Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Battery Measurement Frequency - v02
Battery Measurement Frequency - v02
Uploaded by
Joss RamosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Battery Measurement Frequency - v02
Battery Measurement Frequency - v02
Uploaded by
Joss RamosCopyright:
Available Formats
APPLICATION NOTE
Battery Ohmic Measurement AC or DC?
What frequency should be used for ohmic testing? (DC, Low Frequency AC or High Frequency AC)
Ohmic measurements can be performed with AC or DC current. Which provides the
most information about the battery? To answer this we first have to ask what the
characteristics of a battery are.
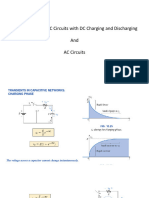
Below is an image of the Randle’s equivalent circuit.
Ri = the resistance of the plates,
electrolyte and inter-cell connections
Rct = the resistance of the charge
transfer
ZW = the Warburg diffusion element.
This models the diffusion process
associated with the charge transfer.
L = the inductance
Cdl = double layer effect
From this equivalency circuit it is clear to see that a battery has resistive, capacitive as
well as some inductive characteristics. (The inductive characteristics are minimal.)
What is the double layer effect (Cdl)?
This double layer effect appears where a conductive
electrode and an adjacent liquid electrolyte meet. At this
boundary two layers of ions with opposing polarity form
when a voltage is applied. The two layers of ions are
separated by a single coating of solvent molecules that
adheres to the surface of the electrode and acts like a
dielectric, forming a capacitor.
This layer can become non uniform and change, often
before resistive changes are seen in the plates or the
electrolyte.
When testing with DC current only the resistive properties of the battery are tested. The
double layer capacitive charge is completely ignored. In addition the Warburg diffusion
element (ZW) is also an impedance measurement.
Megger USA - Valley Forge Corporate Center
2621 Van Buren Avenue, Norristown, Pennsylvania, 19403, USA
T. 1-610 676 8500 F. 1-610-676-8610
APPLICATION NOTE
Battery Ohmic Measurement AC or DC?
An impedance measurement is required in order to evaluate all, the resistive as well as
capacitive and inductive characteristics of a battery.
Where:
Z = Impedance
R = Resistance
X = Inductive Reactance
L
X = Capacitive Reactance
When measuring with high frequency AC the inductive properties
become predominant. The higher the test frequency f the greater XL.
When measuring with low frequency AC the capacitive properties
become predominant.
The lower the test frequency f the greater XC.
In reality the two predominate properties of a battery are resistive and capacitive.
Therefore low frequency AC testing is the preferred method for testing batteries. Low
frequency measurement will measure the changes in plates, electrolytes, inter-cell
connections, double layer capacitance as well as the charge transfer.
By measuring all the characteristics of the battery it is possible to see changes in the
state of health earlier in the batteries aging process. This allows for better maintenance
and reliability.
The BITE product line from Megger performs AC testing of batteries at frequencies
between 50 and 60Hz. Providing a clear view of not only the resistive elements of the
battery but the double layer effect as well. This provides earlier detection of changes in
the state of health of the battery and therefore better reliability.
