Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 - NCP & Drug Analysis
9 - NCP & Drug Analysis
Uploaded by
Florante Aniban0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pages9 - NCP & Drug Analysis
9 - NCP & Drug Analysis
Uploaded by
Florante AnibanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN PHILIPPINES
University Town, Northern Samar
COLLEGE of NURSING and ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
NURSING CARE PLAN
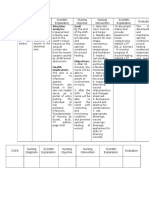
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC OBJECTIVES/ NURSING SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE PLANNING INTERVENTIONS
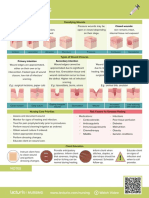
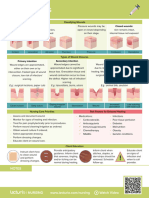
Objective: Impaired skin Burns, or burn Within to 2 days of ▪ Assess the status of the ▪ Knowing exactly the wound After 1 to 2 days of
- Presence of Integrity injuries, result from nursing interventions the burned area, noting the coverage helps in planning for nursing
multiple burn related to the tissue damage due to client maintains an intact degree of tissue care of the patient. interventions the
injury, a small Burn Injury. heat transfer from involvement and extent of
skin integrity with client’s skin
one on the one site to another. In the damage. ▪ There are specific care
regular wound healing integrity was
fingertips of most cases, this heat ▪ Determine the type of requirements for some type of
the right is much more than the process and absence of irritating agent that wounds depending on the nature improved with
second and skin can withstand, wound complications like caused the wound. of injury (i.e., thermal vs. regular healing and
third fingers, leading to disruption keloids, etc. chemical). Knowing these would absence of any
another on the in the skin’s integrity help the nurse in planning complications.
dorsum of the and other problems. appropriate care for the patient.
left hand, and
a third on the
chest. ▪ In some cases, the initial phases
▪ Provide patient support of wound care for burns may be
during the initial phases painful and distressing to the
of wound care. patient, especially when these
involve debridement. Providing
the patient support eases stress
and anxiety and helps the
patient to cooperate in his care
plan.
▪ Stress the importance of
asepsis, especially when ▪ This helps prevent infections at
handling wounds. the wound site.
▪ Administer medications ▪ These substances are prescribed
as prescribed. to the patient to help promote
tissue growth, wound healing
and in some cases, prevent the
formation of keloids.
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC OBJECTIVES/ NURSING SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE PLANNING INTERVENTIONS
Objective: Acute Pain related According to Within 4 hours of nursing ▪ Assess reports of ▪ Pain is nearly always present to some After 4 hours of
- Presence to destruction of NANDA, acute pain interventions the client pain, noting location degree because of varying severity of nursing
of multiple skin/tissues. is an unpleasant will be able to: and character and tissue involvement and destruction interventions, the
burns, a sensory and intensity (0–10 but is usually most severe during
▪ Report the pain is client was able to
small one emotional scale). dressing changes and debridement.
reduced/controlled. report pain was
on the experience ▪ Elevation may be required initially to
fingertips associated with ▪ Display relaxed facial reduce edema formation; thereafter, reduced/controlled
▪ Elevate burned
of the right acute or potential expressions/body extremities changes in position and elevation and was able to
second and tissue damage, or posture. periodically. reduce discomfort and risk of joint display relaxed
third described in terms contractures. facial
fingers, of such damage; expressions/body
another on sudden or slow posture.
the onset of any ▪ Maintain ▪ Temperature regulation may be lost
dorsum of intensity from comfortable with major burns. External heat
the left mild to severe environmental sources may be necessary to prevent
hand, and a with an temperature, provide chilling.
third on anticipated or heat lamps, heat
the chest. predictable end, retaining body
and with a coverings.
duration of less ▪ Reduces severe physical and
▪ Provide medication emotional distress associated with
than 3 months. and/or place in dressing changes and debridement.
hydrotherapy (as
Nerves are tissue appropriate) before
that offers very performing dressing
little resistance to changes and
the passage of an debridement.
electric current. ▪ Provide basic ▪ Promotes relaxation; reduces muscle
When nerves are comfort measures: tension and general fatigue.
affected by an massage of uninjured
electric shock, the areas, frequent
consequences position changes.
include pain, ▪ The burned patient may require
▪ Administer around-the-clock medication and
tingling, analgesics, as
numbness, dose titration. IV method is often
indicated. used initially to maximize drug effect.
weakness or
difficulty moving a Concerns of patient addiction or
limb. These effects doubts regarding degree of pain
may clear up with experienced are not valid during
time or be emergent/acute phase of care, but
narcotics should be decreased as soon
permanent.
as feasible and alternative methods
for pain relief initiated.
