Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics GRoup Activity
Physics GRoup Activity
Uploaded by
AbinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Heat Transfer ProjectDocument68 pagesHeat Transfer ProjectsubratorajNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Heat TransferDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 1 Heat Transferaimanrsln0% (1)
- Bare and LaggedDocument20 pagesBare and Laggedchimikoxd25% (4)
- Heat Transfer MethodDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer MethodSonu BairwaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer - Radiation, Convection and ConductionDocument9 pagesHeat Transfer - Radiation, Convection and Conductionsubham dashNo ratings yet
- Modes of Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and RadiationDocument63 pagesModes of Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and RadiationKelly ObrienNo ratings yet
- HT Lecture 01 Modes of HeatTransferDocument29 pagesHT Lecture 01 Modes of HeatTransferYashaswiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts of Heat TransferDocument27 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts of Heat TransferAbishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Me 372 L02Document30 pagesMe 372 L02gs9e28dfaqfoNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Basic Modes of Heat TransferDocument15 pagesClass 1 Basic Modes of Heat TransferShadmanSakiefHridoyNo ratings yet
- L4 Heat Transfer Mechanisms PDFDocument26 pagesL4 Heat Transfer Mechanisms PDFgebreslassie gereziherNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationDocument29 pagesModule 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationVishnupriya B.No ratings yet
- Basic Modes of Heat TransferDocument15 pagesBasic Modes of Heat Transfermeraj100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Mechanisms 2022Document25 pagesHeat Transfer Mechanisms 2022PABLO VICENTE REBOLLOSO SALINASNo ratings yet
- Chap01 HT 3e LectureDocument19 pagesChap01 HT 3e LectureBanu KayıkçıNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Heat TransferTharusha Eranga RamanayakaNo ratings yet
- B.7-3 Thermal Energy TransferDocument22 pagesB.7-3 Thermal Energy TransferajinnorabahurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Heat TransferJeevanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Conduction Convection RadiationDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Conduction Convection RadiationAMJAD100% (1)
- Presentation On: Heat TransferDocument16 pagesPresentation On: Heat TransfermehediNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lecture NotesDocument66 pagesHeat Transfer Lecture NotesJustin100% (1)
- Lectures Presented by B.K.Roy Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument40 pagesLectures Presented by B.K.Roy Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Departmentreshnalidevi1998No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Transmission of HeatDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Transmission of Heatdinesh11rNo ratings yet
- HT Donot Give Now 8.8.13Document20 pagesHT Donot Give Now 8.8.13Rajib MandalNo ratings yet
- Heat:: Thermal Energy in The Form of Heat Can Move in Three WaysDocument38 pagesHeat:: Thermal Energy in The Form of Heat Can Move in Three WaysSimrah HafeezNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - Vol. 02 - DHARMSINH DESAI UNIVERSITYDocument150 pagesChemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - Vol. 02 - DHARMSINH DESAI UNIVERSITYGustavo Gonzalez ServaNo ratings yet
- Heat 1Document17 pagesHeat 1shotlove56No ratings yet
- Transmision de CalorDocument28 pagesTransmision de Calorversantos3No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer DemonstrationDocument17 pagesHeat Transfer DemonstrationJohn DarylNo ratings yet
- 5MA039 - Introduction To Heat TransferDocument30 pages5MA039 - Introduction To Heat TransferNaveen KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 HeatTransfer - Intro On Conduction Convection RadiationDocument24 pages1.0 HeatTransfer - Intro On Conduction Convection RadiationGharamNo ratings yet
- HT Lecture Notes - 0Document41 pagesHT Lecture Notes - 0SUPRADEEP GNo ratings yet
