Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AD Moradabad Pre Visit
AD Moradabad Pre Visit
Uploaded by
SAHIL JAINCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The City Assembled: By: Spiro KostofDocument29 pagesThe City Assembled: By: Spiro KostofSneha PeriwalNo ratings yet
- Croak by Gina Damico ExcerptDocument29 pagesCroak by Gina Damico ExcerptHoughton Mifflin Harcourt0% (1)
- Shahjahanabad (The Walled City of Delhi)Document27 pagesShahjahanabad (The Walled City of Delhi)Priyesh Dubey94% (18)
- Phases of A ProjectDocument9 pagesPhases of A ProjectRaquel RsuNo ratings yet
- History of IndiaDocument21 pagesHistory of IndiaAbhishek Kadian50% (2)
- Chandni Chowk-Study As Historic DistrictDocument14 pagesChandni Chowk-Study As Historic DistrictRakshita BhattNo ratings yet
- EkisticsDocument34 pagesEkisticsGladys MatiraNo ratings yet
- Joyce Travelbee (1926 Human Relationship ModelDocument4 pagesJoyce Travelbee (1926 Human Relationship ModelHugMoco Moco Locah ÜNo ratings yet
- Master Plans For Delhi The First Master Plan For DelhiDocument6 pagesMaster Plans For Delhi The First Master Plan For DelhiVAISHNAVI KHONDENo ratings yet
- City of ShajahanabadDocument21 pagesCity of ShajahanabadSilpaNo ratings yet
- Ud - WPS OfficeDocument54 pagesUd - WPS OfficeSahil KaziNo ratings yet
- Planning of ShahjahanabadDocument22 pagesPlanning of ShahjahanabadAnirudh BabbarNo ratings yet
- ShahjahanabadDocument2 pagesShahjahanabadDhruv Kumar100% (1)
- City Planning TypesDocument17 pagesCity Planning TypesAlex stuwartNo ratings yet
- Constantinos A.Doxiadis: Islamabad - Town PlanningDocument12 pagesConstantinos A.Doxiadis: Islamabad - Town PlanningDhari KaranNo ratings yet
- City Planning of MaduraiDocument15 pagesCity Planning of MaduraiChanchal Soni100% (1)
- RP 6 ICOA 1602 - Jigyasu - SM-with-warningDocument6 pagesRP 6 ICOA 1602 - Jigyasu - SM-with-warningAjay MelwaniNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh PlanningDocument25 pagesChandigarh PlanningJaskirat SinghNo ratings yet
- Planning of CitiesDocument12 pagesPlanning of CitiesSuvithaNo ratings yet
- Linear City PDFDocument29 pagesLinear City PDFGurpreetSinghKalsiNo ratings yet
- Delhi ShahjahanabadDocument25 pagesDelhi ShahjahanabadMEHTHABNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument32 pagesLecture 1 PDFMuskan JainNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Urban Planning - 2021-1Document70 pagesModule 2 - Urban Planning - 2021-1SREYAS K MNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh Planning (Le Corbousier)Document24 pagesChandigarh Planning (Le Corbousier)Lalima GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mahima Prasad Assignment 2Document17 pagesMahima Prasad Assignment 2Mahima TannuNo ratings yet
- Town PlanningDocument31 pagesTown PlanningAviraj SawanNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document1 pageCase Study 2Shraddha Bahirat100% (1)
- Ekistics Assigmnet-2Document25 pagesEkistics Assigmnet-2mansi bitoliyaNo ratings yet
- Shahjahanabad (Old Delhi) Walled CityDocument14 pagesShahjahanabad (Old Delhi) Walled Cityanasmohd00780% (5)
- Shahjahanabad - Heritage CityDocument23 pagesShahjahanabad - Heritage CityaanchalNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh - BhubaneshwarDocument13 pagesChandigarh - BhubaneshwarAbhishek RustagiNo ratings yet
- HSP - Unit 1presentationDocument23 pagesHSP - Unit 1presentationabc300142No ratings yet
- Doxiadis Islamabad PlanningDocument11 pagesDoxiadis Islamabad PlanningpradisevirtueNo ratings yet
- Urban Space Seminar-Bhopal EditDocument7 pagesUrban Space Seminar-Bhopal EditDavid DanielsNo ratings yet
- Module-1 4Document36 pagesModule-1 4Sanjana SudeepNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning - DelhiDocument61 pagesUrban Planning - DelhiShah Rukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Central Business DistrictDocument193 pagesCentral Business DistrictGhulam Mustafa MughalNo ratings yet
- Project Brief - 21DAHZ210Document6 pagesProject Brief - 21DAHZ210gireesh NivethanNo ratings yet
