Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Valvetronic Servomotor
Valvetronic Servomotor
Uploaded by
Igor PinheiroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chery-Orinoco-M11-Pin Out EculDocument4 pagesChery-Orinoco-M11-Pin Out EculManolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Subaru 4EATDocument2 pagesSubaru 4EATGuilherme Zoboli100% (1)
- MC3336-7250'9650'A850 AC Motor ControllerDocument5 pagesMC3336-7250'9650'A850 AC Motor ControllerDavid Pfuño AguilarNo ratings yet
- SIG Motorized ValveDocument6 pagesSIG Motorized ValveAlexandre FerreiraNo ratings yet
- M6 - C3 - Lesson 1 - System DevelopmentDocument34 pagesM6 - C3 - Lesson 1 - System DevelopmentsanthoshyeruvakaNo ratings yet
- 922 Training Elect.Document108 pages922 Training Elect.leonardo riveroNo ratings yet
- Series EA Electric Actuators Low Torque, Medium Torque, and Spring Return Manual 1321-In-003!0!13Document16 pagesSeries EA Electric Actuators Low Torque, Medium Torque, and Spring Return Manual 1321-In-003!0!13Isaac MonterreyNo ratings yet
- Group 10 Engine Control System: 1. CPU CONTROLLER AND ECM (Electronic Control Module)Document7 pagesGroup 10 Engine Control System: 1. CPU CONTROLLER AND ECM (Electronic Control Module)Saidi JalelNo ratings yet
- DTC P0766 Shift Solenoid "D" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S4)Document4 pagesDTC P0766 Shift Solenoid "D" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S4)marran almarranyNo ratings yet
- Accelerator Pedal Sensor Component DescriptionDocument2 pagesAccelerator Pedal Sensor Component DescriptionMadhav DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Elantra 1.6 Engine Electrical1Document55 pagesHyundai Elantra 1.6 Engine Electrical1MANUALES2000CLNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Loco NoteDocument96 pages3 Phase Loco Noteprasoon tiwariNo ratings yet
- Acaim0073 00Document2 pagesAcaim0073 00zoogleNo ratings yet
- AA51880 - Servo Motor ControlDocument10 pagesAA51880 - Servo Motor ControlhugosaldanoNo ratings yet
- Propvalve eDocument38 pagesPropvalve eMohamed Rashed100% (1)
- Piaggio MP3 400 I.E Service Station Manual-11Document20 pagesPiaggio MP3 400 I.E Service Station Manual-11H. KeithNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Control Unit V-ECU, Specifications: Service InformationDocument3 pagesVehicle Control Unit V-ECU, Specifications: Service InformationMorteza BaratzadehNo ratings yet
- Pinout M52 Siemens MS41 - ADAMO MotorsportDocument1 pagePinout M52 Siemens MS41 - ADAMO Motorsportkorovnikovdenis8No ratings yet
- NISSAN Q02elDocument36 pagesNISSAN Q02elМаксым КовальськыйNo ratings yet
- 01 MDocument2 pages01 MGuilherme ZoboliNo ratings yet
- DIAMANT PRO EngDocument16 pagesDIAMANT PRO Engbeto_juriNo ratings yet
- 1 Design A Protection System Using IDMT Relay To Protect System For Given Fault Currents & Plot The Operating Time Characteristics of The Relay UsedDocument6 pages1 Design A Protection System Using IDMT Relay To Protect System For Given Fault Currents & Plot The Operating Time Characteristics of The Relay UsedMR. SUSHIL BARAPATRENo ratings yet
- Servo MotorsDocument14 pagesServo Motors14 Abhigna dusaNo ratings yet
- Throttle Position Sensor Circuit TestDocument8 pagesThrottle Position Sensor Circuit TestDaniel AmanorNo ratings yet
- Signal Reverser For Railway SignalingDocument23 pagesSignal Reverser For Railway SignalingVikas Srivastav100% (1)
- Jf015e - Rebuild - Manualtcc p0740Document2 pagesJf015e - Rebuild - Manualtcc p0740hitecNo ratings yet
- Group 10 Engine Control System: 1. CPU CONTROLLER AND ECM (Electronic Control Module)Document7 pagesGroup 10 Engine Control System: 1. CPU CONTROLLER AND ECM (Electronic Control Module)douahchia rachedNo ratings yet
- Non-Spring Return Direct-Coupled Damper Actuators For Modulating and Floating / 2-Position ControlDocument8 pagesNon-Spring Return Direct-Coupled Damper Actuators For Modulating and Floating / 2-Position ControlPoyaNo ratings yet
