Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brain Conditions
Brain Conditions
Uploaded by
ALMA BALBINCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Top Tung Acupuncture Points (PDFDrive)Document28 pagesTop Tung Acupuncture Points (PDFDrive)shaukijameel50% (4)
- HeadacheDocument16 pagesHeadacheKevinVunNo ratings yet
- Reversing Autism: Connecting The Pieces With The Latest Research On BT, HG, Octopamine, Succinic Acid, B12, Leptu and BIRM.Document42 pagesReversing Autism: Connecting The Pieces With The Latest Research On BT, HG, Octopamine, Succinic Acid, B12, Leptu and BIRM.autismone100% (3)
- Rain Conditions: Headache StrokeDocument2 pagesRain Conditions: Headache StrokeSameer KshitizNo ratings yet
- Picture of The Brain: Prev NextDocument4 pagesPicture of The Brain: Prev NextMarvinEboraNo ratings yet
- Neck Pain Headache: Brain Diseases: InfectionsDocument2 pagesNeck Pain Headache: Brain Diseases: Infectionsv@r0_5No ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument10 pagesHead InjuryMelia SariNo ratings yet
- Pathologies of Central Nervous SystemDocument51 pagesPathologies of Central Nervous SystemSajjad AliNo ratings yet
- The Brain - Praf Elena CristinaDocument14 pagesThe Brain - Praf Elena CristinaPraf Elena CristinaNo ratings yet
- Brain 2Document2 pagesBrain 2bambangNo ratings yet
- Brain Aneurysm Artery Blood Brain Stroke Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument7 pagesBrain Aneurysm Artery Blood Brain Stroke Subarachnoid Hemorrhagebank bjbNo ratings yet
- ELS 102 Theories of Language Module 12-15Document13 pagesELS 102 Theories of Language Module 12-15LovelyLoey ParkNo ratings yet
- Disease of Nervous System Lect 2Document62 pagesDisease of Nervous System Lect 2Monirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous SystemLola MipezNo ratings yet
- 4 - Perception & Coordination Alterations RVDocument391 pages4 - Perception & Coordination Alterations RVgeng gengNo ratings yet
- Head Injury....Document47 pagesHead Injury....nikowareNo ratings yet
- DEMENTIA-WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesDEMENTIA-WPS OfficeDauda Muize AdewaleNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument7 pagesHead InjuryRoshan Ghimire100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemFernanda AmigoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note On Intracrenial HemorrhageDocument4 pagesLecture Note On Intracrenial HemorrhageLionel EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Nervous System DiseasesDocument16 pagesNervous System DiseasesShahzad ShameemNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous Tissues and The BrainDocument3 pagesDisorders of The Nervous Tissues and The BrainCharls DeimoyNo ratings yet
- Head InjuriesDocument76 pagesHead InjuriesWafa Nabilah KamalNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument18 pagesHemorrhagic StrokeNdan RahmaNo ratings yet
- Neurological System DisordersDocument59 pagesNeurological System DisordersJoanna Ephraim CruzNo ratings yet
- Neurological System DisordersDocument41 pagesNeurological System DisordersJoanna Ephraim CruzNo ratings yet
- Brain Injury: Closed (Blunt) Brain Injury Occurs When The Head Accelerates and ThenDocument7 pagesBrain Injury: Closed (Blunt) Brain Injury Occurs When The Head Accelerates and Thencute_tineeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Hemorrhagic StrokesDocument7 pagesClassification of Hemorrhagic StrokesRavinr9No ratings yet
- Impact of StrokeDocument2 pagesImpact of StrokeFauziah eka santiNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument105 pagesHead Injurypuneetkumar7089No ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument6 pagesHead Injurychuramarak23No ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument19 pagesHead InjuryTauqeer AhmedNo ratings yet
- CCN Lecture Altered PerceptionDocument4 pagesCCN Lecture Altered PerceptionPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PathologyDocument57 pagesNervous System Pathologypatriciasuscking100% (1)