- City FormsDocument27 pagesCity FormsELPIDIO SANGRIANo ratings yet
- Making and Unmaking of ChandigarhDocument5 pagesMaking and Unmaking of Chandigarhmanpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- GARELLAVeenaDocument9 pagesGARELLAVeenaHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Classification of Urban FormDocument5 pagesClassification of Urban FormKittuNo ratings yet
- Theories of Town PlanningDocument15 pagesTheories of Town PlanningNimishaSamadhiyaNo ratings yet
- Planning Theory: City Form in The Context of Developed and Developing CountriesDocument29 pagesPlanning Theory: City Form in The Context of Developed and Developing CountriesVirali GohilNo ratings yet
- Heritage Conservation in Ahmadabad PDFDocument35 pagesHeritage Conservation in Ahmadabad PDFSiddhi VashiNo ratings yet
- Mughal City PDFDocument3 pagesMughal City PDFSwarna AnadhkumarNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh: Nishu Gupta B.ARCH I.A.T.PDocument13 pagesChandigarh: Nishu Gupta B.ARCH I.A.T.PNISHUNo ratings yet
- Towns, Traders and CraftspersonsDocument16 pagesTowns, Traders and CraftspersonsjaanNo ratings yet
- Town Planning in India - Ancient Age - Med PDFDocument22 pagesTown Planning in India - Ancient Age - Med PDFAr Aayush GoelNo ratings yet
- Group PPT IslamabadDocument36 pagesGroup PPT IslamabadMadhu SekarNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh: Urban DesignDocument3 pagesChandigarh: Urban DesignArpan PatelNo ratings yet
- 2013-Ud-Elective-Ashok Bhairi PDFDocument84 pages2013-Ud-Elective-Ashok Bhairi PDFvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Planning History NotesDocument5 pagesPlanning History NotesDinesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Town PlanningDocument17 pagesTown PlanningAastha SainiNo ratings yet
- Morphology of A Sacred Urban NeighborhoodDocument20 pagesMorphology of A Sacred Urban NeighborhoodJubel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument13 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationAbhishek Venkitaraman IyerNo ratings yet
- Islamic City PlanningDocument52 pagesIslamic City Planningqwerty100% (1)
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: Xi'An (Chang'An) : SamarkandDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: Xi'An (Chang'An) : Samarkandkartik chopraNo ratings yet
- Analysing The Re Vitalization of HazratganjDocument14 pagesAnalysing The Re Vitalization of HazratganjRudra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization, Fatehpur Sikri, Jaipur and New DelhiDocument85 pagesIndus Valley Civilization, Fatehpur Sikri, Jaipur and New DelhiVriti SachdevaNo ratings yet
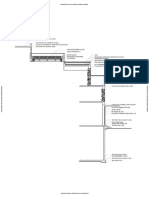
- External Wall SecDocument1 pageExternal Wall SecSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
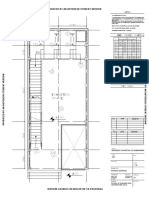
- Key PlanDocument1 pageKey PlanSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Public Service RulesDocument9 pagesPublic Service RulesAnonymous uZbDBWsIcu100% (1)
- Construction and Standardization of Achievement Test in EnglishDocument9 pagesConstruction and Standardization of Achievement Test in EnglishAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Brubaker - 2009 - Ethnicity, Race, and NationalismDocument25 pagesBrubaker - 2009 - Ethnicity, Race, and NationalismGustavo RossiNo ratings yet
- Non Rigid Connector FPDDocument3 pagesNon Rigid Connector FPDIana RusuNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument19 pages1 SMHandika Dwi SaputraNo ratings yet
- The Prayer of Faith by Leonard Boase PDFDocument69 pagesThe Prayer of Faith by Leonard Boase PDF6luke3738No ratings yet
- Plan Implementation and Management - Ii (M.A. E.P.M. 6562)Document22 pagesPlan Implementation and Management - Ii (M.A. E.P.M. 6562)Ahmer KhalilNo ratings yet
- NMTC Test Papers Prelims All Levels 2016Document15 pagesNMTC Test Papers Prelims All Levels 2016tannyNo ratings yet
- AI & Jobs - Advanced News LessonDocument9 pagesAI & Jobs - Advanced News LessonLuis Jaime Castro CintaNo ratings yet
