Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Presentation 1
Untitled Presentation 1
Uploaded by
api-6265415370 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views16 pagesThis document discusses basic electrical components and their symbols. It explains the differences between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), and defines common circuit types like series and parallel. Key components covered include resistors, capacitors, diodes, fuses, LEDs, transistors, integrated circuits, potentiometers, switches, and batteries. Each component has a specific purpose or function within an electrical circuit.
Original Description:
Original Title
untitled presentation 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses basic electrical components and their symbols. It explains the differences between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), and defines common circuit types like series and parallel. Key components covered include resistors, capacitors, diodes, fuses, LEDs, transistors, integrated circuits, potentiometers, switches, and batteries. Each component has a specific purpose or function within an electrical circuit.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views16 pagesUntitled Presentation 1
Untitled Presentation 1
Uploaded by
api-626541537This document discusses basic electrical components and their symbols. It explains the differences between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), and defines common circuit types like series and parallel. Key components covered include resistors, capacitors, diodes, fuses, LEDs, transistors, integrated circuits, potentiometers, switches, and batteries. Each component has a specific purpose or function within an electrical circuit.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 16
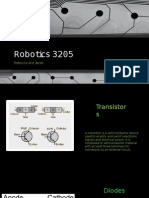
Basic Electrical
Components and Symbols
By Jacob Raymond
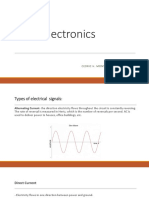
There are two types of electrical signals, those being alternate currents (AC) and direct
currents (DC).
AC
With an AC current, the direction of electricity flows throughout the circuit is
constantly reversing. Is the most cost effective way to transport large amounts of
electricity across distances.
DC
In DC currents electricity only flows in one direction between the power and the
ground. DC circuits can also be referred to as continuity circuits
On a battery:
Red is a positive charge
Black is a negative charge
Series Circuits
Series circuits create and unequal charge across multiple outputs.
Parallel Circuit
Parallel circuits share the electricity to the different outputs resulting in a more
evenly distributed output.
Resistors
● Have no polarity
● Read amount of resistance based on the color of bands
Capacitor
● Store energy in order to keep the amount of energy constant throughout the
circuit.
Diodes
Only allow electricity to flow one way meaning that they have polarity. An example
is an LED
Fuse
Designed to burn and end the circuit if electricity burns to hot. This prevents
damaging other parts of the circuit.
LED
A Light Emitting Diode which releases very little heat.
Transistors
Transistors takes small electrical currents into its base pin and amplifies it in a
much larger current that can pass through its collector and emitter pins.
Integrated Circuits
An integrated circuit is a specialized circuit that has been shrunk into one small
chip where each leg connects to the circuit.
Potentiometers
Potentiometers are variable resistors. It can be manually adjusted to change the
resistance in a circuit.
Switches
Switches are used to open and close circuits.
Batteries
A battery is a container which stores chemical energy and changes it into electrical
energy. Batteries are the power of the circuits.
You might also like
- Basic Electrical Components and Symbols 1Document17 pagesBasic Electrical Components and Symbols 1api-626396965No ratings yet
- Mikael Eury - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument19 pagesMikael Eury - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525646892No ratings yet
- Nithin Danday Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument20 pagesNithin Danday Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-527955670No ratings yet
- Ibrahim Aljanabi - Baisc Electrical TheoryDocument34 pagesIbrahim Aljanabi - Baisc Electrical Theoryapi-472643829No ratings yet
- Paraskevi Hofioni - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument20 pagesParaskevi Hofioni - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525648840No ratings yet
- Elizabeth Lynch - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument20 pagesElizabeth Lynch - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525692684No ratings yet
- Abdullah Mohammedi - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument23 pagesAbdullah Mohammedi - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525970410No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Components and SymbolsDocument15 pagesBasic Electrical Components and Symbolsapi-632266860No ratings yet
- Noor Al-Salehi - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument22 pagesNoor Al-Salehi - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525647046No ratings yet
- Robotics Electrical SchemtaicDocument22 pagesRobotics Electrical Schemtaicapi-382003348No ratings yet
- Robotics Electrical SchemtaicDocument22 pagesRobotics Electrical Schemtaicapi-381999763No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Components and SybolsDocument15 pagesBasic Electrical Components and Sybolsapi-626542959No ratings yet
- Jared Duran - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument19 pagesJared Duran - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525646997No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Components Used For Circuit DesigningDocument24 pagesBasic Electrical Components Used For Circuit DesigningGABRIELA ALEJANDRA LEON GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument20 pagesBasic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-529209276No ratings yet
- Week 4 - Ces - Grade 7 - Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesWeek 4 - Ces - Grade 7 - Basic Electronic ComponentsCarl Michael BermudezNo ratings yet
- Electrical ParametersDocument16 pagesElectrical Parametersapi-295377694No ratings yet
- ComponentsDocument16 pagesComponentsapi-626529144No ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components and SymbolsDocument12 pagesBasic Electronic Components and Symbolsapi-626528859No ratings yet
- Eec 115 Experiment I & IiDocument12 pagesEec 115 Experiment I & IiOreoluwa OmiyaleNo ratings yet
- Essential Electrical Components and How They Work Together To Create Incredible Modern Electrical SystemsDocument13 pagesEssential Electrical Components and How They Work Together To Create Incredible Modern Electrical SystemsSolomon GodwinNo ratings yet
- Electric Symbols: By: Sanchit Kanwar Class: X-C Roll No: 26Document29 pagesElectric Symbols: By: Sanchit Kanwar Class: X-C Roll No: 26Eliza Cortez CastroNo ratings yet
- SchematicsDocument10 pagesSchematicsapi-440143855No ratings yet
- Basic Electric Components and Symbols 1Document14 pagesBasic Electric Components and Symbols 1api-626528846No ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument16 pagesUntitled Presentationapi-626397135No ratings yet
- Electrical Component 2956Document15 pagesElectrical Component 2956api-626828415No ratings yet
- Circuits, EC, Symbols, SchematicDocument7 pagesCircuits, EC, Symbols, SchematicKyle Angelo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument12 pagesUntitled Presentationapi-525646969No ratings yet
- Term Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyDocument15 pagesTerm Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyVictor ImehNo ratings yet
- Cristobal Trujillo Gonzalez - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument22 pagesCristobal Trujillo Gonzalez - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525646588No ratings yet
- Quarter 4: Lesson:7 Testing Electronics ComponentsDocument15 pagesQuarter 4: Lesson:7 Testing Electronics Componentsjohnmel indananNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument9 pagesBasic Electronic ComponentsMackRoss PerezNo ratings yet
- Electroniccomponents-Tugas Menterjemahkan Dan Dibuat Power PointDocument18 pagesElectroniccomponents-Tugas Menterjemahkan Dan Dibuat Power PointTemals Dusngam100% (1)
- Basics of ElectronicsDocument15 pagesBasics of ElectronicsAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Signals, Circuits, and Computers: Part BDocument21 pagesSignals, Circuits, and Computers: Part BVeron Taguinod BungagNo ratings yet
- Jacob Hergert - Basic Electronics Components and Circuits 1Document19 pagesJacob Hergert - Basic Electronics Components and Circuits 1api-534579056No ratings yet
- Types of Diagram and SymbolsDocument7 pagesTypes of Diagram and SymbolsPrince John Rabano100% (1)
- Year 9 Electronics Component Revision 2022Document26 pagesYear 9 Electronics Component Revision 2022BigDaddy GNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument7 pagesPower SupplyAdam Syahmi RashadanNo ratings yet
- Robotics 3205Document7 pagesRobotics 3205api-295212456No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document7 pagesUnit 2api-296499245No ratings yet
- Basic Electric Components and SymbolsDocument13 pagesBasic Electric Components and Symbolsapi-626529107No ratings yet
- Capacitor: Some Publications Still Use The Old Resistor SymbolDocument6 pagesCapacitor: Some Publications Still Use The Old Resistor SymbolSarah Jane EgeraNo ratings yet
- Condenser.: Capacitor - in A Way, A Capacitor Is A Little Like A Battery. Although They Work in Completely Different WaysDocument8 pagesCondenser.: Capacitor - in A Way, A Capacitor Is A Little Like A Battery. Although They Work in Completely Different WaysJuan DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Electricity DefinitionDocument18 pagesElectricity DefinitionSumolmal Srisukri100% (1)
- Attachment - 1434787422739 - Familarization With Discrete ComponentsDocument14 pagesAttachment - 1434787422739 - Familarization With Discrete ComponentsRajan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics NotesDocument5 pagesBasic Electronics NotesRolando Carlos FloresNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component, Uses and SymbolDocument18 pagesElectronic Component, Uses and SymbolMuhammad Fahad LatifNo ratings yet
- Electrical ParametersDocument6 pagesElectrical Parametersapi-295377491No ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument10 pagesBasic ElectronicsCedric MontianoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component, Uses and SymbolDocument19 pagesElectronic Component, Uses and SymbolPrinces Joan JuacallaNo ratings yet
- Physics2 CapacitorsDocument13 pagesPhysics2 CapacitorsRestian Lezlie AlvaranNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Electronic Components: Santosh DasDocument5 pagesActive and Passive Electronic Components: Santosh DasCaroline Nikka M. PitloNo ratings yet
- Electronics For Mechanical EngineersDocument35 pagesElectronics For Mechanical EngineersRamanujam O SNo ratings yet
- Resistors: PotentiometerDocument48 pagesResistors: PotentiometerjojoNo ratings yet
- PW5 ElectronicsDocument29 pagesPW5 ElectronicsMichael KavanaghNo ratings yet
- Wires and ConnectionsDocument22 pagesWires and ConnectionsDanilo AlbayNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit ComponentsDocument3 pagesBasic Circuit ComponentsJhoker SudzNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)