Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Production Decisions at Moore's Tech.: Cost Items For Harding Silicon Enterprises, Inc
Production Decisions at Moore's Tech.: Cost Items For Harding Silicon Enterprises, Inc
Uploaded by
Sahil PuniaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Production Decisions at Moore's Tech.: Cost Items For Harding Silicon Enterprises, Inc
Production Decisions at Moore's Tech.: Cost Items For Harding Silicon Enterprises, Inc
Uploaded by
Sahil PuniaCopyright:
Available Formats
CONSULTING PROJECT
Production Decisions at Moore’s Tech.
Moore’s Tech. produces less than 1% of the world’s supply of 99 TB flash module memory for advanced
electronic devices. The memory modules perform according to globally accepted performance standards.
Moore’s Tech has hired you to do undertake three tasks:
1. Perform a statistical analysis of its short-run production costs to estimate its total variable cost function,
average variable cost function, and marginal cost function. Moore’s Tech believes its total fixed costs
will be $6,500 per month, so you do not need to estimate TFC.
2. Recommend production levels and forecast profits for two module price scenarios:
a. The price of 99 TB flash modules reaches $62 per module, and
b. The price of 99 TB flash modules falls to $35 per module.
3. Determine the price below which Moore’s Tech should shut down operations in the short run.
Moore’s Tech provides you with the following cost and output data for the past 19 months. Over this time
period, inflation has been so low that you do not need to adjust the cost data for the effects of inflation (the CPI
rose only 0.4% over the 19 month time period). Monthly output of modules is given in the second column,
which is titled “Monthly production of finished product.” Costs are reported in seven categories (some are fixed
costs and some are variable costs). HINT: Remember, cost items are part of fixed costs if the costs do not vary
with output, even though fixed cost items may vary over time.
Cost Items for Harding Silicon Enterprises, Inc.
Business Building
Monthly production licenses Insurance lease Materials Energy Wage
Month of finished product & fees premiums payment expenses Telephone expenses expense
Nov-16 875 0 0 3570 9690 945 7230 12250
Dec-16 670 0 0 3570 6700 945 5115 8995
Jan-17 1675 6000 2200 3570 16295 945 12884 23106
Feb-17 1155 0 0 3570 11285 945 9240 15225
Mar-17 1845 0 0 3570 16550 945 14220 24530
Apr-17 1650 0 0 3570 16230 945 12700 21600
May-17 1955 0 0 3570 19626 945 15640 27484
Jun-17 2845 0 0 3570 27410 945 22760 39830
Jul-17 2265 0 2200 3570 20526 945 17244 31225
Aug-17 3470 0 0 3570 34176 830 25760 48564
Sep-17 3665 0 0 3570 36726 830 28720 50094
Oct-17 3750 0 0 3570 42576 830 32000 54474
Nov-17 4595 0 0 3570 48226 830 37260 66414
Dec-17 4060 0 0 3570 41095 830 33155 57840
Jan-18 3575 7200 2450 4200 34550 830 27400 50050
Feb-18 4380 0 0 4200 41800 830 34460 61320
Mar-18 5575 0 0 4200 81750 830 54600 82150
Apr-18 7870 0 0 4200 92360 830 102960 130180
May-18 6750 0 0 4200 89576 830 70000 109774
1. a. Compute total variable cost (TVC) by adding the appropriate columns of cost items. Compute
average variable cost (AVC). [Remember that you are given an estimate of HSE’s future total
fixed costs ($6,500 per month).] Print out the 19 months of data on output (Q) and total variable
cost (TVC) and average variable cost (AVC).
b.
Plot a scatter diagram of TVC on the vertical axis and Q on the horizontal axis. Does the scatter
diagram suggest a functional form for TVC? Explain briefly.
c.
Plot a scatter diagram of AVC on the vertical axis and Q on the horizontal axis. Does the scatter
diagram suggest a functional form for AVC? Explain briefly.
d.
