Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transcription in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Subject:-Zoology
Transcription in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Subject:-Zoology
Uploaded by
Asif Ahmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesTranscription is the first step of gene expression where DNA is copied into RNA. It involves an enzyme called RNA polymerase that binds to a promoter region of DNA and copies the template strand into RNA until reaching a terminator region. There are differences in transcription between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes have a single type of RNA polymerase while eukaryotes have three distinct types, each specialized for synthesizing different RNA molecules. The transcription process consists of initiation, elongation, and termination steps.
Original Description:
Original Title
Transcription Summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTranscription is the first step of gene expression where DNA is copied into RNA. It involves an enzyme called RNA polymerase that binds to a promoter region of DNA and copies the template strand into RNA until reaching a terminator region. There are differences in transcription between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes have a single type of RNA polymerase while eukaryotes have three distinct types, each specialized for synthesizing different RNA molecules. The transcription process consists of initiation, elongation, and termination steps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesTranscription in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Subject:-Zoology
Transcription in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Subject:-Zoology
Uploaded by
Asif AhmedTranscription is the first step of gene expression where DNA is copied into RNA. It involves an enzyme called RNA polymerase that binds to a promoter region of DNA and copies the template strand into RNA until reaching a terminator region. There are differences in transcription between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes have a single type of RNA polymerase while eukaryotes have three distinct types, each specialized for synthesizing different RNA molecules. The transcription process consists of initiation, elongation, and termination steps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
1
Transcription in Prokaryotes and
Eukaryotes
[Summary]
Subject:- Zoology
Course:- BG 4th Semester
Paper:- Core Course 4, Genetics and
Evolutionary Biology
Topic No:- 2.3 –Transcription
Lecture:- Transcription in Prokaryotes
and Eukaryotes
2
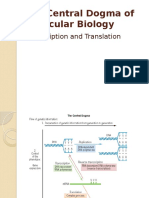
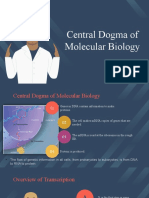
Transcription is the first step in gene expression. It involves copying a
gene's DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule. Transcription is DNA
dependent RNA synthesis. The DNA strand on which RNA is synthesized
is called template strand and the other strand of DNA is called non-
template strand with respect to transcription process. The DNA strand is
copied in 3'-to-5' direction antiparallel to RNA strand which builds in 5'-to-
3' direction. The transcribed segment of DNA is called a transcription unit.
This unit is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that codes for a single RNA
molecule, containing a promoter, an RNA-coding sequence, and a
terminator. An enzyme system converts the genetic information from the
transcription unit of double stranded DNA into a single stranded RNA. The
main enzyme involved in transcription is RNA polymerase (RNA pol). This
enzyme joins the transcription unit at promoter region, then moves along
the RNA coding region to copy the information from template strand to
form primary transcript and then leaves the unit at terminator region. RNA
polymerases have been found in all species, but the number and
composition of these proteins. In bacteria contain a single type of RNA pol
while eukaryotes (multicellular organisms and yeasts) contain three
distinct types, designated I, II, and III. Each polymerase has a specific
function. RNA polymerase I (Pol I) is responsible for the synthesis of only
rRNAs. The principal function of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is synthesis of
mRNAs. RNA polymerase III (Pol III) makes tRNA. DNA-dependent RNA
polymerase, in addition to a DNA template and RNA polymerase, requires
all four ribonucleoside triphosphates as precursors of the nucleotide units
of RNA, as well as Mg2+ ions. The transcription process starts from the
promoter region of transcription unit. First of all RNA pol binds the
promoter region. Then RNA pol polymerizes first few ribonucleotides on
the template strand to initiate the process. After initiation the RNA is
elongated through elongation process where RNA pol moves downstream
along the template strand and adds new ribonucleotide units to the
growing RNA strand. When RNA pol reaches the termination site, both
RNA pol and RNA transcript leaves the transcription unit resulting into
termination of transcription process. In this whole process of transcription
different types of factors are involved which are generally called as
transcription factors.
You might also like
- 2017 Grade 7 Math Challenge Elimination QuestionsDocument2 pages2017 Grade 7 Math Challenge Elimination QuestionsOwen CajarteNo ratings yet
- Stella Adler On America's Master Playwrights,' LecturesDocument6 pagesStella Adler On America's Master Playwrights,' LecturesWwe Full matches100% (1)
- Transcriprion ManuscriptDocument14 pagesTranscriprion ManuscriptAsif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation by Dr. Mesut KarahanDocument26 pagesTranscription and Translation by Dr. Mesut KarahanEmily ClementhNo ratings yet
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument38 pagesTranscription and RNA ProcessingRishi Kumar100% (1)
- Transcription in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: (Frequently Asked Questions)Document6 pagesTranscription in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: (Frequently Asked Questions)Asif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Genetic Information: - Central Dogma - Genetic CodesDocument34 pagesGenetic Information: - Central Dogma - Genetic Codesakhikabir100% (1)
- Unit-3 Transcription in Eukaryotes-IDocument14 pagesUnit-3 Transcription in Eukaryotes-IRickySaptarshi SahaNo ratings yet
- Overview On TranscriptionDocument21 pagesOverview On TranscriptionAli Akand AsifNo ratings yet
- Transcription NotesDocument16 pagesTranscription NotesArathi PillaiNo ratings yet
- 5 11transcription-2013Document30 pages5 11transcription-2013jernsssNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument135 pagesProtein SynthesisCarlaNo ratings yet
- SYBT TranscriptionDocument69 pagesSYBT TranscriptionMeir SabooNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: InstructorDocument20 pagesCell Biology: Instructorahmed mediaNo ratings yet
- Science FairDocument41 pagesScience FairSafanaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 9 Gene Expression THB 2022Document28 pagesKuliah 9 Gene Expression THB 2022Dea puspita DewiNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument35 pagesTranscription and TranslationMing mingNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY PROJECT TranslationDocument24 pagesBIOLOGY PROJECT Translationaryan1906mishraNo ratings yet
- Gift RNADocument13 pagesGift RNAPeter DindahNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Regulation of Gene Expression: By: Lyka Marie C. Falcasantos BSN - 1DDocument16 pagesTranscription and Regulation of Gene Expression: By: Lyka Marie C. Falcasantos BSN - 1DRemzAbdullaNo ratings yet
- Transcription WorkingDocument51 pagesTranscription Workingapi-3858544No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lec.22 (Nucleic Acids 6)Document6 pagesChemistry Lec.22 (Nucleic Acids 6)Muhammed AbdulsamadNo ratings yet
- Transcription 2Document66 pagesTranscription 2Safe BoxNo ratings yet
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument37 pagesTranscription and RNA ProcessingEarl ReyesNo ratings yet
- (L-8) - Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Feb 1, 2020Document48 pages(L-8) - Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Feb 1, 2020AyazNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationDocument37 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationfangirltonNo ratings yet
- What Is RNA PolymeraseDocument15 pagesWhat Is RNA Polymerasemohmedmustafa4No ratings yet
- RNA Transcription and TranslationDocument11 pagesRNA Transcription and TranslationMaiSakurajimaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism AllDocument31 pagesNucleic Acid Metabolism AllRaufur Rahman AkandaNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument9 pagesFrom Gene To ProteincrookedspookNo ratings yet
- Transcription (Semister I MIC)Document117 pagesTranscription (Semister I MIC)Challagandla AnilNo ratings yet
- Transcription in ProkaryotesDocument18 pagesTranscription in ProkaryotesPrakash100% (1)
- Gene Expression 1Document28 pagesGene Expression 1ha88ial88No ratings yet
- 5 1 TranscriptionDocument24 pages5 1 TranscriptionKâmê KêlâhNo ratings yet
- 21 TranscriptionDocument39 pages21 TranscriptioneraasyahirahNo ratings yet
- LECT-09 Transcription in EukaryotesDocument27 pagesLECT-09 Transcription in EukaryotesFAKHRI HUSAINI NASUTION 1No ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument25 pagesTranscriptionYamunaa ElencovanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9Document66 pagesLesson 9Irica Mae CiervoNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Presented by Quratulain (19-Arid-1403) Asadullah (19-Arid-1379)Document32 pagesRegulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Presented by Quratulain (19-Arid-1403) Asadullah (19-Arid-1379)Beauty LiciousNo ratings yet
- Transcriptiontranslation 170210171328Document34 pagesTranscriptiontranslation 170210171328Farah B. BtoushNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- K3 - Central DogmaDocument41 pagesK3 - Central DogmaAditya MuchayatsyahNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument60 pagesProtein Synthesislucky mbaselaNo ratings yet
- Genes AssignmentDocument4 pagesGenes AssignmentKyle Hilary MatundingNo ratings yet
- Rna Biosynthesis (Transicription)Document33 pagesRna Biosynthesis (Transicription)Alaa AlmajedNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument35 pagesCentral Dogmatariqul13017No ratings yet
- Messenger Rnas (Mrnas) : This Class of Rnas Are The Genetic Coding TemplatesDocument8 pagesMessenger Rnas (Mrnas) : This Class of Rnas Are The Genetic Coding TemplatesRavi AlugubelliNo ratings yet
- Transcription Translation - Types of RNA 2022Document20 pagesTranscription Translation - Types of RNA 2022Merey ZiyabekNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Ofelia Solano Saludar: Department of Natural Sciences University of St. La Salle Bacolod CityDocument55 pagesMrs. Ofelia Solano Saludar: Department of Natural Sciences University of St. La Salle Bacolod CitymskikiNo ratings yet
- S2. Transcription Translation Gene RegulationDocument87 pagesS2. Transcription Translation Gene RegulationDeriq Maorenz CruzNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document5 pagesCH 6Jalovi SartiNo ratings yet
- Usanee Anukool (PH.D.) Clinical Microbiology Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences Chiang Mai University 2 July 2009Document60 pagesUsanee Anukool (PH.D.) Clinical Microbiology Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences Chiang Mai University 2 July 2009Suruk UdomsomNo ratings yet
- Studying BiologyDocument62 pagesStudying BiologyNicolas AliasNo ratings yet
- How Cells Work CompilationDocument18 pagesHow Cells Work CompilationJocelyn Diaz AbangNo ratings yet
- Transcripción - 1 Bio 363 Genética Molecular I Semestre 2021 Sergio MarshallDocument43 pagesTranscripción - 1 Bio 363 Genética Molecular I Semestre 2021 Sergio MarshallIgnacioHandyMoralesNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument19 pagesGene Expressionkvicto100% (1)
- RNA Synthesis, Processing SBT 211Document59 pagesRNA Synthesis, Processing SBT 211TADIWANASHE TINONETSANANo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument23 pagesTranscriptionNikhil PularruNo ratings yet
- Report in Cell BiologyIIDocument3 pagesReport in Cell BiologyIIGenessa Agustin BuenafeNo ratings yet
- RNA, DNA Transcription and RNA TranslationDocument5 pagesRNA, DNA Transcription and RNA TranslationHassan AljaberiNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT talks on science for young people: Molecular Biology!: Discover the secrets of life with the help of artificial intelligenceFrom EverandChatGPT talks on science for young people: Molecular Biology!: Discover the secrets of life with the help of artificial intelligenceNo ratings yet
- The Rise of Mixed Martial Arts: 20 Years of The Ultimate Fighting ChampionshipDocument15 pagesThe Rise of Mixed Martial Arts: 20 Years of The Ultimate Fighting Championshiptkaragiannis72100% (2)
- Science Spiral Progression Curriculum: The Factors Affecting Secondary Students' Learning ProgressDocument8 pagesScience Spiral Progression Curriculum: The Factors Affecting Secondary Students' Learning ProgressPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Lorax Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLorax Lesson Planapi-278032450No ratings yet
- The - Effect - of - Tax - Knowledge, - C 2020 Smart PlsDocument16 pagesThe - Effect - of - Tax - Knowledge, - C 2020 Smart PlsahmedNo ratings yet
- English 10-Q4-M7Document13 pagesEnglish 10-Q4-M7Joemar De Pascion NovillaNo ratings yet
- 200 MCQ On Modern Indian History With AnswerDocument23 pages200 MCQ On Modern Indian History With AnswerThokchom Sophia100% (2)
- 1Document4 pages1Surya TejaNo ratings yet
- Science Syllabus Key Stage 2Document79 pagesScience Syllabus Key Stage 2Fathimath NajdhaNo ratings yet
- Aiden and GlennaDocument18 pagesAiden and GlennaDebraDaumierNo ratings yet
- Eye ContactDocument12 pagesEye ContactÁnh Lã NgọcNo ratings yet
- Blood Diamond - SummaryDocument2 pagesBlood Diamond - SummaryKaustubh TirpudeNo ratings yet
- Infrasound Recording SystemDocument7 pagesInfrasound Recording SystemarunpdnNo ratings yet
- Internet: - The Term Internet Has Been Coined From Two Terms, I.e.Document11 pagesInternet: - The Term Internet Has Been Coined From Two Terms, I.e.Jesse JhangraNo ratings yet
- Analysis of MichelinDocument1 pageAnalysis of MichelinreganhinesNo ratings yet
- Ats Menjawab Soal Gin Nov21 Final 50Document14 pagesAts Menjawab Soal Gin Nov21 Final 50anton suponoNo ratings yet
- Birendra Mishra, Strained NepalDocument188 pagesBirendra Mishra, Strained NepaldhimlepNo ratings yet
- The Evil Consequence of Insulting Muhammad ( ) (Notes) - AuthenticTauheed PublicationsDocument17 pagesThe Evil Consequence of Insulting Muhammad ( ) (Notes) - AuthenticTauheed PublicationsAuthenticTauheedNo ratings yet
- Fermented Intoxicants and Other Beverages in Real Audiencia de QuitoDocument32 pagesFermented Intoxicants and Other Beverages in Real Audiencia de QuitoJuan Martínez BorreroNo ratings yet
- The Divine NamesDocument40 pagesThe Divine Namesbahjat62100% (1)
- Launch of A Hair OilDocument13 pagesLaunch of A Hair OilPawan Malve0% (1)
- Chapter 5-Leadership and MotivationDocument62 pagesChapter 5-Leadership and MotivationAklilu GirmaNo ratings yet
- NHS Digital PresentationDocument21 pagesNHS Digital PresentationInclusion NorthNo ratings yet
- Ikea - SwotDocument3 pagesIkea - SwotSerah SalemNo ratings yet
- 15 Shabaan AmaalDocument388 pages15 Shabaan AmaalSyed Zain HaiderNo ratings yet
- Final Report - Foot Orthosis PDFDocument79 pagesFinal Report - Foot Orthosis PDFAdnan4466No ratings yet
- Research ReportDocument6 pagesResearch ReportHidden MaskNo ratings yet
- Tugas Rutin 2 PEMODELANDocument3 pagesTugas Rutin 2 PEMODELANhilanNo ratings yet
- Selection and Grading of ContentDocument36 pagesSelection and Grading of ContentAli Gamil100% (1)