Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classification of Organisms: Name: Class: VII Date: Subject: Science
Classification of Organisms: Name: Class: VII Date: Subject: Science
Uploaded by
Shashi AgnihotriCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Linnaeuss System of ClassificationDocument33 pagesLinnaeuss System of Classificationheartyjune.ortizo0610No ratings yet
- Biodiversity: The Origin of SpeciesDocument19 pagesBiodiversity: The Origin of Speciesnasrin banuNo ratings yet
- CH 03 BiodiversityDocument9 pagesCH 03 BiodiversityZain NoorNo ratings yet
- PP27 Classification Systems UPDATEDDocument59 pagesPP27 Classification Systems UPDATEDnaledimonyela3No ratings yet
- Handout For Week 6Document10 pagesHandout For Week 6Cheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Notes Biology PDFDocument144 pages1st Year Notes Biology PDFmrtweets67% (6)
- Unit 5 Classification-Class NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 5 Classification-Class NotesNatasha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Biology - BiodiversityDocument0 pagesBiology - Biodiversitywww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- Stages of Living ThingsDocument18 pagesStages of Living ThingsJay DansNo ratings yet
- Hierarchical TaxonomicDocument24 pagesHierarchical TaxonomicJoedee NicolasNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Medical EntranceDocument40 pagesBiology Notes For Medical EntranceNickOoPandeyNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy DefinitionDocument7 pagesTaxonomy DefinitionchristinesalasNo ratings yet
- PP27. Classification SystemsDocument44 pagesPP27. Classification SystemsThanyani MavhivhaNo ratings yet
- Living World Class XiDocument32 pagesLiving World Class XivijithamuraliNo ratings yet
- TaxonomicDocument51 pagesTaxonomicAlvin OliverosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 (Biology)Document24 pagesChapter-2 (Biology)pramod peterNo ratings yet
- "Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings WhichDocument11 pages"Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings Whichbrm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living OrganismsDocument29 pagesClassification of Living OrganismsOJ ICONICNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Biodiversity Class 9thDocument18 pagesBiology Notes Biodiversity Class 9thKaka KNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Notes BiologyDocument144 pages1st Year Notes BiologyAkbar Dad BabarNo ratings yet
- Ijso (Diversity in Living Organisms)Document30 pagesIjso (Diversity in Living Organisms)krishna_m47No ratings yet
- Notes BiologyDocument144 pagesNotes BiologySrikanth VsrNo ratings yet
- NCERT Theory Diversity in Living Organisms Class IX temp (With Exercise)Document32 pagesNCERT Theory Diversity in Living Organisms Class IX temp (With Exercise)9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Classificationofanimals 190616135223Document49 pagesClassificationofanimals 190616135223mshahpromoNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document16 pagesCH 1exercisestartNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - BiodiversityDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - BiodiversityShah SaqibNo ratings yet
- Review: Classification ClassificationDocument28 pagesReview: Classification ClassificationGerlie VelascoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Jump ReportDocument17 pages2nd Jump Reportzyan reyesNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy XI Final NewDocument5 pagesTaxonomy XI Final NewPrazwal RegmiNo ratings yet
- Science 8Document1 pageScience 8Clarissa BernalesNo ratings yet
- 4 2 2Document8 pages4 2 2bejeweled1308No ratings yet
- Text 2 Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesText 2 Classification of Living ThingsmisterxNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Taxonomy: DiversityDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Taxonomy: DiversityRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Living World 1Document5 pagesChapter 1 The Living World 1YashiNo ratings yet
- Agri - Fishery Module Notes 2 Plant TaxonomyDocument3 pagesAgri - Fishery Module Notes 2 Plant TaxonomyGale ViernesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Classification in PalaeontologyDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Classification in PalaeontologyPeter MakanjuolaNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 - Class 11Document20 pagesBiology Chapter 1 - Class 11ameena-11173No ratings yet
- Classification - Taxonomy ReadingDocument7 pagesClassification - Taxonomy Readingapi-262368188No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Biology Chapter 1 The Living World Class 11Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Biology Chapter 1 The Living World Class 11santhoshr927tNo ratings yet
