Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Friction Losses in The Pipe Experiment No: 4
Friction Losses in The Pipe Experiment No: 4
Uploaded by
anil kumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Friction Losses in The Pipe Experiment No: 4
Friction Losses in The Pipe Experiment No: 4
Uploaded by
anil kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
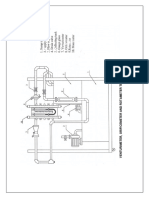
FRICTION LOSSES IN THE PIPE
Experiment No: 4
AIM : To determine the loss of head in a pipe due to (Minor
Losses)
1. Sudden Enlargement
2. Sudden Contraction
APPARATUS : 1. Pipe line fitting apparatus set
2. Stop Watch
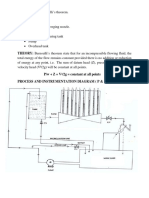
THEORY : When the velocity of flowing liquid changes either
magnitude or direction, there is a large scale of turbulence
ad graduate due to formation of eddies in which a large
portion of the energy processed by flowing liquid is
established which ultimately dissipates as heat. Hence it is
an energy loss. The change in velocity of flow is due to
change in the cross sectional area of flow passage and
change in direction of velocity of flow passage. The loss of
energy due to sudden change is more than that of
graduated changes. The magnitude of these energy losses
was obtained by applying the energy momentum Equation
Loss of head due to sudden Expansion
h1 = (v1-v2)2 / 2g.
Where v1, v2 are mean velocities of flow in small and
large pipes.
Loss of head due to sudden contraction
h1 = 0.33 v12 / 2g.
Where v is the mean velocity of flow in small pipes.
PROCEDURE : 1. Open the inlet valve fully by keeping the outlet closed.
2. Connect the manometeric rubber tubing’s to one of the
pipes and check there is no air bubble entrapping.
3. Open partially the outlet valve of pipe for which loss of
head is to be measured and the outlet valves of other pipes
are closed.
4. Allow the flow to get stabilized, then take manometer
readings.
5. Find out actual discharge by noting time, t taken for
collecting tank the discharge in a measuring tank for
known depth, say 20 cm, using stop watch.
6. Vary the flow rate by adjusting the outlet valve and at least
four readings.
7. Repeat steps 1-6 for different pipe fittings.
FORMULA : H = Differential pressure head between inlet and outlet at
(Expansion valve / Contraction valve).
H = h ((Sm / S) -1) = h ((13.6/1) -1) =12.6 h
h = Difference in Hg level
Q act = AR / T
A = Area of the collecting tank
R = Rise of water level.
T = Time taken for rise of water.
TABULAR FORM:
Type Contraction Expansion
h1 in cm
Manometer
h2 in cm
readings
H= (h1-h2)*12.6
Time taken for 20
cm rise of tank.
Actual Discharge
of the pipe. (Qact)
Velocity of the
flow V2=Q/A2
(m/sec)
Velocity of the
flow V1=Q/A1
(m/sec)
Loss of energy
hv=v2/2g
Loss of energy
H=(v1-v2)2 / 2g.
Loss of coefficient
K=H/ hv
PRECAUTIONS:
Take care that there are no air bubbles entrapped in the apparatus when noting
the manometer readings.
There should be no leakages from any of the pipe fittings.
RESULT: The head loss due to minor (Friction) loss is measured =
OBSERVATIONS:
Diameter of the pipe (D1) =12.7mm =0.0127m.
C/S Area of the pipe (A1) = (∏ / 4)*D 12
= 1.26*10-4 m2.
Enlarged diameter of the pipe (D2) = 25.4mm = 0.0254m.
C/S Area of the pipe (A2) = (∏ / 4)*D 22
=5.06*10-4 m2.
Dimensions of the collecting tank = length =0.3m
Width =0.3m
Area of the collecting tank =l*b =0.3*0.3
=0.09m2.
OBSERVATIONS:
Diameter of the pipe (D1) =12.7mm =0.0127m.
C/S Area of the pipe (A1) = (∏ / 4)*D 12
= 1.26*10-4 m2.
Enlarged diameter of the pipe (D2) = 25.4mm = 0.0254m.
C/S Area of the pipe (A2) = (∏ / 4)*D 22
=5.06*10-4 m2.
Dimensions of the collecting tank = length =0.3m
Width =0.3m
Area of the collecting tank =l*b =0.3*0.3
=0.09m2.
Tabular form:
Type Manometer readings Time Actual Velocity Velocity Loss of Loss
H1. H2. H=(H1- taken Discharg of the of the energy of
cm cm H2)*12.6 for 20 e of the flow. flow. hv= (v1- energy
in cm. cm rise pipe. V2=Q/ V1=Q/ v2)2/2g. hv=v2/
of tank. (Qact) A2 A1 Exp. 2g.
(m/sec) (m/sec) Contra
Contraction 14.5 22.8 104.58 28 7.39*10 -4
1.46 5.87 0.108
16 21.5 69.3 33 6.2*10 -4
1.22 4.92 0.075
Expansion 16.5 21 56.7 30 6.9*10-4 1.36 5.47 0.86
17.5 20 31.5 34 6.08*10 -4
1.20 4.83 0.67
CALCULATIONS:
Contraction:
Actual Discharge (Qact) = (Area of the tank*height of rise of the tank) / time taken.
= (0.1035*0.2)/28
= 7.39*10-4m3/sec.
Velocity of flow (V) = Q/A = 7.39*10-4/5.06*10-4
= 1.46m/sec.
Loss of energy hv=v2/2g
= 1.462/2*9.81
= 0.108.
You might also like
- Participate in Workplace CommunicationDocument8 pagesParticipate in Workplace CommunicationArman Berina CortezNo ratings yet
- LAB MANUAL. EXPERIMENT 2. Calibration of Venturi MeterDocument3 pagesLAB MANUAL. EXPERIMENT 2. Calibration of Venturi Meterjames PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics ExperimentDocument10 pagesFluid Mechanics ExperimentDaniel LohNo ratings yet
- Losses in Fittings ReportDocument7 pagesLosses in Fittings ReportAmartya Mitra100% (1)
- Friction Factor Experiment No: 3Document6 pagesFriction Factor Experiment No: 3anil kumarNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument4 pagesVenturi MeterSyam RajuNo ratings yet
- Venturi Meter: Experiment No: 1Document4 pagesVenturi Meter: Experiment No: 1anil kumarNo ratings yet
- Backup of Flowloss - CSDocument6 pagesBackup of Flowloss - CSSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Lab Manual Hydraulics Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringDocument26 pagesCivil Engineering Lab Manual Hydraulics Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument46 pagesLab ManualAizaz HabibNo ratings yet
- Losses Due To Pipe FrictionDocument8 pagesLosses Due To Pipe FrictionsenthilNo ratings yet
- Elements of Power Systems Laboratory: D.Venugopal Setty, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Iem, RvceDocument46 pagesElements of Power Systems Laboratory: D.Venugopal Setty, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Iem, RvceSnigdha JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Btech4th-CE-Hydraulics & Hydraulic Machine LabDocument26 pagesBtech4th-CE-Hydraulics & Hydraulic Machine LabSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- F.M.H.M.PR.8,9,10 PracticalDocument15 pagesF.M.H.M.PR.8,9,10 PracticalnitinmiskeNo ratings yet
- Friction in Pipes Aim:: FM&HM LabDocument7 pagesFriction in Pipes Aim:: FM&HM Labashoku2No ratings yet
- Ffo Lab Prac... 18bt01051Document30 pagesFfo Lab Prac... 18bt01051Sarthak LathiyaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 4 HM Lab UpdatedDocument4 pagesExperiment No 4 HM Lab Updatedprajwalwanjari5524No ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document12 pagesWa0002.op5857750No ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument12 pagesFluid Mechanicsop5857750No ratings yet
- Fmea ObservationDocument60 pagesFmea Observation20me006No ratings yet
- Discharge CoefficientDocument11 pagesDischarge Coefficientsisai12u2420% (2)
- Fluid Dynamics Student ManualDocument70 pagesFluid Dynamics Student ManualJayachandran SivagurunathanNo ratings yet
- Flowmeter Apparatus (Venturi, Orifice, Rotameter)Document10 pagesFlowmeter Apparatus (Venturi, Orifice, Rotameter)meghaparinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech ManualDocument75 pagesFluid Mech ManualGANESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab 1Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab 1Esra BelhajNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Pump Experiment No: 6Document6 pagesReciprocating Pump Experiment No: 6anil kumarNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument4 pagesVenturi Meterprince.patelNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Venturimeter: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Document6 pagesCalibration of Venturimeter: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Amisha SharonNo ratings yet
- Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument6 pagesCalibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterMUTHUKURU VENKATA GOWTHAM REDDYNo ratings yet
- Orifice Plate Long ReportDocument16 pagesOrifice Plate Long ReportLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- BERNOULLIS THEOREM PracticalDocument4 pagesBERNOULLIS THEOREM PracticalMandeep PathakNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice Meterf20221047No ratings yet
- CE142P-2 Experiment 9Document10 pagesCE142P-2 Experiment 9Faye AnneNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument4 pagesVenturi MeterJorah MormontNo ratings yet
- Multi Stage Centrifugal Pump Experiment No. 5Document6 pagesMulti Stage Centrifugal Pump Experiment No. 5anil kumarNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledIzzat HaziqNo ratings yet
- Friction of Pipe 2Document5 pagesFriction of Pipe 2Ranu GamesNo ratings yet
- FM Manual PDFDocument37 pagesFM Manual PDFSampathkumar MtechNo ratings yet
- Helical Coil FlowDocument4 pagesHelical Coil FlowAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- Ballast Rev 0Document4 pagesBallast Rev 0Rahmat WijanarkoNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's ExperimentDocument11 pagesBernoulli's ExperimentSIMRANNo ratings yet
- User Manual Closed Circuit Pipe Friction ApparatusDocument4 pagesUser Manual Closed Circuit Pipe Friction Apparatusrohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Indo 1Document29 pagesIndo 1Michael TinambunanNo ratings yet
- Friction in PipesDocument7 pagesFriction in PipesCRAZY INDIAN XYZNo ratings yet
- CABINTOYDocument6 pagesCABINTOYMatt Kristopher DiazNo ratings yet
- 1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument5 pages1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterRaghavanNo ratings yet
- Report 7Document10 pagesReport 7Azeezan AlessaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics (Water Distribution System)Document11 pagesHydraulics (Water Distribution System)Saurav GhimireNo ratings yet
- Other 04042022222516671Document8 pagesOther 04042022222516671Yasin EgeNo ratings yet
- Flow Through Triangular NotchDocument7 pagesFlow Through Triangular NotchAbdul Razak KaladgiNo ratings yet
- B21270 - Lab 1 Experiment 1 - ThermofluidDocument4 pagesB21270 - Lab 1 Experiment 1 - Thermofluidb21270No ratings yet
- BGKMECH_HYDRAULIC_LABDocument50 pagesBGKMECH_HYDRAULIC_LABprachetNo ratings yet
- A. Preliminary Design Data: Overtop W Weir 0.667 0.667Document20 pagesA. Preliminary Design Data: Overtop W Weir 0.667 0.667berkely19100% (1)
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsDocument15 pagesFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsAngelica Joyce BenitoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Lab 8Document9 pagesThermal Lab 8Tym pass GmailNo ratings yet
- Lab. Manual Orifice MeterDocument6 pagesLab. Manual Orifice MeterSavan PatelNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab: ST Mary'S Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument36 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab: ST Mary'S Institute of Science and TechnologysidNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement Appratus: Aim of The ExperimentDocument5 pagesFlow Measurement Appratus: Aim of The ExperimentRavi ParikhNo ratings yet
- Fliud Mechanics Exxperiment 5Document2 pagesFliud Mechanics Exxperiment 5Nah Sr AdNo ratings yet
- Falling Head PermeabilityDocument13 pagesFalling Head PermeabilitySitiNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesFrom EverandCase Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesNo ratings yet
