Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EXCEL Coaching 05 Communication Systems
EXCEL Coaching 05 Communication Systems
Uploaded by
Jaydan AdevaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EXCEL Coaching 05 Communication Systems
EXCEL Coaching 05 Communication Systems
Uploaded by
Jaydan AdevaCopyright:
Available Formats
Jaypee M. David, ECE | Holy Angel university | email: j_ypee@yahoo.com | website: www.enjayneer.
com
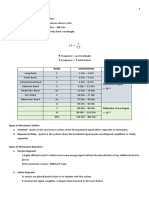
Electronic Systems and Technologies 48. type N connector – lowest attenuation
49. 11 yrs – sunspot cycle radio propagation occurrence
1. 8000 Ix – minimum illumination for reading
50. Mogul-Dellinger fadeout – sudden ionospheric disturbance
2. 2500 ohms – impedance at open end of half wave antenna
frequency
3. 10 Gbps – max data rate of fiber optic system
51. Huffman encoding – most commonly used characters are
4. 8 kbps – data rate of TDMA
represented in fewer bits
5. 500 kbps – 8 Mbps – WiMax
52. acquisition – on time of FETs
6. 27 Mbps – cable Tv internet
53. shared wireless application protocol
7. 32.786 Mbps – H21 broadband ISDN
54. octet – term for byte in ATM
8. 32.28 Mbps – data rate of terrestrial digital TV
55. ISTP cable – used in 10/100 Mbps Ethernet
9. 33.6 kbps – V.34
56. delta modulation – scheme
10. 172.2 kbps – GPRS
57. 460 m – position accuracy of LORAN C/D
11. 72 kbps – Bluetooth
58. 108 MHz – 118 MHz – DME/VOR
12. 10-30 km – max distance bet fiber optic repeaters
59. 108 MHz – 114 MHz – not used in TV
13. 1200 kbps – V.22
60. physical layer – does not use error checking
14. 56 kbps –V.90
61. 28 dB – terminal isolation between subscribers
15. 9.6 kbps – V.32
62. 16 dB – output terminal match
16. 19.2 – speed of cdpp (cellular digital data packet)
63. discriminator – demodulates audio signal in TV
17. 1.23 Mbps – speed of IS-95 CDMA
64. local oscillator – together with mixer
18. 11 Mbps – WiFi / wireless internet service provider
65. balanced detector – not used in mobile tel.
19. IEEE 802.11b – WiFi spec
66. 4 Mhz – guardband of C-band satellite comm.
20. 8-V.58 – standard for digital terrestrial TV
67. basic voice grade – minimum quality circuit available in PTN
21. 9000 ft – spacing between M88 loading coils
68. AWg no. 22 – cable used in customer loop in telephone
22. curve of silence – area above the vertical antenna
exchanges
23. code 39 (bar code ) – discrete code
69. broadband – multichannel
24. near field – under the influence of the induction field
70. scatter angle – dependent in troposcatter propagation
25. local number portability
71. 1000 Hz – standard test tone
26. blocking dynamic range
72. 17 degrees Celsius – reference noise temp
27. 3.5 MHz – FM luminance frequency for VCR recording
73. 4.7 units or sabines– average human absorption
28. PSK digital modulation used for modems
74. acceptance angle = max. critical angle
29. decibel – measure of comparison of sound intensity with
75. internet protocol – software used in preparing packets
another
76. rest frequency – no modulation
30. IMT 2000 – not a 3G wireless system
77. 2520 MHz- U600
31. biphase codes – used in optical system and satellite
78. less than 2 % - CMTS(AMPS)
telemetry links
79. high frequencies – affected by solar cycle
32. facsimile groups – divide into 4 by ITU
80. Speed of longitudinal waves is proportional to the
33. bit oriented protocol – code transparency with frequency
compressibility of the medium
34. 1.6 W – ERP of class 2 cellular mobile
81. EIRP Class II Cellular – 1.6 watts
35. 600 mV – max power for class I analog mobile
82. Electronic Serial Number (ESN) for cellular phone – 32 bits
36. F2 layer – appears at night