- A. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCDocument1 pageA. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCHannah 晗❾No ratings yet
- The Living WorldDocument2 pagesThe Living WorldGayathri Prathima GNo ratings yet
- Biology (Out of Portion)Document51 pagesBiology (Out of Portion)NodiaNo ratings yet
- Classification Introduction 1 Async TaskDocument4 pagesClassification Introduction 1 Async Taskzoha shahzadNo ratings yet
- Acellular LifeDocument20 pagesAcellular LifeMinahil IlyasNo ratings yet
- Five Kingdom SystemDocument8 pagesFive Kingdom SystemsanaullahNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument36 pagesDiversity in Living OrganismsdhruvaNo ratings yet
- Biology F2 M-1Document56 pagesBiology F2 M-1Stanley AkuamoahNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesDiversity in Living Organismssumendra singhNo ratings yet
- Living Organisms and SpeciesDocument2 pagesLiving Organisms and SpeciesmeshNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesClassification of Living ThingsBolu AdediranNo ratings yet
- High School Biology 14-26Document717 pagesHigh School Biology 14-26Saaqib MahmoodNo ratings yet
- CBSE 11th Sample BIOLOGY 1Document17 pagesCBSE 11th Sample BIOLOGY 1ALEENA KANNINo ratings yet
- Beta Monic Ai-MonicaiDocument6 pagesBeta Monic Ai-MonicaiJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismsDocument63 pagesClassification of OrganismsKim DahyunNo ratings yet
- ClassificationsDocument33 pagesClassificationsHi everyoneNo ratings yet
- Life VarityDocument23 pagesLife VaritySubhan ullah TutorialNo ratings yet
- Class Notes of CBSE 9Document8 pagesClass Notes of CBSE 9Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of Our Biological World: Lesson 3Document43 pagesMaking Sense of Our Biological World: Lesson 3Beng QuinnNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument14 pagesBiodiversityameracasanNo ratings yet
- SB KarbonDocument3 pagesSB KarbonAbdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Chinas Legal Strategy To Cope With US Export ContDocument9 pagesChinas Legal Strategy To Cope With US Export Contb19fd0013No ratings yet
- Welspun Linen Customer Price List 2023Document4 pagesWelspun Linen Customer Price List 2023Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Home Office and Branch Accounting Agency 1Document20 pagesHome Office and Branch Accounting Agency 1John Stephen PendonNo ratings yet
- Asfwa Report2008 PDFDocument4 pagesAsfwa Report2008 PDFMesfin DerbewNo ratings yet
- A Kinsha 2013Document698 pagesA Kinsha 2013alexander2beshkovNo ratings yet
- Rat ModelDocument1 pageRat Modelapi-483276188No ratings yet
- View AnswerDocument112 pagesView Answershiv anantaNo ratings yet
- List Peserta Swab Antigen - 5 Juni 2021Document11 pagesList Peserta Swab Antigen - 5 Juni 2021minhyun hwangNo ratings yet
- SPOUSES SALVADOR ABELLA v. SPOUSES ROMEO ABELLADocument2 pagesSPOUSES SALVADOR ABELLA v. SPOUSES ROMEO ABELLAAlia Arnz-Dragon100% (1)
- Accounting For Managers: S. No. Questions 1Document5 pagesAccounting For Managers: S. No. Questions 1shilpa mishraNo ratings yet
- Steve Nison - Candlestick Patterns - RezumatDocument22 pagesSteve Nison - Candlestick Patterns - RezumatSIightlyNo ratings yet
- Talent Acquisition Request Form: EducationDocument1 pageTalent Acquisition Request Form: EducationdasfortNo ratings yet
- English Biofertilizers BrochureDocument2 pagesEnglish Biofertilizers BrochurekerateaNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Toolkit 1Document3 pagesComprehension Toolkit 1api-510893209No ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Selected Ceramic Companies of BangladeshDocument14 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Selected Ceramic Companies of BangladeshmotaazizNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Part 1-Propositional LogicDocument11 pagesUNIT 3 Part 1-Propositional LogicVanshika ChauhanNo ratings yet
- LH - Elementary - Student's Book Answer KeyDocument34 pagesLH - Elementary - Student's Book Answer KeyАнастасия ДанилюкNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 68749835 Electronic Throttle BodyDocument3 pagesData Sheet 68749835 Electronic Throttle BodyDaniel AguirreNo ratings yet
- The Secret Book of JamesDocument17 pagesThe Secret Book of JameslaniNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1: The Terms of An AgreementDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1: The Terms of An AgreementJulieta ImbaquingoNo ratings yet
- Referee Report TemplateDocument2 pagesReferee Report TemplateAna Jufriani100% (1)
