Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Likely To Be Completely New Product or
Likely To Be Completely New Product or
Uploaded by
Ahmed Khalid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesThe document discusses technology management frameworks and processes. It addresses:
- The technology management framework includes identification, selection, acquisition, exploitation, and protection of knowledge.
- Key questions to evaluate a technology opportunity include potential market trends, differences from current technologies, and compatibility with dominant designs.
- Complexity factors in technology management relate to the evolution of science, links between science and technology, and combinations of technologies.
Original Description:
Original Title
Tech Manafesto
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses technology management frameworks and processes. It addresses:
- The technology management framework includes identification, selection, acquisition, exploitation, and protection of knowledge.
- Key questions to evaluate a technology opportunity include potential market trends, differences from current technologies, and compatibility with dominant designs.
- Complexity factors in technology management relate to the evolution of science, links between science and technology, and combinations of technologies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesLikely To Be Completely New Product or
Likely To Be Completely New Product or
Uploaded by
Ahmed KhalidThe document discusses technology management frameworks and processes. It addresses:
- The technology management framework includes identification, selection, acquisition, exploitation, and protection of knowledge.
- Key questions to evaluate a technology opportunity include potential market trends, differences from current technologies, and compatibility with dominant designs.
- Complexity factors in technology management relate to the evolution of science, links between science and technology, and combinations of technologies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Identify technology management State the technology management
this is concerned with managing technologies to framework?
achieve business objectives which require skills in
understanding technology and managing business -Identification
activities
-n Selection
illustrate the fig -Acquisition
-Exploitation
-Protection of knowledge and expertise
embedded in products and manufacturing
The management of technology links engineering,
science and management disciplines to plan, Systems
develop, and implement technological capabilities
State key questions of a tech
to shape and accomplish the strategic and
operational objectives of an organization opportunity?
-What is the potential
What’s the dimensions that attain
competitive advantages for any -What are the market trends?
technology? -What are the differences between the new
technology and the current
- Cost - Quality
- What are the pros and cons for the
- Range of products
client?
- Manufacturing cycle time
-Is it compatible with the dominant design?
- Time to market Can it lead
Complexity factors of technology -to a new dominant design?
management? -What breakthroughs are needed to make
for the technology to emerge? How quickly
-Complexity of the evolution of technology might they develop?
-Complexity of science -What could accelerate or delay its
-Complexity of the links between science and progress?
technology -what scenarios can be envisioned?
-Possible combinations of different technologies to -what are the key threats?
form new technologies
-Fast evolution of customers' needs
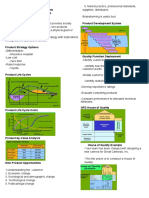
Define Innovation ((أكتب اتنين تالتة
-Some design features are the result of a complex -Likely to be completely new product or
process involving many players service
-Several players influence the evolution of -Could also be a small improvement in
technology existing products or services
CAM→ Computer-Aided Manufacturing
-Might be an improvement in internal processes too
CAD→Computer-Aided Engineering
-Today is likely to have a strong technological
These are a software tools for management
component, e.g software,electronics
the tech.
-Probably for existing market, but may also create
new/ suitable Major function of them
- 3-D Geometric Modeling
Importance of Innovation?
- 2-D Drafting
-Increases opportunity market separation
- Finite Element Analysis
-Good for the economy as a whole (as companies
trade on a global basis) - CNC Programming, Simulation and G-code
Generation
-usually leads to cost reductions-better margins
- Data Exchange
-Should give consumers greater satisfaction and
wider choice - Production Information Management
-Reduces dependency on old products/ services and Procedure to define a CAM model:
technological processes.
-Define the part geometry
Different models of tech innovation and
-Define the machining geometry
draw one of them for example
“integrative parallel process” (p 59~61) -Define machining tools
-Define machining operations and parameters
_product-oriented conversion.
-Simulate machining process
_tech/market-oriented conversion.
-Generate CNC machining codes
_coupling.
