Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RESUME 23 Maret - Amelia Azzahra - 1906357534
RESUME 23 Maret - Amelia Azzahra - 1906357534
Uploaded by
Amelia AzzahraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Stanley Gibbons 'Commonwealth & British Empire Stamp Catalogue 2007' Report and Market UpdateDocument12 pagesStanley Gibbons 'Commonwealth & British Empire Stamp Catalogue 2007' Report and Market Updatepeter smith100% (1)
- prEN 6115Document15 pagesprEN 6115malotNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab: 1Dph BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB ,' BBBBBBBBBBBBBB /de 6Hfwlrq BBBBBBBDocument2 pagesPre-Lab: 1Dph BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB ,' BBBBBBBBBBBBBB /de 6Hfwlrq BBBBBBBAhnafHabibKhanNo ratings yet
- Advac Guerero Chapter 15Document18 pagesAdvac Guerero Chapter 15Drew BanlutaNo ratings yet
- L09 - Reliability EngrgDocument32 pagesL09 - Reliability EngrgU Kyaw Kyaw Naing100% (2)
- BTH780ReliabilityEngineeringLectureMaterial#1 (1) MergedDocument523 pagesBTH780ReliabilityEngineeringLectureMaterial#1 (1) MergedNeuky Els100% (1)
- A Binary Programming Model For SAIFI ConsideringDocument5 pagesA Binary Programming Model For SAIFI ConsideringhanabishimanNo ratings yet
- Design For Reliability Analisa Kegagalan Teknik Mesin USUDocument25 pagesDesign For Reliability Analisa Kegagalan Teknik Mesin USURahman SonowijoyoNo ratings yet
- Bpraps Unit 1Document67 pagesBpraps Unit 120EPS0701No ratings yet
- Project Reliability EngineeringDocument16 pagesProject Reliability EngineeringKartik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Making The Design RobustDocument12 pagesMaking The Design Robustram murthyNo ratings yet
- IE M6-Ktuassist - inDocument11 pagesIE M6-Ktuassist - inHemanth ANo ratings yet
- Maintenance Ass Q1Document6 pagesMaintenance Ass Q1Samatha Farai ZviuyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument7 pagesChapter IShaku SinglaNo ratings yet
- Reliability EngineeringDocument44 pagesReliability EngineeringSarthak RautNo ratings yet
- Reliability Engineering: Kartik Gupta 2K13/PE/016Document15 pagesReliability Engineering: Kartik Gupta 2K13/PE/016Kartik GuptaNo ratings yet
- CGE676 Lect. 1 PDFDocument12 pagesCGE676 Lect. 1 PDFHumaira ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- IE M6 Ktunotes - inDocument9 pagesIE M6 Ktunotes - inAkhil VSNo ratings yet
- Reliability Analysis in Cement Mills ofDocument6 pagesReliability Analysis in Cement Mills ofrecaiNo ratings yet
- Reliability Best Practices: Review TheseDocument18 pagesReliability Best Practices: Review TheseSV SANKARAMOORTHYNo ratings yet
- Pretoria Universiteit Testing RequirementsDocument29 pagesPretoria Universiteit Testing RequirementsChristian NissenNo ratings yet
- 26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations MDocument8 pages26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations Mgagan0312No ratings yet
- State-of-the-Art Predictive Maintenance TechniquesDocument13 pagesState-of-the-Art Predictive Maintenance TechniquesKleber VieiraNo ratings yet
- Repuestos Leer ImportanteDocument23 pagesRepuestos Leer Importantethomas chellewNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Maintenance Policies For A Yaw System Using Reliability-Centered Maintenance and Data-Driven Condition MonitoringDocument9 pagesOptimizing Maintenance Policies For A Yaw System Using Reliability-Centered Maintenance and Data-Driven Condition MonitoringclarkyeahNo ratings yet
- ÇıktıDocument20 pagesÇıktıCanan TAYGURTNo ratings yet
- Summa : of or orDocument3 pagesSumma : of or orSantiago BNo ratings yet
- Reliability & Failure Analysis: BY: Abdullah Omar Mohammed Abou ReashaDocument8 pagesReliability & Failure Analysis: BY: Abdullah Omar Mohammed Abou ReashaAbdullah Omar Abou ReashaNo ratings yet
- Determining The Reliability and Plant Availability of A Production SyztemDocument53 pagesDetermining The Reliability and Plant Availability of A Production SyztemGeorgina SuleNo ratings yet
- Reliability Centered MaintenanceDocument15 pagesReliability Centered MaintenanceEdmund YoongNo ratings yet
- Design For Reliability by AdeshDocument68 pagesDesign For Reliability by AdeshDelhiites AdeshNo ratings yet
- Product and System ReliabilityDocument34 pagesProduct and System ReliabilityRashesh Ambekar100% (1)
- Examining RCM Vs TPMDocument16 pagesExamining RCM Vs TPMcarrot123456No ratings yet
- RCM Alan PrideDocument16 pagesRCM Alan PrideambuenaflorNo ratings yet
- LECTURA 3 - Reliability Aspects of TribologyDocument8 pagesLECTURA 3 - Reliability Aspects of Tribologyeduardoperez.uniNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection PDFDocument12 pagesPower System Protection PDFBala MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Reliablity, Maintainability and AvailablityDocument17 pagesChapter 8 Reliablity, Maintainability and AvailablityabelNo ratings yet
- BTH 780 Reliability EngineeringDocument31 pagesBTH 780 Reliability EngineeringNeuky ElsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document50 pagesUnit 2habte gebreial shrashrNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: 1.1 Historical OverviewDocument72 pagesChapter One: 1.1 Historical OverviewPaulinusNo ratings yet
- RP Tutorial 1Document7 pagesRP Tutorial 1LinuschooNo ratings yet
- Confiabilidad 1Document13 pagesConfiabilidad 1Caviedes SierraNo ratings yet
- Net Protection GuideP11 20Document10 pagesNet Protection GuideP11 20Emmanuel ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Type of Production SystemDocument19 pagesType of Production SystemGeorgina SuleNo ratings yet
- Robustness Valdiation Step by StepDocument36 pagesRobustness Valdiation Step by StepGreenheart OussamaNo ratings yet
- AENG417 (PPT 1 & 2 (Document7 pagesAENG417 (PPT 1 & 2 (keeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Some Fiber Optic Measurement ProceduresDocument6 pagesSome Fiber Optic Measurement ProceduresAmir SalahNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document46 pagesUnit 2habte gebreial shrashrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 and 4 - Reliability, Maintainability, and Availability of Facilities and The Assessment and Control of Product Reliability - 2019Document35 pagesChapter 3 and 4 - Reliability, Maintainability, and Availability of Facilities and The Assessment and Control of Product Reliability - 2019endalkachewNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument13 pagesPresentationabhishekNo ratings yet
- RJS Relibility PPT-1Document61 pagesRJS Relibility PPT-1Ram Janm SinghNo ratings yet
- Abraham Tilahun GSE 6950 15Document13 pagesAbraham Tilahun GSE 6950 15Abraham tilahun100% (2)
- Tribology in Reliability EngineeringDocument8 pagesTribology in Reliability Engineeringeduardoperez.uniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 System Reliability Models and Redundancy Techniques in System DesignDocument47 pagesChapter - 3 System Reliability Models and Redundancy Techniques in System DesignRamana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Reliability EnggDocument20 pagesReliability EnggDipak DeyNo ratings yet
- Reliability Engineering: Chapter OutlineDocument14 pagesReliability Engineering: Chapter OutlineTarandeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Availibility TestDocument16 pagesAvailibility Testrudy_423522658No ratings yet
- Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability: Probability Models For PopulationsDocument8 pagesReliability, Availability, and Maintainability: Probability Models For PopulationsMani KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Design, Verify and Validate Emergency Shutdown SystemsDocument12 pagesHow To Design, Verify and Validate Emergency Shutdown SystemsJacekNo ratings yet
- Power System Reliability Assessment: Keynote Address OnDocument61 pagesPower System Reliability Assessment: Keynote Address OnkuncoroNo ratings yet
- Centaur-Reliability in The Whole Life Cycle of Building SystemsDocument19 pagesCentaur-Reliability in The Whole Life Cycle of Building Systemsmkhanyo46No ratings yet
- Reliability: Theory and ApplicationDocument36 pagesReliability: Theory and ApplicationYogesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Practical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationFrom EverandPractical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationNo ratings yet
- Mec 422 Lecture 4Document37 pagesMec 422 Lecture 4Zhen LinNo ratings yet
- Me Market-StructureDocument3 pagesMe Market-Structurebenedick marcialNo ratings yet
- Service DM Kalibrierung Tab Dienstleistungen enDocument2 pagesService DM Kalibrierung Tab Dienstleistungen enrcnexyNo ratings yet
- Cashless SwedenDocument2 pagesCashless SwedenMariann LieliNo ratings yet
- Final Project MrunalDocument53 pagesFinal Project MrunalPravin RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Brio125-3: Spare Parts CatalogueDocument56 pagesBrio125-3: Spare Parts CatalogueRomanos St.No ratings yet
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting GRE Instructions-OkDocument2 pages7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting GRE Instructions-OkSergio Castañeda100% (1)
- 05968Document4 pages05968Miguel ChaconNo ratings yet
- Bridgestone OTR Product Guide 03-07-2016 PDFDocument80 pagesBridgestone OTR Product Guide 03-07-2016 PDFwillupowersNo ratings yet
- AMT SyllabusDocument5 pagesAMT SyllabuschupchapNo ratings yet
- Japan, US Struggle To Find Crashed Jet and Its 'Secrets': Tokyo (AFP)Document2 pagesJapan, US Struggle To Find Crashed Jet and Its 'Secrets': Tokyo (AFP)Annastasya ParestiNo ratings yet
- GENG 3130 Sec 01 02 Syllabus Full 2022Document14 pagesGENG 3130 Sec 01 02 Syllabus Full 2022pass wordNo ratings yet
- Eutectic 19910: A Hard Nickel-Chromium Coating For Resistance To AbrasionDocument2 pagesEutectic 19910: A Hard Nickel-Chromium Coating For Resistance To AbrasionFactel SANo ratings yet
- 1611 enDocument16 pages1611 enyonestilo1986No ratings yet
- Spatio-Temporal Assessment of Urban Heat Island Effects in Kuala Lumpur Metropolitan City Using Landsat ImagesDocument9 pagesSpatio-Temporal Assessment of Urban Heat Island Effects in Kuala Lumpur Metropolitan City Using Landsat ImagesAshraf RamadanNo ratings yet
- Brief Note On The Trusteeship Approach As Proposed by Mahatma Gandhi - Business Studies - Knowledge HubDocument2 pagesBrief Note On The Trusteeship Approach As Proposed by Mahatma Gandhi - Business Studies - Knowledge HubSagar GavitNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues On Cash Waqf: A Review of The LiteratureDocument26 pagesContemporary Issues On Cash Waqf: A Review of The LiteratureSharifah NurulhudaNo ratings yet
- Afoem Sample Paper Stage B Written Exam Paper 7Document43 pagesAfoem Sample Paper Stage B Written Exam Paper 7Caity YoungNo ratings yet
- BL en BlancoDocument1 pageBL en Blancoana bejaranoNo ratings yet
- TDS EN PluxbentonN PDFDocument1 pageTDS EN PluxbentonN PDFusr1suNo ratings yet
- Adtran HDSL2 H2turDocument90 pagesAdtran HDSL2 H2tursexton hardfortNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle Journal Entries With Chart of AccountsDocument3 pagesAccounting Cycle Journal Entries With Chart of AccountsLala BoraNo ratings yet
- Digital Camer A Remote Control Cell Phone Mp3 Player Telephone Audio System Compac T DiskDocument3 pagesDigital Camer A Remote Control Cell Phone Mp3 Player Telephone Audio System Compac T Diskfelipe100% (1)
- The Impact of National Culture PDFDocument30 pagesThe Impact of National Culture PDFJovanaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology2B (HYOCIB2) Department: Civil Engineering Technology Programme: Bachelor of Engineering Technology (BET) : CivilDocument14 pagesHydrology2B (HYOCIB2) Department: Civil Engineering Technology Programme: Bachelor of Engineering Technology (BET) : CivilnickyNo ratings yet
RESUME 23 Maret - Amelia Azzahra - 1906357534
RESUME 23 Maret - Amelia Azzahra - 1906357534
Uploaded by
Amelia AzzahraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RESUME 23 Maret - Amelia Azzahra - 1906357534
RESUME 23 Maret - Amelia Azzahra - 1906357534
Uploaded by
Amelia AzzahraCopyright:
Available Formats
RESUME KULIAH KAPITA SELEKTRA 23 MARET 2022
Speaker: Prof. Nobuo Mitomo
AMELIA AZZAHRA BERLIANTY
1906357534
RELIABILITY ENGINEERING
Importance of Reliability Engineering
• Improves and guarantees the quality and reliability
• Prevent recurrence and safety problems
THREE COMPONENTS OF RELIABILITY ENGINEERING
Definition of Durability
No matter how great the functionality of a system, if it doesn’t last for a long time, it cannot
be said to have good reliability.
Maintanability
• No failure in the operatuin of the equipment of systems if they can be constantly
monitored for the failures or malfunctions thay can be repaired so can be immediately
used or linked to systems
• Also implies ease of maintenance
Design reliability: maintaine and achieve system functions → based on concepts such as
fall-safe, and foolprof which prevents human negligence
It is an engineering of management technology that is crosscutting and related to specific
engineering disciplines above.
Basic theory of reliability engineering
a. Statistical analysis of reliability data: Example artificial engineering
b. System reliability
c. Maintainability and availability: should complemetnt functional maintenance. To
improve maintainability, important to devise a system that makes it easier to detect
and correct failures and their signs.
Maintanability failure pattern
1. Decreasing failure rate: seen in cases where many failures due to design or
manufacturing defects, which are then eliminated with good lots. Screening by burn-
in is done to overcome
2. CFR (Constant failure rate) : failure rate is constant, independent of time,
incidentally, independent of usage hsistory
3. IFR (Increasing failure rate): seen in failures due to corrosion and deterioration of
solution. Prevention: replacement or overhaul before deterioration progresses is
effective.
COMPLEX SYSTEM FAILURE PATTERN
in the initial failure, failure rate is high due to defects in
parts/materials and variations in the manufacturing process,
but decreases. After that, enters a stable state and become
CFRtype.
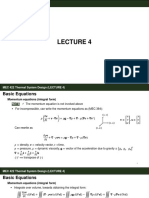
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF RELIABILITY DATA
Reliability test data: obtained by conducting test, controlling conditions, measuring life time,
number of shocks applied
Field Data: lifetime on products and environments in the market places, can be obtained
because it reflects real-world condition
WEIBULL ANALYSIS
Distribution of fracture strength of materials based on
the weakest ring model. Strength distribution that focuses on the fact that the chain breaks.
Asumme based on the empirical support that most lifetime data fits the distribution. Paramtric
methods are used due to small number of data.
Distribution shape →
M: shapre parameter, n : scale parameter. F(t) may have different shapes.
You might also like
- Stanley Gibbons 'Commonwealth & British Empire Stamp Catalogue 2007' Report and Market UpdateDocument12 pagesStanley Gibbons 'Commonwealth & British Empire Stamp Catalogue 2007' Report and Market Updatepeter smith100% (1)
- prEN 6115Document15 pagesprEN 6115malotNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab: 1Dph BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB ,' BBBBBBBBBBBBBB /de 6Hfwlrq BBBBBBBDocument2 pagesPre-Lab: 1Dph BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB ,' BBBBBBBBBBBBBB /de 6Hfwlrq BBBBBBBAhnafHabibKhanNo ratings yet
- Advac Guerero Chapter 15Document18 pagesAdvac Guerero Chapter 15Drew BanlutaNo ratings yet
- L09 - Reliability EngrgDocument32 pagesL09 - Reliability EngrgU Kyaw Kyaw Naing100% (2)
- BTH780ReliabilityEngineeringLectureMaterial#1 (1) MergedDocument523 pagesBTH780ReliabilityEngineeringLectureMaterial#1 (1) MergedNeuky Els100% (1)
- A Binary Programming Model For SAIFI ConsideringDocument5 pagesA Binary Programming Model For SAIFI ConsideringhanabishimanNo ratings yet
- Design For Reliability Analisa Kegagalan Teknik Mesin USUDocument25 pagesDesign For Reliability Analisa Kegagalan Teknik Mesin USURahman SonowijoyoNo ratings yet
- Bpraps Unit 1Document67 pagesBpraps Unit 120EPS0701No ratings yet
- Project Reliability EngineeringDocument16 pagesProject Reliability EngineeringKartik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Making The Design RobustDocument12 pagesMaking The Design Robustram murthyNo ratings yet
- IE M6-Ktuassist - inDocument11 pagesIE M6-Ktuassist - inHemanth ANo ratings yet
- Maintenance Ass Q1Document6 pagesMaintenance Ass Q1Samatha Farai ZviuyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument7 pagesChapter IShaku SinglaNo ratings yet
- Reliability EngineeringDocument44 pagesReliability EngineeringSarthak RautNo ratings yet
- Reliability Engineering: Kartik Gupta 2K13/PE/016Document15 pagesReliability Engineering: Kartik Gupta 2K13/PE/016Kartik GuptaNo ratings yet
- CGE676 Lect. 1 PDFDocument12 pagesCGE676 Lect. 1 PDFHumaira ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- IE M6 Ktunotes - inDocument9 pagesIE M6 Ktunotes - inAkhil VSNo ratings yet
- Reliability Analysis in Cement Mills ofDocument6 pagesReliability Analysis in Cement Mills ofrecaiNo ratings yet
- Reliability Best Practices: Review TheseDocument18 pagesReliability Best Practices: Review TheseSV SANKARAMOORTHYNo ratings yet
- Pretoria Universiteit Testing RequirementsDocument29 pagesPretoria Universiteit Testing RequirementsChristian NissenNo ratings yet
- 26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations MDocument8 pages26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations Mgagan0312No ratings yet
- State-of-the-Art Predictive Maintenance TechniquesDocument13 pagesState-of-the-Art Predictive Maintenance TechniquesKleber VieiraNo ratings yet
- Repuestos Leer ImportanteDocument23 pagesRepuestos Leer Importantethomas chellewNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Maintenance Policies For A Yaw System Using Reliability-Centered Maintenance and Data-Driven Condition MonitoringDocument9 pagesOptimizing Maintenance Policies For A Yaw System Using Reliability-Centered Maintenance and Data-Driven Condition MonitoringclarkyeahNo ratings yet
- ÇıktıDocument20 pagesÇıktıCanan TAYGURTNo ratings yet
- Summa : of or orDocument3 pagesSumma : of or orSantiago BNo ratings yet
- Reliability & Failure Analysis: BY: Abdullah Omar Mohammed Abou ReashaDocument8 pagesReliability & Failure Analysis: BY: Abdullah Omar Mohammed Abou ReashaAbdullah Omar Abou ReashaNo ratings yet
- Determining The Reliability and Plant Availability of A Production SyztemDocument53 pagesDetermining The Reliability and Plant Availability of A Production SyztemGeorgina SuleNo ratings yet
- Reliability Centered MaintenanceDocument15 pagesReliability Centered MaintenanceEdmund YoongNo ratings yet
- Design For Reliability by AdeshDocument68 pagesDesign For Reliability by AdeshDelhiites AdeshNo ratings yet
- Product and System ReliabilityDocument34 pagesProduct and System ReliabilityRashesh Ambekar100% (1)
- Examining RCM Vs TPMDocument16 pagesExamining RCM Vs TPMcarrot123456No ratings yet
- RCM Alan PrideDocument16 pagesRCM Alan PrideambuenaflorNo ratings yet
- LECTURA 3 - Reliability Aspects of TribologyDocument8 pagesLECTURA 3 - Reliability Aspects of Tribologyeduardoperez.uniNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection PDFDocument12 pagesPower System Protection PDFBala MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Reliablity, Maintainability and AvailablityDocument17 pagesChapter 8 Reliablity, Maintainability and AvailablityabelNo ratings yet
- BTH 780 Reliability EngineeringDocument31 pagesBTH 780 Reliability EngineeringNeuky ElsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document50 pagesUnit 2habte gebreial shrashrNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: 1.1 Historical OverviewDocument72 pagesChapter One: 1.1 Historical OverviewPaulinusNo ratings yet
- RP Tutorial 1Document7 pagesRP Tutorial 1LinuschooNo ratings yet
- Confiabilidad 1Document13 pagesConfiabilidad 1Caviedes SierraNo ratings yet
- Net Protection GuideP11 20Document10 pagesNet Protection GuideP11 20Emmanuel ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Type of Production SystemDocument19 pagesType of Production SystemGeorgina SuleNo ratings yet
- Robustness Valdiation Step by StepDocument36 pagesRobustness Valdiation Step by StepGreenheart OussamaNo ratings yet
- AENG417 (PPT 1 & 2 (Document7 pagesAENG417 (PPT 1 & 2 (keeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Some Fiber Optic Measurement ProceduresDocument6 pagesSome Fiber Optic Measurement ProceduresAmir SalahNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document46 pagesUnit 2habte gebreial shrashrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 and 4 - Reliability, Maintainability, and Availability of Facilities and The Assessment and Control of Product Reliability - 2019Document35 pagesChapter 3 and 4 - Reliability, Maintainability, and Availability of Facilities and The Assessment and Control of Product Reliability - 2019endalkachewNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument13 pagesPresentationabhishekNo ratings yet
- RJS Relibility PPT-1Document61 pagesRJS Relibility PPT-1Ram Janm SinghNo ratings yet
- Abraham Tilahun GSE 6950 15Document13 pagesAbraham Tilahun GSE 6950 15Abraham tilahun100% (2)
- Tribology in Reliability EngineeringDocument8 pagesTribology in Reliability Engineeringeduardoperez.uniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 System Reliability Models and Redundancy Techniques in System DesignDocument47 pagesChapter - 3 System Reliability Models and Redundancy Techniques in System DesignRamana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Reliability EnggDocument20 pagesReliability EnggDipak DeyNo ratings yet
- Reliability Engineering: Chapter OutlineDocument14 pagesReliability Engineering: Chapter OutlineTarandeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Availibility TestDocument16 pagesAvailibility Testrudy_423522658No ratings yet
- Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability: Probability Models For PopulationsDocument8 pagesReliability, Availability, and Maintainability: Probability Models For PopulationsMani KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Design, Verify and Validate Emergency Shutdown SystemsDocument12 pagesHow To Design, Verify and Validate Emergency Shutdown SystemsJacekNo ratings yet
- Power System Reliability Assessment: Keynote Address OnDocument61 pagesPower System Reliability Assessment: Keynote Address OnkuncoroNo ratings yet
- Centaur-Reliability in The Whole Life Cycle of Building SystemsDocument19 pagesCentaur-Reliability in The Whole Life Cycle of Building Systemsmkhanyo46No ratings yet
- Reliability: Theory and ApplicationDocument36 pagesReliability: Theory and ApplicationYogesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Practical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationFrom EverandPractical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationNo ratings yet
- Mec 422 Lecture 4Document37 pagesMec 422 Lecture 4Zhen LinNo ratings yet
- Me Market-StructureDocument3 pagesMe Market-Structurebenedick marcialNo ratings yet
- Service DM Kalibrierung Tab Dienstleistungen enDocument2 pagesService DM Kalibrierung Tab Dienstleistungen enrcnexyNo ratings yet
- Cashless SwedenDocument2 pagesCashless SwedenMariann LieliNo ratings yet
- Final Project MrunalDocument53 pagesFinal Project MrunalPravin RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Brio125-3: Spare Parts CatalogueDocument56 pagesBrio125-3: Spare Parts CatalogueRomanos St.No ratings yet
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting GRE Instructions-OkDocument2 pages7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting GRE Instructions-OkSergio Castañeda100% (1)
- 05968Document4 pages05968Miguel ChaconNo ratings yet
- Bridgestone OTR Product Guide 03-07-2016 PDFDocument80 pagesBridgestone OTR Product Guide 03-07-2016 PDFwillupowersNo ratings yet
- AMT SyllabusDocument5 pagesAMT SyllabuschupchapNo ratings yet
- Japan, US Struggle To Find Crashed Jet and Its 'Secrets': Tokyo (AFP)Document2 pagesJapan, US Struggle To Find Crashed Jet and Its 'Secrets': Tokyo (AFP)Annastasya ParestiNo ratings yet
- GENG 3130 Sec 01 02 Syllabus Full 2022Document14 pagesGENG 3130 Sec 01 02 Syllabus Full 2022pass wordNo ratings yet
- Eutectic 19910: A Hard Nickel-Chromium Coating For Resistance To AbrasionDocument2 pagesEutectic 19910: A Hard Nickel-Chromium Coating For Resistance To AbrasionFactel SANo ratings yet
- 1611 enDocument16 pages1611 enyonestilo1986No ratings yet
- Spatio-Temporal Assessment of Urban Heat Island Effects in Kuala Lumpur Metropolitan City Using Landsat ImagesDocument9 pagesSpatio-Temporal Assessment of Urban Heat Island Effects in Kuala Lumpur Metropolitan City Using Landsat ImagesAshraf RamadanNo ratings yet
- Brief Note On The Trusteeship Approach As Proposed by Mahatma Gandhi - Business Studies - Knowledge HubDocument2 pagesBrief Note On The Trusteeship Approach As Proposed by Mahatma Gandhi - Business Studies - Knowledge HubSagar GavitNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues On Cash Waqf: A Review of The LiteratureDocument26 pagesContemporary Issues On Cash Waqf: A Review of The LiteratureSharifah NurulhudaNo ratings yet
- Afoem Sample Paper Stage B Written Exam Paper 7Document43 pagesAfoem Sample Paper Stage B Written Exam Paper 7Caity YoungNo ratings yet
- BL en BlancoDocument1 pageBL en Blancoana bejaranoNo ratings yet
- TDS EN PluxbentonN PDFDocument1 pageTDS EN PluxbentonN PDFusr1suNo ratings yet
- Adtran HDSL2 H2turDocument90 pagesAdtran HDSL2 H2tursexton hardfortNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle Journal Entries With Chart of AccountsDocument3 pagesAccounting Cycle Journal Entries With Chart of AccountsLala BoraNo ratings yet
- Digital Camer A Remote Control Cell Phone Mp3 Player Telephone Audio System Compac T DiskDocument3 pagesDigital Camer A Remote Control Cell Phone Mp3 Player Telephone Audio System Compac T Diskfelipe100% (1)
- The Impact of National Culture PDFDocument30 pagesThe Impact of National Culture PDFJovanaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology2B (HYOCIB2) Department: Civil Engineering Technology Programme: Bachelor of Engineering Technology (BET) : CivilDocument14 pagesHydrology2B (HYOCIB2) Department: Civil Engineering Technology Programme: Bachelor of Engineering Technology (BET) : CivilnickyNo ratings yet