Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mixed Conditionals: Grammar Chart
Mixed Conditionals: Grammar Chart
Uploaded by
takinardiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mixed Conditionals: Grammar Chart
Mixed Conditionals: Grammar Chart
Uploaded by
takinardiCopyright:
Available Formats
Grammar » B2 Grammar lessons and exercises » Mixed conditionals – If I were you, I wouldn’t have done it
1 2 3
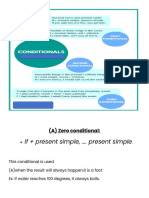
Mixed conditionals
Mixed conditionals are a combination of two types of conditional patterns, usually second and third conditionals. We can have a third conditional in the if
clause and a second conditional in the main clause or a second conditional in the if clause and a third conditional in the main clause.
Grammar chart
Second and third conditionals
In a second conditional we use past in the if clause and would/might/could + infinitive in the main clause. It is used to talk about hypothetical situations
happening in the present or future.
• If I were rich, I‘d buy that house.
In a third conditional we use past perfect in the if clause and would/might/could + have + past participle in the main clause. It is used to talk about
hypothetical situations happening in the past.
• If you had studied more, you would have passed the exam.
A mixed conditional is a combination of second and third conditionals.
Mixed third/second conditional
We use this combination to talk about a hypothetical condition happening in the past (third conditional) with a present result (second conditional). We
use past perfect in the if clause and would/could/might + infinitive in the main clause.
• If I had been elected, I would be the president now.
• If I had won the lottery, I would be rich.
• I might have a better job now if I hadn’t dropped out of school.
Mixed second/third conditional
We use this combination to talk about a hypothetical condition happening in the present (second conditional) with a past result (third conditional). We
use past in the if clause and would/could/might + have + past participle in the main clause.
• If I were a man, they would have given me the job.
• If I didn’t have so much work, I would have gone to the party last night.
• I would have understood them if I spoke German.
Note that in this type of combination, the present condition also existed in the past, when the result in the main clause took place. Let’s take a look, for
example, at the first sentence:
• If I were a man, they would have given me the job.
If I were a man now would mean that I would also have been a man in the past, when I was not given the job. As I’m not a man now (which implies that I
wasn’t a man when I applied for the job either), I didn’t get the job.
You might also like
- First CondDocument4 pagesFirst CondМарта НазаркевичNo ratings yet
- Verb ComplementsDocument19 pagesVerb ComplementsCenobioNo ratings yet
- Focgb4 Ak GQ 6Document2 pagesFocgb4 Ak GQ 6Irma Kiss57% (7)
- Prim 5 - Booklet 1st Term (Macmillan)Document58 pagesPrim 5 - Booklet 1st Term (Macmillan)Essam Selim33% (3)
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument3 pagesMixed ConditionalsDASCALU ANANo ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument1 pageMixed Conditionalsad7120118No ratings yet
- Zero, First, Second, Third and Mixed ConditionalsDocument4 pagesZero, First, Second, Third and Mixed ConditionalschelseaNo ratings yet
- 9-All Conditionals - Mixed Conditionals, Alternatives To If, InversionDocument3 pages9-All Conditionals - Mixed Conditionals, Alternatives To If, InversiontakinardiNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Conditional (Open Condition)Document4 pagesType 1 Conditional (Open Condition)Hung TranNo ratings yet
- All Conditionals - Mixed Conditionals, Alternatives To If', InversionDocument4 pagesAll Conditionals - Mixed Conditionals, Alternatives To If', InversionKiara QuispeNo ratings yet
- Wepik Mastering The Art of Conditional Sentences A Comprehensive Guide To Fluent English Expression 20231022061046ysUEDocument17 pagesWepik Mastering The Art of Conditional Sentences A Comprehensive Guide To Fluent English Expression 20231022061046ysUEGibran MuhmmdNo ratings yet
