Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 EE303 Linear Control Systems
2 EE303 Linear Control Systems
Uploaded by
Jeril jose0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThe document describes a course on linear control systems. The course has 6 modules that cover topics like transfer functions, time and frequency domain analysis, stability analysis using Root Locus and Nyquist criteria. Assessment includes 2 internal exams and an end semester exam with questions from all modules. The course aims to develop students' ability to model dynamic systems and analyze stability of linear time-invariant systems.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes a course on linear control systems. The course has 6 modules that cover topics like transfer functions, time and frequency domain analysis, stability analysis using Root Locus and Nyquist criteria. Assessment includes 2 internal exams and an end semester exam with questions from all modules. The course aims to develop students' ability to model dynamic systems and analyze stability of linear time-invariant systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pages2 EE303 Linear Control Systems
2 EE303 Linear Control Systems
Uploaded by
Jeril joseThe document describes a course on linear control systems. The course has 6 modules that cover topics like transfer functions, time and frequency domain analysis, stability analysis using Root Locus and Nyquist criteria. Assessment includes 2 internal exams and an end semester exam with questions from all modules. The course aims to develop students' ability to model dynamic systems and analyze stability of linear time-invariant systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
KTUQBANK.
COM
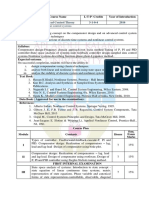
Course Name L-T-P - Year of
Course Credits Introduction
code
EE303 Linear Control Systems 2-1-0-3 2016
Prerequisite: Nil
Course Objectives:
To provide a strong foundation on the analytical and design techniques on classical control theory
and modelling of dynamic systems
Syllabus :
Open loop-and closed loop control systems- Transfer function - Control system components-Steady stare
error- static error coefficient- dynamic error coefficient-Stability Analysis- Root locus- Frequency domain
analysis-Bode plot-polar plot-Nyquist stability criterion- Non-minimum phase system - transportation lag.
Expected outcome.
The students will have the ability to
i. develop mathematical models of various systems.
ii. analyse the stability aspects of linear time invariant systems.
Text Books:
1) Dorf R. C. and R. H. Bishop, Modern Control Systems, Pearson Education, 2011.
2) Nagarath I. J. and Gopal M., Control System Engineering, Wiley Eastern, 2008.
3) Nise N. S., Control Systems Engineering, 6/e, Wiley Eastern, 2010.
4) Ogata K., Modern Control Engineering, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2010.
References:
1) Gibson J. E., F. B. Tuteur and J. R. Ragazzini, Control System Components, Tata McGraw Hill,
2013
2) Gopal M., Control Systems Principles and Design, Tata McGraw Hill, 2008.
3) Imthias Ahamed T P, Control Systems, Phasor Books, 2016
4) Kuo B. C., Automatic Control Systems, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2002.
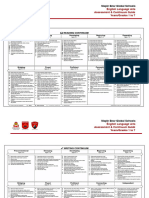
Course Plan
Sem.
Module Contents Hours Exam
Marks
Open loop-and closed loop control systems: Transfer function of LTI
systems-Mechanical and Electromechanical systems – Force voltage and
I force current analogy - block diagram representation - block diagram 8 15%
reduction - signal flow graph - Mason's gain formula - characteristic
equation.
Control system components: DC and AC servo motors – synchro -
gyroscope - stepper motor - Tacho generator.
II Time domain analysis of control systems: Transient and steady state 6 15%
responses - time domain specifications - first and second order systems -
step responses of first and second order systems.
FIRST INTERNAL EXAMINATION
Error analysis - steady state error analysis - static error coefficient of type
0,1, 2 systems - Dynamic error coefficients.
III 7 15%
Concept of stability: Time response for various pole locations - stability of
feedback system - Routh's stability criterion
Root locus - General rules for constructing Root loci – stability from root
IV 7 15%
loci - effect of addition of poles and zeros.
SECOND INTERNAL EXAMINATION
Frequency domain analysis: Frequency domain specifications- Analysis
V 7 20%
based on Bode plot - Log magnitude vs. phase plot,
Credits :- APJ KTU | Fair Use Policy
KTUQBANK.COM
Polar plot- Nyquist stability criterion-Nichols chart - Non-minimum phase
VI 7 20%
system - transportation lag.
END SEMESTER EXAM
QUESTION PAPER PATTERN:
Maximum Marks: 100 Exam Duration: 3Hourrs.
Part A: 8 compulsory questions.
One question from each module of Modules I - IV; and two each from Module V & VI.
Student has to answer all questions. (8 x5)=40
Part B: 3 questions uniformly covering Modules I & II. Student has to answer any 2 from the 3
questions: (2 x 10) =20. Each question can have maximum of 4 sub questions (a,b,c,d), if needed.
Part C: 3 questions uniformly covering Modules III & IV. Student has to answer any 2 from the 3
questions: (2 x 10) =20. Each question can have maximum of 4 sub questions (a,b,c,d), if needed.
Part D: 3 questions uniformly covering Modules V & VI. Student has to answer any 2 from the 3
questions: (2 x 10) =20. Each question can have maximum of 4 sub questions (a,b,c,d), if needed.
Credits :- APJ KTU | Fair Use Policy
You might also like
- Jntuk Eee 4-2 Sem Syllabus Book (R10)Document23 pagesJntuk Eee 4-2 Sem Syllabus Book (R10)Venkat KickNo ratings yet
- Handouts For Inventories: A. This Fact Must Be DisclosedDocument7 pagesHandouts For Inventories: A. This Fact Must Be DisclosedDenver Legarda100% (1)
- Exegetical Dictionary of The New TestamentDocument4 pagesExegetical Dictionary of The New Testamentmung_khat0% (2)
- Course Code: EE303 Linear Control Systems 2-1-0-3 2016 Prerequisite: NilDocument2 pagesCourse Code: EE303 Linear Control Systems 2-1-0-3 2016 Prerequisite: NilSUNOBHAINo ratings yet
- EE484 Control SystemsDocument2 pagesEE484 Control Systemssaheedahmd0112No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Control Engineering Subject B.E. 5 SemesterDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Control Engineering Subject B.E. 5 Semesterishan shahNo ratings yet
- Control Theory SYLLABUSDocument3 pagesControl Theory SYLLABUSjustlearn369963No ratings yet
- CS R-16 SyllabusDocument3 pagesCS R-16 SyllabusSai tejaswiNo ratings yet
- EE304 Advanced Control TheoryDocument2 pagesEE304 Advanced Control TheorySha MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Mechanical Engineering (19) SUBJECT CODE: 2151908Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Mechanical Engineering (19) SUBJECT CODE: 2151908Mulu GirmayNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University II Year B.Tech. ECE. Il-Sem T P 0 C Control SystemsDocument1 pageJawaharlal Nehru Technological University II Year B.Tech. ECE. Il-Sem T P 0 C Control SystemsappuamreddyNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument2 pagesControl SystemsrahulwasthereNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3AADITYA SHAHNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Alok MauryaNo ratings yet
- IC301 Control Engineering-IDocument3 pagesIC301 Control Engineering-IAKSHAY KRISHNA K RNo ratings yet
- CS SyllabusDocument2 pagesCS SyllabusEEE ACEECNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 6 EeeDocument11 pagesSyllabus 6 EeeSUMIT RAJNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control System SyllabusDocument3 pagesFeedback Control System SyllabusDamanMakhijaNo ratings yet
- Control Unit 1Document37 pagesControl Unit 1AnshNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Control Systems ECE R13Document2 pagesSyllabus Control Systems ECE R13tansnvarmaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Aeronautical Engineering Subject CodeDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological University: Aeronautical Engineering Subject CodeHarnil VaghasiyaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus GTU PDFDocument3 pagesSyllabus GTU PDFkalpesh_chandakNo ratings yet
- EE306 Power System AnalysisDocument2 pagesEE306 Power System AnalysisPriyadarshini SahooNo ratings yet
- English TutorialDocument145 pagesEnglish Tutorialkrunal tripathiNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument70 pagesLecture NotesPrathamraj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University Biomedical EngineeringDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University Biomedical EngineeringMandy745No ratings yet
- EE201 Circuits N NetworksDocument2 pagesEE201 Circuits N NetworksArya ANo ratings yet
- 6th Sem EEE 18Document28 pages6th Sem EEE 18Iqbal Ahammed KaladgikarNo ratings yet
- MLRS R20 - CS SyllabusDocument2 pagesMLRS R20 - CS Syllabusrupa kumar dhanavathNo ratings yet
- EE306 Power System Analysis PDFDocument2 pagesEE306 Power System Analysis PDFCharles Joseph LukeNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument160 pagesControl SystemsPintu DeyNo ratings yet
- E2 Linear Control Systems SyllabusDocument2 pagesE2 Linear Control Systems SyllabussasikalaNo ratings yet
- ETR6C3Document3 pagesETR6C3Shikha PatelNo ratings yet
- ME362 Control System EngineeringDocument2 pagesME362 Control System Engineeringrashad kNo ratings yet
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiDocument25 pagesChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- CS Syllabus JntukDocument2 pagesCS Syllabus JntukEEE CRRNo ratings yet
- Control System Ece QB EeeeeeeDocument73 pagesControl System Ece QB EeeeeeeARNI JAYACHANDRANo ratings yet
- Control System EngineeringDocument2 pagesControl System EngineeringGokulNo ratings yet
- Courses of Study: T. Y. B. Tech. (Instrumentation) For The Batch Registering in 2006-07Document20 pagesCourses of Study: T. Y. B. Tech. (Instrumentation) For The Batch Registering in 2006-07Vaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Control System EngineeringDocument3 pagesControl System Engineeringnisarg0% (1)
- Automatic Control (ME1401)Document2 pagesAutomatic Control (ME1401)Mehroos AliNo ratings yet
- CBGS 7 Sem 20-21290521110137Document18 pagesCBGS 7 Sem 20-21290521110137kushagra vashishthaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech, EE, 5th Sem, 2018-19 BatchDocument19 pagesB.Tech, EE, 5th Sem, 2018-19 BatchBijayKumarDasNo ratings yet
- Banasthali University Department of Electronics Course Handout Class: B.Tech. (EC) 6 SemDocument2 pagesBanasthali University Department of Electronics Course Handout Class: B.Tech. (EC) 6 SemVipan SharmaNo ratings yet
- EE311 SyllabusDocument1 pageEE311 SyllabusVenkatesh GogineniNo ratings yet
- Advanced Control Systems SyllabusDocument2 pagesAdvanced Control Systems SyllabusMulu GirmayNo ratings yet
- Autonomous College Under VTU - Accredited by NBA - Approved by AICTEDocument3 pagesAutonomous College Under VTU - Accredited by NBA - Approved by AICTESureshNo ratings yet
- Control Systems (9171)Document5 pagesControl Systems (9171)Victoria Franco0% (1)
- TE Part I Electrical Engg. 2014Document37 pagesTE Part I Electrical Engg. 2014sordfish143No ratings yet
- Modern Control TheoryDocument137 pagesModern Control TheorypragatinareshNo ratings yet
- EED-412 Slide Set-I - ShareDocument74 pagesEED-412 Slide Set-I - ShareDevangi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. Power Systems & Automation PDFDocument17 pagesM.Tech. Power Systems & Automation PDFPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- M.Tech PSADocument17 pagesM.Tech PSASwathi AllipilliNo ratings yet
- Ec1304 Control Systems 3 1 0 100Document1 pageEc1304 Control Systems 3 1 0 100Anupama RaghavendranNo ratings yet
- Third Year 5 Semester Syllabus: (Applicable From The Academic Session 2018-2019)Document23 pagesThird Year 5 Semester Syllabus: (Applicable From The Academic Session 2018-2019)Tignangshu ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- CONTROL SYSTEMS (Core Subject) B.E., VI Semester, Electrical and Electronics Engineering (As Per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Scheme)Document2 pagesCONTROL SYSTEMS (Core Subject) B.E., VI Semester, Electrical and Electronics Engineering (As Per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Scheme)tabassNo ratings yet
- SallyubusDocument61 pagesSallyubusravindra898233No ratings yet
- EC409 Control Systems (CareerYuga)Document3 pagesEC409 Control Systems (CareerYuga)jinto0007No ratings yet
- BME-O533 All Unit AssignmentDocument6 pagesBME-O533 All Unit Assignment216310018No ratings yet
- Multiple Models Approach in Automation: Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy SystemsFrom EverandMultiple Models Approach in Automation: Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy SystemsNo ratings yet
- Mayring 2000 - Qualitative Content AnalysisDocument10 pagesMayring 2000 - Qualitative Content Analysispist81100% (2)
- Transducers Engineering Notes PDFDocument110 pagesTransducers Engineering Notes PDFThamilarasan VNo ratings yet
- 7 Web DesignDocument39 pages7 Web DesignBladdesuriNo ratings yet
- The Socio-Economic Significance of Food DesertsDocument1 pageThe Socio-Economic Significance of Food Desertsapi-466415791No ratings yet
- Gold Sluice Box LegsDocument3 pagesGold Sluice Box LegsEricNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Special Education in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesTimeline of Special Education in The PhilippinesIchien SomelhigNo ratings yet
- Partner PPT VC15Document52 pagesPartner PPT VC15Biswabhusan PradhanNo ratings yet
- 2017 Unesco StyleDocument27 pages2017 Unesco StyleLittlequanNo ratings yet
- Transparent Governance in An Age of AbundanceDocument452 pagesTransparent Governance in An Age of AbundancePamela GaviñoNo ratings yet
- Activity Week 14 PROJECT 2-9ºDocument3 pagesActivity Week 14 PROJECT 2-9ºTheSeul SNo ratings yet
- TERM 1 Half SYLLABUS PDFDocument5 pagesTERM 1 Half SYLLABUS PDFranjanjhallbNo ratings yet
- Modern Methods of ConstructionDocument18 pagesModern Methods of Constructionhiren_1810No ratings yet
- Boppps DetailDocument10 pagesBoppps DetailMUHAMMAD SAYYIDNo ratings yet
- Nucl - Phys.B v.594Document784 pagesNucl - Phys.B v.594buddy72No ratings yet
- ELA Continuum Y1 To Y7Document7 pagesELA Continuum Y1 To Y7meryem rhimNo ratings yet
- CH 01 PPTaccessibleDocument62 pagesCH 01 PPTaccessibleSaltanat ShamovaNo ratings yet
- List of Red-Light Districts: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument32 pagesList of Red-Light Districts: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchsudeepomNo ratings yet
- Atm / Debit Card Application Form: Khumneicha G A O NG NDocument2 pagesAtm / Debit Card Application Form: Khumneicha G A O NG NLalrinpuii Joute0% (1)
- Turning Your Vision Into Reality Worksheet PDFDocument7 pagesTurning Your Vision Into Reality Worksheet PDFSHASHANKNo ratings yet
- BadmintonDocument11 pagesBadmintonIsabel Sanchez80% (5)
- Noise Pollution and Its Control at Construction SiteDocument14 pagesNoise Pollution and Its Control at Construction SiteAbhishek KadianNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Cultural Diversity: Practice TestDocument6 pagesUnit 7. Cultural Diversity: Practice TestLong ĐứcNo ratings yet
- J.w.mackail - Select Epigrams From The Greek Anthology (1890)Document197 pagesJ.w.mackail - Select Epigrams From The Greek Anthology (1890)Ashraf MagedNo ratings yet
- An Exposition of The Seven Church Ages VGRDocument33 pagesAn Exposition of The Seven Church Ages VGREmmanuelNo ratings yet
- The Case For A Post-Tribulation RaptureDocument18 pagesThe Case For A Post-Tribulation RaptureDonovan Neufeldt100% (1)
- Hepatology MRCP1Document87 pagesHepatology MRCP1Raouf Ra'fat SolimanNo ratings yet
- Fifth SunDocument337 pagesFifth Sundhana sekaran100% (6)
- Water PumpsDocument4 pagesWater PumpsEphremHailuNo ratings yet