Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 viewsLo3 Connect Hardware Peripherals
Lo3 Connect Hardware Peripherals
Uploaded by
remose06Installing new hardware peripherals should be done with minimal disruption to clients. Installations are best scheduled during quiet periods like holidays or after hours when clients will not need their computers. All new devices must be thoroughly tested according to a documented test plan to ensure they function properly and meet client needs before use. When connecting new peripherals, drivers may need to be installed and the operating system will detect and configure the new hardware.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Lokotrack LT1213 S N 72964Document368 pagesLokotrack LT1213 S N 72964Carlos Israel Gomez67% (6)
- Student Workbook - ICAICT303A Connect Internal Hardware ComponentsDocument104 pagesStudent Workbook - ICAICT303A Connect Internal Hardware ComponentsSarah ButlerNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument10 pagesSoftwareTalila B. Robsan100% (1)
- Levels of SupportDocument3 pagesLevels of SupportNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Recording Client Support RequirementsDocument65 pagesRecording Client Support RequirementswosenNo ratings yet
- Record Client Support SurviceDocument8 pagesRecord Client Support SurviceGizaw Tadesse100% (1)
- MO 6 Record Client Support RequirementsDocument25 pagesMO 6 Record Client Support RequirementsLusi Abdella100% (1)
- Configuring and Using InternetDocument29 pagesConfiguring and Using Internetm.tsedey2013100% (2)
- Protect Application or System Software INFORMATION SHEETDocument22 pagesProtect Application or System Software INFORMATION SHEETGizaw TadesseNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian TVET-System: Based On May 2011 Occupational StandardsDocument73 pagesEthiopian TVET-System: Based On May 2011 Occupational StandardsendashawNo ratings yet
- Dereja Academy: Worksheet Personal Vision StatementDocument2 pagesDereja Academy: Worksheet Personal Vision StatementGroom AssefaNo ratings yet
- M03 - Build A Small Wireless LANDocument70 pagesM03 - Build A Small Wireless LANabenezer abitiNo ratings yet
- Assist With Policy Development For Client Support For IT HNS Level IV Extension by Jaleto SunkemoDocument19 pagesAssist With Policy Development For Client Support For IT HNS Level IV Extension by Jaleto SunkemoJaleto sunkemo100% (1)
- Activity 7Document3 pagesActivity 7Elias PetrosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Hardware PeripheralsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Computer Hardware PeripheralsedrisNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian TVET-System: Learning Guide # 1Document23 pagesEthiopian TVET-System: Learning Guide # 1Kefelegn Gulint100% (2)
- Build Internet Infrastructure LO1Document8 pagesBuild Internet Infrastructure LO1mohammed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Equipment and ConsumablesDocument31 pagesMaintaining Equipment and ConsumablesTewodros alemuNo ratings yet
- UC6 Maintain Equipment and Software Inventory and DocumentationDocument38 pagesUC6 Maintain Equipment and Software Inventory and DocumentationmulugetaNo ratings yet
- Monitor and Support Data Conversion Abenet DBMS L IVDocument5 pagesMonitor and Support Data Conversion Abenet DBMS L IVAbenet AsmellashNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems Laboratory ManualDocument97 pagesDistributed Systems Laboratory Manualeyob abelNo ratings yet
- TM10 Evaluating and Selecting Web Hosting ServiceDocument55 pagesTM10 Evaluating and Selecting Web Hosting Servicefikadu walkaNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian TVET System: LG CodeDocument6 pagesEthiopian TVET System: LG CodeFitawu TekolaNo ratings yet
- HNS New OS 2021 AdamaDocument184 pagesHNS New OS 2021 AdamabayushNo ratings yet
- M02 - Configuring and Administering ServerDocument77 pagesM02 - Configuring and Administering ServerAlazar walle100% (1)
- LO2 Provide Advice On Software, Hardware or NetworkDocument11 pagesLO2 Provide Advice On Software, Hardware or NetworkTechalew100% (1)
- Install Dspace 7 On WindowsDocument4 pagesInstall Dspace 7 On Windowsdemtec.soptecNo ratings yet
- Mis ExamDocument3 pagesMis ExamchisomoNo ratings yet
- Administering Network and Hardware PeripheralDocument37 pagesAdministering Network and Hardware PeripheralEyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- Answers PDFDocument138 pagesAnswers PDFsfhiybnNo ratings yet
- FPTC Itsm Level V ProjectDocument15 pagesFPTC Itsm Level V Projectmesfin teshomeNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian TVET System: LG CodeDocument4 pagesEthiopian TVET System: LG CodeFitawu TekolaNo ratings yet
- TTLM of Conduct User TrainingDocument21 pagesTTLM of Conduct User TrainingEliyaas Wakjira Hirpha100% (1)
- 2012121009121309-Authoring ToolDocument35 pages2012121009121309-Authoring ToolIrfan FazailNo ratings yet
- Mekelle Institute of Technology: PC Hardware Troubleshooting (CSE501) Lecture - 4Document63 pagesMekelle Institute of Technology: PC Hardware Troubleshooting (CSE501) Lecture - 4Tsehayou SieleyNo ratings yet
- Chimdesa Gedefa Assignment #2 Causal and Entry ConsistencyDocument15 pagesChimdesa Gedefa Assignment #2 Causal and Entry ConsistencyBũ ŚĥNo ratings yet
- Administer Network HardwareDocument62 pagesAdminister Network HardwareMintesnot AdeNo ratings yet
- Maintain Inventory of Information TechnologyDocument36 pagesMaintain Inventory of Information Technologydesta bulatoNo ratings yet