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC OBJECTIVES/ NURSING INTERVENTIONS SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE PLANNING
Objective: Risk for Wound Burn patients have After 2 to 4 days ▪ Assess the wound for any ▪ Assessment aids in planning After 2 to 4 days of
- Presence Infection as lost the primary of nursing signs of infection & identify appropriate intervention. nursing
of multiple evidenced by loss of barrier to interventions, the type, percentage, degree, interventions, the
burns, a infectious & depth of burn.
the skin barrier as the client will client remains free
small one invasion, their ▪ Follow aseptic precautions ▪ To prevent cross infections.
well as remain free from from symptoms of
on the skin. In addition, like hand washing, gloving,
fingertips immunosuppression patients with symptoms of gowning, & mask every infection.
of the right experienced extensive burns infection. patient interaction.
second and because of a develop a ▪ Provide hydrotherapy & ▪ To prevent infection.
third systemic profound wound cleansing
fingers, inflammatory hypermetabolic immediately.
another on response triggered response that ▪ Provide wound dressing by ▪ To prevent wound infection.
the persists for following aseptic precaution.
by the injured
dorsum of months. They are ▪ Apply anti-septic creams like ▪ To aid in healing and prevent
the left tissue. at risk for sepsis Silver sulfadiazine to the infection.
hand, and a and MODS at least wound.
third on as long as the
the chest. wounds remain
open.
UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN PHILIPPINES
University Town, Northern Samar
COLLEGE of NURSING and ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
DRUG ANALYSIS
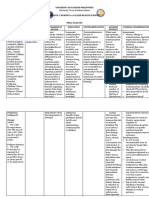
DRUG CLASSIFICATION MECHANISM OF INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING CONSIDERATION
ACTION EFFECTS
Generic Name: Acetaminophen is The exact In general, Contraindications to When used Assessment:
Acetaminophen in a class of mechanism of action acetaminophen the use of appropriately, ▪ History: Allergy to
medications called of acetaminophen is is used for the acetaminophen side effects with acetaminophen, impaired
Brand Names: analgesics and not known. It may treatment of mild include acetaminophen hepatic function, chronic
Tylenol,Acephen, antipyretics. reduce the to moderate pain hypersensitivity to are not alcoholism, pregnancy,
Acetadryl, Allzital, production of and reduction of acetaminophen, common. lactation
Apadaz, Arthriten prostaglandins in fever. It is severe hepatic The most ▪ Physical: Skin color,
Inflammatory the brain. available over impairment, or severe common side lesions; T; liver
Pain, , Cetafen, Prostaglandins are the counter in active hepatic disease. effects are rash, evaluation; CBC, LFTs,
Children's Silapap, chemicals that cause various forms, However, there is a nausea, and renal function tests
Darvocet-N, inflammation and the most general debate among headache. Interventions:
Dayquil Sinex, swelling. common being experts whether Other important ▪ Do not exceed the
Dolofin, Dologen, Acetaminophen oral forms. hepatic impairment is side effects recommended dosage.
Fioricet With relieves pain by Because of its truly a limiting factor, include: ▪ Consult physician if
Codeine, Goody's elevating the pain low risk of as it would likely be ▪ Hypersensiti needed for children < 3
Back & Body Pain threshold, that is, by causing allergic associated with vity yr; if needed for longer
Relief, , Little requiring a greater reactions, this decreased production reactions than 10 days; if continued
Fevers, amount of pain to drug can be of the toxic ▪ Serious skin fever, severe or recurrent
Mersyndol, Midol develop before a administered in metabolite, N-acetyl- reactions pain occurs (possible
Complete, person feels it. It patients who are p-benzoquinoneimine ▪ Kidney serious illness).
Panadol, reduces fever intolerant to (NAPQI). damage ▪ Avoid using multiple
Pediacare through its action on salicylates and ▪ Anemia preparations containing
Children's Fever the heat-regulating those with ▪ Reduced acetaminophen. Carefully
Reducer Pain center of the brain. allergic number of check all OTC products.