- Intracranial Regulation: Scope of ICRDocument7 pagesIntracranial Regulation: Scope of ICRTamanda MushoreNo ratings yet
- Blood Clot in The BrainDocument3 pagesBlood Clot in The BrainHarsh KananiNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Lect 5Document27 pagesHead Injury Lect 5amber tariq100% (1)
- Disorders of NSDocument4 pagesDisorders of NSThe KhanNo ratings yet
- Cerebral StrokeDocument2 pagesCerebral StroketansimktNo ratings yet
- Hand Out2007Document36 pagesHand Out2007Roza IsmarniNo ratings yet
- TBI QuizletDocument4 pagesTBI QuizletLoraine CometaNo ratings yet
- Approach To HeadacheDocument49 pagesApproach To Headachegea pandhita sNo ratings yet
- Convulsion Epilepsy: SeizuresDocument2 pagesConvulsion Epilepsy: SeizuresSuryo PratomoNo ratings yet
- KERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Document67 pagesKERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Tunjung TrihapsariNo ratings yet
- DizzinessDocument3 pagesDizzinesscannatNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Week 10 GlossaryDocument1 pageUnit 1 Week 10 Glossaryscarlettcrawley2007No ratings yet
- Head Injury - FMDocument3 pagesHead Injury - FMSivaani ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- Nar SingDocument14 pagesNar Singbasinang_jangilNo ratings yet
- Cerebral HemorrhageDocument2 pagesCerebral HemorrhageGian TejadaNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities Associated With Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesAbnormalities Associated With Nervous SystemroseNo ratings yet
- SeizureDocument1 pageSeizureMhegz HalconNo ratings yet
- Hemiplegia Resource Book ModifiedDocument60 pagesHemiplegia Resource Book ModifiedAnonymous czrvb3hNo ratings yet
- Head Injury NoteDocument7 pagesHead Injury NoteAi Mio100% (1)
- Head Trauma: George Ayoub - Med3Document23 pagesHead Trauma: George Ayoub - Med3Joe KhdeirNo ratings yet
- Ronny Yusyanto. Head InjuryDocument12 pagesRonny Yusyanto. Head InjuryFerdyNo ratings yet
- Self-Instructional Module Format I. Title: Emergency Management of Head, Spine, and Face Injuries IIDocument21 pagesSelf-Instructional Module Format I. Title: Emergency Management of Head, Spine, and Face Injuries IICharmae NaveaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral EdemaDocument5 pagesCerebral EdemaSimranNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument100 pagesDisorders of The Nervous SystemnipoNo ratings yet
- P1 Types of HeadacheDocument8 pagesP1 Types of Headachebujor2000ajaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesDisorders of The Nervous SystemAgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- LP StrokeDocument33 pagesLP StrokeMiskan FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Edema, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCerebral Edema, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Selected Instructional Course LecturesDocument27 pagesSelected Instructional Course LecturesAhmad ShakirNo ratings yet
- Monoamine Oxidase InhibitorsDocument14 pagesMonoamine Oxidase InhibitorsMary Ann DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument5 pagesCongenital Hip DislocationMonica Aguirre QuilangNo ratings yet
- Kanker Ovarium 2 PDFDocument6 pagesKanker Ovarium 2 PDFhestiNo ratings yet
- Karya Tulis IlmiahDocument50 pagesKarya Tulis IlmiahSayyid SultanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology of The SkinDocument52 pagesAnatomy Physiology of The SkinRune_Zeit100% (1)
- Aortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationDocument2 pagesAortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationArunNo ratings yet
- Localized Treatment of Chronic Buruli Ulcer With v1 Id1035 PDFDocument3 pagesLocalized Treatment of Chronic Buruli Ulcer With v1 Id1035 PDFAnonymous e3TFin8884No ratings yet
- CancerDocument2 pagesCancerkatyaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem ServicesDocument30 pagesBiodiversity and Ecosystem ServicesNick NgNo ratings yet
