Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP - Poliomyelitis
NCP - Poliomyelitis
Uploaded by
Cassey Cureg0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
335 views4 pagesThe nursing care plan addresses a 3-year-old patient with poliomyelitis who has impaired mobility and decreased strength in their right leg. The plan includes 21 interventions to monitor vital signs, assess motor function and pain levels, provide skin care and pressure relief, encourage exercise and activity, and collaborate with other specialists to develop an individualized treatment plan. The short-term goal is to see increased strength and function after 8 hours, and the long-term goal within 1 month is for the patient to maintain their functional position, perform independent activity, and increase their strength.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing care plan addresses a 3-year-old patient with poliomyelitis who has impaired mobility and decreased strength in their right leg. The plan includes 21 interventions to monitor vital signs, assess motor function and pain levels, provide skin care and pressure relief, encourage exercise and activity, and collaborate with other specialists to develop an individualized treatment plan. The short-term goal is to see increased strength and function after 8 hours, and the long-term goal within 1 month is for the patient to maintain their functional position, perform independent activity, and increase their strength.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
335 views4 pagesNCP - Poliomyelitis
NCP - Poliomyelitis
Uploaded by
Cassey CuregThe nursing care plan addresses a 3-year-old patient with poliomyelitis who has impaired mobility and decreased strength in their right leg. The plan includes 21 interventions to monitor vital signs, assess motor function and pain levels, provide skin care and pressure relief, encourage exercise and activity, and collaborate with other specialists to develop an individualized treatment plan. The short-term goal is to see increased strength and function after 8 hours, and the long-term goal within 1 month is for the patient to maintain their functional position, perform independent activity, and increase their strength.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
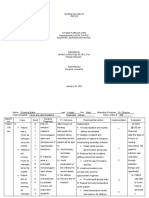
NURSING CARE PLAN
POLIOMYELITIS
Name: CASSEY MAE M. CUREG Year & Section: BSN 3 – C
ASSESSMENT NURSING PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
Subjective Impaired physical Short term: 1. Monitor Vital Signs 1. To note changes and for baseline Short term:
Data: mobility related to After 8 hours of comparison. After 8 hours of
“Parang decreased strength nursing 2. Determine the diagnosis that nursing
lantang gulay and endurance intervention the contributes to immobility. 2. These conditions can cause intervention the
ang kanang secondary to patient will physiological and psychological patient is able to
binti ng anak neuromuscular demonstrate 3. Note factors affecting current problems that can seriously demonstrate
ko. Di niya impairment as increased strength situation and potential time impact physical, social, and increased strength
maigalaw ng evidenced by and function of involved. economic well-being. and function of
maayos at inability to affected body affected body part.
parang purposively move part. 4. Evaluate for presence and 3. Identifies potential impairments
nanghihina.” and lower leg degree of pain, listening to and determines types of Long term:
As verbalized paralysis. Long term: client’s description about interventions needed to provide After 1 month of
by the patient’s After 1 month of manner in which pain limits for client’s safety. nursing
mother. nursing mobility intervention the
intervention the 4. To determine if pain management patient is able to:
Objective patient will be 5. Continually assess motor can improve mobility. Maintain position
Data: able to: function by requesting patient of function as
Age: 3 y/o Maintain to perform certain actions like 5. Evaluates status of individual evidenced by
Gender: position of shrugging shoulders, spreading situation, affecting type and absence of foot
Female function as fingers. choice of interventions. drop.
Height: 95.3 evidenced by Perform physical
cm absence of foot 6. Assess the strength to perform 6. This assessment provides data on activity
Weight: 29 lbs. drop. ROM to all joints. extent of any physical problems independently or
Perform physical and guide therapy. Testing by a within limits of
Ascending activity 7. Ascertain client’s perception of physical therapist may be needed. disease.
Paralysis independently or activity and exercise needs and Increase strength
The patient within limits of impact of current situation. 7. Helps to determine client’s of
is weak disease. Identify cultural beliefs and expectation and beliefs related to unaffected/comp
Have limited Increase expectations affecting recovery activity and potential long-term ensatory body
ROM activity strength of or response to long-term effect of current immobility. Also, parts.
Minimized unaffected/com limitations. identifies barriers that may be Demonstrate
movement pensatory body addressed. techniques/behav
Level of parts. 8. Ascertain nutritional status and iors that enable
functional Demonstrate client’s report or energy level. 8. Deficiencies in nutrients and resumption of
mobility – 2; techniques/beha water, electrolytes, and minerals activity.