Reliever, Tylenol Specifically, it tells tendencies, platelets in ▪ Give drug with food if GI
With Codeine the center to lower including the blood upset occurs.
the body's bronchial (thrombocyt ▪ Discontinue drug if
Pregnancy temperature when asthmatics. openia) hypersensitivity reactions
Category B the temperature is Specific dosing Chronic alcohol occur.
elevated. guidelines should use may also ▪ Treatment of overdose:
Dosage: be followed increase the risk Monitor serum levels
Adults: when of stomach regularly, N-
▪ PO or PR administering bleeding. The acetylcysteine should be
By suppository, acetaminophen most serious available as a specific
325–650 mg q 4– to children. side effect is antidote; basic life
6 hr or PO, 1,000 liver damage support measures may be
mg tid to qid. Do due to large necessary.
not exceed 4 doses, chronic Teaching points:
g/day. use or ▪ Do not exceed
concomitant use recommended dose; do
Pediatric Patients: with alcohol or not take for longer than
▪ PO or PR other drugs that 10 days.
Doses may be also damage the ▪ Take the drug only for
repeated 4–5 liver. complaints indicated; it is
times/day; do not Other serious not an anti-inflammatory
exceed five doses side effects that agent.
in 24 hr; give PO have been ▪ Avoid the use of other
or by suppository. reported over-the-counter
include bleeding preparations. They may
in the intestines contain acetaminophen,
and stomach, and serious overdosage
angioedema, can occur. If you need an
Stevens- over-the-counter
Johnson preparation, consult your
syndrome, and health care provider.
kidney damage. ▪ Report rash, unusual
A reduction in bleeding or bruising,
the number of yellowing of skin or eyes,
white blood changes in voiding
cells has also patterns.
been reported.
DRUG CLASSIFICATION MECHANISM OF INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING CONSIDERATION
ACTION
Generic Name: Silver sulfadiazine The exact Indicated as SILVADENE Cream Common side Examination and
Silver sulfadiazine belongs to a class mechanism by an adjunct 1% (silver effects of Silver Evaluation:
of drugs known as which silver for the sulfadiazine) is Sulfadiazine ▪ Assess the size, depth,
Brand Names: sulfa antibiotics, sulfadiazine exerts prevention contraindicated in include: color, drainage, and
Silvadene, Topical. its anti-infective and patients who are ▪ Pain periwound area to
Thermazene, and activity is treatment of hypersensitive to ▪ Burning document whether drug
SSD Cream. unknown. Both wound sepsis silver sulfadiazine or ▪ Itching therapy is successful in
free silver and the in patients any of the other ▪ Rash decreasing infection and
Pregnancy sulfonamide with second- ingredients in the ▪ Cell death of the promoting wound
Category B moiety may exert and third- preparation. skin healing.
activity, but the degree Because sulfonamide ▪ Localized ▪ Monitor any new or
Dosage: drug does not burns. therapy is known to eruption of the increased skin reactions
Adults, Adolescents inhibit folic acid increase the skin at the site of application,
and Children: synthesis as other possibility of ▪ Transient skin including rash, burning,
▪ After cleansing sulfonamides do. kernicterus, discoloration itching, pain, and
and Silver sulfadiazine SILVADENE Cream ▪ Destruction of necrosis. Report any
debridement, disrupts bacteria 1% should not be used red blood cells suspicious skin reactions
apply topically by damaging the on pregnant women (in patients with to the physician.
to a thickness of cell membrane and approaching or at g6pd deficiency) ▪ Be alert for signs of
approximately the cell wall rather term, on premature ▪ Deficiency of leukopenia, including
1.6 mm (1/16th than by inhibiting infants, or on newborn granulocytes in fever, sore throat, and
of an inch) folic acid synthesis. infants during the first the blood signs of infection. Report
twice per day. Silver sulfadiazine 2 months of life. ▪ Discontinued these signs to the
Reapply the has a wide production of physician.
cream spectrum of blood cells Interventions:
whenever bactericidal ▪ Low blood ▪ Implement wound care
necessary to activity against platelet count procedures (whirlpool,
any affected both gram-positive ▪ Low white pulsed lavage, gentle
areas where and gram-negative blood cell count débridement) as needed
drug removed organisms. ▪ Dermatologic to cleanse burns and
by activity or and ulcers. Make sure the
hydrotherapy. hypersensitivity drug is reapplied and
reactions dressings are changed
Infants > 2 months: (stevens- according to the
▪ Apply topically johnson recommended
to a thickness of syndrome, ten) procedures.
about 1.6 mm ▪ Adverse ▪ When indicated, use
(1/16th of an gastrointestinal appropriate physical
inch) twice per effects agents (ultrasound,
day. ▪ Inflammation of electric stimulation,
the liver ultraviolet light) to
Neonates < 2 (hepatitis) facilitate wound healing
months: ▪ Toxic injury to and augment drug effects.
