Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C9: Ue Neurovascular Structures: Files Term
C9: Ue Neurovascular Structures: Files Term
Uploaded by
not meOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C9: Ue Neurovascular Structures: Files Term
C9: Ue Neurovascular Structures: Files Term
Uploaded by
not meCopyright:
Available Formats
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR
STRUCTURES
Files
Term
Waiters Tip
problem of the nerves
paralysis of the arm caused by injury to the upper group of the arm's main
nerves
severing C5, C6 nerves
the affected UE manifests:
medially roatted
extended
pronated
hangs by px side in adduction
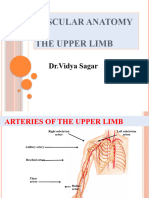
UE ARTERIAL SYSTEM
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 1
BLOOD VESSELS
Arteries - sends blood from the heart
Veins - sends blood away from the heart
Capillaries
Nerve - transmit electrical impulses for movement
*Myocardial Infarction occurs when the LEFT VENTRICLE STOPS
HEART
Left Ventricle - pumps blood out of the heart
Aorta - connects left ventricle to the parts of the body
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 2
3 BRANCHES:
Ascending
Descending
Arch of Aorta
RIGHT: LEFT:
Brachiocephalic Left common carotid artery
Right common carotid artery Left subclavian artery
Right subclavian artery Suprascapular artery
Superficial cervical artery
*Pulse is an artery
Subclavian Artery
main trunk
blood supply to UE
from brachiocephalic to 1st rib
*changes its name after the 1st rib into AXILLARY ARTERY
→ 1st rib to teres major
→ continuation of subclavian artery
→ PARTS
1st part of axillary artery:
Superior Thoracic Artery → upper border of pectoralis minor
2nd part of axillary artery:
Thoracoacromial artery - divides terminal branches
Arterial thoracic artery - lower border of pectoralis minor
3rd part of axillary artery:
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 3
Anterior circumflex humeral artery
Posterior circumflex humeral artery - front and back of surgical neck
Subscapular artery - lower border of subscapularis
*After teres major is the BRACHIAL ARTERY
→ includes the:
Brachial Artery - main arterial supply of the arm from the lower border of teres
major
Nutrient Artery
Profunda Artery - radial collateral → radial recurrent → radial artery
Superior Ulnar collateral Artery - near and follows Ulnar Artery→
anastamose @ elbow joint
Inferior Ulnar collateral Artery
Radial Artery - lateral side
Arterial radialis indicis
Arterial radialis policis
Ulnar Artery - medial side; enters palm through FR
Anterior ulnar recurrent
Posterior ulnar recurrent
Superior palmar arch
- joining or radial and ulnar artery at the palm
- form an arch at the palm
PULSE
same as rate of heartbeat
an artery
if there's no pulse = LEFT VENTRICLE stopped pumping
CUBITAL FOSSA
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 4
front of elbow
Lateral: Brachioradialis Base: 2 condyles of humerus
Medial: Pronator Teres Floor: Supinator, Brachialis
UE VENOUS SYSTEM
from muscles/organs to heart and lungs
brings unoxygenated blood
usually blue
SUPERFICIAL VEIN
Cephalic vein
drains blood from lateral side → ascends cubital fossa → lateral from biceps
converges on subclavian vein
Basilic vein
drains blood from medial side → venae comitantes of brachial artery → axillary
vein
converges on subclavian vein and eventually drain to subclavian vein
Subclavian vein
internal
external
Superior vena cava
on medial side or biceps
medial cubital vein → branch of cephalic vein in cubital fossa
→ runs upward and medially → join basilic vein
medial antecubital vein
Dorsal venous network
hand
drains upward to lateral cephalic vein & medial basilic vein
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 5
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
drain waste products from your body at lateral
Lymph Nodes
sac thics - of axilla - drain at lateral quadrant
Supraclavicular lymph nodes - above the clavicle
Apical lymph nodes - apex
Central lymph nodes
Humeral lymph nodes
TRansverse cervicla chain lymph nodes
Interpectoral lymph nodes
Cubital lymph nodes
Supratrochlear lymph nodes
NERVES
→ sensory innervation to skin and deep structures
→ motor innervation to muscles
Atlas C1 - carrying the load of the skull
Axis C2
C3
C4
C5
Foramen Transversarium
hole on cervical vertebra
houses vetebral artery
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 6
Spinal Cord gives out:
Spinal Nerves:
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
EXITS C - Cervical
CTLS: DUD T - Thoracic
NERVE IMPINGEMENT Ls - Lumbosacral
CTLS: DUU D - Down
U - Up
Nerves of UE
C5 - Superior Trunk
C6 - Superior Trunk
C7 - Middle Trunk
C7 - Inferior Trunk
T1 - Inferior Trunk
Divisions
-Each divides into Anterior Division & Posterior Division
Cords
→ Lateral Cord
→ Posterior Cord
→ Medial Cord
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 7
MNEMONICS: ROTONDA CUBAO 22355
2 nerves come directly from the ROOT
2 nerves come directly from the TRUNK
3 nerves from LATERAL CORD
5 nerves from POSTERIOR CORD
5 nerves from MEDIAL CORD
UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURE
Two structures: Nerves & Vascular structures
Waiter’s Tip
Problem in the nerves
Nerve palsies or Erb’s duchenne Palsy
Affected upper limb is medially rotated, extended, pronated, and hangs by the
patient’s side in adduction
UE ARTERIAL SYSTEM
“Ugat”
Refers to all in the local dialect
Can be nerves or blood vessels
Nerve
Transmits electrical impulses from brain to muscles to make them move
Blood vessels
Contains blood / container of blood
Arteries, veins, capillaries
To send blood from the heart to bring oxygenated & deoxygenated blood to the
organ and away from the organ & to spread nutrients, oxygen, chemicals, &
other elements to tissues
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 8
Artery
Blood vessels that sends oxygenated blood from the heart to organs
Color red (contains oxygenated blood)
Heart
Has four chambers (left & right atrium and ventricle)
Left ventricle
Pumps blood out of the heart