Estimate a quadratic AVC function. Present the estimated equation and evaluate the regression
results (i.e., discuss the algebraic signs of the parameter estimates, the significance levels, and the
R2).
e.
Evaluate the results of your regression equation in part a. Specifically discuss algebraic signs of
parameters, statistical significance, and goodness of fit.
2. a. How many modules should be produced (monthly) if world module prices are $62 per
module? Forecast the Moore’s Tech profit at this output level.
b. How many modules should be produced (monthly) if world module prices are $35 per
module? Forecast the profit at this output level.
3. At what price should Moore’s Tech shut down and produce no modules in the short run?
You might also like
- Kool King Division (A)Document10 pagesKool King Division (A)Rajesh Kumar AchaNo ratings yet
- CIPMADocument31 pagesCIPMAReza HikamatullohNo ratings yet
- Procurement Plan URSIP - Newform - 20181101 (DRAFT)Document22 pagesProcurement Plan URSIP - Newform - 20181101 (DRAFT)Abib Ansari100% (2)
- Chap006 v5Document17 pagesChap006 v5abhishek jainNo ratings yet
- Public Wo Eco SimulationDocument3 pagesPublic Wo Eco Simulationsameeh kadourahNo ratings yet
- Monthly & Yearly ABT DATADocument5 pagesMonthly & Yearly ABT DATAdhaval.patelNo ratings yet
- Sales Comparative AnalysisDocument10 pagesSales Comparative AnalysisAshish PorechaNo ratings yet
- Enter Data in Yellow Fields Workings: 723,658 Slab Amount (Old)Document9 pagesEnter Data in Yellow Fields Workings: 723,658 Slab Amount (Old)HarryNo ratings yet
- Meil Tractable & Adani FY 20-21/AY 21-22 FY 21-22 Month Credited ITR Month Credited Amount As Per F-16Document3 pagesMeil Tractable & Adani FY 20-21/AY 21-22 FY 21-22 Month Credited ITR Month Credited Amount As Per F-16vijay bolisettyNo ratings yet
- Loading... : Product LinksDocument28 pagesLoading... : Product Linkss_lakkoju100% (8)
- Maharashtra State 6PC Arrears Calculator UpdatedDocument9 pagesMaharashtra State 6PC Arrears Calculator UpdatedRajesh Nage100% (15)
- Curvas Prog. 22-06-17 Rev. 0Document18 pagesCurvas Prog. 22-06-17 Rev. 0Milton Illanes OlaveNo ratings yet
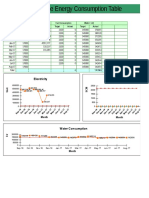
- Reduce Consumption Table-1Document6 pagesReduce Consumption Table-1VictorNo ratings yet
- Long Term PlanDocument10 pagesLong Term Planali MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Part No. Per Day TargetDocument21 pagesPart No. Per Day Targetmechtek 20No ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument11 pagesFinal ExamAnna AnchutinaNo ratings yet
- Investment Management ReportDocument16 pagesInvestment Management ReportMattyNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Marketing StrategiesDocument34 pagesProposal For Marketing StrategiesRifat SultanNo ratings yet
- Reduce Consumption Table-1Document7 pagesReduce Consumption Table-1VictorNo ratings yet
- Untitled 91Document6 pagesUntitled 91Farukh IskalinovNo ratings yet
- Azra Csc134g2Document1 pageAzra Csc134g2Azra FarzanaNo ratings yet
- TN Pay Comm Arrear CalculatorDocument3 pagesTN Pay Comm Arrear CalculatorRAVEEVISHAL100% (1)
- Salary Statement of Snigdha Panda, Assistant Teacher, Govt. High School IRC Village Bhubaneswar For The Assessment Year 2020-21, PAN-AKSPP6871G TAN - BBNO01162ADocument2 pagesSalary Statement of Snigdha Panda, Assistant Teacher, Govt. High School IRC Village Bhubaneswar For The Assessment Year 2020-21, PAN-AKSPP6871G TAN - BBNO01162ASpNo ratings yet
- Project Budgeting in ExcelDocument10 pagesProject Budgeting in Excelw_fibNo ratings yet
- Amena Akter Mim 1620741630 - SCM 320 Individual Assignment 1Document10 pagesAmena Akter Mim 1620741630 - SCM 320 Individual Assignment 1amena aktar MimNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Target Konsumsi BB 23-11-2020Document1 pagePerhitungan Target Konsumsi BB 23-11-2020Andhy AlfharoNo ratings yet
- Operational Matter Meeting 01 - 2023 Energy ReportDocument7 pagesOperational Matter Meeting 01 - 2023 Energy ReportRukshan JayasingheNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics SBA: Name of Candidate: Name of Centre: Centre Number: TitleDocument10 pagesAdditional Mathematics SBA: Name of Candidate: Name of Centre: Centre Number: TitleAndrewNo ratings yet
- Analysis: Calculation of Total Sales of The ProjectDocument7 pagesAnalysis: Calculation of Total Sales of The ProjectShailesh Kumar BaldodiaNo ratings yet
- Ws9 Soln FinalDocument14 pagesWs9 Soln FinaltwofortheNo ratings yet
- Practica MPS Bahena Zagal Luis DanielDocument3 pagesPractica MPS Bahena Zagal Luis DanielLuis DanielNo ratings yet
- Attachment F Sample Report OM Annual Report TemplateDocument7 pagesAttachment F Sample Report OM Annual Report TemplatekarthickNo ratings yet
- PNL YOM727Document8 pagesPNL YOM727Sumit BeniwalNo ratings yet
- 2LM1 Milan Ma YsabellaDocument4 pages2LM1 Milan Ma YsabellaBella AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Ajit Arrear StatementDocument12 pagesAjit Arrear Statementakdas52No ratings yet
- BukuDocument2 pagesBukuRickyNo ratings yet
- Simulasi Bertanam SingkonhDocument2 pagesSimulasi Bertanam SingkonhRickyNo ratings yet
- SSL Cma ReportDocument92 pagesSSL Cma ReportSandhya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Caso 3 MeribagDocument13 pagesCaso 3 MeribagJj OrtegaNo ratings yet
- HR Shee 05-06-024Document3 pagesHR Shee 05-06-024supremepebppcNo ratings yet
- Plan To Start A New BusinessDocument4 pagesPlan To Start A New BusinessPopescuLaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Cs CsaDocument16 pagesCs CsaTamer MohamedNo ratings yet
- Monitoring of Concrete TestingDocument32 pagesMonitoring of Concrete TestingKamen RiderNo ratings yet
- DiarammaaDocument64 pagesDiarammaasamadozoure120No ratings yet
- Cost Machine Shop-April 2015Document18 pagesCost Machine Shop-April 2015azadsingh1No ratings yet
- Taxpnl ZB9854Document35 pagesTaxpnl ZB9854cheenuNo ratings yet
- ES Calculator vs1f (Special Cases)Document40 pagesES Calculator vs1f (Special Cases)Jonnathan Jessus CqNo ratings yet
- Untitled SpreadsheetDocument13 pagesUntitled SpreadsheetBhanu Prakash BoppanaNo ratings yet
- 24 01 22 Data Collection Workbook - Factory v1.3Document59 pages24 01 22 Data Collection Workbook - Factory v1.3Heri HermawanNo ratings yet
- Estrella ECO86501 15Document8 pagesEstrella ECO86501 15Sahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Forecasting PPTDocument58 pagesForecasting PPTojasvinNo ratings yet
- BASELINE ENERGY Glory 2022-2023Document2 pagesBASELINE ENERGY Glory 2022-2023atika kusumondariNo ratings yet
- Grafica Quintuple Tabla Mec. Suelos IIDocument46 pagesGrafica Quintuple Tabla Mec. Suelos IIARTURO DAVID MORAN GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Pc-Arrears-Pb3 - PAY COMMISSION CALCULATORDocument20 pagesPc-Arrears-Pb3 - PAY COMMISSION CALCULATORmohan9813032985@yahoo.com100% (2)
- 09 23 ManpowerDocument8 pages09 23 ManpowerMohamed RizwanNo ratings yet
- Rkbu 2022Document6 pagesRkbu 2022Ganesha GanesNo ratings yet
- Data DrivenDocument13 pagesData Drivenareejsheikh92No ratings yet
- HW 3 Part 2Document7 pagesHW 3 Part 2agonza70No ratings yet
- Gen Target-2017Document22 pagesGen Target-2017SundeepNo ratings yet
- Balram Morla AcpArrDocument1 pageBalram Morla AcpArrvibu613No ratings yet
- United States Census Figures Back to 1630From EverandUnited States Census Figures Back to 1630No ratings yet
- At Its Peak, in The 19th Century, The Empire Extended From The Khyber Pass in The West, To Kashmir in The North, To Sindh in The SouthDocument1 pageAt Its Peak, in The 19th Century, The Empire Extended From The Khyber Pass in The West, To Kashmir in The North, To Sindh in The SouthSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- A Mughal Force in Their City. The Marathas Maintained TheirDocument1 pageA Mughal Force in Their City. The Marathas Maintained TheirSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- At Its Height in 1760, The Maratha Empire Controlled A Large Portion oDocument1 pageAt Its Height in 1760, The Maratha Empire Controlled A Large Portion oSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Amir Khan Umrao Al Udat, To Drive Away TheDocument1 pageAmir Khan Umrao Al Udat, To Drive Away TheSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- British Fought The Pindaris, Bandits Who Had EscapedDocument1 pageBritish Fought The Pindaris, Bandits Who Had EscapedSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- An Impure Kind of Chalcedony Called Jasper Has Bands or Spots of RedDocument1 pageAn Impure Kind of Chalcedony Called Jasper Has Bands or Spots of RedSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Udat To Force The 5,000 Maratha Cavalrymen AwayDocument1 pageUdat To Force The 5,000 Maratha Cavalrymen AwaySahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- The British-Who Created A Trading Station in The West CoastDocument1 pageThe British-Who Created A Trading Station in The West CoastSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- To 1748 Launched Six Campaigns in BengalDocument1 pageTo 1748 Launched Six Campaigns in BengalSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Vassals in A Subsidiary Alliance With The British, FormingDocument1 pageVassals in A Subsidiary Alliance With The British, FormingSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Graphical Solution of LP in Two Variables Example 1 (3.1-9)Document4 pagesGraphical Solution of LP in Two Variables Example 1 (3.1-9)Sahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Them at The Battle of Colachel During The CalcuttaDocument1 pageThem at The Battle of Colachel During The CalcuttaSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Master of Professional Accounting Week 4 Lecture and Tutorial E6.25 Job Costing and Pricing: Interior Decorating FirmDocument32 pagesMaster of Professional Accounting Week 4 Lecture and Tutorial E6.25 Job Costing and Pricing: Interior Decorating FirmSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Trading Posts in Velha Goa, Damaon, Dio Island, andDocument1 pageTrading Posts in Velha Goa, Damaon, Dio Island, andSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1111 Section 10 Fall 2015 Exam 1 Prof. Michael J. Wagner Monday, September 28, 2015Document16 pagesCHEM 1111 Section 10 Fall 2015 Exam 1 Prof. Michael J. Wagner Monday, September 28, 2015Sahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- To: E&Y External Audit Team From: Keith "Ice Cold" Sellers, CFO, CBD, THC Date: February 1, 2019 RE: Testing For Impairment of Goodwill For The First National Bank of VailDocument2 pagesTo: E&Y External Audit Team From: Keith "Ice Cold" Sellers, CFO, CBD, THC Date: February 1, 2019 RE: Testing For Impairment of Goodwill For The First National Bank of VailSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Warning: Course: Financial Accounting (5004) Semester: Spring, 2022 Level: MSC Administrative ScienceDocument11 pagesWarning: Course: Financial Accounting (5004) Semester: Spring, 2022 Level: MSC Administrative ScienceSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- BUS 1103 Macroeconomics AnswersDocument39 pagesBUS 1103 Macroeconomics AnswersSahil PuniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Practice QuestionsDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Practice QuestionshahaheheNo ratings yet