- The Evolution of Google Search Results Pages and Their Effect On User Behaviour PDFDocument81 pagesThe Evolution of Google Search Results Pages and Their Effect On User Behaviour PDFlcm3766lNo ratings yet
- Gentrification in Color and TimeDocument38 pagesGentrification in Color and TimeBNo ratings yet
- Dedication Certificate John Clyde D. Cristobal: This Certifies ThatDocument1 pageDedication Certificate John Clyde D. Cristobal: This Certifies ThatAGSAOAY JASON F.No ratings yet
- Data Sheets Ecc I On AdoraDocument23 pagesData Sheets Ecc I On AdoraAlanAvtoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Memo Workout - Guitar Coach MagDocument28 pagesMuscle Memo Workout - Guitar Coach Magpeterd87No ratings yet
- Frs Whatsapp Chat NotesDocument72 pagesFrs Whatsapp Chat NotesFarai NyaniNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam 2Document5 pagesDiagnostic Exam 2Tomzki Cornelio50% (2)
- AUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea ODocument3 pagesAUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea OdfsdNo ratings yet
Classification of Organisms: Name: Class: VII Date: Subject: Science
Classification of Organisms: Name: Class: VII Date: Subject: Science
Uploaded by
Shashi AgnihotriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classification of Organisms: Name: Class: VII Date: Subject: Science
Classification of Organisms: Name: Class: VII Date: Subject: Science
Uploaded by
Shashi AgnihotriCopyright:
Available Formats
Classification
Name:
of Organisms Class: VII
...w here dreams come true Date:
Subject:
Science
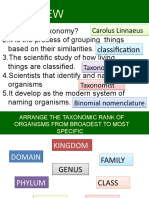
It is difficult to study such a large number of living organism, therefore scientists classified in them
into different categories. The classification system is known as Biological classification or taxonomy. It
was introduced in 1758 by Carolus Linnaeus, a Swedish botanist.
In Linneaus’s time, scientists characterized organisms as either plants or animals. Linnaeus
followed this general rule, dividing all living things into two kingdoms—the Kingdom Plantae (plants) and
the Kingdom Animalia (animals). His system was later modified by other scientists who revealed key
differences among organisms at the cellular level. For example, Linneaus classified fungi and algae in the
plant kingdom. When later scientists noted key differences in the cell structures of these groups, algae and
fungi were reclassified in different kingdoms. By the 1960s, scientists had organized living things into five
kingdoms—the Monera (bacteria), Protista (protozoa and algae), Fungi (mushrooms, yeasts, and molds),
Plantae (plants), and Animalia (animals). The five-kingdom system was widely accepted and used for
many years.
1. Kingdom Monera Bacteria are categorized underneath the Kingdom Monera.
2. Kingdom Protista It is made up of all the eukaryotic unicellular organisms except yeast.
Majorly Protozoans (unicellular eukaryotic organisms) come under the Kingdom Protista. Examples
include paramecium, amoeba, plasmodium, euglena, leishmania etc.
3. Kingdom Fungi The organisms of Kingdom Fungi are mostly saprophytic. It is the only
Kingdom which has multicellular and unicellular organisms. It includes mushrooms, yeast and moulds.
4. Kingdom Plantae All plants and trees we see around us come under this Kingdom. All of them
are autotrophic with chloroplast in their cell.
5. Kingdom Animal Kingdom Animalia is made up of eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic
organisms. Mode of nutrition is holozoic, and they are either herbivores or carnivores. Most animals are
motile, they can move independently in search of food, shelter or mate. Animals are made up of many
organ systems,that aid in performing specific functions that are necessary for the survival of the organism.
The following terms are used in taxonomy.
A kingdom is the highest level of classification which consists of a number of phyla or divisions (in
case of plants) with similar characteristic
Phylum/Division is a level of classification which consists of a
number of classes with similar characteristics.
A class is the level of classification which consists of a number of
orders with similar characteristics.
An order is the level of classification which consists of a number of
families with similar characteristics.
A family is the level of classification which consists of a number of
Genus with similar characteristics.
Genus is the level of classification which consists of a number of
species with similar characteristics.
Species is the level of classification which consists of a number of
organisms with similar characteristics and can interbreed to give
rise to a fertile offspring.
Study the following examples.