When it stops pumping, no more organ that will send blood all over the body
Aorta
From left ventricle, huge blood vessel
connects left ventricle to the rest of the body
shaped like an arch
has 3 branches: Ascending aorta, arch, descemding/thoracic artery
Arch of aorta
or aortic arch
has three main branches; brachiocephalic artery, left common carotid, left
subclavian
Brachiocephalic artery
biggest of the three
right common carotid & right subclavian
a jump off of the right subclavian and right common carotid
Left subclavian & left common carotid
Direct branches of the arch of aorta
in the end we have both right & left subclavian and common carotids
Common carotid artery
as it ascends in front of neck will further divide into external and internal carotid
arteries (both left & right)
left internal/external
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 9
right internal/external
(LEFT)
Arch of aorta
Left common carotid
Eventually branching out into left external & internal carotids
Subclavian Artery
main trunk which will be the blood supply to the upper extremities
left & right subclavians – will be the origin of blood supply to the UE
from brachiocephalic to first rib
Pulse
also an artery
pulsating because of all the blood vessels
pumping of artery (pulse) same as rate of the heartbeat
heart rate is synchronosous w/ arterial pulses as well
To assess if heart is pumping:
a person w/ big breast or large thorax – you can palpate pulse, if there is no
pulse – left ventricle has stopped pumping
B O R D E R S:
Subclavian artery
located in the root of the neck
jumps off the brachiocephalic until the first rib
Axillary artery
from first rib to thee teres major
throughout its course, it is closely related to cords of the brachial plexus and
their branches
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 10
is enclosed in an axillary sheath
pectoralis minor crosses in front of the axillary artery and divides into three: 1, 2,
3
Axillary sheath
connective tissue sheath
continuous with the pre-vertebral fascia in root of the neck
First part
extends from lateral border of first rib to upper border of pectoralis minor
gives off one branch; superior thoracic artery
Second part
lies deep to the pectoralis muscle(pec minor)
gives off two branches; thoracoacromial artery and lateral thoracic artery
Third part
extends from lower border of pectoralis minor to lower border of teres
major
gives off three branches; posterior & anterior circumflex humeral artery
and subscapuar artery
Brachial artery
from lower border of teres major muscle and continues downward – travels
through anterior compartment of arm
its branches supply both anterior & posterior compartment of arm – supplies
entire arm
terminates opposite the neck of the radius dividing into: radial and ulnar arteries
Radial artery
radial pulse that you can palpate near thumb (on lateral side of wrist)
palpated in the anatomic snuff box
Anatomical Snuff box
also known as radial fossa
a triangular depression found on the lateral aspect of the dorsum of hand
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 11
located at the level of the carpal bones and best sen when thumb is
extended
B R A N C H E S:
Muscular branch
To anterior compartment of arm
Nutrient artery
To the humerus
Profunda brachii artery/ arteria profunda brachii
Or deep brachial artery
Arises near the origin of the brachial artery
Accompanies radial nerve through radial (spiral) froove of humerus &
supplies triceps muscles
Anastomoses w/ radial recurrent artery (branch of the radial artery) – to
from part of the collateral circulation around elbow joint
Superior ulnar collateral artery
Arises near middle of arm & follows ulnar nerve
Posterior to medial epicondyle
Anastomoses w/ posterior ulnar recurrent artery ( branch of ulnar arter)
– to form part of the collateral circulation around elbow joint
Inferior ulnar collateral artery
Arises near termination of brachial artery & passes anterior to medial
epicondyle
Anstomoses w/ anterior ulnar recurrent artery (branch of ulnar artery) –
to form part of collateral circulation around elbow joint
Ulnar Artery
larger of two terminal branches of the brachial artery
begins in cubital fossa at level of the neck of the radius
forms superficial palmar arch
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 12
often anastomosing w/ superficial palmar branch of radial artery
In forearm
proximally) lies deep to most of the flexor muscles
(distally) becomes superficial and lies between tendons of flexor carpi
ulnaris & tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis
Forearm Branches
Muscular branches
To neighboring muscles
Anterior & posterior ulnar recurrent branches
Take part in the arterial anastomoses around the elbow joint
Branches taking part in the arterial
Anastomoses around wrist joint
Common interosseous artery
From upper part of ulnar artery and after brief course, divides into anterior and
posterior interosseous arteries
Interosseous arteries
Pass distally on the anterior and posterior surfaces of the interosseous
membrane
Provide nutrient arteries to the radius aand ulna
Supply adjacent muscles in the entrior and posterior compartments
End by taking part in anastomosis around the wrist joint
In Hand
Enters hand superficial to the flexor retinaculum on the lateral side of ulnar nerve
& pisiform bone
Gives off a deep palmar branch then continues into the palm as superficial
palmar arch
Superficial palmar arch
Curves laterally deep to the palmar aponeurosis & superficial to the long flexor
tendons
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 13
Completed on the lateral side of by anastomosing with the superficial palmar
branch of the radial artery
Curve of arch, lies across the palm, level w/ the distal border of the fully
extended thumb
Gives rise to 3 common palmar digital arteries – each dividing into two proper
palmar digital arteries – supply the adjacent sides of two digits
Deep palmar branch
Of UA, arises superficial to the flexor retinaculum
Passes deep between the abductor digiti minimi & the flexor digiti minimi, and