- 03 Teacher's Guide TemplateDocument27 pages03 Teacher's Guide TemplatemeymunaNo ratings yet
- ICT ITS4!04!0811 Monitor and Support Data ConversionDocument5 pagesICT ITS4!04!0811 Monitor and Support Data ConversionMinegezame Getachew LegeNo ratings yet
- InstutionalDocument8 pagesInstutionalhiwot kebedeNo ratings yet
- Year: 4th Semester:7th: Lab ManualDocument26 pagesYear: 4th Semester:7th: Lab ManualMehari Kiros HilufNo ratings yet
- Car Brake Tester Installation PDFDocument67 pagesCar Brake Tester Installation PDFc7oplayNo ratings yet
- Report of Profit PredictionDocument15 pagesReport of Profit PredictionHarsh Garg 24601No ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Communication TechnologyDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Information Communication TechnologyjoNo ratings yet
- MCITP Guide To Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Server Administration (Exam #70-646)Document52 pagesMCITP Guide To Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Server Administration (Exam #70-646)Shane RockafellowNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia Application Form PDFDocument2 pagesEthiopia Application Form PDFRamancoronaNo ratings yet
- LO1 Analyze Client Support IssuesDocument26 pagesLO1 Analyze Client Support IssuesTechalewNo ratings yet
- Application Letter Sample For Fresh Graduate Information TechnologyDocument8 pagesApplication Letter Sample For Fresh Graduate Information TechnologysnnscprmdNo ratings yet
- Update and DocumentDocument53 pagesUpdate and DocumentJaleto sunkemo100% (1)
- Lo2: Process and Organize Data: Important Notes Selecting The Right Technology and SoftwareDocument5 pagesLo2: Process and Organize Data: Important Notes Selecting The Right Technology and SoftwareaduganawNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Web Technology Unit - 1: Tcp/IpDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Web Technology Unit - 1: Tcp/IpLone SomhelmeNo ratings yet
- LO2 Identify IT System Training NeedsDocument13 pagesLO2 Identify IT System Training NeedsTechalewNo ratings yet
- PLAN and OrgDocument20 pagesPLAN and OrgabdiNo ratings yet
- Determining Suitability of Database Functionality and Scalability UC - 7Document10 pagesDetermining Suitability of Database Functionality and Scalability UC - 7Aliyan AmanNo ratings yet
- UC4-LO4. Evaluate and Edit DocumentationDocument12 pagesUC4-LO4. Evaluate and Edit DocumentationmengistuNo ratings yet
- MO7 Apply Problem-Solving Techniques To Routine MalfunctionDocument26 pagesMO7 Apply Problem-Solving Techniques To Routine MalfunctionLusi Abdella100% (1)
- Learning Module 01Document3 pagesLearning Module 01sample name100% (1)
- Halstead Calculator Doc FinalDocument30 pagesHalstead Calculator Doc FinalAlanoobz100% (1)
- 04 - 05-AI-Knowledge and ReasoningDocument61 pages04 - 05-AI-Knowledge and ReasoningderbewNo ratings yet
- My Connect HW Prepheral LO 3Document9 pagesMy Connect HW Prepheral LO 3melaku sabureNo ratings yet
- ER Practical 12rDocument3 pagesER Practical 12rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 6rDocument6 pagesER Practical 6rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 2Document1 pageER Practical 2remose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 3Document4 pagesER Practical 3remose06No ratings yet
- 1 Database Design (25%)Document4 pages1 Database Design (25%)remose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 9rDocument4 pagesER Practical 9rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 8rDocument3 pagesER Practical 8rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 7rDocument5 pagesER Practical 7rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 10rDocument3 pagesER Practical 10rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 11rDocument2 pagesER Practical 11rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 13rDocument4 pagesER Practical 13rremose06No ratings yet
- LO2 - Gather Data Through Formal and Informal ProcessDocument8 pagesLO2 - Gather Data Through Formal and Informal Processremose06No ratings yet
- Its1 Module 4Document43 pagesIts1 Module 4remose06No ratings yet
- Dansa Gauge Nigata SeikiDocument2 pagesDansa Gauge Nigata SeikisssstoretangerangNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Power SupplyDocument33 pagesService Manual: Power SupplyMuhammet CanNo ratings yet
- 2023 06 07 23 24 26 DESKTOP-GPG06PB LogDocument379 pages2023 06 07 23 24 26 DESKTOP-GPG06PB LogTriust XDNo ratings yet
- X Plane 12 Book 1 1 - FinalDocument200 pagesX Plane 12 Book 1 1 - Finalrobert100% (1)
- Afimilk SilentherdsmanDocument80 pagesAfimilk SilentherdsmanlegarciNo ratings yet
- DSD Lab Manuals: Design and Implementation of A Reat Time Clock On FpgaDocument12 pagesDSD Lab Manuals: Design and Implementation of A Reat Time Clock On FpgaAL RIZWANNo ratings yet
- D73668GC21 AppdDocument10 pagesD73668GC21 Appdpraveen2kumar5733No ratings yet
- Infineon-Getting Started REF XDPL8210 U35W DP - vision-GettingStarted-v01 01-ENDocument10 pagesInfineon-Getting Started REF XDPL8210 U35W DP - vision-GettingStarted-v01 01-ENIT JPTOKNo ratings yet
- GV55 Quick Start V1.0Document2 pagesGV55 Quick Start V1.0Charly KureñoNo ratings yet
- Bershka 11776 CC Fashion Mall Tampico - v02 PDFDocument8 pagesBershka 11776 CC Fashion Mall Tampico - v02 PDFCesar TorresNo ratings yet
- Assembly Language Lecture6Document10 pagesAssembly Language Lecture6bmas19692No ratings yet
- Question Papers Solutions: Unit 1Document105 pagesQuestion Papers Solutions: Unit 1Snighda SenNo ratings yet