Megger USA - Valley Forge Corporate Center
2621 Van Buren Avenue, Norristown, Pennsylvania, 19403, USA
T. 1-610 676 8500 F. 1-610-676-8610
You might also like
- Testing, Commissioning, Operation & Maintenances of Electrical Equipment (S - Raho) 6TH Edition PDFDocument1,384 pagesTesting, Commissioning, Operation & Maintenances of Electrical Equipment (S - Raho) 6TH Edition PDFMukesh Kumar95% (59)
- 3TL CatalogDocument44 pages3TL CatalogEduardo Castañares VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Tesla - SekretyDocument82 pagesTesla - SekretyKWojtek80% (5)
- Fundamental of EISDocument70 pagesFundamental of EISLe Quang TrungNo ratings yet
- Physics RevisionDocument5 pagesPhysics RevisionzNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Basic ParametersDocument17 pagesUnit 1: Basic ParametersPeace In YouNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Network Theory - Study NotesDocument16 pagesBasic Concept of Network Theory - Study NotesBORN TO DIENo ratings yet
- Reactance and Impedance: Study UnitDocument74 pagesReactance and Impedance: Study UnitlmpimpaNo ratings yet
- True, Reactive, and Apparent PowerDocument5 pagesTrue, Reactive, and Apparent PowerAwa StelkNo ratings yet
- Autolab Application Note EIS03Document3 pagesAutolab Application Note EIS03Jako SibueaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 HandoutDocument10 pagesTopic 3 HandoutnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Inductor Resistor Learn Definition, Uses & ExamplesDocument1 pageCapacitor Inductor Resistor Learn Definition, Uses & Examples2g2qscbv5pNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8 Reactive Properties of Copper CableDocument29 pagesExercise 8 Reactive Properties of Copper Cableapi-19713349No ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2 Series RLC Circuits: I. DiscussionDocument8 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 2 Series RLC Circuits: I. DiscussionJeffrey JimenezNo ratings yet
- Hewlett-Packard Journal: JANUARY 1967Document20 pagesHewlett-Packard Journal: JANUARY 1967danilo espinozaNo ratings yet
- A192-AE-W6-R, XC & Z - RC circuit-SV-PKPDocument47 pagesA192-AE-W6-R, XC & Z - RC circuit-SV-PKPMuhammad Nurazin Bin RizalNo ratings yet
- E CH Erence Energydiff Ifference Potentiald: Allan RiddickDocument7 pagesE CH Erence Energydiff Ifference Potentiald: Allan RiddickAngel LaoNo ratings yet
- Liebherr Lehr Buch Part - 01Document30 pagesLiebherr Lehr Buch Part - 01Mohammed SaadNo ratings yet
- 20 Electric CircuitsDocument23 pages20 Electric CircuitsquickdannyNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT No 4Document3 pagesEXPERIMENT No 4English words BY Utkarsh johriNo ratings yet
- Click or Tap Here To Enter Text. Click or Tap Here To Enter TextDocument7 pagesClick or Tap Here To Enter Text. Click or Tap Here To Enter Textkylie jonesNo ratings yet
- Ec NotesDocument17 pagesEc Notesss mNo ratings yet
- Capacitors PDFDocument84 pagesCapacitors PDFNaseerUddin100% (1)
- Ece 9Document25 pagesEce 9nachiketaanand20No ratings yet
- 26 Most Asked Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers With PDF CompressedDocument7 pages26 Most Asked Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers With PDF CompressedAishwarya0% (1)
- CT Testing TheoryDocument15 pagesCT Testing TheoryClyde CauchiNo ratings yet
- Th. Floyd-Matje Bazike (2009) (PDF - Io) PDFDocument39 pagesTh. Floyd-Matje Bazike (2009) (PDF - Io) PDFBastri ZekaNo ratings yet
- Bansal Current Electricity PDFDocument27 pagesBansal Current Electricity PDFUttiya SangiriNo ratings yet
- Bansal Current ElectricityDocument27 pagesBansal Current Electricitysudhanva mattupalli100% (1)
- Inductance Without An LCR MeterDocument5 pagesInductance Without An LCR MeterBill AlbertNo ratings yet
- 5reactance and Impedance - R, L, and CDocument22 pages5reactance and Impedance - R, L, and CKassem KallasNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Impedance SpectrosDocument31 pagesElectrochemical Impedance SpectrosDanielPetreNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument36 pagesBasic ElectronicsCarl OlayaNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Impedance of Cables at High and Low FrequenciesDocument11 pagesCharacteristic Impedance of Cables at High and Low FrequenciesoesnuNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit - AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectronic Circuit - AnalysisThivhulawi MukondeleliNo ratings yet
- 5 - Inductance & Capacitance Measurement For DC (Aina P. Marandang)Document17 pages5 - Inductance & Capacitance Measurement For DC (Aina P. Marandang)Klint Suerte CanillaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, SZAB Campus Khairpur Mir'sDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Mehran University of Engineering and Technology, SZAB Campus Khairpur Mir'sAnonymous oXmbHmHNo ratings yet
- 5 - Inductance & Capacitance Measurement For DCDocument17 pages5 - Inductance & Capacitance Measurement For DCKlint Suerte CanillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Electrical Circuits 1Document91 pagesLesson 1 - Electrical Circuits 1Norman AcainNo ratings yet
- SeriesDocument36 pagesSeriesElla KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Phys133 Lab1Document7 pagesPhys133 Lab1api-427609820No ratings yet
- Rectifier Load Analysis For Electric VehicleDocument12 pagesRectifier Load Analysis For Electric Vehiclerock starNo ratings yet
- 06 C Measurement 2Document15 pages06 C Measurement 2Awais MohammedNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and Inductance Measurements Using An Oscilloscope and A Function GeneratorDocument9 pagesCapacitance and Inductance Measurements Using An Oscilloscope and A Function Generatoralex castroNo ratings yet
- Current and Voltage: Q I DQ I DT QT ItDocument20 pagesCurrent and Voltage: Q I DQ I DT QT ItPraneetha InumarthiNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Summary Notes Current Electricity - StuDocument13 pagesUnit 14 Summary Notes Current Electricity - StuWalter WhiteNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document15 pagesLab Report 3WaleedSubhan100% (1)
- General Physics Lab Report: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument19 pagesGeneral Physics Lab Report: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyIzaNo ratings yet
- Capacitance & CapacitorsDocument65 pagesCapacitance & CapacitorsSidhartha ShankarNo ratings yet
- Estimating The State of Charge of A BatteryDocument6 pagesEstimating The State of Charge of A BatteryDarshan KannurNo ratings yet
- Resistance Vs ReactanceDocument3 pagesResistance Vs ReactanceThomas SmithNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics ComponentDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Electronics ComponentNirav PatelNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 6Document4 pagesLab Report 6CattosphereNo ratings yet
- Physics: Force Nmat ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysics: Force Nmat ReviewerMa-anJaneDiamosNo ratings yet
- Resistors: Engr. M Abdul RehmanDocument66 pagesResistors: Engr. M Abdul RehmanZain KhawarNo ratings yet
- Diode Rectifiers, Filters, and Power Supplies: The Solid State DiodeDocument13 pagesDiode Rectifiers, Filters, and Power Supplies: The Solid State DiodeMit MANo ratings yet
- ASU-KALIBO IM - : Aklan State University College of Industrial Technology Kalibo, AklanDocument11 pagesASU-KALIBO IM - : Aklan State University College of Industrial Technology Kalibo, AklanAries PenalosaNo ratings yet
- Up Polytechnic 2nd Semester Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument65 pagesUp Polytechnic 2nd Semester Basic Electrical EngineeringDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Reactance?: Magnetic FieldDocument3 pagesWhat Is Reactance?: Magnetic FieldGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Impedance: Electrical Impedance, or Simply Impedance, Is A Term Coined byDocument8 pagesElectrical Impedance: Electrical Impedance, or Simply Impedance, Is A Term Coined byidigitiNo ratings yet
- Response of Capacitor and Inductor in AC and DC CircuitDocument8 pagesResponse of Capacitor and Inductor in AC and DC CircuitMd Chand AsiqueNo ratings yet