Requires viors that enable 9. Determine degree of can negatively affect activity
assistance resumption of immobility in relation to 0 to 4 tolerance.
when activity. scale, noting muscle strength
walking. and tone, joint mobility, 9. Identifies strengths and deficits
cardiovascular status, balance, and may provide information
RR: 26 and endurance. regarding potential for recovery.
PR: 110
BP: 90/60 10. Discuss discrepancies in 10. May be necessary when the client
TEMP: 36.6 movement noted when client is is using avoidance or controlling
unaware of observations and behavior or is not aware of his or
address methods for dealing her own abilities due to anxiety or
with identified problems. fear.
11. Note emotional/behavioral 11. Feelings of frustration or
responses to problems of powerlessness may impede
immobility. attainment of goal.
12. Determine presence of 12. Effects of immobility are rarely
complications related to confined to one body system and
immobility. can include muscle wasting,
contractures, pressure sores,
13. Assist with the treatment of constipation, aspiration
underlying condition causing pneumonia, thrombotic
pain and/or dysfunction. phenomena, and weakened
immune system functioning.
14. Assist or have client reposition
self on a regular schedule as 13. To maximize the potential for
dictated by individual situation. mobility and function.
15. Perform and encourage regular 14. To reduce pressure on sensitive
skin examination and care. areas and to prevent development
of problems with skin integrity.
16. Provide or recommend
pressure-reducing mattress, 15. Reduces tissue pressure and aids
such as egg crate, or pressure- in maximizing cellular perfusion to
relieving mattress, such as prevent dermal injury.
alternating air pressure, or
water. 16. Promotes well-being and
maximizes energy production.
17. Encourage adequate intake of
fluids and nutritious foods. 17. To permit maximal effort and
involvement in activity.
18. Administer medications prior
to activity as needed for pain 18. Antispasmodic medications may
relief. reduce muscle spasms or
spasticity that interferes with
19. Give medications as mobility; analgesics may reduce
appropriate. pain that impedes movement
20. Collaborate with physical 19. …
medicine specialist and
occupational or physical 20. To develop individual exercise and
therapists in providing range- mobility program, to identify
of-motion exercise (active or appropriate mobility devices, and
passive), isotonic muscle to limit or reduce effects and
contractions, assistive devices, complications of immobility.
and activities.
21. Enhances commit to plan,
21. Encourage client’s/SO’s optimizing outcomes.
involvement in decision-making
as much as possible. 22. May need referral for support and
community services to provide
22. Involve client and SO in care, care, supervision, companionship,
assisting them to learn ways of respite services, nutritional and
managing problems of ADL assistance, adaptive devices
immobility. or changes to living environment,
financial assistance, etc.
You might also like
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Abnormal Psychology 9th Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Abnormal Psychology 9th Edition PDF Scribdvictor.lewis791100% (53)
- HydroxyzineDocument3 pagesHydroxyzineapi-3797941100% (2)
- Cutting HandlingDocument25 pagesCutting HandlingWalid AmdouniNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida NCPDocument3 pagesSpina Bifida NCPShahzad GulfamNo ratings yet
- ClubfootDocument1 pageClubfootBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Nursing Diagnosis and CareDocument1 pageThalassemia Nursing Diagnosis and CareHannah Clarisse Monge IgniNo ratings yet
- GC COURSEWORK (Maternal April 13, 2020) - VARGASDocument5 pagesGC COURSEWORK (Maternal April 13, 2020) - VARGASKathleen VargasNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument3 pagesDischarge PlanDranlie LagdamenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For InflammationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For InflammationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Nitumusiina Billy Admitted With Acute Otitis Media and TonsillitisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Nitumusiina Billy Admitted With Acute Otitis Media and TonsillitisNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Common Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMADocument3 pagesCommon Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMAann camposNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Neonatal PneumoniaDocument1 pageNeonatal PneumoniaAlyssa Rose MacasiebNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanAnnahNo ratings yet
- Rationale: This Will Assess Pain LevelDocument7 pagesRationale: This Will Assess Pain LevelCoreyNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Impetigo: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Impetigo: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Cabuya - PEDIA NCP (IMPERFORATE ANUS)Document3 pagesCabuya - PEDIA NCP (IMPERFORATE ANUS)lorreaNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument5 pagesTetanusBasant karn100% (4)