joins the radial artery to complete the deep palmar arch
Radial Artery
Is the smaller of the two terminal branches of the brachial artery
Begins in the cubital fossa at the level of the neck of the radius and descends
through the lateral (radial) aspect of the anterior compartment of the forearm
Ends by forming the deep palmar arch in hand, often anastomosing with the
deep palmar branch of the ulnar
In forearm
(proximal forearm) radial artery lies deep to the brachioradialis muscle
(middle third of its course) runs medial to the superficial branch of the radial
nerve
(distal forearm) lies on the anterior surface of the radius, between the tendons
of the brachioradialis and flexor carpi radialis muscle
Covered only by the skin and fascia
Ideal site for taking the radial pulse
FOREARM BRANCHES:
Muscular branches
To neighboring muscles
Radial recurrent artery
Takes part in the arterial anastomosis around the elbow joint
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 14
Superficial palmar branch
Arises just proximal to the wrist
Enters the palm of hand and joins the ulnar artery to complete the superficial
palmar arch
In Hand
Radial artery, leaves the forearm by winding around the lateral aspect of the
wrist to reach the posterolateral surface of the hand
Enters the floor of the anatomic snuffbox, lying on the lateral ligament of the
wrist joint and passing deep to the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus &
extensor pollicis brevis muscles
Continues under the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus to reach the interval
between the two heads of the first dorsal interosseous muscles
Artery divides between the muscle heads to enter the deep aspect of the palm of
the hand
(upon entering the palm), RA curves the medially between the oblique and
transverse heads of the adductor pollicis & continues as the deep palmar arch
Deep Palmar Arch
Curves medially deep to the long flexor tendons & superficial to the metcarpal
bones and interosseous muscles
Completed on the medial side by the deep palmar branch of the ulnar artery
Curve of arch, lies at a level of with the proximal border of the external thumb
Sends branches proximally, which take part in anastomoses with wrist joint and
distally to join the digital branches of the superficial palmar arch
Dorsal carpal arch
On the dorsum of the hand, by the radial artery
Before it dives to form the deep palmar arch
TRACE THE BLOOD FLOW FROM LEFT VENTRICLE TO THE RADIAL PULSE
1. Aorta
Ascending, arch, descending/thoracic
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 15
1. Arch of aorta
Brachiocephalic, left common carotid, left subclavian
1. Brachiocephalic
Right common carotid & right subclavian
1. Common carotids
Left and right, ascend in front of neck to brain
Further divides into external and internal carotid artery
1. Subclavian
(left & right) blood suppy for the UE
1. Subclavian artery
From brachiocephalic artery to first rib
1. Axillary artery
First rib to teres major; 3 parts (1, 2, 3)
First (1 branch), second (2 branches), & third (3 branches)
1. Brachial artery
Teres major downwards
Also the brachial pulse w/c can be palpated on medial side of forearm
Further divides into radial & ulnar artery forming superficial palmar arch
Ulnar & radial artery, forms superficial palmar arch
UE VENOUS SYSTEM
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 16
Veins
Travels in the opposite direction from muscles and/or organs will send blood
back to heart to the lungs, so that these blood will exchange CO2 w/ O2 and will
come out again in the form of oxygenated blood
Color blue
Not as complicated as the arterial system; it is simple
Cephalic vein
On lateral side of the dorsal venous rch on the base of hand and winds around
lateral border of foramen
Drains all blood from the lateral side/subclavian
Converge in the area of subclavian vein
Medial cubital vein
A branch of cephalic vein in cubital fossa
Runs forward upward & medially and joins basilica vein
Normally present, but form in w/c it connects cephalic and basilic veins, is
subject to variation
(in cubital fossa) crosses over brachial artery and median nerve, but separated
from them by – bicipital aponeurosis
Basilic & Cephalic vein, likewise will form a network in the hands so that when
on vein is clot the hand will still be drained by the other vein – dorsum venous
network
Veins, always on the medial side
From the subclavian vein it will go down directly into the superior vena cava
(both sides)
In comparison to the arteries which has the brachiocephalic artery in the veins it
is direct
Subclavian Vein Jugular Vein Superior Vena C.
Superior Vena Cava
Drains the head up to the upper extremity
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 17
Ehen there is a clot, there will be congestion and swelling of face, neck, & upper
extremities because blood cannot be drained from finger tips back to the right
atrium
only drains the head through the internal & external jugulars and subclavian vein
(UE) to the superior vena cava
Inferior Vena Cava
From the chest and down
Will drain blood from the top and the legs
Axillary vein
Formed at the lower border of the teres major muscle by the union of the venae
comitantes of the brachial artery & the basilica vein
Runs upward on medial side of axillary artery & ends on lateral border of first rib
becoming the subclavian vei
Receives tributaries, w/c correspond to branches of axillary artery & cephalic
vein
SUMMARY
The venous system is not as complicated as the arterial system, on the lateral side is
the cephalic vein whch goes up & goes to the subclavian vein. On the medial side
is the basilica vein w/c will become an axillary vein & eventually drain in the
subclavian vein – together w/ internal & external jugulars will drain into superior
vena cava
UE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Carries debris, waste products, and infections
Chain of structures that will drain all the waste products from the body
Do not go in one single tube, unlike arteries & veins _ lymphatics
Color green
Lymphatic Veins
“pangadlay”
