanNo ratings yet
- Antibodies, Vaccines, AdjuantsDocument87 pagesAntibodies, Vaccines, AdjuantsBunty Singh MakhanNo ratings yet
- Mappa MicroDocument1 pageMappa MicroCarlotta RanalliNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 20-Jun-2022Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 20-Jun-2022KemNo ratings yet
- 1.05 General Pathology - Diseases of The Immune System (Part 2) - Dr. AleraDocument13 pages1.05 General Pathology - Diseases of The Immune System (Part 2) - Dr. AleraCherry RahimaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics and Resistance 2008Document17 pagesAntibiotics and Resistance 2008Isworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- X0xheather - Principles of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy PDFDocument3 pagesX0xheather - Principles of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy PDFAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- IMSE311 Lec Week-14Document6 pagesIMSE311 Lec Week-14Joanne RemolloNo ratings yet
- Anti-Microbial Resistance PresentationDocument15 pagesAnti-Microbial Resistance Presentationsanish tiwariNo ratings yet
- Review: Antimicrobial Resistance in Hospitals: How Concerned Should We Be?Document8 pagesReview: Antimicrobial Resistance in Hospitals: How Concerned Should We Be?Victor GodwinNo ratings yet
- LL1703 Antibiotics Review PDFDocument15 pagesLL1703 Antibiotics Review PDFAparna DwivediNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #3 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan #3 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJustine Jean GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Antimicrobial ChemotherapyDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Antimicrobial ChemotherapySteven miles PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic - Definition, Types, Side Effects, Resistance, Classification, & Facts - BritannicaDocument13 pagesAntibiotic - Definition, Types, Side Effects, Resistance, Classification, & Facts - Britannicaali khanNo ratings yet
- Serologic Tests Part 3Document2 pagesSerologic Tests Part 3Joshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- 8 - AntibioticsDocument8 pages8 - AntibioticsArshad AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ijms 23 11553Document15 pagesIjms 23 11553Robert StryjakNo ratings yet
- Natural Product Reports: Themed Issue: Novel Antibiotics and Antimicrobial ResistanceDocument73 pagesNatural Product Reports: Themed Issue: Novel Antibiotics and Antimicrobial ResistanceTiannyu WangNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Trigger Words Biology, Virulence and Epidemiology Disease Diagnosis Treatment, Prevention and ControlDocument3 pagesBacteria Trigger Words Biology, Virulence and Epidemiology Disease Diagnosis Treatment, Prevention and ControlEdward IbarraNo ratings yet
- Basics of AntibioticsDocument42 pagesBasics of AntibioticsAsma BakheitNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Its Applications: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenDocument5 pagesBiotechnology and Its Applications: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenJK JHANo ratings yet
- TFG NereidaespinosarubioDocument1 pageTFG NereidaespinosarubioMark WanyamaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Bacterial Infections of The SkinDocument11 pagesSummary of Bacterial Infections of The SkinYna Joy B. LigatNo ratings yet
- 24 Inflammation 1 General HO1Document40 pages24 Inflammation 1 General HO1Hartomo BenxNo ratings yet
- (PHARMA A) 3.3 - Antibiotics I - Dr. Cruz (2024)Document15 pages(PHARMA A) 3.3 - Antibiotics I - Dr. Cruz (2024)Miguel Luis NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Prefinals 301 ReviewerDocument21 pagesPrefinals 301 ReviewerDjayNo ratings yet
- Micro paraDocument2 pagesMicro parafeminaNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument5 pagesMicroDenzyl AcuinNo ratings yet
- Estrategias Antisepticas-2013Document6 pagesEstrategias Antisepticas-2013SaulNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection Related To Insufficient Knowledge To Avoid Exposure To Pathogens As Evidence by Dirty Nails.Document2 pagesRisk For Infection Related To Insufficient Knowledge To Avoid Exposure To Pathogens As Evidence by Dirty Nails.Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - 15Document8 pagesMicrobiology - 15karmylle andradeNo ratings yet