- PCE-Training Manual - Day 2-2 GOVERNING SYSTEMS PDFDocument110 pagesPCE-Training Manual - Day 2-2 GOVERNING SYSTEMS PDFhiralalnhpc100% (1)
- Honeywell ml7420 User ManualDocument8 pagesHoneywell ml7420 User ManualLaurensius ArdiNo ratings yet
- Electric Actuator RHD250 ABBDocument20 pagesElectric Actuator RHD250 ABBQuốc BảoNo ratings yet
- 2012 Chevrolet K2500 HD Pickup Silverado: DTC C0710Document5 pages2012 Chevrolet K2500 HD Pickup Silverado: DTC C0710alberto navasNo ratings yet
- Nm24-Sr Us: Listed 94D5 Temp. Ind & Reg. EquipDocument2 pagesNm24-Sr Us: Listed 94D5 Temp. Ind & Reg. EquipDaniel MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Edc 21bee0321Document16 pagesEdc 21bee0321lakshit.choudhary2021No ratings yet
- Pinout VECUDocument3 pagesPinout VECUcentraltechgvNo ratings yet
- D155A-6 Power Train System: Dubai Training and Demonstration CenterDocument20 pagesD155A-6 Power Train System: Dubai Training and Demonstration CenterMichael DavidNo ratings yet
- NM24 SR US 8Nm 19558Document2 pagesNM24 SR US 8Nm 19558Multiservici Campo EliasNo ratings yet
- Manual EP100 enDocument23 pagesManual EP100 enEBNo ratings yet
- Camshaft Position A ActuatorDocument6 pagesCamshaft Position A ActuatorDannyDDannyDNo ratings yet
- 3 - Telemecanique - Altivar - Atv66 - User - Manual PDFDocument52 pages3 - Telemecanique - Altivar - Atv66 - User - Manual PDFManutençãoNo ratings yet
- Gs Generator TroubleshootingDocument38 pagesGs Generator Troubleshootingகோவி கோபால் ஆர்ட்ஸ்No ratings yet
- MC3336-A850 Series AC Controller Instruction: - DescriptionDocument6 pagesMC3336-A850 Series AC Controller Instruction: - Descriptiontrinh0% (1)
- 5 - Control Panel Training PDFDocument28 pages5 - Control Panel Training PDFbensonNo ratings yet
- MVHF DBL334eDocument2 pagesMVHF DBL334eGOOGLE DISKNo ratings yet
- QsolDocument3 pagesQsolМаксим СабировNo ratings yet
- Manual SO2164430-i1Document80 pagesManual SO2164430-i1Savinda JanszNo ratings yet
- D R Awi N G: Figure1: Generator Earthing ArrangementsDocument7 pagesD R Awi N G: Figure1: Generator Earthing Arrangementsdanniyal acharyaNo ratings yet
- ML7430E/ML7435E: Electric Linear Actuators For Modulating ControlDocument4 pagesML7430E/ML7435E: Electric Linear Actuators For Modulating ControlMarco ReNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Servo SystemDocument33 pagesHydraulic Servo SystemNguyenCanhBaoNo ratings yet
- Pines Ecu Codigos y Pruebas Control Electronico Del Motor Chery Orinoco m11 Service Manual-122-288.PDF Versión 1Document167 pagesPines Ecu Codigos y Pruebas Control Electronico Del Motor Chery Orinoco m11 Service Manual-122-288.PDF Versión 1oscar vergara100% (2)
- Driver Motore Passo PassoDocument12 pagesDriver Motore Passo Passogionp1No ratings yet
- Fuel Rack Solenoid - TestDocument6 pagesFuel Rack Solenoid - TestAdolfo Dario SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Altronics A2-CPU D SRVC Man 04-1991 PDFDocument18 pagesAltronics A2-CPU D SRVC Man 04-1991 PDFSMcNo ratings yet
- Electrical Graphic SymbolDocument5 pagesElectrical Graphic SymbolIslam ShoukryNo ratings yet
- EV-1W Motor ControllerDocument43 pagesEV-1W Motor ControllerMarioNo ratings yet
- Dezurik Precision Electric Control Valves Ppe Technical 14-00-2Document8 pagesDezurik Precision Electric Control Valves Ppe Technical 14-00-2gembirasekaliNo ratings yet
- OcvDocument4 pagesOcvIsmail SetiawanNo ratings yet
- DTC P0500 Corolla Altis 2006Document3 pagesDTC P0500 Corolla Altis 2006ardi agusman100% (2)
- DTC P0A94/553 DC/DC Converter Performance: Circuit DescriptionDocument9 pagesDTC P0A94/553 DC/DC Converter Performance: Circuit Descriptionjermaine tobanNo ratings yet
- Assosa University: Prepared byDocument74 pagesAssosa University: Prepared bySiraj MohammedNo ratings yet
- Heavy Duty Flyer CatalogDocument7 pagesHeavy Duty Flyer CatalogJessie BechaydaNo ratings yet
- Exp-7 111Document4 pagesExp-7 111Dave Pooja DilipkumarNo ratings yet