- Magpantay, Erol Rexel C.Document3 pagesMagpantay, Erol Rexel C.Kenny KenNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Notes .Sme: ThermodynamicsDocument19 pagesUnit-Ii Notes .Sme: Thermodynamicssthavir punwatkarNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument5 pagesHeat TransferZaldy IbanezNo ratings yet
- Chap 13 SAM Transfer of Heat FinalDocument25 pagesChap 13 SAM Transfer of Heat FinalSNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity: Gases Liquids SolidsDocument4 pagesThermal Conductivity: Gases Liquids SolidsAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNo ratings yet
- Comprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementDocument33 pagesComprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementAhmed MobarkiNo ratings yet
- هيت كورس ثانيDocument7 pagesهيت كورس ثانيahmad243809No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer: Lectures 3-4 Introdcution Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Convection Radiation Energy BalanceDocument17 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer: Lectures 3-4 Introdcution Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Convection Radiation Energy BalanceAbdullah RiazNo ratings yet
- Week: 3: Mechanisms of Heat TransferDocument19 pagesWeek: 3: Mechanisms of Heat TransferAhmad AimanadhifNo ratings yet
- HVAC For Course2Document251 pagesHVAC For Course2Anwar Pariyarath0% (1)
- There Are Three Mechanisms by Which Heat (Energy) Is Transferred in The AtmosphereDocument3 pagesThere Are Three Mechanisms by Which Heat (Energy) Is Transferred in The Atmospheremohd firdaus bin ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Heat TransferDocument31 pagesMechanism of Heat Transferedna padreNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document32 pagesModule 1Shivani ManeNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferSquidward TentaclesNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument5 pagesHeat TransferYuli AnaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat Transfer and Conductivity by Engr - Muzaffar Hussain SiyalDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Heat Transfer and Conductivity by Engr - Muzaffar Hussain SiyalMuzaffar Shahnawaz siyalNo ratings yet
- 01 Transmission of Heat Theory1Document33 pages01 Transmission of Heat Theory1Ashok Pradhan100% (1)
- Heat Transfer 1 PDFDocument72 pagesHeat Transfer 1 PDFMerazka FaroukNo ratings yet
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- Final hmt-1 PDFDocument211 pagesFinal hmt-1 PDFPoyyamozhi Nadesan RanjithNo ratings yet
- Review Heat TransferDocument23 pagesReview Heat TransferjameslyNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Lecture Slide: Dr. Paul S. NnamchiDocument34 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Lecture Slide: Dr. Paul S. NnamchilotannaNo ratings yet
- Heat VsDocument9 pagesHeat VsRenuga77No ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter OneDocument16 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter Oneabdi dejeneNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Heat and Mass TransferDocument40 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Heat and Mass TransferHugo MartinsNo ratings yet
- Treatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsFrom EverandTreatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- ANSYS AIM DocumentationDocument306 pagesANSYS AIM DocumentationWilder Molina100% (2)
- Simulation CFD Comparison MatrixDocument2 pagesSimulation CFD Comparison MatrixtalabizNo ratings yet
- Ee Room VentilationDocument7 pagesEe Room VentilationNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection & RadiationDocument19 pagesConduction, Convection & RadiationsanyaNo ratings yet
- Aero 6sem HTDocument232 pagesAero 6sem HTNVNo ratings yet
- Ansys Icepak BrochureDocument4 pagesAnsys Icepak Brochurejagadees21No ratings yet
- Sfpe Handbook OverviewDocument14 pagesSfpe Handbook Overviewcoolsummer1112143No ratings yet
- EHM Lesson 5 FT PDFDocument14 pagesEHM Lesson 5 FT PDFMuhammed NazardeenNo ratings yet
- Thermal Diffusivity Variations of Food Products in Natural Convection CoolingDocument7 pagesThermal Diffusivity Variations of Food Products in Natural Convection CoolingDANIELLY LOPES DE OLIVEIRANo ratings yet