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 18
If you have a tooth infection you will feel you have nodes under your jaw
because the dirt of tooth will be drine in that area
Ex. punctured self (wound in fingers) – lymph adenopathy is in axilla
Lymph nodes
Does not travel in the same manner as the arteries & veins in one pathway
rather, they can travel in different pathways in a mesh-like structure
Supraclavicular lymph nodes
above the clavicle
Interpectoral lymph nodes
Between pectoralis minor & major
Transverse cervical chain of lymph nodes
Cervical (deep), supraclavicular, subclavicular, upper chest, anterior lateral
neck
Apical lymph nodes
Apex or tip of lungs
Central lymph nodes
Axilla
Humeral lymph nodes
Near humerus
Cubital lymph nodes
Near elbows
Supratrochlear lymph nodes
Above the trochlea
Axillary Lymph Nodes
(20 to 30 in number) collect lymoh from a large territory
Drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast, superficial lymph
vessels form the thoracoabdominal walls above level of umbilicus, skin of the
back above level of the iliac crest, & vessels from the upper limb
ARRANGED IN SIX GROUPS
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 19
1. Anterior (pectoral) group
Along lower border of the pectoralis minor, deep to the pectoralis minor
Receive lymph vessels from lateral quadrants of breast and superficial vessels
from the anterolateral abdominal wall above levl of umbilicus
1. Posterior (subscapular) group
In front of subscapularis muscle
Receive superficial lymph vessels from the back, down as far as the level of iliac
crests
1. Lateral group
Along medial side of axillary vein
Receive most of the lymph vessels of the upper limb (except those superficial
vessels draining the lateral side – see infraclavicular nodes below)
1. Central group
In center of axilla, in the axxillary fat deep to the pectoralis minor
Receive lymph from the three groups above
1. Infraclavicular (deltopectoral) group
Not strictly axillary nodes because they are located outside axilla
In deltopectoral groove between deltoid & pectoralis major
Receive superficial lymph vessels from the lateral side of the hand, forearm, &
arm
1. Apical group
At apex of axilla, at internal border of first rib
Receive efferent lymph vessels from all the other axillary nodes
Apical Nodes
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 20
Drain into the subclavian lymph trunk
Subclavian lymph trunks
(left side) drain into the thoracic duct
(right side) drains into right lymph trunk
(alternatively) may drain directly into one of the large veins at the root of the
neck
Superficial lymph vessel
Draining the superficial tissues of the upper limb pass upward to the axilla
Lymph vessels of fingers
Pass along their borders to reach the webs
Vessels ascend onto the dorsum of the hand
Lymph vessels on palm
Form a plexus that is drained by vessels that ascend in front of forearm or
pass around medial and lateral border to join vessels on dorsum of the hand
Lymph vessels, thumb, lateral fingers, and lateral areas of hand,forearm, &
arm – follows the cephalic vein to the infraclavicular group of nodes
Superior vessels from medial fingers & medial areas of hand & forearm
follow basilica vein to cubital fossa
some drain into supratrochlear lymph node, others accompany basilica vein to
the axilla – where they drain into the lateral group of axillary nodes
Supratrochlear lymph nodes
superficial fascia over upper part of the cubital fossa, above the trochlea
Efferent Vessels
also drain into the lateral axillary nodes
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 21
Deep Lymphatic Vessels
draining the muscles & deep structures of the arm
Deep Structures of arm
drain into lateral group of axillary nodes
Brachial Plexus
the entire nerve supply of the upper limb
a complex nerve network formed when the anterior (ventral) rami of the 5
through the 8 cervical & 1 throracic spinal nerves (C8; T1) intermingle with one
another in the posterior triangle of the neck
I M P O R T A N T F U N C T I O N S
sensory innervations to skin & deep structures; joints
motor innervations to muscles
influence over the diameters of the blood vessels by the sympathetic vasomotor
nerves
sympathetic secremotor supply to the sweat glands
C1 – atlas, carrying load of skull ; C2 – axis
Cervical Vertebra
of the spine consist of 7 bony rings that reside in the neck between base of skull
& thoracic vertebrae in trunk
unique because of/ they have foramen transversarium
Foramen Transversarium
hole in the transverse process of cervical vertebra
Houses the vertebral artery
Vertebral artery
Inside hole of vertebra
Die instantaneously if cut because it cuts-off blood supply in the brain
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 22
Spinal Cord
On neck, inside vertebra
Will give out a nerve: C1, C2, C3, C4 nerves
Spine
divided into; thoracic, cervical, lumbar, & sacral area
Nerve Fibers
originate in single segments of the spinal cords
contribute to the composition of multiple individual nerves
each that branches off, carries fibers from multiplbe segments of the spinal cord
Spinal Root
C5, C6, C7, C8; T1 nerves – brachial plexus
Origin of entire brachial plexus
17 nerves in UE
From roots to trunk
C5 & C6 – superior trunk
C7 – middle trunk
C8 & T1 – inferior trunk
From trunks to divisions
Each trunk is divided into anterior & posterior divisions
From divisions to cords
Lateral cord
All division of superior & middle cord
Posterior cord
All posterior divisions of 3 trunks
Medial cord
Anterior divisions of inferior trunk
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 23
Named in relation to the axillary artery (point of reference)
Branches of the brachial plexus
17 branches all together
ROTONDA CUBAO (22355)
Roots (2)
Long thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7)
Dorsal scapular nerve (C5)
Trunks (2)
(both are in the upper/superior trunk)
Suprascapular nerve
Nerve to subclavius
Lateral Cord (3)
Musculocutaneous berve
Lateral pectoral nerve
Median nerve from lateral cord
Posterior Cord (5)
Axillary nerve