- Lenovo Legion 5 17ITH6 SpecDocument7 pagesLenovo Legion 5 17ITH6 SpecCikal MuharramNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalogue: Edition 03/2011Document112 pagesSpare Parts Catalogue: Edition 03/2011Gustavo Astudillo100% (2)
- 01 MS-16R5 v1.0 EnglishDocument56 pages01 MS-16R5 v1.0 Englishanykind1808No ratings yet
- YyyDocument3 pagesYyyBAD CHIPNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PracticeTest 98-365 v2019-07-30 by - Laura - 227qDocument131 pagesMicrosoft PracticeTest 98-365 v2019-07-30 by - Laura - 227qDavis BejaranoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Modern Usb C Speaker ZwartDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Modern Usb C Speaker ZwartDuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP CP: SM-G570M Block DiagramDocument43 pagesAP CP: SM-G570M Block DiagramGilson PereiraNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Routing Engine Technical Introduction: JTAC White Paper Technote ID: TN303 April 2016Document31 pagesNext Generation Routing Engine Technical Introduction: JTAC White Paper Technote ID: TN303 April 2016Ronie SinghNo ratings yet
- Machine LanguageDocument16 pagesMachine LanguageDarwin FerrerNo ratings yet
- ACA - Chapter 6Document75 pagesACA - Chapter 6Praveen YadavNo ratings yet
- Sun Fire X4140 Service Diagnostic GuideDocument80 pagesSun Fire X4140 Service Diagnostic GuidePeterNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics Lec4 Spring 2021-2Document59 pagesDigital Forensics Lec4 Spring 2021-2change abcNo ratings yet
- Installation & Operating Instructions For DU / DC Series Area, Master & Combination Alarm SystemsDocument34 pagesInstallation & Operating Instructions For DU / DC Series Area, Master & Combination Alarm SystemsEsteban PerezNo ratings yet
- Microprogramming - Programmable Digital Microcircuits - CERN (1982) (Motorola 68000)Document34 pagesMicroprogramming - Programmable Digital Microcircuits - CERN (1982) (Motorola 68000)Effervescent FlufferNo ratings yet
- Optiplex 330 Into HackintoshDocument3 pagesOptiplex 330 Into HackintoshorangotaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual of Computer Maintenance and Troubleshooting (C301-3350701) Semester - 5Document59 pagesLab Manual of Computer Maintenance and Troubleshooting (C301-3350701) Semester - 5Spidy SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts List: Electric PokerDocument20 pagesSpare Parts List: Electric PokeralmirNo ratings yet
Lo3 Connect Hardware Peripherals
Lo3 Connect Hardware Peripherals
Uploaded by
remose060 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views8 pagesInstalling new hardware peripherals should be done with minimal disruption to clients. Installations are best scheduled during quiet periods like holidays or after hours when clients will not need their computers. All new devices must be thoroughly tested according to a documented test plan to ensure they function properly and meet client needs before use. When connecting new peripherals, drivers may need to be installed and the operating system will detect and configure the new hardware.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInstalling new hardware peripherals should be done with minimal disruption to clients. Installations are best scheduled during quiet periods like holidays or after hours when clients will not need their computers. All new devices must be thoroughly tested according to a documented test plan to ensure they function properly and meet client needs before use. When connecting new peripherals, drivers may need to be installed and the operating system will detect and configure the new hardware.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views8 pagesLo3 Connect Hardware Peripherals
Lo3 Connect Hardware Peripherals
Uploaded by
remose06Installing new hardware peripherals should be done with minimal disruption to clients. Installations are best scheduled during quiet periods like holidays or after hours when clients will not need their computers. All new devices must be thoroughly tested according to a documented test plan to ensure they function properly and meet client needs before use. When connecting new peripherals, drivers may need to be installed and the operating system will detect and configure the new hardware.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
LO3: CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERALS
3.1. Avoiding Disruption to the Client
Minimal Disruption to the Client
One of the most important considerations when installing a new hardware peripheral is to try and install the device
with the least amount of disruption to the client. A client may not be very happy if you install a piece of hardware
equipment while they are creating an urgent report. It is important to schedule installation times that are:
also suitable to the client’s or computer user’s schedules
sufficient lengths to install and thoroughly test the hardware device.
To achieve this, make sure that you are aware of:
Common organisational procedures that regularly need to be performed on the computer (for example, end of
month processing or weekly backups) and plan installations outside these periods
Current projects, deadlines and schedules of the client/user.
Installations should be scheduled for times such as:
quiet periods (for example, during holiday periods)
before or after normal office hours
while the client/user is out of the office
When the client will not need their computer.
