Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Storage Guildline: Main Purpose of Competible Storage Group
Chemical Storage Guildline: Main Purpose of Competible Storage Group
Uploaded by
applecrushzCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Alkanes AnswersDocument42 pagesAlkanes AnswersSpider Gamer22No ratings yet
- Sanosil Biotech Pvt. LTD.: Material Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesSanosil Biotech Pvt. LTD.: Material Safety Data SheetJainil Panchal50% (2)
- ASTM - 1955 - Tentative Methods of Test For Phosphate in Industrial WaterDocument9 pagesASTM - 1955 - Tentative Methods of Test For Phosphate in Industrial WaterEvelynNo ratings yet
- Structural Plate Astm A36: Plates, Shapes, and Sheet PilingDocument4 pagesStructural Plate Astm A36: Plates, Shapes, and Sheet Pilingeko kusumoNo ratings yet
- Polishing The Basic Principles in EnglishDocument4 pagesPolishing The Basic Principles in EnglishMafteian LiviuNo ratings yet
- 1016 Greenhouse PlansDocument9 pages1016 Greenhouse Planslagumbeg100% (1)
- Chemical Storage Gui Deline: Main Purpose of Comp Atible Storage GroupDocument2 pagesChemical Storage Gui Deline: Main Purpose of Comp Atible Storage GroupapplecrushzNo ratings yet
- Chemical Segregation NIHDocument6 pagesChemical Segregation NIHSundaramoorthy SelvanathanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Introduction To Chemistry Form 4 KSSM (1) StudentDocument43 pagesCH 1 Introduction To Chemistry Form 4 KSSM (1) StudentJASON CHONG CHIA HANG Moe100% (1)
- Chemical Storage TableDocument4 pagesChemical Storage TableMin Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Epa Chemical Segregation ChartDocument2 pagesEpa Chemical Segregation ChartChilaNo ratings yet
- FBMH Table For Chemical StorageDocument4 pagesFBMH Table For Chemical StorageJoan RaquinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Segregation Table 230302 123808Document6 pagesChemical Segregation Table 230302 123808Zaira AsorNo ratings yet
- Almacenamiento y SegregaciónDocument1 pageAlmacenamiento y SegregaciónCecilia Lorena SzymczakNo ratings yet
- Chemical Storage Segregation SchemeDocument3 pagesChemical Storage Segregation Schemesuko winartiNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Safety Measures in Laboratory Science F4 KSSMDocument38 pagesCH 1 Safety Measures in Laboratory Science F4 KSSMfaezahNo ratings yet
- ChemicalsDocument12 pagesChemicalsBryan Monico EnolvaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Storage Guidelines SiDocument2 pagesChemical Storage Guidelines SiIndranil MitraNo ratings yet
- Proper Handling of ChemicalsDocument13 pagesProper Handling of ChemicalsmoriartyNo ratings yet
- Piranha Solution Safety Guidelines: 1. PropertiesDocument7 pagesPiranha Solution Safety Guidelines: 1. PropertiessureshNo ratings yet
- Methanol DatasheetDocument3 pagesMethanol DatasheetJeevanNo ratings yet
- Cedalite Resin Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesCedalite Resin Safety Data SheetAsadNo ratings yet
- Msds Sodium Hydroxide PDFDocument3 pagesMsds Sodium Hydroxide PDFGregoriusNo ratings yet
- Week 5: Safety Management: Name of Lecturer: Ms. Patricia Anne Mateo Notes By: LACDAO, F.M., & Trinidad, C.ADocument7 pagesWeek 5: Safety Management: Name of Lecturer: Ms. Patricia Anne Mateo Notes By: LACDAO, F.M., & Trinidad, C.ADarmayne GraganzaNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Proper Chemical StorageDocument5 pagesProcedure For Proper Chemical StorageDavish GurriahNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hydroxide Naoh CAS No.: 1310-73-2: CLIP, Chemical Laboratory Information ProfileDocument1 pageSodium Hydroxide Naoh CAS No.: 1310-73-2: CLIP, Chemical Laboratory Information ProfileCarolus GazaNo ratings yet
- 2504 MSDS Polymer Polyphosphate Sludge Conditioner Treatment Steam Raising PlantDocument4 pages2504 MSDS Polymer Polyphosphate Sludge Conditioner Treatment Steam Raising Planthendrik subagioNo ratings yet
- Amiduro de Potasio - Data Sheet SeguridadDocument3 pagesAmiduro de Potasio - Data Sheet SeguridadOsvaldo MolinaNo ratings yet
- MRC SafetyDocument40 pagesMRC SafetyIISER MOHALINo ratings yet
- Chaát Thaûi Nguy Haïi Hazardous Waste: Khaùi NieämDocument11 pagesChaát Thaûi Nguy Haïi Hazardous Waste: Khaùi Nieämchauktmt30No ratings yet
- Chemical Storage For Solid and Liquid Compounds in LaboratoryDocument5 pagesChemical Storage For Solid and Liquid Compounds in LaboratoryChilaNo ratings yet
- Color Coded Labeling System For Storing Chemicals in Your LaboratoryDocument5 pagesColor Coded Labeling System For Storing Chemicals in Your LaboratoryRobbi HidayatNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Engineering Technology General Chemistry (Chemb-T)Document6 pagesBachelor of Engineering Technology General Chemistry (Chemb-T)Paul CornejoNo ratings yet
- Sulphamic AcidDocument4 pagesSulphamic AcidAvinash RanaNo ratings yet
- ELGI Airlube XD - MSDSDocument6 pagesELGI Airlube XD - MSDSMuthalagu J (Aravindh)No ratings yet
- SDS ZaDocument5 pagesSDS ZaQuality AssuranceNo ratings yet
- (Tawas) Sodium Aluminate High Performance Coagulant PDFDocument3 pages(Tawas) Sodium Aluminate High Performance Coagulant PDFANNaNo ratings yet
- Product Safety Data Sheet: Ronald Britton LTDDocument8 pagesProduct Safety Data Sheet: Ronald Britton LTDemeka2012No ratings yet
- Sodium-Hypochlorite - MsdsDocument3 pagesSodium-Hypochlorite - MsdsmehrNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Chemical StorageDocument7 pagesGuidelines For Chemical StorageRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Campbells Quick N SDSDocument8 pagesCampbells Quick N SDSMoch Rokhmat Taufiq HidayatNo ratings yet
- 1 - Aluminium MetalDocument2 pages1 - Aluminium MetalChunkyLuverRudyNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Term OneDocument30 pagesGrade 11 Term OnenishantesabatoNo ratings yet
- Alvania r3Document7 pagesAlvania r3Senthil Kumar GanesanNo ratings yet
- Ferric Chloride Specific Gravity & Boiling & Freezing PointsDocument4 pagesFerric Chloride Specific Gravity & Boiling & Freezing PointsbandarNo ratings yet
- MSDS CaO FADocument4 pagesMSDS CaO FANur'aini Virani PutriNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Coal Tar 9942Document4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Coal Tar 9942Rahul S. ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet-Huwasan TR 50Document4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet-Huwasan TR 50Hitesh Kohli100% (1)
- Nickel Sulphate (TG)Document5 pagesNickel Sulphate (TG)awaneeraj78No ratings yet
- Part 1 Planet EarthDocument33 pagesPart 1 Planet EarthKingsley HoNo ratings yet
- High - RiskDocument50 pagesHigh - RiskjovanivanNo ratings yet
- SUN SDS Lead Acid 2019 enDocument10 pagesSUN SDS Lead Acid 2019 engraziellecoutinNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Planet EarthDocument36 pagesPart 1 Planet EarthnsjsNo ratings yet
- Bec 210Document27 pagesBec 210liviciuklNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hypochlorite 6 % MSDSDocument5 pagesSodium Hypochlorite 6 % MSDScataztropherNo ratings yet
- MSDS NaOHDocument2 pagesMSDS NaOHbittNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Sodium HydroxideDocument8 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Sodium HydroxideEarl HernaneNo ratings yet
- MSDS - OxygenDocument5 pagesMSDS - OxygenNishanthNJNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Effect Pigment Paste-SUNRUNSDocument4 pagesMSDS - Effect Pigment Paste-SUNRUNSOnline LearningNo ratings yet
- Potassium Permanganate MSDSDocument4 pagesPotassium Permanganate MSDSImaduddin Yusuf HanifNo ratings yet
- BR150011245Document8 pagesBR150011245helena moorNo ratings yet
- Dynamite SDSDocument4 pagesDynamite SDSMuh HabzNo ratings yet
- Iridium Complexes in Organic SynthesisFrom EverandIridium Complexes in Organic SynthesisLuis A. OroNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens (Part 2)From EverandInorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens (Part 2)A. P. HagenNo ratings yet
- Major Material Requirement: Ruwanpura Expressway Project - Phase 01Document2 pagesMajor Material Requirement: Ruwanpura Expressway Project - Phase 01Shamitha KanchanaNo ratings yet
- FMI51 - Spares PartsDocument6 pagesFMI51 - Spares PartsGustavo PuenteNo ratings yet
- Architectural Connections GuideDocument70 pagesArchitectural Connections GuideTSGSSNo ratings yet
- Aeroshell Fluid 61Document2 pagesAeroshell Fluid 61Jorge MartinsNo ratings yet
- NTN Bearing Part Number System (Nomenclature)Document7 pagesNTN Bearing Part Number System (Nomenclature)Eric AndrésNo ratings yet
- Stationary Price MonthlyDocument4 pagesStationary Price MonthlyAudy Nesya DyaNo ratings yet
- Science G7 SUMMATIVE 2021 EDITEDDocument2 pagesScience G7 SUMMATIVE 2021 EDITEDedwin dumopoyNo ratings yet
- Ullmann Sodium ChlorideDocument48 pagesUllmann Sodium ChlorideNoee CassaniNo ratings yet
- Zinc Oxide and Salicylic Acid PasteDocument1 pageZinc Oxide and Salicylic Acid PasteKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Differenze Tra Le Varie PVD TecniquesDocument3 pagesDifferenze Tra Le Varie PVD TecniquesdavNo ratings yet
- Corrosion On AircraftDocument59 pagesCorrosion On Aircraftprakash100% (2)
- Metals and The Reactivity SeriesDocument11 pagesMetals and The Reactivity SeriesNiya HinksonNo ratings yet
- Moulding MCS FactoryDocument21 pagesMoulding MCS Factorymeet dodhiwalaNo ratings yet
- List of Groundwater Contaminated Sites CPCBDocument4 pagesList of Groundwater Contaminated Sites CPCBParas Singh RajpurohitNo ratings yet
- Final 2013Document1 pageFinal 2013Anonymous BAzcBzWuNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation: Method StatmentDocument12 pagesPile Foundation: Method StatmentDeepak PatilNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Saurabh Shah Code: 1710Document58 pagesPrepared By: Saurabh Shah Code: 1710Openheart Janardan KumarNo ratings yet
- A Forensic Approach For Assessing ModesDocument11 pagesA Forensic Approach For Assessing ModesGadhoumiWalidNo ratings yet
- Nitotile LM : Constructive SolutionsDocument2 pagesNitotile LM : Constructive SolutionsmilanbrasinaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Admixtures HandbookDocument2 pagesConcrete Admixtures HandbookchatnoirNo ratings yet
- UWPR CommonMassSpecContaminantsDocument271 pagesUWPR CommonMassSpecContaminantsBenedito AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- Grinding Technical Questions of Producing Composite CementDocument10 pagesGrinding Technical Questions of Producing Composite CementAziz MalkiNo ratings yet
- Dietanolamina - TDS - DOWDocument2 pagesDietanolamina - TDS - DOWhenriquefxs2926No ratings yet
- Shell Stitch Baby BlanketDocument2 pagesShell Stitch Baby BlanketElizna Koekemoer ErweeNo ratings yet
- Washer Dryer Combination - FAS 3612 FAS 3612X Installation and User Manual PDFDocument72 pagesWasher Dryer Combination - FAS 3612 FAS 3612X Installation and User Manual PDFDavid RossNo ratings yet
Chemical Storage Guildline: Main Purpose of Competible Storage Group
Chemical Storage Guildline: Main Purpose of Competible Storage Group
Uploaded by
applecrushzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Storage Guildline: Main Purpose of Competible Storage Group
Chemical Storage Guildline: Main Purpose of Competible Storage Group
Uploaded by
applecrushzCopyright:
Available Formats
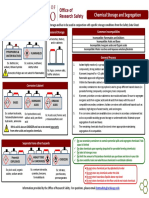
MAKMAL BERPUSAT
CHEMICAL STORAGE GUILDLINE
Main Purpose of Competible Storage Group
Protect exposure to
Protect flammables, Avoid accidental
poisons / cause
explosion & ignition mixing
adverse health effect
G I: Flammable Liquids
G II: Poisons volatile
G III: Acids Oxidizing
Nine Groups Storage
G IV: Acids Organic and
Mineral
System
G V: Bases Liquid
G VI: Oxidizer Liquid
G VII: Poisons Non-volatile
G VIII: Reactives Metal
Hydrides and Pyrophorics
G IX: Dry Solidss
1 Returned to location after each use
2 Do not placed on bench tops
Principles
3 Not in the fume hood
Of Safe
Chemical 4 Not arrange in alphabetical order
Storage
5 Away from sun and heat
6 Not store under the sink
7 Label chemicals properly
8 Carcinogens must be labeled
9 Storage of liquid chemicals is more hazardous than
storage of solids
MAKMAL BERPUSAT
How To Store Chemicals
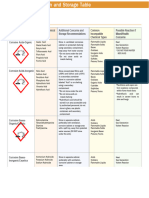
Group Definition Primary Recommended Example
Storage Facilities
Concern
G I: Flammable Liquids To protect from • 1. Flammable All alcohols, acetone, acetonitrile, benzene,
Includes liquids with flashpoints < ignition Cabinet (G I) ether, ethyl acetate, hexane, methyl
21 C 2. Refrigerator: butane, propanol, all silanes, toluene.
for containers
less than 1 liter.
G II: Volatile Poisons To prevent 1. Flammable cabinet (G Chloroform, dimethyl sulfate,
Includes poisons toxics and inhalation II -Toxic) formaldehyde, methylene chloride, phenol.
suspected carcinogens with strong exposures. 2. Refrigerator: for
odor or evaporation rate. containers less than 1
liter.
G III: Oxidizing Acids Preventing Chemical Safety Storage Nitric, sulfuric, perchloric, phosphoric acids,
All oxidizing acids are highly reaction with Cabinet (Each oxidizing and chromic acids.
reactive with most substances and each others and acid must be double
each other. corrosive action contained/secondary
on surfaces. box)
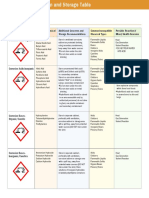
G IV: Organic and Mineral Acids. To prevent Chemical Safety Storage Acetic, butyric, formic, glacial acetic,
reaction with cabinet hydrochloric, isobutyric, trifluoroacetic
bases and acids.
oxidizing acids
and corrosive
action on
surfaces.
G V: Liquid Bases Preventing Chemical storage cabinet Sodium hydroxide, ammonium hydroxide,
contact and (bases) calcium hydroxide, glutaraldehyde.
reaction with
acids.
G VI: Oxidizer – Liquid To isolate from 1. Chemical storage Ammonium persulfate, hydrogen peroxide
Oxidizing liquids react with other materials. cabinet / Flammable (if greater than or equal to 30%)
everything causing cabinet (Oxi)
explosions/corrosion of surfaces. 2. Smaller quantities
must be in secondart
container if kept near
other chemicals
G VII: Poisons Non-Volatile To prevent 1. Toxic Steel Cabinet, Acrylamide solutions;
Includes highly toxic (LD50 oral rat contact and Chemical Storage diethylpyrocarbonate; diisopropyl
< 50 mg/kg) and toxic chemicals reaction with Cabinet (i.e., must be fluorophosphate; uncured epoxy resins;
(LD50 oral rat < 500 mg/kg), known other substances. enclosed) ethidium bromide; triethanolamine
carcinogens, suspected 2. Do not store on
carcinogens and mutagens open shelves in the lab
or cold room
G VIII: Reactives Metal Hydrides and To prevent 1. Water proof double Sodium borohydride, calcium hydride,
Pyrophorics contact and containment according lithium aluminum hydride
Most metal hydrides react reaction with to label instructions.
violently with water, some ignite liquids and, in 2. Isolation from other
spontaneously in air (pyrophoric). some cases, air. storage groups.
3. Under paraffin oil
(metal)
G IX: Dry Solids To prevent Open shelves are Benzidine, cyanogen bromide,
Includes all powders, hazardous contact and acceptable ethylmaleimide, oxalic acid, potassium
and non hazardous. potential reaction cyanide, sodium cyanide
with liquids.
You might also like
- Alkanes AnswersDocument42 pagesAlkanes AnswersSpider Gamer22No ratings yet
- Sanosil Biotech Pvt. LTD.: Material Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesSanosil Biotech Pvt. LTD.: Material Safety Data SheetJainil Panchal50% (2)
- ASTM - 1955 - Tentative Methods of Test For Phosphate in Industrial WaterDocument9 pagesASTM - 1955 - Tentative Methods of Test For Phosphate in Industrial WaterEvelynNo ratings yet
- Structural Plate Astm A36: Plates, Shapes, and Sheet PilingDocument4 pagesStructural Plate Astm A36: Plates, Shapes, and Sheet Pilingeko kusumoNo ratings yet
- Polishing The Basic Principles in EnglishDocument4 pagesPolishing The Basic Principles in EnglishMafteian LiviuNo ratings yet
- 1016 Greenhouse PlansDocument9 pages1016 Greenhouse Planslagumbeg100% (1)
- Chemical Storage Gui Deline: Main Purpose of Comp Atible Storage GroupDocument2 pagesChemical Storage Gui Deline: Main Purpose of Comp Atible Storage GroupapplecrushzNo ratings yet
- Chemical Segregation NIHDocument6 pagesChemical Segregation NIHSundaramoorthy SelvanathanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Introduction To Chemistry Form 4 KSSM (1) StudentDocument43 pagesCH 1 Introduction To Chemistry Form 4 KSSM (1) StudentJASON CHONG CHIA HANG Moe100% (1)
- Chemical Storage TableDocument4 pagesChemical Storage TableMin Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Epa Chemical Segregation ChartDocument2 pagesEpa Chemical Segregation ChartChilaNo ratings yet
- FBMH Table For Chemical StorageDocument4 pagesFBMH Table For Chemical StorageJoan RaquinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Segregation Table 230302 123808Document6 pagesChemical Segregation Table 230302 123808Zaira AsorNo ratings yet
- Almacenamiento y SegregaciónDocument1 pageAlmacenamiento y SegregaciónCecilia Lorena SzymczakNo ratings yet
- Chemical Storage Segregation SchemeDocument3 pagesChemical Storage Segregation Schemesuko winartiNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Safety Measures in Laboratory Science F4 KSSMDocument38 pagesCH 1 Safety Measures in Laboratory Science F4 KSSMfaezahNo ratings yet
- ChemicalsDocument12 pagesChemicalsBryan Monico EnolvaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Storage Guidelines SiDocument2 pagesChemical Storage Guidelines SiIndranil MitraNo ratings yet
- Proper Handling of ChemicalsDocument13 pagesProper Handling of ChemicalsmoriartyNo ratings yet
- Piranha Solution Safety Guidelines: 1. PropertiesDocument7 pagesPiranha Solution Safety Guidelines: 1. PropertiessureshNo ratings yet
- Methanol DatasheetDocument3 pagesMethanol DatasheetJeevanNo ratings yet
- Cedalite Resin Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesCedalite Resin Safety Data SheetAsadNo ratings yet
- Msds Sodium Hydroxide PDFDocument3 pagesMsds Sodium Hydroxide PDFGregoriusNo ratings yet
- Week 5: Safety Management: Name of Lecturer: Ms. Patricia Anne Mateo Notes By: LACDAO, F.M., & Trinidad, C.ADocument7 pagesWeek 5: Safety Management: Name of Lecturer: Ms. Patricia Anne Mateo Notes By: LACDAO, F.M., & Trinidad, C.ADarmayne GraganzaNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Proper Chemical StorageDocument5 pagesProcedure For Proper Chemical StorageDavish GurriahNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hydroxide Naoh CAS No.: 1310-73-2: CLIP, Chemical Laboratory Information ProfileDocument1 pageSodium Hydroxide Naoh CAS No.: 1310-73-2: CLIP, Chemical Laboratory Information ProfileCarolus GazaNo ratings yet
- 2504 MSDS Polymer Polyphosphate Sludge Conditioner Treatment Steam Raising PlantDocument4 pages2504 MSDS Polymer Polyphosphate Sludge Conditioner Treatment Steam Raising Planthendrik subagioNo ratings yet
- Amiduro de Potasio - Data Sheet SeguridadDocument3 pagesAmiduro de Potasio - Data Sheet SeguridadOsvaldo MolinaNo ratings yet
- MRC SafetyDocument40 pagesMRC SafetyIISER MOHALINo ratings yet
- Chaát Thaûi Nguy Haïi Hazardous Waste: Khaùi NieämDocument11 pagesChaát Thaûi Nguy Haïi Hazardous Waste: Khaùi Nieämchauktmt30No ratings yet
- Chemical Storage For Solid and Liquid Compounds in LaboratoryDocument5 pagesChemical Storage For Solid and Liquid Compounds in LaboratoryChilaNo ratings yet
- Color Coded Labeling System For Storing Chemicals in Your LaboratoryDocument5 pagesColor Coded Labeling System For Storing Chemicals in Your LaboratoryRobbi HidayatNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Engineering Technology General Chemistry (Chemb-T)Document6 pagesBachelor of Engineering Technology General Chemistry (Chemb-T)Paul CornejoNo ratings yet
- Sulphamic AcidDocument4 pagesSulphamic AcidAvinash RanaNo ratings yet
- ELGI Airlube XD - MSDSDocument6 pagesELGI Airlube XD - MSDSMuthalagu J (Aravindh)No ratings yet
- SDS ZaDocument5 pagesSDS ZaQuality AssuranceNo ratings yet
- (Tawas) Sodium Aluminate High Performance Coagulant PDFDocument3 pages(Tawas) Sodium Aluminate High Performance Coagulant PDFANNaNo ratings yet
- Product Safety Data Sheet: Ronald Britton LTDDocument8 pagesProduct Safety Data Sheet: Ronald Britton LTDemeka2012No ratings yet
- Sodium-Hypochlorite - MsdsDocument3 pagesSodium-Hypochlorite - MsdsmehrNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Chemical StorageDocument7 pagesGuidelines For Chemical StorageRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Campbells Quick N SDSDocument8 pagesCampbells Quick N SDSMoch Rokhmat Taufiq HidayatNo ratings yet
- 1 - Aluminium MetalDocument2 pages1 - Aluminium MetalChunkyLuverRudyNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Term OneDocument30 pagesGrade 11 Term OnenishantesabatoNo ratings yet
- Alvania r3Document7 pagesAlvania r3Senthil Kumar GanesanNo ratings yet
- Ferric Chloride Specific Gravity & Boiling & Freezing PointsDocument4 pagesFerric Chloride Specific Gravity & Boiling & Freezing PointsbandarNo ratings yet
- MSDS CaO FADocument4 pagesMSDS CaO FANur'aini Virani PutriNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Coal Tar 9942Document4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Coal Tar 9942Rahul S. ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet-Huwasan TR 50Document4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet-Huwasan TR 50Hitesh Kohli100% (1)
- Nickel Sulphate (TG)Document5 pagesNickel Sulphate (TG)awaneeraj78No ratings yet
- Part 1 Planet EarthDocument33 pagesPart 1 Planet EarthKingsley HoNo ratings yet
- High - RiskDocument50 pagesHigh - RiskjovanivanNo ratings yet
- SUN SDS Lead Acid 2019 enDocument10 pagesSUN SDS Lead Acid 2019 engraziellecoutinNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Planet EarthDocument36 pagesPart 1 Planet EarthnsjsNo ratings yet
- Bec 210Document27 pagesBec 210liviciuklNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hypochlorite 6 % MSDSDocument5 pagesSodium Hypochlorite 6 % MSDScataztropherNo ratings yet
- MSDS NaOHDocument2 pagesMSDS NaOHbittNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Sodium HydroxideDocument8 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Sodium HydroxideEarl HernaneNo ratings yet
- MSDS - OxygenDocument5 pagesMSDS - OxygenNishanthNJNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Effect Pigment Paste-SUNRUNSDocument4 pagesMSDS - Effect Pigment Paste-SUNRUNSOnline LearningNo ratings yet
- Potassium Permanganate MSDSDocument4 pagesPotassium Permanganate MSDSImaduddin Yusuf HanifNo ratings yet
- BR150011245Document8 pagesBR150011245helena moorNo ratings yet
- Dynamite SDSDocument4 pagesDynamite SDSMuh HabzNo ratings yet
- Iridium Complexes in Organic SynthesisFrom EverandIridium Complexes in Organic SynthesisLuis A. OroNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens (Part 2)From EverandInorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens (Part 2)A. P. HagenNo ratings yet
- Major Material Requirement: Ruwanpura Expressway Project - Phase 01Document2 pagesMajor Material Requirement: Ruwanpura Expressway Project - Phase 01Shamitha KanchanaNo ratings yet
- FMI51 - Spares PartsDocument6 pagesFMI51 - Spares PartsGustavo PuenteNo ratings yet
- Architectural Connections GuideDocument70 pagesArchitectural Connections GuideTSGSSNo ratings yet
- Aeroshell Fluid 61Document2 pagesAeroshell Fluid 61Jorge MartinsNo ratings yet
- NTN Bearing Part Number System (Nomenclature)Document7 pagesNTN Bearing Part Number System (Nomenclature)Eric AndrésNo ratings yet
- Stationary Price MonthlyDocument4 pagesStationary Price MonthlyAudy Nesya DyaNo ratings yet
- Science G7 SUMMATIVE 2021 EDITEDDocument2 pagesScience G7 SUMMATIVE 2021 EDITEDedwin dumopoyNo ratings yet
- Ullmann Sodium ChlorideDocument48 pagesUllmann Sodium ChlorideNoee CassaniNo ratings yet
- Zinc Oxide and Salicylic Acid PasteDocument1 pageZinc Oxide and Salicylic Acid PasteKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Differenze Tra Le Varie PVD TecniquesDocument3 pagesDifferenze Tra Le Varie PVD TecniquesdavNo ratings yet
- Corrosion On AircraftDocument59 pagesCorrosion On Aircraftprakash100% (2)
- Metals and The Reactivity SeriesDocument11 pagesMetals and The Reactivity SeriesNiya HinksonNo ratings yet
- Moulding MCS FactoryDocument21 pagesMoulding MCS Factorymeet dodhiwalaNo ratings yet
- List of Groundwater Contaminated Sites CPCBDocument4 pagesList of Groundwater Contaminated Sites CPCBParas Singh RajpurohitNo ratings yet
- Final 2013Document1 pageFinal 2013Anonymous BAzcBzWuNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation: Method StatmentDocument12 pagesPile Foundation: Method StatmentDeepak PatilNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Saurabh Shah Code: 1710Document58 pagesPrepared By: Saurabh Shah Code: 1710Openheart Janardan KumarNo ratings yet
- A Forensic Approach For Assessing ModesDocument11 pagesA Forensic Approach For Assessing ModesGadhoumiWalidNo ratings yet
- Nitotile LM : Constructive SolutionsDocument2 pagesNitotile LM : Constructive SolutionsmilanbrasinaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Admixtures HandbookDocument2 pagesConcrete Admixtures HandbookchatnoirNo ratings yet
- UWPR CommonMassSpecContaminantsDocument271 pagesUWPR CommonMassSpecContaminantsBenedito AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- Grinding Technical Questions of Producing Composite CementDocument10 pagesGrinding Technical Questions of Producing Composite CementAziz MalkiNo ratings yet
- Dietanolamina - TDS - DOWDocument2 pagesDietanolamina - TDS - DOWhenriquefxs2926No ratings yet
- Shell Stitch Baby BlanketDocument2 pagesShell Stitch Baby BlanketElizna Koekemoer ErweeNo ratings yet
- Washer Dryer Combination - FAS 3612 FAS 3612X Installation and User Manual PDFDocument72 pagesWasher Dryer Combination - FAS 3612 FAS 3612X Installation and User Manual PDFDavid RossNo ratings yet