Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsObjective: - Understand Fourier Series - Understand DFT and FFT
Objective: - Understand Fourier Series - Understand DFT and FFT
Uploaded by
Jenan NabeelThis document introduces the objective of understanding Fourier series and the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and fast Fourier transform (FFT). It provides an overview of what a Fourier transform is and how it can decompose functions into constituent frequencies. The report section then describes using FFT to analyze a signal with 20Hz and 40Hz components buried in noise, including computing the DFT and power spectrum, plotting frequency and power, producing a 0-centered periodogram, and plotting the phase. The conclusion reflects on applying the Fourier transform concepts learned in theory to analyzing signals in this lab.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- An Introduction to Random Vibrations, Spectral & Wavelet Analysis: Third EditionFrom EverandAn Introduction to Random Vibrations, Spectral & Wavelet Analysis: Third EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- By:-Mr. B.M.Daxini: Unit - Iv Time Frequency Signal Analysis MethodsDocument12 pagesBy:-Mr. B.M.Daxini: Unit - Iv Time Frequency Signal Analysis MethodsBhautik DaxiniNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform ApplicationsDocument17 pagesFourier Transform ApplicationsAbhineet Gupta100% (2)
- Fourier Analysis: Synthesis. For Example, Determining WhatDocument11 pagesFourier Analysis: Synthesis. For Example, Determining WhatEmmanuel TuffetNo ratings yet
- Task-01: Discrete Time Fourier TransformDocument5 pagesTask-01: Discrete Time Fourier TransformAsit44 gleNo ratings yet
- Fourier AnalysisDocument10 pagesFourier Analysiswatson191No ratings yet
- FFT in MatlabDocument5 pagesFFT in MatlabNguyen Quoc DoanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document8 pagesChapter 7Aldon JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lab13Document10 pagesLab13contactdiyan2003No ratings yet
- Lab13Document10 pagesLab13contactdiyan2003No ratings yet
- 3F3 3 Fast Fourier TransformDocument50 pages3F3 3 Fast Fourier TransformChalani PremadasaNo ratings yet
- EE-451 Lab #2 AM and FM Systems Using MATLAB: GeneralDocument4 pagesEE-451 Lab #2 AM and FM Systems Using MATLAB: GeneralGetachew EndrisNo ratings yet
- Sistel - 02 - FourierDocument31 pagesSistel - 02 - FourierRivaldi MhsNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform - WikipediaDocument91 pagesFourier Transform - WikipediaAyad M Al-AwsiNo ratings yet
- 2.continuous Wavelet TechniquesDocument14 pages2.continuous Wavelet TechniquesremaravindraNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform WikiDocument24 pagesFourier Transform Wikibraulio.dantasNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Fourier TransformDocument6 pagesLab 3 - Fourier TransformEd ItrNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform ApplicationsDocument29 pagesFourier Transform ApplicationsAnonymous DBq6p69tANo ratings yet
- BAB 2. FourierDocument31 pagesBAB 2. FourierExioraNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform ApplicationsDocument18 pagesFourier Transform ApplicationsHarmanpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Sampling Theory With Applications Using MATLAB: Anna Maeser April 21, 2008Document16 pagesSampling Theory With Applications Using MATLAB: Anna Maeser April 21, 2008hord72No ratings yet
- Fourier AnalysisDocument9 pagesFourier Analysislolo406No ratings yet
- Signal ProcessingDocument16 pagesSignal ProcessingSatish SirikondaNo ratings yet
- Bioimaging Lab 1 v3Document2 pagesBioimaging Lab 1 v3Henry VelascoNo ratings yet
- A Modified Split-Radix FFT With Fewer Arithmetic OperationsDocument15 pagesA Modified Split-Radix FFT With Fewer Arithmetic Operationssivadanams@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- The Phase Vocoder - Part I: Fig. 1 - Diagram of The Short Term Fourier Transform (STFT)Document8 pagesThe Phase Vocoder - Part I: Fig. 1 - Diagram of The Short Term Fourier Transform (STFT)thenlundbergNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier Transform ReportDocument19 pagesFast Fourier Transform ReportKarabo LetsholoNo ratings yet
- Integral Transforms and Delta FunctionDocument79 pagesIntegral Transforms and Delta FunctionsrrisbudNo ratings yet
- Exp#02 Analysing Biomedical Signal Using DFT and Reconstruct The Signal Using IDFTDocument6 pagesExp#02 Analysing Biomedical Signal Using DFT and Reconstruct The Signal Using IDFTMuhammad Muinul IslamNo ratings yet