- Fire Castable (HACT-180S-250t) at Nozzle Burner (Old Material)Document2 pagesFire Castable (HACT-180S-250t) at Nozzle Burner (Old Material)มิตร อันมาNo ratings yet
- Pta 3287 532676 10215Document8 pagesPta 3287 532676 10215taylan arslanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat Engines 1St Edition Jamil Ghojel Full ChapterDocument51 pagesFundamentals of Heat Engines 1St Edition Jamil Ghojel Full Chapterdavid.brown418100% (14)
- DocumentDocument38 pagesDocumentGEMMALYN BANGAYANNo ratings yet
- Timing BeltDocument28 pagesTiming BeltRaj Bikram MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Omandailyobserver 20231015 1Document20 pagesOmandailyobserver 20231015 1bskpremNo ratings yet
- CX140E Spec SheetDocument6 pagesCX140E Spec SheetthomasNo ratings yet
- Sabreliner Na 265-70 Amm Na 265-80Document2,244 pagesSabreliner Na 265-70 Amm Na 265-80AVIATION TRAINING CENTER SC100% (1)
- Tetraethyllead: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument16 pagesTetraethyllead: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchKenczar RomanoNo ratings yet
- DNIT Vol 2 Part 1Document196 pagesDNIT Vol 2 Part 1JitendraHatwarNo ratings yet
- Review of Maintenance Schedule For PSIDocument108 pagesReview of Maintenance Schedule For PSIsaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Compressed Gas Cylinders Harmonized PolicyDocument4 pagesCompressed Gas Cylinders Harmonized PolicynavierNo ratings yet
- Wood Mackenzie Venezuela Plataforma Deltana Block 4Document7 pagesWood Mackenzie Venezuela Plataforma Deltana Block 4rubenpeNo ratings yet
- MT 03 2023Document78 pagesMT 03 2023Andres Augusto Mesa CastellanosNo ratings yet
- QTT Spare Part Deutz TCD Dan BF6MDocument2 pagesQTT Spare Part Deutz TCD Dan BF6MvirtualakunifnuNo ratings yet
- Orion RKE-B Series ChillerDocument20 pagesOrion RKE-B Series ChillerElias WigunaNo ratings yet
- Harmonic 1Document95 pagesHarmonic 1Abdel-Rahman Saifedin ArandasNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics (PHY 1051)Document11 pagesEngineering Physics (PHY 1051)Harshita GauravNo ratings yet
- CJC Filter DiagramDocument2 pagesCJC Filter DiagrampreciousNo ratings yet
- KS3 LeaP Q4 W8 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMDocument6 pagesKS3 LeaP Q4 W8 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMtolisNo ratings yet
- Ingecon Sun 3825tl C Series enDocument4 pagesIngecon Sun 3825tl C Series enafshin keshtkarNo ratings yet
- Chernobyl Disaster: The Worst Man-Made Disaster in Human HistoryDocument13 pagesChernobyl Disaster: The Worst Man-Made Disaster in Human HistoryGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Part I Autumn 2023-24Document137 pagesThermodynamics Part I Autumn 2023-24itzadisharmaNo ratings yet
- SMM.003E Chief Engineer Handing Over ReportDocument3 pagesSMM.003E Chief Engineer Handing Over ReportAndhityas Piscessandhy PutraNo ratings yet
- General Valve CatalogDocument40 pagesGeneral Valve CatalogAneeshNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lift in The Montrose Field, North Sea: E.G. Jacobs, SPE, Amoco (UK) Exploration CoDocument8 pagesArtificial Lift in The Montrose Field, North Sea: E.G. Jacobs, SPE, Amoco (UK) Exploration Comoh kadNo ratings yet
- Diesel Generator Sets: Output RatingsDocument2 pagesDiesel Generator Sets: Output Ratingsargie gayasNo ratings yet
Valvetronic Servomotor
Valvetronic Servomotor
Uploaded by
Igor PinheiroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Valvetronic Servomotor
Valvetronic Servomotor
Uploaded by
Igor PinheiroCopyright:
Available Formats
Sponsored links
Home / BMW F15 X5 xDrive35i SAV /
Valvetronic servomotor
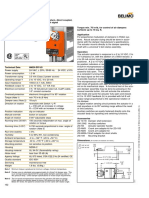
The Valvetronic servomotor also contains the sensor for the position detection of the eccentric shaft. Another
special feature is that the Valvetronic servomotor is surrounded by engine oil. An oil spray nozzle ensures that
the screw drive for the eccentric shaft is lubricated.
Functional description
A brush-less direct current motor with integrated position sensor is used as the Valvetronic servomotor. This
direct current motor is maintenance-free thanks to the contact-free power transformation and is very powerful
(improved efficiency). Thanks to the use of integrated electronic modules, the Valvetronic servomotor can be
controlled very precisely.
The activation of the Valvetronic servomotor is limited to a maximum of 40 amperes. Across a period greater than
200 milliseconds, a maximum of 20 amperes is available. The Valvetronic servomotor is activated via pulse-
width-modulation. The duty cycle is between 5 and 98 %.
Example N20
Index Explanation Index Explanation
1 Oil spray nozzle 2 Eccentric shaft
3 Torsion spring 4 Gate
5 Intake camshaft 6 Intermediate lever
7 Roller cam followers 8 Hydraulic valve clearance
compensation
9 Valve spring 10 Intake valve
11 Valvetronic servomotor 12 Exhaust valve
13 Valve spring 14 Hydraulic valve clearance
compensation
15 Roller cam followers 16 Exhaust camshaft
17 Sealing cup 18 12‐pin plug connection
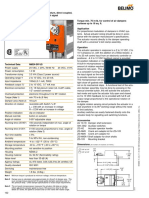
Structure and inner electrical connection
The sensor is supplied with voltage of 5 volt by the TAC module. Via 5 hall effect sensors (= tilt sensors), the TAC
module receives signals and evaluates them. Of the 5 hall effect sensors, 3 are used for approximate
identification and 2 for detailed classification. This means that the angle of rotation of the servomotor can be
determined at less than 7.5°. Thanks to the ratio of the screw drive, this permits a very precise and rapid stroke
adjustment of the valves.
Index Explanation
1 Valvetronic servomotor
2 Tilt sensor (5 hall effect sensors)
Pin assignments
Pin Explanation
U Phase U of the electric servomotor
V Phase V of the electric servomotor
W Phase W of the electric servomotor
SIG Hall effect sensor signal 1
SIG 2 Hall effect sensor signal 2
SIG 3 Hall effect sensor signal 3
SIG 4 Hall effect sensor signal 4
SIG 5 Hall effect sensor signal 5
5V Voltage supply for hall effect sensors
Kl. 31 Ground connection (Terminal 31)
Nominal values
Observe the following setpoint values for the Valvetronic servomotor:
Variable Value
Voltage range 9 to 16 V
Gear ratio 61 : 2
Drive torque 0.4 Nm
Power consumption 40 A
Duty cycle 5 to 98%
Resistance via 2 phases 0,34 Ohm
Temperature range -40 °C to 120 °C
Diagnosis instructions
Dismantling or replacement of the component
After dismantling or replacing the Valvetronic servomotor, there are 2 service functions available:
Learn end stops
Running-in phase
Path: Service Functions > Drive > Digital Motor Electronics > Adjustment Functions
Failure of the component
If the Valvetronic servomotor fails, the following behaviour is to be expected:
Fault entry in the Digital Engine Electronics (DME)
Full Valvetronic stroke
The fixed warning and indicator light lights up in the instrument panel
You might also like
- Chery-Orinoco-M11-Pin Out EculDocument4 pagesChery-Orinoco-M11-Pin Out EculManolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Subaru 4EATDocument2 pagesSubaru 4EATGuilherme Zoboli100% (1)
- MC3336-7250'9650'A850 AC Motor ControllerDocument5 pagesMC3336-7250'9650'A850 AC Motor ControllerDavid Pfuño AguilarNo ratings yet
- SIG Motorized ValveDocument6 pagesSIG Motorized ValveAlexandre FerreiraNo ratings yet
- M6 - C3 - Lesson 1 - System DevelopmentDocument34 pagesM6 - C3 - Lesson 1 - System DevelopmentsanthoshyeruvakaNo ratings yet
- 922 Training Elect.Document108 pages922 Training Elect.leonardo riveroNo ratings yet
- Series EA Electric Actuators Low Torque, Medium Torque, and Spring Return Manual 1321-In-003!0!13Document16 pagesSeries EA Electric Actuators Low Torque, Medium Torque, and Spring Return Manual 1321-In-003!0!13Isaac MonterreyNo ratings yet
- Group 10 Engine Control System: 1. CPU CONTROLLER AND ECM (Electronic Control Module)Document7 pagesGroup 10 Engine Control System: 1. CPU CONTROLLER AND ECM (Electronic Control Module)Saidi JalelNo ratings yet
- DTC P0766 Shift Solenoid "D" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S4)Document4 pagesDTC P0766 Shift Solenoid "D" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve S4)marran almarranyNo ratings yet
- Accelerator Pedal Sensor Component DescriptionDocument2 pagesAccelerator Pedal Sensor Component DescriptionMadhav DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Elantra 1.6 Engine Electrical1Document55 pagesHyundai Elantra 1.6 Engine Electrical1MANUALES2000CLNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Loco NoteDocument96 pages3 Phase Loco Noteprasoon tiwariNo ratings yet
- Acaim0073 00Document2 pagesAcaim0073 00zoogleNo ratings yet
- AA51880 - Servo Motor ControlDocument10 pagesAA51880 - Servo Motor ControlhugosaldanoNo ratings yet
- Propvalve eDocument38 pagesPropvalve eMohamed Rashed100% (1)
- Piaggio MP3 400 I.E Service Station Manual-11Document20 pagesPiaggio MP3 400 I.E Service Station Manual-11H. KeithNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Control Unit V-ECU, Specifications: Service InformationDocument3 pagesVehicle Control Unit V-ECU, Specifications: Service InformationMorteza BaratzadehNo ratings yet
- Pinout M52 Siemens MS41 - ADAMO MotorsportDocument1 pagePinout M52 Siemens MS41 - ADAMO Motorsportkorovnikovdenis8No ratings yet
- NISSAN Q02elDocument36 pagesNISSAN Q02elМаксым КовальськыйNo ratings yet
- 01 MDocument2 pages01 MGuilherme ZoboliNo ratings yet
- DIAMANT PRO EngDocument16 pagesDIAMANT PRO Engbeto_juriNo ratings yet
- 1 Design A Protection System Using IDMT Relay To Protect System For Given Fault Currents & Plot The Operating Time Characteristics of The Relay UsedDocument6 pages1 Design A Protection System Using IDMT Relay To Protect System For Given Fault Currents & Plot The Operating Time Characteristics of The Relay UsedMR. SUSHIL BARAPATRENo ratings yet
- Servo MotorsDocument14 pagesServo Motors14 Abhigna dusaNo ratings yet
- Throttle Position Sensor Circuit TestDocument8 pagesThrottle Position Sensor Circuit TestDaniel AmanorNo ratings yet
- Signal Reverser For Railway SignalingDocument23 pagesSignal Reverser For Railway SignalingVikas Srivastav100% (1)
- Jf015e - Rebuild - Manualtcc p0740Document2 pagesJf015e - Rebuild - Manualtcc p0740hitecNo ratings yet
- Group 10 Engine Control System: 1. CPU CONTROLLER AND ECM (Electronic Control Module)Document7 pagesGroup 10 Engine Control System: 1. CPU CONTROLLER AND ECM (Electronic Control Module)douahchia rachedNo ratings yet
- Non-Spring Return Direct-Coupled Damper Actuators For Modulating and Floating / 2-Position ControlDocument8 pagesNon-Spring Return Direct-Coupled Damper Actuators For Modulating and Floating / 2-Position ControlPoyaNo ratings yet
- PCE-Training Manual - Day 2-2 GOVERNING SYSTEMS PDFDocument110 pagesPCE-Training Manual - Day 2-2 GOVERNING SYSTEMS PDFhiralalnhpc100% (1)
- Honeywell ml7420 User ManualDocument8 pagesHoneywell ml7420 User ManualLaurensius ArdiNo ratings yet