- NCP For ConcussionDocument3 pagesNCP For Concussiontamtam_antonio100% (1)
- Drug Study Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pedia WardCayanne ChuaNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan DyspneaDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan DyspneaMae JavierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanRALPH VINZ NABATARNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)CHRISTIE MONTANO0% (1)
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCj LowryNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute GastroenteritisErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- NCP - NewbornDocument1 pageNCP - NewbornChristine Michelle A. BalancadNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep Pattern Related To Environmental FactorsDocument9 pagesDisturbed Sleep Pattern Related To Environmental Factorsalaisah dimaporoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On SepsisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan On SepsisleoNo ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Comfort NCPDocument2 pagesImpaired Comfort NCPBaironica MindalanoNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InjuryDocument1 pageNCP Risk For InjuryRenz Kier L. ComaNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Needs of A Patient With Acute IllnessDocument3 pagesSpiritual Needs of A Patient With Acute IllnessMarimiel PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Aids/HivDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Aids/HivAdha100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- CHN PTDocument2 pagesCHN PTYzobel Phoebe ParoanNo ratings yet
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanNo ratings yet
- NCP For CHDDocument2 pagesNCP For CHDMonica Rivera100% (1)
- Vanessa LeprosyDocument18 pagesVanessa LeprosyMichael Angelo SeñaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Asthma)Document5 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Asthma)Jann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching PlanAirene Gonzales SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Date and Time Objectives Learning Contents Strategies Target Population Resources Evaluation OutcomeDocument8 pagesDate and Time Objectives Learning Contents Strategies Target Population Resources Evaluation OutcometrizzlecNo ratings yet
- NCP Measles Case PresDocument1 pageNCP Measles Case PresFranz RolfNo ratings yet
- 4 Flow Chart PretermDocument4 pages4 Flow Chart PretermYeni PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveIngrid Eunice ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge Deficient FPDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge Deficient FPDayanaj OngNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Dog Bite InjuryDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Dog Bite Injurykarrey danielNo ratings yet
- CPD Concept MapDocument1 pageCPD Concept MapShandle Dynne Baena100% (1)
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument11 pagesNormal Spontaneous DeliveryAyah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe Assessment of Infant CsepreDocument5 pagesHead To Toe Assessment of Infant CsepreteuuuuNo ratings yet
- VIII. Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesVIII. Discharge PlanPia Therese CabaticNo ratings yet
- Drug Study2Document2 pagesDrug Study2Haifi HunNo ratings yet
- Atrial Septal Defect - 7 Year OldDocument1 pageAtrial Septal Defect - 7 Year OldMSNo ratings yet
- SDL 1Document2 pagesSDL 1Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Femur Fracture Health EducationDocument1 pageFemur Fracture Health EducationMadx VNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPTweenie DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Nursery Drug Study 2 1Document22 pagesNursery Drug Study 2 1Wenalyn Grace Abella LlavanNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Document1 pageDysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Expected Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Expected Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMark Fernandez100% (1)
- NCP - Hip DysplasiaDocument4 pagesNCP - Hip DysplasiaCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- NCP - OsteoporosisDocument4 pagesNCP - OsteoporosisCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- NCP - OsteoporosisDocument4 pagesNCP - OsteoporosisCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Gec 8 - Activity 1Document9 pagesGec 8 - Activity 1Cassey CuregNo ratings yet
- NCP - Hip DysplasiaDocument4 pagesNCP - Hip DysplasiaCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- "My Neck Feels Stiff and There's Pain Coming From It. Every Time I Move It, It Only Gets Worse." As Stated by TheDocument4 pages"My Neck Feels Stiff and There's Pain Coming From It. Every Time I Move It, It Only Gets Worse." As Stated by TheCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- "She Can't Breathe Well Especially During Episodes of Spasms" As Verbalized byDocument2 pages"She Can't Breathe Well Especially During Episodes of Spasms" As Verbalized byCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting COVID 19 Vaccine Acceptance Among Public Market VendorsDocument57 pagesFactors Affecting COVID 19 Vaccine Acceptance Among Public Market VendorsCassey Cureg100% (1)