83. TV horizontal scan – 10.2 us
37. E layer – high frequency daytime propagation
84. Local Oscillator – always accompanied to the mixer
38. hectometric waves – MF range wavelength
85. 10 pulses/sec – pulse dialing
39. X.75 – protocol for packet switching networks
86. Basic Voice Grade – minimum circuit PTN
40. ARQ – error control for HF radio transmission
87. 3-30 MHz – suitable SSB transmission
41. bridge – operates on physical and data link
88. Bay – complete antenna in itself
42. logic 0 – start bit
89. Quarter-wavelength – minimum antenna height
43. elementary doublet – 1/10 wavelength antenna
90. Session layer – OSI layer for sending and reception of
44. 32 bits – Electronic serial number
information
45. 3-30 MHz – suitable for SSb transmission
91. Physical layer – OSI layer for transmission of bits
46. yellow – most luminance
92. Huffman encoding – coding tech. using lesser no. of bits which
47. below 2 MHz – used by Marconi antenna
are frequently occurring
Jaypee M. David, ECE | Holy Angel university | email: j_ypee@yahoo.com | website: www.enjayneer.com
93. Error correction – not function of the physical layer 140. Companding – protect small signals from quantizing distortion
94. Physical and Data-link layer – bridge operation 141. 3.5 MHz – VCR
95. Yellow – most luminance 142. Current Maximum at the base for ¼ wavelength (Marconi
96. H3E – single-sideband full-carrier Antenna)
97. Shared wireless access protocol 143. Synchronous data transfer – CMT
98. Bi-phase coding – coding used in satellite and telemetry 144. 300-3400 Hz – telephone channel BW
99. Blocking dynamic range – 145. Acquisition – time for FET ‘on’
100. Local number portability – retain local number to access 146. 0-4 kHz – ideal passband for voice grade
(migration) 147. Rest frequency – unmodulated FM frequency
101. Decibel – comparing two power levels 148. 25-8000 Hz – electrical signals converted for microphone
102. 32.786 Mbps – ISDN H21 149. 10-30 km – separation for FOC repeaters
103. Induction field – near filed 150. 2520 kHz – master U600 bandwidth
104. Elementary doublet – one-tenth of wavelength 151. R3E – single-sideband reduced carrier
105. Discrete codes – Code 39 152. 1000 Hz – standard test tone
106. Sudden Ionospheric Disturbance – other term for Mogul 153. 0 dBm – reference sound level
Delinger 154. 3 pair of sidebands – Bessel 1.0 mod
107. Less than 2 MHz – operating frequency of Marconi antenna 155. 50Ω and 75Ω - common coaxial characteristic impedance
108. 11 Mbps – Wi-Fi (802.11b) / Wi-Max 156. Curve of silence – area above antenna
109. IMT-2000 – not included in the 3G wireless system 157. Broadband transmission – ‘multichannel’
110. Discriminator – demodulates audio signal in TV 158. Dead space – due to shading of hills and trees
111. 2500 Ω - impedance at the end of ½ wavelength 159. PSK – modulation used by modem
112. E layer – suitable for high-frequency during daytime 160. X.75 – packet switch data
113. F2 layer – only appears at night 161. Formulas:
114. Acceptance angle – max critical angle
115. 460 m – LORAN C/D position accuracy 162. (phase shift)
116. Branch circuit conductor –
117. Header – ‘raceway’
118. Firewire – fastest multimedia peripherals 163.
119. 4 – no. of divisions of facsimile
120. 28 dB – CATV guard / consumers
121. 16 dB – CATV RF output 164. (d in ft)
122. 8 kbps – data rate for TDMA
123. 600 mV – output Class I mobile output minimum
124. 500 kbps to 8 Mbps – Wi-Fi Max
165. (beamwidth), (G = in gain ratio)
125. Packet – smallest unit data for network
126. Frequency translation –
127. Bandwidth efficiency – information density
128. HF waves – affected by the solar cycle
166.
129. Solar cycle – every 11 years
130. UTC – UTA
131. QPSK (DSSS) – mod used for IS-95
132. 577 us – propagation delay for TDM period 167. →Hartley
133. 45 MHz – difference freq for forward and backward
transmission
134. Directivity gain – gain at the direction of the major lobe
135. Bit-oriented protocol – code transparency 168. 1ppm → →crystal
136. ½ wavelength – AM broadcast antenna height
137. Scanning line – synchronization
138. Scatter angle – causes the attenuation using troposcatter 169. BER = (bit error rate)
propagation
139. Faraday rotation – can be eliminated using helical antenna
You might also like
- All Sim Ussd Code ListDocument1 pageAll Sim Ussd Code ListHahahhssu usus50% (2)
- 1PHN Exam Review NotesDocument44 pages1PHN Exam Review NotesKean Xyrem Tialengko100% (1)
- Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesAntenna SpecificationsRobert100% (1)
- EEE4121F - Solution Totutorial - 1 - 2019Document3 pagesEEE4121F - Solution Totutorial - 1 - 2019ObusitseNo ratings yet
- GX Chassis: Alignment ProceduresDocument26 pagesGX Chassis: Alignment ProceduresLuis Arenas BNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 05 Communication SystemsDocument3 pagesEDGE Coaching 05 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- Coaching Notes Communications2Document1 pageCoaching Notes Communications2abcedeNo ratings yet
- EstDocument3 pagesEstNena GonzalesNo ratings yet
- EST3Document4 pagesEST3Juan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- EXCEL Coaching 01 Communication SystemsDocument4 pagesEXCEL Coaching 01 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 04 Communication SystemsDocument5 pagesEDGE Coaching 04 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 03 Communication SystemsDocument3 pagesEDGE Coaching 03 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EST 4 Sectionc4Document7 pagesEST 4 Sectionc4Ruth Abegail de VeraNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 01 Communication SystemsDocument2 pagesEDGE Coaching 01 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- Est Module 22Document4 pagesEst Module 22k baNo ratings yet
- GSM Sys BurstDocument33 pagesGSM Sys Burstmail.akumar100% (1)
- Est Module 20Document4 pagesEst Module 20k baNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Standardization BureauDocument5 pagesTelecommunication Standardization BureauabcedeNo ratings yet
- COACHING NOTES-comm 2Document6 pagesCOACHING NOTES-comm 2Cedric Kasimero BeronyoNo ratings yet
- Couching EstDocument4 pagesCouching EstCedric Kasimero BeronyoNo ratings yet
- Refer To Kennedy Q&A and Excel's EST Standards Mostly Po Dun Galing.Document6 pagesRefer To Kennedy Q&A and Excel's EST Standards Mostly Po Dun Galing.abcedeNo ratings yet
- Harris Falcon III RF 7800m MP Multiband Networking Manpack Radio 2Document2 pagesHarris Falcon III RF 7800m MP Multiband Networking Manpack Radio 2Ilyes Nigro100% (2)
- The Principle of English)Document55 pagesThe Principle of English)sal_owudaNo ratings yet
- A Fully Integrated Radio-Fiber InterfaceDocument3 pagesA Fully Integrated Radio-Fiber InterfaceSana FatimaNo ratings yet
- What Is Wireless and Mobile Communication?Document21 pagesWhat Is Wireless and Mobile Communication?nabilahnazromNo ratings yet
- Mimosa by Airspan B5c Datasheet DS 0008 09Document2 pagesMimosa by Airspan B5c Datasheet DS 0008 09Ceo DataloginNo ratings yet
- Communications Coaching Notes 5Document6 pagesCommunications Coaching Notes 5Ruth DVNo ratings yet
- Coaching 1Document15 pagesCoaching 1abcedeNo ratings yet
- Wireless CommunicationDocument51 pagesWireless CommunicationPhan Minh HảiNo ratings yet
- EXCEL Coaching 09 Communication SystemsDocument1 pageEXCEL Coaching 09 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- Multiband 60-Ghz Wireless Over Fiber Access System With High Dispersion Tolerance Using Frequency Tripling TechniqueDocument7 pagesMultiband 60-Ghz Wireless Over Fiber Access System With High Dispersion Tolerance Using Frequency Tripling TechniqueSourav DebNo ratings yet
- Mimosa B5c DatasheetDocument2 pagesMimosa B5c DatasheetThyeres CanutoNo ratings yet
- L3Harris Falcon Iii® RF-7800M-MP: Wideband Networking Manpack RadioDocument2 pagesL3Harris Falcon Iii® RF-7800M-MP: Wideband Networking Manpack Radio1 pel com Sl SelvaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Physical LayerDocument63 pagesLecture 3 - Physical LayerKhánh Lương TrầnNo ratings yet
- Turner 5ghz Band n79 Wideband MergedDocument3 pagesTurner 5ghz Band n79 Wideband Mergedzeadzizo715No ratings yet
- Notes MSDocument16 pagesNotes MSPatricia SayamanNo ratings yet
- IMS netADC PDFDocument1 pageIMS netADC PDFBraulio ArayaNo ratings yet
- Bai 7 - Da Truy CapDocument5 pagesBai 7 - Da Truy CapDuc VuNo ratings yet
- Power Consumption and Chip Area Reduction Techniques For Mb-Ofdm Uwb RficsDocument4 pagesPower Consumption and Chip Area Reduction Techniques For Mb-Ofdm Uwb RficsOmarFaruqeNo ratings yet
- EST ReviewerDocument2 pagesEST ReviewerEllaineMaeCasilaganNo ratings yet
- Mimosa by Airspan B5c Datasheet DS 0008 02Document2 pagesMimosa by Airspan B5c Datasheet DS 0008 02Mang Iyus RoninNo ratings yet
- An Allcmos Architecture For A Lowpower Frequencyhopped 900 MHZ SDocument4 pagesAn Allcmos Architecture For A Lowpower Frequencyhopped 900 MHZ SSURAJ SINGHNo ratings yet
- Airborne Mesh Radio XK-M353Document5 pagesAirborne Mesh Radio XK-M353EvgeniiNo ratings yet
- FRENZEL3E - INSTRUCTORS MANUAL PartBDocument37 pagesFRENZEL3E - INSTRUCTORS MANUAL PartBamerico079No ratings yet
- OptiX RTN 320 Brochure 01 PDFDocument2 pagesOptiX RTN 320 Brochure 01 PDFMuhammad Sajid100% (1)
- Netwroks All Full FormsDocument4 pagesNetwroks All Full FormsTanishkaNo ratings yet
- Slides 2Document43 pagesSlides 2Ala AwoudaNo ratings yet
- Principles 1Document66 pagesPrinciples 1Swifty SpotNo ratings yet
- Licensure Assessment Review Evaluation 4 Answers: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesLicensure Assessment Review Evaluation 4 Answers: Rizal Technological UniversityAaron Joseph SolanoNo ratings yet
- Komdat Pertemuan-02 Media Komunikasi DataDocument10 pagesKomdat Pertemuan-02 Media Komunikasi DataZulfa RangkutiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document14 pagesLecture 1Martian 07No ratings yet
- ROF For Wireless CommDocument40 pagesROF For Wireless CommVamsi Krishna BNo ratings yet
- SMART Wireless 2 WEBDocument2 pagesSMART Wireless 2 WEBTúlio AbduaniNo ratings yet
- Est Module 25Document8 pagesEst Module 25k baNo ratings yet
- Transmission: Media &systemDocument32 pagesTransmission: Media &systemManoj BorahNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: Presented By: Manish Kumar, SENSEDocument57 pagesTransmission Media: Presented By: Manish Kumar, SENSEIyyaasuu YaadataaNo ratings yet
- WiMAX Technology SolutionsDocument43 pagesWiMAX Technology SolutionsDoriedNo ratings yet
- RTN 320 BrochureDocument2 pagesRTN 320 BrochureGerfrank Gonzalez100% (1)
- Farlink TDDDocument4 pagesFarlink TDDaahmadzamri100% (1)
- 4.0 Communication Systems (Basics) : Prepared By:-Ajay Kumar Kadel, Kathmandu Engg. CollegeDocument5 pages4.0 Communication Systems (Basics) : Prepared By:-Ajay Kumar Kadel, Kathmandu Engg. Collegeajaykumar988No ratings yet
- Investigating 802.11A Wireless Standard For High Speed Network Using Different Modulation TechniquesDocument5 pagesInvestigating 802.11A Wireless Standard For High Speed Network Using Different Modulation TechniqueserpublicationNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDFrom EverandRadio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDNo ratings yet
- MC Data CommunicationDocument8 pagesMC Data CommunicationJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- MC Maritime RadioDocument8 pagesMC Maritime RadioJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- MC Broadcasting Laws and RegulationsDocument8 pagesMC Broadcasting Laws and RegulationsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 07 Communication SystemsDocument1 pageEDGE Coaching 07 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 06 Communication SystemsDocument4 pagesEDGE Coaching 06 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EXCEL Coaching 08 Communication SystemsDocument12 pagesEXCEL Coaching 08 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 05 Communication SystemsDocument3 pagesEDGE Coaching 05 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 04 Communication SystemsDocument5 pagesEDGE Coaching 04 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 01 Communication SystemsDocument2 pagesEDGE Coaching 01 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EXCEL Coaching 09 Communication SystemsDocument1 pageEXCEL Coaching 09 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EXCEL Coaching 07 Communication SystemsDocument10 pagesEXCEL Coaching 07 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EXCEL Coaching 06 Communication SystemsDocument8 pagesEXCEL Coaching 06 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EXCEL Coaching 01 Communication SystemsDocument4 pagesEXCEL Coaching 01 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- EDGE Coaching 03 Communication SystemsDocument3 pagesEDGE Coaching 03 Communication SystemsJaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- Algebra MCQ PERCDC Compilations 03Document12 pagesAlgebra MCQ PERCDC Compilations 03Jaydan AdevaNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication - An IntroductionDocument19 pagesSatellite Communication - An IntroductionThembelanienkosini ChikhambiNo ratings yet
- Zoll AED Plus Operators GuideDocument2 pagesZoll AED Plus Operators GuideZepo DepoNo ratings yet
- Application of GPR Studies For Subsurface Utility Mapping of Panaji Smart City, GoaDocument4 pagesApplication of GPR Studies For Subsurface Utility Mapping of Panaji Smart City, GoaMohammad RafiqNo ratings yet
- Voice Alarm DesignDocument3 pagesVoice Alarm DesignMMMOH200No ratings yet
- Transmission Details - PB2Document3 pagesTransmission Details - PB2Daniel Herrera AstudilloNo ratings yet
- IBS (In Building Solution) Installation Acceptance Checklist: Sap Id Site Name CircleDocument17 pagesIBS (In Building Solution) Installation Acceptance Checklist: Sap Id Site Name CircleShamsuddin Shams100% (1)
- Pronoun Spotting Error BoardDocument10 pagesPronoun Spotting Error Boardsanjaykumar919212No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Multiple Access TechniquesDocument30 pagesChapter 8 - Multiple Access TechniquesDr. Mudita JunejaNo ratings yet
- AcuMesh Wireless RS485 Network User ManualDocument22 pagesAcuMesh Wireless RS485 Network User Manualenergy8001No ratings yet
- 10th Penguin English Practice Book & Question Bank-WatermarkedDocument36 pages10th Penguin English Practice Book & Question Bank-WatermarkedVettrivel V 8th bNo ratings yet
- Adrv 9002Document92 pagesAdrv 9002rajNo ratings yet
- Bop It SmashDocument2 pagesBop It SmashRICARDO FRANCISCO CUZQUEN ALCASNo ratings yet
- Towards An Integrated Photonics-Based RadarDocument4 pagesTowards An Integrated Photonics-Based RadarSuzanne MeloNo ratings yet
- Population Exposure To Radiation Emitted by Mobile Networks in Abidjan Cote DivoireDocument12 pagesPopulation Exposure To Radiation Emitted by Mobile Networks in Abidjan Cote DivoireHoussem TeberNo ratings yet
- L3Harris Rf-5833H Series: 150 Watt HF/VHF Power AmplifiersDocument2 pagesL3Harris Rf-5833H Series: 150 Watt HF/VHF Power Amplifiersfalcom2100% (2)
- CS42448 Audio DAC ADCDocument66 pagesCS42448 Audio DAC ADCQuinta EspNo ratings yet
- MSC ThesisDocument122 pagesMSC ThesisJohnNo ratings yet
- AESA For ShipsDocument14 pagesAESA For Shipsanon_815621938No ratings yet
- QPA2237 Data SheetDocument17 pagesQPA2237 Data SheetBatuhan ALTINKÜPENo ratings yet
- Grundig 55 VLE 9372 SL EN PDFDocument88 pagesGrundig 55 VLE 9372 SL EN PDFMihai IulianaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Generator, Pulse Generation Method, Communication Apparatus and Communication MethodDocument4 pagesPulse Generator, Pulse Generation Method, Communication Apparatus and Communication Methodnthung115No ratings yet
- Afr1056 Flight DispatchDocument41 pagesAfr1056 Flight Dispatchabang fayyadNo ratings yet
- Receptor NE602 DCDocument1 pageReceptor NE602 DCMiguel OyarzabalNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: TA-FB930RDocument24 pagesService Manual: TA-FB930RMaikel Borges IglesiasNo ratings yet
- DCS AJS-37 Viggen GuideDocument135 pagesDCS AJS-37 Viggen GuideAlex WhiteNo ratings yet