- Conditional Clauses - Part 2 (Second Conditional & Third Conditional)Document6 pagesConditional Clauses - Part 2 (Second Conditional & Third Conditional)Shu BhamNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 1&2Document5 pagesConditionals 1&2Monica Adina BaneaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Third and Mixed B1 - B2 GrammarDocument2 pagesConditionals Third and Mixed B1 - B2 GrammarYolimarNo ratings yet
- Conditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFDocument15 pagesConditional Theory N Exercise For Class PDFUmu NeroNo ratings yet
- According To Jeremy Harmer and Hester Lott in TheiDocument10 pagesAccording To Jeremy Harmer and Hester Lott in TheiEka wahyuniNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Conditionals: Zero ConditionalDocument2 pagesGrammar: Conditionals: Zero ConditionalfatimaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences TheoryDocument2 pagesConditional Sentences TheorymariecbaNo ratings yet
- Teori Conditional SentencesDocument3 pagesTeori Conditional SentencesamelianiNo ratings yet
- Tên đề tài:: Trường Đại Học Hải Phòng Khoa Ngoại NgữDocument13 pagesTên đề tài:: Trường Đại Học Hải Phòng Khoa Ngoại Ngữmicheal longdikNo ratings yet
- Mixed Conditionals - Test-EnglishDocument1 pageMixed Conditionals - Test-EnglishMilica MilunovićNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Second Term RevisionDocument20 pagesGrade 11 Second Term RevisionEkbalNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Modul 8Document3 pagesConditional Sentences Modul 8aben djamien prodoNo ratings yet
- If You StudyDocument5 pagesIf You Studyafeky11No ratings yet
- Nazia Inglesthird ConditionalDocument10 pagesNazia Inglesthird ConditionalIsmael César FançaneNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsJaunius AugustisNo ratings yet
- If Clauses & Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesIf Clauses & Conditional Sentencesaarti100% (1)
- If Clause Type I, IIDocument22 pagesIf Clause Type I, IIpintwanNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument4 pagesConditionalsvotaco6503No ratings yet
- Conditional Schue LerDocument14 pagesConditional Schue LerraimodNo ratings yet
- Conditionalsandwishes 160420081955Document47 pagesConditionalsandwishes 160420081955Ali Chahin100% (1)
- Materi Baru Bujing AngadidaDocument5 pagesMateri Baru Bujing Angadidapaulus silalahiNo ratings yet
- Third Conditionals and Mixed ConditionalsDocument2 pagesThird Conditionals and Mixed ConditionalswysacadNo ratings yet
- Conditional Class Full NotesDocument13 pagesConditional Class Full NotesThangavel Raj JNo ratings yet
- IF ClauseDocument5 pagesIF ClauseJuliette Viveros UlibarryNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument3 pagesConditional SentenceRegina MagdaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences 1Document15 pagesConditional Sentences 1w8q6gb5xbfNo ratings yet
- Makalah Conditional SentenceDocument6 pagesMakalah Conditional SentenceSATRIA GNo ratings yet
- Third Conditional WorksheetDocument6 pagesThird Conditional WorksheetHatice AydinNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesAle GarpeNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences & Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesConditional Sentences & Passive Voicesfhrdia19No ratings yet
- English 9 Module 4 - First and Second ConditionalsDocument10 pagesEnglish 9 Module 4 - First and Second ConditionalsPauline Karen Concepcion100% (1)
- 5 Types of Conditional Sentences in EnglishDocument6 pages5 Types of Conditional Sentences in EnglishShaistaNo ratings yet
- "The Unreal Past": ConditionalsDocument3 pages"The Unreal Past": ConditionalsLuisa Fernanda Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- Conditional If PDF To Be SharedDocument21 pagesConditional If PDF To Be SharedMiandy CelestinnNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument8 pagesConditionalsIrene BertoloNo ratings yet