It can be difficult to work out how long it will take to install a peripheral device. It will vary according to the type of
device, current operating system, problems requiring troubleshooting and the experience of the installer. If you will
be regularly performing installations, keeping a log of installations — noting the time required and problems
experienced — could help to estimate the time spent on future installations.
Once you have arranged a suitable time, make sure you adhere to it or give advanced notice if you will be delayed.
Remember that clients may have scheduled their daily workload around the installation.
Also consider the timeframe expected by client when installing new hardware. If you work for a busy organisation it
may be necessary to work out a daily to-do list. Order tasks with priority given to installations that perform critical
functions or have been waiting to be done for the longest amount of time.
3.2. Testing Devices and Creating a Test Plan
3.2.1. Testing
In addition to ensuring a device is able to perform a basic task (such as printing a test page or scanning an image) it is
also necessary that all functionality required by the client is tested. When new peripheral equipment is not tested for
critical functions before being used, it can lead to malfunction, causing large disruptions to clients and potentially
damage other parts of a computer system. If, for example, a new external zip drive has not been tested to check it will
be capable of making backups of specific files, it could mean that vital information of the client’s could be destroyed
if those backups were not successful.
Ensure that all new installations are thoroughly tested after initial setup and prior to use by the client. Depending on
the device, different functions will need to be tested.
Devices that have components that are known to degrade with time, especially printers, should also be tested
periodically. Printers need to be routinely tested, as components such as the ink cartridges and toner can cause
deterioration of print quality and may require maintenance and/or cleaning.
All tests should be completed according to a documented test plan.
Some suggestions of functions that may be tested for a printer, scanner and digital camera devices are included below.
CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERAL 1
LO3: CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERALS
Printer
Printer functions that may be tested are:
Can the printer handle different paper types (for example A4, A5, foolscap, thick, thin, overhead
transparencies)?
Will the printer work successfully on different computers?
Will the printer work successfully with different software packages (for example, word processing,
spreadsheets and desktop publishing)?
Is black and white print quality acceptable to clients?
Is colour print quality acceptable to clients?
Scanner
Scanner functions that may be tested are:
Is the resolution of a scanned image an acceptable quality?
Does the scanner work correctly with different software packages (eg a word processor or desktop publishing
package)?
Can the scanner handle items of unusual size and thickness (eg a large book or cardboard poster)?
Does the OCR software scan a document successfully?
Will the scanner work successfully on other computers?
Digital Camera
Camera functions that may be tested are:
Are all images in the camera transferred correctly from the camera to the computer?
Does the camera software allow sufficient editing of the photo images (eg rotating, cropping, reducing red-
eye)?
Will the digital camera work successfully on other computers?
3.2.2. What is a Test Plan?
A test plan is used to work out a structured process to ensure that a new device will work under all expected
circumstances. It logically describes:
1. functions that need to be tested
2. an example test case scenario
3. expected results for each scenario
4. what actually happened once the test has been performed.
Example test case scenarios should simulate realistic work patterns — ie the scenario should realistically demonstrate
if a function will be satisfactory after implementation.
Because testing is so critical to the successful implementation of the new device, it is important that a test plan is
comprehensive and considers every way a device will need to function after implementation. It is useful to refer back
to the client requirements so that you will remember functions that will regularly be expected by the client.
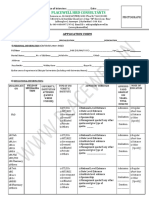
On the next page is a test plan, with selected scenarios, to ensure that a printer is working to acceptable client
requirements.
CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERAL 2
LO3: CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERALS
CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERAL 3
LO3: CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERALS
3.3. Connecting and Configuring Hardware Peripherals
Peripherals will normally connect to an existing interface port or wireless. When connecting peripherals, it is
important for you to understand the role the operating system plays in hardware connectivity. Once you connect
hardware to your system it is the operating system that detects the new hardware and sends the message to the user for
immediate configuration. The operating system detects plug and play hardware without prompting the user.
Note:
The operating system acts as an intermediary between the hardware and the user. If the hardware is not configured it
will not work properly or communicate with the rest of the computer system.
Operating system – software used to manage and control the operations of the hardware.
The following are functions of an operating system that you should note:
It manages the hardware and software resources of the system. In a desktop computer, these resources include
such things as the processor, memory, disk and space
It provides a stable, consistent way for applications to deal with the hardware without having to know all the
details of the hardware
With the large variety of computer systems, operating systems, peripheral types and features, and manufacturers, each
peripheral device will have its own individual installation procedure. It is important to refer to manufacturer guidelines
and manuals when installing any hardware device to ensure that all procedures are correctly followed.
There are three ways that you can configure/install device software (drives). These are:
Automatic Installation
Plug and play
Manual Installation
Automatic Installation - also known as Single exe installation - is one that most people are familiar with.
Plug and Play - Windows performs this function without you noticing that it is taking place. Windows
XP/Vista/7/8/10 all have drives in the package for devices that are compatible to Windows operating system.
Manual Installation - here you are given instructions on how to install a particular drive and you are expected to
follow the steps.
Procedures which are generally followed when installing any new peripheral device include:
1. Plugging in the cables between the device and the computer
2. Installing any drivers
3. Troubleshooting installation when necessary
4. Customising the device
5. Testing the device for satisfying required conditions.
What are Drivers?
Whenever you install a hardware peripheral device, you will also have to install a driver. A driver is a software
program that allows the hardware device to talk to the operating system.