- Isoniazid RifampicinDocument6 pagesIsoniazid RifampicinRYAN CHRISTIAN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Class Summary TableDocument6 pagesAntibiotic Class Summary TableuserherwwweNo ratings yet
- Small Animal SurgeryDocument7 pagesSmall Animal Surgeryhonovezaann.a.campita.ctucvmNo ratings yet
- Controlling Microbial Growth in Vivo Using Antimicrobial AgentsDocument3 pagesControlling Microbial Growth in Vivo Using Antimicrobial AgentsMaria Gloria Aquino BorjaNo ratings yet
- Breaking The Chain of Infections in Chronic Wounds: C.E.O Pedis Care CenterDocument18 pagesBreaking The Chain of Infections in Chronic Wounds: C.E.O Pedis Care Centersyafiul hudaNo ratings yet
- Herbal Antibiotics and Antivirals: Herbal Medicine to Heal Yourself NaturallyFrom EverandHerbal Antibiotics and Antivirals: Herbal Medicine to Heal Yourself NaturallyNo ratings yet
- Vaccination: How Millions of Lives Have Been Saved - Perhaps YoursFrom EverandVaccination: How Millions of Lives Have Been Saved - Perhaps YoursNo ratings yet
- DiseaseResearchProject 1Document3 pagesDiseaseResearchProject 1Racheal MukiriNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Centre: Assignment - 3Document12 pagesDialysis Centre: Assignment - 3grvoneandonlyNo ratings yet
- Success One HSC Biology Online Resource 2019Document35 pagesSuccess One HSC Biology Online Resource 2019Sehasa PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Official Program Superweek 2020Document9 pagesOfficial Program Superweek 2020Christian SagastumeNo ratings yet
- Soap NoteDocument7 pagesSoap Noteapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Mathematical Models in Epidemiology: by Peeyush ChandraDocument50 pagesMathematical Models in Epidemiology: by Peeyush ChandraSachin R10C08No ratings yet
- Select The Base of ScienceDocument4 pagesSelect The Base of SciencesahandNo ratings yet
- Psychology (037) Class - Xii Sample Question Paper - 2019-2020 Time - 3 Hours Max Marks - 70 General InstructionsDocument5 pagesPsychology (037) Class - Xii Sample Question Paper - 2019-2020 Time - 3 Hours Max Marks - 70 General InstructionsTurfa AhmedNo ratings yet
- PranithaDocument15 pagesPranithaKumar VijayNo ratings yet
- 2020 Bidirectional Association Between Tuberculosis and SarcoidosisDocument8 pages2020 Bidirectional Association Between Tuberculosis and SarcoidosisLCCNo ratings yet
- Situation 1: One Day, Dika Hangs Out Alone To Get Some Fresh Air. When She PassesDocument2 pagesSituation 1: One Day, Dika Hangs Out Alone To Get Some Fresh Air. When She PassesDika Pratiwi BudiantoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Learning Activity Sheet No: 1: English For Academic and Professional Purposes (Eapp)Document6 pagesQuarter 2 Learning Activity Sheet No: 1: English For Academic and Professional Purposes (Eapp)YVONE MAE MAYORNo ratings yet
- Febuxostat Vs AlopurinolDocument13 pagesFebuxostat Vs AlopurinolNilson Morales CordobaNo ratings yet
- Polygenic and Monogenic InheritanceDocument5 pagesPolygenic and Monogenic Inheritancekhanmunazah242No ratings yet
- MSDS QuartzDocument4 pagesMSDS QuartzAnchita MitraNo ratings yet
- Hira SMSDocument51 pagesHira SMSAbrar ArijitNo ratings yet
- OMNIBUS Guidelines As of April 3Document22 pagesOMNIBUS Guidelines As of April 3TheSummitExpressNo ratings yet
- Diet and Nutrition A17Document20 pagesDiet and Nutrition A17Syintya eka putriNo ratings yet
- Methotrexate Drug StudyDocument1 pageMethotrexate Drug StudyAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado0% (1)
- COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance and Hesitancy Questionnaire (COV-AHQ)Document3 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance and Hesitancy Questionnaire (COV-AHQ)Shaira Marie BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Emergency Oxygen ProviderDocument64 pagesEmergency Oxygen ProviderzubinNo ratings yet
- Urticaria and Angioedema: Ailing Zou (邹爱玲) 2021.10.18Document24 pagesUrticaria and Angioedema: Ailing Zou (邹爱玲) 2021.10.18AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture and Cancer - David O'Regan, Jacqueine Filshie - The Royal Marsden Hospital, London and Surrey, UKDocument6 pagesAcupuncture and Cancer - David O'Regan, Jacqueine Filshie - The Royal Marsden Hospital, London and Surrey, UKFredericoNo ratings yet
- Portrayal of Psychopathy in The MoviesDocument7 pagesPortrayal of Psychopathy in The MoviesAshish ChandNo ratings yet
- PSSDDocument39 pagesPSSDbenopij556No ratings yet