- Lecture Basics of FTDocument35 pagesLecture Basics of FTmnaNo ratings yet
- DIP Module 3Document61 pagesDIP Module 3sasindhur rNo ratings yet
- Image Enhancement in The Frequency DomainDocument34 pagesImage Enhancement in The Frequency DomainRaaz Key Run ChhatkuliNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Fourier TransformDocument49 pagesDigital Signal Processing: Fourier TransformdeboernNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform and Spectra: G G G GDocument21 pagesFourier Transform and Spectra: G G G GSedat IsterNo ratings yet
- Fourier NotesDocument4 pagesFourier Notesmrlog1No ratings yet
- Discrete Fourier Transform and Signal Spectrum: Advance Digital Signal ProcessingDocument40 pagesDiscrete Fourier Transform and Signal Spectrum: Advance Digital Signal ProcessingSaad AlwashNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) : The FFT in One Dimension The FFT in Multiple DimensionsDocument10 pagesFast Fourier Transform (FFT) : The FFT in One Dimension The FFT in Multiple Dimensionsİsmet BurgaçNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Lecture 22: Sampling and Reconstruction of Band-Limited SignalsDocument5 pagesModule 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Lecture 22: Sampling and Reconstruction of Band-Limited SignalsPrasad KavthakarNo ratings yet
- Signal ProcessingDocument40 pagesSignal ProcessingSamson MumbaNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems: DT e T X F XDocument6 pagesSignals and Systems: DT e T X F XBasim BrohiNo ratings yet
- Short Term Spectral Analysis, Modification Discrete Fourier Transform Synthesis, andDocument4 pagesShort Term Spectral Analysis, Modification Discrete Fourier Transform Synthesis, andDeepak Kumar Singh Res. Scholar., Dept. of Mechanical Engg., IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- Fast Fourier TransformDocument8 pagesFast Fourier TransformnakarshaNo ratings yet
- 111 Signal ProcessingDocument17 pages111 Signal ProcessingDotto KnowsNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transformation of An IR InterferogramDocument12 pagesFourier Transformation of An IR InterferogramIvt RomeroNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform of Coulomb PotentialDocument4 pagesFourier Transform of Coulomb Potentialtutorciecle123No ratings yet
- Lab1 Fourier Analysis of SignalsDocument3 pagesLab1 Fourier Analysis of SignalsAbdelrhman Ahmed AbdelkhaliqNo ratings yet
- GVICDocument157 pagesGVICTemitope OniNo ratings yet
- Lab3 BME321 BSPDocument3 pagesLab3 BME321 BSPAsim BashirNo ratings yet
- Proyecto 04Document6 pagesProyecto 04Scott Backster Clarck0% (1)
- 1016 Hanshaw Road Ithaca, Ny 14850 August 3, 2017Document13 pages1016 Hanshaw Road Ithaca, Ny 14850 August 3, 2017David MartinsNo ratings yet
- Frequency SpaceDocument71 pagesFrequency SpaceHafid ScooteristNo ratings yet
- L15-23 NotesDocument2 pagesL15-23 NotesitasneemNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of The Discrete Fourier Transform: XF Xte DTDocument8 pagesFundamentals of The Discrete Fourier Transform: XF Xte DTho-faNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document11 pagesExperiment 2manikNo ratings yet
- Frequency Domain ProcessingDocument42 pagesFrequency Domain ProcessingInJune YeoNo ratings yet
- Amath 482 Coding Project 2 Report JonathanaaltoDocument13 pagesAmath 482 Coding Project 2 Report Jonathanaaltoapi-615220844No ratings yet
- What Is The Fast Fourier TransformDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Fast Fourier TransformGabriel AguirreNo ratings yet
- Resonance Enhancement in Laser-Produced Plasmas: Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandResonance Enhancement in Laser-Produced Plasmas: Concepts and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
Objective: - Understand Fourier Series - Understand DFT and FFT
Objective: - Understand Fourier Series - Understand DFT and FFT
Uploaded by
Jenan Nabeel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesThis document introduces the objective of understanding Fourier series and the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and fast Fourier transform (FFT). It provides an overview of what a Fourier transform is and how it can decompose functions into constituent frequencies. The report section then describes using FFT to analyze a signal with 20Hz and 40Hz components buried in noise, including computing the DFT and power spectrum, plotting frequency and power, producing a 0-centered periodogram, and plotting the phase. The conclusion reflects on applying the Fourier transform concepts learned in theory to analyzing signals in this lab.
Original Description:
A simple project in Matlab about Fourier Transform
Original Title
Matlab Project
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document introduces the objective of understanding Fourier series and the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and fast Fourier transform (FFT). It provides an overview of what a Fourier transform is and how it can decompose functions into constituent frequencies. The report section then describes using FFT to analyze a signal with 20Hz and 40Hz components buried in noise, including computing the DFT and power spectrum, plotting frequency and power, producing a 0-centered periodogram, and plotting the phase. The conclusion reflects on applying the Fourier transform concepts learned in theory to analyzing signals in this lab.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesObjective: - Understand Fourier Series - Understand DFT and FFT
Objective: - Understand Fourier Series - Understand DFT and FFT
Uploaded by
Jenan NabeelThis document introduces the objective of understanding Fourier series and the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and fast Fourier transform (FFT). It provides an overview of what a Fourier transform is and how it can decompose functions into constituent frequencies. The report section then describes using FFT to analyze a signal with 20Hz and 40Hz components buried in noise, including computing the DFT and power spectrum, plotting frequency and power, producing a 0-centered periodogram, and plotting the phase. The conclusion reflects on applying the Fourier transform concepts learned in theory to analyzing signals in this lab.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
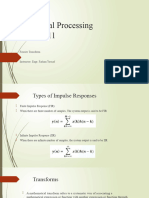
Objective:
- Understand Fourier series
- Understand DFT and FFT
Introduction:
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions depending
on space or time into functions depending on spatial frequency or temporal frequency. That
process is also called analysis. An example application would be decomposing the waveform of
a musical chord into terms of the intensity of its constituent pitches. The term Fourier
transform refers to both the frequency domain representation and the mathematical operation that
associates the frequency domain representation to a function of space or time.
Report:
1- Consider the following data x with two component frequencies of differing amplitude and
phase buried in noise with the following parameters:
a- Sampling frequency = 200hz
b- 20 second samples
c- 20 and 40 hz components
d- Gaussian noise
2- Use FFT to compute DFT y and its power
3- Plot the frequency and power
4- Rearrange the output from fft to produce 0-centered periodogram
5- Create and plot the phase
Conclusion:
This was a short and interesting lab about what we studied earlier in theory, we studied about
Fourier transform and series, in the lab we tested some graphs with different values, looking
forward to more interesting labs.
You might also like
- An Introduction to Random Vibrations, Spectral & Wavelet Analysis: Third EditionFrom EverandAn Introduction to Random Vibrations, Spectral & Wavelet Analysis: Third EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- By:-Mr. B.M.Daxini: Unit - Iv Time Frequency Signal Analysis MethodsDocument12 pagesBy:-Mr. B.M.Daxini: Unit - Iv Time Frequency Signal Analysis MethodsBhautik DaxiniNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform ApplicationsDocument17 pagesFourier Transform ApplicationsAbhineet Gupta100% (2)
- Fourier Analysis: Synthesis. For Example, Determining WhatDocument11 pagesFourier Analysis: Synthesis. For Example, Determining WhatEmmanuel TuffetNo ratings yet
- Task-01: Discrete Time Fourier TransformDocument5 pagesTask-01: Discrete Time Fourier TransformAsit44 gleNo ratings yet
- Fourier AnalysisDocument10 pagesFourier Analysiswatson191No ratings yet
- FFT in MatlabDocument5 pagesFFT in MatlabNguyen Quoc DoanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document8 pagesChapter 7Aldon JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lab13Document10 pagesLab13contactdiyan2003No ratings yet
- Lab13Document10 pagesLab13contactdiyan2003No ratings yet
- 3F3 3 Fast Fourier TransformDocument50 pages3F3 3 Fast Fourier TransformChalani PremadasaNo ratings yet
- EE-451 Lab #2 AM and FM Systems Using MATLAB: GeneralDocument4 pagesEE-451 Lab #2 AM and FM Systems Using MATLAB: GeneralGetachew EndrisNo ratings yet
- Sistel - 02 - FourierDocument31 pagesSistel - 02 - FourierRivaldi MhsNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform - WikipediaDocument91 pagesFourier Transform - WikipediaAyad M Al-AwsiNo ratings yet
- 2.continuous Wavelet TechniquesDocument14 pages2.continuous Wavelet TechniquesremaravindraNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform WikiDocument24 pagesFourier Transform Wikibraulio.dantasNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Fourier TransformDocument6 pagesLab 3 - Fourier TransformEd ItrNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform ApplicationsDocument29 pagesFourier Transform ApplicationsAnonymous DBq6p69tANo ratings yet
- BAB 2. FourierDocument31 pagesBAB 2. FourierExioraNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform ApplicationsDocument18 pagesFourier Transform ApplicationsHarmanpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Sampling Theory With Applications Using MATLAB: Anna Maeser April 21, 2008Document16 pagesSampling Theory With Applications Using MATLAB: Anna Maeser April 21, 2008hord72No ratings yet
- Fourier AnalysisDocument9 pagesFourier Analysislolo406No ratings yet
- Signal ProcessingDocument16 pagesSignal ProcessingSatish SirikondaNo ratings yet
- Bioimaging Lab 1 v3Document2 pagesBioimaging Lab 1 v3Henry VelascoNo ratings yet
- A Modified Split-Radix FFT With Fewer Arithmetic OperationsDocument15 pagesA Modified Split-Radix FFT With Fewer Arithmetic Operationssivadanams@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- The Phase Vocoder - Part I: Fig. 1 - Diagram of The Short Term Fourier Transform (STFT)Document8 pagesThe Phase Vocoder - Part I: Fig. 1 - Diagram of The Short Term Fourier Transform (STFT)thenlundbergNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier Transform ReportDocument19 pagesFast Fourier Transform ReportKarabo LetsholoNo ratings yet
- Integral Transforms and Delta FunctionDocument79 pagesIntegral Transforms and Delta FunctionsrrisbudNo ratings yet
- Exp#02 Analysing Biomedical Signal Using DFT and Reconstruct The Signal Using IDFTDocument6 pagesExp#02 Analysing Biomedical Signal Using DFT and Reconstruct The Signal Using IDFTMuhammad Muinul IslamNo ratings yet
- Lecture Basics of FTDocument35 pagesLecture Basics of FTmnaNo ratings yet
- DIP Module 3Document61 pagesDIP Module 3sasindhur rNo ratings yet
- Image Enhancement in The Frequency DomainDocument34 pagesImage Enhancement in The Frequency DomainRaaz Key Run ChhatkuliNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Fourier TransformDocument49 pagesDigital Signal Processing: Fourier TransformdeboernNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform and Spectra: G G G GDocument21 pagesFourier Transform and Spectra: G G G GSedat IsterNo ratings yet
- Fourier NotesDocument4 pagesFourier Notesmrlog1No ratings yet
- Discrete Fourier Transform and Signal Spectrum: Advance Digital Signal ProcessingDocument40 pagesDiscrete Fourier Transform and Signal Spectrum: Advance Digital Signal ProcessingSaad AlwashNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) : The FFT in One Dimension The FFT in Multiple DimensionsDocument10 pagesFast Fourier Transform (FFT) : The FFT in One Dimension The FFT in Multiple Dimensionsİsmet BurgaçNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Lecture 22: Sampling and Reconstruction of Band-Limited SignalsDocument5 pagesModule 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Lecture 22: Sampling and Reconstruction of Band-Limited SignalsPrasad KavthakarNo ratings yet
- Signal ProcessingDocument40 pagesSignal ProcessingSamson MumbaNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems: DT e T X F XDocument6 pagesSignals and Systems: DT e T X F XBasim BrohiNo ratings yet
- Short Term Spectral Analysis, Modification Discrete Fourier Transform Synthesis, andDocument4 pagesShort Term Spectral Analysis, Modification Discrete Fourier Transform Synthesis, andDeepak Kumar Singh Res. Scholar., Dept. of Mechanical Engg., IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- Fast Fourier TransformDocument8 pagesFast Fourier TransformnakarshaNo ratings yet
- 111 Signal ProcessingDocument17 pages111 Signal ProcessingDotto KnowsNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transformation of An IR InterferogramDocument12 pagesFourier Transformation of An IR InterferogramIvt RomeroNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform of Coulomb PotentialDocument4 pagesFourier Transform of Coulomb Potentialtutorciecle123No ratings yet
- Lab1 Fourier Analysis of SignalsDocument3 pagesLab1 Fourier Analysis of SignalsAbdelrhman Ahmed AbdelkhaliqNo ratings yet
- GVICDocument157 pagesGVICTemitope OniNo ratings yet
- Lab3 BME321 BSPDocument3 pagesLab3 BME321 BSPAsim BashirNo ratings yet
- Proyecto 04Document6 pagesProyecto 04Scott Backster Clarck0% (1)
- 1016 Hanshaw Road Ithaca, Ny 14850 August 3, 2017Document13 pages1016 Hanshaw Road Ithaca, Ny 14850 August 3, 2017David MartinsNo ratings yet
- Frequency SpaceDocument71 pagesFrequency SpaceHafid ScooteristNo ratings yet
- L15-23 NotesDocument2 pagesL15-23 NotesitasneemNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of The Discrete Fourier Transform: XF Xte DTDocument8 pagesFundamentals of The Discrete Fourier Transform: XF Xte DTho-faNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document11 pagesExperiment 2manikNo ratings yet
- Frequency Domain ProcessingDocument42 pagesFrequency Domain ProcessingInJune YeoNo ratings yet
- Amath 482 Coding Project 2 Report JonathanaaltoDocument13 pagesAmath 482 Coding Project 2 Report Jonathanaaltoapi-615220844No ratings yet
- What Is The Fast Fourier TransformDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Fast Fourier TransformGabriel AguirreNo ratings yet
- Resonance Enhancement in Laser-Produced Plasmas: Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandResonance Enhancement in Laser-Produced Plasmas: Concepts and ApplicationsNo ratings yet