Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Needs Needs: Training
Needs Needs: Training
Uploaded by
miqdad balochOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Needs Needs: Training
Needs Needs: Training
Uploaded by
miqdad balochCopyright:
Available Formats
Training - a planned effort by a company to facilitate employees’ learning of job-related
competencies.
Competencies include knowledge, skills or behavior critical for successful job performance.
The goal of training is for employees to master the competencies and apply them to their day-to-
day activities.
High-leverage training
Is linked to strategic business goals and objectives.
Uses an instructional design process to ensure that training is effective.
Compares or benchmarks the company's training programs against training
programs in other companies.
Continuous learning - requires employees to understand the entire work system,
including the relationships among their jobs, their work units, and the company.
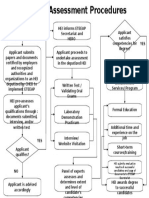
ANALYZING Training Needs:
Training Needs Analysis
Performance Analysis:
Task Analysis: Assessing
Assessing current
new employees’ training
employees’ training
needs
needs
Business strategy: A plan that integrates the company's goals, policies, and actions.
The strategy influences how the company uses:
Physical capital, financial capital, and human capital.
Explicit knowledge – knowledge that can be formalized, codified, and communicated.
Tacit knowledge – personal knowledge based on individual experience that is difficult to
explain to others.
Six Sigma processes - a process of measuring, analyzing, improving, and then controlling
processes once they have been brought within the narrow six sigma quality tolerances or
standards.
ISO 10015 - a quality management tool designed to ensure that training is linked to company
needs and performance.
Training Design Process:
Is sometimes referred to as the ADDIE model because it includes analysis, design,
development, implementation, and evaluation.
Balance scorecard – means of performance measurement that provides managers with a chance
to look at the overall company performance or the performance of departments or functions It
considers four perspectives: customers, internal (processes that influence customer satisfaction),
innovation and learning, and financial.
Learning - a relatively permanent change in human capabilities that is not a result of growth
processes.
Learning Theories:
• Reinforcement theory - emphasizes that people are motivated to perform or avoid
certain behaviors because of past outcomes that have resulted from those behaviors.
– Several processes in reinforcement theory are positive reinforcement, negative
reinforcement, extinction, and punishment.
• Social learning theory - emphasizes that people learn by observing other persons (models)
whom they believe are credible and knowledgeable.
Goal setting theory - assumes that behavior results from a person’s conscious goals and
intentions.
– Goals influence a person’s behavior by:
• directing energy and attention.
• sustaining effort over time.
• motivating the person to develop strategies for goal attainment.
• Need theories
– Helps to explain the value that a person places on certain outcomes.
– Need - a deficiency that a person is experiencing at any point in time.
– Maslow’s and Alderfer’s need theories focused on physiological needs, relatedness
needs, and growth needs.
– The major difference between Alderfer’s and Maslow’s hierarchies of needs is that
Alderfer allows the possibility that if higher-level needs are not satisfied, employees will
refocus on lower-level needs.
– McClelland’s need theory focused primarily on needs for achievement, affiliation, and
power
• Information processing theory
– It highlights how external events influence learning, which include:
• Verbal instructions, pictures, diagrams, and maps suggesting ways to code the
training content so that it can be stored in memory.
Transfer of Training Theory
Transfer of training is more difficult when tasks during training are different from the work
environment.
Closed skills: Training objectives that are linked to learning specific skills that are to be
identically produced by the trainee on their job
Open skills: Linked to more general learning principles
Learning Styles:
Succession planning is a process for identifying and developing new leaders, who can replace
old leaders when they leave, retire or die. Succession planning increases the availability of
experienced and capable employees that are prepared to assume these roles as they become
available.
