Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acetazolamide
Acetazolamide
Uploaded by
Gwyn Rosales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
503 views3 pagesAcetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to treat glaucoma and seizures. It works by inhibiting the carbonic anhydrase enzyme, decreasing fluid secretion in the eyes and altering neuronal firing patterns in the brain. Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and metabolic acidosis. Nurses must monitor for side effects and ensure proper dosing, administration technique, and patient education on diet and fluid intake when using this drug.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAcetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to treat glaucoma and seizures. It works by inhibiting the carbonic anhydrase enzyme, decreasing fluid secretion in the eyes and altering neuronal firing patterns in the brain. Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and metabolic acidosis. Nurses must monitor for side effects and ensure proper dosing, administration technique, and patient education on diet and fluid intake when using this drug.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
503 views3 pagesAcetazolamide
Acetazolamide
Uploaded by
Gwyn RosalesAcetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to treat glaucoma and seizures. It works by inhibiting the carbonic anhydrase enzyme, decreasing fluid secretion in the eyes and altering neuronal firing patterns in the brain. Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and metabolic acidosis. Nurses must monitor for side effects and ensure proper dosing, administration technique, and patient education on diet and fluid intake when using this drug.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Nursing
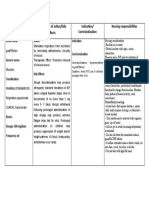
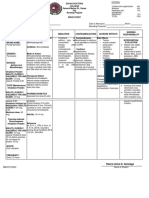
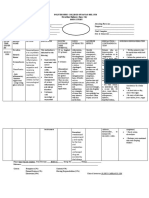
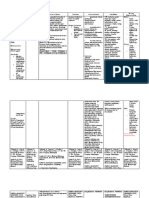
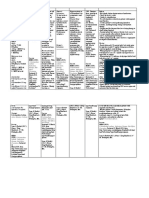
Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects
Responsibilities
Generic Name: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacodynamics General Indication: - Chronic CNS: Ataxia, Before Drug
Acetazolamide Carbonic anhydrase or Mechanism of To treat chronic noncongestive confusion, depression, Administration
inhibitor, Sulfonamide Action: simple (open- closed-angle disorientation, - Store oral
Trade/Brand Name: derivative Inhibits the enzyme angle) glaucoma glaucoma dizziness, drowsiness, preparations at 15°–
Diamox carbonic anhydrase, As short-term - cirrhosis fatigue, fever, flaccid 30° C (59°–86° F)
Therapeutic Class: which normally therapy to treat - hyperchloremic paralysis, headache, unless otherwise
Minimum dose: Anticonvulsant, appears in the eyes’ secondary acidosis lassitude, malaise, directed.
250 mg/day antiglaucoma, diuretic ciliary processes, glaucoma and - hypersensitivity to nervousness, - Check doctor’s order.
brain’s choroid plexus, preoperatively to acetazolamide paresthesia, seizures, - Establish baseline
Maximum dose: and kidneys’ proximal treat acute - hypokalemia tremor, weakness weight before initial
1000 mg/day divided tubule cells. In the congestive - hyponatremia therapy
q8-12hr eyes, enzyme (closed-angle) - severe pulmonary EENT: Altered taste,
inhibition decreases glaucoma obstruction tinnitus, transient During Drug
Patient’s Dose: aqueous humor To induce - severe renal, myopia Administration
500 mg secretion, which diuresis in heart hepatic, or - Ensure right patient,
lowers intraocular failure adrenocortical GI: Anorexia, right drug, right dose,
Route: pressure. In the brain, To treat drug- impairment constipation, diarrhea, right time, and right
PO inhibition may delay induced edema hepatic dysfunction, route.
abnormal, intermittent, To treat seizures, melena, nausea, - Use aseptic
Frequency: and excessive including vomiting techniques when
OD discharge from generalized tonic- administering the
neurons that cause clonic, absence, GU: Crystalluria, medication.
Form: seizures. In the and mixed decreased libido, - Administer diuretic
Tablet kidneys, it increases seizures, and glycosuria, hematuria, dose in morning to
bicarbonate excretion, myoclonic jerk impotence, avoid interrupted
Availability: which carries out patterns nephrotoxicity, sleep.
Tablet; sustained water, potassium, and To prevent or phosphaturia, polyuria, - Give with food or
release capsule; sodium, thus inducing relieve symptoms renal calculi, renal meals to minimize GI
powder for injection diuresis and metabolic of acute mountain colic, urinary upset.
acidosis. This acidosis sickness frequency - Inform patient that
Content: counteracts respiratory acetazolamide tablets
The active substance is alkalosis and reduces Patient’s Indication: HEME: may be crushed and
acetazolamide. Each symptoms of mountain To relieve the inner ear Agranulocytosis, suspended in chocolate
tablet contains 250mg sickness, including fluid build-up thereby hemolytic anemia, or sweet syrup. Or, one
acetazolamide. The headache, dizziness, reducing vertigo leukopenia, tablet may be
other ingredients are nausea, and dyspnea. frequency and avoiding pancytopenia, dissolved in 10 mL hot
dicalcium phosphate, hearing loss progression thrombocytopenia, water and added to 10
corn starch, Pharmacokinetics: of the patient thrombocytopenic ml honey or syrup.
magnesium stearate, Absorption: Well purpura - Maintain adequate
sodium starch absorbed from GI tract. fluid intake (1.5–2.5
glycolate, povidone. SKIN: L/24 h; 1 liter is
Onset: 1-1.5 hr Photosensitivity, approximately equal to
pruritus, rash, Stevens- 1 quart) to reduce risk
Peak: 2-4 hrs Johnson syndrome, of kidney stones.
urticaria - Monitor blood tests
Duration: 8-12 hrs during acetazolamide
Other: Acidosis, therapy to detect
Distribution: hyperuricemia, electrolyte imbalances.
Distributed throughout hypokalemia, weight
body; crosses placenta. loss After Drug
Administration
Elimination: In urine. - Advise patient to eat
potassium-rich diet
Half-Life: 2.4–5.8 h. when taking this drug
in high doses or for
prolonged periods.
- Advise patient to
avoid hazardous
activities if dizziness
or drowsiness occurs.
- Monitor fluid intake
and output every 8
hours and body weight
daily to detect
excessive fluid and
weight loss.
- Monitor for S&S of:
Mild to severe
metabolic acidosis;
potassium loss which
is greatest early in
therapy
- Document procedure
You might also like
- Recombinant Human Erythropoietin Stimulates Erythropoiesis Via Division and Differentiation of Progenitor Cells in Bone MarrowDocument2 pagesRecombinant Human Erythropoietin Stimulates Erythropoiesis Via Division and Differentiation of Progenitor Cells in Bone MarrowGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: A. Overview of The Clinical Use of Diuretics B. Classification of DiureticsDocument22 pagesDiuretics: A. Overview of The Clinical Use of Diuretics B. Classification of DiureticsSteven GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Contraindications: Before:: Diamox, Diamox SequelsDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Contraindications: Before:: Diamox, Diamox SequelsRomwella May AlgoNo ratings yet
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Document2 pagesDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolDocument5 pagesGeneric Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesDrug Study Prednisoloneunnamed personNo ratings yet
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAcyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComJanaica JuanNo ratings yet
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CDocument1 pageDrug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CValerie VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- GlipizideDocument3 pagesGlipizideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument7 pagesDrug Study CaseKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- UROKINASE (Kinlytic)Document4 pagesUROKINASE (Kinlytic)Mikaela Gabrielle GeraliNo ratings yet
- Final ColistinDocument3 pagesFinal ColistinGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study - Calcium GluconatemikErlhNo ratings yet
- Mycophenolate MofetilDocument1 pageMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SulfasalazineDocument2 pagesDrug Study SulfasalazineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For AntaminDocument1 pageDrug Study For AntaminJILLIAN MARIE BARREDO100% (1)
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Document2 pagesFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- MedroxyprogesteroneDocument5 pagesMedroxyprogesteroneunkown userNo ratings yet
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY (Dextromethorphan)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Dextromethorphan)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- THEOPHYLLINE - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTHEOPHYLLINE - Drug Studyeric macabiogNo ratings yet
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHNo ratings yet
- Epirubicin 10Document1 pageEpirubicin 10PdianghunNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilJohn Louie EscardaNo ratings yet
- LABETALOL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLABETALOL Drug StudyLeoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsdeepika kushwah100% (1)
- Drug Study - KetoprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - KetoprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- HydrochlorothiazideDocument2 pagesHydrochlorothiazidekuro hanabusa100% (1)
- FluorouracilDocument2 pagesFluorouracilHyacinth Bueser BondadNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug Study GabapentinDocument3 pagesDrug Study Gabapentinbridget.badiang001No ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyDocument1 pageHydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyTrisha CayabyabNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY SpironolactoneJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet
- MannitolDocument1 pageMannitolAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- PrimidoneDocument6 pagesPrimidoneKim SunooNo ratings yet
- MeclizineDocument2 pagesMeclizineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- ONDANSETRONDocument1 pageONDANSETRONJugen Gumba Fuentes Alquizar0% (1)
- Antidiuretic DrugsDocument4 pagesAntidiuretic DrugsNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Tramadol, Hyoscine-N-Butylbromide, Co-Trimoxazole, Potassium CitrateDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Tramadol, Hyoscine-N-Butylbromide, Co-Trimoxazole, Potassium CitratemissmakaiNo ratings yet
- Sulfamethaxazole, Salbu + IpraDocument5 pagesSulfamethaxazole, Salbu + IpraGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DiphenhydramineDocument3 pagesDiphenhydramineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument6 pagesPhenobarbitalGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- LevetiracetamDocument4 pagesLevetiracetamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Ipratropium SalbutamolDocument2 pagesIpratropium SalbutamolGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- ESOMEPRAZOLEDocument6 pagesESOMEPRAZOLEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- GliclazideDocument5 pagesGliclazideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- NimodipineDocument5 pagesNimodipineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- FenofibrateDocument4 pagesFenofibrateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument3 pagesDexamethasoneGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument4 pagesEnalaprilGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Tetanus ToxoidDocument3 pagesTetanus ToxoidGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- DiazepamDocument3 pagesDiazepamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CeftriaDocument5 pagesCeftriaGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- ColistinDocument2 pagesColistinGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument3 pagesCaptoprilGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- (Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveDocument4 pages(Per System Preferably) : AntihypertensiveGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- AmikacinDocument2 pagesAmikacinGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- Per System PreferablyDocument3 pagesPer System PreferablyGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime 1Document3 pagesCefuroxime 1Gwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument3 pagesCEFUROXIMEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Final Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesFinal Magnesium SulfateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- 6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyDocument2 pages6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaDocument4 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- AcetylcysteineDocument2 pagesAcetylcysteineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Final ColistinDocument3 pagesFinal ColistinGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Final AcetylcysteineDocument2 pagesFinal AcetylcysteineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Final Salbu-IpraDocument3 pagesFinal Salbu-IpraGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Final Opioid (Fentanyl)Document4 pagesFinal Opioid (Fentanyl)Gwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- PCOL 2 - Hypertension and Diuretic Side NotesDocument11 pagesPCOL 2 - Hypertension and Diuretic Side Notes25Lag1Lising, Ryshelle Watz T.No ratings yet
- Anti-Glaucoma Drugs (Ocular Hypotensive Drugs)Document24 pagesAnti-Glaucoma Drugs (Ocular Hypotensive Drugs)aamer niaziNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Chris Hague, PHDDocument29 pagesDiuretics: Chris Hague, PHDranachamanNo ratings yet
- Acetazolamide MDDocument13 pagesAcetazolamide MDhunzala shamirNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 1Document34 pagesDiuretics 1ياسمين مجديNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonDocument28 pagesDiuretics: Dr. Sadat MemonCham PianoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AcetaminophenDocument3 pagesDrug Study AcetaminophenIzza DeloriaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: DR Mozna TalpurDocument33 pagesDiuretics: DR Mozna TalpurShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Principles of Diuretic Therapy: Dr. Rania Magadmi, MBBS, PHDDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Diuretic Therapy: Dr. Rania Magadmi, MBBS, PHDمشاعرمبعثرةNo ratings yet
- PHA 824 The Pharmacodynamics of Diuretic Drugs Dr. M.T. Piascik ObjectivesDocument12 pagesPHA 824 The Pharmacodynamics of Diuretic Drugs Dr. M.T. Piascik ObjectivespriapisNo ratings yet
- Azarga CT 6006Document10 pagesAzarga CT 6006taritariNo ratings yet
- 1 Drugs Acting On The Eye - OkeDocument42 pages1 Drugs Acting On The Eye - OkeSintia AyuningsihNo ratings yet
- Nursing Quiz Topic GlaucomaDocument3 pagesNursing Quiz Topic GlaucomaChieChay Dub100% (1)
- Diuretics: BY-DR. Saurabh Kansal Dept. of Pharmacology Msy Medical College MeerutDocument33 pagesDiuretics: BY-DR. Saurabh Kansal Dept. of Pharmacology Msy Medical College MeerutPrakhar GoelNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Renal SystemDocument58 pagesDrugs Affecting Renal SystemDaniel OkakaNo ratings yet
- Diuretic DrugsDocument62 pagesDiuretic DrugsAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesPharmacology For The Surgical Technologist 4Th Edition Snyder Test Bank Full Chapter PDFCodyDavistgny100% (9)
- DrugDocument13 pagesDrugkhesler BacallaNo ratings yet
- Beige Brown Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20230922 - 184226 - 0000Document25 pagesBeige Brown Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20230922 - 184226 - 0000Mercurio AysonNo ratings yet
- Renal Drugs - Dr. UretaDocument4 pagesRenal Drugs - Dr. UretaAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- 4,5,6 - Diuretic PDFDocument27 pages4,5,6 - Diuretic PDFHely PatelNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument13 pagesDiureticsMohammad ismatNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary PharmacologyDocument11 pagesGenitourinary PharmacologySadia YousafNo ratings yet
- Reflections On Medicinal Chemistry at Merck, West Point: Chapter OneDocument9 pagesReflections On Medicinal Chemistry at Merck, West Point: Chapter OneWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Jurnal GlaukomaDocument6 pagesJurnal GlaukomaIntan NarariaNo ratings yet
- Acetazolamide/diamoxDocument3 pagesAcetazolamide/diamoxjedisay1100% (1)
- DiureticsDocument31 pagesDiureticsRameez ShamounNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used For GlaucomaDocument39 pagesDrugs Used For Glaucomavivilm100% (1)