- Immunology of Dental Caries and Caries Vaccine - Part IDocument6 pagesImmunology of Dental Caries and Caries Vaccine - Part IanviNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms of Type A InfluenzaDocument6 pagesSigns and Symptoms of Type A InfluenzaHoonchyi KohNo ratings yet
- A Technical Study On Biomedical Image Classification Using Mining AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesA Technical Study On Biomedical Image Classification Using Mining AlgorithmsthamilselvanpNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan FormDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan FormChadd Vyllmorr VillarinNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Neonatal EncephalopatyDocument11 pagesDiagnosing Neonatal EncephalopatyLalo LanNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls of Using HbA1c in The Diagnosis and Monitoring of DiabetesDocument5 pagesPitfalls of Using HbA1c in The Diagnosis and Monitoring of DiabetesMihaela RussellNo ratings yet
- Covid AbstracDocument3 pagesCovid AbstracmuhammadmufidNo ratings yet
- DapusDocument2 pagesDapustriNo ratings yet
- AI and ML Lab ManualDocument29 pagesAI and ML Lab ManualNithya NairNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument13 pagesParkinsonVenkatesan VidhyaNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Reproductive Health and RightsDocument57 pagesSexual and Reproductive Health and RightsSharwajit JhaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument9 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFadikaNo ratings yet
- Consent CraniotomyDocument9 pagesConsent CraniotomyAbhinav Gupta100% (1)
- Module 1-Exploring BioethicsDocument76 pagesModule 1-Exploring Bioethicsstlcajun55No ratings yet
- 01 TB Quiz Eng PDFDocument32 pages01 TB Quiz Eng PDFTop Story PostNo ratings yet
- Lesch-Nyhan SyndromeDocument8 pagesLesch-Nyhan SyndromevrindaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Nur Yahya, T 05/1087561/KU/11522Document19 pagesPneumonia: Nur Yahya, T 05/1087561/KU/11522Taufik Nur YahyaNo ratings yet
- Richa Shrivastava Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy BITS PilaniDocument18 pagesRicha Shrivastava Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy BITS PilaniCHOUGULE KISHOR SURYAKANTNo ratings yet
Brain Conditions
Brain Conditions
Uploaded by
ALMA BALBINOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain Conditions
Brain Conditions
Uploaded by
ALMA BALBINCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain Conditions
Headache: There are many types of headaches; some can be serious but most
are not and are generally treated with analgesics/painkillers.
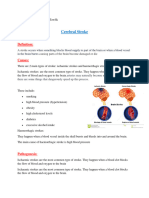
Stroke (brain infarction): Blood flow and oxygen are suddenly interrupted to
an area of brain tissue, which then dies. A blood clot, or bleeding in the brain,
are the cause of most strokes.
Brain aneurysm: An artery in the brain develops a weak area that swells,
balloon-like. A brain aneurysm rupture can causes a stroke.
Subdural hematoma: Bleeding within or under the dura, the lining inside of
the skull. A subdural hematoma may exert pressure on the brain, causing
neurological problems.
Epidural hematoma: Bleeding between the tough tissue (dura) lining the
inside of the skull and the skull itself, usually shortly after a head injury. Initial
mild symptoms can progress rapidly to unconsciousness and death, if
untreated.
Intracerebral hemorrhage: Any bleeding inside the brain.
Concussion: A brain injury that causes a temporary disturbance in brain
function. Traumatic head injuries cause most concussions.
Cerebral edema: Swelling of the brain tissue in response to injury or
electrolyte imbalances.
Brain tumor: Any abnormal tissue growth inside the brain. Whether
malignant (cancer) or benign, brain tumors usually cause problems by the
pressure they exert on the normal brain.
Glioblastoma: An aggressive, malignant brain tumor (cancer). Brain
glioblastomas progress rapidly and are very difficult to cure.
Hydrocephalus: An abnormally increased amount of cerebrospinal (brain)
fluid inside the skull. Usually this is because the fluid is not circulating
properly.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus: A form of hydrocephalus that often causes
problems walking, along with dementia and urinary incontinence. Pressures
inside the brain remain normal, despite the increased fluid.
Meningitis: Inflammation of the lining around the brain or spinal cord, usually
from infection. Stiff neck, neck pain, headache, fever, and sleepiness are
common symptoms.
Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain tissue, usually from infection with a
virus. Fever, headache, and confusion are common symptoms.
Traumatic brain injury: Permanent brain damage from a traumatic head
injury. Obvious mental impairment, or more subtle personality and mood
changes can occur.
Parkinson's disease: Nerves in a central area of the brain degenerate slowly,
causing problems with movement and coordination. A tremor of the hands is a
common early sign.
Huntington's disease: An inherited nerve disorder that affects the brain.
Dementia and difficulty controlling movements (chorea) are its symptoms.
Epilepsy: The tendency to have seizures. Head injuries and strokes may cause
epilepsy, but usually no cause is identified.
Dementia: A decline in cognitive function resulting from death or in the brain.
Conditions in which nerves in the brain degenerate, as well as alcohol abuse
and strokes, can cause dementia. malfunction of nerve cells
Alzheimer’s disease: For unclear reasons, nerves in certain brain areas
degenerate, causing progressive dementia. Alzheimer’s disease is the most
common form of dementia.
Brain abscess: A pocket of infection in the brain, usually by bacteria.
Antibiotics and surgical drainage of the area are often necessary.
You might also like
- Top Tung Acupuncture Points (PDFDrive)Document28 pagesTop Tung Acupuncture Points (PDFDrive)shaukijameel50% (4)
- HeadacheDocument16 pagesHeadacheKevinVunNo ratings yet
- Reversing Autism: Connecting The Pieces With The Latest Research On BT, HG, Octopamine, Succinic Acid, B12, Leptu and BIRM.Document42 pagesReversing Autism: Connecting The Pieces With The Latest Research On BT, HG, Octopamine, Succinic Acid, B12, Leptu and BIRM.autismone100% (3)
- Rain Conditions: Headache StrokeDocument2 pagesRain Conditions: Headache StrokeSameer KshitizNo ratings yet
- Picture of The Brain: Prev NextDocument4 pagesPicture of The Brain: Prev NextMarvinEboraNo ratings yet
- Neck Pain Headache: Brain Diseases: InfectionsDocument2 pagesNeck Pain Headache: Brain Diseases: Infectionsv@r0_5No ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument10 pagesHead InjuryMelia SariNo ratings yet
- Pathologies of Central Nervous SystemDocument51 pagesPathologies of Central Nervous SystemSajjad AliNo ratings yet
- The Brain - Praf Elena CristinaDocument14 pagesThe Brain - Praf Elena CristinaPraf Elena CristinaNo ratings yet
- Brain 2Document2 pagesBrain 2bambangNo ratings yet
- Brain Aneurysm Artery Blood Brain Stroke Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument7 pagesBrain Aneurysm Artery Blood Brain Stroke Subarachnoid Hemorrhagebank bjbNo ratings yet
- ELS 102 Theories of Language Module 12-15Document13 pagesELS 102 Theories of Language Module 12-15LovelyLoey ParkNo ratings yet
- Disease of Nervous System Lect 2Document62 pagesDisease of Nervous System Lect 2Monirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous SystemLola MipezNo ratings yet
- 4 - Perception & Coordination Alterations RVDocument391 pages4 - Perception & Coordination Alterations RVgeng gengNo ratings yet
- Head Injury....Document47 pagesHead Injury....nikowareNo ratings yet
- DEMENTIA-WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesDEMENTIA-WPS OfficeDauda Muize AdewaleNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument7 pagesHead InjuryRoshan Ghimire100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemFernanda AmigoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note On Intracrenial HemorrhageDocument4 pagesLecture Note On Intracrenial HemorrhageLionel EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Nervous System DiseasesDocument16 pagesNervous System DiseasesShahzad ShameemNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous Tissues and The BrainDocument3 pagesDisorders of The Nervous Tissues and The BrainCharls DeimoyNo ratings yet
- Head InjuriesDocument76 pagesHead InjuriesWafa Nabilah KamalNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument18 pagesHemorrhagic StrokeNdan RahmaNo ratings yet
- Neurological System DisordersDocument59 pagesNeurological System DisordersJoanna Ephraim CruzNo ratings yet
- Neurological System DisordersDocument41 pagesNeurological System DisordersJoanna Ephraim CruzNo ratings yet
- Brain Injury: Closed (Blunt) Brain Injury Occurs When The Head Accelerates and ThenDocument7 pagesBrain Injury: Closed (Blunt) Brain Injury Occurs When The Head Accelerates and Thencute_tineeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Hemorrhagic StrokesDocument7 pagesClassification of Hemorrhagic StrokesRavinr9No ratings yet
- Impact of StrokeDocument2 pagesImpact of StrokeFauziah eka santiNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument105 pagesHead Injurypuneetkumar7089No ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument6 pagesHead Injurychuramarak23No ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument19 pagesHead InjuryTauqeer AhmedNo ratings yet
- CCN Lecture Altered PerceptionDocument4 pagesCCN Lecture Altered PerceptionPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PathologyDocument57 pagesNervous System Pathologypatriciasuscking100% (1)
- Intracranial Regulation: Scope of ICRDocument7 pagesIntracranial Regulation: Scope of ICRTamanda MushoreNo ratings yet
- Blood Clot in The BrainDocument3 pagesBlood Clot in The BrainHarsh KananiNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Lect 5Document27 pagesHead Injury Lect 5amber tariq100% (1)
- Disorders of NSDocument4 pagesDisorders of NSThe KhanNo ratings yet
- Cerebral StrokeDocument2 pagesCerebral StroketansimktNo ratings yet
- Hand Out2007Document36 pagesHand Out2007Roza IsmarniNo ratings yet
- TBI QuizletDocument4 pagesTBI QuizletLoraine CometaNo ratings yet
- Approach To HeadacheDocument49 pagesApproach To Headachegea pandhita sNo ratings yet
- Convulsion Epilepsy: SeizuresDocument2 pagesConvulsion Epilepsy: SeizuresSuryo PratomoNo ratings yet
- KERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Document67 pagesKERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Tunjung TrihapsariNo ratings yet
- DizzinessDocument3 pagesDizzinesscannatNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Week 10 GlossaryDocument1 pageUnit 1 Week 10 Glossaryscarlettcrawley2007No ratings yet
- Head Injury - FMDocument3 pagesHead Injury - FMSivaani ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- Nar SingDocument14 pagesNar Singbasinang_jangilNo ratings yet
- Cerebral HemorrhageDocument2 pagesCerebral HemorrhageGian TejadaNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities Associated With Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesAbnormalities Associated With Nervous SystemroseNo ratings yet
- SeizureDocument1 pageSeizureMhegz HalconNo ratings yet
- Hemiplegia Resource Book ModifiedDocument60 pagesHemiplegia Resource Book ModifiedAnonymous czrvb3hNo ratings yet
- Head Injury NoteDocument7 pagesHead Injury NoteAi Mio100% (1)
- Head Trauma: George Ayoub - Med3Document23 pagesHead Trauma: George Ayoub - Med3Joe KhdeirNo ratings yet
- Ronny Yusyanto. Head InjuryDocument12 pagesRonny Yusyanto. Head InjuryFerdyNo ratings yet
- Self-Instructional Module Format I. Title: Emergency Management of Head, Spine, and Face Injuries IIDocument21 pagesSelf-Instructional Module Format I. Title: Emergency Management of Head, Spine, and Face Injuries IICharmae NaveaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral EdemaDocument5 pagesCerebral EdemaSimranNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument100 pagesDisorders of The Nervous SystemnipoNo ratings yet
- P1 Types of HeadacheDocument8 pagesP1 Types of Headachebujor2000ajaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesDisorders of The Nervous SystemAgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- LP StrokeDocument33 pagesLP StrokeMiskan FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Edema, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCerebral Edema, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Selected Instructional Course LecturesDocument27 pagesSelected Instructional Course LecturesAhmad ShakirNo ratings yet
- Monoamine Oxidase InhibitorsDocument14 pagesMonoamine Oxidase InhibitorsMary Ann DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument5 pagesCongenital Hip DislocationMonica Aguirre QuilangNo ratings yet
- Kanker Ovarium 2 PDFDocument6 pagesKanker Ovarium 2 PDFhestiNo ratings yet
- Karya Tulis IlmiahDocument50 pagesKarya Tulis IlmiahSayyid SultanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology of The SkinDocument52 pagesAnatomy Physiology of The SkinRune_Zeit100% (1)
- Aortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationDocument2 pagesAortic Aneurysm Classification: SL No Time Specific Objective Content Av Aids EvaluationArunNo ratings yet
- Localized Treatment of Chronic Buruli Ulcer With v1 Id1035 PDFDocument3 pagesLocalized Treatment of Chronic Buruli Ulcer With v1 Id1035 PDFAnonymous e3TFin8884No ratings yet
- CancerDocument2 pagesCancerkatyaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem ServicesDocument30 pagesBiodiversity and Ecosystem ServicesNick NgNo ratings yet
- Immunology of Dental Caries and Caries Vaccine - Part IDocument6 pagesImmunology of Dental Caries and Caries Vaccine - Part IanviNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms of Type A InfluenzaDocument6 pagesSigns and Symptoms of Type A InfluenzaHoonchyi KohNo ratings yet
- A Technical Study On Biomedical Image Classification Using Mining AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesA Technical Study On Biomedical Image Classification Using Mining AlgorithmsthamilselvanpNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan FormDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan FormChadd Vyllmorr VillarinNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Neonatal EncephalopatyDocument11 pagesDiagnosing Neonatal EncephalopatyLalo LanNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls of Using HbA1c in The Diagnosis and Monitoring of DiabetesDocument5 pagesPitfalls of Using HbA1c in The Diagnosis and Monitoring of DiabetesMihaela RussellNo ratings yet
- Covid AbstracDocument3 pagesCovid AbstracmuhammadmufidNo ratings yet
- DapusDocument2 pagesDapustriNo ratings yet
- AI and ML Lab ManualDocument29 pagesAI and ML Lab ManualNithya NairNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument13 pagesParkinsonVenkatesan VidhyaNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Reproductive Health and RightsDocument57 pagesSexual and Reproductive Health and RightsSharwajit JhaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument9 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFadikaNo ratings yet
- Consent CraniotomyDocument9 pagesConsent CraniotomyAbhinav Gupta100% (1)
- Module 1-Exploring BioethicsDocument76 pagesModule 1-Exploring Bioethicsstlcajun55No ratings yet
- 01 TB Quiz Eng PDFDocument32 pages01 TB Quiz Eng PDFTop Story PostNo ratings yet
- Lesch-Nyhan SyndromeDocument8 pagesLesch-Nyhan SyndromevrindaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Nur Yahya, T 05/1087561/KU/11522Document19 pagesPneumonia: Nur Yahya, T 05/1087561/KU/11522Taufik Nur YahyaNo ratings yet
- Richa Shrivastava Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy BITS PilaniDocument18 pagesRicha Shrivastava Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy BITS PilaniCHOUGULE KISHOR SURYAKANTNo ratings yet