- Electric Actuator RHD250 ABBDocument20 pagesElectric Actuator RHD250 ABBQuốc BảoNo ratings yet
- 2012 Chevrolet K2500 HD Pickup Silverado: DTC C0710Document5 pages2012 Chevrolet K2500 HD Pickup Silverado: DTC C0710alberto navasNo ratings yet
- Nm24-Sr Us: Listed 94D5 Temp. Ind & Reg. EquipDocument2 pagesNm24-Sr Us: Listed 94D5 Temp. Ind & Reg. EquipDaniel MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Edc 21bee0321Document16 pagesEdc 21bee0321lakshit.choudhary2021No ratings yet
- Pinout VECUDocument3 pagesPinout VECUcentraltechgvNo ratings yet
- D155A-6 Power Train System: Dubai Training and Demonstration CenterDocument20 pagesD155A-6 Power Train System: Dubai Training and Demonstration CenterMichael DavidNo ratings yet
- NM24 SR US 8Nm 19558Document2 pagesNM24 SR US 8Nm 19558Multiservici Campo EliasNo ratings yet
- Manual EP100 enDocument23 pagesManual EP100 enEBNo ratings yet
- Camshaft Position A ActuatorDocument6 pagesCamshaft Position A ActuatorDannyDDannyDNo ratings yet
- 3 - Telemecanique - Altivar - Atv66 - User - Manual PDFDocument52 pages3 - Telemecanique - Altivar - Atv66 - User - Manual PDFManutençãoNo ratings yet
- Gs Generator TroubleshootingDocument38 pagesGs Generator Troubleshootingகோவி கோபால் ஆர்ட்ஸ்No ratings yet
- MC3336-A850 Series AC Controller Instruction: - DescriptionDocument6 pagesMC3336-A850 Series AC Controller Instruction: - Descriptiontrinh0% (1)
- 5 - Control Panel Training PDFDocument28 pages5 - Control Panel Training PDFbensonNo ratings yet
- MVHF DBL334eDocument2 pagesMVHF DBL334eGOOGLE DISKNo ratings yet
- QsolDocument3 pagesQsolМаксим СабировNo ratings yet
- Manual SO2164430-i1Document80 pagesManual SO2164430-i1Savinda JanszNo ratings yet
- D R Awi N G: Figure1: Generator Earthing ArrangementsDocument7 pagesD R Awi N G: Figure1: Generator Earthing Arrangementsdanniyal acharyaNo ratings yet
- ML7430E/ML7435E: Electric Linear Actuators For Modulating ControlDocument4 pagesML7430E/ML7435E: Electric Linear Actuators For Modulating ControlMarco ReNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Servo SystemDocument33 pagesHydraulic Servo SystemNguyenCanhBaoNo ratings yet
- Pines Ecu Codigos y Pruebas Control Electronico Del Motor Chery Orinoco m11 Service Manual-122-288.PDF Versión 1Document167 pagesPines Ecu Codigos y Pruebas Control Electronico Del Motor Chery Orinoco m11 Service Manual-122-288.PDF Versión 1oscar vergara100% (2)
- Driver Motore Passo PassoDocument12 pagesDriver Motore Passo Passogionp1No ratings yet
- Fuel Rack Solenoid - TestDocument6 pagesFuel Rack Solenoid - TestAdolfo Dario SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Altronics A2-CPU D SRVC Man 04-1991 PDFDocument18 pagesAltronics A2-CPU D SRVC Man 04-1991 PDFSMcNo ratings yet
- Electrical Graphic SymbolDocument5 pagesElectrical Graphic SymbolIslam ShoukryNo ratings yet
- EV-1W Motor ControllerDocument43 pagesEV-1W Motor ControllerMarioNo ratings yet
- Dezurik Precision Electric Control Valves Ppe Technical 14-00-2Document8 pagesDezurik Precision Electric Control Valves Ppe Technical 14-00-2gembirasekaliNo ratings yet
- OcvDocument4 pagesOcvIsmail SetiawanNo ratings yet
- DTC P0500 Corolla Altis 2006Document3 pagesDTC P0500 Corolla Altis 2006ardi agusman100% (2)
- DTC P0A94/553 DC/DC Converter Performance: Circuit DescriptionDocument9 pagesDTC P0A94/553 DC/DC Converter Performance: Circuit Descriptionjermaine tobanNo ratings yet
- Assosa University: Prepared byDocument74 pagesAssosa University: Prepared bySiraj MohammedNo ratings yet
- Heavy Duty Flyer CatalogDocument7 pagesHeavy Duty Flyer CatalogJessie BechaydaNo ratings yet
- Exp-7 111Document4 pagesExp-7 111Dave Pooja DilipkumarNo ratings yet
- Fire Castable (HACT-180S-250t) at Nozzle Burner (Old Material)Document2 pagesFire Castable (HACT-180S-250t) at Nozzle Burner (Old Material)มิตร อันมาNo ratings yet
- Pta 3287 532676 10215Document8 pagesPta 3287 532676 10215taylan arslanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat Engines 1St Edition Jamil Ghojel Full ChapterDocument51 pagesFundamentals of Heat Engines 1St Edition Jamil Ghojel Full Chapterdavid.brown418100% (14)
- DocumentDocument38 pagesDocumentGEMMALYN BANGAYANNo ratings yet
- Timing BeltDocument28 pagesTiming BeltRaj Bikram MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Omandailyobserver 20231015 1Document20 pagesOmandailyobserver 20231015 1bskpremNo ratings yet
- CX140E Spec SheetDocument6 pagesCX140E Spec SheetthomasNo ratings yet
- Sabreliner Na 265-70 Amm Na 265-80Document2,244 pagesSabreliner Na 265-70 Amm Na 265-80AVIATION TRAINING CENTER SC100% (1)
- Tetraethyllead: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument16 pagesTetraethyllead: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchKenczar RomanoNo ratings yet
- DNIT Vol 2 Part 1Document196 pagesDNIT Vol 2 Part 1JitendraHatwarNo ratings yet
- Review of Maintenance Schedule For PSIDocument108 pagesReview of Maintenance Schedule For PSIsaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Compressed Gas Cylinders Harmonized PolicyDocument4 pagesCompressed Gas Cylinders Harmonized PolicynavierNo ratings yet
- Wood Mackenzie Venezuela Plataforma Deltana Block 4Document7 pagesWood Mackenzie Venezuela Plataforma Deltana Block 4rubenpeNo ratings yet
- MT 03 2023Document78 pagesMT 03 2023Andres Augusto Mesa CastellanosNo ratings yet
- QTT Spare Part Deutz TCD Dan BF6MDocument2 pagesQTT Spare Part Deutz TCD Dan BF6MvirtualakunifnuNo ratings yet
- Orion RKE-B Series ChillerDocument20 pagesOrion RKE-B Series ChillerElias WigunaNo ratings yet
- Harmonic 1Document95 pagesHarmonic 1Abdel-Rahman Saifedin ArandasNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics (PHY 1051)Document11 pagesEngineering Physics (PHY 1051)Harshita GauravNo ratings yet
- CJC Filter DiagramDocument2 pagesCJC Filter DiagrampreciousNo ratings yet
- KS3 LeaP Q4 W8 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMDocument6 pagesKS3 LeaP Q4 W8 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMtolisNo ratings yet
- Ingecon Sun 3825tl C Series enDocument4 pagesIngecon Sun 3825tl C Series enafshin keshtkarNo ratings yet
- Chernobyl Disaster: The Worst Man-Made Disaster in Human HistoryDocument13 pagesChernobyl Disaster: The Worst Man-Made Disaster in Human HistoryGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Part I Autumn 2023-24Document137 pagesThermodynamics Part I Autumn 2023-24itzadisharmaNo ratings yet
- SMM.003E Chief Engineer Handing Over ReportDocument3 pagesSMM.003E Chief Engineer Handing Over ReportAndhityas Piscessandhy PutraNo ratings yet
- General Valve CatalogDocument40 pagesGeneral Valve CatalogAneeshNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lift in The Montrose Field, North Sea: E.G. Jacobs, SPE, Amoco (UK) Exploration CoDocument8 pagesArtificial Lift in The Montrose Field, North Sea: E.G. Jacobs, SPE, Amoco (UK) Exploration Comoh kadNo ratings yet
- Diesel Generator Sets: Output RatingsDocument2 pagesDiesel Generator Sets: Output Ratingsargie gayasNo ratings yet