Upper subscapular nerve
Lower subscapular nerve
Thoracodorsal nerve
Radial nerve
Medial Cord (5)
Medial pectoral nerve
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 24
Medial cutaneous of arm
Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm
Median nerve from medial cord
Ulnar nerve
SUBPARTS
Roots
the anterior rami of the spinal nerves
C5 to T1; C5 & 6 (forms upper trunk), C7 (middle trunk), and C8 & T1 (lower
trunk)
Trunks
Upper, middle, & lower trunk
Divisions
Anterior & posterior
Cords
Lateral, medial, & posterior
Lateral cord
Formed when anterior divisions or the upper & middle trunks unite
Gives rise to the musculocutaneous nerve
Contributes to the formation of the median nerve
Medial cord
Anterior division of lower trunk continues
Gives rise to the ulnar nerve
Contributes to the formation of the median nerve
Posterior cord
Formed when posterior divisions of all three trunks join
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 25
Divides into axillary and radial nerves
Branches
Axillary nerve
Supplies the shoulder region
Supplies teres minor & deltoid muscle
Gives off branches after the shoulder / glenohumeral joint
Can be injured in dislocations of the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint by
compression of the quadrangular space or by pressure of a badly ajudted crutch
pressing upward into armpit
Other four nerves
main branches that distribute through the osseofascial compartment of the upper
limb
Musculocutaneous Nerve
Fisrt muscle it innervates is the coracobracjialis in the axilla down to biceps and
the brachialis (CBB), lower than that has a lateral cutaneous branch – Lateral
cutaneous branch of forearm
Median Nerve
Innervates the wrist flexor muscles in volar surface of arm
Muscles of arm has several layers; upper most – pronator teres
First muscle it innervates is the pronator teres further down it gives off the
muscles in the profundus & flexor pollicis, later on it will supply all the small
muscles of thumb (thenar eminence); flexor pollicis brevis, flexor oponens,
adductor pollicis
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Impingement of median nerve in the wrist
Paralysis of muscle of thethumb
Any condition that decreases size of carpal tunnel & compresses its contets
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 26
Burning pain or “pins and needles” sensation to the lateral 3 ½ fingers &
weakness of the thenar muscles
Decompressing tunner – receives the syndrome
Ape Hand
Median nerve palsy
Condition in which movements of the thumb are severely limited
Ulnar Nerve
Supplies the medial side of the forearm & in sensory division is the lateral 3 ½ is
median and medial 1 ½ is ulnar
First muscle it innervates is the flexor carpi ulnaris & hypothenar muscles (area
below elbow)
Does not give off branches on axillary area and in upper arm as wel
@ ulnar distribution – if patient complains a tingling sensation in lie with little
figer
@ median nerve – tingling of thumb, index, middle, & half of ring finger
BRANCHES
Superficial branch
Supplies skin of palmar surface of medial 1 ½ fingers including nail beds
Supplies Palmaris brevis muscle
Deep branch
Supplies all small muscles of hand except muscles of the thenar compartment
and first two lumbricals which are supplied by median nerve
Froment’s Sign
Adducting thumb is impossible because the adductor pollicis muscle is paralyzed
Patient is asked to grip piece of paper bet. thumb & index (pinching) he/she does
so, by strongly contracting flexor pollicis longus &flexing the terminal phalanx
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 27
Papal’s hand
Or main en griffe, “claw hand”
Hand assumes a characteristic claw-like deformity with clawing more
pronounced on medial (ulnar) aspect of hand
Radial Nerve
Supplies the triceps muscle (medial head, innervated twice)
Eventually goes down to supply muscles of dorsal forearm for wrist extension
Radial nerve palsy
Or Saturday night palsy / sweetheart’s palsy
Paralysis of the radial nerve
Path of radial nerve from axilla
Winds around the radial groove of humerus
Radial groove
Area where radial nerve gets impinged
Wrist drop
Radial nerve palsy
May be caused due to trauma to the radial nerve by way of a cut r stab wound
A pathological condition
OTHER PALSIES:
Erb Duchenne’s Palsy
(C5 & C6) or upper brachial plexus plexus palsy
Present with a typical waiter’s tip deformity
Inability to flex elbow (C5) & wrist extension (C6)
Can occur to babies during birth
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 28
Klumpke’s Palsy
In axillary area
(C8 & T1), or lower brachial plexus injury/palsy
Can be caused by traction – traction injury or stretch injury
“claw like”
ROOTS
Dorsal scapular nerve
C5
Supplies the levator scapula & rhomboid muscles
Long thoracic nerve
C5, 6, 7
arises from the roots of the brachial plexus in the neck and enters the axilla by
passing down over the lateral border of the 1st rib behind the axillary vessels
and brachial plexus
It descends over the lateral surface of the serratus anterior muscle, which it
supplies.
T R U N K S & D I V I S I O N S
Nerve to subclavius
C5, 6
Important clinically, it gives a contribution (C5) to the phrenic nerve
If present, referred to as the accessory phrenic nerve
Suprascapular nerve
C5, 6
Arises in the posterior triangle in the neck and runs downward & laterally to
reach the upper edge of the scapua
It passes through the suprascapular notch, beneath the suprascapular ligament,
to reach the supraspinous fossa
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 29
L A T E R A L C O R D
Lateral pectoral nerve
Supplies the pectoralis major muscle, primarily its clavicular head
Musculocutaneous nerve
Supplies the coracobrachialis muscle & leaves the axilla by piercing that muscle
Lateral root of the median nerve
is the direct continuation of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus
It is joined by the medial root to form the median nerve trunk, and this passes
downward on the lateral side of the axillary artery
The median nerve gives off no branches in the axilla.