▪ Use not the liver Patient/Client-Related
recommended; ▪ Adverse Instruction:
sulfonamides nervous system ▪ Check that the patient
may cause effects and family or caregivers
kernicterus in ▪ Acute kidney understand topical
neonates. failure application and wound
▪ Swelling in the care procedures and
kidney adhere to the
▪ Burning recommended dosing
sensation schedule.
▪ Presence of ▪ Instruct patient and
harmful family/caregivers about
bacteria via prevention of other types
infection of a of skin ulcers and the
wound (sepsis) need for visual inspection
to prevent recurrence or
development of new
ulcers.
DRUG CLASSIFICATION MECHANISM INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING CONSIDERATION
OF ACTION EFFECTS
Generic Names: Clindamycin is in Clindamycin Clindamycin is Clindamycin is Adverse effects Assessment:
Clindamycin, a class of prevents indicated in the contraindicated in are ▪ History: Allergy to
clindamycin medications called peptide bond treatment of patients with a history Diarrhea, nausea, clindamycin, history of
hydrochloride, lincomycin formation, serious of vomiting, asthma or other allergies,
clindamycin antibiotics. thereby infections pseudomembranous abdominal pain; allergy to tartrazine (in 75-
palmitate inhibiting caused by colitis or ulcerative erythema and 150-mg capsules);
hydrochloride, protein susceptible colitis. Care is also multiforme, hepatic or renal dysfunction;
clindamycin synthesis by anaerobic necessary for contact lactation; history of regional
phosphate reversibly bacteria. antibiotic use as dermatitis, enteritis or ulcerative colitis;
binding to 50S Clindamycin is bacterial and fungal exfoliative and history of antibiotic
Brand Names: ribosomal also indicated superinfections may vesiculous associated colitis
Cleocin, Dalacin C subunits. in the occur. It is also dermatitis, ▪ Physical: Site of infection or
(CAN),Cleocin, Depending on treatment of contraindicated in urticaria; acne; skin color, lesions; BP;
Cleocin Phosphate, the organism, serious patients with eosinophilia; local R, adventitious sounds;
Cleocin T, Cleocin infection site, infections due hypersensitivity to irritation, bowel sounds, output, liver
Vaginal Ovules, and drug to susceptible clindamycin, thrombophlebitis. evaluation; CBC, LFTs, renal
Clinda-Derm (CAN), concentration, strains of lincomycin, or any of Potentially Fatal: function tests
Clindagel, clindamycin streptococci, their components. Gasping syndrome Interventions:
ClindaMax, may be a pneumococci, Special care must also (neonates); ▪ Culture infection before
Clindets, Dalacin C bacteriostatic and be taken in patients pseudomembrano therapy.
(CAN) or bactericidal staphylococci. with atopic dermatitis us colitis. ▪ Administer oral drug with a
antibiotic. Its use should as colonization is full glass of water or with
Pregnancy be reserved for more prevalent in this food to prevent esophageal
Category B penicillin- patient population. irritation.
allergic The pathogenicity of ▪ Do not give IM injections of
Dosage: patients or skin infections is more than 600 mg; inject
Adults: other patients higher in this deep into large muscle to
▪ Oral 150–300 for whom, in population; this is avoid serious problems.
mg q 6 hr, up to the judgment of important for future ▪ Do not use for minor
300–450 mg q 6 the physician, a infections as antibiotic bacterial or viral infections.
hr in more penicillin is resistance is a ▪ BLACK BOX WARNING: Be
severe inappropriate. problematic aware that serious to fatal
infections. Because of the complication. colitis can occur; reserve
▪ Parenteral 600– risk of colitis, use, and monitor patient
2,700 mg/day as described in closely.
in two to four the BOXED ▪ Monitor LFTs and renal
equal doses; up WARNING, function tests, and blood
to 4.8 g/day IV before selecting counts with prolonged
or IM may be clindamycin, therapy.
used for life- the physician Teaching Points:
threatening should ▪ Take oral drug with a full
situations. consider the glass of water or with food.
nature of the ▪ Take full prescribed course
Pediatric Patients: infection and of oral drug. Do not stop
▪ Oral the suitability taking without notifying
For clindamycin of less toxic health care provider.
HCl, 8–20 alternatives ▪ You may experience these
mg/kg/day in three (e.g., side effects: Nausea,
or four equal doses. erythromycin). vomiting (eat frequent small
For clindamycin meals); superinfections in
palmitate HCl, 8–25 the mouth, vagina (use
mg/kg/day in three frequent hygiene measures;
or four equal doses; request treatment if severe).
for children ▪ Report severe or watery
weighing < 10 kg, diarrhea, abdominal pain,
use 37.5 mg tid as inflamed mouth or vagina,
the minimum dose. skin rash or lesions.
▪ Parenteral
Neonates: 15–20
mg/kg/day in three
or four equal doses.
> 1 mo: 15–40
mg/kg/day in three
or four equal doses
or 350 mg/m2/day
to 450 mg/m2/day.
You might also like
- Grabovoi NumbersDocument6 pagesGrabovoi NumbersTTimenot820192% (71)
- Nursing Care Plan For Wound HealingDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Wound HealingJobelle Acena50% (2)
- NCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityFlauros Ryu Jabien90% (30)
- Nursing Care Plan For Cesarean SectionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Cesarean SectionJon Gab Paquit85% (33)
- Classification of Malocclusion Angle PDFDocument17 pagesClassification of Malocclusion Angle PDFAndrea Tokumoto100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - BurnDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Burnderic90% (10)
- The Antidote to Suffering: How Compassionate Connected Care Can Improve Safety, Quality, and ExperienceFrom EverandThe Antidote to Suffering: How Compassionate Connected Care Can Improve Safety, Quality, and ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Cc1-Task 4Document8 pagesCc1-Task 4Joshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- University of Eastern Philippines College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesUniversity of Eastern Philippines College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Care PlanFlorante AnibanNo ratings yet
- NCP Rectal AdenocarcinomaDocument3 pagesNCP Rectal AdenocarcinomaReysiela Mae ValinoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityLilet Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationGlare RhayneNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionMao71% (14)
- NCP Template W InferenceDocument5 pagesNCP Template W InferenceVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- NCP Cholelithiasis Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNCP Cholelithiasis Impaired Skin IntegrityReysiela Mae ValinoNo ratings yet
- Asessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAsessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationHikari 光 Shidou50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationValerie FischerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FormDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan FormHanniel MontecalboNo ratings yet
- Phases of The Wound Healing Process: Practice EducatorDocument2 pagesPhases of The Wound Healing Process: Practice EducatorSarah Ariefah SantriNo ratings yet
- NCP BedsoresDocument10 pagesNCP BedsoresFATIMA PANDAOGNo ratings yet
- D. Nemis - Individual NCPDocument3 pagesD. Nemis - Individual NCPDianne NemisNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Wound-Types 01Document1 pageNursing CS Wound-Types 01Jazzmine GuraNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Care PlanDocument10 pagesComprehensive Care Planapi-381124066No ratings yet
- Wound-TypesDocument1 pageWound-TypesJamie W.No ratings yet
- G-CFA Instructor Tab 6-2 Handout 2 Sample Adequate Nursing Care Plan-R6Document2 pagesG-CFA Instructor Tab 6-2 Handout 2 Sample Adequate Nursing Care Plan-R6SriMathi Kasi Malini ArmugamNo ratings yet
- SFP-Vol403 Unit2Document10 pagesSFP-Vol403 Unit2TnchNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 Impaired Skin Integrity EDITEDDocument2 pagesNCP 2 Impaired Skin Integrity EDITEDVincent HermanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Factors Affecting Wound Healing.10-2Document1 pageChecklist For Factors Affecting Wound Healing.10-2indraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanmcrosalesNo ratings yet
- Fernandez, Blessie P. (Bsn-2b) NCPDocument6 pagesFernandez, Blessie P. (Bsn-2b) NCPBlessie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesGroup 3 Diabetes MellitusMary0% (1)
- YumeDocument5 pagesYumeCandrajayantoNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Clinics: Initial Wound ManagementDocument26 pagesVeterinary Clinics: Initial Wound ManagementGuadalupe Cristina Chuchón CáceresNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiology Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiology Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Practice Points: Checklist For Factors Affecting Wound HealingDocument1 pagePractice Points: Checklist For Factors Affecting Wound Healingpka25No ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesImpaired Skin Integritykingpin100% (1)