Generally, driver software will be included within the packaging of a new device. Sometimes operating systems, such
as Windows XP, automatically provide their own drivers if you don’t provide one. At times it may be necessary to
find a newer version of a driver than the one that has been provided by the manufacturer. It is a good idea to regularly
check the manufacturer’s website to see if any new drivers have been developed.
What is Plug and Play?
Plug and play is a hardware technology that enables many operating systems to automatically recognise new hardware
devices and configure them automatically. Most USB devices support plug and play.
CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERAL 4
LO3: CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERALS
3.3.1. Installing a Printer
1. Obtain the Correct Printer Cable
In many cases a printer won’t automatically have a cable included with the original purchase. Check the printer
specifications — you will probably need to buy either a parallel or USB cable.
2. Plug in the Cable
1. Turn off the power to both the printer and the computer.
2. Plug the printer cable into the correct port of the PC — depending on the type of printer the port will most
likely to be either a USB or a parallel port located on the back of the computer. If you are plugging the cable
into a parallel port connection you will need to secure the cable by either tightening small screws or snapping
in wire connectors.
3. Install Ink
Depending on the printer you have you may need to install an ink cartridge (for inkjet printers) or toner cartridge
(for laser printers). Turn the computer’s power on and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to install a new
cartridge.
4. Install the Printer Driver
At some point the computer will either recognise that new hardware has been installed (for example if the
operating system is plug and play compatible) or you will need to tell the computer that a new device has been
added. In either case, you will at some stage be asked for the printer model and a printer driver. Make sure you
install the printer driver at this stage. Sometimes the installation CD will automatically run, installing the printer
driver at the same time.
5. Print a Test Page
Often at the end of the driver installation you will be asked if you would like to print a test page. This is a good
idea because you can quickly determine if the printer is working correctly. If not you can troubleshoot the
installation.
6. Troubleshoot Printer Installation (when necessary)
If a page is not able to print it is necessary to go back and determine why the printer is not working. There are a
number of factors that can contribute to printer problems including:
cables between printer and computer are not properly connected
printer driver is not suitable for the current operating system
paper is loaded incorrectly
ink cartridge or toner is not correctly installed
printer power switch is off.
Suggested Solutions for Common Printer Problems
A blank page is coming out of the printer
You may have run out of ink or toner. Replace ink cartridge or toner.
Make sure that your printer has been set to the default setting.
The document is printing on the wrong part of the page
Check that you have aligned printer to the correct orientation (portrait or landscape).
Make sure the margins have been set correctly in the software program you are using (eg the word
processor or desktop publishing package).
Make sure that the paper has been loaded correctly.
The quality of the printout is poor
If the printer is an inkjet the heads of the ink cartridge may need to be cleaned.
Some printers have software that allows you to change the quality of the printout from draft to best
quality.
CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERAL 5
LO3: CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERALS
Customizing the Printer
Depending on your client’s needs, there may be a need to alter the default printer settings. Some settings that may be
customised include:
Changing the Page Layout — a page may need to be printed in either landscape or portrait orientation.
Changing the Paper Source — depending on the complexity of the printer there may be a variety of trays the
printer has available to use.
Changing the Print Quality — depending on the printer use, a client may require best, normal or draft quality
of print.
Setting the Default Printer — if there is more than one printer attached to a computer, you may need to
change the settings so that the newer model is considered the default model.
3.3.2. Installing a Scanner
Scanners can attach to a computer generally via a USB or a parallel port connection.
1. Turn off the computer and position the scanner
Before commencing installation, turn off power to the computer and place the scanner on a level surface, close
enough to the computer so that the cable will be able to attach to both devices.
2. Unlock the scanner
Many scanners have a lock on the bottom to make sure that components are not dislodged when transporting.
Make sure that you unlock the scanner before commencing installation.
3. Plug in the cable
Plug the cable into either the USB or parallel port connection, depending on the type of scanner.
4. Turn on the scanner
Some scanners will have a power cord that will need to be plugged into a power outlet. Other scanners are
dependent on power from the computer. Some scanners will also have an on/off switch, which will also need to
be turned on.
5. Turn on the PC
When you turn on your computer, most operating systems will recognise that new hardware has been added (eg it
is plug and play compatible). If it hasn’t recognised the new scanner you may need to tell your computer that a
new device has been added.
6. Insert the scanner driver
At some point you will be asked if you have a disk for your scanner. This generally means the computer is
requesting you provide it with the disk containing the driver software.
7. Scan a test image
Ensure that the scanner is working by performing a scan of a book or magazine page.
8. Troubleshoot scanner installation (if necessary)
Suggested Solutions for Common Scanner Problems
Scanner making a clicking sound
Check that the scanner lock is in the unlock position.
Unable to scan anything
Make sure that the scanner is plugged in and all cables are connected properly.
Customize the scanner
Many scanners will also have extra software you can use for scanning. Check the scanner manual to see
whether your scanner has additional software. Install the additional software — it will probably be useful for
scanning text and performing basic image editing functions. The software may also allow you ability to adjust
settings such as dpi (dots per inch), colour, black and white or greyscale. Make sure you modify settings for
normal scanning requirements.
CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERAL 6
LO3: CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERALS
3.3.3. Installing a Digital Camera
1. Check the camera equipment
Before connecting a digital camera to a computer you firstly need to check that it is capable of working on its
own. Measures that need to be taken include:
Inserting a memory card — the majority of digital cameras need you to install a memory card to store
the images that are captured.