- Conditional Clause and Main ClauseDocument5 pagesConditional Clause and Main ClauseRatnaNo ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalsDocument5 pagesMixed ConditionalsCat JonesNo ratings yet
- If Cond 26 NisanDocument15 pagesIf Cond 26 NisanGüray KanselNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 2 3Document12 pagesConditionals 2 3LauGalindoNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument2 pagesConditionalSylvie ChamberlandNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument8 pagesConditionalstehanimariahNo ratings yet
- Conditionals LessonDocument8 pagesConditionals LessonGrace ManuelNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Conditional Sentences-Rules You Need To KnowDocument3 pagesGrammar: Conditional Sentences-Rules You Need To Knowgilca.monicaluizaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument3 pagesConditional SentenceLiwanto LeeNo ratings yet
- English 102 9+10Document16 pagesEnglish 102 9+10moh.ahm3040No ratings yet
- If ClauseDocument3 pagesIf Clauseliziana zaharieNo ratings yet
- If Clause or The Conditional 2023-2024 DR LAHMER MDocument8 pagesIf Clause or The Conditional 2023-2024 DR LAHMER MsolekeNo ratings yet
- If (Conditional) ClauseDocument2 pagesIf (Conditional) ClauseRiza LuthfiNo ratings yet
- Materi 4Document4 pagesMateri 4Ciitraa AggrrNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument10 pagesConditional SentenceschirningshenNo ratings yet
- 23-Inversion With Negative Adverbials - Adding EmphasisDocument3 pages23-Inversion With Negative Adverbials - Adding EmphasistakinardiNo ratings yet
- 31-Asking Questions in English - Question FormsDocument2 pages31-Asking Questions in English - Question FormstakinardiNo ratings yet
- 10-Usually, Used To, Be Used To, Get Used ToDocument2 pages10-Usually, Used To, Be Used To, Get Used TotakinardiNo ratings yet
- TirguinDocument4 pagesTirguintakinardiNo ratings yet
- 30-Prepositions of Movement - Along, Across, Over, Etc.Document1 page30-Prepositions of Movement - Along, Across, Over, Etc.takinardiNo ratings yet
- English ProgrammeDocument15 pagesEnglish ProgrammetakinardiNo ratings yet
- 18-Reported Speech - Indirect SpeechDocument2 pages18-Reported Speech - Indirect SpeechtakinardiNo ratings yet
- Used To, Didn't Use To - Summary ChartDocument2 pagesUsed To, Didn't Use To - Summary CharttakinardiNo ratings yet
- 26-Defining Relative Clauses - Who, Which, That, WhereDocument1 page26-Defining Relative Clauses - Who, Which, That, WheretakinardiNo ratings yet
- 17-Present and Past Simple Passive Be + Past ParticipleDocument2 pages17-Present and Past Simple Passive Be + Past ParticipletakinardiNo ratings yet
- 11-Had Better It's TimeDocument2 pages11-Had Better It's TimetakinardiNo ratings yet
- Second Conditional - Grammar Chart: If Clause and Main ClauseDocument2 pagesSecond Conditional - Grammar Chart: If Clause and Main ClausetakinardiNo ratings yet
- 12-First Conditional, Future Time ClausesDocument3 pages12-First Conditional, Future Time ClausestakinardiNo ratings yet
- 25-Any, No, None - QuantifiersDocument2 pages25-Any, No, None - QuantifierstakinardiNo ratings yet
- 27-Defining and Non-Defining Relative ClausesDocument3 pages27-Defining and Non-Defining Relative ClausestakinardiNo ratings yet
- Second Conditional - Grammar Chart: If Clause and Main ClauseDocument2 pagesSecond Conditional - Grammar Chart: If Clause and Main ClausetakinardiNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs of Deduction - Summary ChartDocument2 pagesModal Verbs of Deduction - Summary CharttakinardiNo ratings yet
- 24-Both, Either, Neither - QuantifiersDocument2 pages24-Both, Either, Neither - QuantifierstakinardiNo ratings yet
- 23-All, Both - QuantifiersDocument2 pages23-All, Both - QuantifierstakinardiNo ratings yet
- 15-First Conditional and Future Time ClausesDocument2 pages15-First Conditional and Future Time ClausestakinardiNo ratings yet
- 16-Gerund or Infinitive - Verb PatternsDocument3 pages16-Gerund or Infinitive - Verb PatternstakinardiNo ratings yet
