Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrochemistry Study Guide
Electrochemistry Study Guide
Uploaded by
jeek ekekOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrochemistry Study Guide
Electrochemistry Study Guide
Uploaded by
jeek ekekCopyright:
Available Formats
Name Date Class
ELECTROCHEMISTRY
Study Guide
A. Matching
Match each term in Column B to the correct description in Column A.
Column A Column B
1. a conductor in a circuit that carries electrons to or from a. anode
a substance other than a metal
2. one part of a voltaic cell, in which either oxidation or b. electrode
reduction occurs
3. a voltaic cell in which the electrolyte is a paste c. cathode
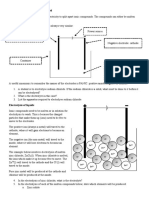
4. the electrode at which reduction occurs d. dry cell
5. a voltaic cell in which a fuel undergoes oxidation and e. battery
from which electrical energy is obtained continuously
6. an electrochemical cell that is used to convert chemical f. electrolysis
energy into electrical energy
7. a tube containing a conducting solution g. voltaic cell
8. a group of cells that are connected together h. half-cell
9. the process in which electrical energy is used to bring
about a chemical change i. salt bridge
10. the electrode at which oxidation occurs j. fuel cell
B. Multiple Choice
Choose the best answer and write its letter on the line.
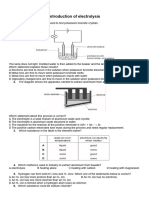
11. In the electrolysis of brine, the substance produced at the cathode is
a. chlorine. c. sodium.
b. oxygen. d. hydrogen.
12. Which of the following describes a dry cell?
a. It can be recharged many times.
b. The graphite rod does not undergo reduction, even though it is the cathode.
c. It contains concentrated sulfuric acid.
d. all of the above
554 Core Teaching Resources
Name Date Class
13. A clean strip of copper is dipped into a solution of magnesium sulfate. Magnesium is above the copper in
the activity series of metals. Predict what you will observe.
a. The copper strip becomes magnesium-plated.
b. Copper dissolves and the solution turns blue.
c. No reaction occurs.
d. Bubbles of hydrogen gas appear on the copper.
14. A clean iron nail is dipped into a solution of silver nitrate. Iron is above silver in the activity series of
metals. Predict what you will observe.
a. The iron will be reduced.
b. Bubbles of nitrogen gas will form on the iron nail.
c. The iron nail will become silver-plated.
d. No reaction occurs.
15. In a fully charged lead storage battery, the cathode grid is packed with
a. spongy lead. c. lead(IV) oxide.
b. lead sulfate. d. sulfuric acid.
16. Which of the following is true about fuel cells?
a. They can be designed so that they emit no pollutants.
b. They are inexpensive.
c. They have never been built or used.
d. They produce energy in short bursts only.
17. Which of the following is true for an electrolytic cell?
a. It changes electrical energy into chemical energy.
b. It is the type of cell used in electroplating.
c. It uses an electric current to make a nonspontaneous reaction go.
d. all of the above
18. When a lead storage battery discharges
a. the concentration of lead sulfate in the battery decreases.
b. the concentration of sulfuric acid increases.
c. the concentration of sulfuric acid decreases.
d. none of the above
19. A zinc-copper cell is constructed:
Zn | Zn2+ (1M) || Cu2+ (1M) | Cu
What occurs to the mass of the copper electrode as the reaction proceeds? (Zinc is above copper in the
activity series of metals.)
a. It increases. c. It decreases.
b. It remains the same.
20. In the cell reaction described in question 19, the negative electrode is
a. Zn(s). c. Zn2+(aq).
b. Cu2+(aq). d. Cu(s).
21. Which half-reaction occurs at the negative electrode in an electrolytic cell in which an object is being
plated with silver?
a. Ag + 1e– → Ag+ c. Ag+ + 1e– → Ag
b. Ag → Ag+ + 1e– d. Ag+ → Ag + 1e–
Chapter 21 Electrochemistry 555
Name Date Class
22. Which metal will react spontaneously with Cu2+(aq) at 25°C?
a. Ag c. Mg
b. Au d. Hg
23. Which reaction occurs when bromine is added to an aqueous solution of iodide ions?
a. 2I– + Br2 → I2 + 2Br– c. 2I– + 2Br– → I2 + Br2
–
b. I2 + 2Br → Br2 + 2I d. I2 + Br2 → 2I– + 2Br–
24. Which ion can be most easily reduced?
a. Cu2+ c. Fe2+
b. Zn2+ d. Ca2+
25. Oxygen and copper are produced during the electrolysis of a CuO solution. Which reaction occurs at the
negative electrode?
a. Oxygen ions are reduced. c. Copper ions are reduced.
b. Oxygen atoms are oxidized. d. Copper atoms are oxidized.
C. True-False
Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
26. During the electrolysis of brine, chlorine gas is produced at the cathode.
27. Copper is above gold in the activity series of metals because copper is less reactive and less easily
oxidized.
28. The oxidation half-reaction in a voltaic cell occurs at the anode.
29. Cell potential is the sum of the reduction potential of the half-cell where reduction occurs and the
reduction potential of the half-cell where oxidation occurs.
30. In an electrolytic cell, oxidation occurs at the cathode, and reduction occurs at the anode.
D. Question
Answer the following question in the space provided.
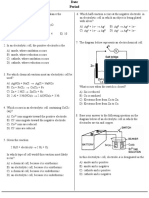
31. Draw a voltaic cell. Label the cathode, anode, salt bridge, and direction of the flow of electrons.
556 Core Teaching Resources
Name Date Class
E. Essay
Write a short essay for the following.
32. State the sign of the electrodes and the reaction that occurs at each electrode for both voltaic and electrolytic cells.
F. Additional Questions
Answer the following questions in the space provided.
33. The standard reduction potential for the cobalt half-cell is –0.28 V. What is the significance of the negative value?
(Refer to the standard hydrogen half-cell in your answer.)
34. What is meant by the reduction potential of a half-cell?
35. Are the following redox reactions spontaneous as written? (Use the information in the Reference Section. Show your
work.)
a. Ni(s) + Zn2+(aq) → Ni2+(aq) + Zn(s)
b. 3Co(s) + 2Al3+(aq) → 3Co2+(aq) + 2Al(s)
Reference Section
Reduction Potentials at 25°C
Electrode Half-Reaction E0(V)
Al3+/Al Al3+ + 3e– → Al –1.66
2+ 2+ –
Zn /Zn Zn + 2e → Zn –0.76
Co2+/Co Co2+ + 2e– → Zn –0.28
2+ 2+ –
Ni /Ni Ni + 2e → Ni –0.25
Chapter 21 Electrochemistry 557
You might also like
- Redox Test 2Document8 pagesRedox Test 2Arhum AliNo ratings yet
- FLR - Heat Losses in Bare and Lagged Pipes and Finned TubesDocument12 pagesFLR - Heat Losses in Bare and Lagged Pipes and Finned TubesNazario Emil Lintag50% (2)
- Revision Test Electrolysis OlevelsDocument5 pagesRevision Test Electrolysis OlevelsMomin BabarNo ratings yet
- Akhilesh Gogikar - Term PaperDocument7 pagesAkhilesh Gogikar - Term PaperdomNo ratings yet
- Redox and Electrochem Review Multiple Choice Eboard AnswersDocument4 pagesRedox and Electrochem Review Multiple Choice Eboard AnswersKhaledEl-MaghallawyNo ratings yet
- Redox QuizzesDocument9 pagesRedox Quizzesoscarball06No ratings yet
- Read These Instructions FirstDocument7 pagesRead These Instructions FirstSalman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 4 NotesDocument18 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 4 Notesaminata13536No ratings yet
- WS4,5,6,7 WK 16-20 Aug Energy and Chemicals Class 10 ZoyaDocument18 pagesWS4,5,6,7 WK 16-20 Aug Energy and Chemicals Class 10 ZoyaUsman AsmatullahNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Reactions: + Battery - Salt BridgeDocument7 pagesElectrochemical Reactions: + Battery - Salt BridgewscienceNo ratings yet
- MT Reviewer Enchem 114 1Document8 pagesMT Reviewer Enchem 114 1Charles Balf CadungoNo ratings yet
- Revision-2 - On ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesRevision-2 - On ElectrochemistryKiro RemonNo ratings yet
- CHM13P Learning Task 5Document6 pagesCHM13P Learning Task 5Paolo Gochingco0% (3)
- Chapter 10 Electrochemistry Text Book ExerciseDocument31 pagesChapter 10 Electrochemistry Text Book ExerciseshahidkakaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 19 MC PracticeDocument18 pagesTopic 9 19 MC PracticeDharmesh Ramnarayan Yadav100% (1)
- Redox Practice Test 1Document21 pagesRedox Practice Test 1Edon BediNo ratings yet
- 4TH QUARTER EXAM ADVANCE CHEM - EditedDocument2 pages4TH QUARTER EXAM ADVANCE CHEM - EditedWilsonNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry With AnswersDocument27 pagesElectrochemistry With AnswersKris CruzNo ratings yet
- AP Unit10 Worksheet AnswersDocument4 pagesAP Unit10 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- 25 E28093 Eletroquimica IDocument22 pages25 E28093 Eletroquimica INatinha32No ratings yet
- There Are 50 Questions in This Paper. Choose The Best Answer For Each QuestionDocument21 pagesThere Are 50 Questions in This Paper. Choose The Best Answer For Each Questionapi-19650882No ratings yet
- SS2 CHEMISTRY TEST ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesSS2 CHEMISTRY TEST Electrolysisforthland consultingNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Notes Top ClassDocument13 pagesElectrochemistry Notes Top ClassSriyansh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit10 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit10 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Gems Genesis: 9caieDocument4 pagesGems Genesis: 9caieBhavya darjiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument5 pagesElectrochemical Cellssanjeevkumarmaner90No ratings yet
- Galvanic CellDocument2 pagesGalvanic Cellpana0048No ratings yet
- Mypchem Ch10answersDocument3 pagesMypchem Ch10answersPikunoShuousNo ratings yet
- Redox Practice Test 2Document22 pagesRedox Practice Test 2Sam KothuriNo ratings yet
- 4 - Electrolysis MCQ SolutionsDocument4 pages4 - Electrolysis MCQ SolutionsNasreen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (1) RevisionDocument10 pagesChemistry (1) RevisionJesse ChimnecheremNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis QuestionsDocument53 pagesElectrolysis QuestionsAahaan ShethNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Lesson (1) EasyDocument12 pagesCh.4 Lesson (1) EasyShahd WaelNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 3Document22 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 3Deepak PradhanNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th ElectrolysisDocument6 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Electrolysisspurohit1991No ratings yet
- CHE1010 Tutorial Sheet 5Document4 pagesCHE1010 Tutorial Sheet 5Chimuka Onson MapikiNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis MasteryDocument8 pagesElectrolysis MasteryDonald ZhuoNo ratings yet
- 2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersDocument9 pages2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersThanabalan MunuswamyNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesExam 3 Review QuestionsJeremy TohNo ratings yet
- LXL - Gr12PhysicalSciences - 27 - Redox Reactions - 02sep2014Document5 pagesLXL - Gr12PhysicalSciences - 27 - Redox Reactions - 02sep2014HNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry and Electrolysis MCQ - Class 10Document11 pagesAnalytical Chemistry and Electrolysis MCQ - Class 10PdkNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument33 pagesElectrolysisborglingchompersNo ratings yet
- Redox WS QB 1Document3 pagesRedox WS QB 1vengateshwaran kNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Electrochemistry QuestionsDocument4 pagesClass 12 Electrochemistry QuestionsShifaNo ratings yet
- Exam Chew 1Document7 pagesExam Chew 1ThilagaNo ratings yet
- Class X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyDocument4 pagesClass X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyToshiGMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- BA 118 Smart Village Revision ModifiedDocument16 pagesBA 118 Smart Village Revision Modifiedhana mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Cmt555: Experiment 1: Galvanic & Electrolytic CellDocument11 pagesLab Report: Cmt555: Experiment 1: Galvanic & Electrolytic CellkuekNo ratings yet
- Your Mistakes Are Proof That You Are TryingDocument10 pagesYour Mistakes Are Proof That You Are TryingAtta ur rafayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Document9 pagesWorksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Dagim YenenehNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Text SolnDocument38 pagesElectrolysis Text Solnhemanth PNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 01 PDFDocument9 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 01 PDFYamini ChandelNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesElectrochemistryDhanush SNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Document4 pagesWorksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Jeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Electrochemistry MCQsDocument29 pagesChapter 3 Electrochemistry MCQssarudarshinij.s123No ratings yet
- S3 THM Chemistry CA2 20 - 21Document6 pagesS3 THM Chemistry CA2 20 - 21Ahnt htoo aungNo ratings yet
- ElecrochemistryDocument7 pagesElecrochemistryffxfuddiNo ratings yet
- 10+2 Assignment-3 - Electrochemistry - ChemistryDocument8 pages10+2 Assignment-3 - Electrochemistry - ChemistrySarthak KawatraNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument6 pagesElectrochemistrytwinkleparmar0064No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry PreparatoryDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry Preparatorynithinkumarin2006No ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Simple Chemical CellsDocument2 pagesChapter 22 Simple Chemical CellssliversniperNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fracture Toughness of CA6NM Alloy, Quenched and Tempered, and of Its Welded Joint Without PWHTDocument8 pagesFracture Toughness of CA6NM Alloy, Quenched and Tempered, and of Its Welded Joint Without PWHTHenry León HenaoNo ratings yet
- HPC 30 - 1 Service ManualDocument76 pagesHPC 30 - 1 Service ManualAlexanderNo ratings yet
- 3314 Ijmech 11Document8 pages3314 Ijmech 11Burak KoyuncuogluNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower JogenderDocument37 pagesCooling Tower JogenderjogedhayalNo ratings yet
- Material and MethodsDocument2 pagesMaterial and MethodsBarinderjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operating Instructions: Busch Produktions GMBH Schauinslandstr. 1 79689 Maulburg GermanyDocument28 pagesInstallation and Operating Instructions: Busch Produktions GMBH Schauinslandstr. 1 79689 Maulburg GermanyRenārs BērtiņšNo ratings yet
- Section Cut in ETABSDocument20 pagesSection Cut in ETABSryan rakhmat setiadiNo ratings yet
- Colloid Chemistry: Lecture 13: EmulsionsDocument55 pagesColloid Chemistry: Lecture 13: Emulsionsgaurav chauhanNo ratings yet
- PumpsDocument33 pagesPumpsSamson HaykonNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - 2.1 Mechanical OperationsDocument34 pagesTopic 2 - 2.1 Mechanical OperationsAmeen HussainNo ratings yet
- Prelims - PPEDocument1 pagePrelims - PPENathanielle AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Elastic CollisionDocument3 pagesElastic CollisionAuden HopeNo ratings yet
- Bearing For Cement Industry - NDocument20 pagesBearing For Cement Industry - NAjanta Bearing100% (1)
- GeowebbDocument48 pagesGeowebbLuis MoralesNo ratings yet
- 4104 A Study - Material 1 (Mossbauer Spectroscopy)Document21 pages4104 A Study - Material 1 (Mossbauer Spectroscopy)GuRi JassalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document149 pagesChapter 2A LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Eagle Brochure 5Document3 pagesEagle Brochure 5Adnan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Technical YLAEDocument16 pagesTechnical YLAEnairam2003No ratings yet
- Physical: MetallurgyDocument4 pagesPhysical: MetallurgySanjanaNo ratings yet
- Main Pattern Part Test-3 (Mpt-3) : Batch: (JP, JPS, JF, JD, JR, JRS, Ep, Ef, Ed, Er) Revision Plan-3Document43 pagesMain Pattern Part Test-3 (Mpt-3) : Batch: (JP, JPS, JF, JD, JR, JRS, Ep, Ef, Ed, Er) Revision Plan-3aditi singhNo ratings yet
- Scalar Wave Energy As WeaponDocument53 pagesScalar Wave Energy As Weapontriple7incNo ratings yet
- IAL Physics SB2 Answers 6CDocument3 pagesIAL Physics SB2 Answers 6CsalmaNo ratings yet
- Design of Semi-Rigid Steel Frames For Failure Mode ControlDocument23 pagesDesign of Semi-Rigid Steel Frames For Failure Mode ControlVincenzo PilusoNo ratings yet
- Coatings 11 01457Document12 pagesCoatings 11 01457Jordan DsNo ratings yet
- Metals Used in ProsthodonticsDocument43 pagesMetals Used in ProsthodonticsnavneetkhanNo ratings yet
- Anti Static Flooring SpecificationDocument1 pageAnti Static Flooring SpecificationSAGAR PAREEKNo ratings yet
- Pump BrochureDocument10 pagesPump Brochuresen_subhasis_58100% (1)