- Multi Stage Centrifugal Pump Experiment No. 5Document6 pagesMulti Stage Centrifugal Pump Experiment No. 5anil kumarNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Pump Experiment No: 6Document6 pagesReciprocating Pump Experiment No: 6anil kumarNo ratings yet
- Venturi Meter: Experiment No: 1Document4 pagesVenturi Meter: Experiment No: 1anil kumarNo ratings yet
- Friction Factor Experiment No: 3Document6 pagesFriction Factor Experiment No: 3anil kumarNo ratings yet
- Special Reference To The Liability of The Internet Service ProviderDocument3 pagesSpecial Reference To The Liability of The Internet Service ProviderGuru PrashannaNo ratings yet
- Crane Control System For Crawler Cranes: Liccon 2Document12 pagesCrane Control System For Crawler Cranes: Liccon 2Krristiian RodrriguezzNo ratings yet
- Vidit JainDocument1 pageVidit JaindasnbdsbNo ratings yet
- FDocument7 pagesFmasheikh1980No ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Computer AlgorithmDocument60 pagesDesign and Analysis of Computer Algorithmshemsedin shukreNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11: Access Layer: Object Storage and Object InteroperabilityDocument8 pagesChapter - 11: Access Layer: Object Storage and Object Interoperabilitydeeparanjini100% (1)
- OCT Retiview 500 Optical Coherence Tomography: FeatureDocument7 pagesOCT Retiview 500 Optical Coherence Tomography: FeatureNurul AminNo ratings yet
- Vortex Breakers in Practice - 201606Document2 pagesVortex Breakers in Practice - 201606JQuest229100% (4)
- Evolution of An EQ Design2Document9 pagesEvolution of An EQ Design2atiqulaNo ratings yet
- Reduction in Average Cycle TimeDocument50 pagesReduction in Average Cycle TimeSean ColferdNo ratings yet
- IPT ReportDocument46 pagesIPT ReportSandeep Kumar YadlapalliNo ratings yet
- Chandrayaan 2Document1 pageChandrayaan 2Mukesh RawatNo ratings yet
- Ashley Withers ResumeDocument1 pageAshley Withers ResumeAshley Danielle DobsonNo ratings yet
- C ProgrammingDocument85 pagesC ProgrammingSudhaRatnamNo ratings yet
- Writingfortelevi00unse PDFDocument328 pagesWritingfortelevi00unse PDFBaran AlinaNo ratings yet
- My Speech at Earth Day 2010, The GambiaDocument2 pagesMy Speech at Earth Day 2010, The GambiaEbrima S. DemNo ratings yet
- Ultramat SiemensDocument39 pagesUltramat Siemensafi1belleNo ratings yet
- REVISTA Europe11Document15 pagesREVISTA Europe11Pancho CorvalánNo ratings yet
- Debug1214 TIPS - JUALAN - CEPAT - LAKU - DI - SHOPEE - 100 - TRI PDFDocument3 pagesDebug1214 TIPS - JUALAN - CEPAT - LAKU - DI - SHOPEE - 100 - TRI PDFAaron BaharyNo ratings yet
- Business Objects: Designer Desktop Intelligence (Reporting) Info View/web Intelligence CMCDocument67 pagesBusiness Objects: Designer Desktop Intelligence (Reporting) Info View/web Intelligence CMCsravan001No ratings yet
- English Workbook 2ND Sem FinalDocument91 pagesEnglish Workbook 2ND Sem FinalMadonna S. AzueloNo ratings yet
- Minelab Go Find 40Document2 pagesMinelab Go Find 40blagoj-1No ratings yet
- 7E Kelas 7 Bab 2 Inggris Semester 1 K13 Revisi 2017Document12 pages7E Kelas 7 Bab 2 Inggris Semester 1 K13 Revisi 2017markhesywan purnoNo ratings yet
- Importance of Marketing Mix in Higher Education InstitutionsDocument13 pagesImportance of Marketing Mix in Higher Education InstitutionsGuna SekarNo ratings yet
- 2009-10 B.tech (Cosmetic)Document28 pages2009-10 B.tech (Cosmetic)Nilesh B ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Fan Coil Units Standard Type: FCU/2020/R1Document3 pagesFan Coil Units Standard Type: FCU/2020/R1Ahmed SohailNo ratings yet
- Technical Handbook RAYCHEM PDFDocument60 pagesTechnical Handbook RAYCHEM PDFSINIŠA PRETKOVIĆNo ratings yet
- Tissue Paper Hot Air Balloon: Andrea Badua Period 2 Physics Ms. BuenconsejoDocument14 pagesTissue Paper Hot Air Balloon: Andrea Badua Period 2 Physics Ms. BuenconsejoAndrea BaduaNo ratings yet
- 74HCT08 Gpu Cmos TTLDocument15 pages74HCT08 Gpu Cmos TTLMehmet KARAHANLINo ratings yet