M E D I A L C O R D
Medial pectoral nerve
supplies and pierces the pectoralis minor muscle, and supplies the pectoralis
major muscle, primarily its sternocostal head
Medial cutaneous nerve of arm
T1
Arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus and is joined by the
intercostobrachial nerve (lateral cutaneous branch of the 2nd intercostal nerve)
supplies the skin and medial side of the arm
Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm
arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus and descends in front of the
axillary artery
supplies the skin and medial side of the forearm
Ulnar nerve
C8; T1
arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus and descends in the interval
between the axillary artery and vein
gives off no branches in the axilla
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 30
Medial root of the median nerve
arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus
crosses in front of the third part of the axillary artery to join the lateral root of the
median nerve & form the median nerve trunk
P O S T E R I O R C O R D
Upper & lower subscapular nerve
Supply the upper and lower parts of the subscapularis muscle
Lower subscapular nerve supplies the teres major muscle
Thoracodorsal nerve
Arise from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus
Runs downward into the axilla and supply the latissimus dorsi muscle
Axillary nerve
(C5, 6)
curves deeply into axilla and passes through the quadrangular space with
posterior circumflex humeral artery
Radial nerve
(C5, 6, 7, 8; T1)
Gives off branches to the heads of the triceps muscle and gives rise to the
posterior cutaneous of the arm
originates from the posterior cord of brachial plexus in the axilla
Named for its pathway along the radial (lateral) side of the upper limb
Is the sole motor nerve to the muscles in the posterior compartments of the arm
and forearm
Also provides extensive cutaneous innervations along the posterior aspect of the
entire limb
Dermatomes of UE
Skin, sensation, sensory contribution in UE
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 31
Area of the skin of the human anatomy that is mainly supplied by branches of a
single spinal sensory nerve root
Myotomes of UE
For strength, a group of actions supplied by a particular group
Brachial Plexus
- the entire nerve supply of the upper limb
- a complex nerve network formed when the anterior (ventral) rami of the 5th through
the 8th cervical & 1st throracic spinal nerves (C8; T1) intermingle with one another in
the posterior triangle of the neck
IMPORTANT FUNCTIONS
sensory innervations to skin & deep structures; joints
motor innervations to muscles
influence over the diameters of the blood vessels by the sympathetic vasomotor
nerves
sympathetic secremotor supply to the sweat glands
Nerve Fibers
- originate in single sements of the spinal cords
- contribute to the composition of multiple individual nerves
- each that branches off, carries fibers from multiplbe segments of the spinal cord
SUB PARTS
Roots
- the anterior rami of the spinal nerves
- C5 to T1; C5 & 6 (forms upper trunk), C7 (middle trunk), and C8 & T1 (lower trunk)
Trunks
- Upper, middle, & lower trunk
Divisions
- Anterior & posterior
Cords
- Lateral, medial, & posterior
Lateral cord
- Formed when anterior divisions or the upper &
middle trunks unite
- Gives rise to the musculocutaneous nerve
- Contributes to the formation of the median nerve
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 32
Medial cord
- Anterior division of lower trunk continues
- Gives rise to the ulnar nerve
- Contributes to the formation of the median nerve
Posterior cord
- Formed when posterior divisions of all three trunks join
- Divides into axillary and radial nerves
Branches
Axillary nerve
- Supplies the shoulder region
Other four nerves
- main branches that distribute through the osseofascial compartment of the upper
limb
ROOTS
Dorsal scapular nerve Long thoracic nerve
- C5 - C5, 6, 7
- Supplies the levator scapula & - arises from the roots of the brachial
rhomboid muscles plexus in the neck and enters the axilla
by passing down over the lateral border
of the 1st rib behind the axillary vessels
and brachial plexus
- It descends over the lateral surface of
the serratus anterior muscle, which it
supplies.
TRUNKS & DIVISIONS
Nerve to subclavius Suprascapular nerve
- C5, 6 - C5, 6
- Important clinically, it gives a - Arises in the posterior triangle in the
contribution (C5) to the phrenic nerve neck and runs downward & laterally to
- If present, referred to as the accessory reach the upper edge of the scapua
phrenic nerve - It passes through the suprascapular
notch, beneath the suprascapular
ligament, to reach the supraspinous
fossa
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 33
LATERAL CORD
Lateral pectoral nerve Musculocutaneous Lateral root of the median
- Supplies the pectoralis nerve nerve
major muscle, primarily - Supplies the - is the direct continuation
its clavicular head coracobrachialis of the lateral cord of the
muscle & leaves the brachial plexus
axilla by piercing that - It is joined by the medial
muscle root to form the median
nerve trunk, and this
Supplies CBB:
passes downward on the
Coracobrachialis lateral side of the axillary
Biceps Brachii artery
- The median nerve gives
Brachialis
off no branches in the
Elbow joint axilla.
