Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rocks and Minerals Test
Rocks and Minerals Test
Uploaded by
Joel Greig0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views6 pagesThe document provides questions and images from 15 stations testing knowledge of rocks, minerals, crystal structures, and geological formations. Questions assess identification of samples, description of properties like crystal structure and luster, and explanations of formation processes. A wide range of samples are presented, from common rocks and minerals to more specialized specimens, covering topics like crystal twinning, metamorphism, and ore deposits.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides questions and images from 15 stations testing knowledge of rocks, minerals, crystal structures, and geological formations. Questions assess identification of samples, description of properties like crystal structure and luster, and explanations of formation processes. A wide range of samples are presented, from common rocks and minerals to more specialized specimens, covering topics like crystal twinning, metamorphism, and ore deposits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views6 pagesRocks and Minerals Test
Rocks and Minerals Test
Uploaded by
Joel GreigThe document provides questions and images from 15 stations testing knowledge of rocks, minerals, crystal structures, and geological formations. Questions assess identification of samples, description of properties like crystal structure and luster, and explanations of formation processes. A wide range of samples are presented, from common rocks and minerals to more specialized specimens, covering topics like crystal twinning, metamorphism, and ore deposits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Rocks and Minerals CSE 2022
~3 minutes per station leaves 5 extra minutes
Team: _________________________ Name(s): __________________________________________________
STATION 1 (16 points)
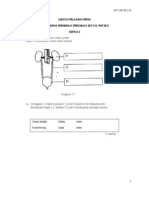
1. What mineral is shown in Image A? (2 points)
2. What crystal structure is exhibited in Image A? (1 point)
3. Briefly describe the formation process of the crystal structure in Image A. (3 points)
4. Frito-Lay, the chip company, has been experimenting with using the crystal structure in Image A to give their salt
more flavor without increasing the amount of salt they use. Why would you be able to taste more salt if it was in
this crystal structure? (3 points)
5. What other mineral from the official SciOly list can create these structures? (2 points)
6. What mineral is shown in Image B? (2 points)
7. What crystal structure is exhibited in Image B? (1 point)
8. What luster does the mineral represented by Image B exhibit? (2 points)
STATION 2 (13 points)
9. What rock is shown in Image C? (2 points)
10. What conditions are this rock formed in? (temperature and pressure) (2 points)
11. What rock is shown in Image D? (2 points)
12. True or False: The rock in Image D is susceptible to be broken down by acids. (1 point)
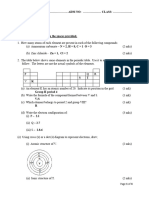
13. What type of Metamorphism is represented by bubble A in Image E? (2 points)
14. What type of Metamorphism is represented by bubble D in Image E? (2 points)
15. What type of Metamorphism is represented by bubble E in Image E? (2 points)
Team: _________________________ Name(s): __________________________________________________
STATION 3 (15 points)
16. What specimen is shown in Image F? (2 points)
17. What element is this specimen the most common ore of? (1 point)
18. What is this specimen’s fracture? (2 points)
19. What specimen is shown in Image G? (2 points)
20. What two elements is this specimen the main ore of? (2 points)
21. Which country produces roughly 1/3rd of this specimen worldwide? (2 points)
22. What specimen is shown in Image G? (2 points)
23. Which element is this specimen the main source of? (1 point)
24. What is this specimen’s tenacity? (1 point)
STATION 4 (17 points)
25. Identify the specimen in Image I (2 points)
26. Identify the specimen in Image J (2 points)
27. Identify the specimen in Image K (2 points)
28. Identify the specimen in Image L (2 points)
29. Identify the specimen in Image M (2 points)
30. Sort specimens I, J, K, L, and M in order from least to most hard following the Mohs hardness scale (5 points)
31. Why is the specimen in Image I especially important to the Mohs hardness scale? (2 points)
STATION 5 (14 points)
32. What mineral is represented in Image N? (2 points)
33. What mineral is represented in Image O? (2 points)
34. Describe the difference between contact twins and penetration twins. (4 points)
35. What is the specific word for a diamond or other crystal that is twinned? (2 points)
36. Define the criteria for the Japan twinning law. (4 points)
STATION 6 (16 points)
37. Identify the yellow mineral in Image P. (1 point)
38. What is a major defining characteristic unique to this mineral? (2 points)
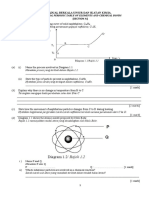
39. Image Q is Halite, also known as table salt, under an electron microscope. What crystal structure does Halite
most commonly exhibit? (2 points)
40. Although Halite normally appears clear or slightly tinted, it fluoresces to what color? (2 points)
41. What rock is represented in Image R? (1 point)
42. Fill in the blank: This rock is notably common, but also happens to be slightly radioactive. The Uranium, Thorium,
and Radium in this rock all decay into _______ (a colorless, odorless and potentially carcinogenic gas). (2 points)
43. Although this rock can be radioactive, it is extremely unlikely to increase annual radioactivity exposure above
safety levels according to the EPA. (2 free points because I’m very happy I got to share fun facts about my
favorite radioactive rock)
44. What compound is the majority constituent of the rock in Image R? (2 points)
45. Which rock is Image R’s extrusive equivalent? (2 points)
Team: _________________________ Name(s): __________________________________________________
STATION 7 (20 points)
46. Identify Image S (2 points)
47. Identify Image T (2 points)
48. Identify Image U (2 points)
49. Identify Image V (2 points)
50. Identify Image W (2 points)
51. Identify Image X (2 points)
52. Identify Image Y (2 points)
53. Identify Image Z (2 points)
54. Identify Image AA (2 points)
55. Identify Image AB (2 points)
STATION 8 (17 points)
56. As seen in Image AC, Ulexite seems to raise text to its surfact. Who first discovered this property, and in what
year? (2 points)
57. What nickname did Ulexite acquire due to this property? (1 point)
58. What element is ulexite mined for as an ore? (2 points)
59. What mineral is represented in Image AD? (2 points)
60. What optical property does this mineral display? (1 point)
61. What causes this otical property? (2 points)
62. What mineral is represented in Image AE? (2 points)
63. What optical property is shown in Image AE? (1 point)
64. Explain how this optical property works. (2 points)
65. Identify at least two other minerals that display this optical property. (2 points)
STATION 9 (16 points + 2 bonus)
66. Identify the mineral in Image AF. (1 point)
67. What causes the purple color of this mineral? (2 points)
68. Identify the mineral in Image AG. (1 point)
69. What causes the orange-yellow color of this mineral? (2 points)
70. Identify the mineral in Image AH. (1 point)
71. What optical property does this mineral uniquely exhibit? (2 points)
72. What causes the aforementioned optical property? (3 points)
73. Identify the mineral in Image AI. (1 point)
74. For bonus points: Name the specific variety of this mineral. (hint: look at the color) (2 bonus points)
75. Identify the mineral in Image AJ. (1 point)
76. Fill in the blank: This mineral is the main component of the _____-rich part of banded iron formations. (2 points)
Team: _________________________ Name(s): __________________________________________________
STATION 10 (16 points)
77. Identify the rock in Image AK. (2 points)
78. What more fine-grained rock does this specimen share a similar composition with? (2 points)
79. Identify the rock in Image AL. (2 points)
80. True or False: This rock is not vesicular. (1 point)
81. This rock is oftenly used for landscaping purposes. Other than its often striking colors, what makes this rock ideal
for landscaping as well as drainage systems. (3 points)
82. Identify the rock in Image AM. (2 points)
83. What word describes this rock’s grain size? (2 points)
84. What is the slow-cooling and coarse-grained equivalent of this rock? (2 points)
STATION 11 (Polymorphs)
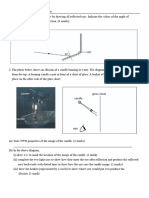
85. Identify the mineral in Image AN (1 point)
86. Identify the mineral in Image AO (1 point)
87. What property is shared between these minerals that can cause what you see in Image AP? (2 points)
88. Why does the process that changes a mineral from AO to AN take place? (3 points)
89. Identify the clear mineral in the top-left of Image AQ (1 point)
90. Identify the brown mineral in the bottom-right on Image AQ. (1 point)
91. What crystal habit does the bottom-right mineral display? (2 points)
92. True or False: Quartz and Tourmaline are polymorphs. (1 point)
STATION 12 (13 points)
93. Identify the specimen in Image AR. (2 points)
94. Why is this rock an ideal host for fossils? (3 points)
95. Identity the specimen in Image AS. (2 points)
96. What makes this rock and other sedimentary rocks so important to archaeologists? (4 points)
97. What is this rock used for outside of science? (2 points)
STATION 13 (20 points)
98. Identify the mineral in Image AT (2 points)
99. Identify the mineral in Image AU (the clear crystal) (2 points)
100. Identify the mineral in Image AV (2 points)
101. Identify the mineral in Image AW (2 points)
102. Identify the mineral in Image AX (2 points)
103. Identify the mineral in Image AY (2 points)
104. Identify the mineral in Image AZ (2 points)
105. Identify the mineral in Image BA (2 points)
106. Identify the mineral in Image BB (2 points)
Team: _________________________ Name(s): __________________________________________________
107. Identify the mineral in Image BC (2 points)
STATION 14 (13 points)
108. Identify the mineral in Image BD. (2 points)
109. What is the chemical formula of the mineral in Image BD? (2 points)
110. What causes this mineral to cleave in paper-thin planes? (3 points)
111. What dictates how crystals will form in a mineral? (2 points)
112. Identify the mineral in Image BE. (2 points)
113. What is the chemical formula of the mineral in Image BE? (2 points)
STATION 15 (15 points)
For questions 114-120, define the word(s). (1 point each)
114. Piezoelectricity
115. Diaphaneity
116. Alluvial Fan
117. Zeolite
118. Recrystallization
119. Evaporite
120. Plane Bedding
For questions 121-128, identify the specimen by its nickname. (1 point each)
121. Bog Iron
122. Kieselguhr
123. Fool’s Gold
124. Yellow Copper
125. Brimstone
126. Antimony Glance
127. Desmine
128. Black Jack
You might also like
- ECM3701 Electronic Communcation Technology: Minor Test No: 01 Year ModuleDocument4 pagesECM3701 Electronic Communcation Technology: Minor Test No: 01 Year ModuleTale Banks0% (1)
- CSS NC II Institutional AssessmentDocument3 pagesCSS NC II Institutional Assessmentdylan tikoyNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 July TestDocument7 pagesScience Form 3 July TestNorafiza Hashim100% (3)
- GCSE Level Optics QuestionsDocument33 pagesGCSE Level Optics QuestionsJayakumar SankaranNo ratings yet
- Chang Chemistry Chapter 1 QuestionsDocument26 pagesChang Chemistry Chapter 1 QuestionsBlanche DauzNo ratings yet
- Losartan Drug StudyDocument1 pageLosartan Drug StudyWenalyn Grace Abella Llavan100% (3)
- Diagram 1.1 Shows A Human Urinary System Rajah 1.1 Menunjukkan Sistem Urinari ManusiaDocument19 pagesDiagram 1.1 Shows A Human Urinary System Rajah 1.1 Menunjukkan Sistem Urinari ManusiaRosializa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Optical Mineralogy - Sample Exam 1Document7 pagesOptical Mineralogy - Sample Exam 1Zarina AdilbekovaNo ratings yet
- Ujian KimiaDocument7 pagesUjian KimiandianaoNo ratings yet
- 6 Elektrokimia SOALAN 2Document2 pages6 Elektrokimia SOALAN 2Noranita HusseinNo ratings yet
- Section A: Structured Questions (30 Marks) : Diagram 1Document6 pagesSection A: Structured Questions (30 Marks) : Diagram 1ndianaoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure QuestionsDocument11 pagesAtomic Structure Questionsemihk626No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01hweta173No ratings yet
- SC 2 Final 08 (F4)Document20 pagesSC 2 Final 08 (F4)Hanif SallehNo ratings yet
- MYP 5 - E-Assessment Revision - Periodic Table (Trends, Periods, Groups) - 43 Marks Q1Document9 pagesMYP 5 - E-Assessment Revision - Periodic Table (Trends, Periods, Groups) - 43 Marks Q1Daria DyabloNo ratings yet
- Chemistry KS4 LZ 2.1Document21 pagesChemistry KS4 LZ 2.1Wreck RalphNo ratings yet
- Science Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02sparsh bagalNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument6 pagesPreviewRochelle BlackNo ratings yet
- SCH 3250 Atomic Structures BondingDocument3 pagesSCH 3250 Atomic Structures BondingPst Kaka ClaranceNo ratings yet
- NTSE Maharashtra 2020 21 SAT Paper With SolutionsDocument18 pagesNTSE Maharashtra 2020 21 SAT Paper With SolutionsDhananjayNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03hweta173No ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Document4 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173No ratings yet
- Light Quiz 3Document2 pagesLight Quiz 3api-339704661No ratings yet
- 4 Atomic Structure: TrilogyDocument13 pages4 Atomic Structure: TrilogyAsmik LogianNo ratings yet
- Kamaishilite Ca Al Sio (Oh)Document1 pageKamaishilite Ca Al Sio (Oh)ramzchileNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Document3 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01garNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 2 End of Term 1 QP 2020Document4 pagesChemistry Form 2 End of Term 1 QP 2020haron murumbaNo ratings yet
- Modul A+ Set 1Document14 pagesModul A+ Set 1ZANARIAH BINTI LIHAT MoeNo ratings yet
- QP - Maharahstra - Ntse Stage 1 (2020-21) - SatDocument14 pagesQP - Maharahstra - Ntse Stage 1 (2020-21) - SatAdarsh GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Sains Ting 3 2014Document22 pagesSains Ting 3 2014abnu98No ratings yet
- Redox Reaction (Past Year)Document5 pagesRedox Reaction (Past Year)Kuryu ZuherlyNo ratings yet
- Report Sheet-Flame TestsDocument4 pagesReport Sheet-Flame TestsVictor DonattoNo ratings yet
- Yr9 Plant Test 2Document4 pagesYr9 Plant Test 2UMAH DEVI M CHANDARNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Revision Practice TestDocument19 pagesCH 7 Revision Practice Testpedro pascalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Johor SET 2 K2 SOALAN 2020 SPM TrialsDocument22 pagesChemistry Johor SET 2 K2 SOALAN 2020 SPM TrialsGloria YongNo ratings yet
- Science Cbse Question Paper Till 2009Document34 pagesScience Cbse Question Paper Till 2009bhargavvnNo ratings yet
- QuetsionsDocument26 pagesQuetsionssuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistryNethul KarunaratneNo ratings yet
- S.3 Physics Exercise 1 - ReflectionDocument7 pagesS.3 Physics Exercise 1 - ReflectionAlex ChenNo ratings yet
- 3.1.11.1 Electrode Potentials + Cells (A-Level Only)Document85 pages3.1.11.1 Electrode Potentials + Cells (A-Level Only)jaisisantosh2007No ratings yet
- f4 Chem Mid-Year Exam 2011Document12 pagesf4 Chem Mid-Year Exam 2011matleNo ratings yet
- PSLE FND Math 2020 Paper 2Document20 pagesPSLE FND Math 2020 Paper 2Chew Pei XuanNo ratings yet
- Sub. Sc. f.2 2012 MidDocument14 pagesSub. Sc. f.2 2012 MidNorzamani NordinNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Practice Booklet-1Document65 pagesInorganic Chemistry Practice Booklet-1godlanshul32No ratings yet
- Set 1-Paper 2 (Soalan)Document20 pagesSet 1-Paper 2 (Soalan)NajwaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sainsf1Document13 pagesSoalan Sainsf1Husna IzaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Eoy Paper 2Document16 pagesGrade 10 Eoy Paper 2vuyelwa.mzileni2021No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Electronic and IctDocument11 pagesChapter 16 Electronic and IctADY2022No ratings yet
- P - 5 Mathematics Mid-Term I ExaminationDocument11 pagesP - 5 Mathematics Mid-Term I Examinationrichardodulai999No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 LightDocument21 pagesChapter 6 LightCart KartikaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Quiz 2015-2020 Past PapersDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Quiz 2015-2020 Past PapersFIKRIYE ONDEROLNo ratings yet
- JEE Main - Growth - Sample Paper-1 - StudentDocument16 pagesJEE Main - Growth - Sample Paper-1 - Studentanurag jaiswalNo ratings yet
- 2022-p5 - Science Rws 2 - Term 4-KeyDocument4 pages2022-p5 - Science Rws 2 - Term 4-KeyDewi PuanNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment (Unit)Document5 pagesSummative Assessment (Unit)Ernesto Berger MarinheiroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 2Document19 pagesChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 2alanisln100% (1)
- Chemical Bond (SPM Q)Document11 pagesChemical Bond (SPM Q)Luna LatisyaNo ratings yet
- 06 Nuclear PhysicsDocument4 pages06 Nuclear PhysicsFrank MalengaNo ratings yet
- 4541/2 Kimia srk2 PHGDocument13 pages4541/2 Kimia srk2 PHGMd Shukri Ab GhaniNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesWorksheet ElectrolysislibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Surface Plasmon Enhanced, Coupled and Controlled FluorescenceFrom EverandSurface Plasmon Enhanced, Coupled and Controlled FluorescenceNo ratings yet
- CAPtain Online ExplainedDocument13 pagesCAPtain Online ExplainedRebekaNo ratings yet
- Fire PreventionDocument2 pagesFire PreventionMarlon Arian Conde AhorroNo ratings yet
- Key Aura FactsDocument17 pagesKey Aura FactspatoNo ratings yet
- Ends With 2 Cells Original Homologous Pairs Separate Ending Human Cells Have 46 Starts With One Cell Sister Chromatids SeparateDocument18 pagesEnds With 2 Cells Original Homologous Pairs Separate Ending Human Cells Have 46 Starts With One Cell Sister Chromatids SeparateProThaThaKing ClashNo ratings yet
- The Word Wall: Chants and Cheers ActivitiesDocument5 pagesThe Word Wall: Chants and Cheers Activitieseva.bensonNo ratings yet
- (Medbook4u Com) IllBaby1Document693 pages(Medbook4u Com) IllBaby1Certificate SurrenderNo ratings yet
- About EthiopianDocument7 pagesAbout EthiopianTiny GechNo ratings yet
- Ageing Aura and Vanitas in Art Greek LauDocument31 pagesAgeing Aura and Vanitas in Art Greek LautaraselbulbaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesRussel RapisoraNo ratings yet
- Hank Kolb 3Document3 pagesHank Kolb 3gr8_amaraNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in The Outdoors 1Document13 pagesRisk Management in The Outdoors 1api-278802103No ratings yet
- UGWT Lecture 1 To 6Document83 pagesUGWT Lecture 1 To 6Meesam AliNo ratings yet
- Mikala Conway - Meal PlanDocument3 pagesMikala Conway - Meal Planmikala conwayNo ratings yet
- Pdvsa: Engineering Design ManualDocument2 pagesPdvsa: Engineering Design ManualElvina Sara Sucre BuenoNo ratings yet
- MatrixDocument30 pagesMatrixauras2065No ratings yet
- IP-16-11-01 Neutral Grounding ResistorsDocument1 pageIP-16-11-01 Neutral Grounding ResistorsHarold Gutierrez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Cyclotron PDFDocument5 pagesCyclotron PDFRaju YadavNo ratings yet
- BI Strategy Roadmap Final v1.3Document201 pagesBI Strategy Roadmap Final v1.3Ange OraudNo ratings yet
- Transform Techniques For Error Control Codes: R. E. BlahutDocument17 pagesTransform Techniques For Error Control Codes: R. E. BlahutFjolla AdemajNo ratings yet
- "The Pedestrian" By: Rey BradburyDocument7 pages"The Pedestrian" By: Rey BradburyGabBragatNo ratings yet
- Math in Focus 3B WorksheetDocument6 pagesMath in Focus 3B WorksheetBobbili PooliNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System StimulantsDocument6 pagesCentral Nervous System StimulantsNathalia CabalseNo ratings yet
- Ethylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process BrochureDocument4 pagesEthylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process Brochurerkapoor584199No ratings yet
- Home Remedies For PneumoniaDocument15 pagesHome Remedies For PneumoniaAljunBaetiongDiazNo ratings yet
- Bad For Democracy How The Presidency Undermines The Power of The PeopleDocument272 pagesBad For Democracy How The Presidency Undermines The Power of The PeoplePaulNo ratings yet
- FLOWERSDocument1 pageFLOWERSikkopal92No ratings yet
- An Anatomy of Serial Killers PDFDocument13 pagesAn Anatomy of Serial Killers PDFHoracio B. RiveraNo ratings yet