- Depressuring Study and Application On BP-A ProjectDocument35 pagesDepressuring Study and Application On BP-A ProjectTruong Minh Hoang100% (6)
- Heat Transfer in Bioreactor: Manam Walait Lecturer FLS, UCP LahoreDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer in Bioreactor: Manam Walait Lecturer FLS, UCP LahoreJawadNo ratings yet
- Unit I IntroductionDocument91 pagesUnit I Introductionsujith100% (3)
- Research On Welding Deformation For Box Girder ofDocument12 pagesResearch On Welding Deformation For Box Girder oframiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perpindahan PanasDocument7 pagesTugas Perpindahan PanasAnonymous DpmprYqkuNo ratings yet
- Manual Thermo IDocument121 pagesManual Thermo IKevin RamiroNo ratings yet
- Locating Levels in Tanks and Silos Using Infrared ThermographyDocument4 pagesLocating Levels in Tanks and Silos Using Infrared ThermographyYeison Camilo Zapata DavidNo ratings yet
- 11P 14 Heat Transfer PDFDocument46 pages11P 14 Heat Transfer PDFkpchakralaNo ratings yet
- Heat Assignment Class 7Document5 pagesHeat Assignment Class 7Anika JoshiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Is The Transition ofDocument11 pagesHeat Transfer Is The Transition of3m3hNo ratings yet
- CH 15 Transmission of HeatDocument53 pagesCH 15 Transmission of HeatCat123No ratings yet
- CFD (Computional Fluid Dynamics) QuizDocument18 pagesCFD (Computional Fluid Dynamics) Quizmsnaghavi100% (1)
- BTech Chemical RevisedDocument46 pagesBTech Chemical RevisedRam Krishan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solidworks Flow Simulation 2012 Tutorial 1Document266 pagesSolidworks Flow Simulation 2012 Tutorial 1Paul Torres J100% (1)
- Olp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Document17 pagesOlp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Shabbir H. KhanNo ratings yet
- 2018 Manual Energy Thermal 12Document35 pages2018 Manual Energy Thermal 12pappadakunduNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy: Abhishek Kumar, Kuljeet Singh, Sunirmit Verma, Ranjan DasDocument15 pagesSolar Energy: Abhishek Kumar, Kuljeet Singh, Sunirmit Verma, Ranjan DasAmandeep RayatNo ratings yet
- 6 Gradient of A Scalar Function: F X F y F ZDocument1 page6 Gradient of A Scalar Function: F X F y F ZakshathNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress MonitoringDocument78 pagesThermal Stress MonitoringSIVA KAVYANo ratings yet
- DLL ScienceDocument5 pagesDLL ScienceMary May LopezNo ratings yet
Physics GRoup Activity
Physics GRoup Activity
Uploaded by
AbinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics GRoup Activity
Physics GRoup Activity
Uploaded by
AbinCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS ACTIVITY
11.9 HEAT TRANSFER
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
Blackbody Radiation
Greenhouse Effect
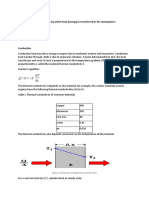
Conduction
The process in which heat flows from objects with higher temperature
to objects with lower temperature.
Conduction Equation
Q = [K.A.(Thot - Tcold)] / d
Where ,
Q is the transfer of heat per unit time
K is the thermal conductivity of the body
A is the area of heat transfer
Thot is the temperature of the hot region
Tcold is the temperature of the cold region
d is the thickness of the body
Conduction Examples
Following are the examples of conduction:
Ironing of clothes is an example of conduction where the heat is
conducted from the iron to the clothes.
Heat is transferred from hands to ice cube resulting in the melting
of an ice cube when held in hands.
Convection
The movement of fluid molecules from higher temperature regions to
lower temperature regions.
Convection Equation
Q = hc . A . (TS – Tf)
Where,
Q is the heat transferred per unit time
Hc is the coefficient of convective heat transfer
A is the area of heat transfer
Ts is the surface temperature
Tf is the fluid temperature
Convection Examples
Examples of convection include:
Boiling of water, that is molecules that are denser move at the
bottom while the molecules which are less dense move upwards
resulting in the circular motion of the molecules so that water
gets heated.
Warm water around the equator moves towards the poles while
cooler water at the poles moves towards the equator.
Radiation
Radiation The process of heat transmission in the form electromagnetic
waves, is called radiation. Radiation do not require any medium for
propagation. It propagates without heating the intervening medium.
Radiation Equation
P = e ∙ σ ∙ A· (Tr – Tc)4
Where,
P is the net power of radiation
A is the area of radiation
Tr is the radiator temperature
Tc is the surrounding temperature
e is emissivity and σ is Stefan’s constant
Radiation Example
Following are the examples of radiation:
Microwave radiation emitted in the oven is an example of
radiation.
UV rays coming from the sun is an example of radiation.
Black Body Radiation
Blackbody radiation is radiation produced by heated objects,
particularly from a blackbody. A blackbody is an object that absorbs all
radiation (visible light, infrared light, ultraviolet light, etc.) that falls on
it. This also means that it will also radiate at all frequencies that heat
energy produces in it
Black Body Radiation Example
Some examples of blackbody radiators that emit visible light or whose
radiation is used for other processes include the electric heaters,
incandescent light bulbs, stoves, the sun, the stars, night vision
equipment, burglar alarms, warm-blooded animals, etc.
Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse effect refers to the phenomenon of increase in the
temperature of the planet on account of emission of gases. This is a
natural process which warms the earth. The radiations coming from the
sun are reflected back by the earth's surface and some of them are
absorbed and re-radiated
Greenhouse Effect Examples
Example of the greenhouse effect that most of us experience in
everyday life is the warming of a car's interior when the vehicle is left
out in the sun. You've probably noticed that your car is always much
hotter inside than the outside temperature if it's been sitting there for a
while.
You might also like
- Heat Transfer ProjectDocument68 pagesHeat Transfer ProjectsubratorajNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Heat TransferDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 1 Heat Transferaimanrsln0% (1)
- Bare and LaggedDocument20 pagesBare and Laggedchimikoxd25% (4)
- Heat Transfer MethodDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer MethodSonu BairwaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer - Radiation, Convection and ConductionDocument9 pagesHeat Transfer - Radiation, Convection and Conductionsubham dashNo ratings yet
- Modes of Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and RadiationDocument63 pagesModes of Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and RadiationKelly ObrienNo ratings yet
- HT Lecture 01 Modes of HeatTransferDocument29 pagesHT Lecture 01 Modes of HeatTransferYashaswiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts of Heat TransferDocument27 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts of Heat TransferAbishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Me 372 L02Document30 pagesMe 372 L02gs9e28dfaqfoNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Basic Modes of Heat TransferDocument15 pagesClass 1 Basic Modes of Heat TransferShadmanSakiefHridoyNo ratings yet
- L4 Heat Transfer Mechanisms PDFDocument26 pagesL4 Heat Transfer Mechanisms PDFgebreslassie gereziherNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationDocument29 pagesModule 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationVishnupriya B.No ratings yet
- Basic Modes of Heat TransferDocument15 pagesBasic Modes of Heat Transfermeraj100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Mechanisms 2022Document25 pagesHeat Transfer Mechanisms 2022PABLO VICENTE REBOLLOSO SALINASNo ratings yet
- Chap01 HT 3e LectureDocument19 pagesChap01 HT 3e LectureBanu KayıkçıNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Heat TransferTharusha Eranga RamanayakaNo ratings yet
- B.7-3 Thermal Energy TransferDocument22 pagesB.7-3 Thermal Energy TransferajinnorabahurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Heat TransferJeevanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Conduction Convection RadiationDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Conduction Convection RadiationAMJAD100% (1)
- Presentation On: Heat TransferDocument16 pagesPresentation On: Heat TransfermehediNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lecture NotesDocument66 pagesHeat Transfer Lecture NotesJustin100% (1)
- Lectures Presented by B.K.Roy Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument40 pagesLectures Presented by B.K.Roy Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Departmentreshnalidevi1998No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Transmission of HeatDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Transmission of Heatdinesh11rNo ratings yet
- HT Donot Give Now 8.8.13Document20 pagesHT Donot Give Now 8.8.13Rajib MandalNo ratings yet
- Heat:: Thermal Energy in The Form of Heat Can Move in Three WaysDocument38 pagesHeat:: Thermal Energy in The Form of Heat Can Move in Three WaysSimrah HafeezNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - Vol. 02 - DHARMSINH DESAI UNIVERSITYDocument150 pagesChemical Engineering For Non-Chemical Engineers - Vol. 02 - DHARMSINH DESAI UNIVERSITYGustavo Gonzalez ServaNo ratings yet
- Heat 1Document17 pagesHeat 1shotlove56No ratings yet
- Transmision de CalorDocument28 pagesTransmision de Calorversantos3No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer DemonstrationDocument17 pagesHeat Transfer DemonstrationJohn DarylNo ratings yet
- 5MA039 - Introduction To Heat TransferDocument30 pages5MA039 - Introduction To Heat TransferNaveen KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 HeatTransfer - Intro On Conduction Convection RadiationDocument24 pages1.0 HeatTransfer - Intro On Conduction Convection RadiationGharamNo ratings yet
- HT Lecture Notes - 0Document41 pagesHT Lecture Notes - 0SUPRADEEP GNo ratings yet
- Magpantay, Erol Rexel C.Document3 pagesMagpantay, Erol Rexel C.Kenny KenNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Notes .Sme: ThermodynamicsDocument19 pagesUnit-Ii Notes .Sme: Thermodynamicssthavir punwatkarNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument5 pagesHeat TransferZaldy IbanezNo ratings yet
- Chap 13 SAM Transfer of Heat FinalDocument25 pagesChap 13 SAM Transfer of Heat FinalSNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity: Gases Liquids SolidsDocument4 pagesThermal Conductivity: Gases Liquids SolidsAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNo ratings yet
- Comprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementDocument33 pagesComprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementAhmed MobarkiNo ratings yet
- هيت كورس ثانيDocument7 pagesهيت كورس ثانيahmad243809No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer: Lectures 3-4 Introdcution Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Convection Radiation Energy BalanceDocument17 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer: Lectures 3-4 Introdcution Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Convection Radiation Energy BalanceAbdullah RiazNo ratings yet
- Week: 3: Mechanisms of Heat TransferDocument19 pagesWeek: 3: Mechanisms of Heat TransferAhmad AimanadhifNo ratings yet
- HVAC For Course2Document251 pagesHVAC For Course2Anwar Pariyarath0% (1)
- There Are Three Mechanisms by Which Heat (Energy) Is Transferred in The AtmosphereDocument3 pagesThere Are Three Mechanisms by Which Heat (Energy) Is Transferred in The Atmospheremohd firdaus bin ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Heat TransferDocument31 pagesMechanism of Heat Transferedna padreNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document32 pagesModule 1Shivani ManeNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferSquidward TentaclesNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument5 pagesHeat TransferYuli AnaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat Transfer and Conductivity by Engr - Muzaffar Hussain SiyalDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Heat Transfer and Conductivity by Engr - Muzaffar Hussain SiyalMuzaffar Shahnawaz siyalNo ratings yet
- 01 Transmission of Heat Theory1Document33 pages01 Transmission of Heat Theory1Ashok Pradhan100% (1)
- Heat Transfer 1 PDFDocument72 pagesHeat Transfer 1 PDFMerazka FaroukNo ratings yet
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- Final hmt-1 PDFDocument211 pagesFinal hmt-1 PDFPoyyamozhi Nadesan RanjithNo ratings yet
- Review Heat TransferDocument23 pagesReview Heat TransferjameslyNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Lecture Slide: Dr. Paul S. NnamchiDocument34 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Lecture Slide: Dr. Paul S. NnamchilotannaNo ratings yet
- Heat VsDocument9 pagesHeat VsRenuga77No ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter OneDocument16 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter Oneabdi dejeneNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Heat and Mass TransferDocument40 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Heat and Mass TransferHugo MartinsNo ratings yet
- Treatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsFrom EverandTreatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- ANSYS AIM DocumentationDocument306 pagesANSYS AIM DocumentationWilder Molina100% (2)
- Simulation CFD Comparison MatrixDocument2 pagesSimulation CFD Comparison MatrixtalabizNo ratings yet
- Ee Room VentilationDocument7 pagesEe Room VentilationNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection & RadiationDocument19 pagesConduction, Convection & RadiationsanyaNo ratings yet
- Aero 6sem HTDocument232 pagesAero 6sem HTNVNo ratings yet
- Ansys Icepak BrochureDocument4 pagesAnsys Icepak Brochurejagadees21No ratings yet
- Sfpe Handbook OverviewDocument14 pagesSfpe Handbook Overviewcoolsummer1112143No ratings yet
- EHM Lesson 5 FT PDFDocument14 pagesEHM Lesson 5 FT PDFMuhammed NazardeenNo ratings yet
- Thermal Diffusivity Variations of Food Products in Natural Convection CoolingDocument7 pagesThermal Diffusivity Variations of Food Products in Natural Convection CoolingDANIELLY LOPES DE OLIVEIRANo ratings yet
- Depressuring Study and Application On BP-A ProjectDocument35 pagesDepressuring Study and Application On BP-A ProjectTruong Minh Hoang100% (6)
- Heat Transfer in Bioreactor: Manam Walait Lecturer FLS, UCP LahoreDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer in Bioreactor: Manam Walait Lecturer FLS, UCP LahoreJawadNo ratings yet
- Unit I IntroductionDocument91 pagesUnit I Introductionsujith100% (3)
- Research On Welding Deformation For Box Girder ofDocument12 pagesResearch On Welding Deformation For Box Girder oframiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perpindahan PanasDocument7 pagesTugas Perpindahan PanasAnonymous DpmprYqkuNo ratings yet
- Manual Thermo IDocument121 pagesManual Thermo IKevin RamiroNo ratings yet
- Locating Levels in Tanks and Silos Using Infrared ThermographyDocument4 pagesLocating Levels in Tanks and Silos Using Infrared ThermographyYeison Camilo Zapata DavidNo ratings yet
- 11P 14 Heat Transfer PDFDocument46 pages11P 14 Heat Transfer PDFkpchakralaNo ratings yet
- Heat Assignment Class 7Document5 pagesHeat Assignment Class 7Anika JoshiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Is The Transition ofDocument11 pagesHeat Transfer Is The Transition of3m3hNo ratings yet
- CH 15 Transmission of HeatDocument53 pagesCH 15 Transmission of HeatCat123No ratings yet
- CFD (Computional Fluid Dynamics) QuizDocument18 pagesCFD (Computional Fluid Dynamics) Quizmsnaghavi100% (1)
- BTech Chemical RevisedDocument46 pagesBTech Chemical RevisedRam Krishan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solidworks Flow Simulation 2012 Tutorial 1Document266 pagesSolidworks Flow Simulation 2012 Tutorial 1Paul Torres J100% (1)
- Olp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Document17 pagesOlp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Shabbir H. KhanNo ratings yet
- 2018 Manual Energy Thermal 12Document35 pages2018 Manual Energy Thermal 12pappadakunduNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy: Abhishek Kumar, Kuljeet Singh, Sunirmit Verma, Ranjan DasDocument15 pagesSolar Energy: Abhishek Kumar, Kuljeet Singh, Sunirmit Verma, Ranjan DasAmandeep RayatNo ratings yet
- 6 Gradient of A Scalar Function: F X F y F ZDocument1 page6 Gradient of A Scalar Function: F X F y F ZakshathNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress MonitoringDocument78 pagesThermal Stress MonitoringSIVA KAVYANo ratings yet
- DLL ScienceDocument5 pagesDLL ScienceMary May LopezNo ratings yet