- 2.0 Community-Health-Survey-11aDocument8 pages2.0 Community-Health-Survey-11aCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Jkms 36 E227 s001Document3 pagesJkms 36 E227 s001Cassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Final - CholeraDocument12 pagesFinal - CholeraCassey Cureg100% (1)
- Final - TYPHOID FEVERDocument13 pagesFinal - TYPHOID FEVERCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Final - Food PoisoningDocument10 pagesFinal - Food PoisoningCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Poliomyelitis: Isabela State UniversityDocument14 pagesPoliomyelitis: Isabela State UniversityCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Hook Worm Infection: Republic of The Philippines City of Ilagan CampusDocument10 pagesHook Worm Infection: Republic of The Philippines City of Ilagan CampusCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Hepatits: Isabela State UniversityDocument11 pagesHepatits: Isabela State UniversityCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Urgensi Kepemimpinan Transformasional Dan Kecerdasan Emosional Pada Perusahaan Dalam Merespons Pandemi Covid-19Document11 pagesUrgensi Kepemimpinan Transformasional Dan Kecerdasan Emosional Pada Perusahaan Dalam Merespons Pandemi Covid-19Inspektorat KubarNo ratings yet
- 8 - Case Studies in Ultrasonic Debridement - Pocket DentistryDocument7 pages8 - Case Studies in Ultrasonic Debridement - Pocket Dentistryfarahpasha16No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MGT340Document1 pageChapter 1 MGT340Normirza HanimNo ratings yet
- Textbook Gen64 125Document76 pagesTextbook Gen64 125Jiraporn AekkhamphanNo ratings yet
- English Module BIG 50 (P2)Document33 pagesEnglish Module BIG 50 (P2)bhanuNo ratings yet
- Prevalensi Parasit Dan Penyakit Ikan AirDocument6 pagesPrevalensi Parasit Dan Penyakit Ikan AirSang PenggodaNo ratings yet
- Trung Tâm Ngoại Ngữ Nq Education Tầng 3, Tòa nhà 29T2 - N05 Hoàng Đạo Thúy - 0961 976 968 1Document6 pagesTrung Tâm Ngoại Ngữ Nq Education Tầng 3, Tòa nhà 29T2 - N05 Hoàng Đạo Thúy - 0961 976 968 1HAnhh TrầnnNo ratings yet
- Approaches To The Study of Hypnotic Dreams: Charles T. TartDocument1 pageApproaches To The Study of Hypnotic Dreams: Charles T. TartIno MoxoNo ratings yet
- Blanche Ely High School Medical Sciences Magnet Program Registration 2022-2023Document2 pagesBlanche Ely High School Medical Sciences Magnet Program Registration 2022-2023aileen higuereyNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors of Anastomotic Leak in Intestinal Surgery AuthorDocument2 pagesRisk Factors of Anastomotic Leak in Intestinal Surgery AuthorluisNo ratings yet
- Turquoise Heart Vector Medical Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesTurquoise Heart Vector Medical Brochure PDFHERNEY LEANDRO PEREZ CADENANo ratings yet
- Physiological, Biomechanical and Medical Aspects of Soldier Load CarriageDocument20 pagesPhysiological, Biomechanical and Medical Aspects of Soldier Load CarriageAnonymous dmhNTyNo ratings yet
- (April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?Document1 page(April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?SNo ratings yet
- Vitamins To CLEAN Your FATTY LIVERDocument5 pagesVitamins To CLEAN Your FATTY LIVERNiloufar GholamipourNo ratings yet
- ECG in Emergency MedicineDocument228 pagesECG in Emergency MedicineM.FADLINo ratings yet
- DIASS Lesson 6Document34 pagesDIASS Lesson 6PBCSSI Ma'am MarizNo ratings yet
- Marram Email BrochureDocument5 pagesMarram Email Brochurethangth1986No ratings yet
- OplerfDocument5 pagesOplerfNdumiso MoyoNo ratings yet
- First Admission List Open (PG 2024)Document163 pagesFirst Admission List Open (PG 2024)13thbatchbphmmihsNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Care 3rd Edition Burke Test BankDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Care 3rd Edition Burke Test BankMatthew Song100% (43)
- Let's Talk About HealthDocument1 pageLet's Talk About HealthAlma Lorena Alonso LinaresNo ratings yet
- Star Comprehensive BrochureDocument1 pageStar Comprehensive BrochureShakti ShivanandNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Premier Plastic Production Company Sop For Emergency Response Plan & PreparednessDocument19 pagesPurpose: Premier Plastic Production Company Sop For Emergency Response Plan & Preparednessimranul haqNo ratings yet
- Oxford Handbook of Rehabilitation Medicine 3rd Edition 2019Document689 pagesOxford Handbook of Rehabilitation Medicine 3rd Edition 2019suzzixx100% (1)
- Key Components of Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesKey Components of Literature Reviewhinlcxtkg100% (1)
- Health 9 Q1 Module 1finalDocument14 pagesHealth 9 Q1 Module 1finalDog GodNo ratings yet
- Try Out 3 2019: Mata Pelajaran: Bahasa Inggris Jenjang: Sma/Ma Ipa Waktu: 120 MenitDocument50 pagesTry Out 3 2019: Mata Pelajaran: Bahasa Inggris Jenjang: Sma/Ma Ipa Waktu: 120 MenitEnglish ClassNo ratings yet
- Health Clinic Floor PlanDocument1 pageHealth Clinic Floor PlanSt_defalco5943No ratings yet