- wrist flexors; volar
surface
CARPAL TUNNEL
gutter converted to
tunnel by flexor
retinaculum
impingement of nerve
at the wrist
paralysis of muscles
of thumb of median
nerve
MEDIAL CORD
Medial pectoral nerve Medial cutaneous Medial cutaneous nerve
- supplies and pierces the nerve of arm of forearm
pectoralis minor muscle, - T1 - arises from the medial
and supplies the - Arises from the cord of the brachial
pectoralis major muscle, medial cord of the plexus and descends in
brachial plexus and is front of the axillary artery
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 34
primarily its sternocostal joined by the - supplies the skin and
head intercostobrachial medial side of the
nerve (lateral forearm
cutaneous branch of
CARPAL TUNNEL
the 2nd intercostal
nerve) gutter converted to
- supplies the skin and tunnel by flexor
medial side of the arm retinaculum
impingement of nerve
at the wrist
paralysis of muscles
of thumb of median
nerve
Ulnar nerve Medial root of the median nerve
- C8; T1 - arises from the medial cord of the
- arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus
brachial plexus and descends in the - crosses in front of the third part of the
interval between the axillary axillary artery to join the lateral root of
artery and vein the median nerve & form the median
- gives off no branches in the axilla nerve trunk
- medial side of arm - wrists flexors; volar surface
suplies:
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Flexor digitorum profundus
Ulnar artery
Muscle of hypothenar eminence
POSTERIOR CORD
Upper & lower subscapular nerve Thoracodorsal nerve
- Supply the upper and lower parts of - Arise from the posterior cord of the
the brachial plexus
subscapularis muscle - Runs downward into the axilla and
- Lower subscapular nerve supplies the supply the latissimus dorsi muscle
teres major muscle
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 35
Axillary nerve Radial nerve
- (C5, 6) - (C5, 6, 7, 8; T1)
- curves deeply into axilla and passes - Gives off branches to the heads of the
through the quadrangular space with triceps muscle and gives rise to the
posterior circumflex humeral artery posterior cutaneous of the arm
supplies: supplies:
deltoid triceps (long head)
teres minor triceps (lateral head)
triceps (medial head)
last: extensor carpi
Wrist Drop/ Saturday Night / Sweet Hearts Palsy
radial nerve palsy
paralysis of radial nerve
impingement of radial nerve
Papal Benediction
ulnar nerve palsy (half of 4th & 5th digits)
Ape Hand
injury of median nerve (1st, 2nd, 3rd & half of 4th digits)
Upper Brachial Plexus Palsy/ Erb-duchenne Palsy
C5, C6 palsy
Lower Brachial Plexus Palsy/ Klumpke's Deformity
Dermatomes
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 36
sensory distribution
strength of muscles
group of actions supplied by a particular nerve/ 1 root
C9: UE NEUROVASCULAR STRUCTURES 37
You might also like
- The Nervous SystemDocument110 pagesThe Nervous SystemZeren Joy C. AngelesNo ratings yet
- Upper Limbs Blood Supply and NervesDocument6 pagesUpper Limbs Blood Supply and Nervesmarksterxxx78% (9)
- Pentagon Reviewer Med SurgDocument31 pagesPentagon Reviewer Med SurgKathy Real VillsNo ratings yet
- Heart & Great Vessels: Structure, Function, DevelopmentDocument57 pagesHeart & Great Vessels: Structure, Function, DevelopmentStefanie GarnerNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument56 pagesCardio Vascular SystemtazebNo ratings yet
- Pedrajeta-Heart and Neck Vessels AssessmentDocument4 pagesPedrajeta-Heart and Neck Vessels AssessmentAndrei PedrajetaNo ratings yet
- Case 1 ObsDocument31 pagesCase 1 ObsMatheesha HerathNo ratings yet
- Common Barnchial Arch: Pulmocutaneous Arch:: ArteryDocument3 pagesCommon Barnchial Arch: Pulmocutaneous Arch:: ArterykleaxeyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18 - The HeartDocument53 pagesLecture 18 - The HeartkiranNo ratings yet
- Samenvatting Anatomie HPDocument11 pagesSamenvatting Anatomie HPndoemdnsNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SDocument110 pagesCirculatory SMohammed HabibNo ratings yet
- Vessels and CirculationDocument67 pagesVessels and CirculationTio UgantoroNo ratings yet
- 3 CVS HeartDocument49 pages3 CVS HeartSepo CaciousNo ratings yet
- The Emotion That Breaks Your Heart Is Sometimes The Very One That Heals It!Document4 pagesThe Emotion That Breaks Your Heart Is Sometimes The Very One That Heals It!A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Anaphy CardioDocument6 pagesAnaphy CardioDianne DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Cardiovascular System - Part IDocument13 pagesAnatomy - Cardiovascular System - Part IVăn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- (H.a.) Chapter 12 - Heart & Neck VesselsDocument9 pages(H.a.) Chapter 12 - Heart & Neck VesselsLevi Sebastian T. CabiguinNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 6-13 (Lec)Document26 pagesPMLS 2 6-13 (Lec)Ricci Gwennmorei TaghapNo ratings yet
- 15.development of Heart - Phanindra Prasad PoudelDocument34 pages15.development of Heart - Phanindra Prasad PoudelPradip ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Heart and Neck VesselsDocument25 pagesAssessment of The Heart and Neck VesselsCuenca LanceNo ratings yet
- NPTE CArdio NotesDocument27 pagesNPTE CArdio NotesAubrey Vale SagunNo ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy Only StudentsDocument34 pagesHeart Anatomy Only Studentscharlene.jadulcoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec CardioDocument12 pagesAnaphy Lec CardioRyan Dave UmayamNo ratings yet
- Concept On Oxygenation: Gas TransportDocument135 pagesConcept On Oxygenation: Gas TransportNikko MelencionNo ratings yet
- 08 Human Physiology The HeartDocument107 pages08 Human Physiology The HeartsuNo ratings yet
- VASCULAR AnatomyDocument19 pagesVASCULAR AnatomyIA CREATIONSNo ratings yet
- 5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2Document29 pages5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2uxdan154No ratings yet
- Blood Vessels CirculationDocument6 pagesBlood Vessels Circulationskyler andradaNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels and CirculationsDocument9 pagesBlood Vessels and Circulationsshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- 4 CVS - Arterial SupplyDocument35 pages4 CVS - Arterial SupplySepo CaciousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BDocument29 pagesChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Trunk Ascending Aorta, Aortic Arch and Its BranchesDocument27 pagesPulmonary Trunk Ascending Aorta, Aortic Arch and Its Branches4dyhm4456qNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Anatomy of The HeartDocument5 pagesChapter 16 Anatomy of The Heartphotojockey18No ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Whole BodyDocument60 pagesBlood Supply of Whole BodyProsanjit Majumder100% (1)