- CapitalizationDocument26 pagesCapitalizationSajalAgrawalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Schedule On TE SurveyDocument42 pagesDetailed Schedule On TE SurveyMatthew AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Markets and CompetitionDocument10 pagesMarkets and CompetitionAnca MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12-Inventory ManagementDocument46 pagesChapter 12-Inventory ManagementMa. Cathleen BalunanNo ratings yet
- Burger CaseDocument15 pagesBurger CaseGaganNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 30 - AnswerDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 30 - Answernash100% (1)
- Malaysian Automotive Demand and Pricing StrategyDocument5 pagesMalaysian Automotive Demand and Pricing StrategyZaraScha HeMoi Hemoy0% (1)
- Amadeus Reservation Ticketing Manual Jan 2011Document245 pagesAmadeus Reservation Ticketing Manual Jan 2011Omar AlyNo ratings yet
- FranchisingDocument36 pagesFranchisingAbderrahim TMIQNo ratings yet
- Thesis Chapter 1Document24 pagesThesis Chapter 1Rohit SinghNo ratings yet
- ch18 - Percentage CompletionDocument49 pagesch18 - Percentage CompletionFrost MintNo ratings yet
- Taganito Mining Corp. vs. CIR CTA 04702 (Full Text)Document14 pagesTaganito Mining Corp. vs. CIR CTA 04702 (Full Text)Ritzchalle Garcia-Oalin100% (1)
- And South-Western Are Trademarks Used Herein Under LicenseDocument31 pagesAnd South-Western Are Trademarks Used Herein Under LicenseAhmed FahmyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Vũ Minh HằngNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NUMBER ONE Nature and Scope of Economics - Definition and Scope of Engineering EconomicsDocument61 pagesLECTURE NUMBER ONE Nature and Scope of Economics - Definition and Scope of Engineering Economicsnickokinyunyu11No ratings yet
- Rediscovered Benjamin Graham - 1945 Lectures - Benjamin GrahamDocument48 pagesRediscovered Benjamin Graham - 1945 Lectures - Benjamin Grahamtatsrus1100% (1)
- Mrunal (Economy) Participatory Notes (P-Notes), Hedge Funds, New Limits On FII, FPI, REFI Explained MrunalDocument8 pagesMrunal (Economy) Participatory Notes (P-Notes), Hedge Funds, New Limits On FII, FPI, REFI Explained Mrunalmerc7inNo ratings yet
- The 2008 VIX Trading Strategies ReportDocument7 pagesThe 2008 VIX Trading Strategies ReportCharles BaronyNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument35 pagesEconomicsKeira FrostNo ratings yet
- Continuation Cost Acctg. Acctg. For MaterialsDocument3 pagesContinuation Cost Acctg. Acctg. For MaterialsKen Ivan HervasNo ratings yet
- AnnualReport2014 2015Document173 pagesAnnualReport2014 2015charlesNo ratings yet
- Engineers' Pay and Financial Performance: Technical FeatureDocument5 pagesEngineers' Pay and Financial Performance: Technical FeatureVinod NairNo ratings yet
- CH 11 FlexiblebudgetsandoverheadanalysisDocument122 pagesCH 11 Flexiblebudgetsandoverheadanalysisamemarlin50% (2)
- Function Reservation ContractDocument1 pageFunction Reservation ContractKamburoto BabykoNo ratings yet
- Scams in India: Presented byDocument12 pagesScams in India: Presented bySharath AndeNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Management PDFDocument47 pagesPortfolio Management PDFbhaumiksawant25No ratings yet
- Service CompanyDocument6 pagesService CompanyMaria Crisol OliciaNo ratings yet