- 28-Comparative and Superlative Adjectives and AdverbsDocument3 pages28-Comparative and Superlative Adjectives and AdverbstakinardiNo ratings yet
- 1-Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument4 pages1-Present Simple Vs Present ContinuoustakinardiNo ratings yet
- 10-How To Use The Verb Go' in EnglishDocument2 pages10-How To Use The Verb Go' in EnglishtakinardiNo ratings yet
- 20 - Infinitives and Gerunds - Verb PatternsDocument2 pages20 - Infinitives and Gerunds - Verb PatternstakinardiNo ratings yet
- 6 Past PerfectDocument2 pages6 Past PerfecttakinardiNo ratings yet
- 27-So, Neither - So Am I, Neither Do I, Etc.Document2 pages27-So, Neither - So Am I, Neither Do I, Etc.takinardiNo ratings yet
- 11-Have To, Don't Have To, Must, Mustn'tDocument4 pages11-Have To, Don't Have To, Must, Mustn'ttakinardiNo ratings yet
- All, Most - Grammar Chart: Quantifiers - All, Most, Both, Either, Neither, Any, No, NoneDocument3 pagesAll, Most - Grammar Chart: Quantifiers - All, Most, Both, Either, Neither, Any, No, NonetakinardiNo ratings yet
- 15-Have Something DoneDocument2 pages15-Have Something DonetakinardiNo ratings yet
- Critical Review About The Differences of The Linguistic Mood Between Arabic and English LanguagesDocument6 pagesCritical Review About The Differences of The Linguistic Mood Between Arabic and English LanguagesJOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN LINGUISTICSNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument52 pagesConditionalsNatasha KHNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Grammar Drills Grammar Guides - 88240Document2 pagesConditional Sentences Grammar Drills Grammar Guides - 88240iñigoNo ratings yet
- THE EXERCISE OF CONDITIONAL SENTENCE FOR 4th STUDENTSDocument2 pagesTHE EXERCISE OF CONDITIONAL SENTENCE FOR 4th STUDENTSlyfia zuliannaNo ratings yet
- First ConditionalDocument2 pagesFirst ConditionalSzilard MateNo ratings yet
- Tink 2 - Unit 6Document10 pagesTink 2 - Unit 6infinityline11102No ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument49 pagesConditionalsapi-252190418100% (1)
- Unit 6B-GrammarDocument11 pagesUnit 6B-GrammarNguyễn Ngọc Tâm NhưNo ratings yet
- Collins: Grammar For IeltsDocument6 pagesCollins: Grammar For IeltsHoàn TrầnNo ratings yet
- LM-0354 Gramatica Inglesa III PresenDocument6 pagesLM-0354 Gramatica Inglesa III PresenLuis MongeNo ratings yet
- Parallel StuctureDocument39 pagesParallel StuctureSintiya Yunisyah SiregarNo ratings yet
- Together 4 Teachers GuideDocument13 pagesTogether 4 Teachers Guidecristinalp8550% (2)
- Conditionals and Reported Speech ReloadedDocument3 pagesConditionals and Reported Speech ReloadedCarlos Andres Ramos CardenasNo ratings yet
- English 9 q1 Module 2 ConditionalsDocument27 pagesEnglish 9 q1 Module 2 ConditionalsAkia SuzukiNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument14 pagesConditionalsVedrana100% (1)
- Lesson PlansDocument4 pagesLesson PlansStoean CristinaNo ratings yet
- Apuntes 2ºbachillerato Conditional SentencesDocument5 pagesApuntes 2ºbachillerato Conditional SentencesPianistasenderistaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument3 pagesConditionalsrascal26No ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument25 pagesConditionalsCamila BalcazaNo ratings yet
- Conditional-Sentences All TypesDocument4 pagesConditional-Sentences All TypesStefania100% (1)
- Conditionals PDFDocument15 pagesConditionals PDFOlene80No ratings yet
- Structure of EnglishDocument4 pagesStructure of Englishseri nuraliaNo ratings yet
- Second Trimester Module For 9th GradersDocument16 pagesSecond Trimester Module For 9th Gradersmelany serranoNo ratings yet
- Test On Unit 9 Text Grammar ExercisesDocument4 pagesTest On Unit 9 Text Grammar ExercisesQuynh NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument6 pagesThe Present Continuous TenselepromNo ratings yet
- Conditionals ExercisesDocument6 pagesConditionals ExercisesangelaNo ratings yet
- First Conditionals WorksheetDocument1 pageFirst Conditionals WorksheetM Paz Pérez García80% (5)