- NCP Skin IntegityDocument3 pagesNCP Skin Integityclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective AdherenceDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective AdherenceTheresa Mae De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment S - O Pt. May ManifestDocument4 pagesNursing Assessment S - O Pt. May Manifestk_a1990No ratings yet
- SJS NCPDocument4 pagesSJS NCPAira Alaro50% (2)
- University of Luzon College of Nursing: Name - Jake Yvan DizonDocument3 pagesUniversity of Luzon College of Nursing: Name - Jake Yvan DizonJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionPebbles PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Debridement PDFDocument4 pagesDebridement PDFWahyu IndraNo ratings yet
- Design A Comprehensive Nursing Care Plans For The Selected Medical, Surgical ConditionsDocument3 pagesDesign A Comprehensive Nursing Care Plans For The Selected Medical, Surgical Conditionskawther mohdNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationBiancaGabatinoAbarcaNo ratings yet
- Xi. Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesXi. Nursing Care PlanSean Lloyd RigonNo ratings yet
- NCP MyomaDocument6 pagesNCP MyomaIzza Mae Ferrancol PastranaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanEliza May Barretto50% (2)
- NCP 1 CSDocument2 pagesNCP 1 CSjuliechan_17mjNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlankingpinNo ratings yet
- Skin Wounds And Wound Healing, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSkin Wounds And Wound Healing, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Surgical Sutures: A Practical Guide of Surgical Knots and Suturing Techniques Used in Emergency Rooms, Surgery, and General MedicineFrom EverandSurgical Sutures: A Practical Guide of Surgical Knots and Suturing Techniques Used in Emergency Rooms, Surgery, and General MedicineRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Cultivating Resilience in the Face of Adversity: Thriving Through ChallengesFrom EverandCultivating Resilience in the Face of Adversity: Thriving Through ChallengesNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcers in the Aging Population: A Guide for CliniciansFrom EverandPressure Ulcers in the Aging Population: A Guide for CliniciansDavid R. Thomas, MDNo ratings yet
- The preparation for the end of the world: A guide for uncertain timesFrom EverandThe preparation for the end of the world: A guide for uncertain timesNo ratings yet
- University of Eastern Philippines College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesUniversity of Eastern Philippines College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Care PlanFlorante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3Document13 pagesCase Study 3Florante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis 9Document6 pagesDrug Analysis 9Florante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Drug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindica Tion Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindica Tion Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesFlorante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classificat ION Action Indicati ON Contraindic Ation Adverse Affect Nursing Considera Tion Generic Name: Chemical Class: Therapeutic ClassDocument17 pagesDrug Name Classificat ION Action Indicati ON Contraindic Ation Adverse Affect Nursing Considera Tion Generic Name: Chemical Class: Therapeutic ClassFlorante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classifica Tion Action Indicati ON Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Body As A Whole: HypersensitivitDocument11 pagesDrug Name Classifica Tion Action Indicati ON Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Body As A Whole: HypersensitivitFlorante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Drug-Ana 3Document6 pagesDrug-Ana 3Florante AnibanNo ratings yet
- LeopoldsDocument2 pagesLeopoldsFlorante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Drug-Ana 4Document14 pagesDrug-Ana 4Florante AnibanNo ratings yet
- University of Eastern PhilippinesDocument2 pagesUniversity of Eastern PhilippinesFlorante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Perineal CareDocument2 pagesPerineal CareFlorante AnibanNo ratings yet
- Sputum ExamDocument14 pagesSputum ExamJuan MorseNo ratings yet
- Cyclosporine For Moderate-To-Severe Alopecia Areata: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Efficacy and SafetyDocument8 pagesCyclosporine For Moderate-To-Severe Alopecia Areata: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Efficacy and Safetysupaidi97No ratings yet