Installing batteries — Make sure to install batteries into the battery component of the camera.
2. Turn on the camera’s power
Make sure that you have switched on the camera before trying to connect the device to the computer.
3. Connect the camera
The majority of digital cameras will connect to the computer with a USB cable.
4. Install the camera software
In most cases your computer will recognise that you have added new hardware. At this stage you may be
prompted to install software (including software drivers) on your computer.
5. Test the connection between camera and computer
Using the software installed on the computer, try to transfer some photos from the camera to the computer.
6. Troubleshoot camera installation (if necessary)
Suggested Solutions for Common Camera Problems
Camera is not recognized by the computer
The camera may not be properly connected to the computer.
Check that the cable and its connectors are in good condition.
Battery charge may not be sufficient. Ensure that batteries are charged sufficiently to allow transfer of photos.
3.3.4. Monitor
A monitor is an output device which displays what’s going on in the system. There are many types of monitors such as
CRT, LCD, PLASMA PANEL, and LED. Each accommodates different technology.
Installation
1. Most monitors come with a tilt-and-swivel base that lets you adjust the angle of the screen and reduce glare
from overhead lighting. If necessary attach the base to the monitor.
2. If necessary, connect the monitor cable to the back of the monitor. The monitor cable is permanently attached on
some monitors.
3. If necessary, connect the power cable to the back of the monitor, the power cable is permanently attached on
some monitors.
4. Connect the monitor cable to the monitor port at the back of the computer. The monitor port is usually located
on the video card.
Troubleshooting
1. The monitor is not working properly.
Check both the power and data cable connected properly.
Change the resolution and colors.
Check the refresh rate of the display adapter.
2. The screen is discolored or it can’t display the text’s\image’s real color.
There is a pin or two of the data cable may be bent.
One of the primary colors may be missing. Use the control button on the monitor.
CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERAL 7
LO3: CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERALS
3. In some area of the monitor, the colors are spread.
There must be any magnetic field around the monitor. Remove the magnetic device which causes the
problem. It may be speaker, radio, etc.
Use the degauss function from the controls of monitor.
4. There is no display at all
Check the all cables related to monitor.
Check the monitor is on.
Check whether the system gets the power.
Check the display adapter and press it.
Check the Li battery on the motherboard.
Check the CPU-Fan is revolting. Sometime this also caused the problem
CONNECT HARDWARE PERIPHERAL 8
You might also like
- Lokotrack LT1213 S N 72964Document368 pagesLokotrack LT1213 S N 72964Carlos Israel Gomez67% (6)
- Student Workbook - ICAICT303A Connect Internal Hardware ComponentsDocument104 pagesStudent Workbook - ICAICT303A Connect Internal Hardware ComponentsSarah ButlerNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument10 pagesSoftwareTalila B. Robsan100% (1)
- Levels of SupportDocument3 pagesLevels of SupportNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Recording Client Support RequirementsDocument65 pagesRecording Client Support RequirementswosenNo ratings yet
- Record Client Support SurviceDocument8 pagesRecord Client Support SurviceGizaw Tadesse100% (1)
- MO 6 Record Client Support RequirementsDocument25 pagesMO 6 Record Client Support RequirementsLusi Abdella100% (1)
- Configuring and Using InternetDocument29 pagesConfiguring and Using Internetm.tsedey2013100% (2)
- Protect Application or System Software INFORMATION SHEETDocument22 pagesProtect Application or System Software INFORMATION SHEETGizaw TadesseNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian TVET-System: Based On May 2011 Occupational StandardsDocument73 pagesEthiopian TVET-System: Based On May 2011 Occupational StandardsendashawNo ratings yet
- Dereja Academy: Worksheet Personal Vision StatementDocument2 pagesDereja Academy: Worksheet Personal Vision StatementGroom AssefaNo ratings yet
- M03 - Build A Small Wireless LANDocument70 pagesM03 - Build A Small Wireless LANabenezer abitiNo ratings yet
- Assist With Policy Development For Client Support For IT HNS Level IV Extension by Jaleto SunkemoDocument19 pagesAssist With Policy Development For Client Support For IT HNS Level IV Extension by Jaleto SunkemoJaleto sunkemo100% (1)
- Activity 7Document3 pagesActivity 7Elias PetrosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Hardware PeripheralsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Computer Hardware PeripheralsedrisNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian TVET-System: Learning Guide # 1Document23 pagesEthiopian TVET-System: Learning Guide # 1Kefelegn Gulint100% (2)
- Build Internet Infrastructure LO1Document8 pagesBuild Internet Infrastructure LO1mohammed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Equipment and ConsumablesDocument31 pagesMaintaining Equipment and ConsumablesTewodros alemuNo ratings yet
- UC6 Maintain Equipment and Software Inventory and DocumentationDocument38 pagesUC6 Maintain Equipment and Software Inventory and DocumentationmulugetaNo ratings yet
- Monitor and Support Data Conversion Abenet DBMS L IVDocument5 pagesMonitor and Support Data Conversion Abenet DBMS L IVAbenet AsmellashNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems Laboratory ManualDocument97 pagesDistributed Systems Laboratory Manualeyob abelNo ratings yet
- TM10 Evaluating and Selecting Web Hosting ServiceDocument55 pagesTM10 Evaluating and Selecting Web Hosting Servicefikadu walkaNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian TVET System: LG CodeDocument6 pagesEthiopian TVET System: LG CodeFitawu TekolaNo ratings yet
- HNS New OS 2021 AdamaDocument184 pagesHNS New OS 2021 AdamabayushNo ratings yet
- M02 - Configuring and Administering ServerDocument77 pagesM02 - Configuring and Administering ServerAlazar walle100% (1)
- LO2 Provide Advice On Software, Hardware or NetworkDocument11 pagesLO2 Provide Advice On Software, Hardware or NetworkTechalew100% (1)
- Install Dspace 7 On WindowsDocument4 pagesInstall Dspace 7 On Windowsdemtec.soptecNo ratings yet
- Mis ExamDocument3 pagesMis ExamchisomoNo ratings yet
- Administering Network and Hardware PeripheralDocument37 pagesAdministering Network and Hardware PeripheralEyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- Answers PDFDocument138 pagesAnswers PDFsfhiybnNo ratings yet
- FPTC Itsm Level V ProjectDocument15 pagesFPTC Itsm Level V Projectmesfin teshomeNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian TVET System: LG CodeDocument4 pagesEthiopian TVET System: LG CodeFitawu TekolaNo ratings yet
- TTLM of Conduct User TrainingDocument21 pagesTTLM of Conduct User TrainingEliyaas Wakjira Hirpha100% (1)
- 2012121009121309-Authoring ToolDocument35 pages2012121009121309-Authoring ToolIrfan FazailNo ratings yet
- Mekelle Institute of Technology: PC Hardware Troubleshooting (CSE501) Lecture - 4Document63 pagesMekelle Institute of Technology: PC Hardware Troubleshooting (CSE501) Lecture - 4Tsehayou SieleyNo ratings yet
- Chimdesa Gedefa Assignment #2 Causal and Entry ConsistencyDocument15 pagesChimdesa Gedefa Assignment #2 Causal and Entry ConsistencyBũ ŚĥNo ratings yet
- Administer Network HardwareDocument62 pagesAdminister Network HardwareMintesnot AdeNo ratings yet
- Maintain Inventory of Information TechnologyDocument36 pagesMaintain Inventory of Information Technologydesta bulatoNo ratings yet
- 03 Teacher's Guide TemplateDocument27 pages03 Teacher's Guide TemplatemeymunaNo ratings yet
- ICT ITS4!04!0811 Monitor and Support Data ConversionDocument5 pagesICT ITS4!04!0811 Monitor and Support Data ConversionMinegezame Getachew LegeNo ratings yet
- InstutionalDocument8 pagesInstutionalhiwot kebedeNo ratings yet
- Year: 4th Semester:7th: Lab ManualDocument26 pagesYear: 4th Semester:7th: Lab ManualMehari Kiros HilufNo ratings yet
- Car Brake Tester Installation PDFDocument67 pagesCar Brake Tester Installation PDFc7oplayNo ratings yet
- Report of Profit PredictionDocument15 pagesReport of Profit PredictionHarsh Garg 24601No ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Communication TechnologyDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Information Communication TechnologyjoNo ratings yet
- MCITP Guide To Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Server Administration (Exam #70-646)Document52 pagesMCITP Guide To Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Server Administration (Exam #70-646)Shane RockafellowNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia Application Form PDFDocument2 pagesEthiopia Application Form PDFRamancoronaNo ratings yet
- LO1 Analyze Client Support IssuesDocument26 pagesLO1 Analyze Client Support IssuesTechalewNo ratings yet
- Application Letter Sample For Fresh Graduate Information TechnologyDocument8 pagesApplication Letter Sample For Fresh Graduate Information TechnologysnnscprmdNo ratings yet
- Update and DocumentDocument53 pagesUpdate and DocumentJaleto sunkemo100% (1)
- Lo2: Process and Organize Data: Important Notes Selecting The Right Technology and SoftwareDocument5 pagesLo2: Process and Organize Data: Important Notes Selecting The Right Technology and SoftwareaduganawNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Web Technology Unit - 1: Tcp/IpDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Web Technology Unit - 1: Tcp/IpLone SomhelmeNo ratings yet
- LO2 Identify IT System Training NeedsDocument13 pagesLO2 Identify IT System Training NeedsTechalewNo ratings yet
- PLAN and OrgDocument20 pagesPLAN and OrgabdiNo ratings yet
- Determining Suitability of Database Functionality and Scalability UC - 7Document10 pagesDetermining Suitability of Database Functionality and Scalability UC - 7Aliyan AmanNo ratings yet
- UC4-LO4. Evaluate and Edit DocumentationDocument12 pagesUC4-LO4. Evaluate and Edit DocumentationmengistuNo ratings yet
- MO7 Apply Problem-Solving Techniques To Routine MalfunctionDocument26 pagesMO7 Apply Problem-Solving Techniques To Routine MalfunctionLusi Abdella100% (1)
- Learning Module 01Document3 pagesLearning Module 01sample name100% (1)
- Halstead Calculator Doc FinalDocument30 pagesHalstead Calculator Doc FinalAlanoobz100% (1)
- 04 - 05-AI-Knowledge and ReasoningDocument61 pages04 - 05-AI-Knowledge and ReasoningderbewNo ratings yet
- My Connect HW Prepheral LO 3Document9 pagesMy Connect HW Prepheral LO 3melaku sabureNo ratings yet
- ER Practical 12rDocument3 pagesER Practical 12rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 6rDocument6 pagesER Practical 6rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 2Document1 pageER Practical 2remose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 3Document4 pagesER Practical 3remose06No ratings yet
- 1 Database Design (25%)Document4 pages1 Database Design (25%)remose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 9rDocument4 pagesER Practical 9rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 8rDocument3 pagesER Practical 8rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 7rDocument5 pagesER Practical 7rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 10rDocument3 pagesER Practical 10rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 11rDocument2 pagesER Practical 11rremose06No ratings yet
- ER Practical 13rDocument4 pagesER Practical 13rremose06No ratings yet
- LO2 - Gather Data Through Formal and Informal ProcessDocument8 pagesLO2 - Gather Data Through Formal and Informal Processremose06No ratings yet
- Its1 Module 4Document43 pagesIts1 Module 4remose06No ratings yet
- Dansa Gauge Nigata SeikiDocument2 pagesDansa Gauge Nigata SeikisssstoretangerangNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Power SupplyDocument33 pagesService Manual: Power SupplyMuhammet CanNo ratings yet
- 2023 06 07 23 24 26 DESKTOP-GPG06PB LogDocument379 pages2023 06 07 23 24 26 DESKTOP-GPG06PB LogTriust XDNo ratings yet
- X Plane 12 Book 1 1 - FinalDocument200 pagesX Plane 12 Book 1 1 - Finalrobert100% (1)
- Afimilk SilentherdsmanDocument80 pagesAfimilk SilentherdsmanlegarciNo ratings yet
- DSD Lab Manuals: Design and Implementation of A Reat Time Clock On FpgaDocument12 pagesDSD Lab Manuals: Design and Implementation of A Reat Time Clock On FpgaAL RIZWANNo ratings yet
- D73668GC21 AppdDocument10 pagesD73668GC21 Appdpraveen2kumar5733No ratings yet
- Infineon-Getting Started REF XDPL8210 U35W DP - vision-GettingStarted-v01 01-ENDocument10 pagesInfineon-Getting Started REF XDPL8210 U35W DP - vision-GettingStarted-v01 01-ENIT JPTOKNo ratings yet
- GV55 Quick Start V1.0Document2 pagesGV55 Quick Start V1.0Charly KureñoNo ratings yet
- Bershka 11776 CC Fashion Mall Tampico - v02 PDFDocument8 pagesBershka 11776 CC Fashion Mall Tampico - v02 PDFCesar TorresNo ratings yet
- Assembly Language Lecture6Document10 pagesAssembly Language Lecture6bmas19692No ratings yet
- Question Papers Solutions: Unit 1Document105 pagesQuestion Papers Solutions: Unit 1Snighda SenNo ratings yet
- Lenovo Legion 5 17ITH6 SpecDocument7 pagesLenovo Legion 5 17ITH6 SpecCikal MuharramNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalogue: Edition 03/2011Document112 pagesSpare Parts Catalogue: Edition 03/2011Gustavo Astudillo100% (2)
- 01 MS-16R5 v1.0 EnglishDocument56 pages01 MS-16R5 v1.0 Englishanykind1808No ratings yet
- YyyDocument3 pagesYyyBAD CHIPNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PracticeTest 98-365 v2019-07-30 by - Laura - 227qDocument131 pagesMicrosoft PracticeTest 98-365 v2019-07-30 by - Laura - 227qDavis BejaranoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Modern Usb C Speaker ZwartDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Modern Usb C Speaker ZwartDuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP CP: SM-G570M Block DiagramDocument43 pagesAP CP: SM-G570M Block DiagramGilson PereiraNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Routing Engine Technical Introduction: JTAC White Paper Technote ID: TN303 April 2016Document31 pagesNext Generation Routing Engine Technical Introduction: JTAC White Paper Technote ID: TN303 April 2016Ronie SinghNo ratings yet
- Machine LanguageDocument16 pagesMachine LanguageDarwin FerrerNo ratings yet
- ACA - Chapter 6Document75 pagesACA - Chapter 6Praveen YadavNo ratings yet
- Sun Fire X4140 Service Diagnostic GuideDocument80 pagesSun Fire X4140 Service Diagnostic GuidePeterNo ratings yet
- Digital Forensics Lec4 Spring 2021-2Document59 pagesDigital Forensics Lec4 Spring 2021-2change abcNo ratings yet
- Installation & Operating Instructions For DU / DC Series Area, Master & Combination Alarm SystemsDocument34 pagesInstallation & Operating Instructions For DU / DC Series Area, Master & Combination Alarm SystemsEsteban PerezNo ratings yet
- Microprogramming - Programmable Digital Microcircuits - CERN (1982) (Motorola 68000)Document34 pagesMicroprogramming - Programmable Digital Microcircuits - CERN (1982) (Motorola 68000)Effervescent FlufferNo ratings yet
- Optiplex 330 Into HackintoshDocument3 pagesOptiplex 330 Into HackintoshorangotaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual of Computer Maintenance and Troubleshooting (C301-3350701) Semester - 5Document59 pagesLab Manual of Computer Maintenance and Troubleshooting (C301-3350701) Semester - 5Spidy SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts List: Electric PokerDocument20 pagesSpare Parts List: Electric PokeralmirNo ratings yet