- Resilience To Academic Stress The Key Towards SuccessDocument4 pagesResilience To Academic Stress The Key Towards SuccessEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Geology of Burma (DGSE)Document126 pagesGeology of Burma (DGSE)Anonymous d1CGjMTi100% (3)
- Math Lesson 23Document5 pagesMath Lesson 23api-461550649No ratings yet
- Philippine Materials in International LawDocument108 pagesPhilippine Materials in International LawAgent BlueNo ratings yet
- WorkationDocument2 pagesWorkationNadiia BeleiNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exersise - HistoryDocument29 pagesNcert Exersise - HistoryTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Playground Design: Bridges in Mathematics Grade 4 Unit 8Document2 pagesPlayground Design: Bridges in Mathematics Grade 4 Unit 8api-289120259No ratings yet
- Tanuj Bohra - HRM - Individual Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesTanuj Bohra - HRM - Individual Assignment PDFTanuj BohraNo ratings yet
- Partisan Politics and Public Finance: Changes in Public Spending in The Industrialized Democracies, 1955-1989Document21 pagesPartisan Politics and Public Finance: Changes in Public Spending in The Industrialized Democracies, 1955-1989SumardiNo ratings yet
- Sugar Analysis Using Ion ChromatographyDocument7 pagesSugar Analysis Using Ion ChromatographyJohn QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Pradip BhalekarDocument11 pagesPradip BhalekarSandeep NaikNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: PRACTICE PAPER (2018-19) Class: Xii Max. Marks:70 Subject: Chemistry Time: 3 HoursDocument8 pagesGeneral Instructions:: PRACTICE PAPER (2018-19) Class: Xii Max. Marks:70 Subject: Chemistry Time: 3 HoursHINDI CARTOONSNo ratings yet
- Lonnie Melvin Murray v. United States, 419 U.S. 942 (1974)Document3 pagesLonnie Melvin Murray v. United States, 419 U.S. 942 (1974)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- EngG8 Q4 Module 4Document12 pagesEngG8 Q4 Module 4Abi Ramirez Ramos-SadangNo ratings yet
- Metabolizam KreatininaDocument21 pagesMetabolizam KreatininahareNo ratings yet
- Modernity-An Incomplete Project: Jurg en Habe RM AsDocument8 pagesModernity-An Incomplete Project: Jurg en Habe RM AsLouis DysonNo ratings yet
- The Lived Experiencesof Lesbian Gayand Bisexual Youth During Their Secondary EducationDocument28 pagesThe Lived Experiencesof Lesbian Gayand Bisexual Youth During Their Secondary EducationFranci CerezaNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Nursing Syllabus and RegulationDocument145 pagesM.Sc. Nursing Syllabus and RegulationSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
AD Moradabad Pre Visit
AD Moradabad Pre Visit
Uploaded by
SAHIL JAINOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AD Moradabad Pre Visit
AD Moradabad Pre Visit
Uploaded by
SAHIL JAINCopyright:
Available Formats
MORADABAD:
URBAN MORPHOLOGY
“Festivals such as Diwali, Eid, Lohri, Durga Puja and Chhat Puja are celebrated with equal
anticipation and joy. The monuments of Moradabad depict the essence of both Hindu and
Muslim cultures. Throughout history, the city has attracted eminent musicians, dancers
and painters who have contributed to the cultural treasures of the city.”
The internal structure of Moradabad, the spatial distribu-
tion of its functional localities — the urban regions cannot
be formulated according to any theoretical arrangement
of urban expansion. It is actually a combination of hetero-
geneous pockets of different functions. The pre-urban nu-
cleus of Moradabad was the fort of Chaupala, situated on
the ridge by the right bank of the Ramganga. Four oth-
er villages also existed on the ridge around Chaupala (old Najibudaulah’s Fort
Moradabad).
The city of Moradabad, which now covers an area of nearly
4 sq. miles, has absorbed all the five villages. For efficiency
of administration and government the, site of the old mud
fort was chosen for the new brick fort. The present city has
its core shifted from the river bank to the northwest. The
core of the old town was the fortthe administrative cente,
and Faiz Ganj- the central business district.
Ancient coins found during a
search
MORADABAD- PRE VISIT STUDY SUBMITTED BY: SECTION:
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN ASHIMA SAINI RANA DAKSHIL 2A
MOHEED HASAN SAHIL JAIN
KOLATA TEJASWI
The surrounding areas served as the
residential quarters for the elite, being
near to the core, and those away from
it, lying tovrards the suburbs, for the
poor and menial service-class people.
The present core or the City Centre is
the area where the Town Hall, Tahsil,
male and female hospitals, municipal
offices, and other public buildings are.
The central business district is located
to the south and southeast of the core.
The old core and the central business district have now decayed, and the site of the core-
the fort, has been occupied by the buildings of the Government Inter College. The urban
regions of the present city have no definite and very clear picture.
THREE GENERALISATIONS OF THE INTERNAL STRUCTURES
MORADABAD- PRE VISIT STUDY SUBMITTED BY: SECTION:
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN ASHIMA SAINI RANA DAKSHIL 2A
MOHEED HASAN SAHIL JAIN
KOLATA TEJASWI
MORADABAD- PRE VISIT STUDY SUBMITTED BY: SECTION:
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN ASHIMA SAINI RANA DAKSHIL 2A
MOHEED HASAN SAHIL JAIN
KOLATA TEJASWI
As regards the spatial distribution of the res-
idential quarters the whole of the old town is
mainly occupied by this function. A special fea-
ture of the residential quarters is the presence
of the manufactories in the residential houses.
The buildings of the old town mainly belonging
to Muslim master craftsmen and artisans are
partly used as the factories for manufacturing
brasswares and partly for the residences. Hence
it is difficult to demarcate any area which is oc-
cupied exclusively by residential quarters. An-
other feature of the residential quarters is the
strong internal differentiation, that of the separate quarters for various castes”, and fol-
lowers of different creeds.
The residential quarters can be divided into the following categories: (a) Old Residential
Quarters. (b) New Residential Quarters. (c) Suburban Residential Developments. (d)
Civil Lines, Police Lines and Railway Settlements. nt.
(a) Old Residential Quarters: From its origin as a fort in 1624 to its cession to the British
Government in 1801, the nucleus of the city was the fort and the Jama Masjid. The res-
idential houses were located around them which usually belonged to Muslim chiefs and
men of rank. Their attendants also resided in the same houses. These houses were very
spacious erected in large gardens. Some of them exist to this day but in a deserted condi-
tion like enclaves. At present there is mixed type of buildings in this quarter.
(b) New Residential Quarters: With the expansion of the city and shift of the nucleus,
many residential quarters have grown besides the old ones and the Civil Lines. The hous-
es are spacious, built according to the plan approved by the local authorities, and provid-
ing all amenities.
(c)Suburban Residential Developiaents: In the northern outskirts Harthala, formerly a
village, has developed into a new suburban residential quarter. Many such suburban res-
idential developments are coming up in the west in Hathala, Majholi, Dhakka, Kanpur,
Narainpur, etc. These residential quarters provide better housing facilities.
(d) Civil Lines, Police Lines and Railway Settlement: Most of the residential buildings of
the Civil Lines and Police Lines usually being a governmental undertaking and construct-
ed generally under the supervision of the Public Works department are of a set pattern.
The architecture is standard with economy as the watchword.
MORADABAD 2019
MORADABAD- PRE VISIT STUDY SUBMITTED BY: SECTION:
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN ASHIMA SAINI RANA DAKSHIL 2A
MOHEED HASAN SAHIL JAIN
KOLATA TEJASWI
SHOPPING AREAS As regards the spatial
distribution of the shopping areas, the cen-
tral business district and other shopping ar-
eas have distinct locations. These have been
distinguished into: (a) Central Business Dis-
trict. (b) Wholesale Shopping Areas. (c) Re-
tail Shopping Areas. (d) Weekly Markets.
(a)Central Business District: The central
business district of old Moradabad was lo-
cated at the crossing of the thorughfares
known as Sambhal Road, Mandi Bans and
Faiz Ganj. At present it has shifted more to-
wards the west near the Town Hall.
(b)Wholesale Shopping Areas; As the factories are generally located mixed with the res-
idential houses, the commercial firms dealing in wholesale business of their products are
also present in every nook and corner of the town.
PARSVNATH SHOPPING MALL
(c) Retail Shopping Areas
(d) Weekly Market Centres: A large number of neighbouring settlements from where
people come to this day to gather at one market place on the fixed days to consign trans-
actions for their periodic requirements.
MORADABAD- PRE VISIT STUDY SUBMITTED BY: SECTION:
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN ASHIMA SAINI RANA DAKSHIL 2A
MOHEED HASAN SAHIL JAIN
KOLATA TEJASWI
INDUSTRIAL AREAS Moradabad is famous for
its brassware industry. By an analysis of the popu-
lation figures it is evident that 96.4% of the total
population of the city derives its living from non-ag-
ricultural occupations, mainly manufacturing brass-
wares and other allied industries.
• Moradabad Cast Metal: The master craftsmen
and labourers engaged in this type of manufactur-
ing are generally Muslims. The manufactory is usu-
ally located in the house of the artisans.
• Moradabad Sheet Brass: There is a considerable
industry of manufacturing domestic utensils out of
imported sheet brass. This branch is mostly in the
hands of the Hindu ‘thateras’ or smiths. So the lo-
calities of this specialised industry are the Chaura-
ha Gali, Thatera, Tambakuwaia, Diwan Ka Bazaar,
and Kath Darwaza. Some modern rolling mills have
been erected to manufacture ‘katoras’ or bowls,
spoons and other vessels out of metal sheets by
cutting and pressing machines. Articles like thalis,
trays, tiffin carriers, etc., are manufactured with the
help of power lathes.
• Moradabad Art Brass: The factory system has still
further developed in the manufacture of art brasswares. The artisians are seen doing this
exquisitely beautiful work, sitting before their doors out in the lanes and along the streets.
Thus, this type of manufacturing is also mixed with the residential quarters. • Food In-
dustries: Flour milling pulse splitting, oil expelling and paddy husking are the basic food
industries, which are located in a scattered fashion throughout the residential quarters.
Their dispersed location makes them accessible to the residents of the city’s different
residential quarters.
• Carpentry and Woodwork: The location of the wood-working establishments is gov-
erned by the transportation factor. So the light articles like stands, etc., are manufactured
near the brassware factories in the city. The heavy furniwure and other articles are gener-
ally made in the factories located along the Station Road and the Bareilly Road outside
the city.
Along the bylanes of Lal Masjid and Bada Shah Safa area in Moradabad, a sense of hopelessness was palpable
among craftsmen who in ordinary circumstances would swear by a profession passed down generations.
MORADABAD- PRE VISIT STUDY SUBMITTED BY: SECTION:
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN ASHIMA SAINI RANA DAKSHIL 2A
MOHEED HASAN SAHIL JAIN
KOLATA TEJASWI
ADMINISTRATIVE CENTRES
Nearly all of the administrative buildings are located in the Civil Lines. Only the Police
Stations and police outposts, Municipal offices and a few other offices are located in the-
other parts of the city.
The fort had been the administrative centre and nucleus of the old town in the past. With
the change of the government the administrative headquarters have shifted to the west
and tne northwest of the old town, where the present TownHall and the Civil Lines have
been established. There is a separate entity in the Civil Lines known as the Police Lines.
This is the area occupied by the Provincial Auxiliary Corps, Police Training College, and
other police establishments.
TRANSPORTATION AREAS • Railway Stations: There are four Bailway Stations in
Moradabad. The most important of them is the Main Junction which is situated in the
mmiddle-west of the city. Moradabad City Railway Station is a terminus passenger sta-
tion for the North-Eastern Railway which is situated to the southeast of the goods shed
of the main station.
RECREATIONAL CENTERS There are a few cinema houses, mostly situated along the
Station Road. The now closed cinema buildings are used for staging dramas and other
recreational progranmas sponsored by the Railway and Rotary clubs. The open space
near Budh Ka Bazaar(a weekly market) to the south of the Station Road and the north-
west of Asalat Pura residential quarters is used for staging the Circus. The city lacks in
recreational centres and so the inhabitants depend for their recreation onccinemas only.
EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTES The city has a large number of educational institutions,
which provide art education from priffiary standard to post-graduate degrees. They are
well distributed in all the residential quarters. Their dispersed locations serve the purpose
of accessibility. The number of Primary and nursery Schools is more than 80 in this city.
These basic institutions are also scattered in the whole city. Moradabad has the biggest
Police Training College of the State of Uttar Pradesh. It is situated in the Police Lines in
a spacious area.
GREEN SPOTS, OPEN SPACES AND AGRICULTURAL FRINGES Moradabad is
very deficient in green spots and open spaces. Its residential quarters and the built-up ar-
eas are so congested that very little open space is available inside the city. It is only in the
Civil Lines that land has been occupied by gardens, parks, lawns and play grounds.
MEDICAL CENTRES There are many hospitals, dispensaries, clinics, maternity yards,
and veterinary hospitals in the city. Besides the hospitals and dispensaries run ty the State
Government, and the Local administration, there are many private clinics and dispensa-
ries wheree facilities are provided for indoor as well as outdoor patients which arewell
distributed throughout the residential quarters of the city and the Civil Lines. A veteri-
nary hospital is also situated in Kanjari Sarai along the Kachehri Road.
BURIAL GROUNDS As the majority of the inhabitants of this city are Muslims, it has
many grave yards. Christians have also inhabited the city for the last two centuries, hence
cemeteries are also found here. The burial grounds as a tradition are always located out-
side the built-up areas and so they make the boundary of the city. With the expansion of
the habitation of the city these burial grounds became the parts of the city proper. Many
residential quarters and other functional developments have taken place beyond the old
grave-yards. The cremation ground for the Hindus is provided by the Ramganga ghats
MORADABAD- PRE VISIT STUDY SUBMITTED BY: SECTION:
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN ASHIMA SAINI RANA DAKSHIL 2A
MOHEED HASAN SAHIL JAIN
KOLATA TEJASWI
You might also like
- The City Assembled: By: Spiro KostofDocument29 pagesThe City Assembled: By: Spiro KostofSneha PeriwalNo ratings yet
- Croak by Gina Damico ExcerptDocument29 pagesCroak by Gina Damico ExcerptHoughton Mifflin Harcourt0% (1)
- Shahjahanabad (The Walled City of Delhi)Document27 pagesShahjahanabad (The Walled City of Delhi)Priyesh Dubey94% (18)
- Phases of A ProjectDocument9 pagesPhases of A ProjectRaquel RsuNo ratings yet
- History of IndiaDocument21 pagesHistory of IndiaAbhishek Kadian50% (2)
- Chandni Chowk-Study As Historic DistrictDocument14 pagesChandni Chowk-Study As Historic DistrictRakshita BhattNo ratings yet
- EkisticsDocument34 pagesEkisticsGladys MatiraNo ratings yet
- Joyce Travelbee (1926 Human Relationship ModelDocument4 pagesJoyce Travelbee (1926 Human Relationship ModelHugMoco Moco Locah ÜNo ratings yet
- Master Plans For Delhi The First Master Plan For DelhiDocument6 pagesMaster Plans For Delhi The First Master Plan For DelhiVAISHNAVI KHONDENo ratings yet
- City of ShajahanabadDocument21 pagesCity of ShajahanabadSilpaNo ratings yet
- Ud - WPS OfficeDocument54 pagesUd - WPS OfficeSahil KaziNo ratings yet
- Planning of ShahjahanabadDocument22 pagesPlanning of ShahjahanabadAnirudh BabbarNo ratings yet
- ShahjahanabadDocument2 pagesShahjahanabadDhruv Kumar100% (1)
- City Planning TypesDocument17 pagesCity Planning TypesAlex stuwartNo ratings yet
- Constantinos A.Doxiadis: Islamabad - Town PlanningDocument12 pagesConstantinos A.Doxiadis: Islamabad - Town PlanningDhari KaranNo ratings yet
- City Planning of MaduraiDocument15 pagesCity Planning of MaduraiChanchal Soni100% (1)
- RP 6 ICOA 1602 - Jigyasu - SM-with-warningDocument6 pagesRP 6 ICOA 1602 - Jigyasu - SM-with-warningAjay MelwaniNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh PlanningDocument25 pagesChandigarh PlanningJaskirat SinghNo ratings yet
- Planning of CitiesDocument12 pagesPlanning of CitiesSuvithaNo ratings yet
- Linear City PDFDocument29 pagesLinear City PDFGurpreetSinghKalsiNo ratings yet
- Delhi ShahjahanabadDocument25 pagesDelhi ShahjahanabadMEHTHABNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument32 pagesLecture 1 PDFMuskan JainNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Urban Planning - 2021-1Document70 pagesModule 2 - Urban Planning - 2021-1SREYAS K MNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh Planning (Le Corbousier)Document24 pagesChandigarh Planning (Le Corbousier)Lalima GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mahima Prasad Assignment 2Document17 pagesMahima Prasad Assignment 2Mahima TannuNo ratings yet
- Town PlanningDocument31 pagesTown PlanningAviraj SawanNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document1 pageCase Study 2Shraddha Bahirat100% (1)
- Ekistics Assigmnet-2Document25 pagesEkistics Assigmnet-2mansi bitoliyaNo ratings yet
- Shahjahanabad (Old Delhi) Walled CityDocument14 pagesShahjahanabad (Old Delhi) Walled Cityanasmohd00780% (5)
- Shahjahanabad - Heritage CityDocument23 pagesShahjahanabad - Heritage CityaanchalNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh - BhubaneshwarDocument13 pagesChandigarh - BhubaneshwarAbhishek RustagiNo ratings yet
- HSP - Unit 1presentationDocument23 pagesHSP - Unit 1presentationabc300142No ratings yet
- Doxiadis Islamabad PlanningDocument11 pagesDoxiadis Islamabad PlanningpradisevirtueNo ratings yet
- Urban Space Seminar-Bhopal EditDocument7 pagesUrban Space Seminar-Bhopal EditDavid DanielsNo ratings yet
- Module-1 4Document36 pagesModule-1 4Sanjana SudeepNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning - DelhiDocument61 pagesUrban Planning - DelhiShah Rukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Central Business DistrictDocument193 pagesCentral Business DistrictGhulam Mustafa MughalNo ratings yet
- Project Brief - 21DAHZ210Document6 pagesProject Brief - 21DAHZ210gireesh NivethanNo ratings yet
- City FormsDocument27 pagesCity FormsELPIDIO SANGRIANo ratings yet
- Making and Unmaking of ChandigarhDocument5 pagesMaking and Unmaking of Chandigarhmanpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- GARELLAVeenaDocument9 pagesGARELLAVeenaHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Classification of Urban FormDocument5 pagesClassification of Urban FormKittuNo ratings yet
- Theories of Town PlanningDocument15 pagesTheories of Town PlanningNimishaSamadhiyaNo ratings yet
- Planning Theory: City Form in The Context of Developed and Developing CountriesDocument29 pagesPlanning Theory: City Form in The Context of Developed and Developing CountriesVirali GohilNo ratings yet
- Heritage Conservation in Ahmadabad PDFDocument35 pagesHeritage Conservation in Ahmadabad PDFSiddhi VashiNo ratings yet
- Mughal City PDFDocument3 pagesMughal City PDFSwarna AnadhkumarNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh: Nishu Gupta B.ARCH I.A.T.PDocument13 pagesChandigarh: Nishu Gupta B.ARCH I.A.T.PNISHUNo ratings yet
- Towns, Traders and CraftspersonsDocument16 pagesTowns, Traders and CraftspersonsjaanNo ratings yet
- Town Planning in India - Ancient Age - Med PDFDocument22 pagesTown Planning in India - Ancient Age - Med PDFAr Aayush GoelNo ratings yet
- Group PPT IslamabadDocument36 pagesGroup PPT IslamabadMadhu SekarNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh: Urban DesignDocument3 pagesChandigarh: Urban DesignArpan PatelNo ratings yet
- 2013-Ud-Elective-Ashok Bhairi PDFDocument84 pages2013-Ud-Elective-Ashok Bhairi PDFvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Planning History NotesDocument5 pagesPlanning History NotesDinesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Town PlanningDocument17 pagesTown PlanningAastha SainiNo ratings yet
- Morphology of A Sacred Urban NeighborhoodDocument20 pagesMorphology of A Sacred Urban NeighborhoodJubel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument13 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationAbhishek Venkitaraman IyerNo ratings yet
- Islamic City PlanningDocument52 pagesIslamic City Planningqwerty100% (1)
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: Xi'An (Chang'An) : SamarkandDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: Xi'An (Chang'An) : Samarkandkartik chopraNo ratings yet
- Analysing The Re Vitalization of HazratganjDocument14 pagesAnalysing The Re Vitalization of HazratganjRudra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization, Fatehpur Sikri, Jaipur and New DelhiDocument85 pagesIndus Valley Civilization, Fatehpur Sikri, Jaipur and New DelhiVriti SachdevaNo ratings yet
- External Wall SecDocument1 pageExternal Wall SecSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Key PlanDocument1 pageKey PlanSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Produced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToDocument1 pageProduced by An Autodesk Student Version: S.N. Date Issued ToSAHIL JAINNo ratings yet
- Public Service RulesDocument9 pagesPublic Service RulesAnonymous uZbDBWsIcu100% (1)
- Construction and Standardization of Achievement Test in EnglishDocument9 pagesConstruction and Standardization of Achievement Test in EnglishAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- Brubaker - 2009 - Ethnicity, Race, and NationalismDocument25 pagesBrubaker - 2009 - Ethnicity, Race, and NationalismGustavo RossiNo ratings yet
- Non Rigid Connector FPDDocument3 pagesNon Rigid Connector FPDIana RusuNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument19 pages1 SMHandika Dwi SaputraNo ratings yet
- The Prayer of Faith by Leonard Boase PDFDocument69 pagesThe Prayer of Faith by Leonard Boase PDF6luke3738No ratings yet
- Plan Implementation and Management - Ii (M.A. E.P.M. 6562)Document22 pagesPlan Implementation and Management - Ii (M.A. E.P.M. 6562)Ahmer KhalilNo ratings yet
- NMTC Test Papers Prelims All Levels 2016Document15 pagesNMTC Test Papers Prelims All Levels 2016tannyNo ratings yet
- AI & Jobs - Advanced News LessonDocument9 pagesAI & Jobs - Advanced News LessonLuis Jaime Castro CintaNo ratings yet
- Resilience To Academic Stress The Key Towards SuccessDocument4 pagesResilience To Academic Stress The Key Towards SuccessEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Geology of Burma (DGSE)Document126 pagesGeology of Burma (DGSE)Anonymous d1CGjMTi100% (3)
- Math Lesson 23Document5 pagesMath Lesson 23api-461550649No ratings yet
- Philippine Materials in International LawDocument108 pagesPhilippine Materials in International LawAgent BlueNo ratings yet
- WorkationDocument2 pagesWorkationNadiia BeleiNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exersise - HistoryDocument29 pagesNcert Exersise - HistoryTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Playground Design: Bridges in Mathematics Grade 4 Unit 8Document2 pagesPlayground Design: Bridges in Mathematics Grade 4 Unit 8api-289120259No ratings yet
- Tanuj Bohra - HRM - Individual Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesTanuj Bohra - HRM - Individual Assignment PDFTanuj BohraNo ratings yet
- Partisan Politics and Public Finance: Changes in Public Spending in The Industrialized Democracies, 1955-1989Document21 pagesPartisan Politics and Public Finance: Changes in Public Spending in The Industrialized Democracies, 1955-1989SumardiNo ratings yet
- Sugar Analysis Using Ion ChromatographyDocument7 pagesSugar Analysis Using Ion ChromatographyJohn QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Pradip BhalekarDocument11 pagesPradip BhalekarSandeep NaikNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: PRACTICE PAPER (2018-19) Class: Xii Max. Marks:70 Subject: Chemistry Time: 3 HoursDocument8 pagesGeneral Instructions:: PRACTICE PAPER (2018-19) Class: Xii Max. Marks:70 Subject: Chemistry Time: 3 HoursHINDI CARTOONSNo ratings yet
- Lonnie Melvin Murray v. United States, 419 U.S. 942 (1974)Document3 pagesLonnie Melvin Murray v. United States, 419 U.S. 942 (1974)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- EngG8 Q4 Module 4Document12 pagesEngG8 Q4 Module 4Abi Ramirez Ramos-SadangNo ratings yet
- Metabolizam KreatininaDocument21 pagesMetabolizam KreatininahareNo ratings yet
- Modernity-An Incomplete Project: Jurg en Habe RM AsDocument8 pagesModernity-An Incomplete Project: Jurg en Habe RM AsLouis DysonNo ratings yet
- The Lived Experiencesof Lesbian Gayand Bisexual Youth During Their Secondary EducationDocument28 pagesThe Lived Experiencesof Lesbian Gayand Bisexual Youth During Their Secondary EducationFranci CerezaNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Nursing Syllabus and RegulationDocument145 pagesM.Sc. Nursing Syllabus and RegulationSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet