Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Revision Notes Edited
Biology Revision Notes Edited
Uploaded by
Ainey MaiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Combined Science NotesDocument61 pagesCombined Science NotesShawn ChimbwandaNo ratings yet
- SC - Plants ExerciseDocument3 pagesSC - Plants ExerciseDewi100% (2)
- Daily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Document24 pagesDaily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Carol Gelbolingo100% (2)
- General and Unique Characteristics of The Different Organ Systems in Representative AnimalsDocument51 pagesGeneral and Unique Characteristics of The Different Organ Systems in Representative AnimalsAliah Jeonelle Ramos100% (2)
- THE Guide: Water-Based Paint Marker For All SurfacesDocument9 pagesTHE Guide: Water-Based Paint Marker For All SurfacesJustin DrewNo ratings yet
- Igcse Notes Biology UpdatedDocument8 pagesIgcse Notes Biology UpdatedAlfy YuleNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision Notes Edited (Repaired)Document5 pagesBiology Revision Notes Edited (Repaired)Ainey MaiNo ratings yet
- All of Biology Paper 1 IGCSE EdexcelDocument30 pagesAll of Biology Paper 1 IGCSE EdexcelzakariyahmurshedNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument7 pagesBiology NotesZiya JiwaniNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - BIO - CLASS 10 - NOTESDocument10 pagesLife Processes - BIO - CLASS 10 - NOTESvaarunisaxenaNo ratings yet
- 2 Structure and Functions in Living OrganismsDocument36 pages2 Structure and Functions in Living OrganismsSam ShohetNo ratings yet
- 6 Life ProcessesDocument28 pages6 Life Processeshaswinthkrishna1511No ratings yet
- Biology Class 9 Kerala Notes Part 1 (English Medium) by OdakkalDocument13 pagesBiology Class 9 Kerala Notes Part 1 (English Medium) by Odakkalmariyu palakkot tms100% (5)
- Biology NoteDocument6 pagesBiology NoteGUO JIAYI 22S203No ratings yet
- Life Processes QuestionsDocument58 pagesLife Processes QuestionsAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology: Biology Teaching Team Telkom University 2020Document40 pagesAnimal Physiology: Biology Teaching Team Telkom University 2020IndahMutiahUtamiNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - CH - 5 Life Processes1Document8 pagesBiology Notes - CH - 5 Life Processes1AISHA AMAL ANDIKATTILASSLAM ANDIKATTILNo ratings yet
- Life Processes: Chapter - 6Document13 pagesLife Processes: Chapter - 6milind dhamaniyaNo ratings yet
- Life Process.Document43 pagesLife Process.Anzar100% (1)
- Bio NotesDocument18 pagesBio Notesfariyausman100No ratings yet
- 2e Nutrition GlossaryDocument4 pages2e Nutrition Glossarysony reactsNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Respiratory SubstrateDocument8 pagesRespiration: Respiratory SubstrateEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- Life Processes NotesDocument87 pagesLife Processes Notesashtosh1418No ratings yet
- Biology SimplifiedDocument59 pagesBiology Simplifiedoussama6928No ratings yet
- IGCSE BiologyDocument12 pagesIGCSE BiologyLe KhanhNo ratings yet
- Notes Part Two (Chapter 3 Nutrition)Document40 pagesNotes Part Two (Chapter 3 Nutrition)Kaviish AnandanNo ratings yet
- Class X Chapter 6 (Life Processes-Nutrition) - 1 PDFDocument11 pagesClass X Chapter 6 (Life Processes-Nutrition) - 1 PDFtiaNo ratings yet
- Science Revision Guide SheetDocument81 pagesScience Revision Guide SheetNam ThanhNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Revision BookDocument65 pagesIGCSE Revision BookTANDON Aditya0% (1)
- Biology NotesDocument9 pagesBiology NotesMinal Shahbaz saeedNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Sep 05, 2021iytzitst88txdDocument8 pagesAdobe Scan Sep 05, 2021iytzitst88txdKumari KNo ratings yet
- BSC2011 Animals Exam 2 ReviewDocument72 pagesBSC2011 Animals Exam 2 ReviewDan TranNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1Document57 pagesBiology Paper 1Matty PNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer (1) - CompressedDocument61 pagesBiology Reviewer (1) - CompressedkevinNo ratings yet
- HSB Section A Living OrganismDocument7 pagesHSB Section A Living OrganismliltrashNo ratings yet
- Notes ch6 BioDocument13 pagesNotes ch6 BioHimayu RanpariaNo ratings yet
- No Test Problem From - Bring Pencil WednesdayDocument7 pagesNo Test Problem From - Bring Pencil WednesdayTene JohnsonNo ratings yet
- b2 Summary Notes - Sets 1-5Document31 pagesb2 Summary Notes - Sets 1-5api-320022467No ratings yet
- Prelecture Questions 2Document7 pagesPrelecture Questions 2kaslana kianaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Syllabus NotesDocument22 pagesPrelim Syllabus NotesChamsNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Class X - NotesDocument9 pagesLife Processes - Class X - Notesgeetanshmaheshwari1009sasNo ratings yet
- Biology RevisionDocument92 pagesBiology Revisionsohaila ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Biology Key TermsDocument11 pagesBiology Key Terms4DBLNo ratings yet
- B1.1 Nutrition - 2018Document49 pagesB1.1 Nutrition - 2018Wayne DayataNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes CH 6 Class 10Document14 pagesBio Notes CH 6 Class 10khushi.kashyap0468No ratings yet
- Life Process 1Document4 pagesLife Process 1tanishqmalik20No ratings yet
- Biology B2 Year 11 NotesDocument28 pagesBiology B2 Year 11 NotesNevin MaliekalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 6010, Revision NotesDocument119 pagesIGCSE Biology 6010, Revision NotesIan MartinNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument25 pagesBiologycarlotarubioperez123No ratings yet
- Respiration.Document39 pagesRespiration.Thee Kinyanjui'sNo ratings yet
- Science Revision NoteDocument68 pagesScience Revision Notebrandon.aryeeNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Revision NoteDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesis Revision NoteUsman Mukhtar AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Kisi2 Biology Fe s4 Sem 2Document15 pagesKisi2 Biology Fe s4 Sem 2Livia XoxoNo ratings yet
- Additional Science B2 (Biology) SpecificationDocument6 pagesAdditional Science B2 (Biology) Specificationgunslinger78No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument16 pagesRespirationTeacher AlexNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes PDFDocument79 pagesBiology Notes PDFSaket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Biology SPM With Cikgu Heery: 1. Density of 3 Cell Components & Specialised Cell Functions - FAMOUS SPM!Document21 pagesSeminar Biology SPM With Cikgu Heery: 1. Density of 3 Cell Components & Specialised Cell Functions - FAMOUS SPM!黎筱淳No ratings yet
- Oswal RMT Life ProcessDocument24 pagesOswal RMT Life ProcessatjatjNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam Saviour by Kalel WilsonDocument15 pagesBiology Exam Saviour by Kalel WilsonKalel WilsonNo ratings yet
- Fe ConceptDocument177 pagesFe ConceptIvan MaximusNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Mastery SheetDocument48 pagesIGCSE Mastery SheetKexinNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS FORMULA CombsciDocument6 pagesPHYSICS FORMULA CombsciAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS FORMULA Combsci Edited FinalDocument8 pagesPHYSICS FORMULA Combsci Edited FinalAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision Notes Edited (Repaired)Document5 pagesBiology Revision Notes Edited (Repaired)Ainey MaiNo ratings yet
- Week 17 English ActivitiesDocument6 pagesWeek 17 English ActivitiesAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperDocument13 pagesCSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1 Rheo Leaf CLS-XDocument2 pagesExperiment - 1 Rheo Leaf CLS-Xsatyajit ojhaNo ratings yet
- Te-Life Processes Final Revisor (2022-23)Document88 pagesTe-Life Processes Final Revisor (2022-23)Gautam SharrmaNo ratings yet
- Pas Bahasa Inggris Kls Xii Ips 1-6 SMT 1Document10 pagesPas Bahasa Inggris Kls Xii Ips 1-6 SMT 1CHANNEL TUMBALNo ratings yet
- FABACEAEDocument5 pagesFABACEAEFitrie Sii Bismaniac100% (1)
- Second Periodical Test in Science Vi Table of Specification Objectives No. of Days Taught Percent No. of Items Item PlacementDocument14 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science Vi Table of Specification Objectives No. of Days Taught Percent No. of Items Item PlacementNida Espinas FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Hagnaya VineDocument6 pagesHagnaya VineAnonette RamosNo ratings yet
- Ordinar Y LevelDocument12 pagesOrdinar Y Levelhelenanamb26No ratings yet
- GENED Science1Document78 pagesGENED Science1Mary-Rose CasuyonNo ratings yet
- System in Plants PDFDocument1 pageSystem in Plants PDFbarfan chhetriNo ratings yet
- The Indian High School (Junior), Dubai Grade: 4 General Science RA 2 PRACTICE SHEET-2020-2021 - Name: - DivDocument2 pagesThe Indian High School (Junior), Dubai Grade: 4 General Science RA 2 PRACTICE SHEET-2020-2021 - Name: - Div༒No ratings yet
- Epithelantha IdentificaçãoDocument9 pagesEpithelantha Identificaçãoays003No ratings yet
- What Is Transpiration?Document5 pagesWhat Is Transpiration?Brandly NyamapnziNo ratings yet
- PracticalDocument5 pagesPracticalsasmitswati0% (1)
- Weed FamiliesDocument4 pagesWeed FamiliesSolomon MbeweNo ratings yet
- 1981 BritishAscomycetesSupplement DennisDocument46 pages1981 BritishAscomycetesSupplement DennisAm MaNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument3 pagesGeneral BiologyPrecious QuiledoroNo ratings yet
- LAB7 IntroDocument3 pagesLAB7 IntroAngela Joyce MartinNo ratings yet
- Using The Tea Evaluation SheetDocument4 pagesUsing The Tea Evaluation SheetAndre CandraNo ratings yet
- (Rangoon Creeper,) : Quisqualis IndicaDocument4 pages(Rangoon Creeper,) : Quisqualis IndicaAshish VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- 0610 s17 QP 62 PDFDocument12 pages0610 s17 QP 62 PDFAnonymous pQ1Z6R29K9No ratings yet
- Biology G9 Q1 W8 D2Document11 pagesBiology G9 Q1 W8 D2MARIANNE OPADANo ratings yet
- Corn Pest Surveillance Pre-Inception MeetingDocument41 pagesCorn Pest Surveillance Pre-Inception MeetingMarcJunardJoverNo ratings yet
- Exploring The NatureDocument20 pagesExploring The NatureSujayJainNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1 Mod5 Ecosystem Life Energy - Science Quarter 1 - LIVING THINGS Module 5 - Ecosystem - Life - StudocuDocument1 pageScience 9 Q1 Mod5 Ecosystem Life Energy - Science Quarter 1 - LIVING THINGS Module 5 - Ecosystem - Life - Studocuzhemon97No ratings yet
- Class 9 Bio PracticalsDocument23 pagesClass 9 Bio PracticalsRaj PandeyNo ratings yet
Biology Revision Notes Edited
Biology Revision Notes Edited
Uploaded by
Ainey MaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Revision Notes Edited
Biology Revision Notes Edited
Uploaded by
Ainey MaiCopyright:
Available Formats
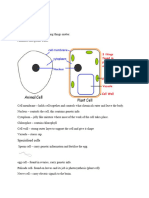
BIOLOGY RBC in water – cell burst (no cell wall to protect the
cell)
Plant Cell Animal Cell
Has cell wall No cell wall Plat cell in water – cell will not burst(thick cell wall to
Has chloroplast No chloroplast protect the cell).
Has large vacuole No vacuole
Conditions for osmosis to takes place:
Function of parts: 1. Presence of water molecules
Cell membrane – control the movement of substances 2. Semi permeable membrane
in and out of the cell. 3. Difference in concentration of water
Cytoplasm – carries out all chemical reactions in the
cell. Enzymes – protein substances which speed up the
Vacuole – mainly filled with water and controls the chemical reactions in the body.
hardness of plant cell. An optimum temperature 37OC – 40OC is needed for
Cell wall – give shape and protect the cell. enzyme action.
Below 37OC – reaction is too slow.
Root Hair Cell : To absorb water from the soil. Above 37OC – enzyme will be destroyed.
Structural Adaptation PH 6-10 enzyme work best.
1. Grow outwards – has larger surface area to Low PH – reaction is low.
absorb more water. Above PH 10 – stops and denatured.
2. Large vacuole – increase the surface area to
absorb more water. Animal nutrition
Xylem: Carries water from the roots to the stems and 7 Classes of food – fats, carbohydrates, protein,
leaves. vitamin, water, fibre & mineral.
Phloem: Carries food. Balanced diet – diet that contain the right proportions
of food to maintain healthy diet.
Red blood cell (RBC) : Transport oxygen to all parts of Malnutrition – poor nutrition
the body. Example:
Contain haemoglobin. Obesity – more fats
Structural Adaptation Constipation – less fibre
1. Biconcave disc shape – provides large surface
area to carry oxygen. Complex food Enzyme Simple
2. No nucleus – more haemoglobin and more food(product)
oxygen to be transported. Starch/carbohydrates Amylase Maltose
Protein Protease Amino acids
White blood cell : Produce antibodies fight against Fat Lipase Fatty acid and
germs glycerol
1. Phagocytes – engulf and digest bacteria
2. Lymphocytes – produce antibodies to fight The end product of protein digestion – amino acid
against the germs The end product of starch digestion – glucose.
Platelets – helps in blood clotting. Human Alimentary Canal
Platelets produce substance which converts Stomach – produce enzyme to digest protein.
fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin net stops blood to flow. Small intestine (duodenum) – digested food is
absorbed into the blood.
Diffusion – movement of molecules from high region Large intestine (ileum) – absorbs water from
to low region. Example: movement of soluble undigested food and store as faeces.
molecule into blood stream, oxygen into cell.
Osmosis – movement of water molecules from a Functions of saliva
region of higher concentration to a region of lower 1. To smoothen the food
concentration through a semi permeable membrane. 2. Contains salivary amylase which convert
Example: movement of water into root hair cell. starch to glucose.
Functions of liver 1. Light – increase in light intensity increase in
1. Produce bile which helps in digestion of fat. the rate of photosynthesis.
2. Breakdown alcohol to carbohydrates and 2. Temperature – increase in temperature
water increase in the rate of photosynthesis.
Changes excess amino acids to carbohydrates and
urea(removed by kidney as urine). Stomata – exchanges of gases (carbon dioxide and
oxygen) takes place through stomata.
Peristalsis – contraction and relaxation of muscles in Guard cell – control the opening and closing of
food pipe. stomata.
The process by which food moves along the walls of Palisade cell – site of photosynthesis.(contain more
alimentary canal – Peristalsis. chlorophyll)
Nutrient needed for plant growth – Nitrate (nitrogen)
Transpiration – loss of water from the lower surface of
Ingestion – Taking in of food. (mouth) a leaf.
Digestion – Breaking down of large food particles into Wilting – A process in which the leaves lose water
smaller food particles. (mouth, stomach, small faster than the roots absorb water.
intestine)
Absorption – Passage of digested food into blood. Uses of water:
(small intestine) It's a reactant used in photosynthesis
Assimilation – use of digested food by all parts of It supports leaves and shoots by keeping
body. the cells rigid
Egestion – removal of undigested food as faeces. It cools the leaves by evaporation
It transports dissolved minerals around
(anus)
the plant
Respiration – Process by which energy released from
food in living cells.
Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration
Presence of oxygen Absence of oxygen
Release large amount of Release small amount of
energy energy
Word equation: Word equation:
Glucose + oxygen Animals
carbon dioxide + water + Glucose lactic acid +
large amount of energy small amount of energy
Plants
Glucose alcohol +
carbon dioxide
The substance produced when muscle cells respire
anaerobically – lactic acid. To remove lactic acid –
need to take in more oxygen.
Difference between inspired air air and expired air:
Plant Nutrition Inspired Air Expired Air
Photosynthesis – Process by which green plants make Contains more Less oxygen
food by using carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, oxygen
chlorophyll. Less carbon dioxide More carbon dioxide
Word equation for photosynthesis: Less water vapour More water vapour
chlorophyll/sunlight Less warmer More warmer
Carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen
Organ through which carbon dioxide is excreted –
Light - as a source of energy Lungs.
Chlorophyll – to trap sunlight Process by which carbon dioxide is excreted –
Diffusion.
2 factors affecting photosynthesis:
Structure In the lungs through which gaseous
exchange takes place – alveoli/airsacs.
Excretion – Removal of harmful waste products of
metabolism from the body.
3 excretory products in body – carbon dioxide, urea
and water.
The lungs are the excretory organs for removing
carbon dioxide from the blood.
The kidneys are the excretory organs for removing
excess water and urea.
Renal artery – brings blood containing urea and excess
water to kidney.
Renal vein – takes the blood cleared of urea and
excess water away from kidney.
Near Objects – Ciliary muscles contract, suspensory
ligaments loose, lens fat
Distant objects – Ciliary muscles relaxes, suspensory
ligaments tight, lens thin
Bright light – Circular muscles contract, radial muscles
relax, pupil smaller
Dim light – Circular muscles relax, radial muscles
contract, pupil bigger
Hormone – chemical substance – made by an
endocrine gland – carried by the blood – changes the
activity of one or more specific target organs –
destroyed by the liver after use.
Veins: carry deoxygenated blood form all parts of the
body back to the heart.
Has valve (prevent backflow of bood), large lumen,
thin muscular wall, blood flow with low pressure.
Artery: carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
to all parts of the body.
No valve, small lumen, thick muscular wall, blood
flow with high pressure.
The left ventricle has a thicker wall than the right
ventricle because it has to pump blood around the
heart.
Coronary heart disease- when fatty substance is
deposited on the wall of arteries blocking the supply
of oxygen to the heart.
Possible cause of heart disease: smoking, obesity,
smoking, overweight, lack of exercise.
Gonorrhoea Syphlis
- thick greenish yellow - painless sore on parts
liquid comes out of penis of the body
- burninf feeling when pass - skin rash which lead to
urine inflammation
- cure by antibiotics - cure by antibiotics
Drug – externally administered substance when taken
into the body changes the chemical reactions in the
body.
Ovary – develops into fruit.
Ovule – develops into seed. Alcohol – a depressant that slows down the working
of the brain and the nervous system.
Dispersal of seed – transportation of seeds and fruits Effects: reduced self control, reduced the ability to
away from parent plant. Example of fruit dispersal: think clearly, difficulty in speaking, seeing and walking,
Wind, animals. injury due to accidents, liver damage, stomach ulcers,
Why? Prevent overcrowding and competition for malnutrition, social problems.
water, nutrients and sunlight.
Heroin – a powerful depressant that slows down the
Germination – the growth of a plant from a seed. working of the nervous and respiratory system.
Condition for germination: a) water b) oxygen c) Effects: sense of well being, drowsiness, social
temperature problems(crime), weight loss, lung damage, brain
damage.
Asexual reproduction – new individual develops or
grow from single parent. Producers – green plants which make food using light
- individuals formed are identical to the parent. energy and two raw materials, water and carbon
dioxide, during the process of photosynthesis.
Sexual reproduction - new individual develops from
cells produced by two parents Consumers – animals which feed on other living
- individuals formed are not identical to either its organisms.
parents.
Decomposers – organism which break down dead
Fertilization – the fusion of a male sex cell(sperm) plant and animal matter into simpler substances and
with a female sex cell(egg) to form a zygote. return them to the soil.
- normally occurs in the fallopian tube.
Food chain – series of organisms through which
Menstruation – the shedding of the womb lining energy is transferred in the form of food (chemical
together with the unfertilized egg and blood through energy).
the vagina. Menstrual cycle – 28 days.
Short food chain:
Breast Feeding Bottle-feeding - energy transfer more efficient
Contains all the Does not contain all the - enough energy for the last consumer.
nutrients nutrients
Contains antibodies Does not contain Deforestation- the cutting down of large area of
antibodies forests.
Easily digested Cannot digest Effects:
Increase bonding Does not increase bonding - soil erosion
between mother and between mother and child - reduction in rainfall
child Famine- shortage of food over a long period of time.
Problems contribute to famines:
Methods of birth control: - droughts
the natural or rhythm method, chemical control - floods
(spermicides), the use of barriers (condoms and - unequal distribution of food
diaphragm), hormonal control (with pills), surgical - overpopulation
sterilization (vasectomy and ligation).
Processes that remove carbon dioxide form the
atmosphere:
- photosynthesis
- dissolving of carbon dioxide in water
Process that return carbon dioxide to the atmosphere:
- respiration
- decay
- combustion or burning
- giving up of carbon dioxide by bodies of water
You might also like
- Combined Science NotesDocument61 pagesCombined Science NotesShawn ChimbwandaNo ratings yet
- SC - Plants ExerciseDocument3 pagesSC - Plants ExerciseDewi100% (2)
- Daily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Document24 pagesDaily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Carol Gelbolingo100% (2)
- General and Unique Characteristics of The Different Organ Systems in Representative AnimalsDocument51 pagesGeneral and Unique Characteristics of The Different Organ Systems in Representative AnimalsAliah Jeonelle Ramos100% (2)
- THE Guide: Water-Based Paint Marker For All SurfacesDocument9 pagesTHE Guide: Water-Based Paint Marker For All SurfacesJustin DrewNo ratings yet
- Igcse Notes Biology UpdatedDocument8 pagesIgcse Notes Biology UpdatedAlfy YuleNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision Notes Edited (Repaired)Document5 pagesBiology Revision Notes Edited (Repaired)Ainey MaiNo ratings yet
- All of Biology Paper 1 IGCSE EdexcelDocument30 pagesAll of Biology Paper 1 IGCSE EdexcelzakariyahmurshedNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument7 pagesBiology NotesZiya JiwaniNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - BIO - CLASS 10 - NOTESDocument10 pagesLife Processes - BIO - CLASS 10 - NOTESvaarunisaxenaNo ratings yet
- 2 Structure and Functions in Living OrganismsDocument36 pages2 Structure and Functions in Living OrganismsSam ShohetNo ratings yet
- 6 Life ProcessesDocument28 pages6 Life Processeshaswinthkrishna1511No ratings yet
- Biology Class 9 Kerala Notes Part 1 (English Medium) by OdakkalDocument13 pagesBiology Class 9 Kerala Notes Part 1 (English Medium) by Odakkalmariyu palakkot tms100% (5)
- Biology NoteDocument6 pagesBiology NoteGUO JIAYI 22S203No ratings yet
- Life Processes QuestionsDocument58 pagesLife Processes QuestionsAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology: Biology Teaching Team Telkom University 2020Document40 pagesAnimal Physiology: Biology Teaching Team Telkom University 2020IndahMutiahUtamiNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - CH - 5 Life Processes1Document8 pagesBiology Notes - CH - 5 Life Processes1AISHA AMAL ANDIKATTILASSLAM ANDIKATTILNo ratings yet
- Life Processes: Chapter - 6Document13 pagesLife Processes: Chapter - 6milind dhamaniyaNo ratings yet
- Life Process.Document43 pagesLife Process.Anzar100% (1)
- Bio NotesDocument18 pagesBio Notesfariyausman100No ratings yet
- 2e Nutrition GlossaryDocument4 pages2e Nutrition Glossarysony reactsNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Respiratory SubstrateDocument8 pagesRespiration: Respiratory SubstrateEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- Life Processes NotesDocument87 pagesLife Processes Notesashtosh1418No ratings yet
- Biology SimplifiedDocument59 pagesBiology Simplifiedoussama6928No ratings yet
- IGCSE BiologyDocument12 pagesIGCSE BiologyLe KhanhNo ratings yet
- Notes Part Two (Chapter 3 Nutrition)Document40 pagesNotes Part Two (Chapter 3 Nutrition)Kaviish AnandanNo ratings yet
- Class X Chapter 6 (Life Processes-Nutrition) - 1 PDFDocument11 pagesClass X Chapter 6 (Life Processes-Nutrition) - 1 PDFtiaNo ratings yet
- Science Revision Guide SheetDocument81 pagesScience Revision Guide SheetNam ThanhNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Revision BookDocument65 pagesIGCSE Revision BookTANDON Aditya0% (1)
- Biology NotesDocument9 pagesBiology NotesMinal Shahbaz saeedNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Sep 05, 2021iytzitst88txdDocument8 pagesAdobe Scan Sep 05, 2021iytzitst88txdKumari KNo ratings yet
- BSC2011 Animals Exam 2 ReviewDocument72 pagesBSC2011 Animals Exam 2 ReviewDan TranNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1Document57 pagesBiology Paper 1Matty PNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer (1) - CompressedDocument61 pagesBiology Reviewer (1) - CompressedkevinNo ratings yet
- HSB Section A Living OrganismDocument7 pagesHSB Section A Living OrganismliltrashNo ratings yet
- Notes ch6 BioDocument13 pagesNotes ch6 BioHimayu RanpariaNo ratings yet
- No Test Problem From - Bring Pencil WednesdayDocument7 pagesNo Test Problem From - Bring Pencil WednesdayTene JohnsonNo ratings yet
- b2 Summary Notes - Sets 1-5Document31 pagesb2 Summary Notes - Sets 1-5api-320022467No ratings yet
- Prelecture Questions 2Document7 pagesPrelecture Questions 2kaslana kianaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Syllabus NotesDocument22 pagesPrelim Syllabus NotesChamsNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Class X - NotesDocument9 pagesLife Processes - Class X - Notesgeetanshmaheshwari1009sasNo ratings yet
- Biology RevisionDocument92 pagesBiology Revisionsohaila ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Biology Key TermsDocument11 pagesBiology Key Terms4DBLNo ratings yet
- B1.1 Nutrition - 2018Document49 pagesB1.1 Nutrition - 2018Wayne DayataNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes CH 6 Class 10Document14 pagesBio Notes CH 6 Class 10khushi.kashyap0468No ratings yet
- Life Process 1Document4 pagesLife Process 1tanishqmalik20No ratings yet
- Biology B2 Year 11 NotesDocument28 pagesBiology B2 Year 11 NotesNevin MaliekalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 6010, Revision NotesDocument119 pagesIGCSE Biology 6010, Revision NotesIan MartinNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument25 pagesBiologycarlotarubioperez123No ratings yet
- Respiration.Document39 pagesRespiration.Thee Kinyanjui'sNo ratings yet
- Science Revision NoteDocument68 pagesScience Revision Notebrandon.aryeeNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Revision NoteDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesis Revision NoteUsman Mukhtar AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Kisi2 Biology Fe s4 Sem 2Document15 pagesKisi2 Biology Fe s4 Sem 2Livia XoxoNo ratings yet
- Additional Science B2 (Biology) SpecificationDocument6 pagesAdditional Science B2 (Biology) Specificationgunslinger78No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument16 pagesRespirationTeacher AlexNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes PDFDocument79 pagesBiology Notes PDFSaket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Biology SPM With Cikgu Heery: 1. Density of 3 Cell Components & Specialised Cell Functions - FAMOUS SPM!Document21 pagesSeminar Biology SPM With Cikgu Heery: 1. Density of 3 Cell Components & Specialised Cell Functions - FAMOUS SPM!黎筱淳No ratings yet
- Oswal RMT Life ProcessDocument24 pagesOswal RMT Life ProcessatjatjNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam Saviour by Kalel WilsonDocument15 pagesBiology Exam Saviour by Kalel WilsonKalel WilsonNo ratings yet
- Fe ConceptDocument177 pagesFe ConceptIvan MaximusNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Mastery SheetDocument48 pagesIGCSE Mastery SheetKexinNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS FORMULA CombsciDocument6 pagesPHYSICS FORMULA CombsciAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS FORMULA Combsci Edited FinalDocument8 pagesPHYSICS FORMULA Combsci Edited FinalAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision Notes Edited (Repaired)Document5 pagesBiology Revision Notes Edited (Repaired)Ainey MaiNo ratings yet
- Week 17 English ActivitiesDocument6 pagesWeek 17 English ActivitiesAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperDocument13 pagesCSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1 Rheo Leaf CLS-XDocument2 pagesExperiment - 1 Rheo Leaf CLS-Xsatyajit ojhaNo ratings yet
- Te-Life Processes Final Revisor (2022-23)Document88 pagesTe-Life Processes Final Revisor (2022-23)Gautam SharrmaNo ratings yet
- Pas Bahasa Inggris Kls Xii Ips 1-6 SMT 1Document10 pagesPas Bahasa Inggris Kls Xii Ips 1-6 SMT 1CHANNEL TUMBALNo ratings yet
- FABACEAEDocument5 pagesFABACEAEFitrie Sii Bismaniac100% (1)
- Second Periodical Test in Science Vi Table of Specification Objectives No. of Days Taught Percent No. of Items Item PlacementDocument14 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science Vi Table of Specification Objectives No. of Days Taught Percent No. of Items Item PlacementNida Espinas FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Hagnaya VineDocument6 pagesHagnaya VineAnonette RamosNo ratings yet
- Ordinar Y LevelDocument12 pagesOrdinar Y Levelhelenanamb26No ratings yet
- GENED Science1Document78 pagesGENED Science1Mary-Rose CasuyonNo ratings yet
- System in Plants PDFDocument1 pageSystem in Plants PDFbarfan chhetriNo ratings yet
- The Indian High School (Junior), Dubai Grade: 4 General Science RA 2 PRACTICE SHEET-2020-2021 - Name: - DivDocument2 pagesThe Indian High School (Junior), Dubai Grade: 4 General Science RA 2 PRACTICE SHEET-2020-2021 - Name: - Div༒No ratings yet
- Epithelantha IdentificaçãoDocument9 pagesEpithelantha Identificaçãoays003No ratings yet
- What Is Transpiration?Document5 pagesWhat Is Transpiration?Brandly NyamapnziNo ratings yet
- PracticalDocument5 pagesPracticalsasmitswati0% (1)
- Weed FamiliesDocument4 pagesWeed FamiliesSolomon MbeweNo ratings yet
- 1981 BritishAscomycetesSupplement DennisDocument46 pages1981 BritishAscomycetesSupplement DennisAm MaNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument3 pagesGeneral BiologyPrecious QuiledoroNo ratings yet
- LAB7 IntroDocument3 pagesLAB7 IntroAngela Joyce MartinNo ratings yet
- Using The Tea Evaluation SheetDocument4 pagesUsing The Tea Evaluation SheetAndre CandraNo ratings yet
- (Rangoon Creeper,) : Quisqualis IndicaDocument4 pages(Rangoon Creeper,) : Quisqualis IndicaAshish VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- 0610 s17 QP 62 PDFDocument12 pages0610 s17 QP 62 PDFAnonymous pQ1Z6R29K9No ratings yet
- Biology G9 Q1 W8 D2Document11 pagesBiology G9 Q1 W8 D2MARIANNE OPADANo ratings yet
- Corn Pest Surveillance Pre-Inception MeetingDocument41 pagesCorn Pest Surveillance Pre-Inception MeetingMarcJunardJoverNo ratings yet
- Exploring The NatureDocument20 pagesExploring The NatureSujayJainNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1 Mod5 Ecosystem Life Energy - Science Quarter 1 - LIVING THINGS Module 5 - Ecosystem - Life - StudocuDocument1 pageScience 9 Q1 Mod5 Ecosystem Life Energy - Science Quarter 1 - LIVING THINGS Module 5 - Ecosystem - Life - Studocuzhemon97No ratings yet
- Class 9 Bio PracticalsDocument23 pagesClass 9 Bio PracticalsRaj PandeyNo ratings yet