You might also like
- Linnaeuss System of ClassificationDocument33 pagesLinnaeuss System of Classificationheartyjune.ortizo0610No ratings yet
- Biodiversity: The Origin of SpeciesDocument19 pagesBiodiversity: The Origin of Speciesnasrin banuNo ratings yet
- CH 03 BiodiversityDocument9 pagesCH 03 BiodiversityZain NoorNo ratings yet
- PP27 Classification Systems UPDATEDDocument59 pagesPP27 Classification Systems UPDATEDnaledimonyela3No ratings yet
- Handout For Week 6Document10 pagesHandout For Week 6Cheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Notes Biology PDFDocument144 pages1st Year Notes Biology PDFmrtweets67% (6)
- Unit 5 Classification-Class NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 5 Classification-Class NotesNatasha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Biology - BiodiversityDocument0 pagesBiology - Biodiversitywww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- Stages of Living ThingsDocument18 pagesStages of Living ThingsJay DansNo ratings yet
- Hierarchical TaxonomicDocument24 pagesHierarchical TaxonomicJoedee NicolasNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Medical EntranceDocument40 pagesBiology Notes For Medical EntranceNickOoPandeyNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy DefinitionDocument7 pagesTaxonomy DefinitionchristinesalasNo ratings yet
- PP27. Classification SystemsDocument44 pagesPP27. Classification SystemsThanyani MavhivhaNo ratings yet
- Living World Class XiDocument32 pagesLiving World Class XivijithamuraliNo ratings yet
- TaxonomicDocument51 pagesTaxonomicAlvin OliverosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 (Biology)Document24 pagesChapter-2 (Biology)pramod peterNo ratings yet
- "Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings WhichDocument11 pages"Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings Whichbrm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living OrganismsDocument29 pagesClassification of Living OrganismsOJ ICONICNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Biodiversity Class 9thDocument18 pagesBiology Notes Biodiversity Class 9thKaka KNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Notes BiologyDocument144 pages1st Year Notes BiologyAkbar Dad BabarNo ratings yet
- Ijso (Diversity in Living Organisms)Document30 pagesIjso (Diversity in Living Organisms)krishna_m47No ratings yet
- Notes BiologyDocument144 pagesNotes BiologySrikanth VsrNo ratings yet
- NCERT Theory Diversity in Living Organisms Class IX temp (With Exercise)Document32 pagesNCERT Theory Diversity in Living Organisms Class IX temp (With Exercise)9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Classificationofanimals 190616135223Document49 pagesClassificationofanimals 190616135223mshahpromoNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document16 pagesCH 1exercisestartNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - BiodiversityDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - BiodiversityShah SaqibNo ratings yet
- Review: Classification ClassificationDocument28 pagesReview: Classification ClassificationGerlie VelascoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Jump ReportDocument17 pages2nd Jump Reportzyan reyesNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy XI Final NewDocument5 pagesTaxonomy XI Final NewPrazwal RegmiNo ratings yet
- Science 8Document1 pageScience 8Clarissa BernalesNo ratings yet
- 4 2 2Document8 pages4 2 2bejeweled1308No ratings yet
- Text 2 Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesText 2 Classification of Living ThingsmisterxNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Taxonomy: DiversityDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Taxonomy: DiversityRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Living World 1Document5 pagesChapter 1 The Living World 1YashiNo ratings yet
- Agri - Fishery Module Notes 2 Plant TaxonomyDocument3 pagesAgri - Fishery Module Notes 2 Plant TaxonomyGale ViernesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Classification in PalaeontologyDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Classification in PalaeontologyPeter MakanjuolaNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 - Class 11Document20 pagesBiology Chapter 1 - Class 11ameena-11173No ratings yet
- Classification - Taxonomy ReadingDocument7 pagesClassification - Taxonomy Readingapi-262368188No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Biology Chapter 1 The Living World Class 11Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Biology Chapter 1 The Living World Class 11santhoshr927tNo ratings yet
- A. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCDocument1 pageA. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCHannah 晗❾No ratings yet
- The Living WorldDocument2 pagesThe Living WorldGayathri Prathima GNo ratings yet
- Biology (Out of Portion)Document51 pagesBiology (Out of Portion)NodiaNo ratings yet
- Classification Introduction 1 Async TaskDocument4 pagesClassification Introduction 1 Async Taskzoha shahzadNo ratings yet
- Acellular LifeDocument20 pagesAcellular LifeMinahil IlyasNo ratings yet