- AC Power (Part Three) - AC Circuit Loads - Pumps & SystemsDocument7 pagesAC Power (Part Three) - AC Circuit Loads - Pumps & SystemschalaNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- BURNDY ConectoresDocument75 pagesBURNDY ConectoresJoss RamosNo ratings yet
- AVTM82318 Rev 4 May 2016Document70 pagesAVTM82318 Rev 4 May 2016Joss RamosNo ratings yet
- Contenido 2 SF6 Gas 2016Document42 pagesContenido 2 SF6 Gas 2016Joss RamosNo ratings yet
- TRANSLINK IW Washgun Brochure4 VIPER VARADocument4 pagesTRANSLINK IW Washgun Brochure4 VIPER VARAJoss RamosNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Check Lists Iw Tele BoomsDocument6 pagesMaintenance Check Lists Iw Tele BoomsJoss RamosNo ratings yet
- Iw Maintenance Schedule To 2000 HoursDocument6 pagesIw Maintenance Schedule To 2000 HoursJoss RamosNo ratings yet
- Insulator Washing Water QualityDocument4 pagesInsulator Washing Water QualityJoss RamosNo ratings yet
- ADC08831 /ADC08832 8-Bit Serial I/O CMOS A/D Converters With Multiplexer and Sample/Hold FunctionDocument32 pagesADC08831 /ADC08832 8-Bit Serial I/O CMOS A/D Converters With Multiplexer and Sample/Hold FunctionJuan HernándezNo ratings yet
- Circuit CharacterizationDocument48 pagesCircuit Characterizationatindra1234No ratings yet
- Delta VFD M User ManualDocument173 pagesDelta VFD M User ManualIsidro QuirozNo ratings yet
- Voltage Doubler ADocument2 pagesVoltage Doubler AErole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technical Bulletin: Other ModelsDocument88 pagesTechnical Bulletin: Other ModelsSid Ahmed GANANo ratings yet
- May2016 Physics Paper 2 HL MarkschemeDocument19 pagesMay2016 Physics Paper 2 HL MarkschemeAnanya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Di-143 Design Idea Topswitch-Hx: High Effi Ciency Inkjet Power Supply Provides Up To 80 Watts of Peak PowerDocument2 pagesDi-143 Design Idea Topswitch-Hx: High Effi Ciency Inkjet Power Supply Provides Up To 80 Watts of Peak PowerJose BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Aneng AN113D ManualDocument2 pagesAneng AN113D Manualalfa3dNo ratings yet
- VT1730 PDFDocument161 pagesVT1730 PDFCristian BobaruNo ratings yet
- Catálogo NutekDocument20 pagesCatálogo Nutekoyauga123No ratings yet
- Distribution System HandbookDocument346 pagesDistribution System HandbookAyan Mandal100% (2)
- ISRO Electronics and Electrical Questions and Answers With Detailed ExplanationsDocument12 pagesISRO Electronics and Electrical Questions and Answers With Detailed ExplanationsGirdhar Gopal Gautam100% (1)
- AMT Module 5-Ktunotes - inDocument20 pagesAMT Module 5-Ktunotes - inJithin GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To: ABB Machines Service CapabilitiesDocument60 pagesIntroduction To: ABB Machines Service CapabilitiessihamuNo ratings yet
- The Real Biefeld Brown EffectDocument3 pagesThe Real Biefeld Brown EffectaxtimeNo ratings yet
- Product End-of-Life Disassembly InstructionsDocument2 pagesProduct End-of-Life Disassembly InstructionsBajlamoNo ratings yet
- 10A45 SimerahDocument8 pages10A45 Simerahega nur aziesNo ratings yet
- Manual Radarmel650Document70 pagesManual Radarmel650ANGELNo ratings yet
- Metal DetectorDocument24 pagesMetal Detectorramlala2591100% (1)
- Optocoupler Input Drive CircuitsDocument7 pagesOptocoupler Input Drive CircuitsLuis Armando Reyes Cardoso100% (1)
- Electrostatic AccelaratorDocument18 pagesElectrostatic AccelaratorPradeepNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting CircuitDocument29 pagesAdaptive Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Circuitgangad_1No ratings yet
- Bakari Trade Project-4Document46 pagesBakari Trade Project-4kenjaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Disturbances in LV Networks Due To Energization of MV NetworksDocument5 pagesElectrical Disturbances in LV Networks Due To Energization of MV NetworksAlejandro Solis GomezNo ratings yet
- MC34262-D-Power Factor Controller-ON-SEMI PDFDocument19 pagesMC34262-D-Power Factor Controller-ON-SEMI PDFnightreader99No ratings yet
- LC Mos High Speed 4-And 8-Channel 8-Bit Adcs Ad7824/Ad7828Document16 pagesLC Mos High Speed 4-And 8-Channel 8-Bit Adcs Ad7824/Ad7828meroka2000No ratings yet