- PRC Cases TemplateeeeeeDocument15 pagesPRC Cases TemplateeeeeeWinter KimNo ratings yet
- Aerobic ExercisesDocument6 pagesAerobic ExercisesAerl XuanNo ratings yet
- Mpower WhoDocument41 pagesMpower Whonewsand webNo ratings yet
- Ca1 Pen SyllabusDocument6 pagesCa1 Pen SyllabusJoseph Bahian-AbangNo ratings yet
- Wound Closure ManualDocument127 pagesWound Closure ManualDougyStoffell100% (6)
- The Michigan Appropriateness Guide For Intravenous Catheters (MAGIC)Document48 pagesThe Michigan Appropriateness Guide For Intravenous Catheters (MAGIC)Suren VishvanathNo ratings yet
- Emergency Evacuation Plan For CradleDocument5 pagesEmergency Evacuation Plan For CradleAbraar AhmedhNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0033350622003468 MainDocument3 pages1 s2.0 S0033350622003468 MainAmrita Heart CareNo ratings yet
- Wadz Mapeh Grade 10 Third Grading Mapeh 10 Sy 2019-2020 (Boooklet)Document8 pagesWadz Mapeh Grade 10 Third Grading Mapeh 10 Sy 2019-2020 (Boooklet)Edward YagoNo ratings yet
- Birth Control Effectiveness & Safety Guide 6-15-2015bDocument2 pagesBirth Control Effectiveness & Safety Guide 6-15-2015bapi-286375746No ratings yet
- The Role of The Gerontological NurseDocument4 pagesThe Role of The Gerontological Nursesusan100% (1)
- CancerTreatment Chinese HerbsDocument8 pagesCancerTreatment Chinese HerbsExcelita SyahraniNo ratings yet
- PRC IV SutureDocument4 pagesPRC IV SutureFreyjaa MabelinNo ratings yet
- Title: Ethical Considerations of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Introduction: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the landscape of healthcare, promising advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. However, as AI becomes increasingly integrated into medical practice, ethical considerations emerge. This paper examines the ethical implications of AI in healthcare, focusing on issues of patient privacy, algorithm bias, transparency, and the ethical responsibilities of healthcare providers. Patient Privacy: One of the primary ethical concerns surrounding AI in healthcare is the protection of patient privacy. As AI systems analyze vast amounts of sensitive medical data, ensuring patient confidentiality and data security becomes paramount. Healthcare organizations must implement robust data protection measures and adhere to strict privacy regulations to safeguard patient information from unauthorized access or misuse. Algorithm Bias: Another ethical challenge in ADocument1 pageTitle: Ethical Considerations of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Introduction: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the landscape of healthcare, promising advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. However, as AI becomes increasingly integrated into medical practice, ethical considerations emerge. This paper examines the ethical implications of AI in healthcare, focusing on issues of patient privacy, algorithm bias, transparency, and the ethical responsibilities of healthcare providers. Patient Privacy: One of the primary ethical concerns surrounding AI in healthcare is the protection of patient privacy. As AI systems analyze vast amounts of sensitive medical data, ensuring patient confidentiality and data security becomes paramount. Healthcare organizations must implement robust data protection measures and adhere to strict privacy regulations to safeguard patient information from unauthorized access or misuse. Algorithm Bias: Another ethical challenge in AVyblova AnimationNo ratings yet
- Whatis Critical AppraisalDocument8 pagesWhatis Critical Appraisalapi-3861522No ratings yet
- SadsadDocument3 pagesSadsadDalo ZeronNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3Document9 pagesLesson 1.3MarkNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesDiseases of Muscular SystemChari Mae Tamayo PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Basic Organization: Diagnostic Microbiology LaboratoryDocument33 pagesBasic Organization: Diagnostic Microbiology Laboratorytummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Day 15 Short Writing - 1Document1 pageDay 15 Short Writing - 1Internship Reports BdNo ratings yet
- Elise Wurst: Associate of Science in NursingDocument3 pagesElise Wurst: Associate of Science in Nursingapi-348450052No ratings yet
- Dental Caries Vaccine Availability Challenges For The 21st CenturyDocument7 pagesDental Caries Vaccine Availability Challenges For The 21st CenturyandiNo ratings yet
- NCP Altered Bowel EleminationDocument2 pagesNCP Altered Bowel EleminationDianna RoseNo ratings yet
- NHMSFAP As Post Anesthesia CareDocument11 pagesNHMSFAP As Post Anesthesia CareOktavia PutriNo ratings yet
- 017 0 BBDocument1 page017 0 BBCristina Duran GarcíaNo ratings yet