- Five Kingdom SystemDocument8 pagesFive Kingdom SystemsanaullahNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument36 pagesDiversity in Living OrganismsdhruvaNo ratings yet
- Biology F2 M-1Document56 pagesBiology F2 M-1Stanley AkuamoahNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesDiversity in Living Organismssumendra singhNo ratings yet
- Living Organisms and SpeciesDocument2 pagesLiving Organisms and SpeciesmeshNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesClassification of Living ThingsBolu AdediranNo ratings yet
- High School Biology 14-26Document717 pagesHigh School Biology 14-26Saaqib MahmoodNo ratings yet
- CBSE 11th Sample BIOLOGY 1Document17 pagesCBSE 11th Sample BIOLOGY 1ALEENA KANNINo ratings yet
- Beta Monic Ai-MonicaiDocument6 pagesBeta Monic Ai-MonicaiJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismsDocument63 pagesClassification of OrganismsKim DahyunNo ratings yet
- ClassificationsDocument33 pagesClassificationsHi everyoneNo ratings yet
- Life VarityDocument23 pagesLife VaritySubhan ullah TutorialNo ratings yet
- Class Notes of CBSE 9Document8 pagesClass Notes of CBSE 9Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of Our Biological World: Lesson 3Document43 pagesMaking Sense of Our Biological World: Lesson 3Beng QuinnNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument14 pagesBiodiversityameracasanNo ratings yet
- SB KarbonDocument3 pagesSB KarbonAbdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Chinas Legal Strategy To Cope With US Export ContDocument9 pagesChinas Legal Strategy To Cope With US Export Contb19fd0013No ratings yet
- Welspun Linen Customer Price List 2023Document4 pagesWelspun Linen Customer Price List 2023Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Home Office and Branch Accounting Agency 1Document20 pagesHome Office and Branch Accounting Agency 1John Stephen PendonNo ratings yet
- Asfwa Report2008 PDFDocument4 pagesAsfwa Report2008 PDFMesfin DerbewNo ratings yet
- A Kinsha 2013Document698 pagesA Kinsha 2013alexander2beshkovNo ratings yet
- Rat ModelDocument1 pageRat Modelapi-483276188No ratings yet
- View AnswerDocument112 pagesView Answershiv anantaNo ratings yet
- List Peserta Swab Antigen - 5 Juni 2021Document11 pagesList Peserta Swab Antigen - 5 Juni 2021minhyun hwangNo ratings yet
- SPOUSES SALVADOR ABELLA v. SPOUSES ROMEO ABELLADocument2 pagesSPOUSES SALVADOR ABELLA v. SPOUSES ROMEO ABELLAAlia Arnz-Dragon100% (1)
- Accounting For Managers: S. No. Questions 1Document5 pagesAccounting For Managers: S. No. Questions 1shilpa mishraNo ratings yet
- Steve Nison - Candlestick Patterns - RezumatDocument22 pagesSteve Nison - Candlestick Patterns - RezumatSIightlyNo ratings yet
- Talent Acquisition Request Form: EducationDocument1 pageTalent Acquisition Request Form: EducationdasfortNo ratings yet
- English Biofertilizers BrochureDocument2 pagesEnglish Biofertilizers BrochurekerateaNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Toolkit 1Document3 pagesComprehension Toolkit 1api-510893209No ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Selected Ceramic Companies of BangladeshDocument14 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Selected Ceramic Companies of BangladeshmotaazizNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Part 1-Propositional LogicDocument11 pagesUNIT 3 Part 1-Propositional LogicVanshika ChauhanNo ratings yet
- LH - Elementary - Student's Book Answer KeyDocument34 pagesLH - Elementary - Student's Book Answer KeyАнастасия ДанилюкNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 68749835 Electronic Throttle BodyDocument3 pagesData Sheet 68749835 Electronic Throttle BodyDaniel AguirreNo ratings yet
- The Secret Book of JamesDocument17 pagesThe Secret Book of JameslaniNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1: The Terms of An AgreementDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1: The Terms of An AgreementJulieta ImbaquingoNo ratings yet
- Referee Report TemplateDocument2 pagesReferee Report TemplateAna Jufriani100% (1)
- The Evolution of Google Search Results Pages and Their Effect On User Behaviour PDFDocument81 pagesThe Evolution of Google Search Results Pages and Their Effect On User Behaviour PDFlcm3766lNo ratings yet
- Gentrification in Color and TimeDocument38 pagesGentrification in Color and TimeBNo ratings yet
- Dedication Certificate John Clyde D. Cristobal: This Certifies ThatDocument1 pageDedication Certificate John Clyde D. Cristobal: This Certifies ThatAGSAOAY JASON F.No ratings yet
- Data Sheets Ecc I On AdoraDocument23 pagesData Sheets Ecc I On AdoraAlanAvtoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Memo Workout - Guitar Coach MagDocument28 pagesMuscle Memo Workout - Guitar Coach Magpeterd87No ratings yet
- Frs Whatsapp Chat NotesDocument72 pagesFrs Whatsapp Chat NotesFarai NyaniNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam 2Document5 pagesDiagnostic Exam 2Tomzki Cornelio50% (2)
- AUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea ODocument3 pagesAUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea OdfsdNo ratings yet