Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quantities Report - NAA
Quantities Report - NAA
Uploaded by
asamselaseCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Standard BoQ (UAE - DoT) - CESMM4 PDFDocument554 pagesStandard BoQ (UAE - DoT) - CESMM4 PDFNektarios Matheou87% (45)
- Engineering Measurement and Evaluation Cec214Document12 pagesEngineering Measurement and Evaluation Cec214Hussaini bobo65% (17)
- Part 1 - General: Important Note Regarding "Document9 pagesPart 1 - General: Important Note Regarding "MohamedNo ratings yet
- QS For Graduate Level - C & GDocument39 pagesQS For Graduate Level - C & GDushan Senarathne100% (1)
- Manual de Taller Tractor l4100Document120 pagesManual de Taller Tractor l4100Jorge Puentes SeoaneNo ratings yet
- How to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionFrom EverandHow to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Unit I - IntroductionDocument7 pagesUnit I - IntroductionBAGUMA NELSONNo ratings yet
- 2 - TOPIC 1 - Principle of MeasurementDocument27 pages2 - TOPIC 1 - Principle of MeasurementNUR SYAQIRAH TAJUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Bill of Quantity - 02.12.2022Document8 pagesLecture 11 - Bill of Quantity - 02.12.2022Timothy GodwinNo ratings yet
- Quantity SurveyingDocument111 pagesQuantity Surveyingsakshi singhNo ratings yet
- Technical Terms: Module-1Document33 pagesTechnical Terms: Module-1Gireesh Gowda GiriNo ratings yet
- Siddiq Khan - Bill of QuantitiesDocument10 pagesSiddiq Khan - Bill of Quantitiesguyii86100% (1)
- ADocument46 pagesADushan SenarathneNo ratings yet
- Work Descriptions Package 3BDocument41 pagesWork Descriptions Package 3BAlireza entNo ratings yet
- CESMM MalaysiaDocument50 pagesCESMM Malaysialaurenjia83% (6)
- Quant TTTTT TTTTTDocument10 pagesQuant TTTTT TTTTTasamselaseNo ratings yet
- 01 Billing - Introduction To Billing v2Document9 pages01 Billing - Introduction To Billing v2Daniel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Civil MeasurementDocument47 pagesCivil MeasurementEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Standard Method of MeasurementsDocument24 pagesCivil Engineering Standard Method of MeasurementsRatnesh Patel100% (1)
- Case Study Preparation Bill of QuantitiesDocument6 pagesCase Study Preparation Bill of QuantitiesMuhd FaiqNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Costing (A70138) : Lecture NotesDocument73 pagesEstimation and Costing (A70138) : Lecture Noteshakim imtiyazNo ratings yet
- EN-2023 0005 a13+-+Lot+2+-+Template+for+technical+offer+1.00+New 001Document19 pagesEN-2023 0005 a13+-+Lot+2+-+Template+for+technical+offer+1.00+New 001niyascaNo ratings yet
- QSCM Upto 1st I.A.Document10 pagesQSCM Upto 1st I.A.Md.saifaadil AttarNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction To Elemental Cost AnalysisDocument17 pages1.0 Introduction To Elemental Cost AnalysisMon Luffy100% (1)
- 1.0 Introduction To Elemental Cost AnalysisDocument17 pages1.0 Introduction To Elemental Cost AnalysisMon LuffyNo ratings yet
- TTLM L-III M03 Preparing Bill of QuantitiesDocument61 pagesTTLM L-III M03 Preparing Bill of Quantitiesfayera letaNo ratings yet
- Drawing StandardsDocument12 pagesDrawing StandardsAgung Bayu100% (1)
- Ce2402 Eqs NotesDocument160 pagesCe2402 Eqs NotesrajNo ratings yet
- Long Report TemplateDocument23 pagesLong Report TemplateSardar Hamid ullahNo ratings yet
- Composing Descriptions For Bills of Quantities in Accordance WithDocument18 pagesComposing Descriptions For Bills of Quantities in Accordance WithdduffyNo ratings yet
- Standard Methods of Measurement For Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesStandard Methods of Measurement For Civil EngineeringRajanRanjan83% (12)
- Malaysian Standard Methods of Measurement For Civil Engineering WorksDocument23 pagesMalaysian Standard Methods of Measurement For Civil Engineering Worksrosmarina_rahma9813100% (18)
- Iare E&c Lecture Notes PDFDocument110 pagesIare E&c Lecture Notes PDFRichik MondalNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Costing (A70138) : Lecture NotesDocument110 pagesEstimation and Costing (A70138) : Lecture NotesRakshith Gowda100% (1)
- Estimation and Costing PDFDocument51 pagesEstimation and Costing PDFPARVATHANENI SAI KRISHNANo ratings yet
- BTQS 3044 - Measurement of External Works L1b IntroDocument27 pagesBTQS 3044 - Measurement of External Works L1b IntroLE PEI CHIANo ratings yet
- Section 01270-UNIT PRICESDocument2 pagesSection 01270-UNIT PRICESIm ChinithNo ratings yet
- Method of MeasurementsDocument41 pagesMethod of MeasurementsKrishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Tractor: TracteurDocument118 pagesTractor: TracteuryogismNo ratings yet
- AQS 4204 Assignments Bouquet 2020Document7 pagesAQS 4204 Assignments Bouquet 2020Pasipanodya TsambatareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction of SMM For Civil Eng WorksDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction of SMM For Civil Eng WorksTerwabe WapagovskiNo ratings yet
- Handbook-for-Preparing-Bill-of-Quantities-for Civil-Engineeering-Works PDFDocument248 pagesHandbook-for-Preparing-Bill-of-Quantities-for Civil-Engineeering-Works PDFcheewingyuenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Introduction+types of Tender)Document15 pagesChapter 1 (Introduction+types of Tender)saifulsabdin100% (1)
- Week 9 - Bill of QuantitiesDocument17 pagesWeek 9 - Bill of QuantitiesNUR FATINAH BINTI ZOLKIFLI 5ENo ratings yet
- Draft, SBD, Services (Non-Consultant)Document67 pagesDraft, SBD, Services (Non-Consultant)Muhammad Umair KabeerNo ratings yet
- QS 002 Midterm CompilationDocument443 pagesQS 002 Midterm CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- QS 002 Module 3 CompilationDocument200 pagesQS 002 Module 3 CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Part-2 (A) Scope of WorksDocument249 pagesPart-2 (A) Scope of Worksjai karanNo ratings yet
- B.O.Q PreparationDocument7 pagesB.O.Q PreparationYelisa Danny DenzelNo ratings yet
- Victorious Staff ESB 300Document5 pagesVictorious Staff ESB 300Chikwason Sarcozy MwanzaNo ratings yet
- Quantity Take OffDocument26 pagesQuantity Take OffTien Ngo Minh100% (1)
- Business Management for Scientists and Engineers: How I Overcame My Moment of Inertia and Embraced the Dark SideFrom EverandBusiness Management for Scientists and Engineers: How I Overcame My Moment of Inertia and Embraced the Dark SideNo ratings yet
- Static Analysis of Software: The Abstract InterpretationFrom EverandStatic Analysis of Software: The Abstract InterpretationNo ratings yet
- Codification of Statements on Standards for Attestation Engagements, January 2018From EverandCodification of Statements on Standards for Attestation Engagements, January 2018No ratings yet
- Rainfall-Induced Slope Instability PRESENTATIONDocument15 pagesRainfall-Induced Slope Instability PRESENTATIONasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Rose S$DDocument22 pagesRose S$DasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Induction Training Report - Planning Division: AcknowledgementDocument44 pagesInduction Training Report - Planning Division: AcknowledgementasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Induction Training Report - Naa Koshie LampteyDocument21 pagesAcknowledgement: Induction Training Report - Naa Koshie LampteyasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Contracts Naa (Repaired)Document26 pagesContracts Naa (Repaired)asamselaseNo ratings yet
- U-Drain 900Document2 pagesU-Drain 900asamselaseNo ratings yet
- Quant TTTTT TTTTTDocument10 pagesQuant TTTTT TTTTTasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Measurement Sheet: Project: EarthworksDocument57 pagesMeasurement Sheet: Project: EarthworksasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SOURCES & FOUNDATIONS OF HUMAN RIGHTS LAWDocument6 pagesChapter 2 SOURCES & FOUNDATIONS OF HUMAN RIGHTS LAWI Lobeu My CaratNo ratings yet
- Tabelas Roscas TrapezoidaisDocument49 pagesTabelas Roscas TrapezoidaisDesenvolvimento MHNo ratings yet
- Growth of Robotics in IndiaDocument14 pagesGrowth of Robotics in Indianitul deoriNo ratings yet
- Chziri Zjr2 User ManualDocument51 pagesChziri Zjr2 User ManualJosé Henríquez V.No ratings yet
- Building Chatbots in Python Chapter2 PDFDocument41 pagesBuilding Chatbots in Python Chapter2 PDFFgpeqwNo ratings yet
- Miama: A Small Introduction To The Free Font Miama by Linus Romer, AugustDocument5 pagesMiama: A Small Introduction To The Free Font Miama by Linus Romer, Augustjose chaveroNo ratings yet
- StudyGuide CosmonautDocument25 pagesStudyGuide CosmonautAzuWillDieNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training ReportDocument6 pagesIndustrial Training Reportmayank guptaNo ratings yet
- Revision On Unit 1,2 First Secondry (Hello)Document11 pagesRevision On Unit 1,2 First Secondry (Hello)Vivian GendyNo ratings yet
- Anthropomorphic Hand PresentationDocument22 pagesAnthropomorphic Hand PresentationAnshulNo ratings yet
- Hindalco ReportDocument42 pagesHindalco ReportAman RoyNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Construction of Urban Intersections With Portlandcement Concrete Pavement (PCCP)Document3 pagesAccelerated Construction of Urban Intersections With Portlandcement Concrete Pavement (PCCP)A-16 RUSHALINo ratings yet
- Tutorial Materials SelectionDocument2 pagesTutorial Materials SelectionSyahmiNo ratings yet
- The Ethnography of Communication: Mădălina MATEIDocument8 pagesThe Ethnography of Communication: Mădălina MATEIamir_marzbanNo ratings yet
- UPNMG Press Statement-Unemployed Nurses and MidwivesDocument1 pageUPNMG Press Statement-Unemployed Nurses and MidwivesClavia NyaabaNo ratings yet
- Pineal Gland A Spiritual Third Eye An OdDocument4 pagesPineal Gland A Spiritual Third Eye An OdAsli Melek DoenerNo ratings yet
- Sensor Manual 1Document11 pagesSensor Manual 1Tame PcAddictNo ratings yet
- The Microsoft-Nokia Strategic Alliance PDFDocument25 pagesThe Microsoft-Nokia Strategic Alliance PDFmehedee129No ratings yet
- Gear Agma IIDocument49 pagesGear Agma IInathNo ratings yet
- Final 2 PLSQLDocument16 pagesFinal 2 PLSQLBadri Mahmoud AliNo ratings yet
- 19Document227 pages19Miguel José DuarteNo ratings yet
- Cut Out ValveDocument64 pagesCut Out ValveHoang L A TuanNo ratings yet
- Ecs 2ar FDocument39 pagesEcs 2ar FĐức LêNo ratings yet
- Product 043 UMDocument31 pagesProduct 043 UMPankaj MauryaNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesDocument5 pagesComparative and Superlative AdjectivesYoussef BrsNo ratings yet
- Kuwait Business Directory SampleDocument1 pageKuwait Business Directory SampleDrMohamed RifasNo ratings yet
- BUS203 Term Paper - Section 04Document16 pagesBUS203 Term Paper - Section 04Sumaiya Selim SushmeNo ratings yet
- SS Disco Check Valve (Size 15-100)Document2 pagesSS Disco Check Valve (Size 15-100)rudirstNo ratings yet
- Colah Github Io Posts 2015 08 Understanding LSTMsDocument16 pagesColah Github Io Posts 2015 08 Understanding LSTMsMithun PantNo ratings yet
- Cable Gland HAWKER - CatalogueDocument87 pagesCable Gland HAWKER - CatalogueJean SantosNo ratings yet
Quantities Report - NAA
Quantities Report - NAA
Uploaded by
asamselaseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quantities Report - NAA
Quantities Report - NAA
Uploaded by
asamselaseCopyright:
Available Formats
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
Table of Contents
1.0 INTRODUCTION..............................................................................................................1
2.0 ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE:...............................................................................2
FIG 1: ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE..........................................................................2
3.0 CIVIL ENGINEERING MEASUREMENTS...............................................................3
3.1 Introduction to CESSM3....................................................................................................3
3.1.1 General items...................................................................................................................4
3.1.2 Work classification..........................................................................................................4
3.1.3 Coding and numbering....................................................................................................4
3.1.4 Item numbers...................................................................................................................5
3.1.5 Coding of unclassified items...........................................................................................5
3.1.6 Mode of description.........................................................................................................6
3.1.7 Unit of measurement.......................................................................................................6
3.1.8 Additional description rules............................................................................................6
3.2 Introduction to Bill of Quantity (BOQ)..............................................................................6
3.2.1 Purpose of Bill of Quantities...........................................................................................6
3.2.2 Content of Bills of Quantities..........................................................................................7
Section A: List of Principal Quantities........................................................................................7
Section B: Preamble.....................................................................................................................7
Section C: Day Works..................................................................................................................8
Section D: Works items and Classifications................................................................................8
Section E: Grand Summary..........................................................................................................8
FIG 2: SECTIONS OF BOQ....................................................................................................8
3.2.3 Production of Bill of Quantities......................................................................................9
4.0 Taking off 1km Road…………………………………………………………………12
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page i
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
CHAPTER 1
1.0 INTRODUCTION
The Quantities Division is one of the eight divisions of the development department of Ghana
Highway Authority. The division is headed by a director who is assisted by two managers:
Quantities Manager Development and Quantities Manager Maintenance. The Division is charged
with the responsibility of:
1. Preparation and checking of tender documents
2. Vetting of payment certificates
3. Estimation of road works
4. Advising other divisions on issues relating to costing
During my two months induction training with the Quantities Division I was scheduled to
receive training in the form of lectures and discussions and this was undertaken by surveyors in
the Quantities section. This report elaborates on my experience with the Quantities Division.
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 1
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
CHAPTER TWO
2.0 ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE:
FIG 1: ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 2
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
CHAPTER THREE
3.0 CIVIL ENGINEERING MEASUREMENTS
3.1 Introduction to CESSM3
Quantities of Civil Engineering works are normally measured in accordance with the standard
method of measurement of civil engineering quantities (CESMM3).
The civil engineering standard method of measurements (CESMM) helps to secure a more
comprehensive, uniform and rationalized approach to measurement with its standardized
terminology and three levels of description.
The method of measurement seeks to:
Standardize the layout and content of Bills of Quantities
Bring about a systematic structure and uniformity of items measured by means of
standard phrases and method related instructions
Increase the number of work and revise the type, nature and subdivision of work into
measurement items
Update the measurement code to make it easier with new techniques
Allow the Contractor to ‘write in’ items relating to special constructional techniques or to
particular provisions which directly affect construction methods and therefore should be
reflected in tenders
Provide a list of brief identifying descriptions that do not repeat information found on the
drawings or in the specifications and will be available for use in the preparation of
valuations.
One of the main functions of a civil engineering bill of quantities is to provide a basis on which
tenders can be obtained and, when the bills are priced, they afford a means of comparing the
various tenders received, both as regard totals and individual rates. After the contract has been
signed, the rate in the priced bill of quantities can be used to assess the value of the work as
executed, and help in the preparation of interim statements.
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 3
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
3.1.1 General items
These are works not part of the permanent works. i.e. contractual, specific requirements, method
rated charges.
Contractual –for contractors
Specific requirements-for engineers.ie they are required to facilitate smooth flow of work
Method related charges-facilitate the method contractors will work with.
Examples
Provide performance bond code A110
Provide third party insurance A130
Provide third party against injury to personnel A130.1
Provide third party personnel against injury to equipment A130.2
3.1.2 Work classification
The works encountered in civil engineering contracts are classified into 26 main classes. i.e. A-Z
Each class is further sub-divided into three (3) divisions which classify works at successive
levels of detail. Each division comprises a list of 8 descriptive features of work.
An example
Class F (in –situ concrete) contains three divisions of classification. The first classifies different
types of in situ concrete.
The second classifies the strength and location and the third division classifies the aggregate size
and thickness of cross sectioned area.
3.1.3 Coding and numbering
Each item in the work classification is coded for easy identification starting from A-Z and
numbered.
The letters represent the classes while digits give the position of the item. These positions are in
the first second and third divisions.
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 4
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
An example
Code E322 identifies an item as follows:
Class: E Earthworks
First division: 3 Excavation of foundations
Second division: 2 Material other than top soil, rock or artificial
Third division 2 Maximum depth 0.25-0.5m
Sometimes the symbol * is used to Indicate all numbers in the appropriate division
An example
A27* meaning group of code numbers from A 271 toA278 inclusive
3.1.4 Item numbers
Code numbers could be used in the bill of quantities (BOQ).this is done in ascending code
number. When code numbers are used as item numbers in BOQ, they should not be part of item
description.
Example
Item Description Qty Unit Rate Amount
No
A110 Performance bond
A120 Insurance of work
3.1.5 Coding of unclassified items
In coding of unclassified items, digit shall be used in the appropriate positions in the code
number where feature of item is not listed in the work classification.
Example
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 5
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
Item A339 –where digit 9 is used as plant for mixing chippings.
Item E120 - where digit 0 is used when the division of classification is open ended.(excavation
by dredging)
3.1.6 Mode of description
Item description should identify the component of works not the task to be carried out by the
contractor.
An example
High yield steel bar reinforcement to BS 4449 nominal size 20mm not supply, deliver, cut bend
high yield bar reinforcement to BS4449 nominal size 20mm.
3.1.7 Unit of measurement
The unit of measurement stated against a descriptive feature should be the same for all items to
which that descriptive feature applies.
3.1.8 Additional description rules
These are additional description rules used in describing items of work.
A separate item would be given in some instances where additional description is given for
component of work exhibiting different additional features.
They are normally separated with a decimal.
Example
Item D310.1 which might be “stump removal 150-500mm diameter and backfill hole with gravel
Item D310.2 which might be “stump removal 150-500mm diameter and backfill hole with clay
material.
3.2 Introduction to Bill of Quantity (BOQ)
3.2.1 Purpose of Bill of Quantities
The bill of quantities of a contract assists in the engineering field in the following ways:
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 6
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
It enables all contractors tendering for a contract to price on exactly the same information
with a minimum of effort.
It provides a basis for the evaluation of variations which often occur during the progress
of work.
It gives an itemized list of the component parts of projects, with a full description and the
quantity of each part, and this may assist the successful contractor in ordering materials
and assessing his labour requirement for the contract.
After being priced, it provides a good basis for a cost analysis, which subsequently will
be of use on future contracts in cost panning work.
3.2.2 Content of Bills of Quantities
The CESSM3 presents a standard format for Bills of Quantities. Bills are to have five sections as
follows:
Section A: List of Principal Quantities
Section B: Preamble
Section C: Day Works
Section D: Works items and Classifications
Section E: Grand summary
Section A: List of Principal Quantities
The first section of the Bill of Quantities is the list of principal quantities.
This list is to precede the preamble to the bill of quantities.The early part of the specification
should describe the nature, magnitude, output or size of the principal components of the works so
that the extent of the works required is defined and readily appreciated. This is also useful if the
cost of the contract is to be of value for cost analysis purposes in the tendering process.
Section B: Preamble
The preamble can be grouped into three items:
Inclusions and narrating of any other standard method of measurement used in measuring
ancillary works on the contract
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 7
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
Any amendment to the CESSM adopted by the Measurement Engineer or Quantity
Surveyor for the Contract
Where excavation, boring or driving is included, a definition of Rock is given in the
preamble to aid measurement.
Section C: Day Works
Day work means the method of valuing work on the basis of time spent by the workmen, the
materials used and the plant employed.
Section D: Works items and Classifications
Work item Class A: General work items
The standard method has five main divisions or categories of items that can be put in the Class A
preliminaries bill:
Contractual requirements
Specified requirements
The ‘Method-related charges’
Provisional sums
‘Nominated subcontractors’, which include or exclude work on site
Work items Class B-Z:
This is related to measured quantities. Under this we have:
Classification and number of items
Items Coding, Numbering, Headings and Subheadings
Section E: Grand Summary
The Grand Summary contains a tabulation of the parts of the Bill of Quantities with provision for
insertion of the total of the amounts brought forward from the Part Summaries.
FIG 2: SECTIONS OF BOQ
Section Description
A List of Principal Quantities
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 8
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
B Preamble:
States the edition of CESMM being used and items with measurements
that varies with the CESMM. clauses 5.4 and 5.5
C Day work Schedule
This is a list of labour, plant and material with or without nominal
quantities inserted in the document.
D Works Items
Class A: General Items (preliminaries)
Contractual requirements fixed
Specified requirements fixed, time related, quantity related
Method Related Charges fixed, time related
Provisional Sums
Price cost (PC) items
Class B to Z: Work Items
Related to measured quantities
E Grand Summary
Collection and totaling of Part summaries
General contingency allowance
Adjustment item: Addition to or deduction from the total of complete
works: not adjustable on final certificates – paid or recovered by
proportional installments in interim certificates
3.2.3 Production of Bill of Quantities
The traditional method of preparing bill of quantities is in the following sequence of operations:
Taking off dimensions from drawings
Working up
- Squaring
- Abstracting
- Billing
- Editing
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 9
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
- Typing
- Reading over
- Printing
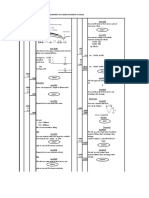
Below is a sample of a typical dimension sheet used for taking off
A B C D E A B C D E
A - Binding column
B - Multiplying column
C - Dimension column
D - Squaring column
E - Description column
Order of entering dimension at the Dimension Column is as follows:
Length
Width/breadth
Height/depth
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 10
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
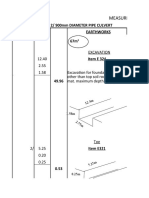
Example: entries for excavation for foundation of box culvert.
10.00 Excavation
1.20 Item: E 323
1.00 12.00m3 Excavation for foundations of material other than
topsoil, rock or artificial hard material not exceeding
1.0m
2
Ditto Apron
3.60
0.60
E 532
1.00
Disposal of excavated material
16.32m3
16.32m3
Typical bill of quantity sheet is shown below
Binding Item Item Item Item Rate Amount
Column Number Description Unit Quantity Column Column
1 m3 16.32
Excavation
2 Disposal of m3 16.32
excavated
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 11
INDUCTION TRAINING-QUANTITIES DIVISION
material
CHAPTER FOUR
4.0 Taking off for a 1km roadway
As part of my training, I was guided on how to take off for a one km stretch of a presumed road.
This assignment is completed in the appendix attached to this report.
NAA KOSHIE LAMPTEY
Page 12
You might also like
- Standard BoQ (UAE - DoT) - CESMM4 PDFDocument554 pagesStandard BoQ (UAE - DoT) - CESMM4 PDFNektarios Matheou87% (45)
- Engineering Measurement and Evaluation Cec214Document12 pagesEngineering Measurement and Evaluation Cec214Hussaini bobo65% (17)
- Part 1 - General: Important Note Regarding "Document9 pagesPart 1 - General: Important Note Regarding "MohamedNo ratings yet
- QS For Graduate Level - C & GDocument39 pagesQS For Graduate Level - C & GDushan Senarathne100% (1)
- Manual de Taller Tractor l4100Document120 pagesManual de Taller Tractor l4100Jorge Puentes SeoaneNo ratings yet
- How to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionFrom EverandHow to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Unit I - IntroductionDocument7 pagesUnit I - IntroductionBAGUMA NELSONNo ratings yet
- 2 - TOPIC 1 - Principle of MeasurementDocument27 pages2 - TOPIC 1 - Principle of MeasurementNUR SYAQIRAH TAJUDDINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Bill of Quantity - 02.12.2022Document8 pagesLecture 11 - Bill of Quantity - 02.12.2022Timothy GodwinNo ratings yet
- Quantity SurveyingDocument111 pagesQuantity Surveyingsakshi singhNo ratings yet
- Technical Terms: Module-1Document33 pagesTechnical Terms: Module-1Gireesh Gowda GiriNo ratings yet
- Siddiq Khan - Bill of QuantitiesDocument10 pagesSiddiq Khan - Bill of Quantitiesguyii86100% (1)
- ADocument46 pagesADushan SenarathneNo ratings yet
- Work Descriptions Package 3BDocument41 pagesWork Descriptions Package 3BAlireza entNo ratings yet
- CESMM MalaysiaDocument50 pagesCESMM Malaysialaurenjia83% (6)
- Quant TTTTT TTTTTDocument10 pagesQuant TTTTT TTTTTasamselaseNo ratings yet
- 01 Billing - Introduction To Billing v2Document9 pages01 Billing - Introduction To Billing v2Daniel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Civil MeasurementDocument47 pagesCivil MeasurementEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Standard Method of MeasurementsDocument24 pagesCivil Engineering Standard Method of MeasurementsRatnesh Patel100% (1)
- Case Study Preparation Bill of QuantitiesDocument6 pagesCase Study Preparation Bill of QuantitiesMuhd FaiqNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Costing (A70138) : Lecture NotesDocument73 pagesEstimation and Costing (A70138) : Lecture Noteshakim imtiyazNo ratings yet
- EN-2023 0005 a13+-+Lot+2+-+Template+for+technical+offer+1.00+New 001Document19 pagesEN-2023 0005 a13+-+Lot+2+-+Template+for+technical+offer+1.00+New 001niyascaNo ratings yet
- QSCM Upto 1st I.A.Document10 pagesQSCM Upto 1st I.A.Md.saifaadil AttarNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction To Elemental Cost AnalysisDocument17 pages1.0 Introduction To Elemental Cost AnalysisMon Luffy100% (1)
- 1.0 Introduction To Elemental Cost AnalysisDocument17 pages1.0 Introduction To Elemental Cost AnalysisMon LuffyNo ratings yet
- TTLM L-III M03 Preparing Bill of QuantitiesDocument61 pagesTTLM L-III M03 Preparing Bill of Quantitiesfayera letaNo ratings yet
- Drawing StandardsDocument12 pagesDrawing StandardsAgung Bayu100% (1)
- Ce2402 Eqs NotesDocument160 pagesCe2402 Eqs NotesrajNo ratings yet
- Long Report TemplateDocument23 pagesLong Report TemplateSardar Hamid ullahNo ratings yet
- Composing Descriptions For Bills of Quantities in Accordance WithDocument18 pagesComposing Descriptions For Bills of Quantities in Accordance WithdduffyNo ratings yet
- Standard Methods of Measurement For Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesStandard Methods of Measurement For Civil EngineeringRajanRanjan83% (12)
- Malaysian Standard Methods of Measurement For Civil Engineering WorksDocument23 pagesMalaysian Standard Methods of Measurement For Civil Engineering Worksrosmarina_rahma9813100% (18)
- Iare E&c Lecture Notes PDFDocument110 pagesIare E&c Lecture Notes PDFRichik MondalNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Costing (A70138) : Lecture NotesDocument110 pagesEstimation and Costing (A70138) : Lecture NotesRakshith Gowda100% (1)
- Estimation and Costing PDFDocument51 pagesEstimation and Costing PDFPARVATHANENI SAI KRISHNANo ratings yet
- BTQS 3044 - Measurement of External Works L1b IntroDocument27 pagesBTQS 3044 - Measurement of External Works L1b IntroLE PEI CHIANo ratings yet
- Section 01270-UNIT PRICESDocument2 pagesSection 01270-UNIT PRICESIm ChinithNo ratings yet
- Method of MeasurementsDocument41 pagesMethod of MeasurementsKrishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Tractor: TracteurDocument118 pagesTractor: TracteuryogismNo ratings yet
- AQS 4204 Assignments Bouquet 2020Document7 pagesAQS 4204 Assignments Bouquet 2020Pasipanodya TsambatareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction of SMM For Civil Eng WorksDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction of SMM For Civil Eng WorksTerwabe WapagovskiNo ratings yet
- Handbook-for-Preparing-Bill-of-Quantities-for Civil-Engineeering-Works PDFDocument248 pagesHandbook-for-Preparing-Bill-of-Quantities-for Civil-Engineeering-Works PDFcheewingyuenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Introduction+types of Tender)Document15 pagesChapter 1 (Introduction+types of Tender)saifulsabdin100% (1)
- Week 9 - Bill of QuantitiesDocument17 pagesWeek 9 - Bill of QuantitiesNUR FATINAH BINTI ZOLKIFLI 5ENo ratings yet
- Draft, SBD, Services (Non-Consultant)Document67 pagesDraft, SBD, Services (Non-Consultant)Muhammad Umair KabeerNo ratings yet
- QS 002 Midterm CompilationDocument443 pagesQS 002 Midterm CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- QS 002 Module 3 CompilationDocument200 pagesQS 002 Module 3 CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Part-2 (A) Scope of WorksDocument249 pagesPart-2 (A) Scope of Worksjai karanNo ratings yet
- B.O.Q PreparationDocument7 pagesB.O.Q PreparationYelisa Danny DenzelNo ratings yet
- Victorious Staff ESB 300Document5 pagesVictorious Staff ESB 300Chikwason Sarcozy MwanzaNo ratings yet
- Quantity Take OffDocument26 pagesQuantity Take OffTien Ngo Minh100% (1)
- Business Management for Scientists and Engineers: How I Overcame My Moment of Inertia and Embraced the Dark SideFrom EverandBusiness Management for Scientists and Engineers: How I Overcame My Moment of Inertia and Embraced the Dark SideNo ratings yet
- Static Analysis of Software: The Abstract InterpretationFrom EverandStatic Analysis of Software: The Abstract InterpretationNo ratings yet
- Codification of Statements on Standards for Attestation Engagements, January 2018From EverandCodification of Statements on Standards for Attestation Engagements, January 2018No ratings yet
- Rainfall-Induced Slope Instability PRESENTATIONDocument15 pagesRainfall-Induced Slope Instability PRESENTATIONasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Rose S$DDocument22 pagesRose S$DasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Induction Training Report - Planning Division: AcknowledgementDocument44 pagesInduction Training Report - Planning Division: AcknowledgementasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Induction Training Report - Naa Koshie LampteyDocument21 pagesAcknowledgement: Induction Training Report - Naa Koshie LampteyasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Contracts Naa (Repaired)Document26 pagesContracts Naa (Repaired)asamselaseNo ratings yet
- U-Drain 900Document2 pagesU-Drain 900asamselaseNo ratings yet
- Quant TTTTT TTTTTDocument10 pagesQuant TTTTT TTTTTasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Measurement Sheet: Project: EarthworksDocument57 pagesMeasurement Sheet: Project: EarthworksasamselaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SOURCES & FOUNDATIONS OF HUMAN RIGHTS LAWDocument6 pagesChapter 2 SOURCES & FOUNDATIONS OF HUMAN RIGHTS LAWI Lobeu My CaratNo ratings yet
- Tabelas Roscas TrapezoidaisDocument49 pagesTabelas Roscas TrapezoidaisDesenvolvimento MHNo ratings yet
- Growth of Robotics in IndiaDocument14 pagesGrowth of Robotics in Indianitul deoriNo ratings yet
- Chziri Zjr2 User ManualDocument51 pagesChziri Zjr2 User ManualJosé Henríquez V.No ratings yet
- Building Chatbots in Python Chapter2 PDFDocument41 pagesBuilding Chatbots in Python Chapter2 PDFFgpeqwNo ratings yet
- Miama: A Small Introduction To The Free Font Miama by Linus Romer, AugustDocument5 pagesMiama: A Small Introduction To The Free Font Miama by Linus Romer, Augustjose chaveroNo ratings yet
- StudyGuide CosmonautDocument25 pagesStudyGuide CosmonautAzuWillDieNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training ReportDocument6 pagesIndustrial Training Reportmayank guptaNo ratings yet
- Revision On Unit 1,2 First Secondry (Hello)Document11 pagesRevision On Unit 1,2 First Secondry (Hello)Vivian GendyNo ratings yet
- Anthropomorphic Hand PresentationDocument22 pagesAnthropomorphic Hand PresentationAnshulNo ratings yet
- Hindalco ReportDocument42 pagesHindalco ReportAman RoyNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Construction of Urban Intersections With Portlandcement Concrete Pavement (PCCP)Document3 pagesAccelerated Construction of Urban Intersections With Portlandcement Concrete Pavement (PCCP)A-16 RUSHALINo ratings yet
- Tutorial Materials SelectionDocument2 pagesTutorial Materials SelectionSyahmiNo ratings yet
- The Ethnography of Communication: Mădălina MATEIDocument8 pagesThe Ethnography of Communication: Mădălina MATEIamir_marzbanNo ratings yet
- UPNMG Press Statement-Unemployed Nurses and MidwivesDocument1 pageUPNMG Press Statement-Unemployed Nurses and MidwivesClavia NyaabaNo ratings yet
- Pineal Gland A Spiritual Third Eye An OdDocument4 pagesPineal Gland A Spiritual Third Eye An OdAsli Melek DoenerNo ratings yet
- Sensor Manual 1Document11 pagesSensor Manual 1Tame PcAddictNo ratings yet
- The Microsoft-Nokia Strategic Alliance PDFDocument25 pagesThe Microsoft-Nokia Strategic Alliance PDFmehedee129No ratings yet
- Gear Agma IIDocument49 pagesGear Agma IInathNo ratings yet
- Final 2 PLSQLDocument16 pagesFinal 2 PLSQLBadri Mahmoud AliNo ratings yet
- 19Document227 pages19Miguel José DuarteNo ratings yet
- Cut Out ValveDocument64 pagesCut Out ValveHoang L A TuanNo ratings yet
- Ecs 2ar FDocument39 pagesEcs 2ar FĐức LêNo ratings yet
- Product 043 UMDocument31 pagesProduct 043 UMPankaj MauryaNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesDocument5 pagesComparative and Superlative AdjectivesYoussef BrsNo ratings yet
- Kuwait Business Directory SampleDocument1 pageKuwait Business Directory SampleDrMohamed RifasNo ratings yet
- BUS203 Term Paper - Section 04Document16 pagesBUS203 Term Paper - Section 04Sumaiya Selim SushmeNo ratings yet
- SS Disco Check Valve (Size 15-100)Document2 pagesSS Disco Check Valve (Size 15-100)rudirstNo ratings yet
- Colah Github Io Posts 2015 08 Understanding LSTMsDocument16 pagesColah Github Io Posts 2015 08 Understanding LSTMsMithun PantNo ratings yet
- Cable Gland HAWKER - CatalogueDocument87 pagesCable Gland HAWKER - CatalogueJean SantosNo ratings yet