Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 5.5 Glasgow Coma Scale
Table 5.5 Glasgow Coma Scale
Uploaded by
Ymon Tualla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views6 pagesThis document provides information on assessing neurological function including:
1) A neurologic assessment tool that outlines how to test motor function, reflexes, sensory function, and cerebellar function and what normal findings should be.
2) Tables listing the cranial nerves, their locations and functions to aid in cranial nerve examination.
3) The Glasgow Coma Scale which is used to assess level of consciousness.
Original Description:
Original Title
Table 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on assessing neurological function including:
1) A neurologic assessment tool that outlines how to test motor function, reflexes, sensory function, and cerebellar function and what normal findings should be.
2) Tables listing the cranial nerves, their locations and functions to aid in cranial nerve examination.
3) The Glasgow Coma Scale which is used to assess level of consciousness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views6 pagesTable 5.5 Glasgow Coma Scale
Table 5.5 Glasgow Coma Scale
Uploaded by
Ymon TuallaThis document provides information on assessing neurological function including:
1) A neurologic assessment tool that outlines how to test motor function, reflexes, sensory function, and cerebellar function and what normal findings should be.
2) Tables listing the cranial nerves, their locations and functions to aid in cranial nerve examination.
3) The Glasgow Coma Scale which is used to assess level of consciousness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Table 5.
5 Glasgow Coma Scale
• Appearance: Neat, clean; clothes appropriate to occasion, season, and sex
• Affect: Attentive, cooperative, pleasant
• Speech : Articulate, fluent, readily answers questions
• Memory: Responds appropriately to questions:
o Immediate: “Why are you here?”
o Recent: “What did you eat for breakfast?”
o Remote: “Where were you born?”
• Orientation :
o Person (self, others)
o Place
o Time
• General knowledge/intellectual level:
o Responds appropriately to general questions like “Who is the president of the Philippines?”
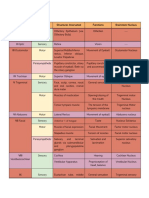
MNEMONICS MNEMONICS
CN 1 OLFACTORY OH SENSORY SOME
CN 2 OPTIC OH SENSORY SAYS
CN3 OCULOMOTOR OH MOTOR MARRY
CN4 TROCHLEAR TO MOTOR MONEY
CN5 TRIGEMINAL TOUCH BOTH BUT
CN6 ABDUCENS AND MOTOR MY
CN7 FACIAL FEEL BOTH BROTHER
CN8 ACOUSTIC A SENSORY SAYS
CN9 GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL GIRLS BOTH BIG
CN10 VAGUS VAGINA BOTH BOOBS
CN11 SPINAL ACCESORY SO MOTOR MATTER
CN12 HYPOGLOSSAL HEAVEN MOTOR MOST
Table 5.6 Cranial Nerves Assessment Tool
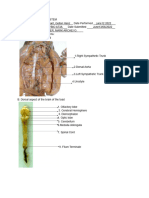
I Olfactory Cribiform Plate Special Sensory: Smell
II Optic Optic Canal Special Sensory: Sight Vision
III Oculomotor Superior Orbital Somatic Motor: Superior, Medial, Inferior Rectus,
Fissure Inferior Oblique ; Visceral Motor: Sphincter Pupillae
Pupil Constriction, elevation of upper lid
IV Trochlear Superior Orbital Somatic Motor: Superior Oblique Eye movement
Fissure
V Trigeminal Sup Orbital Somatic Sensory: Face
Fissure Somatic Motor: Mastication, Tensor Tympani, Tensor
V1: Palati Controls muscle of chewing
V2: Foramen
Rotundum
V3: Foramen
Ovale
VI Abducens Superior Orbital Somatic Motor: Lateral Rectus Eye movement,
Fissure
VII Facial Internal Auditory Somatic sensory: Posterior External Ear Canal
Canal Special Sensory: Taste (Anterior 2/3 of Tongue)
Somatic Motor: Muscles Of Facial Expression
Visceral Motor: Salivary Glands, Lacrimal Glands
Controls muscle for facial expression
VIII Acoustic Internal Auditory Special Sensory: Auditory/Balance Maintain equilibrium;
Canal hearing
IX Glossopharyngeal Jugular Foramen Somatic Sensory: Posterior 1/3 Tongue, Middle Ear
Visceral Sensory: Carotid Body/Sinus
Special Sensory: Taste
Somatic Motor: Stylopharyngeus Visceral Motor:
Parotid Controls muscle of throat
X Vagus Jugular Foramen Somatic Sensory: External Ear ; Visceral Sensory:
Aortic Arch/Body ; Special sensory: Taste Over
Epiglottis
Somatic Motor: Soft Palate, Pharynx, Larynx
(Vocalization and Swallowing)
Visceral Motor: Bronchoconstriction, Peristalsis,
Bradycardia, Vomitting Controls muscle of throat,
thoracic and abdominal organs
XI Spinal Jugular Foramen Somatic Motor: Trapezius, Sternocleidomastoid
Accessory Controls neckmuscles
XII Hypoglossal Hypoglossal Somatic Motor: Tongue Tongue movement
Canal
Table 5.7 Cranial Nerve Locations and Functions
Neurologic Assessment Assessment Tool Normal Findings Significant Findings
Motor Function Muscle strength. • Equal size on both sides NOTE: Tics, tremors,
assessment of the Flexion and extension. of body fasciculations
motor system Muscle tone • Usually firm may suggest neurologic
involves testing for • Equal strength on both involvement.
muscle size, tone, sides of
and strength the body
under voluntary • Smooth , coordinated
movements movements
Reflexes Scale Response Blink reflex NOTE: Diminished or
0 Absent Gag and swallow reflex absent reflexes may
+ Present but diminished Plantar response (Babinski suggest upper or lower
++ Normal reflex) motor neuron disease;
+++ Mildly increased but Deep tendon reflex however, this may also be
not pathologic Biceps found in normal people.
++++ Markedly hyperactive; Triceps (Reinforcement by
clonus may be Brachioradialis isometric contraction such
present Patellar – NORMAL: as asking patient to push
extension of his or her hands together
leg below the knee while knee reflex is checked
Achilles – Normal: plantar may increase reflex
flexion activity.)
of feet A positive Babinski’s reflex
Plantar (babinski) – may be seen in pyramidal
Normal: bending of toes tract disease or in the
downward unconscious patient
Sensory Function Asses for: (done after Normal sensations NOTE: Inappropriate
symmetric testing of the response
arms, legs, and trunk) indicates neurologic
Pain: “Sharp or dull?” disorder.
Temperature: “Hot or cold?”
Light touch: “Feel touch?”
Vibration: “Feel tuning fork
vibrating against joint?”
Position sense
(proprioception): “Am I
moving your toe up or
down?”
Cerebellar Function Perform Romberg’s test: Note the client’s ability to NOTE: Loss of balance is
o ask the client to maintain balance with eyes termed
stand open and closed for 20 “positive Romberg test”
erect, feet together and seconds with minimum (indicates sensory ataxia).
arms at side, first with swaying Uncoordinated gait may
eyes open, then closed. suggest cerebral palsy,
The nurse should stand parkinsonism, or drug side
close to the client to effect. Inappropriate
catch the client in the movements suggest
event of a fall cerebellar disease
Table 5.8 Neurologic Assessment Tool and Finding
Assessment Assessment Normal Significant
Tool Findings Findings
Head Inspection : Normocephalic Hydrocephalic
Size or contour Microcephalic
Asymmetric
Scalp Inspection Smooth, nontender NOTE: Scaling,
masses, tenderness
Head circumference Measuring Tape : Between 5th and Exceeds chest
(measured at largest 95th percentile on circumferenceby 1–2
point above eyebrow standardized growth cm until 18 mo.
and behind occiput) chart.
Anterior fontanel 3–4 cm in length and2– NOTE: Unusually
3 cm in width until large fontanel may
9–12 mo of age. indicate hydrocephaly
Soft, flat; bulges while (faulty circulation or
crying. Closes between absorption of
9 and 18 mo. CSF).
Unusually small
fontanel may indicate
craniosynostosis
(premature closure of
sutures).
Posterior fontanel 0.5–1 cm across. May Delayed closure may
be closed at birth or indicate hydrocephaly.
by 3 months of age.
Table 5.9 Head Assessment
Assessment Assessment Normal Significant
Tool Findings Findings
Face Inspection Symmetric, Asymmetric, weak; involuntary
with relaxed movements; tense or
facial expressions expressionless facies
Sinuses Frontal and Tenderness
maxillary
sinuses nontender
Cranial nerve: Able to smile, puff Unable to purposely and
(CN)VII:facial, cheeks, symmetrically
motor frown, raise use facial muscles
eyebrows,
with symmetry noted
CN V: trigeminal: Bilateral contractions Weak or asymmetric contraction of
Motor of temporal and muscles
masseter
muscles when teeth
are
clenched
CN V: trigeminal: Able to distinguish Unable to distinguish
sensory touch on type and location of
both sides of touch
face
Table 5.10 Face Assessment
You might also like
- Mental Health Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesMental Health Practice QuestionskathypinzonNo ratings yet
- NCM 101A H.A Theory Module 7Document21 pagesNCM 101A H.A Theory Module 7Munira HatibbonNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment: NeuroDocument34 pagesHealth Assessment: Neuroiamjennykim76No ratings yet
- Physiology of Autonomous Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesPhysiology of Autonomous Nervous SystemBelay MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Neurological Exam: H.Khorrami PH.DDocument89 pagesNeurological Exam: H.Khorrami PH.DHossein KhorramiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesChapter - 3 Autonomic Nervous SystemjarssooNo ratings yet
- 1 Olfactory Sensory 2 Optic Sensory: Cranial Nerve Name Function Specific Function Test Exit OpeningDocument2 pages1 Olfactory Sensory 2 Optic Sensory: Cranial Nerve Name Function Specific Function Test Exit OpeningDelilah BlackNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Disorders:: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument9 pagesNeurologic Disorders:: Anatomy & PhysiologyMaria Erlene SantosNo ratings yet
- Horner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationDocument3 pagesHorner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationVictorija Evania Lucille DeldioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in HADocument3 pagesReviewer in HAjulia.caballero0107No ratings yet
- NS Physiology For PC-IIDocument168 pagesNS Physiology For PC-IItemesgen belayNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Altered PerceptionDocument129 pages7.1 Altered PerceptionAlexander Blanche PajelaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesPeripheral Nervous SystemPaula Maryvette Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular: Cranial NervesDocument30 pagesNeuromuscular: Cranial NerveswanderlastNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial NervesakexisNo ratings yet
- Baca PDFDocument167 pagesBaca PDFHani Nur Hayani100% (1)
- Nurologic Ass Faculty - 2023 1st Term-1Document29 pagesNurologic Ass Faculty - 2023 1st Term-1cwley64No ratings yet
- Neurological Exam: H.Khorrami PH.DDocument74 pagesNeurological Exam: H.Khorrami PH.Dkhorrami4100% (1)
- Cranial Nerve TableDocument1 pageCranial Nerve TableAnna DangNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System - Lec 1Document6 pagesNeurologic System - Lec 1Farmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: I O Olfactory II O OpticDocument2 pagesCranial Nerves: I O Olfactory II O OpticDraw BackNo ratings yet
- PNCDocument2 pagesPNClovelove DayoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology With PhatophysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With PhatophysiologyJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- SISTEM SARAF MOTORIK - PD - SMT - 5 - ArdaniDocument24 pagesSISTEM SARAF MOTORIK - PD - SMT - 5 - ArdaniAlexander FernandoNo ratings yet
- The Cranial Nerves: Nerve Number and Name Composition Some FunctionsDocument3 pagesThe Cranial Nerves: Nerve Number and Name Composition Some FunctionsRoy Mitz BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument2 pagesNervous System - Anatomy & PhysiologykathzheinNo ratings yet
- 1cranial NervesDocument62 pages1cranial Nervesmyka brilliant cristobalNo ratings yet
- Harle-Sas 22 - Ponce, Kristel Mae O.Document11 pagesHarle-Sas 22 - Ponce, Kristel Mae O.Ponce Kristel Mae ONo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Originates From Edinger Westphal NucleusDocument5 pagesParasympathetic Originates From Edinger Westphal NucleusChristine NathaliaNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial NervesDomalaon, Princess Sophia B.No ratings yet
- STUDENT IndividualWorksheet Week4CNBSDocument30 pagesSTUDENT IndividualWorksheet Week4CNBSZoe FormosoNo ratings yet
- Act 14 (Gollon, Hanz. Chua Valiant) NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument3 pagesAct 14 (Gollon, Hanz. Chua Valiant) NERVOUS SYSTEMs9036282No ratings yet
- 6 Parts: o Mental Status o Cranial Nerves o Sensory Function o Motor Function o Cerebellar Function o Reflexes 1. Cranial NervesDocument3 pages6 Parts: o Mental Status o Cranial Nerves o Sensory Function o Motor Function o Cerebellar Function o Reflexes 1. Cranial NervesTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Intensive ReviewerDocument10 pagesNeurologic Intensive ReviewerAllysa PrestonNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing ReviewerDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing ReviewerDavid Brillo0% (1)
- Guess What?: Vision Technicians Bausch & Lomb School of Optometry Kismatpur CampusDocument43 pagesGuess What?: Vision Technicians Bausch & Lomb School of Optometry Kismatpur Campusyaad_aks4851No ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument9 pagesAnaphy ReviewerPrince Chester CamaliganNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument38 pagesNervous Systemrand200507No ratings yet
- CNS AhnDocument190 pagesCNS Ahni am sigmaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic SystemDocument6 pagesNeurologic SystemNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- 1 - Head and Neck Anatomy Review LiteDocument34 pages1 - Head and Neck Anatomy Review LiteDiana MitreaNo ratings yet
- Lesson11 Neurological AssessmentDocument4 pagesLesson11 Neurological AssessmentDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves NeuroanatomyDocument57 pagesCranial Nerves NeuroanatomyArvin TanNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Testing in PedsDocument2 pagesCranial Nerve Testing in PedsNicole GreeneNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument3 pagesHealth Assessmentathenaethereal9201No ratings yet
- Sanket ProjectDocument45 pagesSanket ProjectSanket JainNo ratings yet
- General Psychology 4: THE Physiological Basis OF Behavior: Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MANDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology 4: THE Physiological Basis OF Behavior: Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MANMariel EfrenNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Lab ReportDocument7 pagesNervous System Lab Reportapi-331455890No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemAmr KhalilNo ratings yet
- Assessing Neurologic System - FinalDocument66 pagesAssessing Neurologic System - FinalAngelo EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument17 pagesCranial Nervesdankirsh100% (17)
- Cns AnesthesiaDocument12 pagesCns AnesthesiaVIGNESH AJNo ratings yet
- Why, . Sign and Symptom!!!: Anwar Wardy, MD - Neu Department of Neurology FKK UmjDocument29 pagesWhy, . Sign and Symptom!!!: Anwar Wardy, MD - Neu Department of Neurology FKK UmjNurul Wandasari SNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 1Document10 pagesStudy Unit 1Kayleigh MastersNo ratings yet
- Responses To Altered PerceptionDocument74 pagesResponses To Altered PerceptionANDREA JUSTINE CARDEÑONo ratings yet
- NER4 and 5 NotesDocument11 pagesNER4 and 5 NotesjasminNo ratings yet
- NeuroPHY FINALS - ANS + SensationDocument3 pagesNeuroPHY FINALS - ANS + SensationlycolinniNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves TransDocument4 pagesCranial Nerves Transchynne ongNo ratings yet
- A monograph on sleep and dream: their physiology and psychologyFrom EverandA monograph on sleep and dream: their physiology and psychologyNo ratings yet
- Practise Book Oet Listening Set1 Audio LinksDocument1 pagePractise Book Oet Listening Set1 Audio LinksYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Plan 1.pdf - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Document1 page1.1 Plan 1.pdf - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Ymon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Leadership and ManagementDocument5 pagesLeadership and ManagementYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Plan 3.pdf - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Document1 page1.2 Plan 3.pdf - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Ymon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Cle Notes 2ND PeriodicalDocument3 pagesCle Notes 2ND PeriodicalYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- PinterestDocument3 pagesPinterestYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- ELearning Manual Handling Tutorial V 9 - June 2015 - ACN Approved Feb 2016Document29 pagesELearning Manual Handling Tutorial V 9 - June 2015 - ACN Approved Feb 2016Ymon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research: I. DefinitionsDocument7 pagesNursing Research: I. DefinitionsYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- 8Document8 pages8Ymon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Lecture 59 Pages Pg. 274 332Document59 pagesPediatric Nursing Lecture 59 Pages Pg. 274 332Ymon TuallaNo ratings yet
- 3Document5 pages3Ymon TuallaNo ratings yet
- A. Probability Sampling MethodsDocument6 pagesA. Probability Sampling MethodsYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- B. Scheduling Schedule: Be Determined With A Simple Worker-Patient Ratio or FormulaDocument7 pagesB. Scheduling Schedule: Be Determined With A Simple Worker-Patient Ratio or FormulaYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Visual Acuity: Eye AssessmentDocument3 pagesVisual Acuity: Eye AssessmentYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Agusan Del Sur Food and veggies-SADocument2 pagesAgusan Del Sur Food and veggies-SAYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Handout in MAPEH Grade 1 ABCDEDocument2 pagesHandout in MAPEH Grade 1 ABCDEYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- ManageDocument6 pagesManageYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Determinants:: Blood PressureDocument3 pagesDeterminants:: Blood PressureYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- PULSEDocument3 pagesPULSEYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh3 PDFDocument2 pagesMapeh3 PDFYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Form - Membership Registration For Regular MemberDocument1 pageForm - Membership Registration For Regular MemberYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- I. Health, Wellness and Illness: Self-Esteem Love and Belongingness Self-ActualizationDocument3 pagesI. Health, Wellness and Illness: Self-Esteem Love and Belongingness Self-ActualizationYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Form - Membership Registration For Associate MemberDocument1 pageForm - Membership Registration For Associate MemberYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs: PurposeDocument3 pagesVital Signs: PurposeYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Assessment TechniquesDocument3 pagesAssessment TechniquesYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Computer Answer KeyDocument2 pagesComputer Answer KeyYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Fourth Mastery Test: Handout in COMPUTER Grade 1 ABCDEDocument2 pagesFourth Mastery Test: Handout in COMPUTER Grade 1 ABCDEYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word: Handout in COMPUTER 4 Quarterly Examination Grade 1 ABCDEDocument3 pagesMicrosoft Word: Handout in COMPUTER 4 Quarterly Examination Grade 1 ABCDEYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Practice TypingDocument1 pagePractice TypingYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Urine TherapyDocument5 pagesUrine TherapyMichal SladekNo ratings yet
- Adult Health Nursing-I.unit PlanDocument19 pagesAdult Health Nursing-I.unit PlanAnindita mitraNo ratings yet
- Sepsis PowerPointDocument49 pagesSepsis PowerPointWonyenghitari GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Skin Rashes: An Emerging Symptom of COVID-19: What Clinicians Need To Know About Cutaneous Manifestations of COVID-19Document3 pagesSkin Rashes: An Emerging Symptom of COVID-19: What Clinicians Need To Know About Cutaneous Manifestations of COVID-19littlemisseeeNo ratings yet
- Pjo 29 64 PDFDocument2 pagesPjo 29 64 PDFibanggNo ratings yet
- CreatePDF 3Document66 pagesCreatePDF 3Re GLNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Student Version The Nervous System 2020 (1138)Document21 pagesChapter 7 Student Version The Nervous System 2020 (1138)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Samphire2003 PDFDocument9 pagesSamphire2003 PDFYacine Tarik AizelNo ratings yet
- Pancuronium: "Pavulon - Bromurex"Document33 pagesPancuronium: "Pavulon - Bromurex"Bahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive Disorder: Continuing Education ActivityDocument9 pagesMajor Depressive Disorder: Continuing Education Activityaluri venkatarajaNo ratings yet
- Treating and Monitoring Hypomagnesaemia For Non-Critical Areas of TrustDocument3 pagesTreating and Monitoring Hypomagnesaemia For Non-Critical Areas of Trustramy.elantaryNo ratings yet
- 2006 Lange OutlineDocument570 pages2006 Lange Outlinemequanint kefieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Paintings: by Cathy ChangDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Paintings: by Cathy ChangSameer MehtaNo ratings yet
- Drugs AffectingDocument5 pagesDrugs Affectingjoeneil pascua100% (1)
- ICD 10 Rujukan Non SpesialistikDocument19 pagesICD 10 Rujukan Non SpesialistikKISNINGSIHNo ratings yet
- GI QuestionsDocument3 pagesGI QuestionsYusif ElmiNo ratings yet
- .Lagundi (Vitex Negundo) : Uses & PreparationDocument4 pages.Lagundi (Vitex Negundo) : Uses & PreparationClarette GutierrezNo ratings yet
- DR Bravo: When To Suspect Ehlers-Danlos SyndromeDocument6 pagesDR Bravo: When To Suspect Ehlers-Danlos Syndromesnowgrouse100% (1)
- Management of Meniere's Disease - An Analytical Ayurveda PerspectiveDocument3 pagesManagement of Meniere's Disease - An Analytical Ayurveda PerspectiveAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Lymphadenopathy in ChildrenDocument5 pagesLymphadenopathy in ChildrenMaria PaulaNo ratings yet
- MCQ PaperDocument23 pagesMCQ PaperJapleen SinghNo ratings yet
- Pulse PDFDocument11 pagesPulse PDFB. Vineeth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Paper C 2019 With Key andDocument28 pagesPaper C 2019 With Key andaizaz100% (1)
- Last Exams Questions Papers 2018 Dr. Gopika PDFDocument111 pagesLast Exams Questions Papers 2018 Dr. Gopika PDFrhea100% (1)
- Practice TestDocument6 pagesPractice TestJulie May SuganobNo ratings yet
- Krajcovicova octoberSEPDocument35 pagesKrajcovicova octoberSEPParvesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology Notes: Ankit Gupta Home 1/1/2008Document33 pagesOral Pathology Notes: Ankit Gupta Home 1/1/2008Jitendra PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Manual Hematology GamalDocument189 pagesManual Hematology GamalJeri BerongoyNo ratings yet
- DR - Dilip MMS GIT NotesDocument263 pagesDR - Dilip MMS GIT NotesKoushik Sharma AmancharlaNo ratings yet