_integrative. Procedure to define a CAE model:
_integrative system. -Define the geometry of a part or an assembly
_integrative parallel. -Select materials
-Specify restraints and loads
-Create meshes
-Run the analysis
-View the analysis results
Benefits of CAD and CAM
-Product quality -Shorter design time
-Production cost reductions
CAD→ Computer-Aided Design
-Database availability Advantages of ERP:
-New range of capabilities
-Provides integration of supply-chain,
-Reduces need for "similar" parts production and administrative processes
What is the Flexible Manufacturing -Creates commonality of databases
System (FMS)? -Can incorporate improved, redesigned, “best
processes:
It’s a system which Using automated machines (DNC)
& materials handling equipment together, often -Increases communication and collaboration
connected to centralized computer, also called worldwide
automated work cell. -Helps integrate multiple sites and business
units
Advantages:
-Is packaged with a software core that is off-
-Faster, lower-cost changes from one part to another the-shelf coding
-Lower direct labor costs -Can provide a strategic advantage over
-Reduced inventory competitors
-Consistent, and perhaps better quality Disadvantages of ERP
Disadvantages: -Is very expensive to purchase, and even
more costly to customize
-Limited ability to adapt to product or product mix
changes -Requires major changes in the company and
its processes to implement
-Requires substantial preplanning and capital
expenditures -Is such a complex program that many
companies cannot adjust to it
-Technological problems of exact component
positioning and precise timing -Involves an ongoing process for
implementation, which is often never
-Tooling and fixture requirements completed
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): -Expertise in ERP is limited, with staffing an
ongoing problem
-Packaged business software systems that allow
companies to: Innovation dimensions
-Automate and integrate the majority of their business -form -function -extent -timing
processes
-Share common data and practices across the entire Sources of innovative opportunity
enterprise -the unexpected -inconsistency
-Produce and access information in a real-time -process need -market structure
environment
-demographics - perception
-now knowledge
CHARACTERISTICS OF KNOWLEDGE-
BASED INNOVATIONS
(1) The longest lead time of all innovations (e.g., 25-30
years)
(2) Almost always based on the convergence of
several different kinds of knowledge
SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS OF
KNOWLEDGE-BASED INNOVATION:
(1) Careful analysis of all of the necessary factors
(2) A clear focus on the strategic position
(3) Ability to learn and practice entrepreneurial
management
UNIQUE RISKS OF KNOWLEDGE-BASED
INNOVATION:
(1) The window of opportunity for establishing a
position is small
(2) A "shake-out" sets in as soon as the window of
opportunity closes
(3) There must be receptivity to the knowledge-based
innovation
System Dynamics Modeling
- Identify a problem
-Develop a dynamic hypothesis explaining the cause
of the problem
- Create a basic causal graph
- Augment the causal graph with more information
Convert the augmented causal graph to a System
Dynamics flow graph
- Translate a System Dynamics flow graph into
DYNAMO programs or equations
- Simulate the DYNAMO programs or equations
You might also like
- Software Development Processes and MethodologiesDocument31 pagesSoftware Development Processes and MethodologiesChristian Lloyd Salon100% (1)
- MIL-HDBK-23 Structural Sandwich CompositesDocument491 pagesMIL-HDBK-23 Structural Sandwich Compositeslider402114716No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Operation Management (Design of Goods and Services)Document7 pagesChapter 5 Operation Management (Design of Goods and Services)syaarose80% (5)
- Neumoinsuflador Lut Service ManualDocument65 pagesNeumoinsuflador Lut Service Manualandres2013bio0% (1)
- Digital Field ProsperDocument31 pagesDigital Field ProsperRonaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 OMDocument6 pagesChapter 6 OMAngel Jasmin TupazNo ratings yet
- PLM Fundamentals: Where Did It Come From?Document130 pagesPLM Fundamentals: Where Did It Come From?Anup ShokhwalNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument84 pagesProduct Life Cycle ManagementTRIBHUWAN TYAGINo ratings yet
- FEA For All EngineersDocument14 pagesFEA For All EngineersMarta TanaskovicNo ratings yet
- 91social Company Overview and CapabilitiesDocument22 pages91social Company Overview and CapabilitiesMahesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Top Solid Integration 2003 UsDocument12 pagesTop Solid Integration 2003 Usapi-3725036No ratings yet
- CS330 L1Document101 pagesCS330 L1dorathiNo ratings yet
- GEOPLM Siemens PLM Tecnomatix Process DesignerDocument2 pagesGEOPLM Siemens PLM Tecnomatix Process DesignerbehnyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1mimi nurfikriyahNo ratings yet
- AI Based Layout Planning SolutionDocument11 pagesAI Based Layout Planning SolutionrameshinreallifeNo ratings yet
- GIS - Campus Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesGIS - Campus Job Descriptioneue99332No ratings yet
- 2007+ +Skills+&+Knowledge+of+Cost+Engineering1.61 88Document28 pages2007+ +Skills+&+Knowledge+of+Cost+Engineering1.61 88Naveen LopesNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems NotesDocument21 pagesManagement Information Systems NoteszainebkhanNo ratings yet
- Celsius Tech Case Study SummaryDocument15 pagesCelsius Tech Case Study SummaryPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Enabling Digital Transformation Through A Collaborative Approach Between Design and ManufacturingDocument7 pagesEnabling Digital Transformation Through A Collaborative Approach Between Design and Manufacturingmakdeep2012No ratings yet
- Part 2: Defining PLM - Critical "Must Have" CapabilitiesDocument7 pagesPart 2: Defining PLM - Critical "Must Have" CapabilitiesSandeep BelurNo ratings yet
- 2511-Industry4.0 Demystifying The Digital TwinDocument16 pages2511-Industry4.0 Demystifying The Digital TwinAnonymous zwnFXURJNo ratings yet
- Driving High Performance: Case StudyDocument6 pagesDriving High Performance: Case StudyRajendra ThakurNo ratings yet
- Moving From One System To Many: Software Product Lines: Re-Using Architectural AssetsDocument13 pagesMoving From One System To Many: Software Product Lines: Re-Using Architectural AssetsjayasreeNo ratings yet
- Name-Roll No. - Assignment No. DateDocument6 pagesName-Roll No. - Assignment No. DatePratik Vitthalrao Jagtap-PatilNo ratings yet
- Simufact BR Product Lines enDocument4 pagesSimufact BR Product Lines enBryan BritoNo ratings yet
- Se Slide Revison NDocument31 pagesSe Slide Revison Nphongth779No ratings yet
- Intro Software EnggDocument29 pagesIntro Software EnggdfdfdNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing and Service TechnologiesDocument5 pagesManufacturing and Service TechnologiesSandunika DevasingheNo ratings yet
- Product Lifecycle Management: Dhirendra Kulkarni Technical Account Manager - PTCDocument14 pagesProduct Lifecycle Management: Dhirendra Kulkarni Technical Account Manager - PTCMahesh Karande (KOEL)No ratings yet
- Erp Keda Sap ImplementationDocument28 pagesErp Keda Sap ImplementationAksa DindeNo ratings yet
- Full Funnel Lead Nurturing: Microsoft Windows 10 OSDocument5 pagesFull Funnel Lead Nurturing: Microsoft Windows 10 OSVandan JainNo ratings yet
- Based Manufacturing: Kiowledge Distributed Product Design and IDocument6 pagesBased Manufacturing: Kiowledge Distributed Product Design and ITrinh VtnNo ratings yet
- Production PlanningDocument47 pagesProduction Planningsurendra0028No ratings yet
- Module 1Document17 pagesModule 1zain asroyNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Analysis For A Software ProjectDocument21 pagesFeasibility Analysis For A Software ProjectpushtiwalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document44 pagesLesson 1John LagmanNo ratings yet
- Automation Hand BookDocument310 pagesAutomation Hand BookPul50No ratings yet
- Module 1 Intro of ManagementDocument21 pagesModule 1 Intro of ManagementCarljohari Hussein AriffNo ratings yet
- The Catia Design Process, Design and Manufacture in AviationDocument3 pagesThe Catia Design Process, Design and Manufacture in AviationVigneshkumarNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Strategic Cost Management Linked With StrategiesDocument8 pagesWeek 3 - Strategic Cost Management Linked With StrategiesXandra AbitriaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Operations Management & TQM, MidtermsDocument6 pagesReviewer in Operations Management & TQM, MidtermsBellela DumpNo ratings yet
- 3 SS 1.1 Tech IntroDocument15 pages3 SS 1.1 Tech Introakhil reddy kalvaNo ratings yet
- Journey Towards A Model-Based EnterpriseDocument9 pagesJourney Towards A Model-Based EnterpriseAsish KumarNo ratings yet
- COMP 211 Introduction To Software EngineeringDocument18 pagesCOMP 211 Introduction To Software EngineeringsirmadamstudentNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Design & Methodology CS 312 OO Modeling CS 214 Fall 2011Document58 pagesObject-Oriented Design & Methodology CS 312 OO Modeling CS 214 Fall 2011From Zero To HeroNo ratings yet
- Siemens PLM Fibersim BR X44Document20 pagesSiemens PLM Fibersim BR X44Big FloresNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Circuit Technology Is On The MarketDocument36 pagesAsynchronous Circuit Technology Is On The MarketspotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Technology and Operations ManagementDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Technology and Operations ManagementChristian De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- RISE OF MODELING AND SIMULATION IN MANUFACTURING - HarmanDocument7 pagesRISE OF MODELING AND SIMULATION IN MANUFACTURING - Harmanharman04No ratings yet
- Denken A 2007Document6 pagesDenken A 2007Pay SohilauwNo ratings yet
- Automotive Design: ErgonomicsDocument56 pagesAutomotive Design: Ergonomicsravisb2958No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 (B) - Automation of Production SystemsDocument31 pagesLecture 6 (B) - Automation of Production Systemsdub911No ratings yet
- Operations Decisions 1Document7 pagesOperations Decisions 1raheemeeaaishaNo ratings yet
- Automation Solution Guide 2008 by Schneider Electric 1655790068Document300 pagesAutomation Solution Guide 2008 by Schneider Electric 1655790068Lacramioara VisnyeiNo ratings yet
- Management.: Chapter 2: Product, Process, and Schedule DesignDocument4 pagesManagement.: Chapter 2: Product, Process, and Schedule DesignHazel MosotNo ratings yet
- L4 Technology and Innovation ManagementDocument27 pagesL4 Technology and Innovation ManagementMaria seidNo ratings yet
- Operations Management TQMDocument18 pagesOperations Management TQMGweeenchanaNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument9 pagesOperations ManagementMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Computed Radiography (CR) : Dosen: Anak Agung Aris Diartama, S.ST, M.TR - IDDocument28 pagesComputed Radiography (CR) : Dosen: Anak Agung Aris Diartama, S.ST, M.TR - IDKevin TagahNo ratings yet
- Imperial Remnant Rules SheetDocument1 pageImperial Remnant Rules SheetJd DibrellNo ratings yet
- SS Disco Check Valve (Size 15-100)Document2 pagesSS Disco Check Valve (Size 15-100)rudirstNo ratings yet
- HZ 01Cpr: Material Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesHZ 01Cpr: Material Safety Data SheetFakhreddine BousninaNo ratings yet
- UPNMG Press Statement-Unemployed Nurses and MidwivesDocument1 pageUPNMG Press Statement-Unemployed Nurses and MidwivesClavia NyaabaNo ratings yet
- ATR72 Freighter VersionDocument6 pagesATR72 Freighter Versiontomay777No ratings yet
- Chavan Avinash-Resume 2Document1 pageChavan Avinash-Resume 2Adinath Baliram ShelkeNo ratings yet
- DM Assignment 1Document5 pagesDM Assignment 1Mai Anh TrầnNo ratings yet
- John Deere - Parts Catalog - Frame 5 v-3103Document2 pagesJohn Deere - Parts Catalog - Frame 5 v-3103eliasNo ratings yet
- Unit Test-II (SOM) 1Document2 pagesUnit Test-II (SOM) 1hasanNo ratings yet
- Capstone Project Proposal: My Inquiry Question IsDocument7 pagesCapstone Project Proposal: My Inquiry Question Isapi-491542571No ratings yet
- Adu Gloria WorkDocument68 pagesAdu Gloria WorkAiman UsmanNo ratings yet
- 5S (Methodology) : 5S Is The Name of A Workplace Organization Methodology That Uses A List of FiveDocument3 pages5S (Methodology) : 5S Is The Name of A Workplace Organization Methodology That Uses A List of FiveRoberto DiyNo ratings yet
- Numeral System Indian and InternationalDocument4 pagesNumeral System Indian and Internationalsatya 1No ratings yet
- File DisksDocument22 pagesFile DisksAlana PetersonNo ratings yet
- Ecs 2ar FDocument39 pagesEcs 2ar FĐức LêNo ratings yet
- CIO 308 Data Sheet 4921240554 UKDocument10 pagesCIO 308 Data Sheet 4921240554 UKWaseem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Module-5Document56 pagesVlsi Module-5Phanindra ReddyNo ratings yet
- C.S. Sharma and Kamlesh Purohit - Theory of Mechanisms and Machines-PHI Learning Private Limited (2006)Document723 pagesC.S. Sharma and Kamlesh Purohit - Theory of Mechanisms and Machines-PHI Learning Private Limited (2006)tp coephNo ratings yet
- How To Write History Coursework GcseDocument4 pagesHow To Write History Coursework Gcsexokcccifg100% (2)
- Chapter 2 SOURCES & FOUNDATIONS OF HUMAN RIGHTS LAWDocument6 pagesChapter 2 SOURCES & FOUNDATIONS OF HUMAN RIGHTS LAWI Lobeu My CaratNo ratings yet
- Types of ShoringDocument9 pagesTypes of ShoringAzil14100% (10)
- Schema Refinement and Normal Forms: Database Management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1Document19 pagesSchema Refinement and Normal Forms: Database Management Systems, 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1PRADNYA KASHIKARNo ratings yet
- Statement of Claim Form PDFDocument3 pagesStatement of Claim Form PDFWalla MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Quizapp: 15It324E Mini Project ReportDocument24 pagesQuizapp: 15It324E Mini Project ReportSubroto DasNo ratings yet
- One Love Executive Business Plan 4Document62 pagesOne Love Executive Business Plan 4Rocio CarrascalNo ratings yet
- DISS Q2 Week1 Learning-Activity-SheetDocument2 pagesDISS Q2 Week1 Learning-Activity-SheetBryanNo ratings yet
- Quality Control ManagementDocument4 pagesQuality Control Managementkriss WongNo ratings yet