- Reviewer 2 Health AssessmentDocument13 pagesReviewer 2 Health AssessmentchristinejeancenabreNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemadnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Introduction To The Cardiovascular System: Away From To BetweenDocument6 pagesChapter 20 - Introduction To The Cardiovascular System: Away From To Betweentomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument8 pagesHEARTJoyce OmegaNo ratings yet
- Heart and Blood Vessels, BloodDocument13 pagesHeart and Blood Vessels, BloodDaniel DanielNo ratings yet
- Axillary ContentsDocument44 pagesAxillary Contentsbravestone974No ratings yet
- Activity of Circulatory (Anaphy)Document3 pagesActivity of Circulatory (Anaphy)maglangitjoannamarie1920No ratings yet
- Lecture 19 - Vessels and CirculationDocument67 pagesLecture 19 - Vessels and CirculationSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Circulatory SystemDocument131 pagesAnatomy Circulatory Systemanduamlakmolalgn332No ratings yet
- مذكرة فرست الزمالة المجمعةDocument160 pagesمذكرة فرست الزمالة المجمعةmahi_elsemary7011100% (1)
- CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Hand Out)Document15 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Hand Out)79ctq9xpf7No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, LudhianaDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, Ludhianapreet kaurNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASDocument3 pagesCARDIOVASFrama Intan MiguelNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument38 pagesCardiovascular SystemShyn BaldostamonNo ratings yet
- Anaphy HeartDocument6 pagesAnaphy HeartAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The CvsDocument43 pagesIntroduction To The CvsParmesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Physio Study Guide - The HeartDocument3 pagesPhysio Study Guide - The HeartEmily ChanNo ratings yet
- Aorta AnatomyDocument41 pagesAorta AnatomySingey LhendupNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System BSN 1Document16 pagesCardiovascular System BSN 1Arianne Jen GenotivaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument114 pagesThe Circulatory SystemKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Cardiovascular SystemluaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1Document54 pagesLecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1hafiz patah100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Heart & Circulation KeyDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Heart & Circulation KeyJenn YumulNo ratings yet
- MS CVS ReviewDocument41 pagesMS CVS ReviewShayesra-Radina Laja SahibadNo ratings yet
- Mediastinal Anatomy: Superior Mediastin Um Middle Mediastin Um PericardiumDocument2 pagesMediastinal Anatomy: Superior Mediastin Um Middle Mediastin Um PericardiumBenjamin ChosichNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of The Body: Cardiovascular SystemDocument74 pagesMaintenance of The Body: Cardiovascular Systemdania mauriyanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter I IntroductionDocument58 pagesChapter I Introductionnot meNo ratings yet
- C9: Upper Limb, Breast and AxillaDocument27 pagesC9: Upper Limb, Breast and Axillanot meNo ratings yet
- C6: Pelvic Wall: Files TermDocument12 pagesC6: Pelvic Wall: Files Termnot meNo ratings yet
- C9: Ue Bones & Joints: Upper LimbsDocument21 pagesC9: Ue Bones & Joints: Upper Limbsnot meNo ratings yet
- An Segmental AnatomyDocument374 pagesAn Segmental AnatomyJorge Lucas Jimenez100% (1)
- Coding and Billing Facet Joint InjectionsDocument3 pagesCoding and Billing Facet Joint InjectionsMischelle Pittman HenryNo ratings yet
- ASIA ScoreDocument14 pagesASIA Scorezloncar3No ratings yet
- Anatomy One LinersDocument10 pagesAnatomy One Linersridin007100% (2)
- Case Presentation On GbsDocument23 pagesCase Presentation On GbsRucHi ShArmaNo ratings yet
- (BCA HSB) Anatomy of The Back (Dr. Vibar) Meowstic 2022Document5 pages(BCA HSB) Anatomy of The Back (Dr. Vibar) Meowstic 2022Ronel MonterozoNo ratings yet
- Cross Sectional Anatomy of SpineDocument37 pagesCross Sectional Anatomy of SpineAvinash Gupta50% (2)
- Autonomic CH 15Document34 pagesAutonomic CH 15sawalekatumbo1No ratings yet
- Anatomi Neurology 2Document22 pagesAnatomi Neurology 2LindaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord ExternalDocument33 pagesSpinal Cord ExternalCosplay AccountNo ratings yet
- 5Document2 pages5Academic ServicesNo ratings yet
- Lab3 Human Anatomy 1 YearDocument51 pagesLab3 Human Anatomy 1 Yearnatheer ayedNo ratings yet
- Erler Zimmer (Watermark) - PasswordDocument260 pagesErler Zimmer (Watermark) - Passwordmat kool100% (1)
- 2009 The Neuroanatomic Basis of The Acupuncture Principal MeridiansDocument21 pages2009 The Neuroanatomic Basis of The Acupuncture Principal MeridiansAna Maria MartinsNo ratings yet
- HeadDocument360 pagesHeadfeliciostenio100% (1)
- Print Chapter 13 Flashcards - Easy NotecardsDocument18 pagesPrint Chapter 13 Flashcards - Easy NotecardsoyamaNo ratings yet
- Pier Paolo Maria Menchetti-Cervical Spine - Minimally Invasive and Open Surgery-Springer International Publishing (2015) PDFDocument258 pagesPier Paolo Maria Menchetti-Cervical Spine - Minimally Invasive and Open Surgery-Springer International Publishing (2015) PDFLorena BurdujocNo ratings yet
- Narayana Medical Academy, A.PDocument23 pagesNarayana Medical Academy, A.PSK M BashaNo ratings yet
- Mcem Anatomy MCQDocument37 pagesMcem Anatomy MCQMOHAMMED ANEEZNo ratings yet
- Oina MusclesDocument73 pagesOina MusclesShen AndradeNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument110 pagesThe Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- SPINAL CORD (External Features)Document39 pagesSPINAL CORD (External Features)Drravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- Neurological AssessmentDocument47 pagesNeurological AssessmentMangayarkarasi Chandrakasan100% (5)
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemAnonymous hYMWbANo ratings yet
- Asda JKLMNDocument185 pagesAsda JKLMNBikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Chapter # 7Document69 pagesNervous System: Chapter # 7saddam ud dinNo ratings yet
- 511-525chapter 6-8 (5) The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal ReflexesDocument4 pages511-525chapter 6-8 (5) The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexestomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet