Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Price Level: Sras 1 2
Price Level: Sras 1 2
Uploaded by
mongCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Introduction International Economics From SalvatoreDocument9 pagesIntroduction International Economics From SalvatoreEric James Abarro0% (1)
- Economics IB - Inflation EssayDocument6 pagesEconomics IB - Inflation Essaymykiri79100% (2)
- Question and Answer - 2Document30 pagesQuestion and Answer - 2acc-expertNo ratings yet
- Gann and Market CycleDocument12 pagesGann and Market CycleMukeshChauhanNo ratings yet
- Inward and Outward Looking Trade PoliciesDocument8 pagesInward and Outward Looking Trade Policieszainablakhani100% (17)
- Lecture 3, Tutorial 5Document6 pagesLecture 3, Tutorial 5KAREN WONGNo ratings yet
- Explanation of ADAS Diagram 2023Document6 pagesExplanation of ADAS Diagram 2023Jay Teng (Sajc)No ratings yet
- PhaoDocument4 pagesPhaoThuỳ Hương LêNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Macroeconomic Shocks On Asset Prices: Appendix To Web Appendix 1 To ChapterDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Macroeconomic Shocks On Asset Prices: Appendix To Web Appendix 1 To ChapterhlcarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Macro Tutorial 2Document5 pagesMacro Tutorial 2Nayama NayamaNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document21 pagesChap 3nida younasNo ratings yet
- 2022 A Level H2 CSQ1 - For APDocument8 pages2022 A Level H2 CSQ1 - For APKelly ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 - Monetary Policy, InflationDocument66 pagesLecture 17 - Monetary Policy, InflationEricNo ratings yet
- EJC J2 H2 Econs P2 Prelims MSDocument35 pagesEJC J2 H2 Econs P2 Prelims MSSimrah Sultanah (Njc)No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Issue - InflationDocument1 pageMacroeconomics Issue - InflationYing Ying LeeNo ratings yet
- Understanding Aggregate Demand (AD)Document4 pagesUnderstanding Aggregate Demand (AD)Nuri HaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Mankiw Macroeconomics PDDocument11 pagesSolution Manual Mankiw Macroeconomics PDClerisha DsouzaNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Monetary Policy:: A SummaryDocument43 pagesThe Effects of Monetary Policy:: A SummaryhumaidjafriNo ratings yet
- Pidilite 3R Aug11 2022Document8 pagesPidilite 3R Aug11 2022Arka MitraNo ratings yet
- Economics Commentary (Macro)Document3 pagesEconomics Commentary (Macro)Akshat JainNo ratings yet
- NBKKuwait Economic Brief Quarterly April 2021 EDocument9 pagesNBKKuwait Economic Brief Quarterly April 2021 ERaj Kishor PathakNo ratings yet
- Part IIIDocument47 pagesPart IIICoutinhoNo ratings yet
- Bk1 Ch5 Pastpaper AnsDocument9 pagesBk1 Ch5 Pastpaper AnsavawkNo ratings yet
- MacroScenario-BRAZIL Feb22Document5 pagesMacroScenario-BRAZIL Feb22Matheus AmaralNo ratings yet
- Final Economics Commentary 3 (Macroeconomics)Document6 pagesFinal Economics Commentary 3 (Macroeconomics)malik.krittikaNo ratings yet
- Investor Digest: HighlightDocument23 pagesInvestor Digest: HighlightArianto ThesmanNo ratings yet
- File SementaraDocument10 pagesFile SementaraHilih KintilNo ratings yet
- Ecfin Forecast Summer 10-07-19 Ro enDocument1 pageEcfin Forecast Summer 10-07-19 Ro enClaudiuNo ratings yet
- Bài Thi Kết Thúc Học Phần Tên học phần: …Kinh tế vĩ mô 1……………………………Document4 pagesBài Thi Kết Thúc Học Phần Tên học phần: …Kinh tế vĩ mô 1……………………………Anh Nguyễn VânNo ratings yet
- 44-45. Demand and Supply Side Causes of Unemployment 2Document12 pages44-45. Demand and Supply Side Causes of Unemployment 2ryan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Construction Cost SG 2022 Q1Document13 pagesQuarterly Construction Cost SG 2022 Q1quict.handongecNo ratings yet
- Facts About The Business Cycle: Aggregate Demand IDocument50 pagesFacts About The Business Cycle: Aggregate Demand ISahul HameedNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 3Document21 pagesIndividual Assignment 3Giang ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument52 pagesAggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyTonny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-05 at 8.09.02 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2024-03-05 at 8.09.02 PMemmanuelkakayayaNo ratings yet
- Economic OutlookDocument10 pagesEconomic OutlookedgarmerchanNo ratings yet
- FPDocument13 pagesFPKenny KwokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 & 10 - : Solutions To Problem Set # 8Document11 pagesChapter 9 & 10 - : Solutions To Problem Set # 8rashiNo ratings yet
- 2019 HCI C2H2 Econs Prelim CSQ 1 Suggested Answers and Mark SchemeDocument8 pages2019 HCI C2H2 Econs Prelim CSQ 1 Suggested Answers and Mark SchemeRaymond YimNo ratings yet
- P1 On InflationDocument6 pagesP1 On Inflationeleni.nikolaouNo ratings yet
- 1920 DSE Econ Assignment 02 Macro Chapter 07 AnswersDocument2 pages1920 DSE Econ Assignment 02 Macro Chapter 07 AnswersKen ElpídaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Update: The Saudi Economy: On A Very Firm FootingDocument9 pagesMacroeconomic Update: The Saudi Economy: On A Very Firm FootingAdeel ShaikhNo ratings yet
- LRASDocument15 pagesLRASMethon BaskNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy Lecture - PGP 26Document23 pagesFiscal Policy Lecture - PGP 26Parth BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 National Income REAL Vs NominalDocument24 pagesLecture 4 National Income REAL Vs NominalElshaddaiNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Submitted To: Sir Ikarm UllahDocument3 pagesMicroeconomics: Submitted To: Sir Ikarm UllahNadia ZahraNo ratings yet
- Ad-AsDocument52 pagesAd-AsNavneet ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Deal Pro - Financial Investment Competition Team: K-Drei: Ram Prasath T Vishwath S Padma Shravan MDocument2 pagesDeal Pro - Financial Investment Competition Team: K-Drei: Ram Prasath T Vishwath S Padma Shravan MMini ClipsNo ratings yet
- Topic F STD VerDocument38 pagesTopic F STD Verwgg5774No ratings yet
- Ki BBTN 20240212Document8 pagesKi BBTN 20240212muh.asad.amNo ratings yet
- Topic Review 1Document11 pagesTopic Review 1Afifah Abd WahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 InflationDocument25 pagesChapter 9 InflationĐỉnh Kout NamNo ratings yet
- Factor Payments Y Consumption of Domestically Produced Goods and Services (C)Document25 pagesFactor Payments Y Consumption of Domestically Produced Goods and Services (C)Johanne TangeNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Jll-Q1-2022-Market-Intelligence-Update-Mea-ConstructionDocument5 pages2022 - Jll-Q1-2022-Market-Intelligence-Update-Mea-ConstructionYi JieNo ratings yet
- Economics Strategy - 12MP Developmental Boost-Hong Leong Investment Bank Sep 28 2021Document11 pagesEconomics Strategy - 12MP Developmental Boost-Hong Leong Investment Bank Sep 28 2021tlin0035No ratings yet
- PNJ Update 20201207Document7 pagesPNJ Update 20201207Khoa PhamNo ratings yet
- BU204 10 Finley Joey Unit 9Document18 pagesBU204 10 Finley Joey Unit 9Rosey FinleyNo ratings yet
- Revision 2nd PartDocument48 pagesRevision 2nd PartSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Ecfin Forecast Winter 2021 Ro enDocument1 pageEcfin Forecast Winter 2021 Ro enVirban RobertNo ratings yet
- HW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewDocument5 pagesHW #1: Solutions: Questions For Reviewantonhaye100% (2)
- HW 1 Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesHW 1 Solutions PDFThe oneNo ratings yet
- HW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewDocument5 pagesHW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewantonhayeNo ratings yet
- HW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewDocument5 pagesHW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewantonhayeNo ratings yet
- 2001 Econ. Paper 2 (Original)Document19 pages2001 Econ. Paper 2 (Original)peter wongNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Finserv AMC - Factsheet - June 2024Document33 pagesBajaj Finserv AMC - Factsheet - June 2024mayank.cxNo ratings yet
- Literature Review GDPDocument6 pagesLiterature Review GDPbctfnerif100% (1)
- Introduction To Finance Markets Investments and Financial Management 15th Edition Melicher Solutions Manual 1Document13 pagesIntroduction To Finance Markets Investments and Financial Management 15th Edition Melicher Solutions Manual 1samanthahortoncbdsetjaxr100% (30)
- Statistical Appendix Economic Survey 2022-23Document217 pagesStatistical Appendix Economic Survey 2022-23vijay krishnaNo ratings yet
- Icici Bank: Key Financial RatiosDocument2 pagesIcici Bank: Key Financial RatiosSriharsha KrishnaprakashNo ratings yet
- MPRA Paper 26856 PDFDocument64 pagesMPRA Paper 26856 PDFabdouuntd7No ratings yet
- Annual Reports 2015Document128 pagesAnnual Reports 2015Fuaad DodooNo ratings yet
- Princ ch35 PresentationDocument33 pagesPrinc ch35 PresentationJ.JEFRI CHENNo ratings yet
- Eco MS 1 CSSC WDocument9 pagesEco MS 1 CSSC WSM THIRUMURUGANNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments: International FinanceDocument42 pagesBalance of Payments: International FinanceSoniya Rht0% (1)
- 2-The Global EconomyDocument8 pages2-The Global EconomyWynnie RondonNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 PDFDocument64 pagesChapter8 PDFbigdigdaddyyNo ratings yet
- Bilderberg Meetings Conference Report 1979Document58 pagesBilderberg Meetings Conference Report 1979bilderbergboysNo ratings yet
- Political Economy, Vol. 108 No. 1, 1-33: Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesPolitical Economy, Vol. 108 No. 1, 1-33: Daftar PustakaRian SopianNo ratings yet
- Foreign Reserve 2Document6 pagesForeign Reserve 2cakartikayNo ratings yet
- Top of Mind - Stagflation RiskDocument25 pagesTop of Mind - Stagflation RiskalysomjiNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 National Income Accounting: Reference: Ahuja - PG 15-35Document31 pagesModule - 4 National Income Accounting: Reference: Ahuja - PG 15-35chunmaina10mbaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Planning in SAPDocument24 pagesFlexible Planning in SAPharinikrishnaNo ratings yet
- PakistanDocument4 pagesPakistanAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics Final ReportDocument14 pagesMacro Economics Final ReportSaad FarooqNo ratings yet
- IC3 Nov 2012 023Document24 pagesIC3 Nov 2012 023Rizwan ShahidNo ratings yet
- CAD EssayDocument4 pagesCAD Essayshelterman14No ratings yet
- Economics Paper 2 SLDocument6 pagesEconomics Paper 2 SLneraxew739No ratings yet
- Exchane Rate RegimesDocument17 pagesExchane Rate RegimesAvinash SupkarNo ratings yet
- ECON 352 Problem Set 3 (With Key)Document18 pagesECON 352 Problem Set 3 (With Key)Ceylin SenerNo ratings yet
Price Level: Sras 1 2
Price Level: Sras 1 2
Uploaded by
mongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Price Level: Sras 1 2
Price Level: Sras 1 2
Uploaded by
mongCopyright:
Available Formats
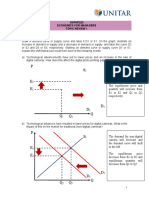
4.
Using the aggregate demand and aggregate supply (AD-SRAS) diagram, explain what will
happen to the equilibrium price level and Real GDP when each of the following events
occurs:
(i) A depreciation of Ringgit Malaysia (RM)
Price level
SRAS 1 Depreciation of Ringgit Malaysia cause the net export
E2 growth which leads to increase in real GDP and price
P2 E1 level. The equilibrium price level increase from P1 to
P1
AD 2 P2 and the aggregate demand of real GDP increase from
AD 1 Q1 to Q2. This causes the aggregate demand curve shift
Q1 Q 2 Real GDP rightward from AD1 to AD2.
(i) An increase in labour productivity
Price level
SRAS 1
SRAS 2
An increase in labour productivity will help the factory
E1 or business able to produce more outputs in the market.
P1 E2 The equilibrium price level falls from P1 to P2 and the
P2
aggregate supply of real GDP increase from Q1 to Q2.
AD 1
Therefore, the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift
Real GDP
Q1 Q2 rightward from SRAS1 to SRAS2.
(ii) Bank Negara Malaysia
(BNM) announced a raise in interest rate to reduce inflation.
Price level Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM) announce a raise in
SRAS 1 interest to reduce inflation will cause less people want to
borrow loan from BNM because they not willing to pay
E1
P1 high interest. The equilibrium price level falls from P1 to
E2
P2 P2 and the aggregate demand of real GDP decrease from
AD 1 Q1 to Q2. This causes the aggregate demand curve shift
AD 2
Q1
Real GDP leftward from AD1 to AD2.
Q2
You might also like
- Introduction International Economics From SalvatoreDocument9 pagesIntroduction International Economics From SalvatoreEric James Abarro0% (1)
- Economics IB - Inflation EssayDocument6 pagesEconomics IB - Inflation Essaymykiri79100% (2)
- Question and Answer - 2Document30 pagesQuestion and Answer - 2acc-expertNo ratings yet
- Gann and Market CycleDocument12 pagesGann and Market CycleMukeshChauhanNo ratings yet
- Inward and Outward Looking Trade PoliciesDocument8 pagesInward and Outward Looking Trade Policieszainablakhani100% (17)
- Lecture 3, Tutorial 5Document6 pagesLecture 3, Tutorial 5KAREN WONGNo ratings yet
- Explanation of ADAS Diagram 2023Document6 pagesExplanation of ADAS Diagram 2023Jay Teng (Sajc)No ratings yet
- PhaoDocument4 pagesPhaoThuỳ Hương LêNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Macroeconomic Shocks On Asset Prices: Appendix To Web Appendix 1 To ChapterDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Macroeconomic Shocks On Asset Prices: Appendix To Web Appendix 1 To ChapterhlcarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Macro Tutorial 2Document5 pagesMacro Tutorial 2Nayama NayamaNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document21 pagesChap 3nida younasNo ratings yet
- 2022 A Level H2 CSQ1 - For APDocument8 pages2022 A Level H2 CSQ1 - For APKelly ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 - Monetary Policy, InflationDocument66 pagesLecture 17 - Monetary Policy, InflationEricNo ratings yet
- EJC J2 H2 Econs P2 Prelims MSDocument35 pagesEJC J2 H2 Econs P2 Prelims MSSimrah Sultanah (Njc)No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Issue - InflationDocument1 pageMacroeconomics Issue - InflationYing Ying LeeNo ratings yet
- Understanding Aggregate Demand (AD)Document4 pagesUnderstanding Aggregate Demand (AD)Nuri HaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Mankiw Macroeconomics PDDocument11 pagesSolution Manual Mankiw Macroeconomics PDClerisha DsouzaNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Monetary Policy:: A SummaryDocument43 pagesThe Effects of Monetary Policy:: A SummaryhumaidjafriNo ratings yet
- Pidilite 3R Aug11 2022Document8 pagesPidilite 3R Aug11 2022Arka MitraNo ratings yet
- Economics Commentary (Macro)Document3 pagesEconomics Commentary (Macro)Akshat JainNo ratings yet
- NBKKuwait Economic Brief Quarterly April 2021 EDocument9 pagesNBKKuwait Economic Brief Quarterly April 2021 ERaj Kishor PathakNo ratings yet
- Part IIIDocument47 pagesPart IIICoutinhoNo ratings yet
- Bk1 Ch5 Pastpaper AnsDocument9 pagesBk1 Ch5 Pastpaper AnsavawkNo ratings yet
- MacroScenario-BRAZIL Feb22Document5 pagesMacroScenario-BRAZIL Feb22Matheus AmaralNo ratings yet
- Final Economics Commentary 3 (Macroeconomics)Document6 pagesFinal Economics Commentary 3 (Macroeconomics)malik.krittikaNo ratings yet
- Investor Digest: HighlightDocument23 pagesInvestor Digest: HighlightArianto ThesmanNo ratings yet
- File SementaraDocument10 pagesFile SementaraHilih KintilNo ratings yet
- Ecfin Forecast Summer 10-07-19 Ro enDocument1 pageEcfin Forecast Summer 10-07-19 Ro enClaudiuNo ratings yet
- Bài Thi Kết Thúc Học Phần Tên học phần: …Kinh tế vĩ mô 1……………………………Document4 pagesBài Thi Kết Thúc Học Phần Tên học phần: …Kinh tế vĩ mô 1……………………………Anh Nguyễn VânNo ratings yet
- 44-45. Demand and Supply Side Causes of Unemployment 2Document12 pages44-45. Demand and Supply Side Causes of Unemployment 2ryan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Construction Cost SG 2022 Q1Document13 pagesQuarterly Construction Cost SG 2022 Q1quict.handongecNo ratings yet
- Facts About The Business Cycle: Aggregate Demand IDocument50 pagesFacts About The Business Cycle: Aggregate Demand ISahul HameedNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 3Document21 pagesIndividual Assignment 3Giang ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument52 pagesAggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyTonny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-05 at 8.09.02 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2024-03-05 at 8.09.02 PMemmanuelkakayayaNo ratings yet
- Economic OutlookDocument10 pagesEconomic OutlookedgarmerchanNo ratings yet
- FPDocument13 pagesFPKenny KwokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 & 10 - : Solutions To Problem Set # 8Document11 pagesChapter 9 & 10 - : Solutions To Problem Set # 8rashiNo ratings yet
- 2019 HCI C2H2 Econs Prelim CSQ 1 Suggested Answers and Mark SchemeDocument8 pages2019 HCI C2H2 Econs Prelim CSQ 1 Suggested Answers and Mark SchemeRaymond YimNo ratings yet
- P1 On InflationDocument6 pagesP1 On Inflationeleni.nikolaouNo ratings yet
- 1920 DSE Econ Assignment 02 Macro Chapter 07 AnswersDocument2 pages1920 DSE Econ Assignment 02 Macro Chapter 07 AnswersKen ElpídaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Update: The Saudi Economy: On A Very Firm FootingDocument9 pagesMacroeconomic Update: The Saudi Economy: On A Very Firm FootingAdeel ShaikhNo ratings yet
- LRASDocument15 pagesLRASMethon BaskNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy Lecture - PGP 26Document23 pagesFiscal Policy Lecture - PGP 26Parth BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 National Income REAL Vs NominalDocument24 pagesLecture 4 National Income REAL Vs NominalElshaddaiNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Submitted To: Sir Ikarm UllahDocument3 pagesMicroeconomics: Submitted To: Sir Ikarm UllahNadia ZahraNo ratings yet
- Ad-AsDocument52 pagesAd-AsNavneet ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Deal Pro - Financial Investment Competition Team: K-Drei: Ram Prasath T Vishwath S Padma Shravan MDocument2 pagesDeal Pro - Financial Investment Competition Team: K-Drei: Ram Prasath T Vishwath S Padma Shravan MMini ClipsNo ratings yet
- Topic F STD VerDocument38 pagesTopic F STD Verwgg5774No ratings yet
- Ki BBTN 20240212Document8 pagesKi BBTN 20240212muh.asad.amNo ratings yet
- Topic Review 1Document11 pagesTopic Review 1Afifah Abd WahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 InflationDocument25 pagesChapter 9 InflationĐỉnh Kout NamNo ratings yet
- Factor Payments Y Consumption of Domestically Produced Goods and Services (C)Document25 pagesFactor Payments Y Consumption of Domestically Produced Goods and Services (C)Johanne TangeNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Jll-Q1-2022-Market-Intelligence-Update-Mea-ConstructionDocument5 pages2022 - Jll-Q1-2022-Market-Intelligence-Update-Mea-ConstructionYi JieNo ratings yet
- Economics Strategy - 12MP Developmental Boost-Hong Leong Investment Bank Sep 28 2021Document11 pagesEconomics Strategy - 12MP Developmental Boost-Hong Leong Investment Bank Sep 28 2021tlin0035No ratings yet
- PNJ Update 20201207Document7 pagesPNJ Update 20201207Khoa PhamNo ratings yet
- BU204 10 Finley Joey Unit 9Document18 pagesBU204 10 Finley Joey Unit 9Rosey FinleyNo ratings yet
- Revision 2nd PartDocument48 pagesRevision 2nd PartSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Ecfin Forecast Winter 2021 Ro enDocument1 pageEcfin Forecast Winter 2021 Ro enVirban RobertNo ratings yet
- HW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewDocument5 pagesHW #1: Solutions: Questions For Reviewantonhaye100% (2)
- HW 1 Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesHW 1 Solutions PDFThe oneNo ratings yet
- HW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewDocument5 pagesHW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewantonhayeNo ratings yet
- HW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewDocument5 pagesHW #1: Solutions: Questions For ReviewantonhayeNo ratings yet
- 2001 Econ. Paper 2 (Original)Document19 pages2001 Econ. Paper 2 (Original)peter wongNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Finserv AMC - Factsheet - June 2024Document33 pagesBajaj Finserv AMC - Factsheet - June 2024mayank.cxNo ratings yet
- Literature Review GDPDocument6 pagesLiterature Review GDPbctfnerif100% (1)
- Introduction To Finance Markets Investments and Financial Management 15th Edition Melicher Solutions Manual 1Document13 pagesIntroduction To Finance Markets Investments and Financial Management 15th Edition Melicher Solutions Manual 1samanthahortoncbdsetjaxr100% (30)
- Statistical Appendix Economic Survey 2022-23Document217 pagesStatistical Appendix Economic Survey 2022-23vijay krishnaNo ratings yet
- Icici Bank: Key Financial RatiosDocument2 pagesIcici Bank: Key Financial RatiosSriharsha KrishnaprakashNo ratings yet
- MPRA Paper 26856 PDFDocument64 pagesMPRA Paper 26856 PDFabdouuntd7No ratings yet
- Annual Reports 2015Document128 pagesAnnual Reports 2015Fuaad DodooNo ratings yet
- Princ ch35 PresentationDocument33 pagesPrinc ch35 PresentationJ.JEFRI CHENNo ratings yet
- Eco MS 1 CSSC WDocument9 pagesEco MS 1 CSSC WSM THIRUMURUGANNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments: International FinanceDocument42 pagesBalance of Payments: International FinanceSoniya Rht0% (1)
- 2-The Global EconomyDocument8 pages2-The Global EconomyWynnie RondonNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 PDFDocument64 pagesChapter8 PDFbigdigdaddyyNo ratings yet
- Bilderberg Meetings Conference Report 1979Document58 pagesBilderberg Meetings Conference Report 1979bilderbergboysNo ratings yet
- Political Economy, Vol. 108 No. 1, 1-33: Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesPolitical Economy, Vol. 108 No. 1, 1-33: Daftar PustakaRian SopianNo ratings yet
- Foreign Reserve 2Document6 pagesForeign Reserve 2cakartikayNo ratings yet
- Top of Mind - Stagflation RiskDocument25 pagesTop of Mind - Stagflation RiskalysomjiNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 National Income Accounting: Reference: Ahuja - PG 15-35Document31 pagesModule - 4 National Income Accounting: Reference: Ahuja - PG 15-35chunmaina10mbaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Planning in SAPDocument24 pagesFlexible Planning in SAPharinikrishnaNo ratings yet
- PakistanDocument4 pagesPakistanAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics Final ReportDocument14 pagesMacro Economics Final ReportSaad FarooqNo ratings yet
- IC3 Nov 2012 023Document24 pagesIC3 Nov 2012 023Rizwan ShahidNo ratings yet
- CAD EssayDocument4 pagesCAD Essayshelterman14No ratings yet
- Economics Paper 2 SLDocument6 pagesEconomics Paper 2 SLneraxew739No ratings yet
- Exchane Rate RegimesDocument17 pagesExchane Rate RegimesAvinash SupkarNo ratings yet
- ECON 352 Problem Set 3 (With Key)Document18 pagesECON 352 Problem Set 3 (With Key)Ceylin SenerNo ratings yet