Training Methods:
Traditional training methods
Require an instructor or facilitator
Involve face-to-face interactions
Presentation Methods
Trainees are passive recipients of information, which may include:
Facts or information
Processes
Problem-solving methods
Includes lectures and audio-visual techniques
Lecture: Trainers communicate through spoken words
Least expensive and least time-consuming ways to present information
Hands-on Methods
Require trainee to be actively involved in learning
On-the-job training (OJT) New or inexperienced employees learn work by:
Observing peers or managers performing the job
Trying to imitate their behavior
Needs less investment in terms of time or money
Simulation: Represents a real-life situation
Trainees’ decisions and the resulting outcomes mirror what would happen in real work
situations Replicates the physical equipment that employees use on the job
Is used to teach production, process skills, management, and interpersonal skills
Case studies: Description about how employees or an organization dealt with a difficult
situation.
Business games: Require trainees to gather information, analyze it, and make decisions
Primarily used for management skill development
Mimic the competitive nature of business
Designed to demonstrate understanding or application of knowledge, skill, or behavior and
provides several alternative courses of action
Rules limit participant behavior
Role plays: Trainees act out characters assigned to them. Trainees need to engage in several
activities before, during, and after the role play
Behavior modeling: Demonstrates key behaviors to replicate.
Provides trainees with the opportunity to practice the key behaviors
Based on the principles of social learning theory
More appropriate for teaching skills and behaviors than factual information
Modeling display: Key behaviors that the trainees will practice to develop the same set of
behaviors.
Application planning: Prepares trainees to use the key behaviors on the job Involves
identifying specific situations in which to use the key behaviors
You might also like
- TMA01 Handout Planner For Final Work 1Document11 pagesTMA01 Handout Planner For Final Work 1Eland ExamsNo ratings yet
- TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT AT Mahindra & MahindraDocument6 pagesTRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT AT Mahindra & MahindraUpadhayayAnkurNo ratings yet
- Succeed in Cambridge Cae 10 Practice Tests Key Scribd PDFDocument3 pagesSucceed in Cambridge Cae 10 Practice Tests Key Scribd PDFGiulia ChireaNo ratings yet
- HRM 2Document66 pagesHRM 2Deepa SelvamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document18 pagesChapter 4AYNETU TEREFENo ratings yet
- T&D MidDocument9 pagesT&D MidM. Naziur SardarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 HR and OB AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter 8 HR and OB AnswersAny RoseNo ratings yet
- By Mrs - Saylee JoshiDocument42 pagesBy Mrs - Saylee Joshisayleejoshi17No ratings yet
- TrainingdevelopmentDocument60 pagesTrainingdevelopmentveeramanivelNo ratings yet
- HRM 1Document66 pagesHRM 1Deepa SelvamNo ratings yet
- TrainingDocument34 pagesTrainingHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- What Is Training?Document39 pagesWhat Is Training?morjagdishNo ratings yet
- Training & DevelopmentDocument42 pagesTraining & Development匿匿No ratings yet
- Cognitive Methods Are More of Giving Theoretical Training To TheDocument5 pagesCognitive Methods Are More of Giving Theoretical Training To Theshameena07No ratings yet
- Module-3 - Training and Developing Human ResourcesDocument27 pagesModule-3 - Training and Developing Human Resourcesamrj27609No ratings yet
- Training & Development: - Manisha Vijayran Nain Asstt - Prof.-HRDocument22 pagesTraining & Development: - Manisha Vijayran Nain Asstt - Prof.-HRAbhishek ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document22 pagesChapter 8doha safwatNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 5 Alagappa UniversityDocument39 pagesUNIT - 5 Alagappa UniversitySe SathyaNo ratings yet
- Iii Needs AssessmentDocument9 pagesIii Needs AssessmentGem TanqueridoNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument60 pagesHuman Resource ManagementvibgorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document13 pagesChapter 02ImrannkhanNo ratings yet
- Functions of Manangement STAFFING TabinasDocument27 pagesFunctions of Manangement STAFFING TabinasAlden AzanzaNo ratings yet
- Revision For The Training 0 DevelopmentDocument23 pagesRevision For The Training 0 Developmentيوسف سعيد العنزيNo ratings yet
- Human Resource DevelopmentDocument26 pagesHuman Resource DevelopmentThomas KenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Training and DevelopmentDocument39 pagesChapter 7 - Training and DevelopmentMoshmi MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Training and Development: Here We Will DiscussDocument25 pagesTraining and Development: Here We Will DiscussAlemayehu CEromo ADNo ratings yet
- Training Framework For An OrganisationDocument19 pagesTraining Framework For An OrganisationSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument34 pagesResearch Paperanugya jainNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Employee Training and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 7 Employee Training and Developmentjames.carltaypaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Training: at The End of This Lesson, You Should Be Able ToDocument15 pagesLesson 5: Training: at The End of This Lesson, You Should Be Able ToRuby SparksNo ratings yet
- Agrib 8 - Chapter 3Document24 pagesAgrib 8 - Chapter 3respineda240000000256No ratings yet
- Presentation (Training and DevelopmmentDocument24 pagesPresentation (Training and DevelopmmentAtreya Terry VyasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Management: Understanding Management Tools in Performance ManagementDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Management: Understanding Management Tools in Performance ManagementCarraa BaqqalaaNo ratings yet
- HRM - Unit 3Document16 pagesHRM - Unit 3Tanisha SarrafNo ratings yet
- Training Need Analysis & Experiential Training MethodsDocument17 pagesTraining Need Analysis & Experiential Training Methodspravin shivaji jadhavNo ratings yet
- Employee Training & Management DevelopmentDocument22 pagesEmployee Training & Management DevelopmentPrabakar UnicNo ratings yet
- Developing Individuals and TeamsDocument20 pagesDeveloping Individuals and TeamsEyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- 6 Chapter Six - Training and DevelopmentXDocument29 pages6 Chapter Six - Training and DevelopmentXEbsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- Joey R. MiñanoDocument37 pagesJoey R. MiñanoarshadalicaNo ratings yet
- 4training and DevelopmentDocument3 pages4training and DevelopmentAlcaraz Paul JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Training and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesTraining and DevelopmentMARC URRUTIA MIRÓNo ratings yet
- 1.1 About The TrainingDocument48 pages1.1 About The Trainingindu priyaNo ratings yet
- Socializing, Orienting, and Developing EmployeesDocument36 pagesSocializing, Orienting, and Developing EmployeesridaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 TrainingDocument43 pagesChapter 7 TrainingKayeMeryl FernandezNo ratings yet
- TrainingDocument39 pagesTrainingvermakrishna1118No ratings yet
- Training and DevelopmentDocument60 pagesTraining and Developmentfarhanahmednagda100% (1)
- 1 - Intro. of TrainingDocument12 pages1 - Intro. of TrainingmayankNo ratings yet
- HRM460 SEC-2 Final AssignmentDocument6 pagesHRM460 SEC-2 Final AssignmentTayeb KhanNo ratings yet
- HRPD 13 March 11Document22 pagesHRPD 13 March 11Suneeta WarrierNo ratings yet
- Training: Pallavi TyagiDocument25 pagesTraining: Pallavi TyagiVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- M M M MDocument36 pagesM M M MPriyanka Rutul PatelNo ratings yet
- T&D Module1Document9 pagesT&D Module197vb7z6ccsNo ratings yet
- Effect of TrainingDocument45 pagesEffect of Trainingindu priyaNo ratings yet
- Training MethodsDocument36 pagesTraining MethodsKhushbu Bavishi50% (2)
- Chapter Three: The Development of HRDocument76 pagesChapter Three: The Development of HRethnan lNo ratings yet
- Ink & Insights: Mastering Business Coaching in the Digital AgeFrom EverandInk & Insights: Mastering Business Coaching in the Digital AgeNo ratings yet
- Coaching and Mentoring Learning Resource ManualFrom EverandCoaching and Mentoring Learning Resource ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Coaching Skills for Managers: The No Waffle Guide To Getting The Best From Your TeamFrom EverandCoaching Skills for Managers: The No Waffle Guide To Getting The Best From Your TeamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Ultimate Employee Training Guide- Training Today, Leading TomorrowFrom EverandThe Ultimate Employee Training Guide- Training Today, Leading TomorrowNo ratings yet
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsFrom EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsNo ratings yet
- Accelerate Your Leadership Development in Training Domain: Proven Success Strategies for New Training & Learning ManagersFrom EverandAccelerate Your Leadership Development in Training Domain: Proven Success Strategies for New Training & Learning ManagersNo ratings yet
- Principle of Marketing VivaDocument19 pagesPrinciple of Marketing Vivamiqdad balochNo ratings yet
- BM VivaDocument15 pagesBM Vivamiqdad balochNo ratings yet
- HRM Viva Notes-1Document9 pagesHRM Viva Notes-1miqdad baloch100% (1)
- VIVA QuestionsDocument10 pagesVIVA Questionsmiqdad balochNo ratings yet
- Supervisor Observation 1 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesSupervisor Observation 1 Lesson Planapi-325281014No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Results-Based Performance Management SystemDocument72 pagesDepartment of Education: Results-Based Performance Management Systemjhancelle golosindaNo ratings yet
- Personal Philosophy of Teaching That Is Learner-CenteredDocument2 pagesPersonal Philosophy of Teaching That Is Learner-CenteredDonna Welmar Tuga-on67% (3)
- Republic of The Philippines: Libon Community CollegeDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Libon Community Collegepayno gelacioNo ratings yet
- From Head To ToeDocument5 pagesFrom Head To Toeapi-500025821No ratings yet
- ETEEAP AssessmentDocument1 pageETEEAP AssessmentfringedNo ratings yet
- ShsDocument4 pagesShsKhristine Khate Odiaman MendezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Tle Drafting 2024Document5 pagesLesson Plan in Tle Drafting 2024Kimarie ApaoNo ratings yet
- Gender Differences in Reading Strategies Among Vocational High School StudentsDocument7 pagesGender Differences in Reading Strategies Among Vocational High School StudentsReko upbNo ratings yet
- DLL Feb 12-16Document10 pagesDLL Feb 12-16Rodrigo Salon Jr.No ratings yet
- CT: Biennial Report On School Districts' EffortsDocument108 pagesCT: Biennial Report On School Districts' EffortsPatricia DillonNo ratings yet
- 01st of June 2017 To 28 of June 2017Document2 pages01st of June 2017 To 28 of June 2017AyushNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Grade Level Standard: Rooted in Christ DoctrineDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Grade Level Standard: Rooted in Christ DoctrineroseNo ratings yet
- ILMPDocument9 pagesILMPChelle Pangan - SansanoNo ratings yet
- DLP Science 7 Quarter 2 - Microscope and Their FunctionDocument2 pagesDLP Science 7 Quarter 2 - Microscope and Their FunctionLudi Jane TorrefrancaNo ratings yet
- Boat Lesson Plan-2Document4 pagesBoat Lesson Plan-2api-539924409No ratings yet
- Results-Based Performance Management System (RPMS) For TeachersDocument6 pagesResults-Based Performance Management System (RPMS) For TeachersCristina Rhain WinterNo ratings yet
- Buku Teks Digital - English Kelas PeralihanDocument195 pagesBuku Teks Digital - English Kelas PeralihanMohammad Saiful100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1ZaIm HaFiziNo ratings yet
- Section 7 4 Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesSection 7 4 Lesson Planapi-272198179No ratings yet
- The Role of Teaching PracticeDocument12 pagesThe Role of Teaching PracticeKim LabradorNo ratings yet
- Seminar in Teaching: Osias College, IncDocument4 pagesSeminar in Teaching: Osias College, Incclara dupitasNo ratings yet
- Subspace Regularizers For Few-Shot Class Incremental LearningDocument18 pagesSubspace Regularizers For Few-Shot Class Incremental LearningDerry WijayaNo ratings yet
- Clemencia Espiritu, PH.D.: The Provision Are As FollowsDocument4 pagesClemencia Espiritu, PH.D.: The Provision Are As FollowsLadymae Barneso SamalNo ratings yet
- Preschool CurricularDocument24 pagesPreschool CurricularSca Jalpaiguri100% (1)
- There Is No Application Fee PayableDocument1 pageThere Is No Application Fee PayableMamello Meme BolofoNo ratings yet
- DR Assignment 01Document1 pageDR Assignment 01علیزہ علیNo ratings yet
- Boosting (Machine Learning)Document6 pagesBoosting (Machine Learning)Javier Garcia RajoyNo ratings yet